The Effects of Preoperative Irradiation
|
|
|
- Edmund Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Effects of Preoperative Irradiation on Primary Tracheal Anastomosis N. Tsubota, M.D., W. J. Simpson, M.D., A. W. P. Van Nostrand, M.D., and F. G. Pearson, M.D. ABSTRACT Preoperative radiotherapy was used in the management of selected patients with cancer of the lung or trachea who might subsequently require segmental resection of bronchus or trachea and reconstruction by primary anastomosis. This study was designed to determine the effects of varying dosages of preoperative irradiation on anastomotic healing. Two rings were resected from the cervical trachea of 20 dogs following irradiation with varying doses of cesium. There were no important adverse effects on healing of the trachea or adjacent organs in dogs receiving up to 3,500 rads. All dogs receiving a higher dose than this developed some anastomotic stenosis, which was severe in 6 of 8 animals. Similar adverse efects were observed in 2 patients managed by preoperative radiotherapy (4,000 rads in three weeks) and tracheal resection with primary anastomosis. n some patients with primary carcinoma of the lung or trachea, it may be evident prior to operation that dissection lines will be close to the margins of gross tumor and that microscopic tumor may remain following resection. This problem frequently occurs in patients with primary carcinoma of the trachea (adenoid cystic carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma) since nonresectable structures such as the aortic arch and its branches, and the vena cava, lie immediately adjacent to the mediastinal trachea. Both squamous cell carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma are responsive to current techniques of irradiation [ 1-6, 81. Theoretically, radiation therapy is most likely to ablate tumor on the periphery or margin of a neoplasm, and preoperative irradiation should reduce the incidence of local recurrence 151. This study evaluates the effects of varying doses of preoperative irradiation on healing of the tracheal anastomosis and adjacent tissues of the esophagus and spinal cord. Materials and Methods Mongrel dogs were irradiated by means of a cesium teletherapy unit with a source-to-skin distance of 50 cm, using 8 x 10 cm right and left lateral neck fields From the Division of Thoracic Surgery, Department of Radiotherapy, and Department of Pathology, University of Toronto and Toronto General Hospital, Toronto, Ont., Canada. Supported by Grant no. 288, Ontario Cancer Treatment and Research Foundation, Toronto, Ont., Canada. We thank Dr. N. B. Rewcastle, Dr. J. Smialek, and Mr. K. Eken for the neuropathology studies, Mr. J. Crocker for his assistance with Microfil studies, and Mi-. S. Rae for his meticulous technical assistance. Presented at the Eleventh Annual Meeting of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Montreal, Que., Canada, Jan , Address reprint requests to Dr. Pearson, Room 120 University Wing, Toronto General Hospital, Toronto, Ont., Canada M5G 1L THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
2 Preoperative Irradiation for Tracheal Anastomosis centered on the cervical trachea and including the adjacent esophagus and anterior aspect of the spinal cord. The field for irradiation extended 4 cm on either side of the tracheal segment to be resected. Both fields were treated daily, and fifteen treatments were given over a period of three weeks. The radiation dose was relatively uniform throughout the entire treatment course. The dogs weighed between 17 and 22 kg. The animals were divided into five groups of 4 each: a control group receiving no radiotherapy and four groups receiving 3,000,3,500,4,000 and 5,000 rads of preoperative irradiation, respectively. Three weeks after completion of radiation therapy, a short segment of cervical trachea consistingof the eighth and ninth cartilages was resected and reconstructed by primary anastomosis using interrupted sutures of 3-0 chromic catgut. There was no tension on this anastomosis. Postoperatively the dogs were examined for clinical evidence of tracheal obstruction, which, when present, was characterized by labored breathing on effort, wheezing respiration, and a characteristic hoarse cough. Bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy were done three and six weeks after operation, and again at six months in long-term experiments. Contrast tracheograms using powdered tantalum [7] were obtained shortly before the animals were killed. The postmortem gross appearance and histology of the irradiated and adjacent tissues were recorded. In 8 dogs the tracheal circulation was examined following injection of Microfil* - an orange colored, radiopaque, high-viscosity dilutant - into the arterial side of the circulation. Between 75 and 100 ml of liquid Microfil was injected into each carotid artery immediately after the animals were killed with 10 ml of Lethol (nembutal and alcohol). Prior to Microfil injection, the carotid vessels were ligated inferiorly at the level of the sternal notch and superiorly close to the base of the skull. Better filling of small arterioles was obtained by injecting 1,500 IU of heparin intravenously three minutes before the animals were killed. In each of the five study groups, 3 animals were killed six weeks after tracheal resection and 1 animal was killed after six months. Aside from changes developing at the tracheal anastomosis, no significant anesthetic or postoperative complications were observed, and all animals completed the study protocol. Following postmortem examination the resected tracheal segments were examined by means of paraffin-embedded blocks sectioned both vertically and horizontally. The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The trachea and esophagus obtained from each dog was fixed in 10% formalin, and multiple paraffin-embedded blocks were obtained. These blocks included sections through the anastomosis site, through irradiated trachea and esophagus away from the anastomosis site, and from nonirradiated trachea and esophagus both above and below the irradiated area. On examination of histological sections, specific note was made of the presence or absence of mucosal ulceration and edema, granulation tissue, vascular or lymphatic dilatation, infiltration with acute or chronic inflammatory cells, and the presence of increased collagen and fibrous connective tissue. Eight specimens were injected with Microfil and roentgenograms made. *Microfil silicone rubber injection compounds, Canton Biomedical Products, Boulder, Colo. VOL. 20, NO. 2, AUGUST,
3 ~ ~~ TSUBOTA ET AL. EFFECTS OF PREOPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY ON TRACHEAL HEALING IN 20 DOGS Clinical Stenosis Group Signs None Mild Severe Control ,000 rads ,500 rads ,000 rads ,000 rads They were then subjected to a clearing technique* designed to demonstrate more precisely the vascular changes in the region of the anastomosis. Since Microfil is radiopaque it is readily discernible on standard roentgenograms, and its bright orange color makes it clearly visible to the naked eye and through the dissecting microscope once the specimen has been cleared. Results The gross effects of preoperative radiotherapy on tracheal healing are summarized in the Table. The tracheal anastomosis healed well in the 4 control dogs without evidence of ulceration or granulation tissue at interval bronchoscopy ; it was identified as a thin, linear scar without stenosis in the tantalum bronchogram and upon postmortem examination (Fig. 1). In animals receivingup to 3,500 rads preoperatively, no differences were observed from the control group at interval endoscopy or postmortem examination, except in 1 dog that developed mild, asymptomatic stenosis at the anastomosis. The contrast tracheogram and gross appearance of the anastomosis in a dog receiving 3,500 rads preoperatively and killed six weeks after tracheal resection are illustrated in Figure 2. All animals receiving either 4,000 or 5,000 rads of preoperative radiotherapy developed a stricture at the tracheal anastomosis that produced clinical evidence of tracheal obstruction in 7 of the 8 dogs. In 3 of the 4 dogs receiving 5,000 rads the stenosis was severe (Fig. 3). In the 5 animals (1 from each study group) maintained for six months following tracheal resection, no differences were observed in the bronchoscopic or roentgenographic appearance of the anastomosis from the changes documented at six weeks. None of the animals developed radiation esophagitis as evaluated by esophagoscopy and postmortem studies. It appears that the dog esophagus is less sensitive to radiation therapy than the human esophagus, since a dose of 3,000 rads delivered over three weeks frequently produces radiation esophagitis in man. The cervical spinal cord was removed during postmortem examination, using a posterior approach for the dissection. Sections from multiple levels of the cervical cord were stained and processed in paraffin. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and Lux01 fast blue and then examined with light microscopy. In 1 specimen a focal lesion of acute arteritis was identified, but it is doubtful *The specimens were dehydrated using increasing concentrations of alcohol and then cleared using cedarwood oil. After examination and photography, the specimens were embedded in paraffin wax and sectioned ip the usual manner. 154 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
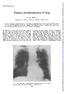
4 Preoperative Irradiation fm Tracheal Anastomosis FIG. 1. (A) Contrast tracheogram in a control animal killed six weeks after tracheal anastomosis. There is no significant stenosis. (B) Gross appearance of tracheal anastomosis (arrow) in the same animal. The anastomosis is seen as a line of pale, linear scar without stricture. that this was related to the radiation therapy. In the remaining specimens no abnormality was identified that could not be explained on the basis of manipulative and processing artifacts. Specifically, no differences were seen between the control specimens and the cord segments of irradiated animals. It should be noted, however, that the field for irradiation did not extend to the posterior aspect of the spinal cord, and the cord may not have received the same full dosage levels that were delivered to the trachea and esophagus. FIG. 2. (A) Contrast tracheopam six weeks after tracheal anastomosis in an animal receiuing?,500 rads of preoperative irradiation. There is no signafxant stenosis. (B) Gross appearance.f the anastomosis (arrow) in the same animal. VOL. 20, NO. 2, AUGUST,
5 TSUBOTA ET AL. FIG. 3. (A) Contrast tracheogram six weeks after tracheal anastomosis in animal receiving 5,000 rads of preoperative irradiation. Severe stenosis with clinical signs of airway obstruction is present. (B) Gross appearance of tracheal anastomosis in the same animal. A diaphragm of scar tissue is present at the anastornosix HISTOLOGY OF THE TRACHEA Histological sections from irradiated areas of the trachea and esophagus in dogs receiving 3,000 and 3,500 rads showed a minor degree of edema of the tracheal mucosa associated with a sprinkling of chronic inflammatory cells when compared with sections from control dogs. The anastomosis site in these dogs was a thin, flat scar covered with normal respiratory mucosa and showing no increase in vascularity, chronic inflammation, or fibrosis when compared with the controls (Fig. 4A). Sections taken from dogs receiving 4,000 and 5,000 rads revealed increasing degrees of edema and inflammation. The most striking differences, however, were at the site of anastomosis. Those animals which exhibited clinical signs of tracheal stenosis had developed a buildup of capillary-rich granulation tissue at the anastomosis site that protruded into the tracheal lumen and in some cases remained denuded of epithelium (Figs. 4B, 5). The vascular network adjacent to the anastomosis site remained markedly dilated. Edema, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis were all increased at the anastomosis site. All these observations support the contention that the effects of irradiation on sites of tissue injury (in this study, surgical trauma) are due to an alteration in the vascular response that promotes the development of granulation tissue, delays the healing process, and produces increased amounts of connective tissue when healing occurs. In this dog model the critical dose appeared to be between 3,500 and 4,000 rads. Comment It is apparent from this study that, in dogs, preoperative radiotherapy in doses greater than 3,500 rads given over three weeks impairs healing of a tracheal 156 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
6 Preoperative Irradiation for Tracheal Anastomosis FIG. 4. Photomicrographs of longitudinal sections of the trachea. (A) Anastomosis in a dog that received 3,000 rads of preoperative irradiation. The anastomosis is a thin line of scar with intact epathelial cover and without luminal stenosis. (B) Anastomosis in a dog that received 5,000 rads of preoperative irradiation. There is an excess of vascular granulation tissue and fibroplasia at the anastomosis, some death and destruction of one ofthe tracheal cartilages, and obvious compromise ofthe tracheal lumen which resulted in moderately severe stenosis. (Both H t3 E, X 15; reduced 20% for reproduction.) anastomosis and results in a high incidence of marked stenosis. There is some evidence that anastomotic stenosis in man may result from preoperative irradiation at dosage levels similar to those described in the present experiment. In 1970, 1 of our patients underwent carinal resection for adenoid cystic carcinoma with reconstruction by primary anastomosis between the two bronchial stumps and distal trachea. She received 4,000 rads of radiotherapy during three weeks as a preoperative measure. Surgical treatment was delayed for three months after VOL. 20, NO. 2, AUGUST,
7 TSUBOTA ET AL. FIG. 5. (A) Photograph of opened trachea in a control animal killed six weeks after tracheal anastomosis. The circulation was injected with Microfil. There is no important increase in the number ofsmall vessels at the anastomotic site (arrows).(b) Photograph of opened trachea in an animal that received 4,000 rads of preoperative irradiation and was killed six weeks after tracheal anastomosis. Microfil injection demonstrates a very pronounced increase in the number of small vessels at the margins of ths anastomosis (arrows). completion of radiation therapy because of severe and prolonged esophagitis and tracheobronchitis in the irradiated field. Following resection and reconstruction she developed a clearly demarcated band of necrosis on the tracheal side of the anastomosis. This ultimately healed with a moderate stricture that required repeated dilation to maintain a satisfactory airway. Abbey-Smith has reported troublesome anastomotic strictures following sleeve lobectomy and bronchoplasty 158 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
8 Preoperative Irradiation for Tracheal Anastomosis in patients receiving high doses of preoperative radiotherapy (5,000 rads over four or five weeks).* Since 1970 we have treated 7 patients requiring tracheal or bronchoplastic anastomosis with 3,500 rads of preoperative irradiation delivered during three weeks, followed by resection three weeks after completion of treatment. Three patients had adenoid cystic carcinoma of the trachea requiring segmental resection and reconstruction by primary anastomosis. Three patients had squamous cell carcinoma of the bronchus and required sleeve lobectomy and bronchotracheal anastomosis. One patient with squamous cell carcinoma involving the carina had a carinal resection with right pneumonectomy and reconstruction by anastomosis of the left main bronchus to the distal trachea. In none of these 7 patients were there any significant problems with healing at the anastomosis, and none developed marked stenosis. The theoretical rationale for using preoperative irradiation in such patients has been outlined. Assuming that preoperative radiotherapy may reduce the incidence of local recurrence in selected patients, it is still not known whether 3,000 or 3,500 radsadministered during three weeks is an adequate dose. We have reported limited evidence supporting the effectiveness of such dosage levels in the management of a small number of patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma of the trachea [5]. Adequate evaluation will require a longer period of follow-up and greater numbers of patients treated in this fashion. References 1. Attar, S. A., Hankins, J., Turney, S., Mason, G. R., Ramirez, R., and McLaughlin, J. Tracheal obstruction. Ann Thorac Surg 16:555, Grillo, H. C. Reconstruction of the trachea: Experience in 100 consecutive cases. Thorax 28:667, Hajdu, S. I., and Koss, L. G. Cytology of carcinoma of the trachea. Actu Cytol 3:255, Lewit, P., Karman, S., Terracina, S., and Beemer, A. M. Malignant tumors of the trachea. Chest 60:498, Pearson, F. G., Thompson, D. W., Weissberg, D., Simpson, W. J. K., and Kergin, F. G. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the trachea. Ann Thoruc Surg 18:16, Richardson, J. D., Grover, F. L., and Trinkle, J. K. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the trachea: Response to cobalt 60. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 66:311, Wood, P. B., Nagy, E., Pearson, F. G., and Rae, S. Measurement of mucociliary clearance from the lower respiratory tract of normal dogs. Can Anaesth SOC J 20: 192, Zenker, H. O., Moore, R. L., Baker, D. C., and Lattes, R. Adenoid cystic carcinoma (cylindroma) of the trachea: Case report with nine-year follow-up. Cancer 23:699,1969. Discussion DR. ROBERT J. JENSIK (Chicago, Ill.): At Rush-Presbyterian-St. Luke s Medical Center over the past ten years, tracheal resection with pneumonectomy and tracheobronchial anastomosis for carcinoma has been carried out in 28 patients: 24 synchronous right pneumonectomies, 1 prior right pneumonectomy, and 3 prior left pneumonectomies. *R. Abbey-Smith, personal communication. VOL. 20, NO. 2, AUGUST,
9 TSUBOTA ET AL. Prior radiotherapy was given to 24 patients with a tumor dose usually limited to 4,000 rads, although in 1 patient as much as 6,000 rads was administered. Of 12 patients surviving less than six months, stenosis developed in 1 following a leak. In 15 patients surviving six months to ten years there were no instances of stenosis. I cannot explain the untoward results in the example cited by Dr. Tsubota. This complication has seldom been seen in our surviving patients, which has allowed us to attempt these procedures after prior radiotherapy without any reluctance. DR. PEARSON: In Dr. Jensik's patients, a dosage of 4,000 rads was administered over a period of four weeks. This isequivalent to slightly less than 3,500 rads administered during a three week period. I believe this explains the discrepancy in their observation concerning the absence of adverse effects of preoperative irradiation in patients undergoing tracheal resection with pneumonectomy. 160 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea ORIGINAL ARTICLES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea and Bronchus: The Case for Conservative Resection Robert H. Breyer, M.D., John R. Dainauskas, M.D., Robert J. Jensik, M.D., and L. Penfield Faber,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea and Bronchus: The Case for Conservative Resection Robert H. Breyer, M.D., John R. Dainauskas, M.D., Robert J. Jensik, M.D., and L. Penfield Faber,
A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy for carinal resection and reconstruction
 Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis. The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University
 The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis ) The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University Named also: endobronchial tuberculosis,ebtb defined as tuberculous
The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis ) The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University Named also: endobronchial tuberculosis,ebtb defined as tuberculous
The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction
 The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction Alaa Gaafar-MD, Ahmed Youssef-MD, Mohamed Elhadidi-MD A l e x a n d r i a F a c u l t y o f
The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction Alaa Gaafar-MD, Ahmed Youssef-MD, Mohamed Elhadidi-MD A l e x a n d r i a F a c u l t y o f
External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other
 Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized
 Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis
 Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Efficacy of Polydioxanone Monof Tracheal Anastomosis Kawahara, Katsunobu; Yamasaki, Naoy Takeshi; Kusano, Hiroyuki; Akamine, Masao Citation Acta medica
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Efficacy of Polydioxanone Monof Tracheal Anastomosis Kawahara, Katsunobu; Yamasaki, Naoy Takeshi; Kusano, Hiroyuki; Akamine, Masao Citation Acta medica
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy
 Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review
 Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
Reconstructive Airway Operation After Irradiation
 Reconstructive Airway Operation After Irradiation Derek D. Muehrcke, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, and Douglas J. Mathisen, MD General Thoracic Surgical Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and the Harvard
Reconstructive Airway Operation After Irradiation Derek D. Muehrcke, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, and Douglas J. Mathisen, MD General Thoracic Surgical Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and the Harvard
March The patients, two men and nine. an average of 54 years. In 10 of these patients. the cervical trachea was affected.
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 378-386 Resection of thyroid carcinoma infiltrating the trachea T. ISHIHARA, K. KIKUCHI, T. IKEDA, H. INOUE, S. FUKAI, K. ITO', AND T. MIMURA' From the Department of Surgery, School of
Thorax, 1978, 33, 378-386 Resection of thyroid carcinoma infiltrating the trachea T. ISHIHARA, K. KIKUCHI, T. IKEDA, H. INOUE, S. FUKAI, K. ITO', AND T. MIMURA' From the Department of Surgery, School of
Carcinoma of the Lung
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Sleeve lobectomy for lung adenocarcinoma treated with neoadjuvant afatinib
 Case Report Sleeve lobectomy for lung adenocarcinoma treated with neoadjuvant afatinib Ichiro Sakanoue 1, Hiroshi Hamakawa 1, Reiko Kaji 2, Yukihiro Imai 3, Nobuyuki Katakami 2, Yutaka Takahashi 1 1 Department
Case Report Sleeve lobectomy for lung adenocarcinoma treated with neoadjuvant afatinib Ichiro Sakanoue 1, Hiroshi Hamakawa 1, Reiko Kaji 2, Yukihiro Imai 3, Nobuyuki Katakami 2, Yutaka Takahashi 1 1 Department
Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection
 Original Article on Thoracic Surgery Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection Qianli Ma, Deruo Liu Department of Thoracic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing
Original Article on Thoracic Surgery Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection Qianli Ma, Deruo Liu Department of Thoracic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1985, 30
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Experimental Study on Sleeve Anasto Hemodynamics Takada, Toshio Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1985, 30 Issue Date 1985-10-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15682
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Experimental Study on Sleeve Anasto Hemodynamics Takada, Toshio Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1985, 30 Issue Date 1985-10-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15682
Lobectomy with sleeve resection in the
 Thorax (970), 25, 60. Lobectomy with sleeve resection in the treatment of bronchial tumours G. M. REES and M. PANETH Brompton Hospital, London, S.W3 Fortysix patients with malignant tumours involving the
Thorax (970), 25, 60. Lobectomy with sleeve resection in the treatment of bronchial tumours G. M. REES and M. PANETH Brompton Hospital, London, S.W3 Fortysix patients with malignant tumours involving the
Primary Tumors of Ribs
 Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Carinal resections. Leonidas Tapias, Michael Lanuti. Clinical vignette
 Masters of Cardiothoracic Surgery Carinal resections Leonidas Tapias, Michael Lanuti Division of Thoracic Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence to: Michael Lanuti, MD.
Masters of Cardiothoracic Surgery Carinal resections Leonidas Tapias, Michael Lanuti Division of Thoracic Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence to: Michael Lanuti, MD.
Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction
 Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (2010) 26:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s12055-010-0021-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction Mohamed Abdel Hamied Regal & Yasser Ahmed
Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (2010) 26:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s12055-010-0021-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction Mohamed Abdel Hamied Regal & Yasser Ahmed
Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
The Role of Radiation Therapy
 The Role of Radiation Therapy and Surgery in the Treatment of Bronchogenic Carcinoma R Adams Cowley, M.D., Morris J. Wizenberg, M.D., and Eugene J. Linberg, M.D. A study of the combined use of preoperative
The Role of Radiation Therapy and Surgery in the Treatment of Bronchogenic Carcinoma R Adams Cowley, M.D., Morris J. Wizenberg, M.D., and Eugene J. Linberg, M.D. A study of the combined use of preoperative
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Tracheal Stenosis or Tracheal Injury
 Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Histological evaluation of cancer e cancer. Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Ka Hsieh, Chia-Ming; Oka, Tadayuki; Ts Taniguchi, Hideki; Touchika, Hirono
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Histological evaluation of cancer e cancer. Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Ka Hsieh, Chia-Ming; Oka, Tadayuki; Ts Taniguchi, Hideki; Touchika, Hirono
Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases
 Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Tracheal Adenocarcinoma Treated with Adjuvant Radiation: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Published online: May 23, 2013 1662 6575/13/0062 0280$38.00/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Published online: May 23, 2013 1662 6575/13/0062 0280$38.00/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma
 Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
CROSS CODER. Sample page. Anesthesia. codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS. Essential links from CPT. Power up your coding optum360coding.
 CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS
 Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type A Acute coronary syndrome, perioperative oxygen in, 599 600 Acute lung injury (ALI). See Lung injury and Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type A Acute coronary syndrome, perioperative oxygen in, 599 600 Acute lung injury (ALI). See Lung injury and Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Case Report. Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* Abstract. Introduction.
 121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005
 Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
bronchopleural fistula
 Role of automatic staplers in the aetiology of bronchopleural fistula MOHSIN HAKIM, BB MILSTEIN From the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Papworth Hospital, Cambridge Thorax 1985;40:27-31 ABSTRACT
Role of automatic staplers in the aetiology of bronchopleural fistula MOHSIN HAKIM, BB MILSTEIN From the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Papworth Hospital, Cambridge Thorax 1985;40:27-31 ABSTRACT
Region: 11. Clinic6patholo cal Studies
 Tumors of the Thvmus and ThVIIliC Region: 11. Clinic6patholo cal Studies on Hodgkin s Disease of Re Thymus N. P. Bergh, M.D., P. Gatzinsky, M.D., S. Larsson, M.D., P. Lundin, M.D., and B. Ridell, M.D.
Tumors of the Thvmus and ThVIIliC Region: 11. Clinic6patholo cal Studies on Hodgkin s Disease of Re Thymus N. P. Bergh, M.D., P. Gatzinsky, M.D., S. Larsson, M.D., P. Lundin, M.D., and B. Ridell, M.D.
Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for complicated pulmonary resections
 Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for complicated pulmonary resections Ding-Pei Han, Jie Xiang, Run-Sen Jin, Yan-Xia Hu, He-Cheng Li Jiaotong University School
Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for complicated pulmonary resections Ding-Pei Han, Jie Xiang, Run-Sen Jin, Yan-Xia Hu, He-Cheng Li Jiaotong University School
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft
 Redacement of Superior Vena Cava with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft A Versatile Technique C. J. Chiu, M.D., J. Terzis, M.D., and M. L. MacRae, B.S. ABSTRACT A technique to construct a spiral vein graft
Redacement of Superior Vena Cava with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft A Versatile Technique C. J. Chiu, M.D., J. Terzis, M.D., and M. L. MacRae, B.S. ABSTRACT A technique to construct a spiral vein graft
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment. Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS
 Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
years old female with paratracheal lymph nodes infiltration and mediastinal extension, who presented
 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour of the Trachea with Paratracheal Lymph Nodes and Mediastinal Invasion Salina Husain From Department of Otolaryngology, Univerti Kebengsaan, Malaysia. Received:
Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour of the Trachea with Paratracheal Lymph Nodes and Mediastinal Invasion Salina Husain From Department of Otolaryngology, Univerti Kebengsaan, Malaysia. Received:
Right sleeve pneumonectomy via uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic approach
 Case Report Right sleeve pneumonectomy via uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic approach Chenlu Yang, Firas Abu Akar, Jian Chen, Lei Jiang Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tongji University Affiliated
Case Report Right sleeve pneumonectomy via uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic approach Chenlu Yang, Firas Abu Akar, Jian Chen, Lei Jiang Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tongji University Affiliated
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Combined esophagectomy and carinal pneumonectomy
 Case Report Combined esophagectomy and carinal pneumonectomy Hon Chi Suen, Cody Wayne Smith Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Mercy Hospital Jefferson, Festus, MO 63028, USA Correspondence to: Hon
Case Report Combined esophagectomy and carinal pneumonectomy Hon Chi Suen, Cody Wayne Smith Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Mercy Hospital Jefferson, Festus, MO 63028, USA Correspondence to: Hon
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
4/24/2017. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis Endoscopic & Surgical Management
 Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
Carcinoma of the Lung in Women
 Carcinoma of the Lung in Marvin M. Kirsh, M.D., Jeanne Tashian, M.A., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT The 5-year survival of 293 men and of 78 women undergoing pulmonary resection and mediastinal lymph
Carcinoma of the Lung in Marvin M. Kirsh, M.D., Jeanne Tashian, M.A., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT The 5-year survival of 293 men and of 78 women undergoing pulmonary resection and mediastinal lymph
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
2 Li et al. Surgical techniques of VATS using non-intubated anesthesia
 Surgical Technique Video-assisted transthoracic surgery resection of a tracheal mass and reconstruction of trachea under non-intubated anesthesia with spontaneous breathing Shuben Li 1,2,3 *, Jun Liu 1,2,3
Surgical Technique Video-assisted transthoracic surgery resection of a tracheal mass and reconstruction of trachea under non-intubated anesthesia with spontaneous breathing Shuben Li 1,2,3 *, Jun Liu 1,2,3
The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma G. A. Patterson, M.D., R. Ilves, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., J. D. Cooper, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D.,
The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma G. A. Patterson, M.D., R. Ilves, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., J. D. Cooper, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D.,
Needle Biopsy. Transcarinal Bronchoscopic. Robert T. Fox, M.D., William M. Lees, M.D., + and Thomas W. Shields, M.D.I
 Transcarinal Bronchoscopic Needle Biopsy Robert T. Fox, M.D., William M. Lees, M.D., + and Thomas W. Shields, M.D.I B KONCHOSCOPIC EXAMINATION has for years been one of the major aids in diagnosis and
Transcarinal Bronchoscopic Needle Biopsy Robert T. Fox, M.D., William M. Lees, M.D., + and Thomas W. Shields, M.D.I B KONCHOSCOPIC EXAMINATION has for years been one of the major aids in diagnosis and
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis
 Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY
 EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY Morihito Okada, MD Noriaki Tsubota, MD Masahiro Yoshimura, MD Yoshifumi Miyamoto, MD Hidehito Matsuoka, MD, Shinsuke Satake, MD
EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY Morihito Okada, MD Noriaki Tsubota, MD Masahiro Yoshimura, MD Yoshifumi Miyamoto, MD Hidehito Matsuoka, MD, Shinsuke Satake, MD
Transbronchial fine needle aspiration
 Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis
 Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis Cameron D. Wright, MD ubglottic stenosis is usually due to either endotracheal S tube ischemic necrosis or idiopathic larygotracheal stenosis. The ischemic area
Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis Cameron D. Wright, MD ubglottic stenosis is usually due to either endotracheal S tube ischemic necrosis or idiopathic larygotracheal stenosis. The ischemic area
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma
 Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
Robotic-assisted McKeown esophagectomy
 Case Report Page 1 of 8 Robotic-assisted McKeown esophagectomy Dingpei Han, Su Yang, Wei Guo, Runsen Jin, Yajie Zhang, Xingshi Chen, Han Wu, Hailei Du, Kai Chen, Jie Xiang, Hecheng Li Department of Thoracic
Case Report Page 1 of 8 Robotic-assisted McKeown esophagectomy Dingpei Han, Su Yang, Wei Guo, Runsen Jin, Yajie Zhang, Xingshi Chen, Han Wu, Hailei Du, Kai Chen, Jie Xiang, Hecheng Li Department of Thoracic
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Slide Tracheoplasty
 90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy Etiology - Benign Stenosis Post - intubation Trauma Post - operative Inflammatory Idiopathic
 Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Trachea: a Report of Seven Cases and Literature Review
 Original Article 357 Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Trachea: a Report of Seven Cases and Literature Review Po-Yi Yang, MD; Maw-Sen Liu, MD; Chih-Hung Chen 1, MD; Chin-Ming Lin, MD; Thomas Chang Yao Tsao
Original Article 357 Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Trachea: a Report of Seven Cases and Literature Review Po-Yi Yang, MD; Maw-Sen Liu, MD; Chih-Hung Chen 1, MD; Chin-Ming Lin, MD; Thomas Chang Yao Tsao
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis
 Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis Noel H. Fishman, M.D., Herbert H. Dedo, M.D., William K. Hamilton, M.D., Warren A. Hinchcliffe, M.D., and Benson B. Roe, M.D. D uring the past three years, 12 patients
Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis Noel H. Fishman, M.D., Herbert H. Dedo, M.D., William K. Hamilton, M.D., Warren A. Hinchcliffe, M.D., and Benson B. Roe, M.D. D uring the past three years, 12 patients
Esophageal anastomotic techniques
 Esophageal anastomotic techniques Raphael Bueno, MD, Brigham and Women s Hospital Slide 1 Good afternoon, I would like thank the association and Dr and Dr for inviting me to speak today. Slide 2 I am trying
Esophageal anastomotic techniques Raphael Bueno, MD, Brigham and Women s Hospital Slide 1 Good afternoon, I would like thank the association and Dr and Dr for inviting me to speak today. Slide 2 I am trying
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF)
 Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF) Abstract The results of 25 cases underwent a pedicled pericardial flap coverage for the bronchial
Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF) Abstract The results of 25 cases underwent a pedicled pericardial flap coverage for the bronchial
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Subglottic stenosis, with involvement of the lower larynx
 Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction
 Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction Analysis and Comparison of Findings in 27 Patients and 22 Controls WILLIAM C. ROBERTS, M.D., AND ANCIL
Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction Analysis and Comparison of Findings in 27 Patients and 22 Controls WILLIAM C. ROBERTS, M.D., AND ANCIL
Tracheal Obstruction. G. Robert Mason, M.D., Ralph Ramirez, M.D., and. Safuh Attar, M.D., John Hankins, M.D., Stephen Turney, M.D.
 Tracheal Obstruction Safuh Attar, M.D., John Hankins, M.D., Stephen Turney, M.D., G. Robert Mason, M.D., Ralph Ramirez, M.D., and Joseph McLaughlin, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal obstruction, a life-threatening
Tracheal Obstruction Safuh Attar, M.D., John Hankins, M.D., Stephen Turney, M.D., G. Robert Mason, M.D., Ralph Ramirez, M.D., and Joseph McLaughlin, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal obstruction, a life-threatening
DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA
 Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Left Upper Division Sleeve Segmentectomy for Early Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Segmental Bronchus: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report Left Upper Division Sleeve Segmentectomy for Early Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Segmental Bronchus: Report of Two Cases Junzo Shimizu, MD, 1 Yoshinori Ishida, MD, 1 Takahiro Kinoshita,
Case Report Left Upper Division Sleeve Segmentectomy for Early Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Segmental Bronchus: Report of Two Cases Junzo Shimizu, MD, 1 Yoshinori Ishida, MD, 1 Takahiro Kinoshita,
Long-Term Survival After Resection of Primary Adenoid Cystic and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea and Carina
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Long-Term Survival After Resection of Primary Adenoid Cystic and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea and Carina Henning A. Gaissert, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, M. Behgam Shadmehr,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Long-Term Survival After Resection of Primary Adenoid Cystic and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea and Carina Henning A. Gaissert, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, M. Behgam Shadmehr,
Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma
 CASE REPORTS Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Bronchus Graham Fallon, M.D., Medad Schiller, M.D., and James W. Kilman, M.D. ABSTRACT A 6-year-old child with an unresectable rhabdomyosarcoma of the right
CASE REPORTS Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Bronchus Graham Fallon, M.D., Medad Schiller, M.D., and James W. Kilman, M.D. ABSTRACT A 6-year-old child with an unresectable rhabdomyosarcoma of the right
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon
 Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
9/18/2015. Disclosures. Objectives. Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C. I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest
 Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings
 Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Ormond C. Mendes, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT The lymphatic sump of Borrie is
Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Ormond C. Mendes, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT The lymphatic sump of Borrie is
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER
 MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction. of the esophagogastric junction at. Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D.
 Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Novatech Products for Interventional Pulmonology
 Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
