COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY-GUIDED BIOPSY OF MEDIASTINAL LESIONS: FINE VERSUS CUTTING NEEDLES
|
|
|
- Marian White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, 2003 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY-GUIDED BIOPSY OF MEDIASTINAL LESIONS: FINE VERSUS CUTTING NEEDLES André Piovesan de Farias 1, Daniel Deheinzelin 2, Riad N.Younes 2,3 and Rubens Chojniak 1 FARIAS AP de et al. Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions: fine versus cutting needles. Rev. Hosp. Clín. Fac. Med. S. Paulo 58(2):69-74, PURPOSE: To report the experience of a radiology department in the use of computed tomography guided biopsies of mediastinal lesions with fine and cutting needles, describing the differences between them. The results of adequacy of the sample and histologic diagnoses are presented according to the type of needle used. METHODS: We present a retrospective study of mediastinal biopsies guided by computed tomography performed from January 1993 to December Eighty-six patients underwent mediastinal biopsy in this period, 37 with cutting needles, 38 with fine needles, and 11 with both types (total of 97 biopsies). RESULTS: In most cases, it was possible to obtain an adequate sample (82.5%) and specific diagnosis (67.0%). Cutting-needle biopsy produced a higher percentage of adequate samples (89.6% versus 75.5%, P = 0.068) and of specific diagnosis (81.3% versus 53.1%, P = 0.003) than fine-needle biopsy. There were no complications that required intervention in either group. CONCLUSION: Because they are practical, safe, and can provide accurate diagnoses, image-guided biopsies should be considered the procedure of choice in the initial exploration of patients with mediastinal masses. In our experience, cutting needles gave higher quality samples and diagnostic rates. We recommend the use of cutting needles as the preferred procedure. DESCRIPTORS: Mediastinal masses. Tomography, computed axial. Needle biopsy. INTRODUCTION Image-guided percutaneous needle biopsy is a reliable technique for the diagnosis of thoracic diseases, particularly for the assessment of mediastinal lesions. Computed tomography (CT) is established as the best imaging method for needle biopsy guidance 1 ; CT provides detailed images for even small lesions located in any part of the mediastinum, which allows for accurate planning, avoiding inadvertent puncture of vascular structures or the lung. In most cases, the lesions are successfully reached, avoiding invasive procedures like bronchoscopy, mediastinoscopy, or even thoracotomy. The major concern has been the inherent risk of pneumothorax, reported to occur in as many as 10% to 23% 2,3 of procedures, although this complication usually requires treatment in only From the Departments of Radiology 1 and Thoracic Surgery 2 of the Cancer Hospital A. C. Camargo ; Paulista University (UNIP) and LIM Received for publication on June 10, % of cases. There are variations in needle biopsy technique among institutions, the most important difference being the type of needle used. While fine-needle biopsy (FNA) uses cytological techniques for analysis, cutting-needle biopsy provides larger tissue samples that are suitable for histologic study. The present study evaluates the results of CT-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions, as well as its impact on final diagnosis and management, comparing fine-needle and cutting-needle biopsies. 69
2 Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, 2003 METHODS We reviewed all biopsies of mediastinal masses performed between January 1993 and December Eighty-six patients underwent mediastinal biopsy during the study period, 38 with fine needles, 37 with cutting needles, and 11 with both types (total of 97 biopsies). Some authors recommend cutting needles according to the suspected diagnosis 1. In our practice, the size and the relationship of the lesion to adjacent structures determine the type of needle chosen. We use cutting needles when the lesion is larger than 20 mm and there is a low possibility of puncture of the lung or vascular structures. The study included 43 women and 43 men, ranging in age from 1 to 95 years (median = 34 years). We did not repeat biopsies in the same patient. Masses from all parts of mediastinum were included. The size of the lesions ranged from 12 to 140 mm (median = 35 mm), and the distance from the skin ranged from 18 to 140 mm (median = 50 mm). The biopsies were performed with the CT scanners GE Pace Plus and GE Pro Speed. Lesions were localized with contiguous scans 5 or 10 mm thick. The best path was displayed on the computer monitor, and electronic cursors were used to measure the distance from the skin and from a body marker, information that allowed calculation of the degree of inclination needed. The location for needle entry was marked on the patient s skin by correlating the light beam from the CT scanner. After preparation of skin with antiseptic solution, local anesthesia was performed on this site using 1% lidocaine. Children under 5 years of age underwent general anesthesia. The biopsy needle was then introduced, and new scans were obtained to modify or confirm the needle position. The fine-needle biopsies were performed with 22-gauge Chiba needles. The aspiration sample was smeared onto glass slides and immersed in 90% alcohol. A new puncture was performed when the sample obtained was judged insufficient. One to five aspirations were performed in each individual case and were then sent to the pathology department. The cutting-needle biopsies were performed with an 18-gauge Tru-Cut â (MD Tech) needle. When the tissue was obtained, it was placed in formalin and sent to the pathology department for final histological diagnosis. For pathologic analysis, the sample was stained in hematoxylin-eosin and classified as adequate or inadequate by the pathologist. The results of cytology and histology of the adequate sample were designated by the pathologist as the specific diagnosis, or when this was not possible, as positive or negative for malignancy. The rates of adequate sampling and specific diagnosis for the 2 different needle types were compared using the chi-square test, and the results were considered significant when P <0.05. RESULTS Adequate sampling for diagnosis was obtained in 80 biopsies (82.5%). The final diagnoses were 65 specific diagnoses, and 7 classified as positive and 8 negative for malignancy. The specific diagnoses of these procedures are listed in table 1. In the group undergoing cuttingneedle biopsy (n = 48), there were 43 (89.6%) with an adequate sample and 5 with inadequate samples (10.4%). The sample tissue provided for 39 (81.3%) specific diagnoses, as well as for 2 classified as positive and 2 negative for malignancy. In the group with specific diagnoses, lymphoma was the most frequent diagnosis (18 cases), followed by lung cancer, teratoma, seminoma, normal thymus, and mesenchymal neoplasms. In the 2 cases classified as positive for malignancy, the diagnoses were later confirmed as lymphoma and metastatic adenocarcinoma. For the 2 biopsies classified as negative for malignancy, further investigation established the diagnosis of ganglioneuroma and lymphoma. In 5 cases of inadequate sampling, the patients underwent thoracotomy, which revealed 3 cases of lymphoma, 1 bronchogenic cyst, and 1 mesothelioma. The fine-needle biopsies (n = 49) produced 37 (75.5%) adequate sample punctures. There were 26 (53.1%) specific diagnoses. Lymphoma was the most common histologic diagnosis, followed by lung cancer and others (thymoma, liposarcoma, seminoma, and metastasis). All 5 cases classified Table 1 - Distribution of specific diagnoses in 80 fine- or cutting-needle biopsies of mediastinal tumors. Lymphoma 22 Thymic hyperplasia 2 Lung carcinoma 10 Neuroendocrine tumor 1 Metastasis (lung and breast cancer) 7 Fibrosis 2 Thymoma 3 Liposarcoma 1 Seminoma 2 Mesenchymal neoplasm 1 Teratoma 2 Hürthle cell tumor 1 Normal thymus 2 Esophageal carcinoma 1 70
3 REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, 2003 Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions as positive for malignancy were confirmed as lymphoma or lung cancer. There were 6 cases classified as negative for malignancy, with 3 of them later confirmed as benign tumors, while the other 3 were actually malignant disease (lymphoma). In the 12 cases of inadequate sampling, subsequent investigation led to diagnosis of 5 cases of lymphoma, 3 of lung cancer, and 1 of bronchogenic cyst. In 3 other cases of this category, clinical diagnosis of benign masses was suspected, and they are still being followed up with no evidence of malignancy. The results of all punctures, including those for which specific diagnosis was not possible and those of inadequate sampling, are described according to the needle type and shown in tables 2 and 3. Cutting-needle biopsy was more successful. There was a statistically significant difference in the rate of specific diagnosis (P = 0.003), and there were more adequate sample punctures (P = 0.068), although these did not reach statistical significance. There were no complications that required any kind of intervention in the patients of both groups. However, minor complications such as small pneumothorax and hematoma could be underestimated in our series, because this is a retrospective study, and this information could be incompletely recorded in the radiology reports or subsequent clinical evaluations. DISCUSSION The potential for malignancy and the possibility of severe complications, such as respiratory or circulatory compression, mandate the fast and sometimes urgent diagnosis and treatment for mediastinal masses. Exploratory thoracotomy, mediastinoscopy, and anterior mediastinotomy are still widely used, despite potential morbidity and even mortality associated with these procedures. With dedicated and experienced pathologists, percutaneous biopsies can provide adequate diagnosis in most cases, independent of the type of needle used, whether fine or cutting. Either needle type is an adequate alternative that is well tolerated by the patients. Table 2 - Adequacy of results with cutting- vs fine-needle biopsy. Adequate Inadequate Cutting needle (n=48) 43 ( 89.6%) 5 (10.4%) Fine needle (n=49) 37 (75.5%) 12 (24.5%) Total (n=97) 80 (82.5%) 17 (17.5%) P = Table 3 - Specific diagnosis: Comparison between cutting- and fine-needle biopsies. Specific diagnosis Nonspecific diagnosis Cutting needle (n = 48) 39 (81.3%) 9 (18.8%) Fine needle (n = 49) 26 (53.1%) 23 (46.9%) Total (n = 97) 65 (67.0%) 32 (33.0%) P = These procedures are cost effective because they shorten the period from admission to diagnosis, decrease the number of surgical operations, and shorten the time of hospital stay, which reduces overall treatment costs 4. Unfortunately, some contraindications exist that preclude the use of percutaneous biopsies in every case. The absolute contraindications include uncontrollable cough and suspicion of hydatid cyst, whereas relative contraindications include bleeding diathesis, vascular lesions, pulmonary hypertension, uncooperative patient, and advanced emphysema 4. Fluoroscopy, CT, and more recently ultrasound can guide the punctures 5,6. The last method has the advantage of real-time imaging, but is limited in the evaluation of parts of mediastinum hidden by bone or air. Computed tomography can show more details than fluoroscopy, and provides complete evaluation of the thoracic cavity. Our success rate for adequate sampling (82.5%) and specific diagnosis (67.0%) was similar to the rates reported in the literature, ranging from 72% to 100% 4,7,11. Our high rate of malignancies is probably due to the patient population referred to our cancer hospital. As expected, we found more cases of adequate sampling in the cuttingneedle group (89.6% versus 75.5%). The tissue samples obtained with these needles also resulted in more specific diagnosis than in the fine-needle group (81.3% versus 53.1%). Fine-needle biopsy has long been recognized as useful because it is easily performed and provides adequate samples from deeply seated lesions. Fine-needle biopsy has a high sensitivity and specificity for metastatic disease 11,12. Morrisey et al. 10 reported a slightly higher sensitivity of cuttingneedle biopsy (96%) for diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma comparing to the 71
4 Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, % sensitivity of FNA. Fine-needle biopsy is also useful for cystic masses 13 and germ cell tumors 8. However, cytopathology with FNA samples requires a considerable amount of experience from the pathologist in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis based on few aspirated cells. On the other hand, the quality of the tissue sample provided by cuttingneedle biopsy is superior compared to that by FNA. Because more tissue is available, histologic diagnosis can be made and further pathologic investigations can be performed if necessary 9. This technique is also useful for other histologic types, such as lymphoma, thymoma, and benign tumors. With the sample obtained by FNA, a pathologist may suspect these diagnoses but may not be able to differentiate among them. Recent reports describe the higher accuracy of cutting-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of lymphoma 14,15, with the possibility of also determining the histologic subtype in most cases 16, which is fundamental information required to determine the subsequent treatment modality. A disadvantage of cutting-needle biopsies is local pain due to the larger gauge. Nowadays, the number of punctures is reduced, and the rapid sampling with the biopsy gun decreases the likelihood of pain. Our results confirm the advantages of cutting-needle biopsy for histologic diagnosis, but in some cases, we recommend the use fine needles instead. Fine needles are preferable when there is pulmonary parenchyma between the tumor and the chest wall, when the lesions are located adjacent to great vessels, and when highly vascular lesions are suspected. In these cases, and if metastatic carcinoma is suspected, FNA should be the initial method 1,11,17. The safety of these procedures was confirmed by the low incidence of complications in both groups, which concurs with reports from the literature 10. The absence of complications in our series also can be associated with the low number of punctures through the lung parenchyma or pleura, which can be avoided in most cases by using CT guidance. In conclusion, because they are minimally invasive, safe, cost effective, and have a high rate of success in providing adequate tissue sample, percutaneous needle biopsies guided by CT should be considered as the procedure of choice in the investigation of mediastinal masses. Both types of needle produced satisfactory results, but the higher quality sample of cutting needles provided more histologic diagnoses. The use of the cutting-needle biopsy can lead to more specific diagnosis without an increased incidence of complications; therefore, we recommend cutting-needle biopsy as the preferred method whenever possible. RESUMO FARIAS AP de e col. - Biópsia de massas mediastinais guiadas por Tomografia Computadorizada: agulhas finas versus cortantes. Rev. Hosp. Clín. Fac. Med. S. Paulo 58(2): 69-74, OBJETIVO: Apresentar a experiência de um serviço de radiologia na prática de punções biópsias de massas mediastinais guiadas por tomografia computadorizada com agulhas finas ou cortantes, descrevendo as diferenças entre elas. Os resultados referentes a material suficiente e diagnóstico histológico são apresentados de acordo com o tipo de agulha utilizado. MÉTODOS: Apresentamos um estudo retrospectivo de biópsias mediastinais guiadas por tomografia computadorizada realizadas em nosso hospital no período de janeiro de 1993 a dezembro de Oitenta e seis pacientes foram submetidos a biópsia mediastinal neste período, sendo 37 realizadas com agulhas cortantes, 38 com agulhas finas e 11 com ambas, (total de 97 biópsias). RESULTADOS: Na maioria dos casos foi possível se obter material adequado (82.5% ) e diagnóstico específi- 72
5 REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, 2003 Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions co (67 %). As agulhas cortantes apresentaram maior porcentagem de material suficiente (89.6% versus 75,5%, P=0,068) e de diagnóstico específico (81,3% versus 53,1%, p=0,003 ) do que as agulhas finas. Não houveram complicações que requisessem intervenção em nenhum dos grupos. CONCLUSÃO: Pela praticidade, segurança e grande probabilidade de diagnóstico acurado sem procedimentos mais invasivos, as biópsias guiadas por imagem devem ser consideradas como a primeira etapa na investigação de massas mediastinais. Pela nossa experiência as agulhas cortantes fornecem material de maior qualidade e maior taxa de diagnóstico. Nós recomendamos o uso das agulhas cortantes como procedimento preferencial. DESCRITORES: Massa mediastinal. Biópsia por agulha. Tomografia computadorizada. REFERENCES 1. PROTOPAPAS Z, WESTCOTT JL - Transthoracic hilar and mediastinal biopsy. Radiol Clin North Am 2000; 38(2): MOINUDDIN SM, LEE LH, MONTGOMERY JH - Mediastinal needle biopsy. AJR 1984; 143: BELFIORE G, CAMERA L, MOGGIO G, SALVATORE M et al. - Middle mediastinum lesions: preliminary experience with CT-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy with a suprasternal approach. Radiology 1997; 202: ZAFAR N, MOINUDDIM S - Mediastinal needle biopsy. Cancer 1995; 76: HEILO A - Tumors in the mediastinum: US-guided histologic core needle biopsy. Radiology 1993; 189: WERNECKE K, VASSALO P, VON BASSEWITZ DB et al. - Mediastinal tumors: biopsy under US guidance. Radiology 1989; 172: BRESSLER EL, KIRKHAM JA - Mediastinal masses: alternative approach to CT-guided needle biopsy. Radiology 1994; 191: HERMAN SJ, HOLUB RV, CHAMBERLEIN DW et al. - Anterior mediastinal masses: utility of transthoracic needle biopsy. Radiology 1991; 180: PARKER SH, HOPPER KD, CARTER TE et al. - Image-directed percutaneous biopsies with a biopsy gun. Radiology 1989; 171: MORRISEY B, ADAMS H, CRANE MD et al. - Percutaneous needle biopsy of the mediastinum: review of 94 procedures. Thorax 1993; 48: ADLER OB, ROSENBORG A, PELEG H Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of mediastinal masses: evaluation of 136 experiences. AJR 1983; 140:
6 Computed tomography-guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(2):69-74, PROTOPAPAS, WESTCOTT JL - Transthoracic needle biopsy of mediastinal lymph nodes for staging lung cancers. Radiology 1996; 199: KUHLMAN JE, FISHMAN EK, WANG KP et al. - Mediastinal cysts: Diagnostic by CT and needle aspiration. AJR 1988; 150: BEM-YEHUDA D, POLLIACK A, OKON E et al. - Image guided core needle biopsy in malignant lymphoma: Experience with 100 patients that suggests the technique is reliable. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: PAPA VI, HUSSAIN HK, REZNEK RH et al. - Role of image guided core needle biopsy in the management of patients with lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: MOULTON JS, MOORE PT - Coaxial percutaneous biopsy technique with automated biopsy devices: Value in improving accuracy and negative predictive value. Radiology 1993; 186: WESCOTT JL - Percutaneous needle aspiration of hilar and mediastinal masses. Radiology 1981; 141:
Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit
 Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis)
 Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Computed tomography-guided transthoracic needle biopsy of pulmonary nodules *
 Transthoracic REVIEW needle ARTICLE biopsy of pulmonary nodules Computed tomography-guided transthoracic needle biopsy of pulmonary nodules * Biópsia transtorácica de nódulos e massas pulmonares dirigida
Transthoracic REVIEW needle ARTICLE biopsy of pulmonary nodules Computed tomography-guided transthoracic needle biopsy of pulmonary nodules * Biópsia transtorácica de nódulos e massas pulmonares dirigida
Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Biopsies of Suspected Mediastinal Lesions
 Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Biopsies of Suspected Mediastinal Lesions SA Samad, FRCR* N.A. Sharifah, DCP** M.A. Zulfiqar, M. Med. (Radiology)* A. Maimunah, M. Med. (Radiology)* A. Yahya, FRCS*** W.
Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Biopsies of Suspected Mediastinal Lesions SA Samad, FRCR* N.A. Sharifah, DCP** M.A. Zulfiqar, M. Med. (Radiology)* A. Maimunah, M. Med. (Radiology)* A. Yahya, FRCS*** W.
Mediastinal Tumors: Imaging
 Mediastinal Tumors: Imaging References Imaging in Oncology, Husband and Reznek Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance of the thorax, Naidich, Zerhouni, Siegelman, Mediastinal compartments Anterior:
Mediastinal Tumors: Imaging References Imaging in Oncology, Husband and Reznek Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance of the thorax, Naidich, Zerhouni, Siegelman, Mediastinal compartments Anterior:
Comparison of CT-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy with and Without Registration of Prior PET/CT Images to Diagnose Mediastinal Tumors
 Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (2014) 37:1306 1311 DOI 10.1007/s00270-013-0793-x CLINICAL INVESTIGATION NON-VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS Comparison of CT-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy with and Without Registration
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (2014) 37:1306 1311 DOI 10.1007/s00270-013-0793-x CLINICAL INVESTIGATION NON-VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS Comparison of CT-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy with and Without Registration
Abstract. Introduction. Salah Abobaker Ali
 Sensitivity and specificity of combined fine needle aspiration cytology and cell block biopsy versus needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of sonographically detected abdominal masses Salah Abobaker Ali
Sensitivity and specificity of combined fine needle aspiration cytology and cell block biopsy versus needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of sonographically detected abdominal masses Salah Abobaker Ali
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Endobronchial Ultrasound in the Diagnosis & Staging of Lung Cancer
 Endobronchial Ultrasound in the Diagnosis & Staging of Lung Cancer Dr Richard Booton PhD FRCP Lead Lung Cancer Clinician, Consultant Respiratory Physician & Speciality Director Manchester University NHS
Endobronchial Ultrasound in the Diagnosis & Staging of Lung Cancer Dr Richard Booton PhD FRCP Lead Lung Cancer Clinician, Consultant Respiratory Physician & Speciality Director Manchester University NHS
Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach
 ProceedingS.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 9(3-1) 1995, pp. 78-82. Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach M.A. Rahim Khan, Bilquees A. Suleman,
ProceedingS.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 9(3-1) 1995, pp. 78-82. Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach M.A. Rahim Khan, Bilquees A. Suleman,
Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices
 Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices PHILLIP GUICHET, B.A. 1, FEREIDOUN ABTIN, M.D. 2, CHRISTOPHER LEE, M.D. 1 1 KECK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OF USC, DEPT OF
Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices PHILLIP GUICHET, B.A. 1, FEREIDOUN ABTIN, M.D. 2, CHRISTOPHER LEE, M.D. 1 1 KECK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OF USC, DEPT OF
The Role of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis and Management of Thymic Neoplasia
 MALIGNANCIES OF THE THYMUS The Role of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis and Management of Thymic Neoplasia Maureen F. Zakowski, MD, James Huang, MD, and Matthew P. Bramlage, MD Background:
MALIGNANCIES OF THE THYMUS The Role of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis and Management of Thymic Neoplasia Maureen F. Zakowski, MD, James Huang, MD, and Matthew P. Bramlage, MD Background:
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL
 The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
T masses continues to evolve as newer imaging modalities
 Thoracoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of Mediastinal Masses John A. Kern, MD, Thomas M. Daniel, MD, Curtis G. Tribble, MD, Mark L. Silen, MD, and Bradley M. Rodgers, MD Divisions of Pediatric and Thoracic
Thoracoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of Mediastinal Masses John A. Kern, MD, Thomas M. Daniel, MD, Curtis G. Tribble, MD, Mark L. Silen, MD, and Bradley M. Rodgers, MD Divisions of Pediatric and Thoracic
Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary?
 Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary? Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Hayter, T. Berkmen; New
Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary? Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Hayter, T. Berkmen; New
Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 970813, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/970813 Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy William
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 970813, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/970813 Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy William
Investigation of correlation between cytological and histological findings in suspected carcinoma of thyroid
 original article J Bras Patol Med Lab. 2018 Dec; 54(6): 407-411. Investigation of correlation between cytological and histological findings in suspected carcinoma of thyroid Investigação da correlação
original article J Bras Patol Med Lab. 2018 Dec; 54(6): 407-411. Investigation of correlation between cytological and histological findings in suspected carcinoma of thyroid Investigação da correlação
Karoline Nowillo, MD. February 1, 2008
 Case Presentation Karoline Nowillo, MD SUNY Downstate t February 1, 2008 Case Presentation Chief complaint enlarging goiter x 8 months History of present illness shortness of breath, heaviness in chest
Case Presentation Karoline Nowillo, MD SUNY Downstate t February 1, 2008 Case Presentation Chief complaint enlarging goiter x 8 months History of present illness shortness of breath, heaviness in chest
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center
 Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy induced complications - how to cut back?
 CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy induced complications - how to cut back? Poster No.: C-0560 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Boskovic, M. Stojanovic, S. Pena Karan, G. Vujasinovi#;
CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy induced complications - how to cut back? Poster No.: C-0560 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Boskovic, M. Stojanovic, S. Pena Karan, G. Vujasinovi#;
Transbronchial fine needle aspiration
 Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1
 Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1 In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Ki-Suck Jung, M.D. 2, Hyoung June Im,
Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1 In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Ki-Suck Jung, M.D. 2, Hyoung June Im,
PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS Abdur Rehman Khan, Arshad Javed, Mohammad Ejaz Department of Radiology and Department of Pulmonology, Postgraduate Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS Abdur Rehman Khan, Arshad Javed, Mohammad Ejaz Department of Radiology and Department of Pulmonology, Postgraduate Medical
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES LungCancerAlliance.org
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org CONTENTS What is a Biopsy?...2 Non-Surgical Biopsies...3 Surgical Biopsies...5 Biopsy Risks...6 Biopsy Results...6 Questions
UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org CONTENTS What is a Biopsy?...2 Non-Surgical Biopsies...3 Surgical Biopsies...5 Biopsy Risks...6 Biopsy Results...6 Questions
EBUS-TBNA in PET-positive lymphadenopathies in treated cancer patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG IMAGING EBUS-TBNA in PET-positive lymphadenopathies in treated cancer patients Juliana Guarize 1, Monica Casiraghi 1, Stefano Donghi 1, Chiara Casadio 2, Cristina Diotti 1, Niccolò
ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG IMAGING EBUS-TBNA in PET-positive lymphadenopathies in treated cancer patients Juliana Guarize 1, Monica Casiraghi 1, Stefano Donghi 1, Chiara Casadio 2, Cristina Diotti 1, Niccolò
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
May-Lin Wilgus. A. Study Purpose and Rationale
 Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer
 The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer Gerard A. Silvestri, MD,MS, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC silvestri@musc.edu Staging Lung
The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer Gerard A. Silvestri, MD,MS, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC silvestri@musc.edu Staging Lung
Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs
 Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs Fine needles for cytology have been used >50 years in all parts of the human body with no to very little harm Gold Anchor comes pre-loaded in needles of the
Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs Fine needles for cytology have been used >50 years in all parts of the human body with no to very little harm Gold Anchor comes pre-loaded in needles of the
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
MATERIALS AND METHODS. We retrospectively reviewed a consecutive series
 Huanqi Li1 Phillip M. Boiselle1 2 Jo-Anne 0. Shepard1 Beatrice Trotman-Dickenson1 Theresa C. McLoud1 Received January 2, 1996; accepted after revision Febru ary 19, 1996. tchest Division, Department of
Huanqi Li1 Phillip M. Boiselle1 2 Jo-Anne 0. Shepard1 Beatrice Trotman-Dickenson1 Theresa C. McLoud1 Received January 2, 1996; accepted after revision Febru ary 19, 1996. tchest Division, Department of
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions
 Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
Assessing the lung and mediastinum in cancer-is tissue the issue? George Santis
 1 Assessing the lung and mediastinum in cancer-is tissue the issue? George Santis Optimal management of Cancer Histological diagnosis & accurate staging at presentation Molecular analysis of primary tumour
1 Assessing the lung and mediastinum in cancer-is tissue the issue? George Santis Optimal management of Cancer Histological diagnosis & accurate staging at presentation Molecular analysis of primary tumour
Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy
 Original Article Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy * Atheer A. Fadhil** FICMS-CABMS-FICMS (Pulm.), DMRD, FIBMS (Rad.), Fac Med Baghdad 2012; Vol. 54, No. 1 Received Dec.2011
Original Article Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy * Atheer A. Fadhil** FICMS-CABMS-FICMS (Pulm.), DMRD, FIBMS (Rad.), Fac Med Baghdad 2012; Vol. 54, No. 1 Received Dec.2011
MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro
 MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro Paul E. Van Schil, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic and Vascular Surgery University of Antwerp, Belgium Mediastinal staging Invasive techniques lymph node mapping cervical
MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro Paul E. Van Schil, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic and Vascular Surgery University of Antwerp, Belgium Mediastinal staging Invasive techniques lymph node mapping cervical
Mediastinoscopy, Mediastinotomy And Thoracoscopy For Mediastinal Lesions. Alper Toker, MD
 Mediastinoscopy, Mediastinotomy And Thoracoscopy For Mediastinal Lesions Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery The mediastinum is a complex anatomic
Mediastinoscopy, Mediastinotomy And Thoracoscopy For Mediastinal Lesions Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery The mediastinum is a complex anatomic
Primary mediastinal tumours
 Primary mediastinal tumours Thorax (1974), 29, 475. YOUSF D. AL-NAAMAN, MOHAMAD S. AL-AN, and MUAYYAD M. AL-OMER Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad,
Primary mediastinal tumours Thorax (1974), 29, 475. YOUSF D. AL-NAAMAN, MOHAMAD S. AL-AN, and MUAYYAD M. AL-OMER Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad,
Pathology of Mediastinal Tumors
 SAMO Meeting Lucerne 2009 Pathology of Mediastinal Tumors Alex Soltermann Most common lesions (adults) Clinical presentation 50% of the patients are asymptomatic, lesion discovered incidentally Symptoms
SAMO Meeting Lucerne 2009 Pathology of Mediastinal Tumors Alex Soltermann Most common lesions (adults) Clinical presentation 50% of the patients are asymptomatic, lesion discovered incidentally Symptoms
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for mediastinal
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for mediastinal
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery
 Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy is a common finding in
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for the Diagnosis of Intrathoracic Lymphadenopathy in Patients with Extrathoracic Malignancy A Multicenter Study Neal Navani,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for the Diagnosis of Intrathoracic Lymphadenopathy in Patients with Extrathoracic Malignancy A Multicenter Study Neal Navani,
CT-guided biopsy of lung lesions: defining the best needle option for a specific diagnosis
 CLINICAL SCIENCE CT-guided biopsy of lung lesions: defining the best needle option for a specific diagnosis Marcos Duarte Guimarães, I Edson Marchiori, II Bruno Hochhegger, III Rubens Chojniak, I Jefferson
CLINICAL SCIENCE CT-guided biopsy of lung lesions: defining the best needle option for a specific diagnosis Marcos Duarte Guimarães, I Edson Marchiori, II Bruno Hochhegger, III Rubens Chojniak, I Jefferson
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience
 CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
Computed tomography guided fine needle aspiration cytology of thoracic lesions: A retrospective analysis of 114 cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 47-52 Computed tomography guided fine needle aspiration cytology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 47-52 Computed tomography guided fine needle aspiration cytology
Standardized transbronchial needle aspiration procedure for intrathoracic lymph node staging of non-small cell lung cancer
 Original Article on Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (TBNA) Standardized transbronchial needle aspiration procedure for intrathoracic lymph node staging of non-small cell lung cancer Xu-Ru Jin 1 *, Min
Original Article on Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (TBNA) Standardized transbronchial needle aspiration procedure for intrathoracic lymph node staging of non-small cell lung cancer Xu-Ru Jin 1 *, Min
Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis
 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2303.2006.00336.x Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis S. Smojver-Ježek*, T. Peroš-Golubičić, J. Tekavec-Trkanjec, I. Mažuranić
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2303.2006.00336.x Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis S. Smojver-Ježek*, T. Peroš-Golubičić, J. Tekavec-Trkanjec, I. Mažuranić
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases
 Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases 2014 Date: October 2014 Version: Owner: Status: v01 Ministry of Health Cancer Services Final Citation: Ministry of Health. 2014. Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators:
Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases 2014 Date: October 2014 Version: Owner: Status: v01 Ministry of Health Cancer Services Final Citation: Ministry of Health. 2014. Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators:
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes
 Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes Evan A. Alston, MD 1 ; Sejong Bae, PhD 2 ; and Isam A. Eltoum, MD, MBA 1 BACKGROUND:
Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes Evan A. Alston, MD 1 ; Sejong Bae, PhD 2 ; and Isam A. Eltoum, MD, MBA 1 BACKGROUND:
Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy Junji Uchida, MD, Fumio Imamura, MD, Akemi Takenaka, CT, Mana Yoshimura, MD, Kiyonobu Ueno, MD, Kazuyuki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy Junji Uchida, MD, Fumio Imamura, MD, Akemi Takenaka, CT, Mana Yoshimura, MD, Kiyonobu Ueno, MD, Kazuyuki
Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month. Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA
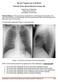 May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC. Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017
 Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017 To describe patient referral & triage for the patient with suspected lung cancer To describe the initial
Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017 To describe patient referral & triage for the patient with suspected lung cancer To describe the initial
Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules
 Original article Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules Samuel Copeland MD, Shrinivas Kambali MD, Gilbert Berdine MD, Raed Alalawi MD Abstract Background:
Original article Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules Samuel Copeland MD, Shrinivas Kambali MD, Gilbert Berdine MD, Raed Alalawi MD Abstract Background:
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
UCLA General Surgery Residency Program Rotation Educational Policy Goals and Objectives
 UPDATED: July 2009 ROTATION: THORACIC SURGERY UCLA General Surgery Residency Program ROTATION DIRECTOR: Mary Maish, M.D. CHIEF OF CARDIAC SURGERY: Robert Cameron, M.D. SITES: UCLA Medical Center - Westwood
UPDATED: July 2009 ROTATION: THORACIC SURGERY UCLA General Surgery Residency Program ROTATION DIRECTOR: Mary Maish, M.D. CHIEF OF CARDIAC SURGERY: Robert Cameron, M.D. SITES: UCLA Medical Center - Westwood
Consensus of Percutaneous Lung Needle Biopsy Statement from Japanese Society of Lung Needle Biopsy
 IVR Jpn J Intervent Radiol 22:256-261, 2007. Consensus of Percutaneous Lung Needle Biopsy Statement from Japanese Society of Lung Needle Biopsy 2000CT CT 5 IVR CT 100 Europian radiology 5 CT EBM IC 1 2
IVR Jpn J Intervent Radiol 22:256-261, 2007. Consensus of Percutaneous Lung Needle Biopsy Statement from Japanese Society of Lung Needle Biopsy 2000CT CT 5 IVR CT 100 Europian radiology 5 CT EBM IC 1 2
Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy
 Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy Charles R. Thomas, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiation Medicine Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Medical
Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy Charles R. Thomas, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiation Medicine Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Medical
Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System. Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center
 Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center Thyroid Nodules Frequent occurrence Palpable: 4-7% of adults Ultrasound: 10-31% Majority benign
Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center Thyroid Nodules Frequent occurrence Palpable: 4-7% of adults Ultrasound: 10-31% Majority benign
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Francisco Jose Rodrigues de Moura Filho 1. Marilza Oliveira 2. ABSTRACT RESUMO
 28 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Francisco Jose Rodrigues de Moura Filho 1. Marilza Oliveira 2. 1 Médico, graduado em Medicina na Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC), com Especialidade Médica em Radiologia e Diagnóstico
28 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Francisco Jose Rodrigues de Moura Filho 1. Marilza Oliveira 2. 1 Médico, graduado em Medicina na Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC), com Especialidade Médica em Radiologia e Diagnóstico
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
THORACIC MALIGNANCIES
 THORACIC MALIGNANCIES Summary for Malignant Malignancies. Lung Ca 1 Lung Cancer Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnostic Evaluation for Non-Small Lung Cancer 1. History and Physical examination. 2. CBCDE,
THORACIC MALIGNANCIES Summary for Malignant Malignancies. Lung Ca 1 Lung Cancer Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnostic Evaluation for Non-Small Lung Cancer 1. History and Physical examination. 2. CBCDE,
Ultrasound-guided FNA Biopsy. American Thyroid Association 2017
 Ultrasound-guided FNA Biopsy American Thyroid Association 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth University Disclosures: No relevant
Ultrasound-guided FNA Biopsy American Thyroid Association 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth University Disclosures: No relevant
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER
 MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
Mediastinal Staging. Samer Kanaan, M.D.
 Mediastinal Staging Samer Kanaan, M.D. Overview Importance of accurate nodal staging Accuracy of radiographic staging Mediastinoscopy EUS EBUS Staging TNM Definitions T Stage Size of the Primary Tumor
Mediastinal Staging Samer Kanaan, M.D. Overview Importance of accurate nodal staging Accuracy of radiographic staging Mediastinoscopy EUS EBUS Staging TNM Definitions T Stage Size of the Primary Tumor
PET/CT in lung cancer
 PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
EBUS-FNAB: HOW TO OPTIMIZE YOUR CYTOLOGY SAMPLES, LHSC EXPERIENCE. Dr. Mariamma Joseph Division Head of Cytopathology LHSC and Western University
 EBUS-FNAB: HOW TO OPTIMIZE YOUR CYTOLOGY SAMPLES, LHSC EXPERIENCE Dr. Mariamma Joseph Division Head of Cytopathology LHSC and Western University Objectives Brief overview of EBUS-FNA Strategies to optimize
EBUS-FNAB: HOW TO OPTIMIZE YOUR CYTOLOGY SAMPLES, LHSC EXPERIENCE Dr. Mariamma Joseph Division Head of Cytopathology LHSC and Western University Objectives Brief overview of EBUS-FNA Strategies to optimize
Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions
 Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
 Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Basic Data. Sex:Male 31 years old Occupation: 搬家工人
 Basic Data Sex:Male 31 years old Occupation: 搬家工人 Chief Complaint Intermittent chest pain with shortness of breath for 2-3 months. Present Illness 4 months ago, he started having occasional chest pain
Basic Data Sex:Male 31 years old Occupation: 搬家工人 Chief Complaint Intermittent chest pain with shortness of breath for 2-3 months. Present Illness 4 months ago, he started having occasional chest pain
Blood path technique to reduce pneumothorax after CT guided lung biopsy
 Blood path technique to reduce pneumothorax after CT guided lung biopsy Poster No.: C-0753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: G. J. Mallarajapatna, N. Ramanna; Bangalore/IN Keywords: Interventional
Blood path technique to reduce pneumothorax after CT guided lung biopsy Poster No.: C-0753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: G. J. Mallarajapatna, N. Ramanna; Bangalore/IN Keywords: Interventional
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 19 Effective Health Care Program Comparative Effectiveness of Core-Needle and Open Surgical Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Breast Lesions Executive Summary Background
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 19 Effective Health Care Program Comparative Effectiveness of Core-Needle and Open Surgical Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Breast Lesions Executive Summary Background
Preoperative Evaluation
 Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015
 Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions
 ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
Computed tomography-guided percutaneous biopsy of bone lesions: rate of diagnostic success and complications *
 Original Article Maciel MJS et al. / CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of bone lesions Computed tomography-guided percutaneous biopsy of bone lesions: rate of diagnostic success and complications * Biópsia
Original Article Maciel MJS et al. / CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of bone lesions Computed tomography-guided percutaneous biopsy of bone lesions: rate of diagnostic success and complications * Biópsia
SCBT-MR 2015 Incidentaloma on Chest CT
 SCBT-MR 2015 Incidentaloma on Chest CT Reginald F. Munden MD, DMD, MBA I have no conflicts of interest to report Incidentaloma Pulmonary Nodule Mediastinal Lymph Node Coronary Artery Calcium Incidental
SCBT-MR 2015 Incidentaloma on Chest CT Reginald F. Munden MD, DMD, MBA I have no conflicts of interest to report Incidentaloma Pulmonary Nodule Mediastinal Lymph Node Coronary Artery Calcium Incidental
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Outcomes of Biopsies of Small Pulmonary Nodules Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sang Hyun Choi 1 Eun Jin Chae Ji-Eun Kim Eun Young Kim Sang
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Outcomes of Biopsies of Small Pulmonary Nodules Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sang Hyun Choi 1 Eun Jin Chae Ji-Eun Kim Eun Young Kim Sang
Running Title: Utility of HCG Washout in Cervical LND FNA
 AACE Clinical Case Reports Rapid Electronic Articles in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited,
AACE Clinical Case Reports Rapid Electronic Articles in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited,
Case Scenario 1: Breast
 Case Scenario 1: Breast A 63 year old white female presents with a large mass in her left breast. 4/15/13 Mammogram/US: 1. Left breast mammographic and sonographic at 3:00 measuring 7.1 cm highly suggestive
Case Scenario 1: Breast A 63 year old white female presents with a large mass in her left breast. 4/15/13 Mammogram/US: 1. Left breast mammographic and sonographic at 3:00 measuring 7.1 cm highly suggestive
USGFNA of thyroid nodules
 US Guided FNA (USGFNA) of neck masses INTERVENTIONAL HEAD & NECK ULTRASOUND Brendan C. Stack, Jr., MD., FACS, FACE Professor Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Indications Technique Interpretation Results
US Guided FNA (USGFNA) of neck masses INTERVENTIONAL HEAD & NECK ULTRASOUND Brendan C. Stack, Jr., MD., FACS, FACE Professor Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Indications Technique Interpretation Results
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
OBJECTIVES. Solitary Solid Spiculated Nodule. What would you do next? Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules.
 Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Study of image guided fine needle aspirates from lesions of liver: A two year study in a tertiary care center
 Original article Study of image guided fine needle aspirates from lesions of liver: A two year study in a tertiary care center Vijay Subhashrao Bonde 1, Nanda J. Patil 2 Department of Pathology, 2 nd floor,
Original article Study of image guided fine needle aspirates from lesions of liver: A two year study in a tertiary care center Vijay Subhashrao Bonde 1, Nanda J. Patil 2 Department of Pathology, 2 nd floor,
American College Of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria WORK-UP OF THE SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE
 This document is provided to you by the American College of Radiology. We strive to deliver this information in a convenient and effective manner. After you finish reviewing the criteria, please provide
This document is provided to you by the American College of Radiology. We strive to deliver this information in a convenient and effective manner. After you finish reviewing the criteria, please provide
Case Scenario 1. Pathology report Specimen from mediastinoscopy Final Diagnosis : Metastatic small cell carcinoma with residual lymphatic tissue
 Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD. November 18, 2017
 Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD November 18, 2017 Disclosures I do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations
Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD November 18, 2017 Disclosures I do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
