6. Describe relevant outcome criteria for evaluating nursing care of clients with substance-use
|
|
|
- Barnaby Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3037: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH NURSING THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE ABUSE, CODEPENDENCY, AND IMPAIRED NURSE Sheryl F. Banak, MSN, RN 2007 Q1 LECTURE OBJECTIVES: 1. Define abuse, dependence, intoxication, and withdrawal. 2. Discuss the predisposing factors implicated in the etiology of substance-related disorders. 3. Identify symtomatology and use the information in assessment of clients with various substanceuse disorders and substance-induced disorders. 4. Identify nursing diagnoses common to clients with substance-use disorders and substance-induced disorders, and select appropriate nursing interventions for each. 5. Identify topics for client and family teaching relevant to substance-use disorders and substanceinduced disorders. 6. Describe relevant outcome criteria for evaluating nursing care of clients with substance-use disorders and substance-induced disorders. 7. Discuss the issue of substance-related disorders within the profession of nursing. 8. Define codependency and identify behavioral characteristics associated with the disorder. 9. Discuss treatment of codependency. 10. Describe various modalities relevant to treatment of individuals with substance-use disorders and substance-induced disorders. READING ASSIGNMENT: STUDY TIPS: 1. Townsend, chapter Townsend Pocket Guide, Chapter 4 1. COMPLETE ALL of the READING ASSIGNMENTS. 2. USE the OBJECTIVES as study questions. 3. REALIZE that, when you are studying, you are studying for: a. THIS TEST b. HESI c. N-CLEX d. EXCELLENCE in YOUR NURSING PRACTICE 4. Study REVIEW QUESTIONS at the end of the CHAPTER. 5. NOTE: TEST QUESTIONS are derived from READING ASSIGNMENTS AND LECTURE. 6. Study related material from NCLEX-RN Exam Review Book 7. DEFINE words in VOCABULARY LIST at beginning of chapter; most are in the glossary.
2 Q2 LECTURE OUTLINE: I. Introduction A. Two groups 1. Substance-use disorders a. Abuse b Dependence 2. Substance-induced disorders a. Intoxication b. Withdrawal c. Delirium d. Dementia e. Amnesia f. Psychosis g. Mood disorder h. Anxiety disorder i. Sexual dysfunction j. Sleep disorders B. Some illegal substances accepted in various degrees by subcultures in society II. Substance-use disorders A. Substance abuse. DSM-IV-TR criteria for substance abuse: 1. Recurrent substance use resulting in failure to fulfill major role obligations at work, school, home 2. Recurrent substance use in physically hazardous situations 3. Recurrent substance-related legal problems 4. Continued substance use despite persistent/recurrent social/interpersonal problems caused/exacerbated by effects of a substance B. Substance dependence 1. Physical dependence is manifested by a. The need for increasing amounts of substance t produce desired effects b. Syndrome of withdrawal with cessation of substance 2. Psychological dependence: Overwhelming desire to repeat use of a particular drug to: a. Produce pleasure, or b. Avoid discomfort 3. DSM-IV-TR criteria a. Evidence of tolerance, defined by either (1) Markedly increased amounts of substance to achieve intoxication or desired effects, or (2) Markedly diminished effect with continued use of same amount of substance b. Evidence of withdrawal symptoms, as manifested by either (1) The characteristic withdrawal syndrome for the substance, or (2) The same (or a closely related) substance is taken to relieve or avoid withdrawal symptoms. c. The substance is often taken (1) In larger amounts than intended (2) Over a longer period than was intended d. Persistent desire/unsuccessful efforts to decrease/eliminate substance use e. Much time is spent in activities to (1) Obtain substance (2) Use substance, or (3) Recover from substance s effects
3 f. Substance use results in reduced or elimination of important (1) Social activities (2) Occupational activities (3) Recreational activities g. Substance use is continued despite the person s knowledge that the substance has most likely caused/exacerbated a (1) Persistent or recurrent physical problem, or a (2) Persistent or recurrent psychological problem Q3 III. IV. Substance-Induced disorders A. Substance intoxication DSM-IV-TR: 1. The development of a reversible substance-specific syndrome caused by recent ingestion of (or exposure to) a substance. 2. Clinically significant maladaptive behavior or psychological changes due to effect of a substance on the CNS and develop during or shortly after use of the substance. 3. The symptoms a. are not due to a general medical condition, and, b. are not better accounted for by another mental disorder. B. Substance withdrawal DSM-IV-TR criteria: 1. The development of a substance-specific syndrome caused by the cessation of (or reduction in) heavy and prolonged substance use. 2. The substance-specific syndrome causes a. clinically significant distress, or b. impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. 3. The symptoms a. are not due to a general medical condition, and, b. are not better accounted for by another mental disorder. Classes of Psychoactive Substances A. Alcohol B. Amphetamines and related substances C. Caffeine D. Cannabis E. Cocaine F. Hallucinogens G. Inhalants H. Nicotine I. Opioids J. Phencyclidine and related substances K. Sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics V. Predisposing factors A. Biological 1. Genetics. Apparent hereditary factor, esp with alcoholism. 2. Biochemical. Alcohol may produce morphine-like substances in the brain; responsible for alcohol addiction. B. Psychological 1. Developmental influences. Focus is on a. a punitive superego, and b. fixation at the oral stage of psychsocial development. 2. Personality factors. a. Personality traits suggested to play a part in tendency toward addictive behavior 1) Low self-esteem 2) Frequent depression
4 Q4 3) Passivity 4) Inability to delay or defer gratification 5) Inability to communicate effectively C. Sociocultural 1. Social learning. a. Increased child and adolescent use w/parents who use; modeling. b. Substance use promoted in peer groups. 2. Conditioning. Pleasurable effects from substance use act as positive reinforcement for continued use. 3. Cultural and ethnic influences. Some cultures more prone to substance use than others. VI. The Dynamics of Substance-related Disorders A. Alcohol abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance. 2. Historical aspects. 3. Patterns of use/abuse: a. Phase I. Prealcoholic phase. b. Phase II. Early alcoholic phase. c. Phase III. Crucial phase. d. Phase IV. Chronic phase. 4. Effects on body: a. Peripheral neuropathy b. Alcoholic myopathy c. Wernicke s encephalopathy d. Korsakoff s psychosis e. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy f. Esophagitis g. Gastritis h. Pancreatitis i. Alcoholic hepatitis j. Cirrhosis of the liver: 1) Portal hypertension 2) Ascites 3) Esophageal varices 4) Hepatic encephalopathy k. Leukopenia l. Thrombocytopenia m. Sexual dysfunction B. Alcohol intoxication 1. Occurs with blood levels of mg/dL C. Alcohol withdrawal 1. Occurs within 4-12 hours of cessation of (or reduction in) heavy and prolonged alcohol use. D. Sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance: a. Barbiturates b. Nonbarbiturate hypnotics c. Antianxiety agents 2. Historical aspects 3. Patterns of use/abuse
5 4. Effects on body: a. Effects on sleep and dreaming b. Respiratory depression c. Cardiovascular effects d. Renal function e. Hepatic effects f. Body temperature g. Sexual functioning E. Sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic intoxication 1. Intoxication with these CNS depressants ranges from a. disinhibition and aggressiveness, to b. coma and death (with increasing amounts of drug) F. Sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic withdrawal 1. Onset of symptoms depends on half-life of the drug from which withdrawing. 2. Severe withdrawal from CNS depressants can be life-threatening. G. CNS stimulant abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance. a. Amphetamines b. Nonamphetamine stimulants c. Cocaine d. Caffeine e. Nicotine 2. Historical aspects 3. Patterns of use/abuse 4. Effects on body: a. CNS effects b. Cardiovascular/pulmonary effects c. Gastrointestinal and renal effects d. Sexual functioning H. CNS stimulant intoxication 1. Amphetamine and cocaine intoxication causes: a. Euphoria b. Impaired judgment c. Anxiety d. Changes in vital signs e. Nausea and vomiting f. Psychomotor agitation g. Muscular weakness h. Respiratory depression i. Cardiac arrhythmias j. Confusion k. Seizures l. Dyskinesias m. Dystonias n. Coma 2. Caffeine intoxication usually occurs after consumption of 250mg a. Most common symptoms: 1) Restlessness 2) Insomnia Q5
6 Q6 I. CNS stimulant withdrawal 1. Amphetamines and cocaine a. Dysphoria b. Fatigue c. Sleep disturbances d. Increased appetite 2. Caffeine a. Headache b. Fatigue c. Anxiety d. Irritability e. Nausea and vomiting 3. Nicotine a. Dysphoria b. Anxiety c. Irritability d. Difficulty with concentration e. Restlessness f. Increased appetite J. Inhalant abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance a. Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons b. Examples 1) Gasoline 2) Varnish remover 3) Lighter fluid 4) Airplane glue 5) Rubber cement 6) Cleaning fluid 7) Spray paint 8) Shoe conditioner 9) Typewriter ribbon correction fluid 2. Patterns of use/abuse 3. Effects on the body a. CNS effects b. Respiratory effects c. GI effects d. Renal system effects K. Inhalant intoxication 1. DSM-IV-TR definition: Clinically significant maladaptive behavioral or psychological changes that developed during, or shortly after, use of or exposure to volatile inhalants. 2. Symptoms include a. Dizziness b. Nystagmus c. Incoordination d. Slurred speech e. Unsteady gait f. Lethargy g. Depressed reflexes h. Psychomotor retardation i. Tremor j. Generalized muscle weakness k. Blurred vision or diplopia l. Stupor or coma m..euphoria
7 Q7 L. Opioid abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance a. Opioids of natural origin b. Opioid derivatives c. Synthetic opioid-like drugs 2. Historical aspects 3. Patterns of use/abuse 4. Effects on the body a. CNS b. GI c. CV d. Sexual M. Opioid intoxication 1. Symptoms are consistent with the half-life of most opioid drugs and usually last several hours. 2. Severe opioid intoxication can lead to respiratory depression, coma, and death. N. Opioid withdrawal 1. Symptoms a. Occur within 6 to 12 hrs after last dose; b. Peak with 1 to 3 days, and, c. Gradually subside over a period of 5 to 12 days, depending on half-life. d. Include 1) Dysphoric mood 2) Nausea, vomiting 3) Muscle aches 4) Lacrimation 5) Rhinorrhea 6) Dilatation of pupils 7) Piloerection 8) Sweating 9) Abdominal cramping 10) Diarrhea 11) Yawning 12) Fever 13) Insomnia O. Hallucinogen abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance a. Naturally occurring hallucinogens 1) Mescaline 2) Psilocybin and psilocyn 3) Ololiugui b. Synthetic compounds 1) LSD 2) Dimethyltryptamine 3) STP 4) Phencyclidine 5) Designer drugs 2. Historical aspects 3. Patterns of use/abuse 4. Effects on the body
8 Q8 VII. P. Hallucinogen intoxication 1. Occurs within minutes to a few hours after using drug 2. Symptoms a. Perceptual alteration b. Depersonalization c. Derealization d. Tachycardia e. Palpitations f. Symptoms of PCP intoxication also include 1) Belligerence 2) Combativeness 3) May proceed to seizures or coma Q. Cannabis abuse and dependence 1. A profile of the substance a. Marijuana b. Hashish 2. Historical aspects 3. Patterns of use/abuse 4. Effects on the body a. CV b. Respiratory c. Reproductive d. CNS e. Sexual functioning R. Cannabis intoxication 1. Symptoms include a. Impaired motor coordination b. Euphoria c. Anxiety d. A sensation of slowed time e. Impaired judgment 2. Impairment of motor skills lasts for 8-12 hours Application of Nursing Process A. Nurse must begin relationship development with a substance abuser by examining own attitudes and personal experiences with substances. B. Assessment tools for determining extent of problem pt has include 1. Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST) 2. CAGE Questionnaire C. Dual diagnosis: 1. Coexisting substance disorder and mental illness. 2. Patient assigned to special program, targeting both. D. Nursing diagnoses are formulated from data gathered during assessment phase: Outcome criteria established for each. E. Nursing intervention for client with substance use disorder is aimed at: 1. Acceptance of use of substances as a problem 2. Acceptance of personal responsibility for use of substances 3. Identification of more adaptive coping strategies, and 4. Restoration of nutritional status. 5. Care is provided in three phases: a. Detoxification b. Intermediated care c. Rehabilitation
9 F. Client/family education G. Evaluation of care is based on achievement of outcome criteria. Q9 VIII. IX. The Impaired Nurse A. Estimate that 10-20% of nurses suffer from disease of chemical dependency B. Alcohol is most widely abused drug; narcotics follow close behind. C. Clues that may identify an impaired nurse: 1. High absenteeism (if substance source outside of work area) 2. Rarely misses work (if substance source is at work) 3. Problems with relationships 4. Irritability 5. Tendency to isolate 6. Elaborate excuses for behavior 7. Unkempt appearance 8. Impaired motor coordination 9. Frequent trips to the bathroom 10. Patient complaints of inadequate pain control 11. Discrepancies in documentation. D. Peer assistance program developed by American Nurses Association in To assist impaired nurses to recognize their impairments. 2. To obtain necessary treatment. 3. To regain accountability within their profession. 4. Contract is drawn up: a. To detail method of treatment. b. To establish guidelines for monitoring course of treatment. 5. Usually lasts for period of 2 years. Codependency A. Definition: emotional, psychological, and behavioral condition that develops as a result of an individual s prolonged exposure to (and practice of) a set of oppressive rules rules that prevent the open expression of feeling as well as direct discussion of personal and interpersonal problems. B. Derives self-worth from others C. Feels responsible for happiness of others D. Denial that problems exist is common E. Feelings are kept in control; Anxiety may be released in the form of stress-related illnesses, or compulsive behaviors such as a. eating, b. spending, c. working, or d. use of substances F. The codependent nurse 1. Characteristics of some nurses who often have a tendency to fulfill everyone s needs but their own: a. Caretaking. Meeting needs of others to the point of neglecting their own. b. Perfectionism Low self-esteem and fear of failure drive codependent nurses to strive for an unrealistic level of achievement. c. Denial Refusal to acknowledge that any personal problems or painful issues exist. d. Poor communication Rarely express their true feelings.
10 Q10 G. Treating codependence 1. Stage I: Survival Stage. Letting go of the denial that a problems exist. 2. Stage II: Reidentification Stage. Taking responsibility for own dysfunctional behavior. 3. Stage III: Core Issues Stage. Facing the fact that relationships cannot be managed by force of will. 4. Stage IV: Reintegration Stage. Accepting self and willingness to change. X. Treatment Modalities for Substance-Related Disorders A. Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) B. Various support groups patterned after AA for persons with other substance-related problems C. Pharmacotherapy D. Counseling E. Group therapy F. Psychopharmacology for substance intoxication and substance withdrawal XI. XII. Summary (pp in text) Critical Thinking Exercise Source: Townsend, M.C. (2003). Instructor s guide for psychiatric mental health nursing: Concepts of care,(4th ed), Philadelphia: F.A.Davis. January,07/SFBanakkMSN,RN
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH
 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
Substance Use Disorders. A Major Problem. Defining Addiction 2/24/2009. Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 %
 Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders
 Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders
 SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Substance Use Disorder This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and
Substance Use Disorders Substance Use Disorder This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and
ADDICTIONS. Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry
 ADDICTIONS Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Addictions-terminology drug abuse drug dependence drug addiction intoxication withdrawal tolerance
ADDICTIONS Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Addictions-terminology drug abuse drug dependence drug addiction intoxication withdrawal tolerance
Main Questions. Why study addiction? Substance Use Disorders, Part 1 Alecia Schweinsburg, MA Abnromal Psychology, Fall Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders. By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP
 Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP History of Psychoactive Substances Used by people in almost all cultures since prehistoric times Produce effects in the
Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP History of Psychoactive Substances Used by people in almost all cultures since prehistoric times Produce effects in the
1. Townsend (2006) chapter 39 (pp ). 2. Townsend Pocket Guide (2004) chapter 18 (pp ).
 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3037: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH NURSING POPULATIONS AT RISK FOR ALTERATIONS IN HEALTH: PERSONS WITH HIV/AIDS and TERMINAL ILLNESS Sheryl F. Banak, MSN,RN Y1 LECTURE
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3037: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH NURSING POPULATIONS AT RISK FOR ALTERATIONS IN HEALTH: PERSONS WITH HIV/AIDS and TERMINAL ILLNESS Sheryl F. Banak, MSN,RN Y1 LECTURE
Drugs and the School Aged Child. Objectives. Substance Abuse. Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN. n List signs of drug use in children
 Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
7/3/2013 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER ELEVEN CHAPTER OUTLINE. Substance Use Disorders. Oltmanns and Emery
 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
Important Information
 Important Information Please work through the following pages with your patient or the patient s chart as necessary. Fax completed documents to 1 888 629-4722. Keep the original in your chart / file. Fee:
Important Information Please work through the following pages with your patient or the patient s chart as necessary. Fax completed documents to 1 888 629-4722. Keep the original in your chart / file. Fee:
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both?
 substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both? Stephen Strobbe, PhD, RN, PMHCNS-BC, CARN-AP Dawn Farm Education Series St. Joe s Education Center, Ypsilanti, MI Tuesday, January 27, 2015
substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both? Stephen Strobbe, PhD, RN, PMHCNS-BC, CARN-AP Dawn Farm Education Series St. Joe s Education Center, Ypsilanti, MI Tuesday, January 27, 2015
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment
 Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders. DATE: 11/14/2017 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD
 Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders DATE: 11/14/2017 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD Disclosure Information Speaker: John Mahan, MD has nothing to disclose Learning Objectives Understand
Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders DATE: 11/14/2017 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD Disclosure Information Speaker: John Mahan, MD has nothing to disclose Learning Objectives Understand
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, AND THE DSM-5: A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW
 TMH Professionals, LLC, American College of Psychotherapy & LPCA present PSYCHOPATHOLOGY, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, AND THE DSM-5: A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW Module 4: Substance Use Disorders, Impulse Control
TMH Professionals, LLC, American College of Psychotherapy & LPCA present PSYCHOPATHOLOGY, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, AND THE DSM-5: A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW Module 4: Substance Use Disorders, Impulse Control
Initial Substance Use Assessment
 Date of Assessment: Source of Referral: Choose an item. Persons Present: Client and Provider only Transportation Assistance Needed: Yes No Member has a Primary Care Physician (PCP)? Yes No If yes PCP,
Date of Assessment: Source of Referral: Choose an item. Persons Present: Client and Provider only Transportation Assistance Needed: Yes No Member has a Primary Care Physician (PCP)? Yes No If yes PCP,
AACN PCCN Review. Behavioral
 AACN PCCN Review Behavioral Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com 0 Behavioral I. INTRODUCTION PCCN
AACN PCCN Review Behavioral Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com 0 Behavioral I. INTRODUCTION PCCN
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2)
 Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) دکتر راد گودرزی
 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) 1 Expanded to include Gambling Disorder Cannabis Withdrawal and Caffeine Withdrawal are new disorders Caffeine Withdrawal
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) 1 Expanded to include Gambling Disorder Cannabis Withdrawal and Caffeine Withdrawal are new disorders Caffeine Withdrawal
(consciousness) (monitor) (control)
 : (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
: (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
Clinical Assessment. Client Name (Last, First, MI) ID # Medicaid # DOB: Age:
 Clinical Assessment Client Name (Last, First, MI) ID # Medicaid # DOB: Age: Sex: Ethnic Group: Marital Status: Occupation: Education: Multiaxial Diagnosis Axis I: Clinical Disorders / Other Conditions
Clinical Assessment Client Name (Last, First, MI) ID # Medicaid # DOB: Age: Sex: Ethnic Group: Marital Status: Occupation: Education: Multiaxial Diagnosis Axis I: Clinical Disorders / Other Conditions
*IN10 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT*
 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders. Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder
 Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
GOALS FOR THE PSCYHIATRY CLERKSHIP
 GOALS FOR THE PSCYHIATRY CLERKSHIP GOALS - The aim of the core psychiatry clerkship is to expose students to patients with mental illness and to prepare them to provide psychiatric care at a basic level.
GOALS FOR THE PSCYHIATRY CLERKSHIP GOALS - The aim of the core psychiatry clerkship is to expose students to patients with mental illness and to prepare them to provide psychiatric care at a basic level.
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
MOOD (AFFECTIVE) DISORDERS and ANXIETY DISORDERS
 MOOD (AFFECTIVE) DISORDERS and ANXIETY DISORDERS Shelley Klipp AS91 Spring 2010 TIP 42 Pages 226-231 and 369-379 DSM IV-TR APA 2000 Co-Occurring Substance Abuse and Mental Disorders by John Smith Types
MOOD (AFFECTIVE) DISORDERS and ANXIETY DISORDERS Shelley Klipp AS91 Spring 2010 TIP 42 Pages 226-231 and 369-379 DSM IV-TR APA 2000 Co-Occurring Substance Abuse and Mental Disorders by John Smith Types
Live A Life Above The Influence!
 Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Clinical Assessment. Client Name (Last, First, MI) ID # Medicaid # DOB: Age: Sex: Ethnic Group: Marital Status: Occupation: Education:
 Sex: Ethnic Group: Marital Status: Occupation: Education: Multiaxial Diagnosis Axis I: Clinical Disorders / Other Conditions That May Be a Focus of Clinical Attention Diagnostic Code DSM-IV Name Axis II:
Sex: Ethnic Group: Marital Status: Occupation: Education: Multiaxial Diagnosis Axis I: Clinical Disorders / Other Conditions That May Be a Focus of Clinical Attention Diagnostic Code DSM-IV Name Axis II:
Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They?
 Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They? Yngvild Olsen, MD, MPH Cecil County Board of Health Workgroup Meeting Elkton, MD October 8, 2013 Objectives
Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They? Yngvild Olsen, MD, MPH Cecil County Board of Health Workgroup Meeting Elkton, MD October 8, 2013 Objectives
Withdrawal.
 Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Director, Adult Burns & Trauma Psychiatry Division of Psychiatry and Medicine Medical Director, Addiction Consultation Team MGH Center for Addiction Medicine Massachusetts General
Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Director, Adult Burns & Trauma Psychiatry Division of Psychiatry and Medicine Medical Director, Addiction Consultation Team MGH Center for Addiction Medicine Massachusetts General
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
Chapter 33. The Child with an Emotional or Behavioral Condition
 Chapter 33 The Child with an Emotional or Behavioral Condition Objectives Differentiate among the following terms: psychiatrist, psychoanalyst, clinical psychologist, and counselor. Discuss the impact
Chapter 33 The Child with an Emotional or Behavioral Condition Objectives Differentiate among the following terms: psychiatrist, psychoanalyst, clinical psychologist, and counselor. Discuss the impact
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450
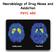 Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450 Healthy Control Drug Abuser Illicit drug use, lifetime and past year, in Canada 50 Canabis only Any drug Any of 5 drugs (without canabis) (CADUMS 2012)
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450 Healthy Control Drug Abuser Illicit drug use, lifetime and past year, in Canada 50 Canabis only Any drug Any of 5 drugs (without canabis) (CADUMS 2012)
Cincinnati Christian University Drug and Alcohol Prevention Program
 Cincinnati Christian University Drug and Alcohol Prevention Program Standards of Conduct for Employees & Students Employees It is a violation of University policy to use or be under the influence of alcohol
Cincinnati Christian University Drug and Alcohol Prevention Program Standards of Conduct for Employees & Students Employees It is a violation of University policy to use or be under the influence of alcohol
Prepared by: Dr. Elizabeth Woodward, University of Toronto Resident in Psychiatry
 Prepared by: Dr. Elizabeth Woodward, University of Toronto Resident in Psychiatry In broad terms, substance use disorders occur when a substance is used in a compulsive manner with a lack of control over
Prepared by: Dr. Elizabeth Woodward, University of Toronto Resident in Psychiatry In broad terms, substance use disorders occur when a substance is used in a compulsive manner with a lack of control over
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use
 Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Substance Misuse and Abuse
 CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH
 PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH OVERVIEW: PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders Psychotic Disorders Personality Disorders PTSD Eating Disorders EXAMPLE What is the diagnosis?
PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH OVERVIEW: PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders Psychotic Disorders Personality Disorders PTSD Eating Disorders EXAMPLE What is the diagnosis?
Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996)
 APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
Page 1 of 5. Policy Statement: II. General Policy Statement
 Page 1 of 5 Title: Drug-Free Schools Policy Statement Category: President Applies to: Staff, Faculty, Student, Department Contact: UCO Office of Legal Counsel (405) 974-3377 Purpose: I. Purpose A. The
Page 1 of 5 Title: Drug-Free Schools Policy Statement Category: President Applies to: Staff, Faculty, Student, Department Contact: UCO Office of Legal Counsel (405) 974-3377 Purpose: I. Purpose A. The
A look at Marijuana in 2014
 A look at Marijuana in 2014 Paul Snyder MA., LADC Overview and Objectives Discuss the mental and physical effects of marijuana use Describe the criteria for Cannabis use disorder according to the DSM 5
A look at Marijuana in 2014 Paul Snyder MA., LADC Overview and Objectives Discuss the mental and physical effects of marijuana use Describe the criteria for Cannabis use disorder according to the DSM 5
THE ADDICTED BRAIN: WHAT S GOING ON IN THERE? 3 CE hours. Sandra Morgenthal, PCC-S, CCFC, RN Copyright 2016 Sandra Morgenthal All rights Reserved
 THE ADDICTED BRAIN: WHAT S GOING ON IN THERE? 3 CE hours Sandra Morgenthal, PCC-S, CCFC, RN Copyright 2016 Sandra Morgenthal All rights Reserved You can contact this author at sandymorgenthal@yahoo.com
THE ADDICTED BRAIN: WHAT S GOING ON IN THERE? 3 CE hours Sandra Morgenthal, PCC-S, CCFC, RN Copyright 2016 Sandra Morgenthal All rights Reserved You can contact this author at sandymorgenthal@yahoo.com
Drug abuse: Drug misuse Dependence abuse
 Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
Defining Drugs. Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions
 Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders. DATE: 4/17/18 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD
 Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders DATE: 4/17/18 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD Disclosure Information Speaker: John Mahan, MD has nothing to disclose Planning Committee: The members
Co-Occurring Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders DATE: 4/17/18 PRESENTED BY: John Mahan, MD Disclosure Information Speaker: John Mahan, MD has nothing to disclose Planning Committee: The members
Clinical Evaluation: Assessment Goals
 Clinical Evaluation: Assessment Goals 1. Define Assessment Process 2. Identify Assessment Instruments 3. Define DSM-5 criteria for Substance Abuse and Dependence, specifiers and multi-axial assessment
Clinical Evaluation: Assessment Goals 1. Define Assessment Process 2. Identify Assessment Instruments 3. Define DSM-5 criteria for Substance Abuse and Dependence, specifiers and multi-axial assessment
Geriatric Alterations Associated with Neurological Conditions
 Geriatric Alterations Associated with Neurological Conditions I have no conflicts of interest. Julie Bronson The Older Adult According to the World Health Organization Africa 50-55 or 50-65 United Nations
Geriatric Alterations Associated with Neurological Conditions I have no conflicts of interest. Julie Bronson The Older Adult According to the World Health Organization Africa 50-55 or 50-65 United Nations
Drugs in American Society CHD 601. Legal Drugs Alcohol
 Drugs in American Society CHD 601 Legal Drugs Alcohol Unit 2 Last updated April 12, 2017 Edward Pierce, LCSW Overview From the last class Counseling videos Quiz 1 Process Other items Alcohol Biochemical
Drugs in American Society CHD 601 Legal Drugs Alcohol Unit 2 Last updated April 12, 2017 Edward Pierce, LCSW Overview From the last class Counseling videos Quiz 1 Process Other items Alcohol Biochemical
Admit date: 1-WM 2-WM 3.2-WM 3.7-WM 4-WM DSM-V diagnoses: Please list all diagnoses (psychiatric, chemical dependency and medical)
 https://providers.amerigroup.com Substance Use Disorder Withdrawal Management Prior Authorization and Continued Care Request (Use for American Society of Addiction Medicine [ASAM] withdrawal management
https://providers.amerigroup.com Substance Use Disorder Withdrawal Management Prior Authorization and Continued Care Request (Use for American Society of Addiction Medicine [ASAM] withdrawal management
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 31. Behavioral Emergencies & Substance Abuse
 Chapter 31 & Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to form field impression & implement management plan for patients with behavioral or drug abuse emergencies Learning Objectives Distinguish between normal
Chapter 31 & Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to form field impression & implement management plan for patients with behavioral or drug abuse emergencies Learning Objectives Distinguish between normal
SOCI221. Session 11. Crisis and Trauma Issues: Alcohol and other drugs; Eating disorders and Referrals. Department of Social Science
 SOCI221 Session 11 Crisis and Trauma Issues: Alcohol and other drugs; Eating disorders and Referrals Department of Social Science Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Session Aim The
SOCI221 Session 11 Crisis and Trauma Issues: Alcohol and other drugs; Eating disorders and Referrals Department of Social Science Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Session Aim The
Organic Mental Disorders. Organic Mental Disorders. Axes. Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine
 Organic Mental Disorders Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine www.metadon.net 1 Organic Mental Disorders In DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders), OMD includes Delirium,
Organic Mental Disorders Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine www.metadon.net 1 Organic Mental Disorders In DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders), OMD includes Delirium,
Adolescent Substance Abuse
 Adolescent Substance Abuse WHY IT S A PROBLEM AND WHAT WE NEED TO KNOW AS ANESTHESIA PROVIDERS BRIDGET L. MULDOWNEY MD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF ANESTHESIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN- SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Adolescent Substance Abuse WHY IT S A PROBLEM AND WHAT WE NEED TO KNOW AS ANESTHESIA PROVIDERS BRIDGET L. MULDOWNEY MD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF ANESTHESIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN- SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Substance Abuse Protracted Withdrawal
 Substance Abuse Protracted Withdrawal Overview 1. Acute and Protracted Withdrawal 2. Withdrawal Potential Kate Speck, PhD, MAC, LADC 3. Recovery Reinforcers 1 2 3 Addiction Addiction is a primary, chronic,
Substance Abuse Protracted Withdrawal Overview 1. Acute and Protracted Withdrawal 2. Withdrawal Potential Kate Speck, PhD, MAC, LADC 3. Recovery Reinforcers 1 2 3 Addiction Addiction is a primary, chronic,
A Handbook on Drug and Alcohol Abuse
 A Handbook on Drug and Alcohol Abuse THE BIOMEDICAL ASPECTS THIRD EDITION Gail Winger Frederick G. Hofmann James H. Woods New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1992 1. Introduction 3 The Problem of Drug
A Handbook on Drug and Alcohol Abuse THE BIOMEDICAL ASPECTS THIRD EDITION Gail Winger Frederick G. Hofmann James H. Woods New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1992 1. Introduction 3 The Problem of Drug
BASIC VOLUME. Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
 BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children. Jackie McReynolds Washington State University
 Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Like us on Facebook (JU Nursing Leaders) & check our website
 Like us on Facebook (JU Nursing Leaders) & check our website www.junursingleaders.wordpress.com nurseslabs.com/nclex- Questions Substance and eating disorders test bank The nurse is assessing a 19 year-old
Like us on Facebook (JU Nursing Leaders) & check our website www.junursingleaders.wordpress.com nurseslabs.com/nclex- Questions Substance and eating disorders test bank The nurse is assessing a 19 year-old
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: PSYC 1400: Abnormal Psychology CREDITS: 3 (3Lec 0 / Lab) PREREQUISITES: PSYC 1205: General Psychology CATALOG DESCRIPTION: Abnormal Psychology
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: PSYC 1400: Abnormal Psychology CREDITS: 3 (3Lec 0 / Lab) PREREQUISITES: PSYC 1205: General Psychology CATALOG DESCRIPTION: Abnormal Psychology
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information
 Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS
 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
Psychotropic Drugs 0, 4-
 0, 4- } -v Psychotropic Drugs NORMAN L. KELTNER, Ed D, RN Associate Professor, Graduate Program, University of Alabama School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama DAVID
0, 4- } -v Psychotropic Drugs NORMAN L. KELTNER, Ed D, RN Associate Professor, Graduate Program, University of Alabama School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama DAVID
CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND
 Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSHYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH
 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSHYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION FOR PEOPLE WITH ADJUSTMENT AND IMPULSE CONTROL DISORDERS LECTURE OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe various types of
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSHYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION FOR PEOPLE WITH ADJUSTMENT AND IMPULSE CONTROL DISORDERS LECTURE OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe various types of
Trends, Tactics and Toxicity: Marijuana Movement on Missouri College Campuses. Janice Putnam PhD, RN Amy Kiger MS, ABD Kelly Skinner DNP, FNP-C
 Trends, Tactics and Toxicity: Marijuana Movement on Missouri College Campuses Janice Putnam PhD, RN Amy Kiger MS, ABD Kelly Skinner DNP, FNP-C 1 Marijuana/Cannabis Marijuana use is growing in popularity
Trends, Tactics and Toxicity: Marijuana Movement on Missouri College Campuses Janice Putnam PhD, RN Amy Kiger MS, ABD Kelly Skinner DNP, FNP-C 1 Marijuana/Cannabis Marijuana use is growing in popularity
Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders
 Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders Kishore Desagani, MD General Adult and Forensic Psychiatrist Consultant Psychiatrist Medical Assessment and Policy Team
Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders Kishore Desagani, MD General Adult and Forensic Psychiatrist Consultant Psychiatrist Medical Assessment and Policy Team
Common poly-substance abuse: MDMA, Ketamine, & Methamphetamine Clinical detection and management
 Common poly-substance abuse: MDMA, Ketamine, & Methamphetamine Clinical detection and management Prepared by Dr. S.P. LEUNG Castle Peak Hospital 27th January 2001 Medical practitioner should provide care
Common poly-substance abuse: MDMA, Ketamine, & Methamphetamine Clinical detection and management Prepared by Dr. S.P. LEUNG Castle Peak Hospital 27th January 2001 Medical practitioner should provide care
OBJECTIVES PLAN OF LESSON
 Unit: Behavioral Health Nursing Implementation:Keltner et al., Ch. 1, 2, 3, & Appendix; PowerPoint Presentation; Lesson: 1 Handouts; Lecture/Discussion; Transparencies Title: Historic Perspective of Mental
Unit: Behavioral Health Nursing Implementation:Keltner et al., Ch. 1, 2, 3, & Appendix; PowerPoint Presentation; Lesson: 1 Handouts; Lecture/Discussion; Transparencies Title: Historic Perspective of Mental
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
Chapter 25 Outline. Chapter 25: Drug Abuse. Chapter 25 Outline. Drug Abuse. Drug Abuse. Drug Abuse. Drug abuse. Drug abuse
 Chapter 25: Drug Abuse Drug abuse Chapter 25 Outline General considerations Definitions Psychologic dependence Physical dependence Tolerance Addiction, habituation, and dependence Central nervous system
Chapter 25: Drug Abuse Drug abuse Chapter 25 Outline General considerations Definitions Psychologic dependence Physical dependence Tolerance Addiction, habituation, and dependence Central nervous system
Understanding Drug and Alcohol Abuse and Addiction
 Understanding Drug and Alcohol Abuse and Addiction Peter R. Martin, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry and Pharmacology Vanderbilt Addiction Center Substance Use, Abuse, and Addiction Inexorably intertwined
Understanding Drug and Alcohol Abuse and Addiction Peter R. Martin, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry and Pharmacology Vanderbilt Addiction Center Substance Use, Abuse, and Addiction Inexorably intertwined
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Module II Opioids 101 Opiate Opioid
 BUPRENORPHINE TREATMENT: A TRAINING FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY ADDICTION PROFESSIONALS Module II Opioids 101 Module II Goals of the Module This module reviews the following:! Opioid addiction and the brain!
BUPRENORPHINE TREATMENT: A TRAINING FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY ADDICTION PROFESSIONALS Module II Opioids 101 Module II Goals of the Module This module reviews the following:! Opioid addiction and the brain!
DSM-5 UPDATE. Supplement to DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS, FIFTH EDITION
 DSM-5 UPDATE Supplement to DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS, FIFTH EDITION October 2017 DSM-5 Update October 2017 Supplement to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,
DSM-5 UPDATE Supplement to DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS, FIFTH EDITION October 2017 DSM-5 Update October 2017 Supplement to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,
Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014
 Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014 OVERVIEW Definitions Disease concept Anatomy and neurochemistry Risk Factors Defenses, statistics, comorbidity Professionals and treatment
Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014 OVERVIEW Definitions Disease concept Anatomy and neurochemistry Risk Factors Defenses, statistics, comorbidity Professionals and treatment
Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies
 CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
High Risk Medications. University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing
 High Risk Medications University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this module, participants will be better able to: 1. Define Gain high risk medications
High Risk Medications University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this module, participants will be better able to: 1. Define Gain high risk medications
PART VI: TAPERING OPIOIDS ROBERT JENKINSON MD MARCH 7, 2018
 PART VI: TAPERING OPIOIDS ROBERT JENKINSON MD MARCH 7, 2018 TAPERING OPIOIDS GETTING STARTED ON OPIOIDS IS EASY BUT GETTING PATIENTS OFF IS HARD WE ARE ARE OBLIGED TO TAPER PATIENTS DOWN AND OFF OPIOIDS
PART VI: TAPERING OPIOIDS ROBERT JENKINSON MD MARCH 7, 2018 TAPERING OPIOIDS GETTING STARTED ON OPIOIDS IS EASY BUT GETTING PATIENTS OFF IS HARD WE ARE ARE OBLIGED TO TAPER PATIENTS DOWN AND OFF OPIOIDS
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT
 MEDICATION MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT The goal of this agreement is to ensure that you and your physician comply with all state and federal regulations concerning the prescribing of controlled substances. The
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT The goal of this agreement is to ensure that you and your physician comply with all state and federal regulations concerning the prescribing of controlled substances. The
Chapter 23. Medicines and Drugs
 Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
ROLE OF HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE RELATED PROBLEMS
 ROLE OF HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE RELATED PROBLEMS Dr. Anita Rao? ASK SCREEN Refer HELP T T Ranganathan Clinical Research Foundation TTK Hospital IV Main Road, Indira
ROLE OF HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE RELATED PROBLEMS Dr. Anita Rao? ASK SCREEN Refer HELP T T Ranganathan Clinical Research Foundation TTK Hospital IV Main Road, Indira
Table of Contents VOLUME 1
 VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
Clinician's Guide to Substance Abuse
 Questions from chapter 1 Clinician's Guide to Substance Abuse 1) Past medical paradigms of addiction include all EXCEPT a) addiction as a manifestation of underlying psychopathology b) addiction as untreatable
Questions from chapter 1 Clinician's Guide to Substance Abuse 1) Past medical paradigms of addiction include all EXCEPT a) addiction as a manifestation of underlying psychopathology b) addiction as untreatable
Sedative Hypnotics. Isopropyl Alcohol H H H H OH H. H H Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol)
 Sedative Hypnotics Alcohol - The most commonly used Sedative- Hypnotic. Probably the oldest psychoactive drug used by humans. Alcohol use is common our society. 2/3 of people drink. 10% are problem drinkers
Sedative Hypnotics Alcohol - The most commonly used Sedative- Hypnotic. Probably the oldest psychoactive drug used by humans. Alcohol use is common our society. 2/3 of people drink. 10% are problem drinkers
Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement
 Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement You and your provider have agreed on the use of controlled substance medications to treat your: We want to make sure you know how to manage your new prescription(s)
Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement You and your provider have agreed on the use of controlled substance medications to treat your: We want to make sure you know how to manage your new prescription(s)
What is a DRE. Introduction to Drugged Driving
 Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16
 Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Lorazepam Tablets, USP
 Lorazepam Tablets, USP DESCRIPTION: Lorazepam, an antianxiety agent, has the chemical formula, 7-chloro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H -1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one: Cl H N N O Cl OH It is a white
Lorazepam Tablets, USP DESCRIPTION: Lorazepam, an antianxiety agent, has the chemical formula, 7-chloro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H -1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one: Cl H N N O Cl OH It is a white
Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE
 Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE Dr. Brian L. Bethel Child and Family Therapist Independent Trainer and Consultant LPCC-S, LCDC III, RPT-S www.brianlbethel.com INTERPLAY COUNSELING & CONSULTING
Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE Dr. Brian L. Bethel Child and Family Therapist Independent Trainer and Consultant LPCC-S, LCDC III, RPT-S www.brianlbethel.com INTERPLAY COUNSELING & CONSULTING
Mental Health Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives
 Mental Health Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives Mental illness is prevalent in the general population and is commonly seen and treated in the office of the primary care provider. Educational experiences
Mental Health Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives Mental illness is prevalent in the general population and is commonly seen and treated in the office of the primary care provider. Educational experiences
Legalized Marijuana: Uses, Misuses & Abuses. Disclosures. Objectives. Kennon Heard University of Colorado SOM Dept Of Emergency Medicine
 Legalized Marijuana: Uses, Misuses & Abuses Kennon Heard University of Colorado SOM Dept Of Emergency Medicine Disclosures Research grants McNeil Consumer Healthcare (Acetaminophen) Rare Disease Therapeutics
Legalized Marijuana: Uses, Misuses & Abuses Kennon Heard University of Colorado SOM Dept Of Emergency Medicine Disclosures Research grants McNeil Consumer Healthcare (Acetaminophen) Rare Disease Therapeutics
European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE. Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam
 European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam 4.2 Posology and method of administration Unless otherwise prescribed by the physician, the following dosages
European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam 4.2 Posology and method of administration Unless otherwise prescribed by the physician, the following dosages
Drug & Alcohol Detox:
 Drug & Alcohol Detox: Beginning Stages of Addiction Treatment If you ve tried to detox on your own and failed, you are not alone. The good news is that research shows those who commit to a rehabilitation
Drug & Alcohol Detox: Beginning Stages of Addiction Treatment If you ve tried to detox on your own and failed, you are not alone. The good news is that research shows those who commit to a rehabilitation
Psychosocial Assessment
 Florida Department of Corrections Substance Abuse Program Services Psychosocial Assessment General Information: Inmate Name: DC #: Age: Gender: Race: DOB: Last City of Residence: Length of Sentence: Referred
Florida Department of Corrections Substance Abuse Program Services Psychosocial Assessment General Information: Inmate Name: DC #: Age: Gender: Race: DOB: Last City of Residence: Length of Sentence: Referred
