BASIC VOLUME. Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
|
|
|
- Shona Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
2 BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE 3 Principles of CBT and relapse prevention strategies Biology of drug dependence Addiction and the brain Principles of drug dependence treatment and care Basic counselling skills for drug dependence treatment Special considerations when involving families in drug dependence treatment Principles of motivational interviewing Introduction to Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Basics of pharmacological treatment
3 MODULE 1 DRUG DEPENDENCE CONCEPT AND PRINCIPLES OF DRUG TREATMENT
4 Module 1 Training goals Increase knowledge about narcotics and psychoactive substances Understand the mechanisms leading to the vulnerability to start using drugs and develop drug dependence Learn about the reasons why people use drugs Increase knowledge of the biology of drug dependence Learn about the principles of drug dependence treatment and care 4
5 Module 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment Biology of drug dependence Addiction and the brain Principles of drug dependence treatment and care
6 Pre-assessment
7 Icebreaker
8 Icebreaker Please share some or all of the following information with your group (if you don t feel comfortable, then you may pass): a) My name is. b) My family is originally from. c) I am currently living in. d) I am a student at ; a volunteer at ; or work for. e) I became interested in my field because. f) The thing I like most about what I do is. g) I am attending this training because. 8
9 Workshop 1 Biology of drug dependence
10 Training objectives At the end of this workshop you will be able to: Understand characteristics and effects of major classes of psychoactive substances Identify the main defining characteristics of drug dependence and addiction 10
11 Introduction to psychoactive drugs
12 What are psychoactive drugs? Any chemical substance which, when taken into the body, alters its function physically and/ or psychologically... World Health Organization, 1989 Any substance people consider to be a drug, with the understanding that this will change from culture to culture and from time to time. Krivanek,
13 What are psychoactive drugs? Psychoactive drugs interact with the central nervous system (CNS) affecting: Mental processes and behaviour Perceptions of reality Level of alertness, response time and perception of the world 13
14 Why do people initiate drug use? There is a believe that drug use is motivated (at least initially) by the pursuit of pleasure. However, according to scientific evidence, there are factors such as exposure to abuse, neglect, violence, etc., especially in childhood, leading to vulnerabilities to initiate drug use. 14
15 Why do people initiate drug use? Drug use INITIATION starts through: Vulnerability conditions due to abuse, violence and neglect in early childhood Exposure to abuse, neglect and violence in early childhood Peer pressure Personality disorder Comorbid psychiatric disorder Experimental use Key MOTIVATORS & conditioning factors: Stress/pain amelioration Functional (purposeful) Fun (pleasure) Psychiatric disorders Social/educational disadvantages 15
16 Why do people continue drug use? After repeated drug use, deciding to use drugs is no longer voluntary because DRUGS AFFECT THE BRAIN! 16
17 What is drug addiction? Drug addiction is a complex illness characterised by compulsive and at times, uncontrollable drug craving, seeking, and use that persist even in the face of extremely negative consequences. (NIDA, 1999) Substance dependence is not a failure of will or of strength of character but a medical disorder that could affect any human being. Dependence is a chronic and relapsing disorder, often co-occurring with other physical and mental conditions" (WHO, 2004) 17
18 Characteristics of drug addiction Compulsive behaviour Behaviour is reinforcing (rewarding or pleasurable) Loss of control in limiting intake 18
19 Important terminology Psychological craving Tolerance Withdrawal symptoms 19
20 Psychological craving Craving refers to the desire or urge to re-experience the effect of a previously experienced psychoactive substance It is often described as the subjective experience (psychological) of the motivational state that increases the likelihood of drug use (although it is not directly responsible for it) Cravings are most apparent during drug withdrawal and when exposed to triggers 20
21 Psychological craving Craving can also be described as the conscious/subjective experience of the following: Feelings of urge Physical/physiological sensations (heart rate increase, perspiration, etc.) Actual temptation Uncontrollable thoughts 21
22 Psychological craving features Craving tends to be highly associated with the context Triggers are stimuli previously associated with drug use: people places paraphernalia money certain days of the week, etc. Craving can persist far beyond the cessation of drug use 22
23 Psychological craving Psychological craving is a complex phenomenon Craving report and drug use is not as tightly related as initially thought Craving report and cue reactivity (heart rate, sweatgland activity, blood pressure, temperature, etc.) don t show a systematic co-variation among studies More research is needed to clarify this complex phenomenon in order to improve treatment programs 23
24 Tolerance Tolerance is a state in which a person no longer gets the expected responses from a drug as it was experienced before. A higher dose is now required to achieve the same effect. 24
25 Withdrawal symptoms Physiological reactions that occur when after a period of using a drug this habit is discontinued. The reaction could be mild e.g., tobacco to life threatening e.g., alcohol. 25
26 Withdrawal symptoms The following symptoms may occur when drug use is reduced or discontinued: Tremors, chills Cramps Emotional problems Cognitive and attention deficits Hallucinations Convulsions Death 26
27 DSM-5 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM 5: American Psychiatric Association made changes to the DSM Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders SUD defined: SUD is defined a problematic pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress as manifested by at least two criteria occurring in a 12-month period 27
28 WHO ICD-10 Substance Use Disorders: Harmful Use and Dependence Syndrome 28
29 Drug categories
30 Classifying psychoactive drugs The following classification is based on the psychoactive effects of drugs. It is intended as a general guide to better understand relative drug effects, harms and potential withdrawal features. Psychoactive drugs DEPRESSANTS STIMULANTS HALLUCINOGENS Variations in effects and intensity for drugs in the same category may occur for drugs within the same class. 30
31 Classifying psychoactive drugs Depressants Slow down the CNS and body functions, such as heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, etc. and behaviour e.g., slow/uncoordinated movements, slurred speech, etc. Stimulants Hallucinogens Speed up the CNS and body functions. It can be noticed on mood happy, excited, euphoria; cognitive performance better concentration, increased alertness; and behaviour insomnia, fast movements/speech, etc. Alter states of perception and feelings, there are 3 types. Psychedelics: feeling new ways of relating with their inner mind. Dissociative: feelings of being separated from one s body and environment. Delirants: confusional state and problems to focus attention. 31
32 Classifying psychoactive drugs Depressants Stimulants Hallucinogens Alcohol (high doses) Alcohol (low doses) LSD, DMT Benzodiazepines Amphetamines Mescaline Opioids Methamphetamine PCP Solvents Cocaine Ketamine Barbiturates Nicotine Cannabis (high doses) Cannabis (low doses) Khat Magic mushrooms MDMA MDMA 32
33 Alcohol
34 Alcohol: basic facts Description Alcohol or ethylalcohol (ethanol) is present in varying amounts in beer, wine, and liquors Route of administration Oral Acute psychological effects Sedation, euphoria, slowed reaction time, impaired coordination Acute physiological effects Lower heart rate and respiration, coma, death 34
35 Alcohol: basic facts Withdrawal Symptoms: Tremors, chills Cramps Hallucinations Convulsions Delirium tremens Death 35
36 Long-term effects of regular use/abuse of alcohol Decrease in blood cells leading to anaemia, slowhealing wounds and other diseases Brain damage, loss of memory, blackouts, poor vision, slurred speech, and decreased motor control Increased risk of high blood pressure, hardening of arteries, and heart disease 36
37 Long-term effects of regular use/abuse of alcohol Liver cirrhosis, jaundice, and diabetes Immune system dysfunction Stomach ulcers, haemorrhaging, and gastritis Thiamine (and other) deficiencies Testicular and ovarian atrophy Harm to a foetus during pregnancy Increased risk for different types of cancer 37
38 Tobacco
39 Tobacco: basic facts Description Tobacco products contain nicotine plus more than 4,000 chemicals and a dozen gases (mainly carbon monoxide) Route of administration Smoking, chewing Acute psychological effects Relaxation, pleasure, increased concentration Acute physiological effects Release of glucose, increased blood pressure, respiration and heart rate 39
40 Tobacco: basic facts Withdrawal symptoms: Cognitive/attention deficits Sleep disturbance Increased appetite Hostility Irritability Low energy Headaches 40
41 Long-term effects of tobacco use Aneurysm Cataracts Cancer (lung and other types) Obstructive pulmonary diseases Heart disease (stroke, heart attack) Vascular disease Chronic bronchitis Emphysema Asthma symptoms Harm to a foetus during pregnancy, low weight at birth 41
42 Break
43 Cannabis
44 Cannabis: basic facts Description The active ingredient in cannabis is delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Marijuana: Tops and leaves of the plant Cannabis sativa Hashish: More concentrated resinous form of the plant Route of administration Smoked as a cigarette or in a pipe Oral, brewed as a tea or mixed with food 44
45 Let s think! What are the names for marijuana in your community? How is this drug is consumed? 45
46 Cannabis: basic facts Acute PHYSIOLOGICAL effects: Increased heart rate and blood pressure Increased appetite Dry mouth Bloodshot eyes Reduced nausea Acute PSYCHOLOGICAL effects: Altered time sense Mood changes Impaired short-term memory Reduced cognitive capacity (e.g. judgment, attention) Paranoid ideation/psychotic episodes Impairs coordination and balance 46
47 Cannabis: basic facts Withdrawal Symptoms: Insomnia Restlessness Loss of appetite Irritability Sweating Tremors Nausea Diarrhoea 47
48 Long-term effects of cannabis use Long-term effects of cannabis use: Increase in activation of stress-response system Amotivational syndrome Changes in neurotransmitter levels Psychosis in vulnerable individuals Increased risk for cancer, especially lung, head and neck Respiratory illnesses (cough, phlegm) and lung infections Immune system dysfunction Harm to a foetus during pregnancy 48
49 Stimulants, ATS and cocaine
50 Types of stimulants Amphetamine Type Stimulants (ATS): Methamphetamine Speed, crystal, ice, yaba, shabu Amphetamine Pharmaceutical products used for ADD and ADHD Methamphetamine half-life: 8-10 hours. 50
51 Types of stimulants Cocaine Powder cocaine (Hydrochloride salt) Smokeable cocaine Crack Rock Freebase Cocaine half-life: 1-2 hours. 51
52 Let s think! What stimulants are used in your community and how are they consumed? 52
53 Stimulants: basic facts Description Stimulants increase alertness and arousal by stimulating the central nervous system. They include: A group of synthetic drugs (ATS) Plant-derived compounds (cocaine) Route of administration Smoked, injected, snorted or administered by mouth or rectum 53
54 Stimulants: basic facts Acute PSYCHOLOGICAL effects: Euphoria, rush or flash Wakefulness, insomnia Irritability Anxiety Paranoia Aggressiveness Acute PHYSIOLOGICAL effects: Decreased appetite Increased respiration Increased physical activity Hyperthermia Tremors, convulsions 54
55 Stimulants: basic facts Withdrawal symptoms: Dysphoric mood (sadness, anhedonia) Fatigue Insomnia or hypersomnia Psychomotor agitation or retardation Craving Increased appetite Vivid, unpleasant dreams 55
56 Long-term effects of stimulants Strokes, seizures, headaches Depression, anxiety, irritability, anger Memory loss, confusion, attention problems Insomnia, hypersomnia, fatigue Paranoia, hallucinations, panic reactions Suicidal ideation 56
57 Long-term effects of stimulants Nosebleeds, chronic runny nose, hoarseness, sinus infection Dry mouth, burned lips, worn teeth Chest pain, cough, respiratory failure Disturbances in heart rhythm and heart attack Loss of libido Weight loss, anorexia, malnourishment Skin problems 57
58 Methamphetamine use 58
59 Methamphetamine use Serious and permanent scars caused by scratching in a Methamphetamine user 59
60 Methamphetamine use Scars from infected injection sites are often referred to as tracks 60
61 Methamphetamine use Methamphetamine use leads to severe tooth decay Meth Mouth 61
62 Opioids
63 Opioids Buprenorphine Codeine Heroin Hydrocodone Methadone Morphine Opium Oxycodone Thebaine Tramadol 63
64 Opioids: basic facts Description Opium-derived or synthetic compounds that relieve pain, produce morphine-like addiction, or relieve symptoms during withdrawal from morphine addiction. Route of administration Intravenous, smoked, chased, intranasal, oral and intrarectal. 64
65 Opioids: basic facts Acute PSYCHOLOGICAL effects: Euphoria Pain relief Sense of well-being Acute PHYSIOLOGICAL effects: Suppresses cough reflex Histamine release Warm flushing of the skin Dry mouth Drowsiness and lethargy Depression of the central nervous system (mental functioning clouded) 65
66 Opioids: basic facts Withdrawal symptoms: Intensity of withdrawal varies with level and chronicity of use Cessation of opioids causes a rebound in functions depressed by chronic use Withdrawal symptoms usually start a few hours after the last dose* For short-acting opioids (e.g., heroin), major withdrawal symptoms peak between 24 to 48 hours after the last dose Acute symptoms subside over 3 to 7 days Ongoing symptoms may linger for weeks or months 66
67 Long-term effects of opioids Not easy reversible changes in the physical structure and physiology of the brain Fatal overdose Collapsed veins (intravenous) Infectious diseases (intravenous) Higher risk of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis Infection of the heart lining and valves 67
68 Long-term effects of opioids Pulmonary complications & pneumonia Respiratory problems Abscesses Liver disease Low birth weight and developmental delay Spontaneous abortion Cellulitis 68
69 Other drugs Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Club drugs (MDMA-ecstasy, GHB, poppers, etc.) Hallucinogens (LSD, mushrooms, PCP, ketamine) Hypnotics (quaaludes, mandrax) Inhalants petroleum products, glue, paint, paint removers aerosols, sprays, gases, amyl nitrite Khat (Catha edulis) Steroids 69
70 Let s discuss! What drugs are consumed in your area? How are they consumed both by youth and adults? 70
71 Questions
72 Wrap-up Why people start using drugs? What are the 3 main defining characteristics of drug addiction? What are the major types of psychoactive substances?
73 Thank you for your time! End of workshop 1
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use
 Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Live A Life Above The Influence!
 Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Main Questions. Why study addiction? Substance Use Disorders, Part 1 Alecia Schweinsburg, MA Abnromal Psychology, Fall Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Activation-synthesis hypothesis. compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences. Addition. Amphetamines. Barbiturates.
 Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
CARD TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff
 CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
Defining Drugs. Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions
 Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996)
 APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
4 CATEGORIES. Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs
 DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. RG 5c
 PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children. Jackie McReynolds Washington State University
 Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes.
 Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs
 Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Substance Use Disorders. A Major Problem. Defining Addiction 2/24/2009. Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 %
 Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29
 PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
Please review the following slides prior to class. Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared!
 Please review the following slides prior to class Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared! Alcohol and Opiate Dependence Reference Slides Substances of Abuse A
Please review the following slides prior to class Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared! Alcohol and Opiate Dependence Reference Slides Substances of Abuse A
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER:
 NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
States of Consciousness
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs. Alcohol
 XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
Module II Opioids 101 Opiate Opioid
 BUPRENORPHINE TREATMENT: A TRAINING FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY ADDICTION PROFESSIONALS Module II Opioids 101 Module II Goals of the Module This module reviews the following:! Opioid addiction and the brain!
BUPRENORPHINE TREATMENT: A TRAINING FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY ADDICTION PROFESSIONALS Module II Opioids 101 Module II Goals of the Module This module reviews the following:! Opioid addiction and the brain!
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information
 Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
The causes of misuse:
 The Drug Misuse The causes of misuse: Availability of drugs. A vulnerable personality. Adverse social environment. Regular drug taking play a role. Determining misuse and dependence, it is unclear whether
The Drug Misuse The causes of misuse: Availability of drugs. A vulnerable personality. Adverse social environment. Regular drug taking play a role. Determining misuse and dependence, it is unclear whether
Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs
 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders
 Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
Alcohol. Fits Hallucinations. Hallucinations Brain damage. Cirrhosis Gastritis. Diabetes Vomiting blood
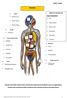 Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
Cocaine. How Is Cocaine Abused? How Does Cocaine Affect the Brain?
 Cocaine Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant drug. The powdered hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and then injected. Crack is the street name given to the form
Cocaine Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant drug. The powdered hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and then injected. Crack is the street name given to the form
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2)
 Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Drug abuse: Drug misuse Dependence abuse
 Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS
 CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Cannabis 101 What is cannabis? Cannabis is a product derived from the Cannabis sativa plant. Cannabis contains hundreds
CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Cannabis 101 What is cannabis? Cannabis is a product derived from the Cannabis sativa plant. Cannabis contains hundreds
People inject, sniff, snort, or smoke heroin. Some people mix heroin with crack cocaine, a practice called speedballing.
 What is heroin? Heroin is an opioid drug made from morphine, a natural substance taken from the seed pod of the various opium poppy plants grown in Southeast and Southwest Asia, Mexico, and Colombia. Heroin
What is heroin? Heroin is an opioid drug made from morphine, a natural substance taken from the seed pod of the various opium poppy plants grown in Southeast and Southwest Asia, Mexico, and Colombia. Heroin
Drug Abuse in America. the United States in Now days there is a lot of help to prevent drug use, like anti drug
 1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
Chapter 23. Medicines and Drugs
 Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS
 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
Drugs and the School Aged Child. Objectives. Substance Abuse. Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN. n List signs of drug use in children
 Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
Current Drug Trends Among Youth. Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol
 Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Co-Occurring Disorders & Drug Addiction Basics: Identifying, Listening & Linking
 Co-Occurring Disorders & Drug Addiction Basics: Identifying, Listening & Linking Sherry Larkins, Ph.D UCLA Integrated Substance Abuse Program June 24, 2011 1 Roadmap Overview of Co-Occurring Disorders
Co-Occurring Disorders & Drug Addiction Basics: Identifying, Listening & Linking Sherry Larkins, Ph.D UCLA Integrated Substance Abuse Program June 24, 2011 1 Roadmap Overview of Co-Occurring Disorders
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT
 ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
NIDA s Drug Health Effects
 NIDA s Drug Cannabis (Marijuana) Greenish-gray mixture of the dried, shredded leaves, stems, seeds, and/or flowers of Cannabis sativa or cannabis indica the hemp plant Heightened sensory perception; euphoria,
NIDA s Drug Cannabis (Marijuana) Greenish-gray mixture of the dried, shredded leaves, stems, seeds, and/or flowers of Cannabis sativa or cannabis indica the hemp plant Heightened sensory perception; euphoria,
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES
 DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
Research Paper 21/08/
 Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens
 Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens 2 Abuse Facts The fourth most commonly misused type of addictive substance among teens in the United States is controlled prescription drugs The likelihood of misusing
Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens 2 Abuse Facts The fourth most commonly misused type of addictive substance among teens in the United States is controlled prescription drugs The likelihood of misusing
Substance Misuse and Abuse
 CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
*IN10 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT*
 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
Knowing Your Drugs. Drugs Defined. Substance Abuse. Substance Abuse: Substance Abuse: Stage One. Substance Abuse: Stage Three
 Knowing Your Drugs Drugs Defined Anything other than food that effects the way your mind and body operates. Breakout Session John Gardner, Captain Travelers Rest Police Department, SC Abuse Defined: The
Knowing Your Drugs Drugs Defined Anything other than food that effects the way your mind and body operates. Breakout Session John Gardner, Captain Travelers Rest Police Department, SC Abuse Defined: The
CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND
 Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They?
 Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They? Yngvild Olsen, MD, MPH Cecil County Board of Health Workgroup Meeting Elkton, MD October 8, 2013 Objectives
Medications in the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: Methadone and Buprenorphine What Really Are They? Yngvild Olsen, MD, MPH Cecil County Board of Health Workgroup Meeting Elkton, MD October 8, 2013 Objectives
Substance Abuse. Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances.
 Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE
 DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1
 Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
Analgesia for Patients with Substance Abuse Disorders. Lisa Jennings CN November 2015
 Analgesia for Patients with Substance Abuse Disorders Lisa Jennings CN November 2015 Definitions n Addiction: A pattern of drug use characterised by aberrant drug-taking behaviours & the compulsive use
Analgesia for Patients with Substance Abuse Disorders Lisa Jennings CN November 2015 Definitions n Addiction: A pattern of drug use characterised by aberrant drug-taking behaviours & the compulsive use
Table of Contents VOLUME 1
 VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
Drug and Alcohol Impairment. Alabama DRE / SFST Program
 Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
A Prescription for Education. Hillary Dubois, Director of Prevention Services Amanda Sandoval, Asst. Director of Prevention Services
 A Prescription for Education Hillary Dubois, Director of Prevention Services Amanda Sandoval, Asst. Director of Prevention Services Addiction Release of abnormally large amounts of neurotransmitters, mainly
A Prescription for Education Hillary Dubois, Director of Prevention Services Amanda Sandoval, Asst. Director of Prevention Services Addiction Release of abnormally large amounts of neurotransmitters, mainly
Substances under Surveillance
 Substances under Surveillance The following substances are under surveillance by the World Health Organization (WHO) as they are considered to have the potential to cause public health harm. For ease of
Substances under Surveillance The following substances are under surveillance by the World Health Organization (WHO) as they are considered to have the potential to cause public health harm. For ease of
The Art of being Human
 Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Consumer Information Cannabis (Marihuana, marijuana)
 Consumer Information Cannabis (Marihuana, marijuana) The courts in Canada have ruled that the federal government must provide reasonable access to a legal source of marijuana for medical purposes. The
Consumer Information Cannabis (Marihuana, marijuana) The courts in Canada have ruled that the federal government must provide reasonable access to a legal source of marijuana for medical purposes. The
Drugs and the Brain. Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso
 Drugs and the Brain Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso What are drugs? DRUG: any substance which, when ingested in relatively small amounts, induces a physiological change LD50 lethal dose 50% = dose
Drugs and the Brain Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso What are drugs? DRUG: any substance which, when ingested in relatively small amounts, induces a physiological change LD50 lethal dose 50% = dose
BASIC VOLUME. Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
 BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment Module 3 Principles of CBT and relapse prevention strategies Introduction to Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Basics of pharmacological treatment Workshop
BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment Module 3 Principles of CBT and relapse prevention strategies Introduction to Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Basics of pharmacological treatment Workshop
Understanding Addiction: Why Can t Those Affected Just Say No?
 Understanding Addiction: Why Can t Those Affected Just Say No? 1 The Stigma of Addiction There continues to be a stigma surrounding addiction even among health care workers. Consider the negative opinions
Understanding Addiction: Why Can t Those Affected Just Say No? 1 The Stigma of Addiction There continues to be a stigma surrounding addiction even among health care workers. Consider the negative opinions
Observations of Drug Impaired Drivers. Winona County Deputy Chad Myers DRE/SFST Instructor Law Enforcement Phlebotomist Winona Co.
 Observations of Drug Impaired Drivers Winona County Deputy Chad Myers DRE/SFST Instructor Law Enforcement Phlebotomist Winona Co. TZD Coordinator How do I know it is drugs??? Do not have to be a DRE to
Observations of Drug Impaired Drivers Winona County Deputy Chad Myers DRE/SFST Instructor Law Enforcement Phlebotomist Winona Co. TZD Coordinator How do I know it is drugs??? Do not have to be a DRE to
Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy
 Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy Robert Davis, MD / r.w.davismd@gmail.com ❶ Statistics ❷ Pregnancy Concerns ❸ Postpartum Concerns ❹ Basic Science ❺ Best Practice Guidelines ❻ Withdrawal ❼ Recovery
Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy Robert Davis, MD / r.w.davismd@gmail.com ❶ Statistics ❷ Pregnancy Concerns ❸ Postpartum Concerns ❹ Basic Science ❺ Best Practice Guidelines ❻ Withdrawal ❼ Recovery
Drugs. Cocaine is most commonly found in powder form and is snorted. Cocaine is a drug derived from the coca plant.
 SECTION: COCAINE AND CRACK Overview Cocaine is a stimulant and is extremely addictive. Cocaine is most commonly found in powder form and is snorted. Cocaine is a drug derived from the coca plant. Crack
SECTION: COCAINE AND CRACK Overview Cocaine is a stimulant and is extremely addictive. Cocaine is most commonly found in powder form and is snorted. Cocaine is a drug derived from the coca plant. Crack
Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement
 Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement You and your provider have agreed on the use of controlled substance medications to treat your: We want to make sure you know how to manage your new prescription(s)
Controlled Substance and Wellness Agreement You and your provider have agreed on the use of controlled substance medications to treat your: We want to make sure you know how to manage your new prescription(s)
Heroin. What is heroin?
 What is heroin? Heroin Heroin is an opioid drug made from morphine, a natural substance taken from the seed pod of the Asian opium poppy plant. Heroin can be a white or brown powder, or a black sticky
What is heroin? Heroin Heroin is an opioid drug made from morphine, a natural substance taken from the seed pod of the Asian opium poppy plant. Heroin can be a white or brown powder, or a black sticky
(consciousness) (monitor) (control)
 : (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
: (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
CANAM INTERVENTIONS. Addiction
 CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
COMPETENCY. Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel. Wednesday, January 14, 2015
 COMPETENCY Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel Wednesday, January 14, 2015 Extent of the Problem Substantial percentage of the population will be substance abusers
COMPETENCY Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel Wednesday, January 14, 2015 Extent of the Problem Substantial percentage of the population will be substance abusers
A substance that reduces pain and may or may not have psychoactive properties.
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS AMPHETAMINE-TYPE STIMULANTS (ATS) A group of substances, mostly synthetic, with closely related chemical structure which have, to varying degrees, a stimulating effect on the central
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AMPHETAMINE-TYPE STIMULANTS (ATS) A group of substances, mostly synthetic, with closely related chemical structure which have, to varying degrees, a stimulating effect on the central
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Tobacco Notes. An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums)
 Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
What parents need to know about drugs
 What parents need to know about drugs Most commonly used drugs and their effects For many people, the term drug tends to suggest illegal activity. However, the use of tobacco and alcohol is legal for people
What parents need to know about drugs Most commonly used drugs and their effects For many people, the term drug tends to suggest illegal activity. However, the use of tobacco and alcohol is legal for people
CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT AMERICAN INDIAN... 20
 CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT... 10 AMERICAN INDIAN... 20 ASIAN OR ASIAN-AMERICAN Chinese... 30 (East) Indian... 31 Filipino... 32 Japanese... 33 Other (Specify):... 34 BLACK African American... 40
CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT... 10 AMERICAN INDIAN... 20 ASIAN OR ASIAN-AMERICAN Chinese... 30 (East) Indian... 31 Filipino... 32 Japanese... 33 Other (Specify):... 34 BLACK African American... 40
Drug & Alcohol Detox:
 Drug & Alcohol Detox: Beginning Stages of Addiction Treatment If you ve tried to detox on your own and failed, you are not alone. The good news is that research shows those who commit to a rehabilitation
Drug & Alcohol Detox: Beginning Stages of Addiction Treatment If you ve tried to detox on your own and failed, you are not alone. The good news is that research shows those who commit to a rehabilitation
Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies
 CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
What is pregabalin? Pregabalin tablets. Pregabalin misuse. National Drug Treatment Centre Research. Administration
 What is pregabalin? Pregabalin is a prescription drug used to manage a number of long-term conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain and generalised anxiety disorder. Similar to benzodiazepines,
What is pregabalin? Pregabalin is a prescription drug used to manage a number of long-term conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain and generalised anxiety disorder. Similar to benzodiazepines,
A. Definition and Categories of Drugs Instructor Led Presentations B. Incidence and Characteristics of Reading Assignments
 Briefly review the objectives, content and activities of this session. Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Define the term drug in the context of this course. Name the seven
Briefly review the objectives, content and activities of this session. Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Define the term drug in the context of this course. Name the seven
THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES. Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM
 THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM DrSteve@DrSteveAlbrecht.com 866-261-5150 @DrSteveAlbrecht REALITY IS NOT A RIVER IN EGYPT... Some Caveats... I m not
THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM DrSteve@DrSteveAlbrecht.com 866-261-5150 @DrSteveAlbrecht REALITY IS NOT A RIVER IN EGYPT... Some Caveats... I m not
Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI
 Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI Psychoactive drugs created to avoid existing laws Modify existing drugs or new drugs with different chemical structures >200 new drugs and 8 classes of drugs since 2009 80 new
Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI Psychoactive drugs created to avoid existing laws Modify existing drugs or new drugs with different chemical structures >200 new drugs and 8 classes of drugs since 2009 80 new
Peripheral Nervous System
 Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
The Dangers of Methamphetamine Abuse
 METH ABUSE Methamphetamine is often referred to as meth, speed, crank, crystal, glass and ice. Depending on the chemical composition, methamphetamine can look like shredded glass pieces or ice. Colors
METH ABUSE Methamphetamine is often referred to as meth, speed, crank, crystal, glass and ice. Depending on the chemical composition, methamphetamine can look like shredded glass pieces or ice. Colors
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern. Chapter 12
 Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders
 SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
ADA PRESENTATION CATHERINE AMULUNDU CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST. University of Nairobi ISO 9001: Certified
 ADA PRESENTATION CATHERINE AMULUNDU CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST University of Nairobi ISO 9001:2008 1 Certified http://www.uonbi.ac.ke Drugs & Substance Abuse OBJECTIVES Help the participants understand the
ADA PRESENTATION CATHERINE AMULUNDU CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST University of Nairobi ISO 9001:2008 1 Certified http://www.uonbi.ac.ke Drugs & Substance Abuse OBJECTIVES Help the participants understand the
Unit II Problem 7 Pharmacology: Substance Abuse, Dependence and Addiction
 Unit II Problem 7 Pharmacology: Substance Abuse, Dependence and Addiction Drugs are classified as being Used (medically approved) abused (medically NOT approved) - What is the difference between dependence
Unit II Problem 7 Pharmacology: Substance Abuse, Dependence and Addiction Drugs are classified as being Used (medically approved) abused (medically NOT approved) - What is the difference between dependence
A look at Marijuana in 2014
 A look at Marijuana in 2014 Paul Snyder MA., LADC Overview and Objectives Discuss the mental and physical effects of marijuana use Describe the criteria for Cannabis use disorder according to the DSM 5
A look at Marijuana in 2014 Paul Snyder MA., LADC Overview and Objectives Discuss the mental and physical effects of marijuana use Describe the criteria for Cannabis use disorder according to the DSM 5
6800$5< /,)(7,0( ',$*126(6 &+(&./,67 'DWH RI &XUUHQW BBBB BBBB BBBBBB
 Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
A handful of dangerous new legal drugs has public health experts worried
 Page 1 of 8 A handful of dangerous new legal drugs has public health experts worried MATTHEW SPEISER AUG. 11, 2015, 5:00 PM Over the past 20 years, the drug world has seen the rise of new psychoactive
Page 1 of 8 A handful of dangerous new legal drugs has public health experts worried MATTHEW SPEISER AUG. 11, 2015, 5:00 PM Over the past 20 years, the drug world has seen the rise of new psychoactive
1 STUDYING THE STUDY DRUG: ADDERALL. iaddiction.com
 1 STUDYING THE STUDY DRUG: ADDERALL Societal Impact of the Drug A stimulant often prescribed for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, Adderall has become a drug of choice for
1 STUDYING THE STUDY DRUG: ADDERALL Societal Impact of the Drug A stimulant often prescribed for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, Adderall has become a drug of choice for
DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES
 DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES In compliance with the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for
DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES In compliance with the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for
