Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the sublingual gland: case report and literature review
|
|
|
- Owen Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 DOI: / Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the sublingual gland: case report and literature review Filippos Thomopoulos 1, Nikolaos G. Nikitakis 2, Argyrios Daskalopoulos 2, Evangelia Piperi 2, Nikolaos Kolomvos 3, Alexandra Sklavounou 2 1 Undergraduate student, School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens 11527, Greece. 2 Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens 11527, Greece. 3 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens 11527, Greece. Correspondence to: Dr. Argyrios Daskalopoulos, Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, 2 Thivon St., Athens 11527, Greece. adaskal@hotmail.gr How to cite this article: Thomopoulos F, Nikitakis NG, Daskalopoulos A, Piperi E, Kolomvos N, Sklavounou A. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the sublingual gland: case report and literature review. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8. Received: 23 Dec 2017 First Decision: 4 Apr 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 Accepted: 18 May 2018 Published: 19 Jul 2018 Science Editor: Athanasios Poulopoulos Copy Editor: Jun-Yao Li Production Editor: Cai-Hong Wang Abstract Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (CSS) is a chronic inflammatory condition of uncertain etiology, primarily affecting the submandibular glands. It has recently been proposed that CSS belongs to the immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease spectrum, although the exact relationship between these two entities requires further elucidation. Our aim is to present a case of bilateral CSS of the sublingual glands and discuss the possible underlying pathogenetic mechanisms. A 66-year-old woman presented with a 7-month history of an asymptomatic firm swelling of the floor of the mouth. Clinically, a diffuse, multinodular swelling of elastic to firm consistency was observed across the sublingual folds bilaterally. An incisional biopsy revealed a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with lymphoid follicle formation, along with acinar degeneration, fibrosclerosis and ductal dilation. Immunohistochemical investigation ruled out lymphoproliferative diseases revealing a polyclonal lymphoplasmacytic population with only a few scattered IgG4-positive plasma cells. IgG4 serum levels were also normal. No treatment was administered with progressive spontaneous resolution of the swelling and no evidence of recurrence at 2 years follow-up. CSS is a benign salivary gland disorder, which, at least in a subset of cases, may represent an IgG4-associated disorder. Therefore, immunohistochemical evaluation of the IgG4/IgG plasma cell ratio and the IgG4 serum levels is a recommended investigation in the diagnostic work-up of CSS cases. Keywords: Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis, immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis, sialolithiasis, sublingual salivary gland The Author(s) Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
2 Page 2 of 9 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I INTRODUCTION Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (CSS) is a chronic fibrosing inflammatory condition, first described by Ku ttner [1] in 1896, most commonly affecting the submandibular glands [2-4]. Clinically, CSS may present as a unilateral or rarely bilateral, asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic firm swelling of the involved gland, often mimicking a neoplasm [2,3,5]. Histologically, CSS shows marked lymphocytic infiltration with reactive lymphoid follicle formation, periductal fibrosis, acinar atrophy and interlobular sclerosis [3,5,6]. Although the pathogenesis of CSS remains uncertain, a wide range of etiologic factors has been proposed including sialolithiasis, secretory disorders, infectious agents, ductal abnormalities and immunopathologic reactions [2,5]. Kitagawa et al. [7] suggested that CSS belongs to the immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) spectrum, a recently described, systemic, immune mediated disease with multi-organ involvement. Since then, the possible association between chronic sclerosing sialadenitis and IgG4-RD has been postulated. Here we report a very rare case of bilateral CCS of the sublingual glands in a 66-year-old woman. The clinical, microscopic and immunopathological features are presented and the possible underlying pathogenetic mechanisms of this, possibly under-recognized, condition are also discussed. CASE REPORT A 66-year-old female presented to the Oral Medicine Clinic, School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece for evaluation of a mildly painful swelling of the floor of the mouth of 2 weeks duration. At the onset, the patient visited the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinic of a local hospital, where broad-spectrum antibiotics (amoxicillin 1 g bid plus metronidazole 500 mg tid) were administered for 1 week with only minimal improvement of the swelling. According to the patient, the first episode of swelling at the area was observed approximately 7 months ago. At that time, panoramic radiograph, computed tomography (CT) scan and ultrasound (US) imaging were performed without remarkable pathologic findings. However, imaging of the sublingual gland region with CT scan was distorted due to the metal artifacts produced by the patient s dental prosthetic appliances. Antibiotic treatment was prescribed and the swelling subsided within 1 week. The medical history was remarkable for a papillary thyroid carcinoma, developing in the context of Hashimoto s thyroiditis, diagnosed 3 years ago and managed with thyroidectomy without radioactive iodine treatment. Since then, the patient was on levothyroxine 75 mg qd. Moreover, she had hypertension treated with a combination of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist and a thiazide diuretic (olmesartan medoxomil 20 mg plus hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg qd) for the last year and hypercholesterolemia, for which she was receiving atorvastatin (20 mg qd) for the last 7 months. She also reported cardiac arrhythmia managed with a non-selective competitive beta-adrenergic receptor blocker I (class III antiarythmic, sotalol hydrochloride 80 mg tabs qd) for the last 2 years. A recent complete blood cell count showed mild anemia and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Clinically, a diffuse, firm, non-tender on palpation swelling was noticed across the sublingual folds bilaterally, more prominently on the left side [Figure 1]. Saliva production from all major salivary glands and unstimulated whole saliva flow rate at 5 min were within normal limits. The remaining of the oral mucosa was also normal, no dental pathology in the lower teeth was identified and no cervical lymphadenopathy was noted. The differential diagnosis included chronic sialadenitis, salivary gland neoplasms, granulomatous disorders (e.g., sarcoidosis), Sjogren's syndrome (although the salivary flow rate was normal) and deposition diseases, such as amyloidosis.
3 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Page 3 of 9 Figure 1. Diffuse, firm, palpable swelling across the sublingual folds bilaterally, more prominently on the left A B Figure 2. Occlusal (A) and panoramic (B) radiographs did not reveal any pathologic findings Occlusal and panoramic radiographs were non-contributory [Figure 2], while a new US and magnetic resonance imaging [Figure 3] of the sublingual/submandibular region did not reveal any evidence of a spaceoccupying or other lesion. An incisional biopsy of the left sublingual gland swelling was performed under topical anesthesia. Histopathologic examination revealed a dense diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of the salivary gland parenchyma with prominent lymphoid follicle formation and preservation of lobular architecture, extensive acinar degeneration, ductal dilation and dense interlobular fibrosis [Figure 4]. Although several serial sections were examined, no signs of sialolith (as a possible cause of obstructive sialadenitis) were noted. Further, the lymphoid cells did not demonstrate atypia and immunohistochemical investigation revealed a polyclonal
4 Page 4 of 9 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Figure 3. Magnetic resonance imaging did not reveal evidence of a space occupying or other lesion in the sublingual-submandibular area Figure 4. Photomicrograph of sublingual gland biopsy showing diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with acinar degeneration, dense fibrosis and ductal dilation in the absence of sialolith formation (HE, 200 ) lymphoplasmacytic population, ruling out a lymphoproliferative disorder. Moreover, lymphoepithelial lesions (suggestive of Sjögren s syndrome) were absent. Based on the clinical and microscopic findings, a provisional diagnosis of CSS was rendered. To exclude the possibility of an IgG4-related disease, further immunohistochemical studies were performed, showing only a few scattered IgG4 positive plasma cells with a low IgG4/IgG ratio. In addition, serological examination, including IgG subtypes, was normal with the exception of an elevated IgG2 level [Table 1]. The post-operative course was uneventful with complete resolution of symptoms and a significant decrease of the swelling within 2 weeks. The residual swelling was spontaneously resolved in the course of the next few weeks. During regular follow up examination for the next 2 years, no signs of recurrences were noticed; only a minimal asymptomatic firmness was palpable along the left sublingual fold, possibly due to scar tissue from the previous biopsy procedure. DISCUSSION CSS usually affects middle aged or elderly patients with a slight male predominance[8-10]. Clinically, it may present as a unilateral or rarely bilateral, asymptomatic or mildly painful, firm swelling of the involved salivary gland[2,3,5]. Salivary flow rate is usually normal or slightly decreased[8]. CSS typically affects the submandibular gland; however, involvement of the parotid, the sublingual gland and the minor salivary glands has also been reported[3,11,12]. To the best of our knowledge, CSS affecting the sublingual gland is exceedingly rare[12].
5 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Page 5 of 9 Table 1. Results of serological examination Test Results Normal rates ANA Negative Negative < 1/40 Anti-Ro, anti-la Negative Negative < 0.8 RF 12 IU/mL 0-30 IU/mL CRP 1.8 mg/l < 5 mg/l IgA 250 mg/dl mg/dl IgM 161 mg/dl mg/dl IgG 1450 mg/dl mg/dl IgG1 805 mg/dl mg/dl IgG2 549 mg/dl mg/dl IgG mg/dl mg/dl IgG mg/dl mg/dl Histopathologically, the lesions of CSS, similar to our case, show marked lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with formation of reactive lymphoid follicles, extensive fibrosis, ductal dilatation, acinar degeneration and, in some cases, obliterative phlebitis [8,13]. Seifert and Donath [14] in 1977 proposed four histological stages of progressive inflammation in CSS. At the initial stage, lymphocytic infiltration around dilated ducts containing inspissated material is observed. Stage 2 is characterized by an increased lymphocytic infiltration with formation of lymphoid follicles, interstitial fibrosis, acinar atrophy and inspissated secretions in the ductal system, while ductal epithelium may show focal metaplasia with proliferation. At stage 3, the lymphocytic infiltration is even more intense, accompanied by lymphoid follicle formation, parenchymal atrophy, periductal hyalinization and sclerosis, while ductal epithelium metaplasia may also be present. At the last stage, inflammation leads to the destruction of the gland with parenchymal loss and sclerosis [14]. The microscopic findings of our case were more consistent with stage 2. The histopathologic differential diagnosis of CSS includes mainly Sjӧgren s syndrome and malignant lymphomas. Features such as presence of dense fibrosis, absence of lymphoepithelial lesions and infiltration by abundant plasma cells help distinguish CSS from Sjӧgren s syndrome [8]. CSS must also be differentiated from malignant lymphomas, especially non-hodgkin B-cell lymphomas, which, albeit rare, represent the most common type of lymphoma affecting the salivary glands. In contrast to lymphomas, cellular atypia in CSS is absent and B-cell polyclonality is revealed immunohistochemically, as shown in our case. On the other hand, a rare case of extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type arising on the grounds of CSS has been described and, as such, regular follow-up until complete resolution of CSS may be indicated [15]. The pathogenesis of CSS remains obscure. Initially, sialoliths were considered the most likely etiologic factor; it has been reported that, approximately 29% up to 83% of CSS cases, are related to the presence of sialoliths [4,10,11]. In cases of chronic obstructive sialadenitis, the microscopic appearance is characterized by mild interlobular fibrosis with lack of the characteristic lymphoid follicle formation and intense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration [7,8]. However, it remains unclear whether the development of sialoliths is the cause or the result of the inflammatory process [4,11]. In addition, in 70% of cases in which a sialolith was present, surgical excision did not result in resolution of the swelling [3]. Moreover, the progressive character of the inflammation observed in CSS, cannot be explained solely by the obstructive process [5]. Hence, it appears more likely that sialolithiasis is a secondary process to sialadenitis that may not be implicated in the pathogenesis of CSS [11,16]. Although our patient was treated with a thiazide diuretic drug that may cause decreased salivary flow and dehydration predisposing to chronic obstructive sialadenitis, serial histopathologic sections did not reveal any findings suggestive of either inspissated material or sialolith formation. Further, normal salivary flow rate from all major salivary glands was noted.
6 Page 6 of 9 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Table 2. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disorder (modified from Okazaki and Umehara [13], 2012) Criteria 1. Clinical examination shows characteristic diffuse/localized swelling or masses in single or multiple organs 2. Hematological examination shows elevated serum IgG4 concentrations ( 135mg/dL) 3. Histopathologic examination shows: (1) marked lymphocyte and plasmacyte infiltration and fibrosis; (2) infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells: ratio of IgG4/IgG positive plasma cells > 40% and > 10 IgG4-positive plasma cells/hpf Definite: Probable: Possible: Other authors suggest that in patients with CSS (or Ku ttner s tumor), a possible underlying secretory disorder of the affected gland may lead to the presence of inspissated saliva in the small ducts and subsequent chronic inflammation. This type of inflammation is called obstructive electrolyte sialadenitis [5,7,17]. In our patient, although sialectasia was present, no inspissated material was observed histopathologically in the ductal system, while unstimulated whole saliva rate was normal. On the other hand, the histopathological appearance of CSS lesions characterized by the presence of dense lymphocytic infiltration with lymphoid follicle formation and destruction of the gland, suggests that immunopathological reactions may be responsible for CSS [5]. Kitagawa et al. [7] in 2005 gave a new insight into the pathogenesis of CSS suggesting that it belongs to the IgG4- related disease (IgG4-RD) spectrum, a recently recognized systemic disease with multi-organ involvement. IgG4-RD is a distinct condition characterized by diffuse enlargement or nodular/hyperplastic lesions of the involved organs, due to a prominent infiltration by lymphocytes and abundant IgG4-positive plasma cells, accompanied by a variable degree of fibrosis. Increased serum IgG4 levels and a good responsiveness to corticosteroids are also observed. Patients with IgG4-RD may have, either simultaneously or subsequently, multi-organ lesions or only single organ involvement [7,13]. This entity came into light first by Hamano et al. [18] in 2001, who reported that the high serum concentrations of IgG4 in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis were reduced effectively with corticosteroid treatment, resulting in clinical remission. In Table 2, the diagnostic criteria proposed by Okazaki and Umehara [13] in 2012 for IgG4-RD have been summarized. The systemic nature of IgG4-RD was revealed by later studies that reported the involvement of numerous organs, including the lacrimal/salivary glands, thyroid gland, bile ducts, lung, kidney, retroperitoneum, central nervous system, liver, lymph nodes, prostate gland, skin and arteries. In Table 3, the IgG4-related disease spectrum is summarized [13]. As a result, over the last decade, the spectrum of IgG4-RD has been broadened comprising a variety of previously described diseases that seemed to be unrelated, such as Mikulicz s disease (MD), Ku ttner s tumor, autoimmune pancreatitis, inflammatory pseudotumor of the orbit, retroperitoneal fibrosis, Riedel thyroiditis and a subtype of Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT) [19,20]. MD, formerly considered to be a part of Sjӧgren s syndrome (SS) clinical spectrum, is characterized by the persistent symmetrical swelling of at least two lacrimal and major salivary glands for more than three months [8]. Recent studies have revealed that SS and MD are two distinct entities, the latter exhibiting the characteristic features of IgG4-RD [17,21]. In addition, Ku ttner s tumor and MD both show salivary gland involvement with similar histopathological features, but CSS lesions exhibit more intense fibrosis [8,19]. In contrast, other authors suggest that CSS and MD may actually represent two variants of IgG4-associated sialadenitis [8]. Although IgG4-RD is a well recognized disease, its pathogenesis and the role of IgG4 remain unclear. Autoimmunity has been speculated as the most probable pathogenetic mechanism. Lactoferrin and carbonic anhydrase, expressed in exocrine organs such as salivary gland and pancreas are considered potential autoantigens. Although autoantibodies against these antigens are the most often detectable ones in the serum of IgG4-RD patients, autoantibodies against the IgG4 molecule have not been detected [19,22]. It still remains
7 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Page 7 of 9 Table 3. IgG4-related disease spectrum (modified from Okazaki and Umehara [13], 2012) Spectrum Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1 (AIP) IgG4-related dacryoadenitis IgG4-related sialadenitis IgG4-related sclerosing cholangiitis IgG4-related kidney disease IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis IgG4-related thyroiditis IgG4-related lypmhadenopathy IgG4-related pulmonary disease IgG4-related prostatitis IgG4-related gastrointestinal disease IgG4-related skin disease IgG4-related aortitis IgG4-related pachymeningitis IgG4-related hypophysitis unclear whether IgG4 is implicated directly or is just a bystander in the course of pathogenesis of IgG4-RD, during which an unknown primary inflammatory process leads to a secondary IgG4 over expression [22,23]. Recent studies have shown that IgG4-RD is characterized by the predominant activation of T-helper type 2 (Th2) and regulatory T-lymphocytes (Treg cells) [19,22-24]. The Th2 cells produce interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL- 13,while Treg cells produce IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) [19,22]. IL-10 has the ability to direct B cells to produce IgG4 and, as a result, to induce an IgG4 class switch, while TGF-β induces fibroplasias [19,22-24]. At present, there is an increasing evidence that CSS is an IgG4-RD [8,9,19]. Although our case did not meet the serological and histopathological diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease, as proposed by Okazaki and Umehara [13] in 2012 [Table 2], a rare case of IgG4-RD-like multi-organ condition with involvement of the salivary glands, absence of IgG4 plasma cell infiltration and normal serum IgG4 levels has been reported recently by Hara et al. [23] in The authors hypothesized that a possible abnormality of the IL-10 signaling might have not allowed the IgG4 class switch. Another aspect of IgG4-RD that has attracted a strong attention recently is the relationship between IgG4 and malignancy. Sporadic cases of tumors occurring in a background of IgG4-RD have been reported. Ito et al. [25] in 2011 described a case of thyroid papillary carcinoma accompanied by HT in a patient with IgG4-RD disease that involved the salivary glands, the pancreas and the biliary tract. They also reported that IgG4 positive plasma cells and fibrosis surrounded solid tumor nests, both at the primary tumor site and the metastatic lymph nodes [25,26]. As mentioned before, a subtype of HT is considered to be IgG4-related [20]. Moreover, HT is considered a risk factor for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Taşli et al. [27] in 2014 investigated the possible role of IgG4 in the relationship between these two entities and reported an increased papillary carcinoma prevalence in IgG4 positive HT cases, compared to the IgG4 negative ones, suggesting that IgG4 plasma cells may be implicated in carcinogenesis [27]. Interestingly, our patient had a history of thyroidectomy due to a papillary thyroid carcinoma on the grounds of HT 3 years before the diagnosis of CSS, although the relationship between IgG4 positive levels and the underlying thyroiditis had not been investigated. Concerning the treatment of CSS, there is a lack of specific protocols in the literature. However, the treatment options that have been reported so far vary between conservative to more aggressive. In cases of CSS due to sialolithiasis, surgery is the treatment of choice [2]. Spontaneous regression of the lesions in the absence of sialolithiasis has also been reported [3]. Since an IgG4-related process has been considered to be implicated in the CSS pathogenesis and a favorable response to corticosteroid treatment has been observed in IgG4-RD cases, this treatment option has also been applied with good results [23,28-30].
8 Page 8 of 9 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I In conclusion, CCS is an under-recognized benign salivary gland disorder of unknown etiology that may represent, at least in some cases, an IgG4-associated disease [30,31]. In this regard, immunohistochemical evaluation of the IgG4/IgG positive plasma cell ratio and the IgG4 serum levels should be performed in all cases although histopathologic examination remains the main diagnostic procedure [32]. Although our case did not meet the immunohistochemical and serological diagnostic criteria of IgG4-related sialadenitis, a rare case of IgG4-RD-like lesions with normal serum and scanty IgG4 tissue positivity has been described. Additionally, no sialoliths were observed nor any other cause could be identified. Therefore, long term follow-up in all CSS cases, even in the absence of typical IgG4-RD features, is recommended. DECLARATIONS Acknowledgments The authors would like to thank Dr. Dimitra Rondogianni, Head, Department of Pathology, Evaggelismos General Hospital, Athens, for her expert opinion. Authors contributions Case report concepts: Nikitakis NG, Sklavounou A Diagnosis and management: Nikitakis NG, Daskalopoulos A Quality control of data: Piperi E, Sklavounou A Data analysis and interpretation: Thomopoulos F, Nikitakis NG, Piperi E, Sklavounou A Literature review: Thomopoulos F, Daskalopoulos A, Kolomvos N Manuscript preparation: Thomopoulos F, Nikitakis NG, Daskalopoulos A, Piperi E Manuscript editing: Nikitakis NG, Daskalopoulos A, Piperi E, Kolomvos N Availability of data and materials Not applicable. Financial support and sponsorship None. Conflicts of interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this study. Ethical approval and consent to participate The patient's consent was provided to us. The study was approved by the Review Board of the affiliated University while no ethical issues were considered during the study. Consent for publication Not applicable. Copyright The Author(s) REFERENCES 1. Ku ttner H. U ber entzu ndliche tumoren der submaxillar-speicheldru se. Bruns Beitr Klin Chir 1896;15: (in German) 2. Pandarakalam C, Goebel WM, Seyer B. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis or Ku ttner s tumor associated with a giant sialolith: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2013;115:e Williams HK, Connor R, Edmondson H. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the submandibular and parotid glands: a report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2000;89: de Vicente JC, López-Arranz E, García J, López-Arranz JS. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med
9 Thomopoulos et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:8 I Page 9 of 9 Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2003;96: Tiemann M, Teymoortash A, Schrader C, Werner JA, Parwaresch R, Seifert G, Klöppel G. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the submandibular gland is mainly due to a T lymphocyte immune reaction. Mod Pathol 2002;15: Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders, Elsevier; p Kitagawa S, Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Sato Y, Minato H, Watanabe K, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Masuda S, Niwa H, Tsuneyama K, Saito K, Haratake J, Takagawa K, Nakanuma Y. Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration characterizes chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Ku ttner s tumor). Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29: Geyer JT, Deshpande V. IgG4-associated sialadenitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23: Laco J, Ryska A, Celakovsky P, Dolezalova H, Mottl R, Tucek L. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis as one of the immunoglobulin G4- related diseases: a clinicopathological study of six cases from Central Europe. Histopathol 2011;58: Ellis GL. Lymphoid lesions of salivary glands: malignant and benign. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2007;12:E Blanco M, Mesko T, Cura M, Cabello-Inchausti B. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Ku ttner s tumor): unusual presentation with bilateral involvement of major and minor salivary glands. Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7: Flaitz CM. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis of the sublingual gland. Am J Dent 2001;14: Okazaki K, Umehara H. Are classification criteria for IgG4-RD now possible? The concept of IgG4-related disease and proposal of comprehensive diagnostic criteria in Japan. Int J Rheumatol 2012;2012: Seifert G, Donath K. On the pathogenesis of the Ku ttner tumor of the submandibular gland. Analysis of 349 cases with chronic sialadenitis of the submandibular. HNO 1977;25: Ochoa ER, Harris NL, Pilch BZ. Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the salivary gland arising in chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Ku ttner tumor). Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25: Harrison JD, Epivatianos A. Immunoprofile of Küttner tumor (chronic sclerosing sialadenitis). Int J Surg Pathol 2010;18: Takano K, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Himi T. Clinicopathologic similarities between Mikulicz disease and Ku ttner tumor. Am J Otolaryngol 2010;31: Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, Kiyosawa K. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2001;344: Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Sumida T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y, Tsubota K, Yoshino T, Kawa S, Suzuki R, Takegami T, Tomosugi N, Kurose N, Ishigaki Y, Azumi A, Kojima M, Nakamura S, Inoue D. Research Program for Intractable Disease by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) Japan G4 team. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol 2012;22: Kakudo K1, Li Y, Hirokawa M, Ozaki T. Diagnosis of Hashimoto s thyroiditis and IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Pathol Int 2011;61: Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Shinomura Y, Imai K. A new conceptualization for Mikulicz s disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol 2006;16: Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23: Hara S, Kawano M, Mizushima I, Yamada K, Fujita K, Matsumura M, Yamagishi M, Sato Y, Yamaguchi Y, Nakanuma Y, Nagata M. A condition closely mimicking IgG4-related disease despite the absence of serum IgG4 elevation and IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration. Mod Rheumatol 2014;2: Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake K, Hayashida JN, Maehara T, Shinozaki S, Kubo Y, Nakamura S. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64: Ito M, Naruke Y, Mihara Y, So K, Miyashita T, Origuchi T, Nakashima M, Livolsi V. Thyroid papillary carcinoma with solid sclerosing change in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Pathol Int 2011;61: Gill J, Angelo N, Yeong ML, McIvor N. Salivary duct carcinoma arising in IgG4-related autoimmune disease of the parotid gland. Hum Pathol 2009;40: Taşli F, Ozkök G, Argon A, Ersöz D, Yağci A, Uslu A, Erkan N, Salman T, Vardar E. The role of IgG4 (+) plasma cells in the association of Hashimoto s thyroiditis with papillary carcinoma. APMIS 2014;122: Abe T, Sato T, Tomaru Y, Sakata Y, Kokabu S, Hori N, Kobayashi A, Yoda T. Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing sialadenitis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2009;108: Doe K, Nozawa K, Okada T, Tada K, Yamaji K, Tamura N, Takasaki Y. Usefulness of minor salivary gland biopsy in the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7: Gallo A, Martellucci S, Fusconi M, Pagliuca G, Greco A, De Virgilio A, de Vincentiis M. Sialendoscopic management of autoimmune sialadenitis: a review of literature. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2017;37: Putra J, Ornstein DL. Ku ttner tumor: IgG4-related disease of the submandibular gland. Head Neck Pathol 2016;10: Witte T, Schulze-Koops H. IgG4-related sialadenitis: IgG4 is helpful, but biopsies are still crucial. Arthritis Res Ther 2015;17:368.
Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular Glands and Extraocular Muscles
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc. Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz
 Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci
 CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
IgG4-related sclerosing disease
 IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin G4-related Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Sjögren s Syndrome
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
IgG4 Disease. General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman
 IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
Case Report Usefulness of minor salivary gland biopsy in the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(5):2673-2677 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000175 Case Report Usefulness of minor salivary gland biopsy in the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease: a case report Kentaro
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(5):2673-2677 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000175 Case Report Usefulness of minor salivary gland biopsy in the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease: a case report Kentaro
Key words: diagnosis, immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin G4-related diseases, immunohistochemistry, pseudolymphoma. CASE HISTORY
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
Renal Pathology Case Conference. Case 2
 Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease
 International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
Overview of the Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Spectrum
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Chronic Sclerosing Sialadenitis (Küttner s tumour) of the Parotid Gland
 Case Report Chronic Sclerosing Sialadenitis (Küttner s tumour) of the Parotid Gland Güçlü Kaan Beriat 1, Sefik Halit Akmansu 1, Sinan Kocatürk 1, Ömür Ataoğlu 2 Submitted: 4 Dec 2009 Accepted: 18 Mar 2010
Case Report Chronic Sclerosing Sialadenitis (Küttner s tumour) of the Parotid Gland Güçlü Kaan Beriat 1, Sefik Halit Akmansu 1, Sinan Kocatürk 1, Ömür Ataoğlu 2 Submitted: 4 Dec 2009 Accepted: 18 Mar 2010
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis
 Ohta et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:67 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0459-z WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related
Ohta et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:67 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0459-z WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator
 Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
IgG4 ᛶ ᝈ䛸 ᶫᮏ ᕫච ᛶ ⅖ ḷᒣ Ꮫ య Ꮫ ぬ㐨
 IgG4 Autoimmune pancreatitis Histopathological features: Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration Stromal fibrosis Acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis 1. Hamano et al reported that serum IgG4 levels were
IgG4 Autoimmune pancreatitis Histopathological features: Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration Stromal fibrosis Acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis 1. Hamano et al reported that serum IgG4 levels were
Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis
 Li et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2015) 17:186 DOI 10.1186/s13075-015-0698-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis Wei Li 1, Yan
Li et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2015) 17:186 DOI 10.1186/s13075-015-0698-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis Wei Li 1, Yan
Salivary Glands. The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major
 Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis of Other Etiology
 94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
Sialadenitis without Stones. Case. University of California, San Francisco 11/6/2014
 Andrew H. Murr, MD Professor and Chairman Roger Boles, MD Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education Department of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery Sialadenitis without Stones: RAI, Autoimmune, and
Andrew H. Murr, MD Professor and Chairman Roger Boles, MD Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education Department of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery Sialadenitis without Stones: RAI, Autoimmune, and
Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy
 Sakai and Imamura Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:3 DOI 10.1186/s13000-017-0681-9 CASE REPORT Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy Yasuhiro Sakai 1,2*
Sakai and Imamura Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:3 DOI 10.1186/s13000-017-0681-9 CASE REPORT Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy Yasuhiro Sakai 1,2*
Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP Sun Young Choi 1, Sanghui Park 2
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report
 Zhang et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:44 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0041-6 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report Hui Zhang
Zhang et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:44 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0041-6 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report Hui Zhang
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease
 Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis
 Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
A case of mantle cell lymphoma presenting as IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz sdisease
 Hayashi et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:225 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0644-0 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of mantle cell lymphoma presenting as IgG4-related
Hayashi et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:225 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0644-0 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of mantle cell lymphoma presenting as IgG4-related
Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal
 CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES. Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation
 ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Churg-Strauss Syndrome Concomitant with Chronic Symmetrical Dacryoadenitis Suggesting Mikulicz s Disease
 CASE REPORT Churg-Strauss Syndrome Concomitant with Chronic Symmetrical Dacryoadenitis Suggesting Mikulicz s Disease Yusuke Hanioka 1, Keiko Yamagami 1, Katsunobu Yoshioka 2, Tomomi Nakamura 1, Masatsugu
CASE REPORT Churg-Strauss Syndrome Concomitant with Chronic Symmetrical Dacryoadenitis Suggesting Mikulicz s Disease Yusuke Hanioka 1, Keiko Yamagami 1, Katsunobu Yoshioka 2, Tomomi Nakamura 1, Masatsugu
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):2560-2568 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1309012 Case Report Occurrence of anaplastic large cell lymphoma following IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis and cholecystitis
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):2560-2568 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1309012 Case Report Occurrence of anaplastic large cell lymphoma following IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis and cholecystitis
A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details
 Modern Rheumatology ISSN: 1439-7595 (Print) 1439-7609 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/imor20 A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details
Modern Rheumatology ISSN: 1439-7595 (Print) 1439-7609 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/imor20 A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details
Case Report Concomitant occurrence of IgG4-related pleuritis and periaortitis: a case report with review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(2):808-814 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1312050 Case Report Concomitant occurrence of IgG4-related pleuritis and periaortitis: a case report with review of the literature
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(2):808-814 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1312050 Case Report Concomitant occurrence of IgG4-related pleuritis and periaortitis: a case report with review of the literature
Kazuichi Okazaki 1 and Hisanori Umehara Introduction. 2. The Concept of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
How 5 Diseases Became One. Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University
 How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details
 Mod Rheumatol (2012) 22:1 14 DOI 10.1007/s10165-011-0508-6 REVIEW ARTICLE A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details Hisanori Umehara Kazuichi Okazaki Yasufumi
Mod Rheumatol (2012) 22:1 14 DOI 10.1007/s10165-011-0508-6 REVIEW ARTICLE A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details Hisanori Umehara Kazuichi Okazaki Yasufumi
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Department of Radiology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;79(5):276-281 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.5.276 Sequential CT Findings in Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease:
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;79(5):276-281 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.5.276 Sequential CT Findings in Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease:
Thyroiditis in the differential diagnosis of lymphoma
 Thyroiditis in the differential diagnosis of lymphoma 2nd Pannonia Congress of Pathology Siofok, Hungary, May 17-19, 2012 Božo Krušlin, M.D., Ph.D., Dpt of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of
Thyroiditis in the differential diagnosis of lymphoma 2nd Pannonia Congress of Pathology Siofok, Hungary, May 17-19, 2012 Božo Krušlin, M.D., Ph.D., Dpt of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of
Clinical Study Is IgG4-Related Disease a Cause of Xerostomia? A Cohort Study of 60 Patients
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 303506, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/303506 Clinical Study Is IgG4-Related Disease a Cause of Xerostomia? A Cohort Study of 60 Patients M. Hermet, 1 M. André,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 303506, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/303506 Clinical Study Is IgG4-Related Disease a Cause of Xerostomia? A Cohort Study of 60 Patients M. Hermet, 1 M. André,
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore
 IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with
 A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease 1)*, Yasuharu Sato 1) 2)*, Koh-ichi Ohshima 3), Katsuyoshi Takata 1), Tomoko Miyata-Takata 1), Mai
A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease 1)*, Yasuharu Sato 1) 2)*, Koh-ichi Ohshima 3), Katsuyoshi Takata 1), Tomoko Miyata-Takata 1), Mai
Original Article CT features and pathologic characteristics of IgG4-related systemic disease of submandibular gland
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(12):16111-16116 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014889 Original Article CT features and pathologic characteristics of IgG4-related systemic disease of submandibular gland
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(12):16111-16116 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014889 Original Article CT features and pathologic characteristics of IgG4-related systemic disease of submandibular gland
Objectives. Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System. Role of Salivary Gland FNA 04/26/2018
 Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Nozomu Kurose. Key Words: IgG4-related disease, comprehensive diagnostic criteria, fibrosis grade, IL-6. J Kanazawa Med Univ , 2016
 J Kanazawa Med Univ 41 76 85, 2016 Clinicopathological Analysis between IgG4-related and Non-IgG4-related Diseases Occurring in Various Organs and Tissues: Re-evaluation of Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria
J Kanazawa Med Univ 41 76 85, 2016 Clinicopathological Analysis between IgG4-related and Non-IgG4-related Diseases Occurring in Various Organs and Tissues: Re-evaluation of Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria
An Unexpected Cause of Hypoglycemia
 An Unexpected Cause of Hypoglycemia Stacey A. Milan, MD FACS Surgical Oncology Nothing to disclose Disclosures Objectives Identify indications for workup of hypoglycemia Define work up for hypoglycemic
An Unexpected Cause of Hypoglycemia Stacey A. Milan, MD FACS Surgical Oncology Nothing to disclose Disclosures Objectives Identify indications for workup of hypoglycemia Define work up for hypoglycemic
IgG4-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients
 IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease
 CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy
 Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders. Raymond P. Wood. History
 Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
IgG4-related disease and its pathogenesis cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity
 International Immunology, Vol. 26, No. 11, pp. 585 595 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu074 Advance Access publication 14 July 2014 The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese
International Immunology, Vol. 26, No. 11, pp. 585 595 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu074 Advance Access publication 14 July 2014 The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese
INFECTION. HIV Infection DWI
 HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis
 J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease: Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Extrapancreatic
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma Yasuko Oshima 1, Ryosuke Usui 1, Shun Manabe 1, Naoki Hasegawa 2, Yukio Kakuta 2, Kosaku Nitta
CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma Yasuko Oshima 1, Ryosuke Usui 1, Shun Manabe 1, Naoki Hasegawa 2, Yukio Kakuta 2, Kosaku Nitta
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus
 Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Diagnostic dilemma of IgG4-related primary localized cervical lymphadenopathy associated with aberrant IL-6 expression level
 Nakamura et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2016) 11:43 DOI 10.1186/s13000-016-0493-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Diagnostic dilemma of IgG4-related primary localized cervical lymphadenopathy associated with aberrant
Nakamura et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2016) 11:43 DOI 10.1186/s13000-016-0493-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Diagnostic dilemma of IgG4-related primary localized cervical lymphadenopathy associated with aberrant
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone Phenomenon in Patients With IgG4-Related Disease
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
155.2 Malignant neoplasm of liver not specified as primary or secondary. C22.9 Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary
 ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
 Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Papule in the Right Floor of the Mouth
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Papule in the Right Floor of the Mouth Course Author(s): H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Anne Cale Jones, DDS; Michaell A. Huber, DDS; Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-070
Continuing Education Brought to you by Papule in the Right Floor of the Mouth Course Author(s): H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Anne Cale Jones, DDS; Michaell A. Huber, DDS; Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-070
IgG4-related lung disease showing high standardized uptake values on FDG-PET: report of two cases
 Kitada et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery 2013, 8:160 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related lung disease showing high standardized uptake values on FDG-PET: report of two cases Masahiro Kitada 1,3*,
Kitada et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery 2013, 8:160 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related lung disease showing high standardized uptake values on FDG-PET: report of two cases Masahiro Kitada 1,3*,
Received for Publication: August 7, 2006
 447 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 34, pp. 447 453, 2006 Analysis of Interleukin 2 Receptor IL-2R and Type III Procollagen-N-peptide P-III-P in a Case of Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Haruyuki Takama
447 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 34, pp. 447 453, 2006 Analysis of Interleukin 2 Receptor IL-2R and Type III Procollagen-N-peptide P-III-P in a Case of Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Haruyuki Takama
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Case Reports in Clinical Pathology, 2015, Vol. 2, No. 1
 CASE REPORT A case of IgG4-related interstitial lung disease showing usual interstitial pneumonia pattern: Unusual case for histological features with pathological proof Seidai Sato 1, Masaki Hanibuchi
CASE REPORT A case of IgG4-related interstitial lung disease showing usual interstitial pneumonia pattern: Unusual case for histological features with pathological proof Seidai Sato 1, Masaki Hanibuchi
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS. Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3
 PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion and Thrombophlebitis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features
 gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features Poster No.: C-2603 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Kawamura, Y. Kikuchi, I.
gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features Poster No.: C-2603 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Kawamura, Y. Kikuchi, I.
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms
 My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
A case of Epstein Barr virus-related lymphadenopathy mimicking the clinical features of IgG4-related disease
 Mod Rheumatol (2013) 23:597 603 DOI 10.1007/s10165-012-0695-9 CASE REPORT A case of Epstein Barr virus-related lymphadenopathy mimicking the clinical features of IgG4-related disease Yoko Wada Masaru Kojima
Mod Rheumatol (2013) 23:597 603 DOI 10.1007/s10165-012-0695-9 CASE REPORT A case of Epstein Barr virus-related lymphadenopathy mimicking the clinical features of IgG4-related disease Yoko Wada Masaru Kojima
A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass
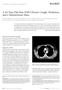 [ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
[ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7816-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Yoji Komiya 1, Makoto Soejima
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7816-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Yoji Komiya 1, Makoto Soejima
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology. Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016
 Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Case of the Day Chest
 Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
