D. T. Li and G. R. Her* Department of Chemistry, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
|
|
|
- Emily Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF MASS SPECTROMETRY J. Mass. Spectrom. 33, 644È652 (1998) Structural Analysis of Chromophore-labeled Disaccharides and Oligosaccharides by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry and High-performance Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry D. T. Li and G. R. Her* Department of Chemistry, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Disaccharides and linear oligosaccharides were labeled with p-aminobenzoic ethyl ester (ABEE) chromophore and analyzed by negative ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESIMS). The formation of glycosylamines rather than reductive amination in the labeling reaction produced many characteristic fragment ions under insource collision-induced dissociation (CID). These ions provided unambiguous assignment of the position of the glycosidic linkages. This approach was extended to the analysis of linkages and the sequence of the linkages of several linear oligosaccharides. Additionally, the anomeric conðguration of ABEE-labeled 1 3-, 1 4- and 1 6- linked glucose disaccharides could be di erentiated according to the relative abundance of characteristic ions. Disaccharides with the same linkage but di erent monosaccharide compositions could be analyzed by on-line coupling of high-performance liquid chromatography with ESIMS. ( 1998 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. KEYWORDS: disaccharides; chromophore; linkage; anomeric conðguration; high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry INTRODUCTION A considerable part of the biological functions of glycoproteins and glycolipids depends on their carbohydrate moiety; for example, cell-to-cell interactions, di erentiation of cells and metastasis are associated with the structure of oligosaccharides present on the cell surface. The structural elucidation of complex carbohydrates requires the determination of the sugar sequence, sugar branching, monosaccharide composition, interglycosidic linkages and anomeric conðguration. The most common method in linkage analysis is the permethylation procedure, where the saccharide is methylated at the free hydroxyl groups, total hydrolysis to monosaccharides is brought about, the carbonyl groups are reduced and Ðnally the hydroxyl groups liberated are derivatized. The mixture obtained is usually analyzed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS).1 This well standardized technique is, in * Correspondence to: G. R. Her, Department of Chemistry, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan grher=mail.ch.ntu.edu.tw Contract/grant sponsor: National Research Council of the Republic of China. general, time-consuming, labor extensive and requires larger sample amounts. Mass spectrometric techniques, especially the combination of soft ionization methods such as fast atom bombardment (FAB) with collision-induced dissociation (CID), have been used for linkage determination of underivatized oligosaccharides.2h9 Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) is another technique which has been reported to allow structural analysis of underivatized oligosaccharide. Garozzo et al.10 used negative-ion ESI-MS and in-source fragmentation to di erentiate the linkage position of reducing disaccharides. Traeger and co-workers11 extended the study of Garozzo et al. to anomeric isomer analysis using selected diagnostic peaks and their relative intensities. Fura and Leary12 used ESI-MS/MS to investigate the branching of Ca2`- and Mg2`-coordinated branched trisaccharides. From the CID spectrum of the intact cationized species, the branching point located on the reducing moiety of an oligosaccharide could be determined. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has been a fundamental technique for the separation and recovery for oligosaccharides.13 It has been recognized that MS may be used as a universal and sensitive detector for HPLC. On-line HPLC/MS and HPLC/ MS/MS have been implemented and shown great potential for the analysis of underivatized oligosac- CCC 1076È5174/98/070644È09 $17.50 Received 29 September 1997 ( 1998 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Accepted 5 March 1998
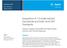
2 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CHROMOPHORE-LABELED SUGARS BY ESI-MS 645 charides, especially using ESI.14,15 Although MS may be powerful for oligosaccharide analysis following HPLC separation, it is common to Ðnd separation conditions with a UV detector prior to MS detection. However, the UV sensitivity for most sugars is generally poor because of the lack of a chromophore in oligosaccharide samples. To solve this problem, precolumn derivatization at the reducing end with UV-absorbing or Ñuorescent chromophores has received considerable attention.16h21 Reductive amination is the most popular labeling procedure. This procedure reduces the reducing sugar and an open-ring derivative is produced. In addition to the very popular reductive amination procedure, the formation of glycosylamine in labeling reactions has demonstrated its great potential in HPLC separations and in linkage analysis.22 Unlike in reductive amination, reducing sugars maintained a closed ring structure in the glycosylamine approach. Based on our previous study,22 closed-ring derivatives (glycosylamines) provided much more linkage information than open-ring products under FAB/CID conditions. In this study, disaccharides and linear oligosaccharides were derivatized using the glycosylamine approach and were studied by ESI-MS and HPLC/ESI-MS. The merits of this approach are discussed. EXPERIMENTAL Chemicals Table 1 lists the sugars analyzed in this study. Panose, sophorose and lactose were purchased from Tokyo Kasei (Tokyo Japan), Serva (Heidelberg, Germany) and Aldrich Chemical (Milwaukee, WI, USA), respectively. All other sugars were obtained from Sigma Chemical (St Louis, MO, USA). p-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester was purchased from Aldrich Chemical. Preparation of chromophore-labeled oligosaccharides Closed-ring (glycosylamine) derivatives were prepared. The procedure of Reinhold and co-workers16 was Table 1. List of sugars analyzed Sophorose Nigerose Laminaribiose Maltose Cellobiose Isomaltose Gentiobiose Melibiose Maltotriose Isomaltotriose Panose Maltopentaose Glcb1 2Glc Glca1 3Glc Glcb1 3Glc Mana1 3Man Glca1 4Glc Glcb1 4Glc Gala1 4Gal Galb1 4Man Glca1 6Glc Glcb1 6Glc Gala1 6Glc Glcaa 4Glca1 4Glc Glca1 6Glca1 6Glc Glca1 6Glca1 4Glc Glca1 (4Glca1) 4Glc 3 adopted for the preparation of ABEE derivatives. For ABEE glycosylamines, the sugars (up to 1 mg) were dissolved in 20 ll of water and 80 ll of reagent solution (prepared by dissolving 1 g of ABEE in 0.5 ml of methanol at 60 C) and reacted at 80 C for 6 h. The solution was washed with 2 ml of ethyl ester to remove the excess ABEE reagent before the HPLC separation. Instrumentation HPLC separation was performed with a system consisting of two Microtech pumps (Microtech ScientiÐc, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), a Rheodyne (Cotati, CA, USA) model 7725 injector with a 5 ll sample loop, and a Linear (Reno, NV, USA) UVIS 200 variable-wavelength detector. A Spherisorb 3-NH column (25 cm ] 2 mm i.d.) was used for the separation 2 of the chromophorelabeled disaccharide mixture. The Ñow rate on-column was 300 ll min~1 and this Ñow was split post-column. A splitting ratio of 1 : 1 delivered 150 ll min~1 into the electrospray ionization source. Before the mobile phase Ñowed into the ionization source, 2-propanolÈwater (1 : 1) containing 0.5% ammonia was added at a Ñow rate of 20 ll min~1 to increase the negative ion ESI sensitivity. Negative ion ESI mass spectra were collected on a Fisons Platform mass spectrometer (VG Bio Tech, Altrincham, UK). The potential of the capillary was set to 2.5 kv and the counter electrode was held at 0 V. The ion source temperature was set to 90 C. Insource CID mass spectra were acquired with the cone voltage set to a speciðed value. A mass range between m/z 150 and 550 was scanned and the scan time was set to 2 s. The absorbance at 254 nm was monitored as the remaining 150 ll min~1 eluent Ñowed through a UV cell. The amounts of sample used in HPLC/MS and CID analysis were D10 and 1 nmol, respectively. The analytical conditions for the separation are given in the Ðgure captions. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Linkage analysis of di- and linear oligosaccharides Disaccharides with di erent linkages were derivatized with ABEE and then studied by ESI-MS. Under insource CID condition, many fragment ions were observed. The most prominent fragments in the positive-ion mode mass spectra resulted from the cleavage of the glycosidic bond, which made the mass spectra very similar and therefore not useful for the di erentiation of linkages (data not shown). Unlike positive-ion spectra, the negative-ion mode yielded many characteristic fragment ions (Fig. 1). These fragments appeared to be cross-ring cleavage ions on reducing end monosaccharides. Disaccharide isomers can be seen as a monosaccharide with another monosaccharide as the substituent at di erent positions, and therefore crossring cleavage of the reducing monosaccharide is very helpful for the di erentiation of these isomers (Fig. 1). The characteristic fragment ions are listed in Table 2. Since the only di erence among the four disaccharides resided in the glycosidic linkage, the di erence observed
3 646 D. T. LI AND G. R. HER Figure 1. Negative-ion in-source CID ESI mass spectra of ABEE-labeled (a) sophorose, (b) laminaribiose, (c) cellobiose and (d) gentiobiose. in the negative-ion ESI mass spectra could be used to establish the linkage position in disaccharides. The FAB technique in combination with high-energy CID has been reported for the linkage determination of ABBE labeled disaccharides.22 Although the di erence in collision energies was signiðcant, the ESI mass spectra recorded at 30 V were in general similar to the FAB/ high-energy CID product ion spectra. A notable di erence was the m/z 281 ion in b-1è4- and b-1è6-linked disaccharides. Except at a lower cone voltage, the
4 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CHROMOPHORE-LABELED SUGARS BY ESI-MS 647 Table 2. SpeciÐc fragment ions for ABEE-labeled disaccharides (m/z) Glcb1 2Glc Glcb1 3Glc Glcb1 4Glc Glcb1 6Glc prominent ion at m/z 281 observed in FAB/CID was detected as a minor ion in 1È6- and 1È4-linked disaccharides (Fig. 1(c) and (d)). Fortunately, the m/z 281 ion was not critical for the determination of linkages. UV or Ñuorescence sensitivity has been the most important factor in the selection of labeling reagents. In recent years, attempts have been made not only to achieve sensitive UV or Ñuorescence detection but also improve the ionization efficiency in ESI analysis by labeling oligosaccharides with chromophores of high proton affinity or preformed ions.23h26 The reportedly successful derivative obtained by labeling with 4- aminobenzoic acid 2-(diethylamino) ether ester23 was not chosen in this study mainly because it was designed for positive ionization and the labeling product was not a closed-ring but an open-ring (reductive amination) derivative. Little information on linkages was obtainable from the ESI mass spectra. Several derivatives including PA (2-pyridinamine), ABEE and ABBE (p-aminobenzoic acid butyl ester) were labeled with glycosylamine and studied by negative-ion ESI. ABEE and ABBE had similar sensitivities which were D5È10 times more sensitive than Figure 2. Negative-ion in-source CID ESI mass spectra of ABEE-labeled (a) maltotriose, (b) isomaltotriose and (c) panose.
5 648 D. T. LI AND G. R. HER Figure 3. Negative-ion in-source CID ESI mass spectra of ABEE-labeled maltopentaose. underivatized disaccharides. The resolution of PA sugar was not as good as that of ABEE or ABBE. ABEE was chosen instead of ABBE in this study mainly because it provided better results on anomeric conðguration for some disaccharides. The linkage of disaccharides without precolumn derivatization could also be determined from the ESI mass spectrum.10,11 However, because of the lack of reducing end fragments, it is often not possible to analyze mixtures with more than one linkage by direct infusion analysis. For example, the characteristic ions for 1È2-, 1È3- and 1È4-linked disaccharides are at m/z 221, 263, 323; 221, 281; and 221, 263, 281, respectively;11 the observation of m/z 221, 263, 281 and 323 ions might represent one of the following three possible combinations: 1È2 ] 1È4, 1È2 ] 1È3 and 1È2 ] 1È3 ] 1È4. In contrast, every linkage-isomeric disaccharide had its speciðc ions (Table 2) in this approach, and therefore linkage positions in a mixture containing more than one linkage could be unambiguously assigned by direct infusion analysis. The study of several 1È4- and 1È6-linked linear oligosaccharides suggested that with the cone voltage set at a higher value, this approach could be extended to the analysis of linear oligosaccharides. The in-source CID mass spectra of trisaccharides with the cone voltage set to 40 V are shown in Fig. 2. The m/z 263 ion in Fig. 2(a) indicates that the non-reducing end is a 1È4-linkage; the ion at m/z 425 (162 u above the m/z 263 ion) and reducing end fragments at m/z 308 and 290 and suggest that the reducing end is also a 1È4-linkage. In Fig. 2(b), the presence of the m/z 251 ion indicates that the nonreducing end is a 1È6-linkage; the peak at m/z 413 (162 amu above the peak at m/z 251) and non-reducing end fragment at m/z 236 suggest that the reducing end linkage is also a 1È6-linkage. In Fig. 2(c), the presence of Figure 4. Skimmer cone voltage vs. ion ratio of m/z 221/248 in ABEE-labeled Glca1 4Glc and Glcb1 4Glc. Error bars represent three standard deviations (3s).
6 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CHROMOPHORE-LABELED SUGARS BY ESI-MS 649 Figure 5. Skimmer cone voltage vs. ion ratio of m/z 236/221 in ABEE-labeled Glca1 6Glc and Glcb1 6Glc. Error bars represent three standard deviations (3s). the ion at m/z 251 suggests a 1È6-linkage in the nonreducing end and the peaks at m/z 425, 308 and 290 indicate that the reducing end is a 1È4-linkage. This method was applicable to higher oligomers. The negative-ion ESI mass spectrum of ABEE-labeled maltopentaose with the cone voltage set to 75 V is shown in Fig. 3. The observation of 1È4-linked diagnostic ions at m/z 263, 425, 587 and 749 and reducing end fragments at m/z 308 and 290 suggested that the Ðve linkages in maltopentaose were all 1È4-linkages. Analysis of anomeric conðguration The determination of anomeric conðguration by a combination of chemical and MS methods has been reported by Khoo and Dell.27 The determination of anomeric conðguration by MS directly is limited, however, mainly because stereoisomers often give very similar mass spectra. Recently, Traeger and co-workers11 di erentiated anomeric conðgurations by the relative abun- Figure 6. Skimmer cone voltage vs. ion ratio of m/z 179/260 in ABEE-labeled Glca1 3Glc and Glcb1 3Glc. Error bars represent three standard deviations (3s).
7 650 D. T. LI AND G. R. HER Figure 7. (a) UV, (b) TIC and (c) reconstructed ion chromatograms of four ABEE-labeled disaccharides on an amino column with 5 15% water acetonitrile as eluent at 300 ml miné1 with a 60 min program. dance of selected ions in a negative-ion ESI mass spectrum. When we examined the relative abundance of fragment ions in the ESI mass spectra of ABEE-labeled disaccharides, it appeared that the relative abundances of some fragment ions were sensitive to the anomeric conðgurations. Figure 4 shows the proðles of skimmer cone voltage vs. ion ratio of m/z 221/248 for Glcb1È
8 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CHROMOPHORE-LABELED SUGARS BY ESI-MS 651 Figure 8. TIC chromatograms of the ABEE-labeled (a) Glca1 3Glc, Glcb1 3Glc and Mana1 3Man, (b) Glca1 4Glc, Gala1 4Gal, Glcb1 4Glc and Galb1 4Man and (c) Glca1 6Glc, Glcb1 6Glc and Gala1 6Glc mixtures. The HPLC conditions for (a) were the same as in Fig. 7 and for (b) and (c) the eluent was 5 15% water acetonitrile at 300 ml miné1 with a 120 min program. 4Glc and Glca1È4Glc. Variations in fragment ion abundance were observed; the variation within a week is represented by the 3p error bars. As can be seen, the anomeric conðguration of Glcb1È4Glc and Glca1È4Glc could be unambiguously assigned with the skimmer cone voltage set from 35 up to 75 V. For Glcb1È6Glc and Glca1È6Glc (Fig. 5), although the anomeric con- Ðguration might be determined at both high and low cone voltages, the di erence was more signiðcant at lower voltages. The 3p bars overlap at high voltage for Glcb1È3Glc and Glca1È3Glc (Fig. 6), and the anomeric conðguration was distinguishable only at low voltage. Owing to the lack of standards, 1È2-linked disaccharides were not studied. In comparison with the FAB/CID technique,22 the di erences in relative abundance between a- and b- anomers of 1È3- and 1È6-linked disaccharides were much clearer in negative-ion ESIMS. LC/MS of ABEE-labeled disaccharides In this study, glycosylamine rather than the popular reductive amination was adopted for labeling the
9 652 D. T. LI AND G. R. HER reducing end of di- and oligosaccharides with an ABEE UV tag. In addition to the fact that the negative-ion in-source CID mass spectrum of a closed-ring (glycosylamine) derivative was more characteristic than that of an open-ring (reductive amination) derivative, closed-ring (glycosylamine) derivatives were reported to show better chromatographic behavior than open-ring derivatives on an amine HPLC column.16,22 The separation of a mixture of four ABEE-labeled glucose disaccharides is shown in Fig. 7. Peaks 1, 2, 3 and 4 correspond to laminaribiose, cellobiose, sophorose and gentiobiose, respectively. Disaccharide derivatized with the glycosylamine approach resulted in two anomers,16 thus a total of eight peaks were observed. Figure 7(a) and (b) are the UV and total ion current chromatograms. In Fig. 7(c), ions at m/z 368, 260, 263 and 236, which represent 1È2-, 1È3-, 1È4- and 1È6- linked disaccharides, respectively, were selected for the reconstructed ion chromatogram. The linkages of these disaccharides can be unambiguously assigned. Complete structure information on disaccharide includes linkage, anomeric conðguration and monosaccharide composition. As discussed above, a direct MS analysis could be used to assign linkages unambiguously and also to provide the anomeric conðguration for 1È3-, 1È4- and 1È6-linked glucose disaccharides. Despite the fact that di erences in ion abundance with high reproducibility were observed for disaccharides with the same linkage, the same anomeric conðguration but di erent monosaccharide compositions, clear conclusions on monosaccharide composition could not be drawn because of the lack of disaccharide standards with all possible isomeric combinations (linkage, anomeric conðguration, monosaccharide composition). On-line coupling of HPLC with ESI-MS might provide a solution to this problem. HPLC was used to separate disaccharide isomers followed by MS detection. Disaccharides with the same linkage but di erent anomeric conðgurations and monosaccharide compositions could be resolved on an amine HPLC column. The total ion currents of 1È3-, 1È4- and 1È6-linked ABEE-labeled disaccharides are shown in Fig. 8(a), (b) and (c), respectively. The retention times and resolving power achievable with HPLC are helpful in the analysis of disaccharides. Disaccharide isomers can be identiðed by the combination of retention times and in-source CID mass spectra. CONCLUSION Closed-ring (glycosylamine) derivatization of reducing disaccharides and linear oligosaccharides was analyzed by negative-ion ESI-MS. In comparison with unlabeled disaccharides, a much clearer assignment can be made for the linkages of di- and linear oligosaccharide. The anomeric conðguration of 1È3-, 1È4- and 1È6-linked glucose disaccharides can be assigned based on the relative abundances of speciðc fragment ions. Although monosaccharide composition did play a role in the fragment ion abundance, no clear conclusion could be drawn because of the lack of standard samples. HPLC/ ESI-MS could be used for the di erentiation of disaccharides with the same linkage but di erent monosaccharide compositions. Acknowledgement This work was supported by the National Research Council of the Republic of China. REFERENCES 1. C. G. Hellerqvist, Methods Enzymol. 193, 554 (1990). 2. Z. Zhou, S. Ogden and J. A. Leary, J. Org. Chem. 55, 5444 (1990). 3. G. E. Hofmeister, Z. Zhou and J. A. Leary, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 5964 (1991). 4. D. Garozzo, M. Giffrida, G. Impallomeni, A. Ballistreri and G. Montaudo, Anal. Chem. 62, 279 (1990). 5. R. A. Laine, K. M. Pamidimukkala, A. D. French, R. W. Hall, S. A. Abbas, R. K. Jain and K. L. Matta, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 6931 (1988). 6. R. A. Laine, E. Yoon, T. J. Mahier, S. Abbas, B. de Lappe, R. Jain and K. Matta, Biol. Mass Spectrom. 20, 505 (1991). 7. B. Domon, D. R. Muller and W. J. Richter, Org. Mass Spectrom. 24, 357 (1989). 8. B. Domon, D. R. Muller and W. J. Richter, Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 19, 390 (1990). 9. J. W. Dallinga and W. Heerma, Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 20, 215 (1991). 10. D. Garozzo, G. Impallomeni and E. Spina, Carbohydr. Res. 221, 253 (1991). 11. B. Mulroney, J. C. Traeger and B. A. Stone, J. Mass Spectrom. 30, 127 (1995). 12. A. Fura and J. A. Leary, Anal. Chem. 65, 2805 (1993). 13. S. C. Churms, J. Chromatogr. 500, 555 (1990). 14. M. Kohler and A. J. Leary, Anal. Chem. 67, 3501 (1995). 15. K. L. Duffin, J. K. Welply, E. Huang and J. D. Henion, Anal. Chem. 64, 1440 (1992). 16. G. R. Her, S. Santikarn, V. N. Reinhold and J. C. Williams, J. Carbohydr. Chem. 6, 129 (1987). 17. S. Hase, S. Hara and Y. Matsushima, J. Biochem. 85, 217 (1979). 18. S. Hase, T. Ikenaka and Y. Matsushima, J. Biochem. 90, 407 (1981). 19. W. T. Wang, N. C. LeDonne, B. Ackerman and C. C. Sweeley, Anal. Biochem. 141, 366 (1984). 20. B. L. Gillece-Castro and A. L. Burlingame, in Biological Mass Spectrometry, edited by A. L. Burlingame and J. A. McClosekey, p. 411, Elsevier, Amsterdam (1990). 21. L. Poulter, R. Karrer and A. L. Burlingame, Anal. Biochem. 195, 1 (1991). 22. D. T. Li and G. R. Her, Anal. Biochem. 19, 250 (1993). 23. K. Yoshino, T. Takao, H. Murata and Y. Shimonishi, Anal. Chem. 67, 4028 (1995). 24. J. Gu, T. Hiraga and Y. Wada, Biol. Mass Spectrom. 23, 212 (1994). 25. M. Okamoto, K. Takahashi and T. Doi, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 9, 641 (1995). 26. S. Suzuki, K. Kakehi and S. Honda, Anal. Chem. 68, 2073 (1996). 27. K. H. Khoo and A. Dell, Glycobiology 1, 83 (1990).
One of the most prevalent post-translational
 Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Alkali Cationized Polysaccharides in a Quadrupole Ion Trap Michael R. Asam and Gary L. Glish Department of Chemistry, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill,
Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Alkali Cationized Polysaccharides in a Quadrupole Ion Trap Michael R. Asam and Gary L. Glish Department of Chemistry, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill,
Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents
 No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
Separation of 15 Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards
 Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)*
 ANALYSIS S e p a r a t i o n R e p o r t N o. 7 9 Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)* *Please refer to Separation
ANALYSIS S e p a r a t i o n R e p o r t N o. 7 9 Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)* *Please refer to Separation
Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System
 Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System Keywords Introduction Application Note PHA0413 High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System Keywords Introduction Application Note PHA0413 High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI
 Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI Kate Yu, Eric Block LC/MS Waters Corporation Introduction to polymer additive analysis by LC/MS. Electron Ionization (EI) Advantages Classical spectra Library searchable
Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI Kate Yu, Eric Block LC/MS Waters Corporation Introduction to polymer additive analysis by LC/MS. Electron Ionization (EI) Advantages Classical spectra Library searchable
Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis
 Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS
Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS
Glycosylation is a predominant post-translational modification
 B American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2012 J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. (2012) 23:1408Y1418 DOI: 10.1007/s13361-012-0420-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Linkage and Branch Analysis of High-Mannose Oligosaccharides
B American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2012 J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. (2012) 23:1408Y1418 DOI: 10.1007/s13361-012-0420-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Linkage and Branch Analysis of High-Mannose Oligosaccharides
Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas decomposition products of irradiated DMC.
 200000 C 2 CH 3 CH 3 DMC 180000 160000 140000 Intensity 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 C 2 H 6 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CCH 3 EMC DEC 20000 C 3 H 8 HCCH 3 5 10 15 20 25 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas
200000 C 2 CH 3 CH 3 DMC 180000 160000 140000 Intensity 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 C 2 H 6 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CCH 3 EMC DEC 20000 C 3 H 8 HCCH 3 5 10 15 20 25 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas
MS/MS as an LC Detector for the Screening of Drugs and Their Metabolites in Race Horse Urine
 Application Note: 346 MS/MS as an LC Detector for the Screening of Drugs and Their Metabolites in Race Horse Urine Gargi Choudhary and Diane Cho, Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA Wayne Skinner and
Application Note: 346 MS/MS as an LC Detector for the Screening of Drugs and Their Metabolites in Race Horse Urine Gargi Choudhary and Diane Cho, Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA Wayne Skinner and
Liquid Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry/Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry of Otigosaccharide Anions
 1582 Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1582-1587 Liquid Secondary on Mass Spectrometry/Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry of Otigosaccharide Anions James A. Carroll, Lambert Ngoka, Cindy G. Beggs, and Carlito B.
1582 Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1582-1587 Liquid Secondary on Mass Spectrometry/Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry of Otigosaccharide Anions James A. Carroll, Lambert Ngoka, Cindy G. Beggs, and Carlito B.
Structural analyses of carbohydrates and oligosaccharides
 A Comparative Study of the Fragmentation of Neutral Lactooligosaccharides in Negative- Ion Mode by UV-MALDI-TOF and UV- MALDI Ion-Trap/TOF Mass Spectrometry Tohru Yamagaki, Hiroaki Suzuki, and Kazuo Tachibana
A Comparative Study of the Fragmentation of Neutral Lactooligosaccharides in Negative- Ion Mode by UV-MALDI-TOF and UV- MALDI Ion-Trap/TOF Mass Spectrometry Tohru Yamagaki, Hiroaki Suzuki, and Kazuo Tachibana
UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes
 UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes Catalin E. Doneanu, Weibin Chen, and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F
UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes Catalin E. Doneanu, Weibin Chen, and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F
Essential Lipidomics Experiments using the LTQ Orbitrap Hybrid Mass Spectrometer
 Application Note: 367 Essential Lipidomics Experiments using the LTQ rbitrap Hybrid Mass Spectrometer Thomas Moehring 1, Michaela Scigelova 2, Christer S. Ejsing 3, Dominik Schwudke 3, Andrej Shevchenko
Application Note: 367 Essential Lipidomics Experiments using the LTQ rbitrap Hybrid Mass Spectrometer Thomas Moehring 1, Michaela Scigelova 2, Christer S. Ejsing 3, Dominik Schwudke 3, Andrej Shevchenko
Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS
 The Open Analytical Chemistry Journal, 2011, 5, 27-36 27 Open Access Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS Viorica Lopez-Avila * and George Yefchak
The Open Analytical Chemistry Journal, 2011, 5, 27-36 27 Open Access Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS Viorica Lopez-Avila * and George Yefchak
MASS SPECTROMETRY OF OLIGOSACCHARIDES
 Joseph Zaia* Department of Biochemistry, Boston University School of Medicine, 715 Albany St., R-806, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 Received 20 March 2003; received (revised) 6 August 2003; accepted 6 August
Joseph Zaia* Department of Biochemistry, Boston University School of Medicine, 715 Albany St., R-806, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 Received 20 March 2003; received (revised) 6 August 2003; accepted 6 August
CHM 424L Organic Laboratory, Dr. Laurie S. Starkey Introduction to Mass Spectrometry
 CM 424L rganic Laboratory, Dr. Laurie S. Starkey Introduction to Mass Spectrometry Mass spectrometry is used to determine a sample's molecular mass and molecular formula. Some structural information can
CM 424L rganic Laboratory, Dr. Laurie S. Starkey Introduction to Mass Spectrometry Mass spectrometry is used to determine a sample's molecular mass and molecular formula. Some structural information can
[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector
![[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector [ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector](/thumbs/83/88757464.jpg) Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry. Supporting Information
 Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni
 0 out of 21 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni This monograph
0 out of 21 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni This monograph
Identification of Aromatic Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters
 Chapter 3.2 Identification of Aromatic Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters The only use of gas chromatography is not sufficient to determine which compounds are eluting from the catalytic bed. At the beginning of
Chapter 3.2 Identification of Aromatic Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters The only use of gas chromatography is not sufficient to determine which compounds are eluting from the catalytic bed. At the beginning of
Ion fragmentation of small molecules in mass spectrometry
 Ion fragmentation of small molecules in mass spectrometry Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 Nomenclature: the main names and acronyms used in mass spectrometry Molecular ion: Ion formed by addition
Ion fragmentation of small molecules in mass spectrometry Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 Nomenclature: the main names and acronyms used in mass spectrometry Molecular ion: Ion formed by addition
4.3 Oligosaccharides. trimethylchlorosilane, in pyridine as solvent, provides a sugar derivative with all HO-groups silylated:
 292 4 Carbohydrates trimethylchlorosilane, in pyridine as solvent, provides a sugar derivative with all HO-groups silylated: Monosaccharides form glycosides (cf. 4.2.4.5). When this occurs between the
292 4 Carbohydrates trimethylchlorosilane, in pyridine as solvent, provides a sugar derivative with all HO-groups silylated: Monosaccharides form glycosides (cf. 4.2.4.5). When this occurs between the
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities by LC/MS. Application Note. Christine Miller Agilent Technologies.
 Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Supporting information
 Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS
 New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS Subhra Bhattacharya, Deva H. Puranam, and Stephen C. Roemer Thermo Fisher Scientific Fisher Chemical, One Reagent Lane, Fair Lawn, NJ Material
New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS Subhra Bhattacharya, Deva H. Puranam, and Stephen C. Roemer Thermo Fisher Scientific Fisher Chemical, One Reagent Lane, Fair Lawn, NJ Material
O O H. Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL. LC /MS conditions
 Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
GlycoFragment and GlycoSearchMS: web tools to support the interpretation of mass spectra of complex carbohydrates
 GlycoFragment and GlycoSearchMS: web tools to support the interpretation of mass spectra of complex carbohydrates Klaus Karl Lohmann* and Claus-W. von der Lieth Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, Vol. 32, Web
GlycoFragment and GlycoSearchMS: web tools to support the interpretation of mass spectra of complex carbohydrates Klaus Karl Lohmann* and Claus-W. von der Lieth Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, Vol. 32, Web
High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column
 High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column Application Note BioPharma Authors James Martosella, Phu Duong, and Alex Zhu Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column Application Note BioPharma Authors James Martosella, Phu Duong, and Alex Zhu Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
Fast Separation of Triacylglycerols in Oils using UltraPerformance Convergence Chromatography (UPC 2 )
 Fast Separation of Triacylglycerols in Oils using UltraPerformance Convergence Chromatography (UPC 2 ) Mehdi Ashraf-Khorassani, 1 Larry T. Taylor, 1 Jinchuan Yang, 2 and Giorgis Isaac 2 1 Department of
Fast Separation of Triacylglycerols in Oils using UltraPerformance Convergence Chromatography (UPC 2 ) Mehdi Ashraf-Khorassani, 1 Larry T. Taylor, 1 Jinchuan Yang, 2 and Giorgis Isaac 2 1 Department of
Chapter 6 IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLAVONOIDS BY HPLC AND LC-MS/MS ANALYSIS
 Chapter 6 IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLAVONOIDS BY HPLC AND LC-MS/MS ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the method development carried out for the identification and characterization
Chapter 6 IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLAVONOIDS BY HPLC AND LC-MS/MS ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the method development carried out for the identification and characterization
Determination and pharmacokinetics of manidipine in human plasma by HPLC/ESIMS
 BIOMEDICAL CHROMATOGRAPHY Biomed. Chromatogr. 21: 836 840 (2007) Published 836 online ORIGINAL 12 April RESEARCH 2007 in Wiley InterScience ORIGINAL RESEARCH (www.interscience.wiley.com).827 Determination
BIOMEDICAL CHROMATOGRAPHY Biomed. Chromatogr. 21: 836 840 (2007) Published 836 online ORIGINAL 12 April RESEARCH 2007 in Wiley InterScience ORIGINAL RESEARCH (www.interscience.wiley.com).827 Determination
Structural Characterization of Sulfoquinovosyl, Monogalactosyl and Digalactosyl Diacylglycerols by FAB-CID-MS/MS
 JOURNAL OF MASS SPECTROMETRY, VOL. 32, 968È977 (1997) Structural Characterization of Sulfoquinovosyl, Monogalactosyl and Digalactosyl Diacylglycerols by FAB-CID-MS/MS Young Hwan Kim,1,2* Jong Shin Yoo1
JOURNAL OF MASS SPECTROMETRY, VOL. 32, 968È977 (1997) Structural Characterization of Sulfoquinovosyl, Monogalactosyl and Digalactosyl Diacylglycerols by FAB-CID-MS/MS Young Hwan Kim,1,2* Jong Shin Yoo1
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application
 Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile
 Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile Roxanne E. Franckowski, M.S.* and Robert A. Thompson, Ph.D. U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration Special Testing and Research Laboratory
Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile Roxanne E. Franckowski, M.S.* and Robert A. Thompson, Ph.D. U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration Special Testing and Research Laboratory
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES. Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016
 LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices
 Application ote #LCMS-2 esquire series Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices Introduction The simple monitoring
Application ote #LCMS-2 esquire series Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices Introduction The simple monitoring
Aminoglycoside antibiotics have activity against
 Collisionally Activated Dissociations of Aminocyclitol-Aminoglycoside Antibiotics and Their Application in the Identification of a New Compound in Tobramycin Samples Peifeng Hu, Edward K. Chess, Sean Brynjelsen,
Collisionally Activated Dissociations of Aminocyclitol-Aminoglycoside Antibiotics and Their Application in the Identification of a New Compound in Tobramycin Samples Peifeng Hu, Edward K. Chess, Sean Brynjelsen,
The Analysis of Jojoba Oil by LC-Coordination Ion Spray-MS (LC-CIS-MS)
 The Analysis of Jojoba Oil by LC-Coordination Ion Spray-MS (LC-CIS-MS) K. Lazou 1, A. d Oosterlinck 2, L. De Reu 1, M. Schelfaut 2, and P. Sandra 2 * 1 Department of Chemical Quality Control, Janssen Pharmaceutica,
The Analysis of Jojoba Oil by LC-Coordination Ion Spray-MS (LC-CIS-MS) K. Lazou 1, A. d Oosterlinck 2, L. De Reu 1, M. Schelfaut 2, and P. Sandra 2 * 1 Department of Chemical Quality Control, Janssen Pharmaceutica,
Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ Orbitrap
 Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ rbitrap Donald Daley, Russell Scammell, Argenta Discovery Limited, 8/9 Spire Green Centre, Flex Meadow, Harlow, Essex, CM19 5TR, UK bjectives unknown
Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ rbitrap Donald Daley, Russell Scammell, Argenta Discovery Limited, 8/9 Spire Green Centre, Flex Meadow, Harlow, Essex, CM19 5TR, UK bjectives unknown
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium. Application. Authors. Abstract.
 Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
CarboPac PA-100 Column for Oligosaccharide Analysis
 columns CarboPac PA- Column for Oligosaccharide Analysis HPLC Columns for Oligosaccharide Mapping and Purification Predictable, high resolution separations of oligosaccharides released from glycoproteins
columns CarboPac PA- Column for Oligosaccharide Analysis HPLC Columns for Oligosaccharide Mapping and Purification Predictable, high resolution separations of oligosaccharides released from glycoproteins
LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 EC C18 Column
 Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2419 Diversification of Self-Replicating Molecules Jan W. Sadownik, Elio Mattia, Piotr Nowak, Sijbren Otto* University of Groningen, Center for Systems Chemistry, Stratingh Institute
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2419 Diversification of Self-Replicating Molecules Jan W. Sadownik, Elio Mattia, Piotr Nowak, Sijbren Otto* University of Groningen, Center for Systems Chemistry, Stratingh Institute
C. Randall Clark* and Jack DeRuiter. F. Taylor Noggle. Abstract. Introduction
 Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Methods for the Differentiation of N-Methyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyO^-butanamine from Regioisomeric Derivatives C. Randall Clark* and Jack DeRuiter Department of
Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Methods for the Differentiation of N-Methyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyO^-butanamine from Regioisomeric Derivatives C. Randall Clark* and Jack DeRuiter Department of
An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates
 An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates Alzea Chrisel H. Alea 1, Diane Elaine T. Co 2 and Marissa G Noel 3* 1,2,3Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401
An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates Alzea Chrisel H. Alea 1, Diane Elaine T. Co 2 and Marissa G Noel 3* 1,2,3Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401
Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
 CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2012, 28(1), 31 36 Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS ZHANG Yu-chi 1,2, PI Zi-feng 1*, LIU Chun-ming 2, SONG
CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2012, 28(1), 31 36 Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS ZHANG Yu-chi 1,2, PI Zi-feng 1*, LIU Chun-ming 2, SONG
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D
 LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
Chromatography Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Application Note Differentiation and Determination Differentiation and Determination of Fatty Acid Methyl of Fatty Esters Acid by Gas Methyl Chromatography Esters by Vacuum Gas Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
Application Note Differentiation and Determination Differentiation and Determination of Fatty Acid Methyl of Fatty Esters Acid by Gas Methyl Chromatography Esters by Vacuum Gas Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
application Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS
 application LC/MS Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS Introduction Many kinds of natural colors are used in beverages,
application LC/MS Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS Introduction Many kinds of natural colors are used in beverages,
Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
 Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Michael McCullagh, 1 Kieran Neeson, 2 and Antonietta Gledhill 1 Waters Corporation,
Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Michael McCullagh, 1 Kieran Neeson, 2 and Antonietta Gledhill 1 Waters Corporation,
Automating Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Glycomics using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Reagents with SimGlycan
 PREMIER Biosoft Automating Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Glycomics using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Reagents with SimGlycan Ne uaca2-3galb1-4glc NAcb1 6 Gal NAca -Thr 3 Ne uaca2-3galb1 Ningombam Sanjib
PREMIER Biosoft Automating Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Glycomics using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Reagents with SimGlycan Ne uaca2-3galb1-4glc NAcb1 6 Gal NAca -Thr 3 Ne uaca2-3galb1 Ningombam Sanjib
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Structural Elucidation of N-glycans Originating From Ovarian Cancer Cells Using High-Vacuum MALDI Mass Spectrometry
 PO-CON1347E Structural Elucidation of N-glycans Originating From Ovarian Cancer Cells Using High-Vacuum MALDI Mass Spectrometry ASMS 2013 TP-708 Matthew S. F. Choo 1,3 ; Roberto Castangia 2 ; Matthew E.
PO-CON1347E Structural Elucidation of N-glycans Originating From Ovarian Cancer Cells Using High-Vacuum MALDI Mass Spectrometry ASMS 2013 TP-708 Matthew S. F. Choo 1,3 ; Roberto Castangia 2 ; Matthew E.
GlycanPac AXR-1 Columns
 CHRMATGRAPHY GlycanPac AXR- Columns For High Resolution Glycan Analysis Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXR- columns are highperformance, silica-based HPLC columns for simultaneous
CHRMATGRAPHY GlycanPac AXR- Columns For High Resolution Glycan Analysis Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXR- columns are highperformance, silica-based HPLC columns for simultaneous
Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac PA100 Column
 CHROMTOGRPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac P Column Product Specifications HPLC Columns for Oligosaccharide Mapping and Purification Predictable, high resolution separations of oligosaccharides released
CHROMTOGRPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac P Column Product Specifications HPLC Columns for Oligosaccharide Mapping and Purification Predictable, high resolution separations of oligosaccharides released
Constituents of Enzymatically Modified Isoquercitrin and Enzymatically Modified Rutin (Extract)
 54 J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan Vol. 41, No. 1 Original Constituents of Enzymatically Modified Isoquercitrin and Enzymatically Modified Rutin (Extract) (Received October 6, 1999) Takuml AKIYAMA*1, Tsutomu WASHING*2,
54 J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan Vol. 41, No. 1 Original Constituents of Enzymatically Modified Isoquercitrin and Enzymatically Modified Rutin (Extract) (Received October 6, 1999) Takuml AKIYAMA*1, Tsutomu WASHING*2,
Mass Spectrometry Introduction
 Mass Spectrometry Introduction Chem 744 Spring 2013 What MS is and is not MS is NOT a spectroscopic method. Molecules are not absorbing EM radiation MS is the generation, separation and characterization
Mass Spectrometry Introduction Chem 744 Spring 2013 What MS is and is not MS is NOT a spectroscopic method. Molecules are not absorbing EM radiation MS is the generation, separation and characterization
Chromatographic and Mass Spectral Studies on Methoxymethcathinones Related to 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
 Chromatographic and Mass Spectral Studies on Methoxymethcathinones Related to 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine Tamer Awad, C. Randall Clark*, and Jack DeRuiter Department of Pharmacal Sciences, School
Chromatographic and Mass Spectral Studies on Methoxymethcathinones Related to 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine Tamer Awad, C. Randall Clark*, and Jack DeRuiter Department of Pharmacal Sciences, School
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Materials and Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
Minutes Figure S1. HPLC separation of nucleosides from LC/ESI-MS analysis of a total enzymatic Trp
 100 A % Relative Abundance m m Ø acp 5 m Øm 5 m m 7 m s * 6 ia m * 0 5 10 15 0 5 0 5 40 Minutes Figure S1. HPL separation of nucleosides from L/ESI-MS analysis of a total enzymatic digest of mt trna. V
100 A % Relative Abundance m m Ø acp 5 m Øm 5 m m 7 m s * 6 ia m * 0 5 10 15 0 5 0 5 40 Minutes Figure S1. HPL separation of nucleosides from L/ESI-MS analysis of a total enzymatic digest of mt trna. V
Application Note # FTMS-46 solarix XR: Analysis of Complex Mixtures
 Application Note # FTMS-46 solarix XR: Analysis of Complex Mixtures Introduction Natural organic matter (NOM) as well as crude oil and crude oil fractions are very complex mixtures of organic compounds
Application Note # FTMS-46 solarix XR: Analysis of Complex Mixtures Introduction Natural organic matter (NOM) as well as crude oil and crude oil fractions are very complex mixtures of organic compounds
SACCHARIDES (Liquid Chromatography)
 Corn Syrup Analysis E-61-1 PRINCIPLE SCOPE A corn syrup solution is passed through a metal ion-modified cation exchange column. The individual sugars are separated by molecular exclusion and ligand exchange.
Corn Syrup Analysis E-61-1 PRINCIPLE SCOPE A corn syrup solution is passed through a metal ion-modified cation exchange column. The individual sugars are separated by molecular exclusion and ligand exchange.
Usefulness of Derivatization in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Conjugated Vitamin D Metabolites
 1999 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 619 Usefulness of Derivatization in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Conjugated Vitamin D Metabolites Original Papers Tatsuya
1999 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 619 Usefulness of Derivatization in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Conjugated Vitamin D Metabolites Original Papers Tatsuya
A Fully Integrated Workflow for LC-MS/MS Analysis of Labeled and Native N-Linked Glycans Released From Proteins
 A Fully Integrated Workflow for LC-MS/MS Analysis of Labeled and Native N-Linked Glycans Released From Proteins Udayanath Aich, 1 Julian Saba, 2 Xiaodong Liu, 1 Srinivasa Rao, 1 Yury Agroskin, 1 and Chris
A Fully Integrated Workflow for LC-MS/MS Analysis of Labeled and Native N-Linked Glycans Released From Proteins Udayanath Aich, 1 Julian Saba, 2 Xiaodong Liu, 1 Srinivasa Rao, 1 Yury Agroskin, 1 and Chris
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit
 Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Structural and quantitative analysis of N-linked glycans by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and negative ion nanospray mass spectrometry
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Analytical Biochemistry 376 (2008) 44 60 ANALYTICAL BIOCHEMISTRY www.elsevier.com/locate/yabio Structural and quantitative analysis of N-linked glycans by matrix-assisted
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Analytical Biochemistry 376 (2008) 44 60 ANALYTICAL BIOCHEMISTRY www.elsevier.com/locate/yabio Structural and quantitative analysis of N-linked glycans by matrix-assisted
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry of Carbohydrates Derivatized with Biotinamidocaproyl Hydrazide
 Chapter 4 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry of Carbohydrates Derivatized with Biotinamidocaproyl Hydrazide Stephanie Bank and Petra Kapková Additional information is available at the end of the chapter
Chapter 4 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry of Carbohydrates Derivatized with Biotinamidocaproyl Hydrazide Stephanie Bank and Petra Kapková Additional information is available at the end of the chapter
189,311, , ,561, ,639, ,679, Ch13; , Carbohydrates
 Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 1260 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System
 Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 126 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System Authors Florian Rieck and Jörg Hippler Agilent
Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 126 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System Authors Florian Rieck and Jörg Hippler Agilent
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
Maximizing chromatographic peak capacity with the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC system
 Maximizing chromatographic peak capacity with the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC system A practical guide on how to use parameters to increase peak capacity Application Note Pharmaceutical and Chemical Author
Maximizing chromatographic peak capacity with the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC system A practical guide on how to use parameters to increase peak capacity Application Note Pharmaceutical and Chemical Author
methods Electrospray mass spectrometry of human hair wax esters Mark Fitzgerald and Robert C. Murphy 1
 Electrospray mass spectrometry of human hair wax esters methods Mark Fitzgerald and Robert C. Murphy 1 Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center, Aurora, CO
Electrospray mass spectrometry of human hair wax esters methods Mark Fitzgerald and Robert C. Murphy 1 Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center, Aurora, CO
Determination of Glimepiride in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Determination of Glimepiride in Human Plasma by LC-ESI/MS/MS Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, Vol. 25, No. 1 109 Determination of Glimepiride in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization
Determination of Glimepiride in Human Plasma by LC-ESI/MS/MS Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, Vol. 25, No. 1 109 Determination of Glimepiride in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization
HPLC Analysis of Sugars
 HPLC Analysis of Sugars Pre-Lab Exercise: 1) Read about HPLC, sugars and the experiment and its background. 2) Prepare a flowchart as appropriate for the lab exercise. 3) Note the various sugar concentrations
HPLC Analysis of Sugars Pre-Lab Exercise: 1) Read about HPLC, sugars and the experiment and its background. 2) Prepare a flowchart as appropriate for the lab exercise. 3) Note the various sugar concentrations
University of New Orleans. Yanjie Jiang University of New Orleans
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-21-2004 Oligosaccharide Analysis via Anion Attachment Using Negative Mode Electrospray
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-21-2004 Oligosaccharide Analysis via Anion Attachment Using Negative Mode Electrospray
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS. Application. Authors. Abstract. Experimental. Introduction. Food Safety
 Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Designer Cannabinoids
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-010 Designer Cannabinoids LCMS-8030 Summary A rapid LC-MS-MS method for determination of designer cannabinoids in smokeable herbs was developed. Background
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-010 Designer Cannabinoids LCMS-8030 Summary A rapid LC-MS-MS method for determination of designer cannabinoids in smokeable herbs was developed. Background
Analysis of Fatty Acyl Groups of Diacyl Galactolipid Molecular Species by HPLC/ESI-MS with In-source Fragmentation
 Analysis of Fatty Acyl Groups of Diacyl Galactolipids by HPLC/ESI-MS Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, Vol. 24, No. 8 1163 Analysis of Fatty Acyl Groups of Diacyl Galactolipid Molecular Species by HPLC/ESI-MS
Analysis of Fatty Acyl Groups of Diacyl Galactolipids by HPLC/ESI-MS Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, Vol. 24, No. 8 1163 Analysis of Fatty Acyl Groups of Diacyl Galactolipid Molecular Species by HPLC/ESI-MS
Application Note. Authors: C. Ledesma, M. Gibert, J.R. Gibert Ingenieria Analitica S.L. Extracts from various food products
 High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography coupled with Pulsed Electrochemical Detection as a powerful tool to evaluate lactose content in lactose-free labeled products Application Note Authors: C.
High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography coupled with Pulsed Electrochemical Detection as a powerful tool to evaluate lactose content in lactose-free labeled products Application Note Authors: C.
Carbohydrates. Lecture2
 Carbohydrates Lecture2 Disaccharides Consist of two monosaccharides covalently bound to each other. All of which are isomers with the molecular formula C 12 22 O 11. The differences in these disaccharides
Carbohydrates Lecture2 Disaccharides Consist of two monosaccharides covalently bound to each other. All of which are isomers with the molecular formula C 12 22 O 11. The differences in these disaccharides
Carbohydrates. What are they? What do cells do with carbs? Where do carbs come from? O) n. Formula = (CH 2
 Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them. Cyclopropylfentanyl
 Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them Cyclopropylfentanyl Science for a safer world The in vitro metabolism of cyclopropylfentanyl Simon Hudson & Charlotte Cutler, Sport and Specialised
Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them Cyclopropylfentanyl Science for a safer world The in vitro metabolism of cyclopropylfentanyl Simon Hudson & Charlotte Cutler, Sport and Specialised
DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD
 DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD Kenichi TAKAICHI, Shuji SAITOH, Yoshio KUMOOKA, Noriko TSUNODA National Research Institute of Police Science, Chiba,
DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD Kenichi TAKAICHI, Shuji SAITOH, Yoshio KUMOOKA, Noriko TSUNODA National Research Institute of Police Science, Chiba,
Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards]
![Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards]](/thumbs/86/94003482.jpg) Neosolaniol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of mycotoxins by liquid chromatography/ tandem mass spectrometry [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter 5, Section 1 9.1 ]
Neosolaniol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of mycotoxins by liquid chromatography/ tandem mass spectrometry [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter 5, Section 1 9.1 ]
Type Analysis of Citrus Essential Oils by Multidimensional Supercritical Fluid Chromatography/ Gas Chromatography
 25 Type Analysis of Citrus Essential Oils by Multidimensional Supercritical Fluid Chromatography/ Gas Chromatography Takashi YARITA, Akira NoMURA and Yoshiyuki HoRIMOTo Department of Analytical Chemistry,
25 Type Analysis of Citrus Essential Oils by Multidimensional Supercritical Fluid Chromatography/ Gas Chromatography Takashi YARITA, Akira NoMURA and Yoshiyuki HoRIMOTo Department of Analytical Chemistry,
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids
 Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
SimGlycan. A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows.
 PREMIER Biosoft SimGlycan A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows SimGlycan software processes and interprets the MS/MS and higher
PREMIER Biosoft SimGlycan A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows SimGlycan software processes and interprets the MS/MS and higher
LC-MS Analysis of Botanicals
 Botanical workshop UAB, Sept 11, 26 LC-MS Analysis of Botanicals Jeevan K. Prasain, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology, UAB Purdue-UAB Botanicals Center for Age-related Disease Applications
Botanical workshop UAB, Sept 11, 26 LC-MS Analysis of Botanicals Jeevan K. Prasain, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology, UAB Purdue-UAB Botanicals Center for Age-related Disease Applications
Introduction. and aryl-α-amino ketones, 11
 Enantiomeric Resolution of γ-amino Acids Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 8 3017 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.8.3017 Liquid Chromatographic Resolution of Vigabatrin and Its Analogue γ-amino Acids
Enantiomeric Resolution of γ-amino Acids Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 8 3017 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.8.3017 Liquid Chromatographic Resolution of Vigabatrin and Its Analogue γ-amino Acids
Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids
 PO-CON1576E Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids HPLC 2015 PSB-MULTI-06 Yoshiyuki WATABE, Tetsuo IIDA, Daisuke NAKAYAMA, Kanya TSUJII, Saki
PO-CON1576E Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids HPLC 2015 PSB-MULTI-06 Yoshiyuki WATABE, Tetsuo IIDA, Daisuke NAKAYAMA, Kanya TSUJII, Saki
Mechanistic Insight into Oxidized N,N-Dimethylacetamide as a source of Formaldehyde Related Process Derivatives
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Reaction Chemistry & Engineering. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information to Accompany: Mechanistic Insight into Oxidized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Reaction Chemistry & Engineering. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information to Accompany: Mechanistic Insight into Oxidized
ESI-MS of chondroitin oligosaccharides Possible ions (charge) m/z ( 1) ( 2) ( 3) ( 4) ( 5) ( 6) ( 7) ( 8) Chondroitin oligomers
 RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008; 22: 3526 3530 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3760 Mass spectrometry for the characterization
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008; 22: 3526 3530 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3760 Mass spectrometry for the characterization
Carbohydrates. Chapter 12
 Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Supporting Information. 58 Pages. 6 Figures 4 Tables
 Light-Source-Dependent Effects of Main Water Constituents on Photodegradation of Phenicol Antibiotics: Mechanism and Kinetics Linke Ge, Jingwen Chen, * Xianliang Qiao, Jing Lin, Xiyun Cai Key Laboratory
Light-Source-Dependent Effects of Main Water Constituents on Photodegradation of Phenicol Antibiotics: Mechanism and Kinetics Linke Ge, Jingwen Chen, * Xianliang Qiao, Jing Lin, Xiyun Cai Key Laboratory
MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS. Pavel Aronov. ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010
 MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS Pavel Aronov ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010 Types of Experiments in Metabolomics targeted non targeted Number of analyzed metabolites is limited
MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS Pavel Aronov ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010 Types of Experiments in Metabolomics targeted non targeted Number of analyzed metabolites is limited
Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis
 FEATURED ARTICLES Taking on Future Social Issues through Open Innovation Life Science for a Healthy Society with High Quality of Life Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis Hitachi
FEATURED ARTICLES Taking on Future Social Issues through Open Innovation Life Science for a Healthy Society with High Quality of Life Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis Hitachi
