Primary hyperparathyroidism is the unregulated overproduction of PTH resulting in abnormal calcium homeostasis.
|
|
|
- Abner Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hyperparathyridism Thrugh their secretin f parathyrid hrmne (PTH), the parathyrid glands are primarily respnsible fr maintaining extracellular calcium cncentratins. Hyperparathyridism is a disease characterized by excessive secretin f PTH, an 84 amin acid plypeptide hrmne. The secretin f PTH is regulated directly by the plasma cncentratin f inized calcium. The main effects f PTH are t increase the cncentratin f plasma calcium by increasing the release f calcium and phsphate frm bne matrix, increasing calcium reabsrptin by the kidney, and increasing renal prductin f 1,25- dihydrxyvitamin D-3 (calcitril), which increases intestinal absrptin f calcium. Thus, verprductin f PTH results in elevated levels f plasma calcium. PTH als causes phsphaturia, thereby decreasing serum phsphate levels. Hyperparathyridism is usually subdivided int primary, secndary, and tertiary hyperparathyridism. Usually, 4 parathyrid glands are situated psterir t the thyrid gland. A small number f patients have 3, 5, r ccasinally, mre glands. The glands are identified based n their lcatin as right r left and superir r inferir. The inferir glands are derived frm the third pharyngeal puch. This structure is als the embrylgic rigin f the thymus. Therefre, the inferir glands riginate mre cephalad than the superir glands, but they migrate alng with the thymus t finally becme situated mre inferirly than the superir glands. Because f their embrylgic assciatin with the thymus, the inferir glands are ften fund adjacent t r within the thymus. They are usually lcated near the inferir ple f the thyrid. The superir glands are mre cnsistent in lcatin, usually fund just superir t the intersectin f the inferir thyrid artery and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The superir glands are derived embrylgically frm the furth pharyngeal puch. This structure als gives rise t the C cells f the thyrid gland. Because f their embrylgic rigin, the superir glands are ccasinally fund within the substance f the thyrid gland. Ectpic lcatins f parathyrid glands are discussed in mre detail in "Primary Hyperparathyridism," under surgical care. Definitin f the prblem Primary hyperparathyridism is the unregulated verprductin f PTH resulting in abnrmal calcium hmestasis. Frequency The prevalence f primary hyperparathyridism is slwly decreasing. Mst recently, the prevalence is reprted t be apprximately 4 cases in 100,000 persns. Primary hyperparathyridism affects wmen apprximately twice as frequently as men. Prevalence increases with age, but hyperparathyridism can affect persns f all ages, including children. ١
2 Etilgy In apprximately 85% f cases, primary hyperparathyridism is caused by a single adenma. In 15% f cases, multiple glands are invlved (ie, either multiple adenmas r hyperplasia). Rarely, primary hyperparathyridism is caused by parathyrid carcinma. The etilgy f adenmas r hyperplasia remains unknwn in mst cases. Familial cases can ccur either as part f the multiple endcrine neplasia syndrmes (MEN 1 r MEN 2a), hyperparathyrid-jaw tumr (HPT-JT) syndrme, r familial islated hyperparathyridism (FIHPT). Familial hypcalciuric hypercalcemia and nenatal severe hyperparathyridism als belng t this categry. The mlecular genetic basis f MEN 1 is an inactivating mutatin f the MEN1 gene, lcated n chrmsme band 11q13. MEN 2a is caused by a germline mutatin f the Ret prt-ncgene n chrmsme 10. Germline mutatin f HRPT2 lcalized n chrmsme arm 1q is respnsible fr HPT-JT, while FIHPT is genetically hetergeneus. Pathphysilgy In primary hyperparathyridism due t adenmas, the nrmal feedback n PTH prductin by extracellular calcium seems t be lst, resulting in a change in the set pint. Hwever, this is nt the case in primary hyperparathyridism frm parathyrid hyperplasia. An increase in the cell numbers is prbably the cause. The chrnic excessive resrptin f calcium frm bne caused by excessive PTH can result in stepenia. In severe cases, this may result in steitis fibrsa cystica, which is characterized by subperisteal resrptin f the distal phalanges, tapering f the distal clavicles, salt-and-pepper appearance f the skull, and brwn tumrs f the lng bnes. This is nt cmmnly seen nw. In additin, the chrnically increased excretin f calcium in the urine can predispse t the frmatin f renal stnes. The ther symptms f hyperparathyridism are due t the hypercalcemia itself and are nt specific t hyperparathyridism. These can include muscle weakness, fatigue, vlume depletin, nausea and vmiting, and in severe cases, cma and death. Neurpsychiatric manifestatins are particularly cmmn and may include depressin, cnfusin, r subtle deficits that are ften characterized prly and may nt be nted by the patient. Increased calcium can increase gastric acid secretin, and persns with hyperparathyridism may have a higher prevalence f peptic ulcer disease. Rare cases f pancreatitis have als been attributed t hypercalcemia. ٢
3 Clinical presentatin Histry Symptms related t hyperparathyridism may include bne pain, pathlgic fractures, and nephrlithiasis. Symptms related t hypercalcemia may include muscle weakness, vlume depletin, plyuria and plydipsia, neurpsychiatric symptms, peptic ulcer disease, and pancreatitis. Physical Examinatin Physical examinatin findings are usually nncntributry. Examinatin may reveal muscle weakness and depressin. A palpable neck mass is nt usually expected with hyperparathyridism, althugh in rare cases, it may indicate parathyrid cancer. Differential diagnsis The causes f hypercalcemia that result in a cncmitantly elevated PTH level are few. These include familial benign (hypcalciuric) hypercalcemia (FHH) lithium-induced hypercalcemia, and tertiary hyperparathyridism. A cautinary nte is that a minrity f patients (i.e., 10-15%) with hyperparathyridism have PTH levels at the high end f the reference range, which is inapprpriately high in the presence f elevated calcium. A subset f patients has calcium levels within the reference range with elevated PTH, which is called nrmcalcemic hyperparathyridism. Hwever, fr cnsidering this diagnsis, all ptential causes f secndary hyperparathyridism (eg, lw calcium intake, GI disrders, renal insufficiency, vitamin D deficiency, hypercalciuria f renal rigin) shuld be excluded. Secndary and tertiary hyperparathyridism are typically diagnsed n the basis f their clinical cntext. Cancer-induced hypercalcemia is usually assciated with a lw PTH level but pssibly a high PTH-related peptide level. Labratry studies Ttal serum calcium and albumin levels r inized calcium levels shuld be measured. Hypercalcemia shuld be dcumented n mre than ne ccasin befre a diagnstic wrkup is undertaken. Testing f the intact PTH level is the cre f the diagnsis. An elevated intact PTH level with an elevated inized serum calcium level is diagnstic f primary hyperparathyridism. Older assays measured prtins f the PTH mlecule, such as the C-terminal r N-terminal. These lder assays shuld n lnger be used in rutine clinical practice. The current assay uses 2 different antibdies t 2 different epitpes; therefre, nly the intact mlecules are detected. A secnd-generatin assay that measures the full-length mlecule ٣
4 shuld be used. This is imprtant in detecting nly active PTH, particularly when PTH levels are lw. A 24-hur urine calcium measurement is necessary t rule ut FHH. A markedly elevated level is an indicatin fr surgery. Imaging studies Imaging studies are nt used t make the diagnsis f primary hyperparathyridism (which is based n labratry data) r t decide n surgical therapy (which is based n clinical criteria). Imaging studies are used t guide the surgen nce surgical therapy has been decided. If a limited parathyrid explratin is t be attempted, a lcalizing study is necessary. Other uses f imaging studies in the initial evaluatin f a patient with primary hyperparathyridism are cntrversial. Fr many patients, the recmmendatin remains fr cmplete parathyrid explratin with resectin f all invlved glands. Many surgens agree that imaging studies are nt required when this surgical treatment is chsen. Hwever, in patients wh have recurrent r persistent hyperparathyridism after a previus surgical explratin, an imaging test t lcalize invlved glands is definitely indicated. As mre experience is gained with technetium Tc 99 sestamibi scanning, use f this mdality t guide surgical therapy and even t cnfirm the diagnsis itself is becming rutine. The best initial test is sestamibi nuclear medicine scanning. This radinuclide is cncentrated in parathyrid tissue. The scan is highly specific fr abnrmal parathyrid tissue. It als has a sensitivity f greater than 90% in the case f slitary adenmas. The main weakness f this test is in diagnsing multiglandular disease. In this case, sensitivity drps t apprximately 55%. When cmbined with single-phtn emissin cmputed tmgraphy scanning, it can be used effectively t lcalize ectpic and usual parathyrid adenmas and, therefre, is the imaging study f chice. Ultrasngraphy f the neck may be equivalent r superir t sestamibi scanning. Hwever, it is peratr-dependent and has been reprted t have widely varying degrees f accuracy. One advantage f neck ultrasngraphy is that it can be perfrmed rapidly by the clinician at the time f the initial evaluatin. CT scanning and MRI have als been used, althugh they have nw largely been replaced by sestamibi scanning. CT scanning has inadequate sensitivity. MRI can be useful, particularly in the case f recurrent r persistent disease and in ectpic lcatins such as the mediastinum. A bne mineral density test is a useful tl t dcument stepenia. Nte that hyperparathyridism preferentially affects the crtical bne at the radius (distal third). ٤
5 Prcedures Bilateral internal jugular vein sampling is used t help lcalize ectpic parathyrid adenmas; hwever, this technique shuld generally be reserved fr centers with specialists and fr selected patients. Treatment Medical care The diet f individuals with primary hyperparathyridism shuld include arund mg f calcium per day. Als, 400 IU f vitamin D per day is reasnable. Estrgen therapy in pstmenpausal wmen has been shwn t cause a small reductin in serum calcium and increases in BMD, with stable PTH. Hwever, risks are assciated with estrgen replacement. Ralxifene may be an alternative. Alendrnate has als been shwn t increase the spine BMD in patients with primary hyperparathyridism. Calcimimetic drugs may be an alternative in the future. Other medical therapy is limited t the treatment f hypercalcemia itself. In the acute setting, this can be accmplished by the use f intravascular vlume expansin with sdium chlride and lp diuretics such as fursemide nce the intravascular vlume is restred. In rare cases, hypercalcemia has been treated with bisphsphnate therapy as a temprary measure prir t surgical treatment. Surgical care Indicatins fr surgery Symptmatic hyperparathyridism shuld be treated by surgical excisin f the abnrmal glands. Sme clinicians advcate surgical therapy in all patients with primary hyperparathyridism, mdified nly fr thse patients wh are nt able t tlerate surgery. They argue that the peratin is generally well tlerated and such treatment prevents cmplicatins (eg, steprsis) and may reverse symptms that patients ften d nt realize they have (eg, fatigue, depressin). Others advcate a nnsurgical apprach whenever pssible, such as in patients with a calcium level less than 11.5 mg/dl, patients with n apparent symptms, and patients wh have nrmal 24-hur urine calcium excretin and n steprsis. A Natinal Institutes f Health (NIH) Wrkshp n Asymptmatic Primary Hyperparathyridism in 2002 revisited the key management issues addressed at the 1990 NIH Cnsensus Develpment Cnference. They recmmended new guidelines fr surgery and the cnservative apprach f mnitring patients ٥
6 wh d nt meet the criteria fr surgery. The indicatins fr surgery as per the 2002 guidelines are as fllws: 1.0 mg/dl abve the upper limit f the reference range fr serum calcium 24-hur urinary calcium excretin greater than 400 mg A 30% reductin in creatinine clearance Bne mineral density T-scre belw -2.5 at any site Age less than 50 years Fr mnitring f patients with asymptmatic hyperparathyridism wh d nt underg surgery, the fllwing are recmmended: serum calcium and creatinine levels every 6 mnths and annual bne mineral density (all 3 sites). Chice f surgical treatment The standard perative apprach is cmplete neck explratin with identificatin f all parathyrid glands and remval f all abnrmal glands. In the case f 4-gland hyperplasia, a 3.5-gland (subttal) parathyridectmy is perfrmed. Apprximately mg f the mst nrmal-appearing tissue is left behind. A nnabsrbable suture is left as a tag t identify the gland shuld reperatin be necessary. Apprximately 85% f cases f primary hyperparathyridism are caused by a single adenma. Therefre, mst patients wh underg full neck explratin t evaluate all parathyrids endure sme unnecessary dissectin. Rather than explre all parathyrid glands, a newer technique, directed parathyridectmy, has evlved. This technique relies n preperative imaging studies t lcalize the abnrmal gland. The surgen then remves nly that gland, withut visualizing the ther glands. With either sestamibi scanning r ultrasngraphy, an abnrmal parathyrid may be detected preperatively in 70-80% f cases. Hwever, neither technique is reliable fr detecting multiple abnrmal glands. Therefre, an additinal methd is required t cnfirm that n ther abnrmal glands are present after excisin f the imaged lesin. Fr this purpse, many centers have begun t use the intraperative PTH assay. Because the plasma half-life f PTH is nly apprximately 4 minutes, the level falls quickly after resectin f the surce. If the level fails t fall after resectin f the identified abnrmal gland, the prcedure is extended t allw fr further explratin. Hwever, the intraperative PTH ٦
7 assay is expensive and is usually available nly in centers that perfrm a high vlume f parathyridectmies. A few authrs have advcated radi-guided parathyridectmy, detecting the labeled sestamibi in the abnrmal gland using a handheld prbe. The excised radiactivity in the abnrmal parathyrid is then cmpared with the remaining backgrund t cnfirm excisin f all affected glands. Hwever, mst centers have abandned this technique because (1) if the gland labels well with sestamibi, use f the handheld prbe intraperatively is unnecessary in mst cases and (2) the use f backgrund cunts t cnfirm cmplete excisin f all abnrmal tissue has nt been well validated. Use f directed parathyridectmy results in a mre limited peratin fr mst patients, resulting in a mre rapid recvery. Hwever, it may yield a higher persistence rate than cmplete neck explratin, and it prbably shuld be perfrmed nly in centers with the capability t perfrm the intraperative PTH assay. Fr familial disease, such as MEN 1, ttal parathyridectmy is perfrmed with auttransplantatin t the frearm and crypreservatin f sme parathyrid tissue. Preperative care Parathyridectmy is usually well tlerated. The main risks are thse assciated with anesthesia. Althugh lcal anesthesia has been used successfully fr this prcedure, especially in the directed appraches where a single adenma is lcalized preperatively, general anesthesia is used mst cmmnly. In patients in whm hypercalcemia (and, therefre, dehydratin) has been severe, special attentin must be directed t periperatively restring the fluid balance. Neck mbility must be assessed t ensure prper psitining in the perating rm. If the patient's vice is nrmal, preperative dcumentatin f vcal crd functin is nt necessary. Intraperative details Cmplete parathyrid explratin The mst critical aspect t ensure success in this peratin is identificatin f all 4 parathyrid glands and remval f all abnrmal glands. ٧
8 The patient is placed in the lawn-chair psitin with the neck extended ver a transversely placed shulder rll. This psitin allws full expsure f anterir neck structures and imprves venus drainage. A lw transverse incisin placed within the skin creases prvides the best csmetic result. The length f the incisin must be adequate t allw thrugh explratin f all ptential lcatins f the parathyrid glands; hwever, given the elasticity f the neck skin flaps, a 3- t 5-cm incisin allws safe identificatin f imprtant structures. After hemstasis f the skin incisin is btained, subplatysmal flaps are develped superirly t the ntch f the thyrid cartilage and inferirly t the flat prtin f the manubrium. The sternhyid and sternthyrid (strap) muscles are separated in the midline t expse the thyrid gland. If preperative lcalizatin studies suggest a parathyrid adenma, that side is apprached first. Frequently, a middle thyrid vein may require ligatin t ensure adequate mbilizatin f the thyrid lbe. The thyrid lbe is elevated ff the cmmn cartid artery and retracted medially. The inferir thyrid artery is identified after blunt and sharp dissectin f the arelar tissue anterirly and medially t the cmmn cartid artery and pstermedially t the thyrid lbe. The recurrent laryngeal nerve is identified next, inferir and lateral t the lwer lbe f the thyrid gland. The intersectin f the inferir thyrid artery and the recurrent laryngeal nerve is an imprtant landmark because mst parathyrid glands, superir and inferir, are lcated within 2 cm f this area. The superir parathyrid glands are lcated drsal t the upper tw thirds f the thyrid lbe and psterir t the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The inferir glands, which are less cnsistent in lcatin, can usually be fund inferir t the inferir thyrid artery and ventral t the recurrent laryngeal nerve. They are usually within 1 cm f the inferir lbe f the thyrid gland. Abnrmally enlarged glands are excised after cnfirmatin f the nrmal size f ther glands. During excisin, aviding capsular rupture f the abnrmal gland is imprtant because this may be assciated with implantatin f parathyrid cells in the perative site and subsequent parathyrmatsis. Parathyrids may be identified by highly experienced surgens based n appearance and lcatin. In mst cases, identificatin f ٨
9 the parathyrid glands shuld be cnfirmed histlgically by frzen sectin examinatin. In all cases f subttal r ttal parathyridectmy with auttransplantatin, parathyrid tissue must be crypreserved fr future auttransplantatin if the initial transplants are nt functinal. Directed parathyridectmy In many respects, the perative technique is similar t that described abve fr a cmplete parathyrid explratin. Differences are nted belw. Adequate imaging f the abnrmal gland prir t surgery is essential. In additin, arrangements fr intraperative measurement f PTH shuld be cnfirmed. A line fr sampling f peripheral venus bld shuld be established. Often the distal saphenus vein prvides the mst cnvenient access. Sme surgens mdify the lcatin f the incisin based n the preperative lcatin f the adenma. This authr prefers a small incisin (ie, ~2 cm) in the standard lcatin fr a cllar incisin. This incisin can be readily extended shuld a cmplete explratin prve necessary. A baseline PTH level is drawn immediately prir t skin incisin. Fllwing identificatin and dissectin f the adenma, a preexcisin level is drawn. Manipulatin f the gland ccasinally causes significant increases in the PTH level. Fllwing excisin f the gland, PTH levels are drawn at 5 minutes and 10 minutes pstexcisin. Criteria fr adequate excisin are either: a 50% drp in PTH frm the baseline level t the 10-minute pstexcisin level r a 50% drp in PTH frm the preexcisin level at 10 minutes and a pstexcisin level belw the baseline level. The incisin may be clsed while the last PTH levels are being prcessed, but the patient shuld remain under anesthesia and the sterile field maintained until the PTH assay results are knwn. Ectpic parathyrid glands Occasinally, all parathyrid glands cannt be identified. In such instances, the usual lcatins are reexamined first because mst parathyrid glands are lcated in typical areas. If parathyrid glands are nt identified in thse lcatins, then a systematic search is perfrmed, taking int cnsideratin the path f descent f superir and inferir parathyrid glands. ٩
10 Inferir glands may be lcated in the thyrthymic ligament. They may be difficult t identify, especially after divisin f the inferir thyrid vein, a maneuver that allws the gland t retract int the superir mediastinum. Anther lcatin fr ectpic inferir parathyrid glands is the thymus. The thymus can be visualized thrugh a transverse cervical incisin by retracting the innminate vein drsally with a spnge-stick while elevating the manubrium anterirly. Divisin f the interclavicular ligament imprves visualizatin in the superir mediastinum. Superir parathyrid glands are usually drsal t the upper tw thirds f the thyrid gland. Occasinally, these glands are adjacent t the superir thyrid vessels. Other lcatins include the cartid sheath r psterir t the esphagus r pharynx (retresphageal). Finally, bth superir and inferir parathyrid glands may be lcated aberrantly within the capsule f the thyrid gland. Sme surgens perfrm a thyrid lbectmy n the side harbring the abnrmal gland after an exhaustive search is made in the afrementined lcatins. Median sterntmy is rarely required during the initial neck explratin fr hyperparathyridism. Pstperative care If a directed parathyridectmy is perfrmed successfully, mst f these patients may be safely discharged the day f surgery. Sme practitiners rutinely supplement with ral calcium pstperatively. Fr a full parathyrid explratin, calcium levels must be mnitred pstperatively every 12 hurs until stabilizatin. The nadir f serum calcium usually ccurs hurs pstperatively. Many patients becme hypcalcemic, but few becme symptmatic. Reserve treatment fr hypcalcemia unless it is severe r the patient becmes symptmatic. Hypcalcemia after parathyrid surgery may be due t hungry bne syndrme where calcium and phsphrus are rapidly depsited in the bne. This is characterized by hypparathyridism and transient, but ccasinally severe, hypcalcemia until the nrmal glands regain sensitivity. If hypparathyridism persists, ral supplementatin with calcium and vitamin D is required. Calcium citrate r calcium carbnate may be started at 2 tablets 4 times per day. Sme patients require mre r less. Calcitril is started at 1 mcg/d fr 1 day, 0.5 mcg/d fr 2 days, and then 0.25 mcg/d thereafter. Patients in whm an auttransplantatin is perfrmed require temprary calcium supplementatin. If a recurrent nerve injury is suggested because the patient has develped new harseness, immediate laryngscpy is ١٠
11 indicated. If vcal crd paralysis is bserved, immediate reperatin may be warranted t repair a transected nerve because a few f these may regain functin. Reexplratin after hurs is nt generally indicated because the risks f perating in an inflamed field utweigh the relatively lw likelihd f a benefit. A ptential life-threatening emergency in the pstperative perid is the develpment f an expanding hematma in the pretracheal space. This cmplicatin must be recgnized and treated immediately by pening the wund and evacuating the hematma. If untreated, laryngeal edema may prgress rapidly, causing airway bstructin. Mst small hematmas d nt require treatment. A subplatysmal fluid cllectin may ccasinally frm, and these are usually treated adequately with a single aspiratin. In a few cases, aspiratin may need t be repeated. Rarely, a drain may need t be placed fr recurrent fluid cllectins. Fllw-up Patients are seen 1-2 weeks pstperatively, and serum calcium and PTH levels are btained. PTH levels may be elevated pstperatively in sme patients, but if the serum calcium remains within the reference range it des nt indicate persistent disease in mst patients. After the immediate pstperative perid, fllw-up is limited t peridic determinatins f serum calcium levels t detect the persistence r recurrence f disease r hypparathyridism. Secndary hyperparathyridism Secndary hyperparathyridism is the verprductin f PTH secndary t a chrnic abnrmal stimulus fr its prductin. Typically, this is due t chrnic renal failure. Anther cmmn cause is vitamin D deficiency. Frequency Secndary hyperparathyridism ccurs t sme degree in virtually all patients with dialysis-dependent chrnic renal failure. Vitamin D deficiency is cmmn and is underdiagnsed. Etilgy In renal failure, the stimuli fr verprductin f PTH are multifactrial. Factrs include hypcalcemia, impaired 1,25-dihydrxyvitamin D prductin by the diseased kidneys, and hyperphsphatemia. Hyperphsphatemia appears t be particularly imprtant in the develpment f parathyrid ١١
12 hyperplasia. These stimuli cause multigland hyperplasia, resulting in increased PTH prductin. Pathphysilgy Chrnic verprductin f PTH in patients with renal failure cntributes t the spectrum f bne disease bserved in patients n dialysis. In mst patients n dialysis, the primary bne disease is steitis fibrsa cystica, a disease f increased bne resrptin caused by elevated PTH levels. Skeletal lesins include subperisteal bne ersins, usually bserved best in the distal phalanges. Likewise, the skull has a classic salt-and-pepper r grund-glass appearance. Other bne diseases are cmmn in patients n dialysis, but these d nt appear directly attributable t hyperparathyridism. Clinical presentatin Because virtually all patients with renal failure have hyperparathyridism t sme degree, the clinical presentatin is ften that f renal failure. In patients with secndary hyperparathyridism due t vitamin D deficiency, the symptms are mainly due t the vitamin deficiency (e.g., stemalacia with increased fracture risk, mypathy [rarely]). In advanced cases f secndary hyperparathyridism, sme patients may have bne pain. Labratry studies All patients with renal failure shuld be mnitred regularly with serum calcium, phsphrus, and PTH levels. Patients with secndary hyperparathyridism usually have a lw-nrmal calcium and elevated PTH. The phsphate level may vary based n the etilgy, trending twards high values in renal insufficiency and lw values in vitamin D deficiency. Imaging studies Radigraphic evaluatin is limited t assessments f the bne disease. Obtain radigraphs f sites f bne pain. Hand radigraphs may shw characteristic subperisteal ersins. Imaging f the parathyrid glands is nt indicated unless primary hyperparathyridism is suggested. Treatment Medical care Unlike primary hyperparathyridism, medical management is the mainstay f treatment fr secndary hyperparathyridism. Treatment with calcitril and calcium can either prevent r minimize secndary hyperparathyridism. Cntrl f the serum phsphate levels with a lw-phsphate diet and phsphate-binding agents is essential. ١٢
13 Patients with predialysis renal failure, ie, thse with early-t-mderate renal failure, usually have a mdest elevatin f PTH levels. Suppressin f PTH secretin with lw-dse calcitril (i.e., mcg/d) may prevent subsequent parathyrid gland hyperplasia and secndary hyperparathyridism; hwever, calcitril therapy must be mnitred carefully t ensure that hypercalcemia is nt induced. Patients with dialysis-dependent chrnic renal failure require calcitril, ral calcium supplementatin, calcium in the dialysate, aluminum-free phsphate binders, and cinacalcet (Sensipar) t maintain levels f serum calcium and phsphate within their reference ranges. Because patients n dialysis are relatively resistant t the actins f PTH, a PTH level within the reference range is nt necessarily desirable. A recent survey f patients n dialysis using this therapy fund that 50% had PTH levels at least 3 times the reference range. Surgical care Indicatins include bne pain r fracture, pruritus, and calciphylaxis Failure f medical therapy t cntrl hyperparathyridism is a sft indicatin fr surgery. Generally, if PTH levels f greater than pg/ml persist after crrectin f serum calcium and phsphrus levels and evidence f prgressive bne disease is present, parathyridectmy may be cnsidered. Intraperative details All 4 glands must be expsed, and bipsies are taken if needed t ensure crrect identificatin. In mst cases, diffuse hyperplasia is encuntered, althugh the size f the glands can be significantly hetergeneus. The prcedure f chice is either ttal parathyridectmy with auttransplantatin r 3.5-gland parathyridectmy. In either case, a thymectmy must be included. A 1991 article by Rthmund et al reprted a randmized cntrlled trial f ttal versus subttal parathyridectmy fr secndary hyperparathyridism. The authrs fund that 4 f 17 subjects treated with subttal parathyridectmy develped recurrent hypercalcemia, and 2 required reexplratin. Nne f the subjects treated by ttal parathyridectmy develped recurrent hypercalcemia. Therefre, several authrs prefer ttal parathyridectmy with auttransplantatin. Briefly, parathyrid tissue is cut int apprximately pieces, each f which measures 1 X 1 mm. These are inserted in pckets in the frearm musculature, and each piece is marked with a plyprpylene suture n the fascia. Parathyrid tissue als must be crypreserved in case the primary auttransplant fails. Pstperative details Pstperative care fllws the rutine described abve in Pstperative care fr primary hyperparathyridism. ١٣
14 If ttal parathyridectmy and auttransplantatin are perfrmed, the patient requires a perid f maintenance with calcium and calcitril supplementatin. Outcme and prgnsis Medical treatment f secndary hyperparathyridism is successful in mst patients. Patients wh require parathyridectmy have apprximately a 10% risk f recurrent r persistent disease. This may be due t a hyperfunctining r missed neck gland r hyperplasia f the autgraft. Occasinally, a patient has persistent hypparathyridism after peratin. If tissue has been crypreserved, transplantatin may reverse hypparathyridism. If hypparathyridism is permanent, lifelng calcium and calcitril supplementatin is necessary. Tertiary hyperparathyridism Tertiary hyperparathyridism is secndary t lng-standing secndary hyperparathyridism. Tertiary disease is characterized by the develpment f autnmus hypersecretin f PTH causing hypercalcemia. Etilgy The etilgy is unknwn. A change may ccur in the set pint f the calciumsensing mechanism t hypercalcemic levels. Pathphysilgy Tertiary hyperparathyridism is bserved mst cmmnly in patients with chrnic secndary hyperparathyridism and ften after renal transplantatin. The hypertrphied parathyrid glands fail t return t nrmal and cntinue t versecrete PTH, despite serum calcium levels that are within the reference range r even elevated. In these cases, the hypertrphied glands becme autnmic and cause hypercalcemia, even after withdrawal f calcium and calcitril therapy. This type f tertiary disease is particularly dangerus because the phsphate level is ften elevated. If the calcium value multiplied by the phsphate value yields a high prduct, diffuse calcinsis may ccur. Clinical presentatin The clinical manifestatins f tertiary hyperparathyridism include persistent hyperparathyridism after renal transplantatin r new hypercalcemia in the setting f chrnic secndary hyperparathyridism. Treatment Ttal parathyridectmy with auttransplantatin r subttal parathyridectmy is indicated. ١٤
15 Familial benign (hypcalciuric) hypercalcemia FHH is caused by a lss-f-functin mutatin f ne allele f the gene fr the calcium-sensing receptr (CaR). It causes hypercalcemia, hypphsphatemia, and hypermagnesemia. The PTH level is usually within the reference range r is mildly elevated. It can be distinguished frm primary hyperparathyridism by lw 24-hur urinary calcium excretin. Persns with FHH are asymptmatic. Parathyridectmy is nt indicated. Hypercalcemia f malignancy This disrder is usually caused by tumr release f a hrmne called PTHrelated peptide. Less cmmnly, hypercalcemia f malignancy is caused by lcal stelytic lesins and, rarely, by verprductin f 1,25-dihydrxyvitamin D. This disrder is the mst cmmn cause f hypercalcemia in hspitalized patients. The hypercalcemia f malignancy results in a lw r undetectable intact PTH level. Usually, it is easily distinguished frm hyperparathyridism. Only a few cases f ectpic prductin f true PTH are reprted in the literature. ١٥
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THYROID/PARATHYROID DISEASE
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THYROID/PARATHYROID DISEASE Edsel Kim, M.D. Otlarynglgy-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregn Clinic Prvidence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyrid and Parathyrid Update February
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THYROID/PARATHYROID DISEASE Edsel Kim, M.D. Otlarynglgy-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregn Clinic Prvidence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyrid and Parathyrid Update February
International Myeloma Working Group Guidelines on Imaging Techniques in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Multiple Myeloma 1
 Internatinal Myelma Wrking Grup Guidelines n Imaging Techniques in the Diagnsis and Mnitring f Multiple Myelma 1 Up t 90% f myelma patients develp stelytic lesins, a majr cause f mrbidity and mrtality,
Internatinal Myelma Wrking Grup Guidelines n Imaging Techniques in the Diagnsis and Mnitring f Multiple Myelma 1 Up t 90% f myelma patients develp stelytic lesins, a majr cause f mrbidity and mrtality,
Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2018 Key Messages (as of June 6, 2018)
 Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET
 WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION
 CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING. Public Health Relevance. Highlights.
 HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING Public Health Relevance Cervical cancer is 90% preventable by having regular Papaniclau (Pap) tests. The Pap test, als knwn as a cervical smear,
HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING Public Health Relevance Cervical cancer is 90% preventable by having regular Papaniclau (Pap) tests. The Pap test, als knwn as a cervical smear,
Osteoporosis Fast Facts
 Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
ACRIN 6666 Screening Breast US Follow-up Assessment Form
 Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Obesity/Morbid Obesity/BMI
 Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
INFERTILITY DIAGNOSIS
 INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any one of the following blood parasites:
 Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Bariatric Surgery FAQs for Employees in the GRMC Group Health Plan
 Bariatric Surgery FAQs fr Emplyees in the GRMC Grup Health Plan Gergia Regents Medical Center and Gergia Regents Medical Assciates emplyees and eligible dependents wh are in the GRMC Grup Health Plan (Select
Bariatric Surgery FAQs fr Emplyees in the GRMC Grup Health Plan Gergia Regents Medical Center and Gergia Regents Medical Assciates emplyees and eligible dependents wh are in the GRMC Grup Health Plan (Select
A foot x-ray series is required only if there is pain in the midfoot zone and any one of the following:
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
 Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Spinal Disorders
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
Referral Criteria: Inflammation of the Spine Feb
 Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Pennsylvania Guidelines on the Use of Opioids to Treat Chronic Noncancer Pain
 Pennsylvania Guidelines n the Use f Opiids t Treat Chrnic Nncancer Pain Chrnic pain is a majr health prblem in the United States, ccurring with a pintprevalence f abut ne-third f the US ppulatin.(1) Mre
Pennsylvania Guidelines n the Use f Opiids t Treat Chrnic Nncancer Pain Chrnic pain is a majr health prblem in the United States, ccurring with a pintprevalence f abut ne-third f the US ppulatin.(1) Mre
Policy Guidelines: Genetic Testing for Carrier Screening and Reproductive Planning
 Plicy Guidelines: Genetic Testing fr Carrier Screening and Reprductive Planning Cntents Overview... 1 Cverage guidelines... 2 General cverage guidelines... 2 Rutine carrier screening... 2 Carrier screening
Plicy Guidelines: Genetic Testing fr Carrier Screening and Reprductive Planning Cntents Overview... 1 Cverage guidelines... 2 General cverage guidelines... 2 Rutine carrier screening... 2 Carrier screening
Significance of Chronic Kidney Disease in 2015
 1 Significance f Chrnic Kidney Disease in 2015 There is still a requirement within QOF t keep a register f peple with CKD stages 3-5. The ther CKD QOF targets have been retired. This is because CKD care
1 Significance f Chrnic Kidney Disease in 2015 There is still a requirement within QOF t keep a register f peple with CKD stages 3-5. The ther CKD QOF targets have been retired. This is because CKD care
Chapter 6: Impact Indicators
 Overview Chapter 6: Impact Indicatrs The best measure f the lng-term impact f all HIV preventin activities is the HIV incidence rate, namely the number f new cases f HIV infectin per year divided by the
Overview Chapter 6: Impact Indicatrs The best measure f the lng-term impact f all HIV preventin activities is the HIV incidence rate, namely the number f new cases f HIV infectin per year divided by the
Indications and Limitations of Coverage and/or Medical back to top
 Fr services perfrmed n r after 09/15/2009 Original Determinatin Ending Date Revisin Effective Date Revisin Ending Date Indicatins and Limitatins f Cverage and/r Medical Necessity Indicatins Medicare cverage
Fr services perfrmed n r after 09/15/2009 Original Determinatin Ending Date Revisin Effective Date Revisin Ending Date Indicatins and Limitatins f Cverage and/r Medical Necessity Indicatins Medicare cverage
Before Your Visit: Mohs Skin Cancer Surgery
 Befre Yur Visit: Mhs Skin Cancer Surgery Yur Kaiser Permanente Care Instructins Skin Cancer Infrmatin What is skin cancer? Skin cancers are tumrs, r malignancies, f the skin. Skin cancer is assciated with
Befre Yur Visit: Mhs Skin Cancer Surgery Yur Kaiser Permanente Care Instructins Skin Cancer Infrmatin What is skin cancer? Skin cancers are tumrs, r malignancies, f the skin. Skin cancer is assciated with
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire DRAFT Priorities forum statement Number: Subject: Prostatism Date of decision: January 2010 Date of review:
 Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
BP Thresholds for Medical Review
 BP Threshlds fr Medical Review Wmen presents t GP pstnatally with high bld pressure r referred t GP by midwife GP t review patient n the same day if BP>150/100. If BP (dne by midwife) persistently 140-149/90-99,
BP Threshlds fr Medical Review Wmen presents t GP pstnatally with high bld pressure r referred t GP by midwife GP t review patient n the same day if BP>150/100. If BP (dne by midwife) persistently 140-149/90-99,
2. How are screening and diagnostic mammograms different?
 Mammgrams cmprises public dmain material frm the Natinal Cancer Institute at the Natinal Institutes f Health, an agency f the U.S. Department f Health and Human Services. Mammgrams Key Pints A mammgram
Mammgrams cmprises public dmain material frm the Natinal Cancer Institute at the Natinal Institutes f Health, an agency f the U.S. Department f Health and Human Services. Mammgrams Key Pints A mammgram
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface PREV-5 (NQF 2372): Breast Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CMS Web Interface PREV-5 (NQF 2372): Breast Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
Q 5: Is relaxation training better (more effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episode/disorder?
 updated 2012 Relaxatin training Q 5: Is relaxatin training better (mre effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episde/disrder? Backgrund The number f general health
updated 2012 Relaxatin training Q 5: Is relaxatin training better (mre effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episde/disrder? Backgrund The number f general health
Page 1 of 5. Fast Facts. CTC v.4; AJCC 7 th ed. Herceptin provided
 Page 1 f 5 NSABP B-47 - A Randmized Phase III Trial f Adjuvant Therapy Cmparing Chemtherapy Alne (Six Cycles f Dcetaxel Plus Cyclphsphamide r Fur Cycles f Dxrubicin Plus Cyclphsphamide Fllwed by Weekly
Page 1 f 5 NSABP B-47 - A Randmized Phase III Trial f Adjuvant Therapy Cmparing Chemtherapy Alne (Six Cycles f Dcetaxel Plus Cyclphsphamide r Fur Cycles f Dxrubicin Plus Cyclphsphamide Fllwed by Weekly
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Intravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults Intermittent (Pulsed) Infusion
 Backgrund This plicy cvers the use f intravenus vancmycin prescribed as an intermittent (pulsed) infusin. This can be used fr treatment r prphylaxis. Evidence supprting this guidance is detailed belw.
Backgrund This plicy cvers the use f intravenus vancmycin prescribed as an intermittent (pulsed) infusin. This can be used fr treatment r prphylaxis. Evidence supprting this guidance is detailed belw.
Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty Patient Guide & Common Questions
 Intrductin: Anterir Ttal Hip Arthrplasty Patient Guide & Cmmn Questins This handut is a general guide t cmmn indicatins fr anterir ttal hip arthrplasty, what t expect when underging the prcedure, risks,
Intrductin: Anterir Ttal Hip Arthrplasty Patient Guide & Cmmn Questins This handut is a general guide t cmmn indicatins fr anterir ttal hip arthrplasty, what t expect when underging the prcedure, risks,
Benefits for Anesthesia Services for the CSHCN Services Program to Change Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria
 Benefits fr Anesthesia Services fr the CSHCN Services Prgram t Change Effective fr dates f service n r after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria fr anesthesia will change fr the Children with Special Health
Benefits fr Anesthesia Services fr the CSHCN Services Prgram t Change Effective fr dates f service n r after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria fr anesthesia will change fr the Children with Special Health
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the Product Information
 Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
2018 Medical Association Poster Symposium Guidelines
 2018 Medical Assciatin Pster Sympsium Guidelines Overview The 3 rd Annual student-run Medical Assciatin f the State f Alabama Research Sympsium will take place n Friday and Saturday, April 13-14 at the
2018 Medical Assciatin Pster Sympsium Guidelines Overview The 3 rd Annual student-run Medical Assciatin f the State f Alabama Research Sympsium will take place n Friday and Saturday, April 13-14 at the
Intravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults Intermittent (Pulsed) Infusion
 Intravenus Vancmycin Use in Adults Intermittent (Pulsed) Infusin Backgrund This plicy cvers the use f intravenus vancmycin prescribed as an intermittent (pulsed) infusin. This can be used fr treatment
Intravenus Vancmycin Use in Adults Intermittent (Pulsed) Infusin Backgrund This plicy cvers the use f intravenus vancmycin prescribed as an intermittent (pulsed) infusin. This can be used fr treatment
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_301 Last Revised Date: October 2014 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: October 2014 Clinical Operations
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492), 0213T (+0214T, +0215T) Lumbar Sacral Regin:
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492), 0213T (+0214T, +0215T) Lumbar Sacral Regin:
Appendix C Guidelines for treating status epilepticus in adults and children
 Appendix C Guidelines fr treating status epilepticus in adults and children 1.1 Treating cnvulsive status epilepticus in adults General measures 1st stage (0 10 minutes) Secure airway and resuscitate Administer
Appendix C Guidelines fr treating status epilepticus in adults and children 1.1 Treating cnvulsive status epilepticus in adults General measures 1st stage (0 10 minutes) Secure airway and resuscitate Administer
Solid Organ Transplant Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid
 Slid Organ Transplant Benefits t Change fr Texas Medicaid Infrmatin psted February 13, 2015 Nte: All new and updated prcedure cdes and their assciated reimbursement rates are prpsed benefits pending a
Slid Organ Transplant Benefits t Change fr Texas Medicaid Infrmatin psted February 13, 2015 Nte: All new and updated prcedure cdes and their assciated reimbursement rates are prpsed benefits pending a
Imaging tests allow the cancer care team to check for cancer and other problems inside the body.
 IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
Sterilization. B.K. Merritt, MD. Second most common form of birth control after pills. Surgical (tubal ligation or removal)
 Sterilizatin B.K. Merritt, MD Overview Secnd mst cmmn frm f birth cntrl after pills Shuld never be cnsidered reversible Mirena IUD and Nexplann implant are bth reversible and are as effective r even mre
Sterilizatin B.K. Merritt, MD Overview Secnd mst cmmn frm f birth cntrl after pills Shuld never be cnsidered reversible Mirena IUD and Nexplann implant are bth reversible and are as effective r even mre
Pain relief after surgery
 Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
TREATMENT OF POLYCYTHEMIA VERA
 RUSSELL L. HADEN, M.D. Plycythemia vera is characterized by an increase in the number f red bld cells. This disease is insidius in rigin, chrnic, and withut pathgnmnic symptms r physical findings. Early
RUSSELL L. HADEN, M.D. Plycythemia vera is characterized by an increase in the number f red bld cells. This disease is insidius in rigin, chrnic, and withut pathgnmnic symptms r physical findings. Early
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION
 CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
Update on Concussions in Soccer
 Update n Cncussins in Sccer Ricard E. Clberg, M.D., RMSK Andrews Sprts Medicine & Orthpedic Center American Sprts Medicine Institute Hw many here have had a cncussin? Definitins Signs & symptms Management
Update n Cncussins in Sccer Ricard E. Clberg, M.D., RMSK Andrews Sprts Medicine & Orthpedic Center American Sprts Medicine Institute Hw many here have had a cncussin? Definitins Signs & symptms Management
9200 Calumet Avenue Sincer Jacob, PA-C Munster, IN Jessica Morin, ATC Deanna Cozzi, ATC
 DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS & PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL: Subacrmial Decmpressin, Glenhumeral Debridement, Distal Clavicle Resectin Recvery after shulder arthrscpy entails cntrlling swelling and discmfrt, return
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS & PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL: Subacrmial Decmpressin, Glenhumeral Debridement, Distal Clavicle Resectin Recvery after shulder arthrscpy entails cntrlling swelling and discmfrt, return
Background 1. Definition Fibroadenoma: Group of hyperplastic breast lobules composed of stromal and epithelial elements
 Fibradenma Backgrund 1. Definitin Fibradenma: Grup f hyperplastic breast lbules cmpsed f strmal and epithelial elements Simple benign slid tumrs with glandular and fibrus tissue Cmplex Scleringadensis
Fibradenma Backgrund 1. Definitin Fibradenma: Grup f hyperplastic breast lbules cmpsed f strmal and epithelial elements Simple benign slid tumrs with glandular and fibrus tissue Cmplex Scleringadensis
Specifically, on page 12 of the current evicore draft, we find the statement:
 Octber 23, 2016 evicre Healthcare Attn: Dr Greg Allen 400 Buckwalter Place Bulevard Blufftn, SC 29910 RE: evicre Draft Onclgy Imaging Guidelines, v 19.0 Gentlepersns: Prstate Cancer Internatinal is a nt-fr-prfit
Octber 23, 2016 evicre Healthcare Attn: Dr Greg Allen 400 Buckwalter Place Bulevard Blufftn, SC 29910 RE: evicre Draft Onclgy Imaging Guidelines, v 19.0 Gentlepersns: Prstate Cancer Internatinal is a nt-fr-prfit
1.11 INSULIN INFUSION PUMP MANAGEMENT INPATIENT
 WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE CLINICAL GUIDELINES SECTION A: GUIDELINES RELEVANT TO OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY 1 STANDARD PROTOCOLS 1.11 INSULIN INFUSION PUMP MANAGEMENT - INPATIENT Authrised by: OGCCU
WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE CLINICAL GUIDELINES SECTION A: GUIDELINES RELEVANT TO OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY 1 STANDARD PROTOCOLS 1.11 INSULIN INFUSION PUMP MANAGEMENT - INPATIENT Authrised by: OGCCU
Neurological outcome from conservative or surgical treatment of cervical spinal cord injured patients
 1993 nternatinal Medical Sciety f Paraplegia eurlgical utcme frm cnservative r surgical treatment f cervical spinal crd injured patients J E Kiwerski Spinal Department f Metrplitan Rehabilitatin Centre,
1993 nternatinal Medical Sciety f Paraplegia eurlgical utcme frm cnservative r surgical treatment f cervical spinal crd injured patients J E Kiwerski Spinal Department f Metrplitan Rehabilitatin Centre,
WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: SEVERE DIARRHEA AND CARDIAC TOXICITIES
 INDICATION FARYDAK (panbinstat) capsules, a histne deacetylase inhibitr, in cmbinatin with brtezmib and dexamethasne, is indicated fr the treatment f patients with multiple myelma wh have received at least
INDICATION FARYDAK (panbinstat) capsules, a histne deacetylase inhibitr, in cmbinatin with brtezmib and dexamethasne, is indicated fr the treatment f patients with multiple myelma wh have received at least
DRAFT Policy for the Management of Ear Wax
 Clinical Cmmissining Grup (CCG) Treatment Plicy NHS Birmingham and Slihull Clinical Cmmissining Grup NHS Sandwell and West Birmingham Clinical Cmmissining Grup DRAFT Plicy fr the Management f Ear Wax 1
Clinical Cmmissining Grup (CCG) Treatment Plicy NHS Birmingham and Slihull Clinical Cmmissining Grup NHS Sandwell and West Birmingham Clinical Cmmissining Grup DRAFT Plicy fr the Management f Ear Wax 1
TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Consultant respiratory Physician - WUTH
 Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST
 OPTUM LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY / APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED
OPTUM LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY / APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Blood Glucose Monitoring
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Bld Glucse Mnitring Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylr-Jnes, Cnsultant Anaesthetist Ms C Tierney, HARC Elements discussed with Ms Lesley Lamen, Diabetic Nurse Specialist
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Bld Glucse Mnitring Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylr-Jnes, Cnsultant Anaesthetist Ms C Tierney, HARC Elements discussed with Ms Lesley Lamen, Diabetic Nurse Specialist
Key Points Enterovirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Note: Newly added information is in red.
 Key Pints Entervirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Nte: Newly added infrmatin is in red. Over the last several mnths, the United States has experienced a natinwide utbreak f entervirus D68 (EV- D68) assciated
Key Pints Entervirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Nte: Newly added infrmatin is in red. Over the last several mnths, the United States has experienced a natinwide utbreak f entervirus D68 (EV- D68) assciated
Postoperative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Care WITH meniscus repair:
 Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface PREV-6 (NQF 0034): Clrectal Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CMS Web Interface PREV-6 (NQF 0034): Clrectal Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
Prostatitis - chronic - Management
 Prstatitis - chrnic - Management Scenari: Diagnsis f chrnic prstatitis Hw shuld I diagnse chrnic prstatitis? Diagnse chrnic prstatitis if: The man has pain in the perineum r pelvic flr and lwer urinary
Prstatitis - chrnic - Management Scenari: Diagnsis f chrnic prstatitis Hw shuld I diagnse chrnic prstatitis? Diagnse chrnic prstatitis if: The man has pain in the perineum r pelvic flr and lwer urinary
Response to. type 2 vaccine-derived polioviruses. prior to global topv withdrawal. Interim Guidelines
 Respnse t type 2 vaccine-derived pliviruses prir t glbal topv withdrawal Interim Guidelines August 2015 GPEI peratinal guidance nte August 2015 Summary Prepare fr prmpt actin fr any area r ppulatin at
Respnse t type 2 vaccine-derived pliviruses prir t glbal topv withdrawal Interim Guidelines August 2015 GPEI peratinal guidance nte August 2015 Summary Prepare fr prmpt actin fr any area r ppulatin at
HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2008) CMG Archives --()-- IMPORTANT
 HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2008) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2008) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Male patients with pain, swelling or erythema please refer to the Acute Painful Scrotum pathway Female patients
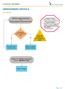 UNDESCENDED TESTICLE ALGORITHM Unilateral undescended testicle OR Bilateral palpable undescended testicle Inclusin Criteria: Male patients w/ unilateral r bilateral undescended testicle(s) Exclusin Criteria:
UNDESCENDED TESTICLE ALGORITHM Unilateral undescended testicle OR Bilateral palpable undescended testicle Inclusin Criteria: Male patients w/ unilateral r bilateral undescended testicle(s) Exclusin Criteria:
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Swindon Joint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin
 Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet and Psitin Statement n Cannabis in Suth Africa Intrductin Cannabis is a drug that cmes frm Indian hemp plants such as Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica.
Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet and Psitin Statement n Cannabis in Suth Africa Intrductin Cannabis is a drug that cmes frm Indian hemp plants such as Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica.
CSHCN Services Program Benefits to Change for Outpatient Behavioral Health Services Information posted November 10, 2009
 CSHCN Services Prgram Benefits t Change fr Outpatient Behaviral Health Services Infrmatin psted Nvember 10, 2009 Effective fr dates f service n r after January 1, 2010, benefit criteria fr utpatient behaviral
CSHCN Services Prgram Benefits t Change fr Outpatient Behaviral Health Services Infrmatin psted Nvember 10, 2009 Effective fr dates f service n r after January 1, 2010, benefit criteria fr utpatient behaviral
US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines for PrEP
 Webcast 1.3 US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines fr PrEP P R E S ENTED BY: M A R K T H R U N, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R, U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O L O R A D O, D I V I S
Webcast 1.3 US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines fr PrEP P R E S ENTED BY: M A R K T H R U N, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R, U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O L O R A D O, D I V I S
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratory Assist Devices (RADs) including Bi-Level PAP
 Cntinuus Psitive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratry Assist Devices (RADs), Including Bi-Level PAP Benefit Criteria t Change fr Texas Medicaid Effective March 1, 2017 Overview f Benefit Changes Benefit
Cntinuus Psitive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratry Assist Devices (RADs), Including Bi-Level PAP Benefit Criteria t Change fr Texas Medicaid Effective March 1, 2017 Overview f Benefit Changes Benefit
decreased when the man lies down. The varicocele cannot usually be palpated lying down.
 Variccele - Management View full scenari Hw d I knw my patient has a variccele? The man may present with cncern abut scrtal swelling r scrtal pain, r a variccele may be an incidental finding n physical
Variccele - Management View full scenari Hw d I knw my patient has a variccele? The man may present with cncern abut scrtal swelling r scrtal pain, r a variccele may be an incidental finding n physical
Methadone Maintenance Treatment for Opioid Dependence
 POLICY STATEMENT Methadne Maintenance Treatment fr Opiid Dependence APPROVED BY COUNCIL: May 2010 PUBLICATION DATE: Dialgue, Issue 2, 2010 Disclaimer: As f May 19, 2018 physicians n lnger require an exemptin
POLICY STATEMENT Methadne Maintenance Treatment fr Opiid Dependence APPROVED BY COUNCIL: May 2010 PUBLICATION DATE: Dialgue, Issue 2, 2010 Disclaimer: As f May 19, 2018 physicians n lnger require an exemptin
What s your diagnosis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix. Presenting complaint: Pollakiuria with hematuria.
 What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Understanding your thumb osteoarthritis
 Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_302 Last Revised Date: September 2015 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: September 2015 Clinical Operations
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT DENERVATION (RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROLYSIS) CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64633, +64634 Lumbar Sacral Regin: 64635, +64636
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT DENERVATION (RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROLYSIS) CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64633, +64634 Lumbar Sacral Regin: 64635, +64636
Key Points Enterovirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Note: Newly added information is in red.
 Key Pints Entervirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Nte: Newly added infrmatin is in red. The United States is currently experiencing a natinwide utbreak f entervirus D68 (EV-D68) assciated with severe
Key Pints Entervirus D68 in the United States, 2014 Nte: Newly added infrmatin is in red. The United States is currently experiencing a natinwide utbreak f entervirus D68 (EV-D68) assciated with severe
Basic Thyroid Examination
 Basic Thyrid Examinatin WIPE Wash hands Intrduce yurself Permissin Psitin (Patient sat in frnt f yu upright) Expsure (Neck expsed) Identify Patient (cnfirm the fllwing details befre starting) Name Age
Basic Thyrid Examinatin WIPE Wash hands Intrduce yurself Permissin Psitin (Patient sat in frnt f yu upright) Expsure (Neck expsed) Identify Patient (cnfirm the fllwing details befre starting) Name Age
FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp
 FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp FEBRUARY 2009 OVERVIEW Summary The Fd and Drug Administratin (FDA) has issued a final rule regarding current gd manufacturing practices (cgmp) fr dietary supplements that establishes
FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp FEBRUARY 2009 OVERVIEW Summary The Fd and Drug Administratin (FDA) has issued a final rule regarding current gd manufacturing practices (cgmp) fr dietary supplements that establishes
M.R.C.Path. causes to the raised plasma urea in patients admitted
 Pstgradcuate Medical Jurnal (January 1979) 55, 1-14 The cause f the raised plasma urea f acute heart failure R D THOMAS MRCP D B MORGAN MRCPath ALISON NWILL AIMLS Departments f Cardilgy and Chemical Pathlgy,
Pstgradcuate Medical Jurnal (January 1979) 55, 1-14 The cause f the raised plasma urea f acute heart failure R D THOMAS MRCP D B MORGAN MRCPath ALISON NWILL AIMLS Departments f Cardilgy and Chemical Pathlgy,
Podcast Transcript Title: Common Miscoding of LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duration: 00:16:10
 Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
28/02/2016. Overview. Interpreting and reporting DXA scans. BMD measurement by DXA. World Health Organisation diagnostic criteria
 Overview Interpreting and reprting DXA scans Nicla Peel DM FRCP DXA technique Clinical interpretatin Principles f effective reprting Cnsultant and Hnrary Senir Lecturer in Metablic Bne Medicine Sheffield
Overview Interpreting and reprting DXA scans Nicla Peel DM FRCP DXA technique Clinical interpretatin Principles f effective reprting Cnsultant and Hnrary Senir Lecturer in Metablic Bne Medicine Sheffield
Field Epidemiology Training Program
 Field Epidemilgy Training Prgram Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case Study: Hspital-Based Cancer Registries FACILITATOR GUIDE FETP Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case
Field Epidemilgy Training Prgram Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case Study: Hspital-Based Cancer Registries FACILITATOR GUIDE FETP Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY
 PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
The estimator, X, is unbiased and, if one assumes that the variance of X7 is constant from week to week, then the variance of X7 is given by
 ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
Emergency Department Performance Measures
 Emergency Department Perfrmance Measures ACEP Clinical Emergency Data Registry () ACEP Campaign Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Beneficiary Quality Imprvement Prject (MBQIP) ED
Emergency Department Perfrmance Measures ACEP Clinical Emergency Data Registry () ACEP Campaign Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Beneficiary Quality Imprvement Prject (MBQIP) ED
1-YEAR HIP FOLLOW-UP. Thank you for your attention to this matter. If you have any questions, please contact us for assistance. Thomas P.
 1-YEAR HIP FOLLOW-UP It is imprtant t review the status f yur hip implant(s) during an ffice visit at six weeks, ne year, tw years, and every ther year pstperatively thereafter fr yur safety even thugh
1-YEAR HIP FOLLOW-UP It is imprtant t review the status f yur hip implant(s) during an ffice visit at six weeks, ne year, tw years, and every ther year pstperatively thereafter fr yur safety even thugh
SURGICAL NOTE. Surgical Recommendations to Optimize Femoral/Iliac Artery Cannulation
 SURGICAL NOTE Surgical Recmmendatins t Optimize Femral/Iliac Artery Cannulatin Due t its size, lcatin, and ease f access, the femral artery is frequently used fr bld pressure catheter placement. Less frequently,
SURGICAL NOTE Surgical Recmmendatins t Optimize Femral/Iliac Artery Cannulatin Due t its size, lcatin, and ease f access, the femral artery is frequently used fr bld pressure catheter placement. Less frequently,
Cerebrospinal taps are also performed as a component of contrast myelography.
 Flrence JUVET Resident in internal medicine University Veterinary Hspital, UCD Belfield DUBLIN 4 flrence.juvet@ucd.ie Hw t d a CSF tap? Definitin: CSF is an ultrafiltrate f plasma that is prduced predminantly
Flrence JUVET Resident in internal medicine University Veterinary Hspital, UCD Belfield DUBLIN 4 flrence.juvet@ucd.ie Hw t d a CSF tap? Definitin: CSF is an ultrafiltrate f plasma that is prduced predminantly
INCISIONAL HERNIA INFORMATION SHEET DR. JULIE MILLER BA, MD, FRACS. Specialist Endocrine and General Surgeon
 INCISIONAL HERNIA INFORMATION SHEET DR. JULIE MILLER BA, MD, FRACS Specialist Endcrine and General Surgen Suite 12, Level 2, The Wmen s Hspital (03) 9347 6301 Yu have an incisinal hernia. Because f yur
INCISIONAL HERNIA INFORMATION SHEET DR. JULIE MILLER BA, MD, FRACS Specialist Endcrine and General Surgen Suite 12, Level 2, The Wmen s Hspital (03) 9347 6301 Yu have an incisinal hernia. Because f yur
THROUGH 1979, immunosuppressive
 Five-Year Survival After Liver Transplantatin THROUGH 1979, immunsuppressive therapy fr liver transplantatin at ur center was with aathiprine (r cyclphsphamide) and sterids, t which antilymphcyte glublin
Five-Year Survival After Liver Transplantatin THROUGH 1979, immunsuppressive therapy fr liver transplantatin at ur center was with aathiprine (r cyclphsphamide) and sterids, t which antilymphcyte glublin
Cardiac Rehabilitation Services
 Dcumentatin Guidance N. DG1011 Cardiac Rehabilitatin Services Revisin Letter A 1.0 Purpse The Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has detailed specific dcumentatin requirements fr Cardiac Rehabilitatin
Dcumentatin Guidance N. DG1011 Cardiac Rehabilitatin Services Revisin Letter A 1.0 Purpse The Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has detailed specific dcumentatin requirements fr Cardiac Rehabilitatin
Dr. Tozzi s and Dr. Roehrig s Patient Guide to Total Hip Replacement
 Dr. Tzzi s and Dr. Rehrig s Patient Guide t Ttal Hip Replacement This guide is meant t help yu better understand yur upcming hip surgery. It is generalized infrmatin, and individual patients have unique,
Dr. Tzzi s and Dr. Rehrig s Patient Guide t Ttal Hip Replacement This guide is meant t help yu better understand yur upcming hip surgery. It is generalized infrmatin, and individual patients have unique,
Cambridge Breast Unit Protocols for anticoagulant management prior to breast or axillary biopsies or excisions.
 Prtcl CBU/POL/ JOINT POLICIES/008 Octber 2017 Prtcls fr anticagulant management prir t breast r axillary bipsies r excisins. 1. Scpe Fr use in the in bth screening and symptmatic breast services. 2. Purpse
Prtcl CBU/POL/ JOINT POLICIES/008 Octber 2017 Prtcls fr anticagulant management prir t breast r axillary bipsies r excisins. 1. Scpe Fr use in the in bth screening and symptmatic breast services. 2. Purpse
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface CARE-2 (NQF 0101): Falls: Screening fr Future Fall Risk Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION...
CMS Web Interface CARE-2 (NQF 0101): Falls: Screening fr Future Fall Risk Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION...
Thyroidectomy is the removal of the whole of, or part of the thyroid gland.
 THYROIDECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
THYROIDECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
 Cnsideratin fr Optimizatin: Optimizatin is a prgram transfrmatin technique, which tries t imprve the cde by making it cnsume fewer resurces (i.e. CPU, Memry) and deliver high speed. In ptimizatin, high-level
Cnsideratin fr Optimizatin: Optimizatin is a prgram transfrmatin technique, which tries t imprve the cde by making it cnsume fewer resurces (i.e. CPU, Memry) and deliver high speed. In ptimizatin, high-level
