A Systematic Approach to Medical Liver Disease
|
|
|
- Shanna Glenn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Systematic Approach to Medical Liver Disease Laura W. Lamps, M.D. Godfrey D. Stobbe Professor and Director of Gastrointestinal Pathology University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI Why do people fear medical liver? Limited number of responses to an infinite number of insults; i.e., many different processes can look alike Morphology is only a single static picture of a dynamic physiologic process Integration with clinical and pathologic data is essential for accurate diagnosis So what are we trying to do, as pathologists? Translate morphologic abnormalities into useful clinical/management data Diagnosis vs. description Management/workup suggestions even if there is no definite diagnosis Give grading/staging info when appropriate 1
2 Understanding the Normal Liver Normal Lobule Liver The Zones Zone 1 Periportal Zone 2 Intermediate (midlobular zone) Zone 3 Centrilobular zone 2
3 2 3 1 Normal Portal Tracts BD HA P Portal vein Hepatic artery Bile duct (interlobular) Lymphatic channels Chronic inflammation Some degree of chronic portal inflammation is normal! Liver Portal Tracts BD Bile Ducts Arterioles accompanied by bile duct 70-93% of time Connected to bile canaliculi by bile ductules and canals of Hering ductules Bile Ductules Found at periphery of portal tracts Ductular reaction is nonspecific response to various processes Often accompanied by neutrophils, also nonspecific 3
4 Hepatic arteriole without duct Normal hepatocytes Sinusoids 4
5 Kupffer cells Ito or stellate cells Normal reticulin framework 5
6 Age Variation Kids Hepatic plates two cells thick Glycogenated nuclei common Extramedullary hematopoiesis (infants) Iron and copper present (infants) Elderly people More striking variation in size of hepatocytes Lipofuscin Larger, more densely fibrotic portal tracts Size variation in older age EMH in infant Lipofuscin -Granular -Zone 3 This is not bile. 6
7 A systematic approach to the liver biopsy My Systematic Approach View slides without history or lab data first Construct a systematic approach that works for you Zone 1 to 3 or 3 to 1 Decide if you need additional stains Construct a morphologic diagnosis Correlate with clinical and lab data Advance or retreat Systematic Approach to Liver Bx Low power Adequacy Overall architecture Lesions Overall inflammatory pattern Fibrosis Higher Power Portal Tracts Size, inflammation, fibrosis, interface activity Bile ducts: are they there, damage, inflammation Lobule Inflammation, cholestasis, fibrosis Don t forget the Kupffer cells and Ito cells Higher power, cont. Hepatocytes Necrosis, reactive changes, accumulations, degeneration Sinusoids Width, congestion, Ito cells, deposits Vessels Inflammation, occlusion, thickening, fibrosis, abnormal morphology 7
8 Basic Classification Liver biopsy Hepatocyte injury predominant Biliary Other Assess Pattern Chronic Not chronic Metabolic, storage Vascular Lobular Portal SH General patterns of hepatitis and associations Portal/periportal Chronic Viral Drug Autoimmune Early biliary disease Lobular Drug Acute viral Autoimmune Nonspecific reactive Cholestatic Drug LDO Granulomatous PBC Infection Sarcoid Drug Unknown Steatohepatitis Alcohol, diabetes, drug, obesity Necrosis predominant Toxin/drug Infection Ischemia/shock Other (non-hepatitis) patterns to recognize Pure cholestasis Drug Systemic illness (sepsis) Storage/metabolic A1AT Glycogen Pigments Iron Copper Vascular abnormalities Outflow obstruction NRH Bile duct injury PBC PSC LDO 8
9 A word about adequacy Depends on the goal: tumor vs. inflammatory liver disease Adequate is however much it takes to make a diagnosis Medical liver: diffuse vs. patchy disease Poor histology/biopsy quality are as or more important than size Crush, fragmentation, sponges really hurt Pathologist must know limitations and communicate them A word about adequacy 1.5cm is considered adequate by some; 2.5cm for medical liver disease by others At least 4 portal tracts for medical liver (some authorities say 11) Wedge-make sure it s more than 1.5cm in depth to avoid subcapsular artifact Subcapsular artifact 9
10 Confirm clinical diagnosis Role of Liver Biopsy in Medical Liver Disease Case 1 32 year old Caucasian man Elevated transaminases on routine physical: AST 56, ALT 102 other liver tests normal History of IV drug use, needle sticks in job as LPN Fatigue but no other symptoms 10
11 11
12 Diagnosis Chronic hepatitis C (antibody/pcr confirmatory) Grade 2-3 Stage 3 Confirm clinical diagnosis Grade and stage (if appropriate) Role of Liver Biopsy in Medical Liver Disease 12
13 Why Grade/Stage? Decide whom to treat* Prognosis 50-80% of HCV patients develop chronic infection Of those, 5-20% progress to cirrhosis Risk factors for progression: Male Older than 40 Drink more than 50g alcohol/day High grade or stage on liver biopsy *Everything has changed with the direct acting antivirals. Why Grade/Stage? Direct acting anti-virals (e.g., Harvoni) Improved rates of SVR and now CURE Effective for all genotypes Minimal toxicity It s crazy expensive (~$95,000 for 12 week course) Histologic criteria for treatment that will be covered by insurance Numerical fibrosis score (Metavir), varies by state Grading-hepatitis* Hepatocyte injury/inflammation=activity Portal inflammation Interface hepatitis (formerly piecemeal necrosis); inflammation and hepatocyte dropout at the limiting plate Lobular inflammation (or spotty necrosis) Necrosis (confluent or lobular) *The following discussion pertains to viral hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis, but not fatty liver disease 13
14 Grading-Descriptive Mild less than half of portal tracts with limiting plate activity; minimal lobular activity Moderate more than half of portal tracts with limiting plate activity; more significant lobular activity Severe bridging necrosis, collapse, really striking inflammatory infiltrate everywhere Batts/Ludwig scoring system 1 (minimal) 2 (mild) 3 (moderate) 4 (marked) Batts KP, Ludwig J. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19(12): Grade 1 Minimal 14
15 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 2 15
16 Grade 3/moderate Grade 3/moderate Grade 4/severe 16
17 Staging Amount of fibrous scarring Portal tract expansion Extension of fibrous tissue beyond usual boundaries of portal tract (periportal) Formation of fibrous septa Formation of nodules Pericentral/perivenular Staging-Descriptive Mild Enlarged, irregular portal tracts Periportal borders get irregular Moderate Fibrous septa and bridging Severe Established cirrhosis Batts Ludwig Scoring System 1 (portal) 2 (periportal) 3 (septal) 4 (cirrhosis) Batts Ludwig, Scheuer and METAVIR systems very similar. 17
18 Stage 0-1 Stage 2-Periportal Stage 2-Periportal 18
19 Stage 3-bridging Stage 3-bridging Stage 4- established cirrhosis 19
20 Histology post-treatment Inflammation persists despite SVR Also true in transplanted livers Early research using non-invasive methods indicates that fibrosis can regress, even advanced fibrosis Putra J. et al. Histopathol 2017 Dec 13 Whitcomb E et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15: Chan J et al. Dig Dis Sci 2018;63: Metavir Scoring System Activity Grade 0: No activity. 1: Mild activity. 2: Moderate activity. 3: Severe activity. Fibrosis stage 0: No fibrosis. 1: Portal fibrosis without septa. 2: Portal fibrosis with few septa. 3: Numerous septa but not cirrhosis. 4: Cirrhosis. Goodman Z. J Hepatol 2007;47: Confirm clinical diagnosis Grade and stage (if appropriate) Role of Liver Biopsy in Medical Liver Disease Look for possible concomitant diseases 20
21 Common Concomitant Diagnoses Fatty liver disease/viral hepatitis Iron overload disorders/viral hepatitis/fatty liver disease HIV coinfection with viral hepatitis HBV coinfection with HCV Adverse drug reaction and anything HCV and/or FLD HCV alone Fatty Liver Disease (ALD or NAFLD) Steatosis, severity Mild to moderate* Mild, moderate, or severe Steatosis, distribution Random Zone 3 predominant Other features of steatohepatitis Absent Variable (ballooning, glycogenated nuclei) Zone 3 fibrosis Absent Variable Lipogranulomas Variable Variable *Genotype 3 has fat as a direct viral cytopathic effect Hepatitis C itself is believed to cause insulin resistance (and thus fatty liver disease) in some patients with other genotypes HCV and NAFLD 21
22 HCV and Iron A lot raises the possibility of iron storage disease, but a little does not exclude it Cirrhosis, alcoholic liver disease, NAFLD also causes of secondary iron overload HFE mutations considered independent risk factors for progression of fibrosis in HCV HCV and hemochromatosis 22
23 HCV and HIV If on HAART: HCV may be more aggressive HAART and DAA may have interactions HAART drugs may also cause steatohepatitis Untreated HCV often more severe in context of HIV as well Things that happen to immunocompromised patients Fibrosing cholestatic variant of HCV Beware neoplasms, infections, granulomas, etc. HAART therapy 23
24 Take-Home Messages HCV is an epidemic Grading/staging essential for prognosis and treatment in HCV Particularly in the age of direct acting antiviral drugs Many patients have more than one coexistent disease process I have wrestled this diagnosis to the ground. Questions? Case 2 29 year old Caucasian female Pre-op blood work prior to elective surgery Ast 58, ALT 111; all else normal ANA 1:80 High cholesterol; markedly obese; does not drink; negative viral markers 24
25 25
26 Diagnosis NASH Extensive bridging fibrosis NOTE: Up to 35% of NASH patients have positive ANA 5-10% may have positive SMA Causes of Fatty Liver Disease Alcohol Metabolic syndrome (includes DM, dysplipidemia, obesity) Gastrointestinal bypass Wilson s disease Drugs Amiodarone Methotrexate? 26
27 Sequelae of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Possible risk factor for cardiovascular disease Contributes to atherogenic dysplipidemia through proinflammatory mediators that affect endothelia Cirrhosis Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, even in noncirrhotic patients Steatosis begins in zone 3 and expands outwards Usually a mix of macro- and microvesicular steatosis 27
28 Ballooning Grading and Staging of Fatty Livers Many pathologists do not assign numerical grade or stage for fatty liver Reserved for research purposes Often institution dependent Descriptive phrases may make it easier to communicate Grading of Steatosis Brunt scheme (add up points for a score) Lobular inflammation 0: none 1: <2 foci/20x field 2: 2-4 foci 3: >4 foci Ballooning 0:none 1:few 2:many Fat 0:less than 5% 1:5-33% 2: >33-66% 3: >66% Simple person s scheme Lobular inflammation A little or a lot Ballooning It s there or it s not Fat Mild-limited to zone 3 Moderate-zones 3 and 2 Severe-panlobular 28
29 Steatofibrosis Begins with central vein sclerosis Zone 3 pericellular fibrosis (chicken-wire) Central-portal fibrous septa Cirrhosis Caveats: Some patients have periportal stellate fibrosis +/- ductular reaction Pediatric patients often don t have zone 3 pericellular fibrosis Steatofibrosis-staging Brunt scheme 1A: Delicate zone 3 perisinusoidal fibrosis 1B: Dense zone 3 perisinusoidal fibrosis 1C: Portal fibrosis only 2: Perisinusoidal and portal fibrosis 3: Bridging fibrosis 4: Cirrhosis Zone 3 pericellular fibrosis 29
30 Bridging fibrosis Cirrhosis Portal Inflammation in NASH Definitely can be present in NASH Associated with higher BMI, female gender, older age, greater insulin resistance Marker of progression in untreated patients Also common in pediatric patients Rule out other things, however Viral, autoimmune 30
31 NAFLD vs. NASH NAFLD: presence of at least 5% steatosis in the liver Much lower rate of progression, particularly if there is no inflammation NASH: more than 5% steatosis + other features Progressive May develop fibrosis and then cirrhosis These patients offered drug therapy 31
32 ALD vs. NASH Seen in both Seen almost exclusively in alcoholic liver disease Steatosis Ballooned hepatocytes Lobular inflammation Mallory bodies Sclerosing hyaline necrosis Satellitosis of neutrophils Cholestatic features Phlebosclerosis of terminal hepatic venules Megamitochondria Pericellular fibrosis EtOH Mallory-Denk bodies 32
33 Satellitosis Sclerosing hyaline necrosis 33
34 Approach to Fatty Liver Biopsies Is there fat? How much? Up to 5% is physiologic Is there steatohepatitis? Constellation of features Is there fibrosis? How much? Is there anything else? Iron Other disease processes Don t miss Wilson s disease! 34
35 Case 3 A 67 year old African-American female with history of CAD and refractory atrial fibrillation Epigastric pain and nausea. AST of 353, ALT 272, alkaline phosphatase 443, bilirubin 5.3. ANA was 1:640, but other autoimmune serologies were negative. Alpha one antitrypsin was also elevated. Viral serologies were negative. Sent home on phenergan. The next week her blood work was rechecked, and her enzymes were higher than before. She ultimately died of liver failure. 35
36 Diagnosis Amiodarone toxicity Amiodarone Effective medical therapy for atrial fibrillation Asymptomatic transaminase elevations in 25% of patients on long term therapy Symptomatic liver dysfunction reportedly in 1-3% Cirrhosis, fatal liver decompensation do occur Lewis JH et al. Hepatology 9:679-85,
37 Amiodarone hepatotoxicity Strongly tissue-bound, so lingers in the body even after drug is stopped Drug withdrawal does not guarantee prompt reversal of toxicity Can happen at any time point during therapy Common drugs that can cause steatosis/steatohepatitis Amiodarone Steroids Tamoxifen Methotrexate Nitrofurantoin Calcium channel blockers Sulfasalazine Halothane Cisplatin Acetaminophen Ibuprofen Tetracycline Oxacillin Valproic acid What is phospholipidosis? A different form of lipid accumulation due to drug binding phospholipid and inhibiting metabolism Enlarged, foamy, or granular hepatocytes EM inclusions similar to inborn disorders of phospholipid metabolism Often, but not always, co-exists with steatohepatitis 37
38 Common drugs that can cause phospholipidosis Amiodarone Amitryptyline Chloroquine Gentamycin Ketoconazole Synthetic estrogens TPN Bactrim Amiodarone hepatotoxicity-pathology Steatosis May be minimal or absent, however Hepatocyte ballooning, Mallory hyaline, satellitosis of neutrophils (pseudoalcoholic liver injury) Phospholipidosis Rarely, granulomas Lewis JH et al. Hum Pathol 21:59-67, Take-Home Messages NAFLD vs. NASH has implications for progression As well as treatment, patient perception Numerical staging more important for research than daily practice Don t miss coexistent diseases Don t miss Wilson s disease Don t forget about amiodarone 38
39 Can I have some fatty food? Please? Case 4 56 year old Caucasian female with nausea and vomiting ALT 1600, AST 900, Alk phos 300 ANA 1:1280 Multiple medications Amitriptyline, lisinopril Viral serologies negative 39
40 Diagnosis Autoimmune hepatitis Moderate to marked activity Bridging fibrosis 40
41 Autoimmune Hepatitis Unresolving autoimmune disease directed at hepatocytes Injury may be zonal or panlobular Transaminases usually markedly elevated Usually chronic presentation, but acute or fulminant presentations are recognized Usually women Autoimmune Hepatitis Lab findings Hypergammaglobulinemia ANA SMA Anti-LKM Anti-LC1 Anti-SLA/LP AMA Less than 5% of patients with apparent AIH have negative ANA and SMA, but titers vary during the course of illness [Bogdanos et al Semin Liver Dis 2009;29:241-53]. Autoimmune Hepatitis-histologoy Periportal lymphoplasmacytic inflammation May be multi or panzonal Lobular disarray Hepatocyte swelling/ballooning or feathery degeneration Necrosis Acidophil bodies Bridging necrosis with collapse Other Cholestasis Rosettes Emperipolesis 41
42 AIH 42
43 Primary biliary cholangitis/cirrhosis Women years old Elevated AMA in 90% Liver enzymes cholestatic Alk phos elevated out of proportion to transaminases Normal ERCP Natural history Progresses to biliary cirrhosis Very low risk of malignancy 43
44 PBC-histology Portal mononuclear infiltrates Lymphs, plasma cells, eosinophils Lymphocytic cholangitis Granulomas near injured ducts Minimal to mild interface and lobular activity Cholate stasis Duct destruction with ductular reaction No necrosis PBC 44
45 Cholate stasis/copper staining 45
46 PBC vs. AIH PBC AIH Plasma cells Yes Yes Interface activity +/- Yes Significant lobular activity No Yes Bridging necrosis No Often Lymphocytic cholangitis Yes +/- Granulomatous cholangitis Yes No Bile duct loss/damage Yes No Copper/cholate stasis Yes No Autoimmune Liver Diseases and Overlap Syndromes Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Overlap AIH/PBC 2-19% PBC Overlap AIH/PSC 7-14% PSC Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis ~18% of AIH patients have an overlap syndrome PBC/AIH Overlap Clearly documented in the literature Incidence depends on stringency of criteria Criteria Ideally both clinical and histologic evidence of both AIH and PBC Alk Phos and AST/ALT elevated x 5 AMA plus ANA/ASMA (usually) Florid duct lesion plus lobular necrosis and interface activity Hypergammaglobulinemia Treatment Urso for the PBC component doesn t hurt Prednisone, other immunosuppressive for AIH component 46
47 PBC/AIH overlap PBC/AIH overlap PBC/AIH overlap 47
48 PBC: Chronic hepatitis-like 48
49 AMA-negative PBC (autoimmune cholangitis) Positive ANA, often SMA Patients more often male Many patients histologically similar to AMA+ PBC Some are more appropriately classified as idiopathic adulthood ductopenia Treatment identical; behavior usually identical Take-Home Messages AIH is a hepatocyte-centric disease that requires immunosuppression Drug almost always in the DDX PBC is a duct-centric disease Alk phos>transaminase elevation Diagnosis of PBC/AIH overlap requires morphologic, clinical, and laboratory evidence of both Behind this closed door is the answer as to whether it s PBC or AIH.or overlap... 49
50 Case 5 34YO Hispanic female presented with weight loss, tachycardia Found to be hyperthyroid, started on propylthiouracil Three months later, presented with nausea, vomiting, jaundice AST 1028, ALT 1039, Bili 6.6, alk phos 586; autoimmune and viral studies negative No evidence of bile duct obstruction 50
51 51
52 Diagnosis Cholestatic hepatitis secondary to adverse drug reaction (propylthiouracil) Approach to Cholestasis Bland cholestasis Hepatocellular and/or canalicular No inflammation or hepatocyte damage Drug, drug, drug, infection/systemic disease, weird stuff 52
53 Approach to Cholestasis Cholestatic hepatitis Hepatocellular and/or canalicular Portal and/or lobular inflammation Hepatocyte damage Drug, viral, autoimmune, large bile duct obstruction, alcohol (if fat is present) LDO 53
54 Approach to Cholestasis Ductular Cholestasis Inspissated bile within ductules Interlobular bile ducts are intact Sepsis (cholangitis lenta; patient is about to die) or rarely drug 54
55 Ductular cholestasis Cholate Stasis Late feature of chronic biliary disease Due to detergent effects of bile (and copper toxicity) Copper often present Periportal hepatocyte ballooning with variably present Mallory hyaline Periportal halo in patients with biliary cirrhosis CK7 positive periportal hepatocytes 55
56 Approach to Cholestasis Cholangiodestructive Often features cholate stasis Portal inflammation with destruction of bile ducts Can lead to biliary cirrhosis Drug, chronic biliary disease (PBC, PSC, etc.) VBDS 56
57 Take-Home Messages Pattern of cholestasis helps narrow differential diagnosis Always consider cholestatic drug reaction in cases of cholestatic hepatitis Almost any form of cholestatic liver disease can be due to adverse drug reaction Hepatitis E is the new player on this block I m just going to lie here until someone gets me some decent clinical information. Henry ponders the causes of cholestasis. 57
58 Other things to keep in mind Sepsis 58
59 Hepatic venous outflow obstruction 59
60 EBV Erythrophagocytosis 60
61 And now a word about reporting.. 61
62 Useless Reporting Liver, needle bx: Triaditis of limited significance. No fibrosis. Pathologist of limited significance Gives no useful information Either call it normal or figure out what it is Useless Reporting Liver, needle bx: Chronic inflammation. See comment Comment: the differential diagnosis includes viral hepatitis, PBC, drug reaction, autoimmune hepatitis, and Coxiella infection. Clinical correlation required. Alternate comment: I am too lazy to do the work of correlating this biopsy with the clinical and lab information. Useful Reporting Liver, needle bx: Chronic hepatitis with mild activity and moderate increase in fibrosis, consistent with hepatitis C. See comment Marked steatosis. Comment: Although nonspecific, these features consistent with chronic hepatitis C; amount of fat suggests possible additional component of fatty liver disease. 62
63 Useful Reporting Liver, needle bx: Lymphocytic cholangitis with ductopenia and copper deposition; see comment Comment: suggestive of primary biliary cirrhosis; correlate with AMA Useful Reporting Liver, needle bx: Steatohepatitis with bridging fibrosis; see comment Comment: Patients with NASH often have positive ANA and/or anti-sma. Features of autoimmune hepatitis are not seen. Somebody wake me up for lunch Alys is exhausted by the subject matter. 63
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology
 Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
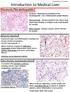 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
DILI PATHOLOGY. PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting
 DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Liver Pathology Symposium - medical livers
 Liver Pathology Symposium - medical livers London, April 13 th 2018 Dr Susan E Davies, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Case 1 SED 65/F Diabetic. Raised ALT, USS fatty. Fibroscan? cirrhosis Reticulin (untoned),
Liver Pathology Symposium - medical livers London, April 13 th 2018 Dr Susan E Davies, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Case 1 SED 65/F Diabetic. Raised ALT, USS fatty. Fibroscan? cirrhosis Reticulin (untoned),
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel. Basel,
 Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology
 REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Acute and Chronic Hepatitis John Hart, M.D. University of Chicago Medical Center
 Acute and Chronic Hepatitis John Hart, M.D. University of Chicago Medical Center Acute Hepatitis Clinical Features Classically acute hepatitis is defined clinically as a significant (at least 2X elevation
Acute and Chronic Hepatitis John Hart, M.D. University of Chicago Medical Center Acute Hepatitis Clinical Features Classically acute hepatitis is defined clinically as a significant (at least 2X elevation
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) Case n 2 ( B 00 / 8249 ) Case n 3 ( B 98 / 8352 )
 Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Case #1. Digital Slides 11/6/ year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests. Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis
 45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Autoimmune hepatitis
 Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Supplemental Tables. Parasitic Schistosomiasis increase < 1. Genetic Hemochromatosis increase < 1. autoimmune Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) increase < 1
 Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
Original Article. Significance of Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Infection INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Bhanthumkomol P, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2013 Vol. 14 No. 1 Jan. - Apr. 2013 29 Bhanthumkomol P 1 Charatcharoenwitthaya P 1 Pongpaiboon A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Significance of liver
Original Article Bhanthumkomol P, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2013 Vol. 14 No. 1 Jan. - Apr. 2013 29 Bhanthumkomol P 1 Charatcharoenwitthaya P 1 Pongpaiboon A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Significance of liver
New insights into fatty liver disease. Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College
 New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
National Liver EQA Scheme. Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004
 National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
Drug Induced Liver Disease Role of the Pathologist. Disclosure. DILI can never be excluded. Romil Saxena, MD. Dr. Saxena has nothing to Disclose
 Drug Induced Liver Disease Role of the Pathologist Romil Saxena, MD Disclosure Dr. Saxena has nothing to Disclose DILI can never be excluded #1 DILI has no specific pattern of injury it can mimic any and
Drug Induced Liver Disease Role of the Pathologist Romil Saxena, MD Disclosure Dr. Saxena has nothing to Disclose DILI can never be excluded #1 DILI has no specific pattern of injury it can mimic any and
21/07/2017. Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease. Changing Role of Liver Biopsy in PBC and PSC. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease Changing Change in Nomenclature for PBC : From Cirrhosis to Cholangitis (EASL Panel, Beuers et al J Hepatol Nov 2015, Gut Nov
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease Changing Change in Nomenclature for PBC : From Cirrhosis to Cholangitis (EASL Panel, Beuers et al J Hepatol Nov 2015, Gut Nov
AASLD: Boston Rob Goldin
 AASLD: Boston 2014 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Autoimmune hepatitis 31 Does genuine acute autoimmune hepatitis have a better prognosis? 32 Patients with Autoimmune Hepatitis and Advanced Disease
AASLD: Boston 2014 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Autoimmune hepatitis 31 Does genuine acute autoimmune hepatitis have a better prognosis? 32 Patients with Autoimmune Hepatitis and Advanced Disease
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Steatohepatitis
 The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
Acute Hepatitis in a Patient with NASH and Elevation of CMV-IgM
 Acute Hepatitis in a Patient with NASH and Elevation of CMV-IgM Uta Drebber, MD Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the
Acute Hepatitis in a Patient with NASH and Elevation of CMV-IgM Uta Drebber, MD Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the
Special stains in liver pathology
 Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Key Points: Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective. Jenny Heathcote, MD. University of Toronto
 Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas
 Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy. Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015.
 Epatite autoimmune e sindrome da "overlap Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015. AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS
Epatite autoimmune e sindrome da "overlap Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015. AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS
Drug-induced liver injury
 Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems
 SHORT COURSE Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems Linda Ferrell, M.D. Department of Anatomic Pathology, University of California San Francisco,
SHORT COURSE Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems Linda Ferrell, M.D. Department of Anatomic Pathology, University of California San Francisco,
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY
 2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern. November 14th, 2018
 Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing?
 Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease. Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC
 Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis. By Dr. Seham Seif
 Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis By Dr. Seham Seif Definition NAFL describe a common clinicopathological conditions characterized by significant lipid deposition in the hepatocytes
Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis By Dr. Seham Seif Definition NAFL describe a common clinicopathological conditions characterized by significant lipid deposition in the hepatocytes
Liver National EQA Scheme. Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005
 Liver National EQA Scheme Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005 Images from circulations Virtualpathology@leeds.ac.uk/uvw View slides from current circulation, Aperio see and navigate whole slide
Liver National EQA Scheme Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005 Images from circulations Virtualpathology@leeds.ac.uk/uvw View slides from current circulation, Aperio see and navigate whole slide
Liver Transplant Pathology a general view
 Liver Transplant Pathology a general view Dr S E Davies Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust ACP/BSG Meeting Leeds 2012 Liver transplantation When and where? Who and why? How?
Liver Transplant Pathology a general view Dr S E Davies Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust ACP/BSG Meeting Leeds 2012 Liver transplantation When and where? Who and why? How?
4/27/2018. Disclosures LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
HIV/AIDS and the Liver : interlinking challenges
 HIV/AIDS and the Liver : interlinking challenges Mark W. Sonderup Division of Hepatology Department of Medicine University of Cape Town & Groote Schuur Hospital Global HIV/AIDS prevalence 37 million people
HIV/AIDS and the Liver : interlinking challenges Mark W. Sonderup Division of Hepatology Department of Medicine University of Cape Town & Groote Schuur Hospital Global HIV/AIDS prevalence 37 million people
Histology. The pathology of the. bile ducts. pancreas. liver. The lecture in summary. Vt-2006
 Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup
 REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017.
 Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017. 1 The 2015 RCPath Stage A curriculum for hepatobiliary pathology and gall bladder. 2 The stage A curriculum
Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017. 1 The 2015 RCPath Stage A curriculum for hepatobiliary pathology and gall bladder. 2 The stage A curriculum
Chewing the Fat on Fatty Liver Mike Kolber MD, CCFP, MSc PEIP 2018
 Chewing the Fat on Fatty Liver Mike Kolber MD, CCFP, MSc PEIP 2018 Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Michael Kolber Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research Support: Alberta College of
Chewing the Fat on Fatty Liver Mike Kolber MD, CCFP, MSc PEIP 2018 Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Michael Kolber Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research Support: Alberta College of
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
(C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes
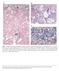 (A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
(A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure
 Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
UC SF. Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update. University of California San Francisco. September 3, 2009
 Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update UC SF University of California San Francisco Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Update in Pathology September 3, 2009 Elizabeth M. Brunt, MD Department of Pathology
Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update UC SF University of California San Francisco Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Update in Pathology September 3, 2009 Elizabeth M. Brunt, MD Department of Pathology
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms?
 Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis
 Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham First described in 1980
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham First described in 1980
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions
 2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2014 Vol. 15 No May - Aug. 2014
 Case Report Poovorawan K, et al. 105 Fatal Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure from Amiodarone Toxicity Poovorawan K 1,2 Wisedopas N 3 Treeprasertsuk S 1 Komolmit P 1 ABSTRACT Background: Drug induced liver
Case Report Poovorawan K, et al. 105 Fatal Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure from Amiodarone Toxicity Poovorawan K 1,2 Wisedopas N 3 Treeprasertsuk S 1 Komolmit P 1 ABSTRACT Background: Drug induced liver
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014
 Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases
 Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases Corporate Presentation March 2019 Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains "forward-looking" statements that involve risks, uncertainties and
Improving the Lives of Patients with Liver Diseases Corporate Presentation March 2019 Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains "forward-looking" statements that involve risks, uncertainties and
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD. April 13, 2012
 NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD Simple Steatosis Fatty hepatocytes Intracellular fat
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD Simple Steatosis Fatty hepatocytes Intracellular fat
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver
 At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver What Can You Tell Your Patients Magnus McLeod MD FRCPC Assistant Professor Dalhousie University 30-NOV-2017 NAFLD Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver What Can You Tell Your Patients Magnus McLeod MD FRCPC Assistant Professor Dalhousie University 30-NOV-2017 NAFLD Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions. American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course
 Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
