Measurement and Improvement of Quality of Cardiovascular Care DR : DEHESTANI
|
|
|
- Tracy Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measurement and Improvement of Quality of Cardiovascular Care DR : DEHESTANI
2 Hospitals For hospitals in the United States, measures of cardiovascular care mandated by the Joint Commission have recently become important foci for quality improvement. These measures are part of a programcalled the ORYXInitiative, which integrates outcomes and other performance measurement data into the accreditation process for hospitals. Two of the core foci of the ORYX initiative are acute myocardialinfarction and heart failure. Comparisons of hospitals on these measurescan be made on the Joint Commission website." Despite broad acceptance
3
4
5
6
7 Incidence 900,000 PEs/ DVTs in USA in Estimated 296,000 PE deaths: 7% treated, 34% sudden and fatal, and 59% undetected ,000 PEs/ DVTs in EU in 2004.
8 Annual # At-Risk for VTE: US Hospitals 7.7 million Medical Service inpatients 3.4 million Surgical Service inpatients Based upon ACCP guidelines for VTE prophylaxis
9 VTE: A Major Source of Mortality and Morbidity 350,000 to 650,000 with VTE per year 100,000 to > 200,000 deaths per year Most are hospital related. VTE is primary cause of fatality in half- More than HIV, Breast CA combined Equals 1 jumbo jet crash / day 10% of hospital deaths May be the #1 preventable cause Huge costs and morbidity (recurrence, post-thrombotic syndrome, chronic PAH) S
10 Failure to Do Simple Things Well Wash Hands 60% Reliable Patients Understand Meds / Problems 40% Reliable Central Lines Placed w/ Proper Technique 60% Reliable Basal Insulin for Inpt Uncontrolled DM 40% Reliable VTE Prophylaxis 50% Reliable
11 Registry Data Highlight the Underuse of Thromboprophylaxis DVT-FREE RIETE IMPROVE BAD NEWS! Only a minority of hospitalized patients receive thromboprophylaxis
12 Out of ~70,000 patients in 358 hospitals, appropriate prophylaxis was administered in: 58.5% of surgical patients 39.5% of medical patients
13 Rationale for DVT Prevention Prevalence Hospitalized patients have risk factors for VTE DVT usually clinically silent, difficult to predict complications Screening is neither effective nor cost-effective Adverse consequences Symptomatic DVT and PE or Fatal PE Costs of testing and treating Increased future risk of recurrent VTE Efficacy and effectiveness of prophylaxis Prophylaxis prevents DVT and PE The prevention of DVT also prevents PE Prophylaxis is cost-effective
14 Outpatient and Inpatient VTE are Linked 74% of VTEs present in outpatients. 42% of outpatient VTE patients have had recent surgery or hospitalization. Only 40% had received VTE prophylaxis.
15 Mortality (%) ICOPER Cumulative Mortality % Days From Diagnosis
16 Cardiovascular Risk Factors and VTE (N=63,552 meta-analysis) RF RR Obesity 2.3 Hypertension 1.5 Diabetes 1.4 Cigarettes 1.2 High Cholesterol 1.2
17 RISK OF PE: BMI Nurses' Health Study JAMA 1997; 277: 642 RR (95% CI) * 1.7 * < > 29 BODY MASS INDEX (kg/m 2 )
18 PE AND CIGARETTE SMOKING Nurses' Health Study (JAMA 1997; 277: 642) * 1.8 * 2.1 RR (95% CI) Never Cigs (ref) 1-14 Cigs Cigs Cigs CIGARETTE SMOKING > 35 Cigs
19 Worldwide Prophylaxis Status for 68,183 Patients 52% at Risk for VTE (50% receive ACCP recommended prophy) Surgical 64% at Risk for VTE Medical 42% at Risk for VTE 59% receive ACCP Rec. Px 40% receive ACCP Rec. Px
20 Risk factors for DVT What are risk factors for DVT in hospitalized patients? What is Virchow s Triad?
21 Virchow s Triad Stasis Trauma Hypercoaguability Virchow RLK (1856). "Thrombose und Embolie. Gefässentzündung und septische Infektion". Gesammelte Abhandlungen zur wissenschaftlichen Medicin. Frankfurt am Main: Von Meidinger & Sohn. pp Translation in Matzdorff AC, Bell WR (1998). Thrombosis and embolie ( ). Canton, Massachusetts: Science History Publications.
22 Risk Factors for DVT Stasis Surgery, trauma, immobility, paresis Increasing age Pregnancy and postpartum Heart or respiratory failure Obesity Vessel Injury Previous DVT Smoking Varicose veins Central venous catheterization Hypercoagulability Increasing age Malignancy Cancer therapy Estrogen therapy (OCP or HRT) Acute medical illness Inflammatory bowel disease Nephrotic syndrome Myeloproliferative disorders Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Inherited or acquired thrombophilia
23 Risk Factors for VTE Age Prior VTE Surgery, trauma Immobility Pregnancy/postpartum Medical illness Cancer & cancer rx Inflammatory Bowel Dz Nephrotic Syndrome Obesity CVL Meds Hormone replacement Tamoxifen, raloxifene Cancer drugs Erythropoetin Thrombophilia Inherited Acquired
24
25
26 Risk Factors for VTE Age Prior VTE Surgery, trauma Immobility Pregnancy/postpartum Medical illness Cancer & cancer rx Inflammatory Bowel Dz Nephrotic Syndrome Obesity CVL Meds Hormone replacement Tamoxifen, raloxifene Almost all inpatients have Cancer 1 drugs RF Erythropoetin 40% of inpatients have 3 RF Thrombophilia Inherited Acquired
27 Absolute Risk of DVT in Hospitalized Patients Patient Group DVT Prevalence, % Medical patients General surgery Major gynecologic surgery Major urologic surgery Neurosurgery Stroke Hip or knee arthroplasty, hip fracture surgery Major trauma Spinal cord injury Critical care patients Chest. 2004;126:338S-400S. PMID:
28 VTE Prophylaxis Guideline Patient admitted Determine risk of VTE Low Moderate Or High Risk of VTE Low risk if all 3: Younger than 40 Mobile No thrombotic risk factors Moderate risk: All other patients High risk: ICU patients Early ambulation Determine bleeding risk Low High Anticoagulant prophylaxis Intermittent pneumatic compression High Bleeding Risk Active gastroduodenal bleed Bleeding within 3 months prior to admission Platelet count of < 50
29 Risk Stratification Risk Type Rx Low Moderate High Minor surgery & medical, mobile Most general surgery & medical patients Ortho & major trauma Early ambulation Medical +/- mechanical Medical +/- mechanical
30 THANKS!
31 Literature Search Cochrane Collaboration National Guideline Clearinghouse Pub Med
32 Guidelines Prevention of venous thromboembolism: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism. A national clinical guideline. Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI). Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. NICE. Venous thromboembolism: reducing the risk of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) in inpatients undergoing surgery.
33 What outcomes do we look for?
34 Outcomes Asymptomatic DVT? Symptomatic DVT? PE? Fatal All PE s? Long-term complications?
35 How can you prevent DVT?
36 Methods of DVT Prophylaxis Mobilization Graduated compression stockings Intermittent pneumatic compression Aspirin Unfractionated heparin Low-molecular weight heparins Enoxaparin, dalteparin Vitamin K antagonists Warfarin, acenocoumarol, phenindione, & dicoumarol Fondaparinux (Factor Xa inhibitor)
37 Mechanical prophylaxis Graduated Compression Stockings (GCS) Prophylaxis DVT Rate None 27% GCS 13% Background Prophylaxis 15% GCS + Background 2%» Elastic compression stockings for prevention of deep vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD PMID:
38 Mechanical prophylaxis Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) Prophylaxis DVT Rate None 29% GCS 15% IPC 8-11%» Am Surg Nov;64: PMID:
39 Mechanical prophylaxis Systematic review surgical patients GCS, IPCs as monotherapy 2/3 reduction in DVT GCS, IPCs added to pharmacotherapy Additional 50% reduction in DVT GCS, IPCs may reduce PE by 40%» Health Technol Assess Dec;9(49):1-78.
40 Mechanical prophylaxis Other issues... Not shown to reduce death Use with caution in vascular insufficiency
41 Clinical Question A 70 male is going to be hospitalized for an inguinal hernia repair. He takes aspirin for vascular prophylaxis. Should he stop ASA for surgery?
42 Aspirin a low-risk measure? Small studies inconclusive PEP study (Lancet. 2000: ) 1700 hip surgery patients, f/u to 35 days ASA vs Placebo Fatal PE.3% vs.6% Symptomatic DVT.9% vs 1.3% Small risk increase in hematemesis and wound bleeding ACCP & ICSI Recommend against relying on aspirin for DVT prevention SIGN Advocates ASA for DVT prevention in surgical patients.
43 Clinical Question A 60 year old female is hospitalized for a COPD exacerbation. Do you need to provide DVT prophylaxis? What do you order?
44 General Medicine LMWH and UFH Reduce DVT and PE by 56-58% No effect demonstrated on death LMWH vs UFH No difference in DVT or PE Lower risk of major bleeding (by 52%) Thromb Haemost Jan;83(1):14-9. PMID:
45 General Medicine Recommendations Ambulation for all patients LMWH or UFH For patients with HF, Respiratory disease, immobility PLUS other risk factors Mechanical prophylaxis If anti-coagulants contraindicated. Consider for all bed-bound patients Chest 2004 Sep;126(3 Suppl):338S-400S. Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI).
46 Non-Orthopedic Surgery General Gynecologic Colorectal Urologic Vascular
47 Clinical Question A 45 year old male was hospitalized for gall bladder disease & his cholecystectomy had to be converted from laparoscopic to open. Does he need DVT prophylaxis? What would you use?
48 General Surgery Meta-analysis: Haemostasis. 1997;27:65. LMWH & UFH reduce DVT & PE risk LMWH reduced minor bleeds 25% Meta-analysis: Br J Surg Jul;88(7):91. LMWH & UFH reduced all DVT, reduced PE Same bleeding risk Meta-analysis: Thromb Res. 2001;102:295. Confirmed LWMH and UFH equally effective & safe for DVT prevention
49 General Surgery ACCP, ICSI, SIGN Low-risk pts (young, non-major surgery) Early and persistent mobilization Moderate-risk pts (major surgery OR > 40 yrs) Use LMWH or UFH High-risk pts (major surgery, > 40 yrs) GCS, plus LMWH or UFH Use GCS if risk of bleeding precludes anti-coagulants. NICE Inpatients having surgery should be offered GCS from the time of admission to hospital unless contraindicated
50 Clinical Question A 70 year old woman with severe DJD and diabetes is having elective hysterectomy for significant uterine prolapse. Do you recommend DVT prophylaxis? What prophylaxis?
51 Major Gynecologic Surgery Cochrane: UFH prevents DVT in women with malignancy Warfarin prevents DVT in women w/o malignancy LMWH just as effective as UFH No studies of ASA Anticoagulant and aspirin prophylaxis for preventing thromboembolism after major gynaecological surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD
52 ACOG Recommendations: Moderate or high risk patients Major surgery, CA, other DVT risk factors GCS or IPC Apply intraoperatively, cont. till ambulatory UFH Start 2-8 hrs pre-op, continue till D/C LMWH Start 12 hrs pre-op, continue till D/C American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Prevention of DVT and pulmonary embolism.
53 Colorectal surgery Both LMWH and UFH reduce DVT risk Adding GCS to either method provides added protection Heparins and mechanical methods for thromboprophylaxis in colorectal surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD001217
54 Other Non-Ortho Surgery Colorectal Both LMWH and UFH reduce DVT risk GCS provide added protection Urologic Minimal evidence UFH, LMWH, GCS, or IPC for pts w/ high DVT Vascular Most are on anti-platelet agents anyway Base prophylaxis on other risk factors
55 Clinical Question You are asked to provide medical consultation on a 75 year old nursing home patient with hypertension and heart disease who needs ORIF of a left hip fracture. What DVT prophylaxis do you recommend?
56 Orthopedics LMWH better & safer than warfarin or UFH» Haemostasis Mar-Apr;27(2): LMWH better & safer than warfarin or UFH for TKR» Thromb Haemost May;79(5): LMWH or IPC better than ASA or warfarin for TKR» J Bone Joint Surg Br Aug;82(6): » J Arthroplasty Apr;16(3): LMWH & UFH similarly effective after hip fx surgery» Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(4):CD LMWH better than Vit K antagonists in ortho surgery» J Thromb Haemost Jul;2(7):
57 Orthopedics No difference in DVT rates between: Pre-op or post-op initiation of LMWH Different currently-accepted LMWH doses» Arch Intern Med Jan 25;159(2): » Thromb Haemost Oct;90(4):
58 Orthopedic Guidelines ACCP and ICSI Elective hip or knee arthroplasty LMWH, vitamin K antagonists, fondaparinux Hip fracture surgery NICE LMWH, vitamin K antagonists, fondaparinux, or UFH Start LMWH or UFH at hospital admission if fracture repair will be delayed. Hip fracture or elective orthopedic surgery LMWH/Fondaparinux + mechanical
59 Trauma High risk of DVT or PE 40 80% DVT ACCP & SIGN LMWH for prophylaxis Mechanical prophylaxis if risk of bleeding precludes anticoagulants.» Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism. Edinburgh (Scotland): Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN); 2002 Oct.» Chest. 2004;126:338S-400S. PMID:
60 Key Messages Both GCS & IPCs significantly reduce DVT rates. UFH and LMWH equally effective and general surgery patients. GCS can provide additional protection for high-risk patients. Use either GCS placed intraoperatively, or UFH or LMWH started preoperatively, gynecologic surgery at risk of DVT Major surgery, malignancy, or other DVT risk factors. Use LMWH, vitamin K antagonists, or fondaparinux after elective major hip or knee surgery. For hip fracture Start LMWH or UFH pre-op if delay until surgery Post-operative DVT prophylaxis: LMWH, UFH, vitamin K antagonists, or fondaparinux.
61 Information for Patients Deep Vein Thrombosis: What You Should Know. mmon-older/800.html (accessed 6 June 2007) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). (accessed 6 June 2007) CG46 Venous thromboembolism: Understanding NICE guidance. (accessed 6 June 2007)
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies
 VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism
 Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
General. Recommendations. Guideline Title. Bibliographic Source(s) Guideline Status. Major Recommendations
 General Guideline Title Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Bibliographic Source(s) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Prevention of deep vein thrombosis
General Guideline Title Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Bibliographic Source(s) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Prevention of deep vein thrombosis
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis
 Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism
 Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism Surgical Care Improvement Project Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH President and CEO Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH Oklahoma Foundation for Medical Quality QIOSC Medical Director
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism Surgical Care Improvement Project Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH President and CEO Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH Oklahoma Foundation for Medical Quality QIOSC Medical Director
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY
 INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales
 Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE)
 DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Outline of This Presentation
 Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Primary VTE Prophylaxis. Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand
 Primary VTE Prophylaxis Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand A 70-yr-old female before THA BMI 31 kg/m 2 with varicose vein What do you recommend for VTE prevention?
Primary VTE Prophylaxis Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand A 70-yr-old female before THA BMI 31 kg/m 2 with varicose vein What do you recommend for VTE prevention?
Getting Started Kit VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PREVENTION. Section 2: Evidence-Based Appropriate VTE Prophylaxis
 Reducing Harm Improving Healthcare Protecting Canadians VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PREVENTION Getting Started Kit Section 2: Evidence-Based Appropriate VTE Prophylaxis January 2017 www.patientsafetyinstitute.ca
Reducing Harm Improving Healthcare Protecting Canadians VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PREVENTION Getting Started Kit Section 2: Evidence-Based Appropriate VTE Prophylaxis January 2017 www.patientsafetyinstitute.ca
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 18 April 2007
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 April 2007 ARIXTRA 2.5 mg/0.5 ml, solution for injection in prefilled syringe Pack of 2 (CIP: 359 225-4) Pack of
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 April 2007 ARIXTRA 2.5 mg/0.5 ml, solution for injection in prefilled syringe Pack of 2 (CIP: 359 225-4) Pack of
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement. Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN
 Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
Venous Thromboembolism. Prevention
 Venous Thromboembolism Prevention August 2010 Venous Thromboembloism Prevention 1 1 Expected Practice Assess all patients upon admission to the ICU for risk factors of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and
Venous Thromboembolism Prevention August 2010 Venous Thromboembloism Prevention 1 1 Expected Practice Assess all patients upon admission to the ICU for risk factors of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked!
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked! William Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Safer
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked! William Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Safer
SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION EFFECTIVE DATE: 06/27/13 DEVICES FOR VENOUS REVISED DATE: 06/26/14 THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS: NON-ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY
 THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS: NON-ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY OBJECTIVE: To outline a practical approach for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients undergoing non-orthopedic surgery. BACKGROUND: VTE is
THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS: NON-ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY OBJECTIVE: To outline a practical approach for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients undergoing non-orthopedic surgery. BACKGROUND: VTE is
Page: 1 of 13. Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Last Review Status/Date: March 2014 Page: 1 of 13 Compression Devices for Venous Description Patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery are at increased risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Patients
Last Review Status/Date: March 2014 Page: 1 of 13 Compression Devices for Venous Description Patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery are at increased risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Patients
Page: 1 of 14. Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Subject: Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Description Patients undergoing major
Subject: Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Description Patients undergoing major
Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures
 1 Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures David Dornbos III, Varun Shah, Blake Priddy, Victoria Schunemann, Ciarán Powers Venous Thromboembolic (VTE) Complications
1 Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures David Dornbos III, Varun Shah, Blake Priddy, Victoria Schunemann, Ciarán Powers Venous Thromboembolic (VTE) Complications
10/8/2012. Disclosures. Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines. Goals and Objectives. Outline
 Disclosures Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines No relevant conflicts of interest related to the topic presented. Cyndy Brocklebank, PharmD, CDE Chronic Disease Management
Disclosures Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines No relevant conflicts of interest related to the topic presented. Cyndy Brocklebank, PharmD, CDE Chronic Disease Management
NICE Guidance: Venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) in patients admitted to hospital 1
 The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project
 Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project Dr. Jonathan Laxton, FRCPC, R5 GIM University of Manitoba
Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project Dr. Jonathan Laxton, FRCPC, R5 GIM University of Manitoba
Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis
 Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis Gregory J. Misky, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine University Of Colorado Denver You recommend the following 72 y.o. man admitted for an elective R hip repair. Patient
Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis Gregory J. Misky, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine University Of Colorado Denver You recommend the following 72 y.o. man admitted for an elective R hip repair. Patient
Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Clinical Position Statement Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Effective: October 2017 Next Review: September 2018 CLINICAL POSITION STATEMENT Postsurgical
Clinical Position Statement Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Effective: October 2017 Next Review: September 2018 CLINICAL POSITION STATEMENT Postsurgical
SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION EFFECTIVE DATE: 06/27/13 DEVICES FOR VENOUS REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
MEDICAL POLICY REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
Cancer and Thrombosis
 Cancer and Thrombosis The close relationship between venous thromboembolism and cancer has been known since at least the 19th century by Armand Trousseau. Thrombosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality
Cancer and Thrombosis The close relationship between venous thromboembolism and cancer has been known since at least the 19th century by Armand Trousseau. Thrombosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality
Tarkten A Pharr, MD, FACS 04/26/2018. VTE Prevention Strategies: Is a One Size Fits all Approach Correct?
 Tarkten A Pharr, MD, FACS 04/26/2018 VTE Prevention Strategies: Is a One Size Fits all Approach No disclosures... Why do we care? Where is this is the realm of public health concerns? Incidence/Prevalence
Tarkten A Pharr, MD, FACS 04/26/2018 VTE Prevention Strategies: Is a One Size Fits all Approach No disclosures... Why do we care? Where is this is the realm of public health concerns? Incidence/Prevalence
Medical Patients: A Population at Risk
 Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
Protocol. Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for (10128) (Formerly Outpatient Use of Limb Pneumatic Compression Devices for ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for (10128) (Formerly Outpatient Use of Limb Pneumatic Compression Devices for ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention
 Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention 7 VTE Risk Assessment: General Patient Population Assess VTE risk at admission, post-op, and transfer See page 2 for VTE risk assessment among Obstetrical (OB) patients
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention 7 VTE Risk Assessment: General Patient Population Assess VTE risk at admission, post-op, and transfer See page 2 for VTE risk assessment among Obstetrical (OB) patients
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Utilization of DVT Prophylaxis in non ICU Hospitalized Patients
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease (2012)S707-S711 707 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease journal homepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/apjtd Document
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease (2012)S707-S711 707 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease journal homepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/apjtd Document
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS
 EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism
 Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT
 Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION DEVICES FOR VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 10/15/15, 06/16/16, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 10/15/15, 06/16/16, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria
Dr. Steve Ligertwood Dr. Roderick Tukker Dr. David Wilton
 Dr. Steve Ligertwood Hospitalist Royal Columbian Hospital Regional Department Head-Hospitalist for Fraser Health Authority Project Lead BC Hospitalist VTE Collaborative Clinical Instructor, UBC School
Dr. Steve Ligertwood Hospitalist Royal Columbian Hospital Regional Department Head-Hospitalist for Fraser Health Authority Project Lead BC Hospitalist VTE Collaborative Clinical Instructor, UBC School
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement or total hip replacement: what can be learnt from root-cause analysis?
 TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2016; 98: 538 542 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0202 Venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement or total hip replacement: what can be learnt from
TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2016; 98: 538 542 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0202 Venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement or total hip replacement: what can be learnt from
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Cancer and the Heparins
 Cancer and the Heparins Wim P Ceelen, MD, PhD, FACS Department of GI Surgery - UZ Gent Senior Clinical Researcher - FWO Overview Mechanisms of cancer induced thrombosis Guidelines for prevention and treatment
Cancer and the Heparins Wim P Ceelen, MD, PhD, FACS Department of GI Surgery - UZ Gent Senior Clinical Researcher - FWO Overview Mechanisms of cancer induced thrombosis Guidelines for prevention and treatment
CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm
 CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm P. Timothy Pollak, MD, PhD University of Calgary Rocky Mountain/ACP Internal Medicine Meeting,
CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm P. Timothy Pollak, MD, PhD University of Calgary Rocky Mountain/ACP Internal Medicine Meeting,
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip/Knee Replacement: A Population-based Taiwan Study
 IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
 Winner of the AAHKS Award Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Greg A. Brown, MD, PhD The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24
Winner of the AAHKS Award Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Greg A. Brown, MD, PhD The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24
*Corresponding Author:
 Audit of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis administered to general surgical patients undergoing elective and emergency operations at National Hospital, Sri Lanka *Migara Seneviratne 1, Asanka Hemachandra
Audit of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis administered to general surgical patients undergoing elective and emergency operations at National Hospital, Sri Lanka *Migara Seneviratne 1, Asanka Hemachandra
Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism
 Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism The AORN Guideline Quick View is a key component of Guideline Essentials, a suite of online implementation tools designed to help the perioperative team translate
Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism The AORN Guideline Quick View is a key component of Guideline Essentials, a suite of online implementation tools designed to help the perioperative team translate
Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis
 Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis Controversies in Hematology 53 rd Annual Meeting of Thai Society of Hematology Bundarika Suwanawiboon, MD Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Faculty of Medicine
Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis Controversies in Hematology 53 rd Annual Meeting of Thai Society of Hematology Bundarika Suwanawiboon, MD Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Faculty of Medicine
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: postsurgical_home_use_of_limb_ compression_devices_for_vte_prophylaxis
Corporate Medical Policy Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: postsurgical_home_use_of_limb_ compression_devices_for_vte_prophylaxis
What evidence exists that describes the efficacy of mechanical prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adult surgical patients?
 July 2015 Rapid Review Evidence Summary McGill University Health Centre: Division of Nursing Research and MUHC Libraries What evidence exists that describes the efficacy of mechanical prophylaxis for venous
July 2015 Rapid Review Evidence Summary McGill University Health Centre: Division of Nursing Research and MUHC Libraries What evidence exists that describes the efficacy of mechanical prophylaxis for venous
Aspirin as Venous Thromboprophylaxis
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Nov 2, 2017 Aspirin as Venous Thromboprophylaxis Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Thromboembolism Consultant, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Disclosures
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Nov 2, 2017 Aspirin as Venous Thromboprophylaxis Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Thromboembolism Consultant, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Disclosures
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS. Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
The Royal College of Emergency Medicine. VTE Risk in Lower Limb Immobilisation in Plaster Cast 2015/2016
 The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Clinical Audits VTE Risk in Lower Limb Immobilisation in Plaster Cast Introduction 2015/2016 EXCELLENCE IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE A significant number of patients attend
The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Clinical Audits VTE Risk in Lower Limb Immobilisation in Plaster Cast Introduction 2015/2016 EXCELLENCE IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE A significant number of patients attend
Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014
 Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014 Case Presentation 75 y/o AAM Rectal bleeding & obstructive symptoms 11/12 Obstructing mass
Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014 Case Presentation 75 y/o AAM Rectal bleeding & obstructive symptoms 11/12 Obstructing mass
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism. João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal
 Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Hospital Acquired VTE: update on national guidance
 Hospital Acquired VTE: update on national guidance Rebecca Chanda Consultant Pharmacist - Thrombosis and Haemostasis Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Chair of the UK Clinical Pharmacy
Hospital Acquired VTE: update on national guidance Rebecca Chanda Consultant Pharmacist - Thrombosis and Haemostasis Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Chair of the UK Clinical Pharmacy
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
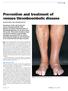 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
1. SCOPE of GUIDELINE:
 Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
CPT only copyright 2014 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. 12/23/2014 Page 66 of 593
 Measure #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2015 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2015 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 02.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 02.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Epidemiology of Thrombosis in Patients with Malignancy. Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism. Chew HK, Arch Int Med, Feb Blom et al, JAMA, Feb 2005
 Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Fatal P.E. Historic 1-2% Current %
 Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora MS (Ortho) DNB (Ortho) Dip SIROT (USA) FAPOA (Korea), FIGOF (Germany), FJOA (Japan) Commonwealth Fellow Joint Replacement (Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, London, UK) Senior
Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora MS (Ortho) DNB (Ortho) Dip SIROT (USA) FAPOA (Korea), FIGOF (Germany), FJOA (Japan) Commonwealth Fellow Joint Replacement (Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, London, UK) Senior
Guidelines for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Adults
 Guidelines for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Adults First Edition (2011) www.savte.com Dear Colleagues, It is our pleasure to introduce this booklet of guidelines for venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Guidelines for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Adults First Edition (2011) www.savte.com Dear Colleagues, It is our pleasure to introduce this booklet of guidelines for venous thromboembolism (VTE)
NoCVA Hospital Engagement Network SSI/VTE Safe Surgery Collaborative. December 13, 2012
 NoCVA Hospital Engagement Network SSI/VTE Safe Surgery Collaborative December 13, 2012 1 Hospital Acquired VTE Preventing a Preventable Problem It takes a commitment from ALL members of the healthcare
NoCVA Hospital Engagement Network SSI/VTE Safe Surgery Collaborative December 13, 2012 1 Hospital Acquired VTE Preventing a Preventable Problem It takes a commitment from ALL members of the healthcare
Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Post-Surgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018
 Prophylaxis Against Venous Thromboemblism (VTE) in Pediatric Trauma Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018 Arash Mahajerin, MD, MSCr Hematology, CHOC Children s Specialists Orange, CA Disclosure
Prophylaxis Against Venous Thromboemblism (VTE) in Pediatric Trauma Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018 Arash Mahajerin, MD, MSCr Hematology, CHOC Children s Specialists Orange, CA Disclosure
Thromboprophylaxis in Adult General Medical Patients - Guidelines for Management
 Thromboprophylaxis in Adult General Medical Patients - Guidelines for Management Adapted from the Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Guideline WAHT-MED-010 Version: Final Ratified by: Provider Quality
Thromboprophylaxis in Adult General Medical Patients - Guidelines for Management Adapted from the Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Guideline WAHT-MED-010 Version: Final Ratified by: Provider Quality
DENOMINATOR: All surgical patients aged 18 years and older undergoing procedures for which VTE prophylaxis is indicated in all patients
 Measure #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Quality ID #23 (NQF 0239): Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Factor Xa Inhibition in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Important Safety Information. Important Safety Information (cont d)
 Factor Xa Inhibition in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism: The Role of Fondaparinux WARNING: SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMAS Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients who are anticoagulated with
Factor Xa Inhibition in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism: The Role of Fondaparinux WARNING: SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMAS Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients who are anticoagulated with
Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
ASHP Therapeutic Position Statement on the Role of Pharmacotherapy in Preventing Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients
 ASHP Therapeutic Position Statements 599 ASHP Therapeutic Position Statement on the Role of Pharmacotherapy in Preventing Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients Position Hospitals should develop
ASHP Therapeutic Position Statements 599 ASHP Therapeutic Position Statement on the Role of Pharmacotherapy in Preventing Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients Position Hospitals should develop
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Policy Number: 1.01.28 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2013 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Policy Number: 1.01.28 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2013 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
TITLE: Acetylsalicylic Acid for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: A Review of Clinical Evidence, Benefits and Harms
 TITLE: Acetylsalicylic Acid for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: A Review of Clinical Evidence, Benefits and Harms DATE: 23 August 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Thromboembolism occurs when a blood
TITLE: Acetylsalicylic Acid for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: A Review of Clinical Evidence, Benefits and Harms DATE: 23 August 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Thromboembolism occurs when a blood
Disclosures. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: What every orthopaedic surgeon needs to know. Published Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: What every orthopaedic surgeon needs to know Paul F. Lachiewicz, MD Chapel Hill Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Consulting Professor Duke Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: What every orthopaedic surgeon needs to know Paul F. Lachiewicz, MD Chapel Hill Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Consulting Professor Duke Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient
 Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients
 Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric
Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge
 Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics Clinical guideline, V2
 Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics 11/11/11 TEMPORARY GUIDANCE There is no prophylactic tinzaparin available in the Trust currently. Please substitute enoxaparin
Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics 11/11/11 TEMPORARY GUIDANCE There is no prophylactic tinzaparin available in the Trust currently. Please substitute enoxaparin
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures
 Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Venous Thrombo-Embolism. John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase <48h)
 Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes
 C l i n i c a l R e v i e w A r t i c l e Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Medical Patients Brian S. Wojciechowski, MD David A. Cohen, MD Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes
C l i n i c a l R e v i e w A r t i c l e Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Medical Patients Brian S. Wojciechowski, MD David A. Cohen, MD Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
LIMB COMPRESSION DEVICES FOR VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 PROPHYLAXIS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
PROPHYLAXIS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
These are guidelines only and can be deviated from if it is thought to be in the patient s best interest.
 Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a recognised complication associated with inactivity and surgical procedures. Therefore, all
Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a recognised complication associated with inactivity and surgical procedures. Therefore, all
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Policy Number: 1.01.28 Last Review: 4/2019 Origination: 4/2013 Next Review: 4/2020 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Policy Number: 1.01.28 Last Review: 4/2019 Origination: 4/2013 Next Review: 4/2020 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
