Egypt Iodine Survey 2014 / Summary Report
|
|
|
- Rosaline Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 Egypt Iodine Survey 2014 / 2015
4
5 Egypt Iodine Survey ACKNOWLEDGMENT The national iodine survey in Egypt was made possible by the commitment and contributions of national and international partners. Funding support was made available through the GAIN-UNICEF USI Partnership Project funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. We would particularly like to acknowledge the support of the following: HE Prof. Dr. Ahmed Emad El-Din Rady the Minister of Health and Population, for his approval, input and continuous support in implementing this study. Ministry of Health and Population, Ministry of Education, National Nutrition Institute,, UNICEF-GAIN, local field teams and Technical and Executive Committees, for their valuable contribution, input, support (fi nancial, technical and logistical), and signifi cant effort that made the study possible. Many thanks to the dedicated MOE, schools, field teams, Central Laboratories and Quality Assurance Team who worked hard under diffi cult and challenging circumstances. We would like to express our sincerest gratitude to all the participants in the current survey including school children, their families and pregnant women. Without their contribution this effort would have been incomplete. Dr. Emad Ezzat Head of PHC and Nursing Sector MOHP Cairo, Egypt 5
6
7 Egypt Iodine Survey Background and Rationale Iodine defi ciency is the single greatest cause of preventable mental impairment globally and also causes many other adverse effects on growth and development due to inadequate thyroid hormone production 1,2. Many of these iodine defi ciency disorders (IDD) result from the effects of iodine defi ciency on fetal brain development during early pregnancy 2,4. Iodizing all salt for human and animal consumption, also known as Universal Salt Iodization (USI), can prevent iodine defi ciency effectively and inexpensively Iodine defi ciency in Egypt has been reported over the past 90 years, starting with an observation of the high prevalence of goiter among Egyptian farmers in A series of studies over the next 70 years revealed some level of iodine defi ciency in different areas across the country The highest prevalence of goiter (82.3%) and lowest urinary iodine concentrations (UIC) were found in Upper Egypt and the New Valley Governorate Egypt was one of six countries that initiated the World Summit for Children in 1990 and one of at least 167 signatories of the overall Declaration and Plan of Action on behalf of the World s Children in which this IDD elimination goal was included 15. In 1996, Egypt passed legislation for the mandatory iodization of table and cooking salt as its main strategy to achieve this goal. Substantial efforts and progress have been made by the Ministry of Health and Population (MOHP) and supporting partners to establish and implement quality-assured USI to prevent the adverse effects of iodine defi ciency among the population 16. In 2003, the Ministry of Industry issued another ministerial decree (Resolution No. 41) that regulated the sale of non-iodized salt and stated that salt for use in households and bakeries should be iodized. This included the requirement for local Baladi bread to be made with iodized salt. Salt used for the animal food industry was exempt from iodization. The Egyptian Organization for Standardization and Quality updated the Egyptian standards for table salt in 2005 and again in 2015 to include salt characteristics, specifi cations and potassium iodate content (30-70 ppm 1 ). The standard now addresses packing, labelling (producer/packer information, iodine logo and potassium iodate level), storage and transport requirements 17. In 2005 a national study was carried that included examination of the relationship between socio-economic characteristics and health status with identifi ed nutritional defi ciencies, IQ and scholastic achievement (Ministry of Health and Population Egypt, 2005). The prevalence of goiter was 36.7% and the median urinary iodine concentration (UIC) was 86 µg/l denoting iodine defi ciency. 43.1% of households in rural areas were using salt that contained no iodine. This indicated that non-iodized salt continued to be available in spite of the legislation requiring all salt to be iodized. Positive correlation was found between urinary iodine concentration and IQ (r = 0.10, P<0.10). 1 Equivalent to ppm iodine 7
8 In , ten years after initiation of USI, the MOHP in collaboration with UNICEF- Egypt implemented the fi rst national school-based iodine survey to evaluate household coverage with iodized salt and iodine nutrition, with regionally-representative data. The results revealed that iodine nutrition status was at optimum levels among schoolage children in all four regions and that 68.3% of households with primary school-age children were using adequately iodized salt (>15ppm), indicating that Egypt was on track to achieve the goal of sustained IDD elimination through salt iodization 18. In summary, through widespread implementation of USI with good compliance by the major salt producers, Egypt made considerable progress from a country with pockets of severe iodine defi ciency, affecting all population groups, to a state of adequate iodine status among PSC at the regional and national levels. However, a study by UNICEF found that, among countries with relatively high overall coverage, Egypt was one of four countries showing the most pronounced disparities in access to quality iodized salt based on wealth. The analysis recommended increased attention to the identifi cation of barriers to the equitable use of adequately iodized salt 19. In , the Egyptian MOHP, in collaboration with GAIN and UNICEF-Egypt, decided to conduct another national survey of household iodized salt coverage and iodine status; to determine progress made since the previous survey towards sustained elimination of IDD among primary school age children (PSC); to verify iodine nutrition among pregnant women (PW), the group most vulnerable to the effect of iodine defi ciency; and to determine current household use of adequately iodized salt. This report presents the fi ndings of the most recent survey. Survey Objectives 1. To assess iodine status in PSC (6 to 12 years of age) through measurement of population median UIC. 2. To assess iodine status among pregnant women (PW) registered within the PHC units/mch of the MOHP through measurement of population median UIC. 3. To determine household use of iodized and adequately iodized salt through quantitative assessment of the iodine content of salt for PSC and PW included in the survey. 4. To determine the relationship between household salt iodine levels and urinary iodine concentrations in both PSC and PW. 5. To investigate changes in iodine status in PSC and in household use of iodized salt since the 2006/2007 survey. 6. To assess knowledge, attitude, and practices of the caretakers of the PSC and of PW regarding iodine defi ciency and the benefi ts of iodized salt use. Methods The survey was a cross sectional multi-stage cluster survey stratifi ed by fi ve regions: Metropolitan, urban Lower Egypt, rural Lower Egypt, urban Upper Egypt and rural Upper Egypt 2. Separate survey sampling procedures were developed to be representative of the two different target populations: primary school children in Egypt, and pregnant women who had registered for antenatal care at a Government primary health care facility. The main outcomes were household salt iodine content assessed by titration and iodine nutrition assessed by median urinary iodine concentration of the population. National results for both indicators were adjusted to account for differences in the proportion of the population in each region. 8 2 Official clearance was not given to conduct the survey in any frontier governorates except El Wadi El Gedid (New Valley). As this governorate is geographically adjacent and culturally similar to the Rural Upper Egypt stratum it was assimilated into this stratum.
9 The target sample size consisted of: i. 3,600 urine samples from primary school children (PSC) 6-12 years of age, together with care-giver completed interviews and salt sample collection conducted at their households; ii. 1,500 urine samples from pregnant women (PW) in their 2 nd or 3 rd trimester 3, with associated completed interviews and collection of household salt samples. In depth training was provided for all fi eld and laboratory staff, including a pilot survey to check all procedures and understanding of the survey teams. Salt and urinary iodine were assessed using quantitative methods with external quality assurance of the laboratory performance. A quality control process was established to check all fi eld work procedures. Double data entry was used with independent review and verifi cation of any discrepancies observed. The Research Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health and Population approved the study. 3 Iodine requirements and level of iodine excretion is expected to be different in each trimester and focusing the study on the 2 nd and 3 rd trimesters provides a more reliable indication of population status in pregnancy. 9
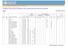
10 Key Findings Characteristics of the survey population - Primary School Aged Children (PSC) There was an even distribution of children by sex and school grade. The majority (80%) of children attended public primary schools, with the remainder split evenly between private and religious (Al Azhar) schools at the national level. At the stratum level, the percent of children attending private schools was highest in Metropolitan areas and Urban Upper Egypt and the percent attending Al Azhar schools was highest in Rural Lower Egypt and lowest in Metropolitan areas. Strata n = completed interviews (unweighted) Variable Sex National Metropolitan Lower Egypt n = 1383 Upper Egypt n = 1306 Urban Rural Urban Rural n = 3284 n = 595 n = 682 n = 701 n = 591 N = 715 Male 53.0% 56.8% 51.3% 53.1% 47.4% 54.0% Female 47.0% 43.2% 48.7% 46.9% 52.6% 46.0% School Grade 3 rd 33.4% 32.9% 34.0% 33.2% 33.0% 33.7% 4 th 33.5% 34.8% 32.1% 33.5% 34.2% 33.1% 5th 33.1% 32.2% 33.9% 33.2% 32.8% 33.1% School Type Public 80.1% 71.1% 87.1% 80.5% 77.5% 83.2% Private 8.8% 25.9% 4.3% 2.6% 14.2% 4.2% Al Azhar 11.2% 3.0% 8.7% 17.0% 8.3% 12.6% Weighted numbers by strata: Metropolitan 612; Lower Egypt: urban 468, rural 1084; Upper Egypt: urban 486, rural
11 The household response rate for completed interviews was 83.5%, for households with analysed salt samples 81.0%, and for urine samples 90.2%.Approximately one-third of primary school children nationally had mothers who were illiterate, one-third had mothers who had intermediate to post-intermediate education and the remainder had mothers who had less than secondary education (15%) or higher education (9%). By strata (not including metropolitan due to high missing rate), the highest level of illiteracy among mothers was in Rural Upper Egypt, which also had the lowest percent of mothers reaching higher education. The median household durable goods score was lowest (indicating poorer household wealth) in Rural Upper Egypt and highest in Metropolitan areas and Urban Upper Egypt. Maternal Level of Education (8.9% missing data nationally) Strata n = completed interviews (unweighted) National Metropolitan 1 Lower Egypt n = 1383 Upper Egypt n = 1306 Variable n = 3284 Urban Rural Urban Rural n = 595 n = 682 n = 701 n = 591 N = 715 Illiterate 33.7% 17.6% 26.1% 26.8% 27.1% 59.2% < Secondary 15.7% 17.6% 13.3% 14.2% 18.4% 15.7% Intermediate to Post Intermediate 32.7% 23.2% 42.3% 44.0% 34.8% 20.2% Higher 9.1% 9.7% 10.4% 10.0% 16.1% 3.5% Household Durable Goods Median Score 2 1 Education level information was missing for 31.8% of all mothers/caretakers in Metropolitan areas. In all other strata it was less than 10%. 2 Durable goods score is a proxy for household wealth, scored 0-14 from a list of household items All further tables present weighted numbers and estimates. 11
12 Characteristics of the survey population Pregnant Women (PW) The majority (>50%) of PW were in the age group years. At the national level approximately 60 of PW were in their 3 rd trimester and this was the same in all regions except for Metropolitan where just over 60% of PW were in their 2 nd trimester. The mean household size, which correlated closely with the durable goods score (a proxy measure of wealth) was lowest in Metropolitan regions and highest in Rural Upper Egypt. National n = 1500 Variable Strata n = completed interviews (unweighted) Metropolitan n = 300 Lower Egypt n = 600 Upper Egypt n = 600 Urban Rural Urban Rural n = 300 n = 300 n = 300 N = % 11.0% 11.0% 13.3% 12.0% 17.7% Age Group 1 (years) % 27.0% 37.7% 38.7% 37.3% 41.0% % 29.3% 28.3% 28.0% 26.7% 25.0% % 19.7% 14.0% 13.3% 16.3% 11.0% % 13.0% 8.6% 6.4% 7.7% 5.3% Pregnancy Trimester 2 nd 39.3% 66.0% 40.0% 31.3% 47.3% 42.0% 3 rd 59.4% 34.3% 59.3% 67.7% 50.7% 56.7% Household Mean Size Weighted numbers by strata: Metropolitan 82; Lower Egypt: urban 132, rural 599; Upper Egypt: urban 120, rural Missing percent at the national level: Age group 0.2%, Pregnancy trimester 1.2% 12
13 The response rate for completed interviews (replacements used) was 100.0%, households with analyzed salt samples 98.0%, and urine samples 99.9%. The level of education varied signifi cantly between strata, with highest levels of education among PW in Lower Egypt. Over 89% of women from all regions reported that they were not in paid employment. Strata n = completed interviews (unweighted) National n = 1500 Variable Metropolitan n = 300 Lower Egypt n = 600 Upper Egypt n = 600 Urban n = 300 Rural n = 300 Urban n = 300 Rural N = 300 Illiterate 15.8% 24.3% 10.3% 9.7% 16.0% 22.3% < Secondary 22.0% 32.4% 21.9% 16.9% 23.7% 25.7% Education Intermediate to Post Intermediate 51.3% 33.6% 55.4% 58.3% 49.0% 46.0% Higher 10.8% 9.7% 12.3% 15.0% 11.3% 6.0% Employment Status 1 2 nd 93.2% 92.0% 93.2% 92.0% 89.3% 95.3% 3 rd 6.6% 7.7% 6.3% 7.7% 10.3% 4.7% 1 Missing percent at the national level: Employment status 0.2%, 13
14 Findings for Iodine Status Primary School Aged Children (PSC) Iodine status among PSC in the survey in Egypt was in the optimal range, indicating adequate iodine intake nationally and in all strata (median Urinary Iodine Concentration (UIC) between 100 and 299µg/L 20 ). Adequate iodine intake has been maintained among PSC since the previous survey (2006-7). There was a signifi cant association between PSC household salt iodine category and median UIC. The median UIC among PSC from households using non-iodized salt (<5ppm iodine) was 110µg/L, compared with a median of 180µg/L among PSC living in households where the salt was adequately iodized (>15ppm iodine). o When data were disaggregated by urban and rural areas, the median UIC among PSC from households using non-iodized salt was below optimal (90µg/L) in rural areas, indicating inadequate iodine intake among PSC in this region. The median UIC was higher among PSC attending private schools and among PSC whose mothers had a higher educational level; however, adequate intake was found in all of these sub-groups of type of school and maternal education. 14
15 Findings for Iodine Status Pregnant Women (PW) Iodine status was assessed nationally among pregnant women for the fi rst time in the survey. The sample represents women who had registered for antenatal care at a Government primary health care facility and were in the 2 nd or 3 rd trimester of pregnancy. The median UIC for PW was slightly below optimum iodine status nationally (median below 150µg/L 21 ). In Metropolitan areas and Urban Upper Egypt however, the median UIC indicated that PW in these areas have adequate iodine intake. Sub-optimum iodine status was found for PW in the remaining three regions, with lowest status among PW in Rural Upper Egypt. There was a signifi cant association between PW household salt iodine category and median UIC. PW from households using non- or inadequately iodized salt (<15ppm iodine) had below-optimal iodine status, while PW from households where the salt iodine content was 15ppm and above had adequate iodine status. The median UIC among PW was higher in the second (150.0µg/L) than the third (137.0µg/L) trimester and increased slightly with improved educational level; however when investigated by education level, the median UIC did not reach 150 µg/l even among PW with higher education. PW in formal employment had optimal iodine status (median UIC 180µg/L); however, the numbers in this group were very small 15
16 Findings for Household Salt Iodine Primary School Age Children (PSC) Results are only presented here for household salt iodine for PSC since this sample was more fully representative of the national population than the sample of pregnant women. Findings for household salt for PW were, overall, very similar to those shown here for PSC 4. Nationally, 74.7% of PSC households were using adequately iodized salt (>15ppm). Only 7.5% of households were using salt with no added iodine (<5ppm). There was a signifi cant difference in the distribution of household salt with different iodine levels between strata: Metropolitan areas had the highest household coverage of adequately iodized salt (82.9%), while Rural Upper Egypt had the lowest coverage (69.6%). Results suggest that household use of adequately iodized salt has increased from 69.1% to 74.7% over 8 years since the survey 5. A particular improvement in household coverage with adequately iodized salt was observed for Lower Egypt as a whole, from 58.2% in to 74.6% in At the national level, the proportion of salt with iodine in the recommended range (15-40ppm) has increased from 31.1% in to 69.5% in All results are presented in the full, long version, survey report 5 Results are not directly comparable due to lack of a weighted estimate for survey.
17 Analysis of key factors associated with iodine status and household salt iodine level A correlation analysis indicated that urinary iodine concentration was strongly infl uenced by household salt iodine level among both population groups (correlation coeffi cient among PSC and among PW). Other factors signifi cantly associated with iodine status among PSC were durable goods score and maternal years of schooling. These factors (durable goods score and woman s own educational level) did not quite reach the level of signifi cance when correlated with UIC among PW. The factor found to be most signifi cantly associated with household salt iodine in PSC households was the durable goods score (correlation coeffi cient 0.223). Maternal education was also a signifi cantly associated factor, but less strongly. Awareness of iodine deficiency and the National Salt Iodization Program. And household salt purchasing practice 6 At the national level, only a minority of mothers of PSC (11.2%) and PW (9.0%) reported to have heard about iodine deficiency as a problem. The level of awareness varied significantly between strata. For mothers of PSC, highest awareness was in Metropolitan regions (19.4%) and lowest in Rural Upper Egypt (5.2%). In contrast, among pregnant women awareness was lowest in Metropolitan regions (5.2%) and highest (about 12%) in both Rural areas. Awareness varied significantly according to educational level and was highest among women with higher education for both PSC mothers (31.8%) and PW (22.2%), and lowest among illiterate women in both groups (<3.5%). At the national level, only 21.4% of PSC mothers and 19.8% of PW were aware that salt has been iodized by governmental decree. Awareness was significantly different by strata. For mothers of PSC, awareness was lowest in Rural Upper Egypt at 10.4%. For PW, awareness was similar among all strata except Metropolitan, where it was at 6.3%. Awareness of government decreed salt iodization increased with increasing educational level from just under 6% for illiterate women (both mothers of PSC and PW) to 43% among mothers of PSC, and 45% among PW with higher education. For mothers of PSC and PW, the main source of information about Governmentdecreed salt iodization was television (44.0% and 39.5% respectively) followed by health care facilities (13.3% and 22.2% respectively) then statements on salt packages (13.1% and 11.3% respectively). Nationally, 86.7% of PW reported using packaged salt for cooking, with 8.1% using loose salt and 5.2% using both packaged and loose. Similarly, 85.6% of mothers of PSC reported to use packaged salt for cooking. Results for the use of packaged cooking salt in households of PW varied significantly across the strata and by education level. By strata: the highest use of packaged salt was reported in Metropolitan areas (95.3%) and lowest use in Rural Upper Egypt (81.7%). By education level: the highest use of packaged salt was reported by PW with higher education (96.9%), with the lowest use in PW who reported they were illiterate (83.5%). 6 Note: the survey technical advisory group has some reservations about the reliability of the resulting data for the knowledge and awareness questions. 17
18 Discussion Points Egypt has made signifi cant progress towards achieving optimal iodine status through universal salt iodization, as shown by the optimal iodine status among primary school children nationally and in all fi ve regions (sustained since the survey). Although iodine intake appears to be just below optimal among the surveyed group of pregnant women at the national level, the fact that intake was adequate in the two most urbanized regions of Egypt indicates that it is possible to achieve adequacy among this most vulnerable group of the population. Of particular note is the fact that adequate intake was achieved among pregnant women living in households that were using adequately iodized salt. The global target for USI, > 90% households using adequately iodized salt, has not yet been achieved, however all regions in the current survey had household coverage rates for adequately iodized salt of at least 70% and less than 5% of households in urban areas were using salt with no added iodine, rising to 10% in the two rural regions. An analysis of the distribution of salt iodine levels indicated large improvements in production quality control since 2006/2007, as well as an apparent overall increase in household use of adequately iodized salt, especially in Upper and Lower Egypt 7. The household iodized salt coverage results from this survey were in line with results from the 2014 DHS 22 which reported that 90.9% of households were using salt with some iodine (compared with 92.5% in this survey). Despite this progress towards achieving optimal iodine nutrition through USI in Egypt, there remains room for improvement in achieving the goal of at least 90% household coverage of adequately iodized salt and adequate iodine nutrition among all population groups, especially in rural areas Available national data for this indicator for are not adjusted for population weight and can therefore not be considered directly comparable with data
19 Iodine Status Cross tabulation and regression analyses of the current survey data show the association between iodine status and household salt iodine content. This association was found to be stronger in rural than in urban areas 8. The regression analysis suggests that, after controlling for the infl uence of household salt iodine level, the most important factors related to iodine status are those related with residence (urban/rural) and socioeconomic status (e.g. household durable goods score). These fi ndings of higher overall iodine intake that is less strongly associated with household salt iodine among PSC from wealthier urban households suggests that these children may have more diverse diets and be obtaining dietary salt, potentially iodized, and other sources of dietary iodine, from a wider variety of sources than just household salt. This is a pattern that has been observed globally, especially in urban and wealthier areas. 30,31,32 Potential sources of additional dietary iodine in Egypt may include the use of iodized salt in certain processed foods (which may be produced using iodized salt even without specifi c regulations requiring this) and dairy products, which are key sources of iodine in some countries due to iodine-supplementation of dairy herds 15 The 2007 Joint Statement from WHO and UNICEF on: Reaching Optimal Iodine Nutrition in Pregnant and Lactating 27, recommended that women living in a population with 50-90% household coverage with adequately iodized salt and a median UIC at or above 100 µg/l in other PSC (which has been sustained for at least two years), are not in need of iodine supplementation in pregnancy. Evidence from this survey indicates that this is the situation applying in most of Egypt, however there may be small subnational areas this is not the case and it should be considered that this survey did not include any information from four frontier governorates. It is currently not common practice in Egypt for Government antenatal facilities to routinely prescribe iodine-containing supplements, most pre-natal supplements do not contain iodine, and women tend to register for antenatal care when already in their second trimester. A recent paper agreeing with the WHO/UNICEF recommendation above 35 provides information which suggests that for the majority of the Egyptian population, the emphasis should be on improving access to adequately iodized salt and on a review of national legislation to consider regulating for iodized salt in a wider variety of food products than bread, to ensure that all major sources of dietary salt are contributing to iodine intake. Iodized Salt The survey illustrated that despite the many changes in Egypt over the past fi ve years, iodized salt producers should be credited with maintaining a consistent supply of quality-assured iodized salt. The high proportion of iodized salt within the nationally regulated range of 15-40ppm iodine represents a signifi cant improvement in production quality control over the past eight years. Despite this, certain supply-related factors remain that are preventing achievement of 90% household coverage with adequately iodized salt. Results from this survey confi rm that inequitable access continues however the gap is decreasing. Further strengthening regulatory monitoring, including of salt re-packers, will help to further improve the iodization quality and packaging of salt supplied to remaining areas with lowest coverage to address this gap. If, as mentioned above, the national legislation is changed to mandate the use of iodized salt iodization in a wider variety of food products, then regulatory monitoring will 8 Not all data are shown 19
20 need to expand to cover food industries. A monitoring system for Baladi bread bakeries piloted by the Ministry of Supply and Internal Trade, with support from WFP and GAIN, found that most bakeries were using adequately iodized salt, indicating the feasibility of iodized salt use and monitoring of relatively small food production units. If other widely consumed food products also included quality controlled iodized salt in their production, the potential iodine intake of the population, including PW, would be expected to increase. Awareness of Iodine Deficiency and Iodized Salt The survey results indicate surprisingly low awareness of iodine defi ciency and iodized salt among women in Egypt. As noted in the results, there are some technical concerns about the questions employed and further qualitative research is recommended to verify the fi ndings. In Egypt, women are usually the decision makers when it comes to the selection of food products for their families. Improving their awareness about the impact of iodine defi ciency and of its prevention through selection of quality iodized salt is one step towards raising the proportion of HH using iodized salt and achieving the goal of sustained optimal iodine nutrition among all population groups. Since salt is a low cost commodity used on a daily basis, an approach based on long-term, multi-channel information is recommended. Information to all age groups via well-informed education personnel, health personnel and retailers, together with appropriate messages on salt packets can be a sustained source of awareness raising about iodine defi ciency and the benefi ts of choosing iodized over non-iodized salt. Summary Recommendations The survey technical advisory group along with the IDD committee made the following recommendations based on the survey results: 1. Ensure sustainability of optimal iodine nutrition and current progress towards USI through a continued multi sector approach and development of a sustainability action plan 2. Review national legislation and standards (use of iodized salt for all human and animal consumption, which would include its use in the processed food industry) 3. Ensure continued quality control and regulatory monitoring of salt iodization and periodic assessments of iodine nutrition. A mechanism of ongoing surveillance should be implemented to identify pockets of low access to adequately iodized salt and of sub-optimal iodine status (particularly among pregnant women), with a plan for follow up action where identifi ed. 4. Assess the impact of community awareness on consumer choice, in the context of lower availability of adequately iodized salt, especially in rural areas. Implement a sustainable (long term) awareness raising strategy through working with the education and health systems and with retailers, in areas where considered appropriate. 5. Further mobilize private sector salt industry (including salt re-packers) and food producers to support, implement and quality-assure any strengthened legislation/ standards. 20
21 Egypt Iodine Survey 2014/ iodine book design MGshort repo.indd 21 10/19/16 10:17 PM
22 References 1. WHO Micronutrient defi ciencies. WHO Available at: en/. (Accessed: 27th May 2016) 2. Delange, F. Iodine defi ciency as a cause of brain damage. Postgrad Med J 77, (2001). 3. World Health Organization. Iodine and Health. Eliminating iodine defi ciency disorders safely through salt iodization. A statement by the World Health Organization. (1994). 4. Pearce, E. N. Effects of iodine defi ciency in pregnancy. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 26, (2012). 5. World Summit for Children -Mid-Decade Goal: Iodine Defi ciency Disorders (IDD). (1994). 6. World Health Organization. Guideline: Fortifi cation of food-grade salt with iodine for the prevention and control of iodine defi ciency disorders. (2014). 7. Dolbey, R. & Omar, M. A note concerning the incidence of goiter in Egypt. Lancet 207, (1924). 8. Abdou, I., Ali, H. & Basioni, A. Nutritional defi ciencies, goiter, dental caries and parasitic infestations among school children in Cairo. Bull Nutr Inst Cairo Egypt 4, (1968). 9. El-Sayed, N., Ismail, H., Hussein, M. & Kamel, A. R. Assessment of the prevalence of IDD among primary school children in Cairo. East. Mediterr. Health J. 1, (1995). 10. Cairo Nutritional Institute and WHO. Report on the prevalence of IDD among school children in Egypt. (1992). 11. High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria University, Maternal and Child Health Care Sector, Ministry of Health and Population, in collaboration with UNICEF. Assessment of the prevalence of IDD and iodized salt use in New Valley Governorate. (1999). 12. Primary Health Care Sector, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria University, Egypt in collaboration with UNICEF. Report on assessment of the prevalence of IDD in El-Minia, Assuit, Sohag and Kafr- El-Sheikh Governorates. (1996). 13. Primary Health Care Sector, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria University, Egypt in collaboration with UNICEF. Report on assessment of the prevalence of IDD in New Valley Governorate. (1993). 14. El-Sayed, N. Iodine defi ciency disorders among school children in upper Egypt: an epidemiologic study. J. Trop. Pediatr. 44, (1998). 15. World Summit for Children (1990). 16. Khallaf, N. Review and in-depth analysis of the existing laws and regulations related to salt iodization in Egypt. (2009). 17. World Trade Organization & Egyptian Organization for Standardization and Quality. Egyptian Standard for Table Salt Fortifi ed with Iodine ES: /2015. (2015). 18. MOHP & UNICEF Egypt. National Iodine Nutrition Survey in Egypt (2008). 19. UNICEF STATISTICS. Percentage of households consuming adequately iodized salt among the richest and poorest quintiles, in 43 countries with available data, Available at: (Accessed: 27th May 2016) 20. Zimmermann, M. B. et al. Thyroglobulin Is a Sensitive Measure of Both Defi cient and Excess Iodine Intakes in Children and Indicates No Adverse Effects on Thyroid Function in the UIC Range of μg/l: A UNICEF/ICCIDD Study Group Report. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, (2013). 21. International Council for Control of Iodine Defi ciency Disorders, UNICEF & World Health Organization. Assessment of iodine defi ciency disorders and monitoring their elimination: a guide for programme managers. (World Health Organization, 2007). 22. Ministry of Health and Population (Egypt), El-Zanaty and Associates (Egypt) & ICF International. Egypt Demographic and Health Survey (2015). 22
23 23
24 UNITED NATIONS CHILDREN S FUND 87 Misr Helwan Agricultural Road. Maadi, Cairo. Egypt Telephone:
iodine book design MG full report v2.indd 1
 iodine book design MG full report v2.indd 1 10/19/16 10:10 PM National Survey of Household Iodised Salt Use and Iodine Status among Primary School Children and Pregnant Women in Egypt 2014/2015 Contents
iodine book design MG full report v2.indd 1 10/19/16 10:10 PM National Survey of Household Iodised Salt Use and Iodine Status among Primary School Children and Pregnant Women in Egypt 2014/2015 Contents
Ministère de la Santé et de l Action Sociale Summary Report
 Ministère de la Santé et de l Action Sociale Summary Report National survey on household utilisation of iodised salt and bouillon and on iodine status of women of reproductive age in Senegal 2014 AUGUST
Ministère de la Santé et de l Action Sociale Summary Report National survey on household utilisation of iodised salt and bouillon and on iodine status of women of reproductive age in Senegal 2014 AUGUST
EGYPT. Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS)
 Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Iodine Deficiency The database on iodine deficiency includes data by country on goitre prevalence and/or urinary iodine concentration
Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Iodine Deficiency The database on iodine deficiency includes data by country on goitre prevalence and/or urinary iodine concentration
Statistical analysis and comments on the USI-IDD survey Azerbaijan 2007
 Statistical analysis and comments on the USI-IDD survey Azerbaijan 2007 Frits van der Haar, PhD Global Public Nutrition Services LLC 2700 Evans Dale Cir Atlanta GA 30340 USA fvander@sph.emory.edu BACKGROUND
Statistical analysis and comments on the USI-IDD survey Azerbaijan 2007 Frits van der Haar, PhD Global Public Nutrition Services LLC 2700 Evans Dale Cir Atlanta GA 30340 USA fvander@sph.emory.edu BACKGROUND
Uganda Fortification Assessment Coverage Tool: (FACT) Overview and Results Kampala, Uganda 23 May 2016
 Uganda Fortification Assessment Coverage Tool: (FACT) Overview and Results Kampala, Uganda 23 May 2016 www.gainhealth.org Background 2 Background and Rationale High burden of malnutrition in Uganda National
Uganda Fortification Assessment Coverage Tool: (FACT) Overview and Results Kampala, Uganda 23 May 2016 www.gainhealth.org Background 2 Background and Rationale High burden of malnutrition in Uganda National
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS); Volume 8, No. 2, May 2011 Special Issue: National Nutrition Survey Papua New Guinea,
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS); Volume 8, No. 2, May 2011 Special Issue: National Nutrition Survey Papua New Guinea,
IODINE DEFICIENCY DISORDERS IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION: SITUATION ANALYSIS AND WAY FORWARD. Report of the Regional Director CONTENTS
 24 June 2008 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-eighth session Yaounde, Republic of Cameroon, 1 5 September 2008 Provisional agenda item 7.5 IODINE DEFICIENCY DISORDERS IN THE WHO AFRICAN
24 June 2008 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-eighth session Yaounde, Republic of Cameroon, 1 5 September 2008 Provisional agenda item 7.5 IODINE DEFICIENCY DISORDERS IN THE WHO AFRICAN
Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela
 Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela 2007-2008 Caballero Luis (*) (*) Physician responsible for the Coordination of the Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control
Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela 2007-2008 Caballero Luis (*) (*) Physician responsible for the Coordination of the Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control
Child and Adult Nutrition
 Children in Egypt 2015 A STATISTICAL DIGEST Chapter 5 Child and Adult Nutrition Children in Egypt 2015 Children in Egypt 2015 is a statistical digest produced by UNICEF Egypt to present updated and quality
Children in Egypt 2015 A STATISTICAL DIGEST Chapter 5 Child and Adult Nutrition Children in Egypt 2015 Children in Egypt 2015 is a statistical digest produced by UNICEF Egypt to present updated and quality
SEA-FHR-1. Life-Course. Promoting Health throughout the. Department of Family Health and Research Regional Office for South-East Asia
 SEA-FHR-1 Promoting Health throughout the Life-Course Department of Family Health and Research Regional Office for South-East Asia the health and development of neonates, children and adolescents
SEA-FHR-1 Promoting Health throughout the Life-Course Department of Family Health and Research Regional Office for South-East Asia the health and development of neonates, children and adolescents
Myanmar Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Myanmar Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Myanmar has experienced growth in Dietary Energy Supply (DES). Dietary quality remains poor, low on protein and vitamins and with high carbohydrates.
Key Indicators Myanmar Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Myanmar has experienced growth in Dietary Energy Supply (DES). Dietary quality remains poor, low on protein and vitamins and with high carbohydrates.
Considerations in calculating flour consumption in a country. Janneke H. Jorgensen, World Bank
 Considerations in calculating flour consumption in a country Janneke H. Jorgensen, World Bank 1 Overview Why calculate flour consumption Factors to be considered Potential sources and quality of data National
Considerations in calculating flour consumption in a country Janneke H. Jorgensen, World Bank 1 Overview Why calculate flour consumption Factors to be considered Potential sources and quality of data National
The Krakow Declaration on Iodine
 The Krakow Declaration on Iodine Tasks and Responsibilities for Prevention Programs Targeting Iodine Deficiency Disorders The EUthyroid Consortium Short running title: Krakow Iodine Declaration of the
The Krakow Declaration on Iodine Tasks and Responsibilities for Prevention Programs Targeting Iodine Deficiency Disorders The EUthyroid Consortium Short running title: Krakow Iodine Declaration of the
NATIONAL STRATEGY on the elimination of iodine deficiency disorders by universal iodization of salt intended for direct human use and for bread baking
 NATIONAL STRATEGY on the elimination of iodine deficiency disorders by universal iodization of salt intended for direct human use and for bread baking 2004-2012 Bucharest, 2005 1 Editura MarLink Tel/Fax:
NATIONAL STRATEGY on the elimination of iodine deficiency disorders by universal iodization of salt intended for direct human use and for bread baking 2004-2012 Bucharest, 2005 1 Editura MarLink Tel/Fax:
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
Fill the Nutrient Gap Pakistan: Rationale, key findings and recommendations. Fill the Nutrient Gap National Consultation Islamabad, 11 April 2017
 Fill the Nutrient Gap Pakistan: Rationale, key findings and recommendations Fill the Nutrient Gap National Consultation Islamabad, 11 April 2017 Meeting nutrient requirements is a prerequisite for preventing
Fill the Nutrient Gap Pakistan: Rationale, key findings and recommendations Fill the Nutrient Gap National Consultation Islamabad, 11 April 2017 Meeting nutrient requirements is a prerequisite for preventing
PHN06: Iodine Deficiency Disorders: Interventions that Worked, Lessons Learnt
 PHN06: Iodine Deficiency Disorders: Interventions that Worked, Lessons Learnt Objectives The last years have seen a worldwide effort to reduce the massive number of people suffering from iodine deficiency
PHN06: Iodine Deficiency Disorders: Interventions that Worked, Lessons Learnt Objectives The last years have seen a worldwide effort to reduce the massive number of people suffering from iodine deficiency
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 Executive Board of the Development Programme, the Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 31 July 2014 Original: English Second regular session 2014 2 to 5 September
Executive Board of the Development Programme, the Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 31 July 2014 Original: English Second regular session 2014 2 to 5 September
Serbia. Historically, goiter and cretinism were significant public health problems in Yugoslavia. The earliest
 Serbia Historically, goiter and cretinism were significant public health problems in Yugoslavia. The earliest studies by Sahovic and coworkers identified endemic areas in Serbia and marked Badovinci, Josanica
Serbia Historically, goiter and cretinism were significant public health problems in Yugoslavia. The earliest studies by Sahovic and coworkers identified endemic areas in Serbia and marked Badovinci, Josanica
CHILDREN IN EGYPT A statistical digest
 CHILDREN IN EGYPT 2015 A statistical digest Statistics contained in this publication are those available to UNICEF Egypt up to June 2015 and refer to 2015 and/ or previous years. UNICEF encourages the
CHILDREN IN EGYPT 2015 A statistical digest Statistics contained in this publication are those available to UNICEF Egypt up to June 2015 and refer to 2015 and/ or previous years. UNICEF encourages the
Myanmar - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Myanmar - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Myanmar has experienced growth in Dietary Energy Supply (DES). Dietary quality remains poor, low on protein and vitamins and with high carbohydrates.
Key Indicators Myanmar - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Myanmar has experienced growth in Dietary Energy Supply (DES). Dietary quality remains poor, low on protein and vitamins and with high carbohydrates.
Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability
 20/3/2012 Food and Agriculture COST Action, Zürich 4-5 June Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability Dr. Maria Andersson Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland 2 3 1993
20/3/2012 Food and Agriculture COST Action, Zürich 4-5 June Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability Dr. Maria Andersson Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland 2 3 1993
UNICEF Nepal Country Office (NCO) Terms of Reference
 UNICEF Nepal Country Office (NCO) Terms of Reference National Consultancy for National Integrated Micronutrients Guideline Development and updating training package on Micronutrients (Vitamin A Deficiency,
UNICEF Nepal Country Office (NCO) Terms of Reference National Consultancy for National Integrated Micronutrients Guideline Development and updating training package on Micronutrients (Vitamin A Deficiency,
Joint project: NDOH, SMHS UPNG, CUSTOMS, NAQIA etc.
 Title of Project: SITUATION ANALYSIS OF IMPORTED SALT AND RICE INTO PNG: NUMBER & QUANTITY OF IMPORTS AND EXTENT OF FORTIFICATION. Joint project: NDOH, SMHS UPNG, CUSTOMS, NAQIA etc. 1 Presented to SMHS
Title of Project: SITUATION ANALYSIS OF IMPORTED SALT AND RICE INTO PNG: NUMBER & QUANTITY OF IMPORTS AND EXTENT OF FORTIFICATION. Joint project: NDOH, SMHS UPNG, CUSTOMS, NAQIA etc. 1 Presented to SMHS
SURVEY AND DETECTION OF IODINE DEFICIENCY
 SURVEY AND DETECTION OF IODINE DEFICIENCY Anwar Dudin, Annie Rambaud-Cousson, Amin Thalji, Ghaleb Zughayer Pediatric department-makassed Hospital-Jerusalem I-AVAILABLE DATA IN THE SOCIETY 1-NEONATAL SCREENING
SURVEY AND DETECTION OF IODINE DEFICIENCY Anwar Dudin, Annie Rambaud-Cousson, Amin Thalji, Ghaleb Zughayer Pediatric department-makassed Hospital-Jerusalem I-AVAILABLE DATA IN THE SOCIETY 1-NEONATAL SCREENING
Improving Programme Implementation through Embedded Research (ipier) EMRO Region PROJECT SUMMARIES
 Egypt Factors contributing to the failure of the health system to regulate private facilities in Egypt Mohammed NOUR EL-DIN and Population Despite efforts by the to increase the proportion of institutional
Egypt Factors contributing to the failure of the health system to regulate private facilities in Egypt Mohammed NOUR EL-DIN and Population Despite efforts by the to increase the proportion of institutional
Evaluation of the Kajiado Nutrition Programme in Kenya. May By Lee Crawfurd and Serufuse Sekidde
 Evaluation of the Kajiado Nutrition Programme in Kenya May 2012 By Lee Crawfurd and Serufuse Sekidde 1 2 Executive Summary This end-term evaluation assesses the performance of Concern Worldwide s Emergency
Evaluation of the Kajiado Nutrition Programme in Kenya May 2012 By Lee Crawfurd and Serufuse Sekidde 1 2 Executive Summary This end-term evaluation assesses the performance of Concern Worldwide s Emergency
The Economic and Social Council, Recalling the United Nations Millennium Declaration13 and the 2005 World Summit Outcome, 1
 Resolution 2010/24 The role of the United Nations system in implementing the ministerial declaration on the internationally agreed goals and commitments in regard to global public health adopted at the
Resolution 2010/24 The role of the United Nations system in implementing the ministerial declaration on the internationally agreed goals and commitments in regard to global public health adopted at the
Iodine and Thyroid Hormones
 Iodine and Thyroid Hormones Iodine and Thyroid Hormones feed-back Iodine Deficiency Characteristics Iodine Deficiency None Mild Mode Severe Median urine iodine >100 50-99 20-49
Iodine and Thyroid Hormones Iodine and Thyroid Hormones feed-back Iodine Deficiency Characteristics Iodine Deficiency None Mild Mode Severe Median urine iodine >100 50-99 20-49
Ethnicity and Maternal Health Care Utilization in Nigeria: the Role of Diversity and Homogeneity
 Ethnicity and Maternal Health Care Utilization in Nigeria: the Role of Diversity and Homogeneity In spite of the significant improvements in the health of women worldwide, maternal mortality ratio has
Ethnicity and Maternal Health Care Utilization in Nigeria: the Role of Diversity and Homogeneity In spite of the significant improvements in the health of women worldwide, maternal mortality ratio has
Visionary Development Goal on Sexual and Reproductive Health & Rights
 Visionary Development Goal on Sexual and Reproductive Health & Rights Sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) are inter-linked to all key development agendas and are central to human health and
Visionary Development Goal on Sexual and Reproductive Health & Rights Sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) are inter-linked to all key development agendas and are central to human health and
CHAPTER 9 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS FRAMEWORK FOR MAKING RECOMMENDATIONS
 CHAPTER 9 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS FRAMEWORK FOR MAKING RECOMMENDATIONS Initially, the prime objective of this study was to assess the anthropometric, vitamin A and iron status in children 6-71 months old
CHAPTER 9 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS FRAMEWORK FOR MAKING RECOMMENDATIONS Initially, the prime objective of this study was to assess the anthropometric, vitamin A and iron status in children 6-71 months old
Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network
 Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network Jonathan Gorstein Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Global Health/ Nutrition
Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network Jonathan Gorstein Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Global Health/ Nutrition
Food fortification in five Southeast Asian countries: SMILING project
 Food fortification in five Southeast Asian countries: SMILING project Pattanee Winichagoon, Ph.D On behalf of the SMILING team Presented at the SMILING Symposium 20 th International Congress of Nutrition,
Food fortification in five Southeast Asian countries: SMILING project Pattanee Winichagoon, Ph.D On behalf of the SMILING team Presented at the SMILING Symposium 20 th International Congress of Nutrition,
Lao PDR. Maternal and Child Health and Nutrition status in Lao PDR. Outline
 Maternal and Child Health and Nutrition status in Lao PDR Outline Brief overview of maternal and child health and Nutrition Key interventions Challenges Priorities Dr. Kopkeo Souphanthong Deputy Director
Maternal and Child Health and Nutrition status in Lao PDR Outline Brief overview of maternal and child health and Nutrition Key interventions Challenges Priorities Dr. Kopkeo Souphanthong Deputy Director
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/MOZ/7 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 18 October 2006 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/MOZ/7 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 18 October 2006 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
A NEW DAWN SHEDS LIGHT ON DIABETES PSYCHOLOGY
 A NEW DAWN SHEDS LIGHT ON PSYCHOLOGY The psychosocial aspect of diabetes may be overlooked as healthcare professionals strive to help people with diabetes meet their glycaemic targets. Three new papers
A NEW DAWN SHEDS LIGHT ON PSYCHOLOGY The psychosocial aspect of diabetes may be overlooked as healthcare professionals strive to help people with diabetes meet their glycaemic targets. Three new papers
Dietary intake profile among Tunisians school children having iodine deficiency or excess
 Dietary intake profile among Tunisians school children having R. Doggui* 1, M. El Ati-Hellal 2, P. Traissac 3, H. Ben Gharbia 4, J. El Ati 1 1 Institut National de Nutrition et de Technologie Alimentaire,
Dietary intake profile among Tunisians school children having R. Doggui* 1, M. El Ati-Hellal 2, P. Traissac 3, H. Ben Gharbia 4, J. El Ati 1 1 Institut National de Nutrition et de Technologie Alimentaire,
3 Indicators of the salt iodization process
 3 Indicators of the salt iodization process 3.1 Factors that determine salt iodine content Appropriate legislation and supportive regulations constitute the point of departure, or cornerstone, of the salt
3 Indicators of the salt iodization process 3.1 Factors that determine salt iodine content Appropriate legislation and supportive regulations constitute the point of departure, or cornerstone, of the salt
MONGOLIA. The 1997 World Vision/Nutrition Research Center (WV/NRC) report showed that 5.8% of infants were born with a low birth weight (<2500 g).
 MONGOLIA Population 1 2 442.540 Infant mortality rate 2 30.4 per 1000 live births Life expectancy at birth 1 65.3 years Fertility rate 1 2.2 Annual population growth 1 1.4% NUTRITION OVERVIEW Major achievements
MONGOLIA Population 1 2 442.540 Infant mortality rate 2 30.4 per 1000 live births Life expectancy at birth 1 65.3 years Fertility rate 1 2.2 Annual population growth 1 1.4% NUTRITION OVERVIEW Major achievements
WFP and the Nutrition Decade
 WFP and the Nutrition Decade WFP s strategic plan focuses on ending hunger and contributing to a revitalized global partnership, key components to implement and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
WFP and the Nutrition Decade WFP s strategic plan focuses on ending hunger and contributing to a revitalized global partnership, key components to implement and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Risk Factors for Hepatitis C Infection in a National Adult Population: Evidence from the 2008 Egypt DHS
 Risk Factors for Hepatitis C Infection in a National Adult Population: Evidence from the 2008 Egypt DHS Jasbir Sangha*, Ann Way*, Fatma El-Zanaty, and Nasr El-Sayed *ICF Macro, Demographic and Health Surveys,
Risk Factors for Hepatitis C Infection in a National Adult Population: Evidence from the 2008 Egypt DHS Jasbir Sangha*, Ann Way*, Fatma El-Zanaty, and Nasr El-Sayed *ICF Macro, Demographic and Health Surveys,
National Nutrition Policy Statement. Operational Plan of Action for Nutrition
 8/6/2008 National Nutrition Policy Statement Operational Plan of Action for Nutrition 2008 2010 Palestinian National Authority Ministry of Health Nutrition Department With technical support from the Nutrition
8/6/2008 National Nutrition Policy Statement Operational Plan of Action for Nutrition 2008 2010 Palestinian National Authority Ministry of Health Nutrition Department With technical support from the Nutrition
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 9 April 2010 Original: English DP/FPA/DCP/PRK/5 Annual session 2010
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 9 April 2010 Original: English DP/FPA/DCP/PRK/5 Annual session 2010
Title: Tanzania national survey on iodine deficiency: impact after twelve years of salt iodation
 Reviewer's report Title: Tanzania national survey on iodine deficiency: impact after twelve years of salt iodation Version: 1 Date: 17 March 2009 Reviewer: Frits van der Haar Reviewer's report: Assey et
Reviewer's report Title: Tanzania national survey on iodine deficiency: impact after twelve years of salt iodation Version: 1 Date: 17 March 2009 Reviewer: Frits van der Haar Reviewer's report: Assey et
Best Practices in Egypt: Mobilizing Community Outreach Workers
 Best Practices in Egypt: Mobilizing Community Outreach Workers Outreach workers receive training on the TAHSEEN/CATALYST project health messages The CATALYST Consortium is a global reproductive health
Best Practices in Egypt: Mobilizing Community Outreach Workers Outreach workers receive training on the TAHSEEN/CATALYST project health messages The CATALYST Consortium is a global reproductive health
Prof. Arnon Baruch Afek Director General of the Ministry of Health of the State of Israel
 Prof. Arnon Baruch Afek Director General of the Ministry of Health of the State of Israel WHO and FAO 19-21 November Thank you, Mr. / Ms. Chair. I am grateful and honored to have the opportunity to address
Prof. Arnon Baruch Afek Director General of the Ministry of Health of the State of Israel WHO and FAO 19-21 November Thank you, Mr. / Ms. Chair. I am grateful and honored to have the opportunity to address
Maldives and Family Planning: An overview
 Maldives and Family Planning: An overview Background The Republic of Maldives is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, located 600 kilometres south of the Indian subcontinent. It consists of 92 tiny islands
Maldives and Family Planning: An overview Background The Republic of Maldives is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, located 600 kilometres south of the Indian subcontinent. It consists of 92 tiny islands
Indonesia-Intensified Iodine Deficiency Control Project. Ministry of Health (MOH)/Ministry of Industry (MOI)
 Project Name Region Sector Project ID Implementing Agency Report No. PIC2866 Indonesia-Intensified Iodine Deficiency Control Project East Asia and Pacific Population and Human Resources IDPA42450 Ministry
Project Name Region Sector Project ID Implementing Agency Report No. PIC2866 Indonesia-Intensified Iodine Deficiency Control Project East Asia and Pacific Population and Human Resources IDPA42450 Ministry
Distinguished Delegates, Officials from various Ministries, Our collaborating partners, Ladies and Gentlemen,
 Opening Speech by the Minister of Health and Social Welfare Honourable Prof. David Mwakyusa at the First African Flour Fortification Initiative Workshop in Arusha, on 17 th November 2008 Distinguished
Opening Speech by the Minister of Health and Social Welfare Honourable Prof. David Mwakyusa at the First African Flour Fortification Initiative Workshop in Arusha, on 17 th November 2008 Distinguished
MAINSTREAMING GENDER EQUALITY. How We Do It
 MAINSTREAMING GENDER EQUALITY How We Do It Access to good nutrition is a universal human right. Nutrition International (NI) believes that good nutrition and gender equality are mutually reinforcing; improving
MAINSTREAMING GENDER EQUALITY How We Do It Access to good nutrition is a universal human right. Nutrition International (NI) believes that good nutrition and gender equality are mutually reinforcing; improving
Nutrition Department
 Ref.: S001.docx National Nutrition Policy, Strategies & Action Plan (NNPSAP) 2011-2013 Palestinian National Authority Ministry of Health Primary Health Care Public Health general directorate Nutrition
Ref.: S001.docx National Nutrition Policy, Strategies & Action Plan (NNPSAP) 2011-2013 Palestinian National Authority Ministry of Health Primary Health Care Public Health general directorate Nutrition
Cambodia Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Although Cambodia has an integrated framework for food and nutrition security, it has not yet achieved the desired nutritional outcomes. Cambodia has experienced rapid growth in per capita
Key Indicators Although Cambodia has an integrated framework for food and nutrition security, it has not yet achieved the desired nutritional outcomes. Cambodia has experienced rapid growth in per capita
Examining trends in inequality in the use of reproductive health care services in Ghana and Nigeria
 Ogundele et al. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2018) 18:492 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-2102-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Examining trends in inequality in the use of reproductive health care services
Ogundele et al. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2018) 18:492 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-2102-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Examining trends in inequality in the use of reproductive health care services
Tuvalu Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Tuvalu Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Tuvalu has experienced a decreasing trend in infant mortality rates, but the country will not meet the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) target.
Key Indicators Tuvalu Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Tuvalu has experienced a decreasing trend in infant mortality rates, but the country will not meet the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) target.
INEQUALITIES IN MATERNAL HEALTH SERVICE UTILISATION IN NEPAL
 INEQUALITIES IN MATERNAL HEALTH SERVICE UTILISATION IN NEPAL An analysis of routine and survey data November 2018 Government of Nepal Ministry of Health and Population Supported by: The contents of this
INEQUALITIES IN MATERNAL HEALTH SERVICE UTILISATION IN NEPAL An analysis of routine and survey data November 2018 Government of Nepal Ministry of Health and Population Supported by: The contents of this
Protecting the growth and development of
 The Best Investment for Viet Nam s National Economic Development Protecting the growth and development of today s children is the key to fuelling tomorrow s economic and social development. But, reports
The Best Investment for Viet Nam s National Economic Development Protecting the growth and development of today s children is the key to fuelling tomorrow s economic and social development. But, reports
Prevalence of Goitre and Iodine Intake in Kanpur
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 2, Issue 1 (Sep. Oct. 2013), PP 22-26 Prevalence of Goitre and Iodine Intake in Kanpur Shailja Singh 1,
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 2, Issue 1 (Sep. Oct. 2013), PP 22-26 Prevalence of Goitre and Iodine Intake in Kanpur Shailja Singh 1,
TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE CONTROL OF A DUAL EPIDEMIC IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Regional Director.
 30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
Review of Approaches to Measuring Food Consumption for Food-based Micronutrient Programming
 Review of Approaches to Measuring Food Consumption for Food-based Micronutrient Programming Jennifer Coates, Brooke Colaiezzi, James Wirth, Jack Fiedler, Bea Rogers MAD Group Food Consumption Measurement
Review of Approaches to Measuring Food Consumption for Food-based Micronutrient Programming Jennifer Coates, Brooke Colaiezzi, James Wirth, Jack Fiedler, Bea Rogers MAD Group Food Consumption Measurement
UNGASS Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS: Core Indicators revision
 UNGASS Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS: Core Indicators revision Updated version following MERG recommendations Context In light of country reports, regional workshops and comments received by a
UNGASS Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS: Core Indicators revision Updated version following MERG recommendations Context In light of country reports, regional workshops and comments received by a
Ph.D. (Statistics), Faculty of Economics & political Sciences, Cairo University, Egypt, 1988.
 Ramadan Hamed, Ph.D. ramadanh@aucegypt.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. (Statistics), Faculty of Economics & political Sciences, Cairo University, Egypt, 1988. M.Sc. (Statistics), Faculty of Economics &political Sciences,
Ramadan Hamed, Ph.D. ramadanh@aucegypt.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. (Statistics), Faculty of Economics & political Sciences, Cairo University, Egypt, 1988. M.Sc. (Statistics), Faculty of Economics &political Sciences,
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/TGO/5 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 12 October 2007 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/TGO/5 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 12 October 2007 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
Nauru Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Nauru Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Nauru has remained stationary in health and child survival outcomes and will not achieve the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) on child mortality.
Key Indicators Nauru Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Nauru has remained stationary in health and child survival outcomes and will not achieve the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) on child mortality.
Investing in Family Planning/ Childbirth Spacing Will Save Lives and Promote National Development
 Investing in Family Planning/ Childbirth Spacing Will Save Lives and Promote National Development Fact Sheet prevents Nigerian families and, in particular, the poor from using FP to improve their well-being.
Investing in Family Planning/ Childbirth Spacing Will Save Lives and Promote National Development Fact Sheet prevents Nigerian families and, in particular, the poor from using FP to improve their well-being.
Demographic and Health Profile. Ethiopia. Nigeria. Population is currently 73 million, annual growth rate is 2.4%
 Adebola Adedimeji Demographic and Health Profile Nigeria Population is currently 150 million, annual growth rate is 2% Political structure- Federal Republic; 36 states, almost 800 local governments Multi-ethnic,
Adebola Adedimeji Demographic and Health Profile Nigeria Population is currently 150 million, annual growth rate is 2% Political structure- Federal Republic; 36 states, almost 800 local governments Multi-ethnic,
Progress in the utilization of antenatal and delivery care services in Bangladesh: where does the equity gap lie?
 Pulok et al. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2016) 16:200 DOI 10.1186/s12884-016-0970-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Progress in the utilization of antenatal and delivery care services in Bangladesh: where
Pulok et al. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2016) 16:200 DOI 10.1186/s12884-016-0970-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Progress in the utilization of antenatal and delivery care services in Bangladesh: where
Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey
 Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey Renuka Jayatissa 1, S M Moazzem Hossain
Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey Renuka Jayatissa 1, S M Moazzem Hossain
Strengthening Maternal Nutrition Data for Policy and Program in Selected ASEAN Countries
 Strengthening Maternal Nutrition Data for Policy and Program in Selected ASEAN Countries Emorn Udomkesmalee Institute of Nutrition, Mahidol University Thailand 4. Be accountable for better, more regular,
Strengthening Maternal Nutrition Data for Policy and Program in Selected ASEAN Countries Emorn Udomkesmalee Institute of Nutrition, Mahidol University Thailand 4. Be accountable for better, more regular,
Global database on the Implementation of Nutrition Action (GINA)
 Global database on the Implementation of Nutrition Action (GINA) National Nutrition Policy of Sri Lanka Published by: Ministry of Healthcare and Nutrition Is the policy document adopted?: Yes Adopted by:
Global database on the Implementation of Nutrition Action (GINA) National Nutrition Policy of Sri Lanka Published by: Ministry of Healthcare and Nutrition Is the policy document adopted?: Yes Adopted by:
FORTIFICATION ASSESSMENT COVERAGE TOOLKIT (FACT) SURVEY IN KAZAKHSTAN NOVEMBER 2017
 REPORT FORTIFICATION ASSESSMENT COVERAGE TOOLKIT (FACT) SURVEY IN KAZAKHSTAN NOVEMBER 2017 DISCLAIMER This report is developed by the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) and the Kazakh Academy
REPORT FORTIFICATION ASSESSMENT COVERAGE TOOLKIT (FACT) SURVEY IN KAZAKHSTAN NOVEMBER 2017 DISCLAIMER This report is developed by the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) and the Kazakh Academy
Does community-driven development build social cohesion or infrastructure?
 Working paper brief Governance G.M.B. Akash / Panos Does community-driven development build social cohesion or infrastructure? In community-driven development (CDD) programmes, community members are in
Working paper brief Governance G.M.B. Akash / Panos Does community-driven development build social cohesion or infrastructure? In community-driven development (CDD) programmes, community members are in
Laos - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Laos - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles In Lao PDR, GDP per capita has increased consistently during recent years, as has Dietary Energy Supply (DES) per person. Nevertheless, undernutrition
Key Indicators Laos - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles In Lao PDR, GDP per capita has increased consistently during recent years, as has Dietary Energy Supply (DES) per person. Nevertheless, undernutrition
Foreword. Steven Shongwe Executive Secretary ECSA Health Community
 Foreword Over the last five years, the East, Central and Southern African Health Community (ECSA-HC) has continued to undertake advocacy and technical assistance to assist member countries to embrace and
Foreword Over the last five years, the East, Central and Southern African Health Community (ECSA-HC) has continued to undertake advocacy and technical assistance to assist member countries to embrace and
Nutrition Policy ( )
 Nutrition Policy (2017-2021) First Informal Consultation 25 November 2016 The Nutrition Team Plus gender expert Heike Wach Why a new Nutrition Policy? Align with the WFP Integrated Road Map WFP Strategic
Nutrition Policy (2017-2021) First Informal Consultation 25 November 2016 The Nutrition Team Plus gender expert Heike Wach Why a new Nutrition Policy? Align with the WFP Integrated Road Map WFP Strategic
Modelling the impact of poverty on contraceptive choices in. Indian states
 Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2, Dublin (Session STS67) p.3649 Modelling the impact of poverty on contraceptive choices in Indian states Oliveira, Isabel Tiago ISCTE Lisbon
Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2, Dublin (Session STS67) p.3649 Modelling the impact of poverty on contraceptive choices in Indian states Oliveira, Isabel Tiago ISCTE Lisbon
Malnutrition Experience in Sultanate of Oman. Dr Salima almamary Family physician Nutrition Department
 Malnutrition Experience in Sultanate of Oman Dr Salima almamary Family physician Nutrition Department Outline Country profile Malnutrition prevalence in Oman and interventions done to reduce it Fortification
Malnutrition Experience in Sultanate of Oman Dr Salima almamary Family physician Nutrition Department Outline Country profile Malnutrition prevalence in Oman and interventions done to reduce it Fortification
SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUTRITION
 SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUTRITION Why an ICN2? Only an inter-governmental conference can provide the mandate and the obligations for governments to globally address global problems To identify
SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUTRITION Why an ICN2? Only an inter-governmental conference can provide the mandate and the obligations for governments to globally address global problems To identify
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/ZMB/8 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 30 June
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/ZMB/8 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 30 June
smoking is not allowed anywhere at home and a corresponding increase in the proportion saying that smoking is allowed in some parts of the house.
 Executive Summary The use of tobacco products is widespread throughout the world. Tobacco use is associated with chronic health problems and is a major cause of death. Although the prevalence of smoking
Executive Summary The use of tobacco products is widespread throughout the world. Tobacco use is associated with chronic health problems and is a major cause of death. Although the prevalence of smoking
Fill the Nutrient Gap Analysis: An introduction. Giulia Baldi, MPH WFP, Nutrition Division
 Fill the Nutrient Gap Analysis: An introduction Giulia Baldi, MPH WFP, Nutrition Division 2 Meeting nutrient requirements is a prerequisite for preventing malnutrition MALNUTRITION Inadequate dietary intake
Fill the Nutrient Gap Analysis: An introduction Giulia Baldi, MPH WFP, Nutrition Division 2 Meeting nutrient requirements is a prerequisite for preventing malnutrition MALNUTRITION Inadequate dietary intake
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/JOR/8 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 6 August
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/JOR/8 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 6 August
Meeting the 2025 salt and raised blood pressure reduction targets
 Meeting the 2025 salt and raised blood pressure reduction targets Dr Timothy Armstrong Coordinator Department of Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases Leading risk factors for global mortality Source:
Meeting the 2025 salt and raised blood pressure reduction targets Dr Timothy Armstrong Coordinator Department of Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases Leading risk factors for global mortality Source:
UHC. Moving toward. Ghana NATIONAL INITIATIVES, KEY CHALLENGES, AND THE ROLE OF COLLABORATIVE ACTIVITIES. Public Disclosure Authorized
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Moving toward UHC Ghana NATIONAL INITIATIVES, KEY CHALLENGES, AND THE ROLE OF COLLABORATIVE ACTIVITIES re Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Moving toward UHC Ghana NATIONAL INITIATIVES, KEY CHALLENGES, AND THE ROLE OF COLLABORATIVE ACTIVITIES re Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Rapid decline of female genital circumcision in Egypt: An exploration of pathways. Jenny X. Liu 1 RAND Corporation. Sepideh Modrek Stanford University
 Rapid decline of female genital circumcision in Egypt: An exploration of pathways Jenny X. Liu 1 RAND Corporation Sepideh Modrek Stanford University This version: February 3, 2010 Abstract Egypt is currently
Rapid decline of female genital circumcision in Egypt: An exploration of pathways Jenny X. Liu 1 RAND Corporation Sepideh Modrek Stanford University This version: February 3, 2010 Abstract Egypt is currently
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
Ending preventable maternal and child mortality
 REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 9.3 Sixty-ninth Session SEA/RC69/11 Colombo, Sri Lanka 5 9 September 2016 22 July 2016 Ending preventable maternal and child mortality There has been a significant
REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 9.3 Sixty-ninth Session SEA/RC69/11 Colombo, Sri Lanka 5 9 September 2016 22 July 2016 Ending preventable maternal and child mortality There has been a significant
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/CIV/6 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 6 October 2008 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/CIV/6 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 6 October 2008 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
Routine Immunization Status among Children under 5 Years of Age living in Rural District of Pakistan
 International Journal of Health Research and Innovation, vol. 3, no. 2, 2015, 13-20 ISSN: 2051-5057 (print version), 2051-5065 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Routine Immunization Status among Children under
International Journal of Health Research and Innovation, vol. 3, no. 2, 2015, 13-20 ISSN: 2051-5057 (print version), 2051-5065 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Routine Immunization Status among Children under
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 29 September 2011 Original:
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 29 September 2011 Original:
Harnessing the Cooperative Advantage to Build a Better World, Global Forum on Cooperatives, UNDESA, Addis Ababa, 4 6 September 2012,
 Harnessing the Cooperative Advantage to Build a Better World, Global Forum on Cooperatives, UNDESA, Addis Ababa, 4 6 September 2012, UN African Union Social Development Policies: Implementation Challenges
Harnessing the Cooperative Advantage to Build a Better World, Global Forum on Cooperatives, UNDESA, Addis Ababa, 4 6 September 2012, UN African Union Social Development Policies: Implementation Challenges
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB5672 Project Name
 PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB5672 Project Name Pakistan - Enhanced Nutrition for Mothers and Children Project Region SOUTH ASIA Sector Health (90%); Other social services
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB5672 Project Name Pakistan - Enhanced Nutrition for Mothers and Children Project Region SOUTH ASIA Sector Health (90%); Other social services
Identifying and addressing inequities in child and maternal health provision. Gian Gandhi Health Section, UNICEF NYHQ
 Identifying and addressing inequities in child and maternal health provision Gian Gandhi Health Section, UNICEF NYHQ 1 On average, global burden has fallen steadily As measured by number of under-five
Identifying and addressing inequities in child and maternal health provision Gian Gandhi Health Section, UNICEF NYHQ 1 On average, global burden has fallen steadily As measured by number of under-five
IODINE CONTENT IN THE MARKETED PRODUCTS OF IODIZED SALT: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY IN SOUTHERN SRI LANKA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/sjdem.v6i2.7308 IODINE CONTENT IN THE MARKETED PRODUCTS OF IODIZED SALT: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY IN SOUTHERN SRI LANKA E De Zoysa 1, M Hettarachchi 2, C Liyanage
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/sjdem.v6i2.7308 IODINE CONTENT IN THE MARKETED PRODUCTS OF IODIZED SALT: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY IN SOUTHERN SRI LANKA E De Zoysa 1, M Hettarachchi 2, C Liyanage
PROVIDING EMERGENCY OBSTETRIC AND NEWBORN CARE
 URGENT RESPONSE: PROVIDING EMERGENCY OBSTETRIC AND NEWBORN CARE Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Introduction Women everywhere face a risk in giving birth. Worldwide, about 15 per cent of
URGENT RESPONSE: PROVIDING EMERGENCY OBSTETRIC AND NEWBORN CARE Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Introduction Women everywhere face a risk in giving birth. Worldwide, about 15 per cent of
The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition
 The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition Marie Ruel Director, Poverty, Health and Nutrition, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) October
The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition Marie Ruel Director, Poverty, Health and Nutrition, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) October
Brunei Darussalam - Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Brunei Darussalam Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Brunei Darussalam has one of the highest rates of GDP per capita and of Dietary Energy Supply (DES) per person in the region. For decades,
Key Indicators Brunei Darussalam Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Brunei Darussalam has one of the highest rates of GDP per capita and of Dietary Energy Supply (DES) per person in the region. For decades,
Cook Islands Food and Nutrition Security Profiles
 Key Indicators Cook Islands Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Mortality in children has shown a constant reduction over the years, but unless further acceleration, Cook Islands will not achieve the
Key Indicators Cook Islands Food and Nutrition Security Profiles Mortality in children has shown a constant reduction over the years, but unless further acceleration, Cook Islands will not achieve the
FGM IN BURKINA FASO: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. December 2015
 FGM IN BURKINA FASO: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY December 2015 Registered Charity: No. 1150379 Limited Company: No: 08122211 E-mail: info@28toomany.org 28 Too Many 2017 COUNTRY PROFILE: FGM IN BURKINA FASO EXECUTIVE
FGM IN BURKINA FASO: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY December 2015 Registered Charity: No. 1150379 Limited Company: No: 08122211 E-mail: info@28toomany.org 28 Too Many 2017 COUNTRY PROFILE: FGM IN BURKINA FASO EXECUTIVE
A Comparative Analysis of Fertility Plateau In Egypt, Syria and Jordan: Policy Implications
 A Comparative Analysis of Fertility Plateau In Egypt, Syria and Jordan: Policy Implications Executive Summary by Hoda Rashad and Hassan Zaky Social Research Center The American University in Cairo March
A Comparative Analysis of Fertility Plateau In Egypt, Syria and Jordan: Policy Implications Executive Summary by Hoda Rashad and Hassan Zaky Social Research Center The American University in Cairo March
