Interleukin-10 (IL-10) Counterregulates IL-4-Dependent Effector Mechanisms in Murine Filariasis
|
|
|
- Nora Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 2004, p Vol. 72, No /04/$ DOI: /IAI Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) Counterregulates IL-4-Dependent Effector Mechanisms in Murine Filariasis Sabine Specht, 1,2 Lars Volkmann, 1 Tom Wynn, 3 and Achim Hoerauf 1,2 * Institute for Medical Parasitology, Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn, Bonn, 1 and Department of Helminthology, Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine, Hamburg, 2 Germany, and Immunology Section, Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 3 Received 18 February 2004/Returned for modification 26 March 2004/Accepted 25 July 2004 Interleukin-10 (IL-10) was at first described as a Th2-associated cytokine, although more recent reports have shown that immunosuppression applies to both Th1 and Th2 cell responses, e.g., when produced by T regulatory cells. This concept when applied to human filariasis would argue that high parasite loads are associated with IL-10, while bona fide Th2 responses, mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, are associated with parasite containment. To prove this relationship in a causal manner, we investigated the roles of IL-4 and IL-10 in a helminth infection model in which mice genetically deficient for IL-4, IL-10, or IL-4 plus IL-10 were infected with the rodent filaria Litomosoides sigmodontis. Compared to C57BL/6 wild-type and IL-10 knockout (KO) mice, IL-4 KO mice remained susceptible, exhibiting a remarkable number of live adult worms. Interestingly however, when the IL-10 gene was knocked out simultaneously with the IL-4 gene, the susceptibility of IL-4 KO mice was reversed. Although production of IFN- was increased in IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout mice, depletion of gamma interferon did not affect worm elimination, so it seems unlikely to be the major factor in mediating resistance in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice. Taken together, the results of this study add proof to the concept that has arisen for human filariasis that IL-10-dependent responses, which are associated with patency, are antagonistic to bona fide Th2 responses, which control parasite loads. The finding that knockout of IL-10 reversed a disease phenotype induced by knockout of IL-4 gives the first causal evidence of an antagonistic activity between IL-4 and IL-10 in an infection in vivo. Filariasis, which affects more than a 180 million people in the tropics, is a major cause of severe morbidity and considerable socioeconomic problems. Animal models are powerful tools to investigate immune mechanisms induced by different parasite developmental stages. The precise immune mechanisms that govern worm control in mice are only partially understood. The current consensus is that the host elicits a mixed T-helper type 1 (Th1) Th2 response, which is essential for the containment of different developmental stages. Thus, the Th1 cytokine IFN- is needed for adult worm control in murine infection with Brugia malayi (3) and Litomosoides sigmodontis (29), apparently through encapsulation and clearance mediated by neutrophils (1, 29). Furthermore, injection of B. malayi microfilariae (MF) into otherwise uninfected mice stimulated the production of IFN- (20, 21, 27, 28). On the other hand, interleukin-5 (IL-5) is essential for vaccine-mediated protection (24) and controls adult worm development and microfilaremia in primary infection (1, 25, 36). Of even more relevance for the present study is that IL-4 mediated pathways are necessary for the control of microfilaremia after full infection with L. sigmodontis L3 organisms that have developed into fertile adult worms (36, 37). In resistant C57BL/6 mice, IL-4 is required to prevent the development of adult worms as well as microfilaremia (22). The recently developed T regulatory concept (10), when * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Institute for Medical Parasitology, Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn, Sigmund-Freud-Str. 25, Bonn, Germany. Phone: (49) Fax: (49) hoerauf@parasit.meb.uni-bonn.de. applied to human and animal filariasis, would argue that in filariasis high worm and microfilarial loads are associated with the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10 (produced by T cells and also a variety of non-t cells), while bona fide Th2 responses, mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, are associated with parasite containment (13, 31, 35). However, direct evidence for IL-10 being antagonistic to IL-4 in regard to parasite loads has not been obtained so far for helminth infection. Thus, in murine schistosomiasis, IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout (KO) mice succumbed earlier to infection than their single-ko littermates but showed equivalent parasite loads (15). In the present study, we infected mice deficient for IL-4, IL-10, or both cytokines with the rodent filaria L. sigmodontis. Confirming earlier data (22), adult worms and MF were recovered from IL-4-deficient mice on the resistant C57BL/6 background. However, the additional knockout of IL-10 led to a reversal in worm load. This indicates a counterregulatory role for IL-10 in the susceptibility conferred by IL-4 deficiency. (This study formed part of a Ph.D. thesis by S. Specht at the Faculty of Biology, University of Hamburg.) MATERIALS AND METHODS Animal maintenance and infection of mice with L. sigmodontis. IL-4/IL-10 KO mice on a C57BL/6 background were obtained from A. Sher and T. Wynn (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md.). IL-10 KO mice on a C57BL/6 background (19) were provided by H. Mossmann (Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology, Freiburg, Germany). IL-4 KO mice and C57BL/6 wild-type (wt) mice (originally from Jackson Laboratories) and the knockout strains mentioned above were housed under specific-pathogen-free conditions in microisolator cages. KO offspring, wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and cotton rats were bred at the 6287
2 6288 SPECHT ET AL. INFECT. IMMUN. animal facilities of the Bernhard Nocht Institute. Natural infections were performed as described previously (2). At least five mice were used for each group. Parasite recovery. Adult worms were removed from the pleural cavity and counted at days 42 and 65 postinfection (p.i.). The thoracic cavity was flushed with 2 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1% fetal calf serum (FCS), and the worms were allowed to sediment. The microfilaria count was determined from 50 l of EDTA-treated peripheral blood or 200 l of pleural cavity flush after staining with Hinkelmann s solution (0.5% [wt/vol] eosin Y, 0.5% [wt/vol] phenol and [vol/vol] formaldehyde in distilled water) as described previously (2). Purification of peripheral blood MF. MF were purified from the peripheral blood of cotton rats on a Percoll gradient as described previously (6). In brief, isosmotic Percoll was prepared by mixing 9 parts of Percoll (density, g/ml) with 1 part of 2.5 M sucrose. Various dilutions of the isosmotic Percoll in 0.25 M sucrose were made to obtain 25, 30, and 35% solutions. The gradient dilutions were layered in 15-ml tubes, and peripheral blood, diluted 1:2, was pipetted onto the Percoll layers. The tubes were then centrifuged at 400 g for 30 min at room temperature. Recovered MF (between the 25 and 30% layers) were washed with RPMI % FCS, and viable MF were injected intravenously into naive mice. Analysis of developmental stages of MF. The fertility of the worms was determined by assessing the presence or absence of embryonic stages in squeeze preparations of individual worms. Formalin-fixed worms were placed in a small volume of PBS on a glass slide and cut in the midpoint. Another glass slide was placed on top of the worm, and the two slides were gently pressed together to force the contents of the worms into the phosphate-buffered solution. Uterine tube contents were examined at a magnification of 40. The stages checked for were morula and fully elongated (stretched) microfilariae. The examiner was blind to the origin of samples. Cell culture. The culture of splenocytes was carried out in 96-well culture plates (Greiner, Frickenhausen, Germany) in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS, glutamine, and gentamicin at 37 C with 5% CO 2. Spleens were teased to single-cell suspension, and erythrocytes were removed by incubation with ammonium chloride. Pleural cavity cells ( ) and whole splenocytes were cultured for 72 h in the presence of medium, 10 g ofl. sigmodontis adult worm antigen per well, or 50 ng of concanavalin A per well. Supernatants were removed and frozen for cytokine determination. Cytokine assays. Concentrations of the cytokines IFN-, IL-10, and IL-4 in the pleural wash, serum (dilution of 1:10), and culture supernatant were determined by specific two-site enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), using standard protocols. The antibody pairs for capture and detection (biotinylated) were purchased from BD PharMingen (Heidelberg, Germany) in the combinations recommended. They were used at a concentration of 1 g/ml. Recombinant cytokines (BD PharMingen) were used as standards. IL-13 ELISA was performed with the Duo ELISA kit (R&D Systems, Wiesbaden, Germany). All ELISAs were developed after incubation with streptavidin-peroxidase complex (1:10,000; Roche-Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany), using 3,5,3,5 -tetramethylbenzidine (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) at 6 mg/ml in dimethyl sulfoxide as the substrate. The sensitivity was 20 pg/ml. Antibody treatment. Monoclonal antibodies were purified from hybridoma culture supernatants (XMG 1.2, anti-ifn- ; TRFK-4, control isotype) by ammonium sulfate precipitation and affinity purification over a protein G column (Pharmacia, Freiburg, Germany) according to standard procedures. Mice were treated at weekly intervals with 1 mg/mouse starting on day 20 until day 41 postinfection. Antibody isotype analysis. Microtiter plates were coated overnight with 10 g of L. sigmodontis adult worm antigen per ml in PBS (ph 9.6). After blocking with 1% bovine serum albumin, sera (1:1,000) were incubated for 5 h at room temperature. After washing, plates were incubated with isotype-specific anti-mouse immunoglobulin antibodies conjugated with biotin (PharMingen) for 1 h. ELISAs were developed after incubation with streptavidin-peroxidase complex (1:10,000; Boehringer), using 3,5,3,5 -tetramethylbenzidine (Roth) at 6 mg/ml in dimethyl sulfoxide as the substrate. Statistical analysis. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test, including Bonferroni correction, was performed to assess the statistical differences in parasite loads, microfilarial clearance, and humoral immunoglobulin G (IgG) production. Furthermore, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine differences attributable to the mouse strains independent of the variance of the single experiments. ANOVA was done for parasite loads, MF counts (which had been log transformed to meet parametric assumptions), and IL-10 and IFN- production by splenocytes. A P value of 0.05 was considered to represent a statistically significant difference. Box plots represent medians and percentiles (10, 25, 50, 75, and 90%). FIG. 1. L. sigmodontis-infected IL-4 KO mice contain significantly (Mann-Whitney U test and Bonferroni correction, P ) more adult parasites than L. sigmodontis-infected C57BL/6, IL-10 KO, or IL-4/IL-10 KO mice at day 65 postinfection. Viable parasites were obtained by pleural lavage and counted. Results from one of six consistent experiments comprising six to eight animals per group are shown. RESULTS Susceptibility of IL-4 KO mice to L. sigmodontis infection is reversed when IL-10 is knocked out. The courses of infection in C57BL/6 wt, IL-4 KO, IL-10 KO, and IL-4/IL-10 double-ko mice were monitored. At day 42 p.i., adult worms were recovered from all mouse strains, with IL-4 KO mice having slightly higher worm loads (data not shown). At day 65 p.i., all worms had been cleared in wild-type mice, whereas IL-4 KO mice still harbored a significant number of worms (Fig. 1). Interestingly, the additional deficiency of IL-10 in IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout mice reversed the susceptibility seen in IL-4 KO mice. Only two out of six double-knockout mice harbored three and five adult worms, respectively, whereas all six IL-4 KO mice contained adult worms (range, 16 to 147). IL-10 KO mice showed worm levels equivalent to those of IL-4/IL-10 KO mice. This finding was reproduced in six additional experiments. ANOVA testing confirmed for all seven experiments that parasite loads were independent from experiment to experiment variation but strictly depended on the single (IL-4 KO) versus double (IL-4/IL-10 KO) deficiency (P ). Worms in IL-4 knockout mice also reached sexual maturity and released microfilariae into the thoracic cavity and eventually in the blood. No microfilariae were detected in the pleural cavity or blood of wild-type, IL-10 KO, or IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout mice (Table 1). Equivalent clearance of intravenously injected microfilariae in all mouse strains. In order to monitor clearance of MF without interference of adult worms, 100,000 MF of L. sigmodontis were injected intravenously. IL-10 KO mice were not available for this experiment but are known to show declines of MF equivalent to those in wild-type C57BL/6 mice (17). All mouse strains cleared the MF with similar kinetics (Fig. 2). A 50% drop in microfilaremia was seen on day 1 following injection in all strains. No microfilaremia was detected past day 6. This indicates that there is no direct effect of cytokine deficiency on MF containment. Filaria-specific antibody responses do not correlate with the parasite load. L. sigmodontis antigen-specific antibodies in the
3 VOL. 72, 2004 ANTAGONISM BETWEEN IL-10 AND IL TABLE 1. Development of patent infection in IL-4 KO mice but not in IL-10 KO strains a Strain No. of MF in b : Pleural lavage fluid (200 l) Blood (50 l) C57BL/6 0 0 IL-4 KO 31 (1 1,982) c 0 (0 113) d IL-10 KO 0 0 IL-4/IL-10 KO 0 0 a Blood and pleural cavity MF statuses in L. sigmodontis-infected C57BL/6 and IL-10-, IL-4, and IL-4/IL-10-deficient mice were assessed at day 65 p.i. b Medians (10 to 90% percentiles) are given. c P by ANOVA of log-transformed pleural lavage fluid MF counts. d P by ANOVA of log-transformed blood MF counts. sera on day 65 p.i. were investigated. Consistent with the fact that IL-4 is a major factor in class switching to IgG1, the two strains deficient for IL-4 produced little to no filaria-specific IgG1 (Fig. 3A). Conversely, these strains displayed elevated levels of IgG2a (Fig. 3B). he fact that immunoglobulin subclass production followed the pattern of IL-4 expression but not that of parasite loads suggests that antifilarial antibodies of these subclasses do not correlate with parasite containment in these mouse strains. Anti-IFN- antibody does not alter parasite loads in IL-4/ IL-10 KO mice. Given that in BALB/c mice an impact of IFN- on the control of adult worms was shown earlier (29), it was of interest to monitor IFN- production in the different mouse strains after L. sigmodontis infection. At day 65 p.i., splenocytes of KO strains in comparison to wild-type mice displayed increased levels of IFN- in vitro upon stimulation with mitogen or L. sigmodontis antigen (Fig. 4), with much larger amounts being produced by the IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout mice than by IL-4 single-knockout mice. In IL-4/IL-10 KO and IL-10 KO mice, elevated basal secretion of IFN- was observed. FIG. 2. There is no difference in the clearance of microfilariae (mean values standard errors of the means) following intravenous injection of 100,000 MF in C57BL/6, IL-4 KO, and IL-4/IL-10 KO mice (n 8 in each group). Results from one of two consistent experiments are shown. FIG. 3. Humoral analysis of C57BL/6, IL-4 KO, IL-4/IL-10 KO, and IL-10 KO mice following infection. Results for filarial specific IgG1 (A) and IgG2a (B) are shown, representing one of two consistent experiments. For each isotype, four or five mice were bled at day 65 p.i. by retro-orbital venipuncture. Sandwich ELISA was performed to determine the filaria-specific concentration of the relevant isotype in serum. *, significant difference in IgG concentration (Mann-Whitney U test and Bonferroni correction, P ). To find out whether the increase in IFN- production in IL-4/IL-10 double-knockout mice was responsible for their resistance to a patent infection, anti-ifn- antibody was injected into the peritoneal cavities of these mice at weekly intervals from day 20 to day 41 p.i. in a separate experiment. Mice were sacrificed and analyzed for their worm containment at 65 days p.i. Consistently, the number of worms found in the thoracic cavities of IL-4 KO mice was significantly higher than that in all other strains. However, in two separate experiments no difference was observed between anti-ifn- -treated and control Ig-treated IL-4/IL-10 KO mice (Fig. 5). There was also no significant difference (determined by ANOVA) when data from the two experiments were combined. An insufficient efficacy of the anti-ifn- antibody treatment is not likely, since rectal prolapse development in the IL-4/IL-10 KO strain (observed in approximately one-third of cases) was reversed each time after the repeated injections. In addition, analysis of IFN- levels at day 65 p.i., i.e., 23 days after the last antibody administration, showed that IFN- levels were highly elevated in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice ( pg/ml [mean standard error) but were reduced to the level of that of IL-4 KO mice (11 9 pg/ml) in anti-ifn- -treated IL-4/IL-10 KO mice (7 6 pg/ml). As a further control experiment, IFN- KO mice on a C57BL/6 background were infected with L. sigmodontis. The
4 6290 SPECHT ET AL. INFECT. IMMUN. FIG. 4. Splenocytes of infected mice with IL-10 deficiency show higher IFN- production at day 65 p.i. after restimulation with filarial antigen (B) or concanavalin A (ConA) (C), as do unstimulated (A) cells. Sandwich ELISA was performed to determine the murine IFN- concentration. Results from two consistent experiments, comprising four or five animals per group, were combined by using ANOVA, which showed that this difference is not due to variations from infections. The asterisks indicate significantly higher IFN- levels in IL-10 and IL-4/IL-10 KO strains compared to wild-type and IL-4 KO mice (P ) (A, B, and C) and in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice compared to IL-10 KO mice (P 0.05) (A and B). course of parasite infection appeared to be equivalent to that in C57BL/6 wt mice in that at day 65 p.i. (i.e., at the time point when IL-4/IL-10 KO mice treated with anti-ifn- were assessed), neither strain contained adult worms (data not shown). This further suggests that in mice on the C57BL/6 background, IFN- is not a major mediator of parasite control. FIG. 5. Treatment of infected IL-4/IL-10 KO mice with anti-ifn- antibodies (horizontal stripes) has no effect on worm load compared to that in IL-4/IL-10 mice treated with control Ig. C57BL/6, IL-10 KO, IL-4 KO, and IL-4/IL-10 KO mice were naturally infected with L. sigmodontis, and the worm load was analyzed 65 days later. *, significant increase in IL-4 KO mice compared to all other genotypes of mice (P 0.05), with four to seven mice per group (four in the antibodytreated groups). IL-4 KO mice permit worm embryogenesis, while IL-4/IL-10 KO mice do not. In order to monitor the effects of IL-4 and IL-10 on worm fertility, adult female worms recovered from the thoracic cavity were subjected to an analysis of embryogenesis, using the squeeze preparation technique. Development from oocytes to stretched and motile micofilariae was accomplished only in IL-4 KO mice. However, embryos prepared from worms recovered from IL-4/IL-10 double-ko mice failed to develop past the morula stage (Table 2). These data suggest that IL-4 and IL-10 exert contrasting effects on embryogenesis in murine filariasis. IL-10 levels in sera are elevated in IL-4 KO mice. The data described above suggested that IL-10 might be involved, probably indirectly, in the embryogenesis and thus in permissivity towards filarial infection in IL-4 KO mice. In support of this, blood was drawn from the animals from three experiments and then analyzed collectively by Student s t test. Sera from IL-4 KO mice showed elevated levels of IL-10 at day 65 p.i. compared to those from C57BL/6 wt mice (Fig. 6). IL-13 is not elevated in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice. In order to look for other possible mechanisms of parasite control in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice, IL-13 levels in serum and pleural lavage fluid were analyzed at day 65 p.i. No significant difference between mouse strains was observed when four independent experiments with TABLE 2. Fertility of Litomosoides worms as determined by squeeze preparations Strain No. of mice No. of worms Embryo development in female worms at day 65 p.i. No. of worms positive for morula stage No. of worms positive for stretched MF C57BL/ IL-4 KO IL-10 KO IL-4/IL-10 KO
5 VOL. 72, 2004 ANTAGONISM BETWEEN IL-10 AND IL FIG. 6. IL-10 levels in sera of mice infected naturally with L. sigmodontis. Significantly (P ) elevated levels were observed in IL-4 KO mice. The data represent the combined analysis of sera from animals of three experiments analyzed with Student s t test. ANOVA confirmed that the significant difference did not arise from variation in the natural infection model. sera (Fig. 7A) (ANOVA, P 0.05) and eight independent experiments with pleural lavage fluid (Fig. 7B) (ANOVA, P 0.05) were analyzed. This argues against the hypothesis that elevated IL-13 mediates resistance in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice compared to full susceptibility in IL-4 KO mice. DISCUSSION Infections with filarial worms in humans and mice typically induce a Th2 response as do other helminth infections, with the classic hallmarks being elevated production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 as well as elevated levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia. For quite some time after the establishment of the Th1-Th2 dichotomy, IL-10 was also considered a Th2 marker, at least in mice, due to its profound antagonistic effects on Th1 responses, while inhibitory effects on IL-5 production by human T cells have been known for a longer time (32, 41, 42). Increasing evidence from animal models of allergic diseases suggests that IL-10 acts as an inhibitor of Th2 responses in vitro and in vivo (8). However, a direct antagonism between IL-4 and IL-10 has not been shown so far. The novel finding in this study is that causal evidence for such an antagonism can be directly demonstrated for parasite loads in a helminth infection. Thus, while deficiency of IL-4 permitted persistence of filarial worms and microfilarial production, this permissivity was reversed in mice deficient in both IL-4 and IL-10 (Fig. 1). The presence of IL-10 and absence of IL-4 in this system were associated with embryo development (Table 2). Our results on the role of IL-10 in compromising Th2 cytokine-mediated protection differ from earlier data for murine T. muris infection, where deficiency of IL-10 and IL-4 led to a failure to eliminate Trichuris muris larvae (33). In this model, IL-4/IL-10 double-ko mice showed neither an increased nor a reduced larval burden in comparison to single-knockout mice. The differences from murine filariasis may be due to (i) the fact that IL-10 per se is essential for worm control in T. muris and (ii) the fact that Th1 responses promote susceptibility to T. muris infection and are similarly induced in mice deficient for IL-10, IL-4, or both cytokines, while in murine filariasis Th1 FIG. 7. IL-13 levels in sera (A) and pleural lavage fluid (B) of mice naturally infected with L. sigmodontis. No significant differences could be observed between C57BL/6, IL-4 KO, IL-10 KO, and IL-4/IL-10 KO mice when analyses of four (A) and eight (B) experiments were combined and analyzed with Student s t test. ANOVA confirmed that the significant difference did not arise from variation in the natural infection model. responses either do not influence parasite loads (C57BL/6 background) or are associated with protection (29). One may conclude from this comparison that different mechanisms of parasite control are effective in different helminth infections. Accordingly, in experimental murine schistosomiasis, mice deficient for either IL-10 or IL-4 or for both cytokines displayed parasite loads that were not different from those of wild-type mice (15, 16, 40). Differences from schistosomiasis were also found in regard to infection-induced IFN- production in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice. While IL-4/IL-10 KO mice had an excessive Th1 response to schistosomiasis and died significantly earlier than did single-ko mice, in our study IL-4/IL-10 KO mice did not succumb to infection, although IFN- levels were strongly elevated compared to those in wt and IL-4 KO mice and were elevated to a lesser extent compared to those in IL-10 KO mice (Fig. 4). In addition, the role of IFN- in parasite control seems to differ between schistosomiasis and filariasis: in BALB/c mice the complete absence of IFN- resulted in increased loads of adult filariae, whereas only small amounts of IFN-, as observed in IL-12 KO mice, were sufficient to limit adult worm loads to the level in BALB/c control mice (29). This is different on the C57BL/6 background, where IFN-
6 6292 SPECHT ET AL. INFECT. IMMUN. deficiency does not result in elevated worm loads (data not shown). Still, the control experiment with C57BL/6 IFN- KO mice does not exclude a protective role for IFN- in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice, all the more since elevated IFN- levels were observed in these mice. Therefore, we administered neutralizing anti- IFN- monoclonal antibody at weekly intervals from day 20 to 41, i.e., at time points when maturation of worms and embryogenesis take place. While the injections did reverse rectal prolapse development, thus demonstrating in vivo efficacy, they did not influence L. sigmodontis infection. Although we cannot fully exclude the possibility that the antibody might have reached the colonic tissue and prevented rectal prolapse but would not affect the local inflammatory environment that controls the worms, our data rather argue against IFN- being the major factor of resistance in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice. Surprisingly, the ratio of IFN- induction by mitogen or specific antigen over medium in splenic cell cultures was rather low (Fig. 4). This correlated with high baseline secretion by cells from IL-10 and IL-4/IL-10 KO strains. This may be due to the existence of T cells, which are already stimulated in vivo by the L. sigmodontis infection, or may reflect the fact the sources other than T cells contribute to IFN- production in these mice. IL-13 is yet another cytokine that could be responsible for the reversion of susceptibility in IL-4/IL-10 compared to IL-4 KO mice. Therefore, the levels of this cytokine in the sera and thoracic cavity fluids of the mice were determined (Fig. 7), but no significant differences were found. This result, however, still does not fully exclude a biological role for IL-13, because its functional efficiency is controlled by expression of an IL-13 decoy receptor (sil-13r 2-Fc). Since IFN- was found (via IL-12) to downregulate decoy receptor expression and thus to increase the functional effect of IL-13 (7), it is possible that elevated IFN- levels in IL-4/IL-10 KO mice might have led to increased function of IL-13. An elegant way to prove such a compensatory effect of IL-13 would have been the treatment with recombinant IL-13 decoy receptor (formerly from Wyeth, Cambridge, Mass.), which unfortunately is no longer available. Deficiency of IL-4 drastically increases susceptibility to filariasis, and in particular to L. sigmodontis infection, in mice of both susceptible BALB/c and resistant C57BL/6 backgrounds. Microfilaremia is enhanced throughout (22, 36, 37), while in IL-4 KO mice on a C57BL/6 background the life span of adult worms also appears to be prolonged (22). The precise mechanism of IL-4 action, however, remains unclear. Antibodies do not play a major role, given that MT KO mice, which have no functional B cells, do not display an altered course of parasite infection (26, 37). A direct effect of IL-4 on worm embryogenesis could be excluded in our earlier work, given that IL-4R KO mice displayed grossly the same phenotype as IL-4 KO mice (36). The finding of elevated levels of IL-10 in sera of IL-4 KO mice in the present study may indicate that IL-10 promotes patency in these mice. This would be in line with our finding of patency reversal by additional deficiency of IL-10 as well as with an earlier study of L. sigmodontis infection in which IL-10 was found to be necessary for microfilariaremia persistence upon transfer of adult fertile female filariae (17). Evidence for antagonistic effects of IL-4 and IL-10 can also be found in human filarial infection. In onchocerciasis, patients with generalized disease and high microfilarial skin loads have peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) that show low proliferation to onchocercal antigen but produce large amounts of IL-10. This is in contrast to the hyperreactive Sowda form of onchocerciasis, in which microfilariae are effectively reduced by Th2-mediated mechanisms and in which PBMC proliferate vigorously and produce highly elevated IL-5 but only little IL-10 upon antigen-specific stimulation (4, 9, 12). In another large survey, IL-5 production in whole blood of patients was inversely related to MF skin loads (5). At least part of the IL-10 response is driven by regulatory T cells (Tr-1 cells), which could be cloned from PBMC as well as from onchocercomas. These Tr-1 cells were shown to inhibit Th1 and Th2 clones in vitro (31). In PBMC from patients with lymphatic filariasis, high MF loads also were positively associated with IL-10 and correlated negatively with IL-5 (18, 23, 30). While a direct interventional study with humans to prove these associations is ethically not possible, our results using the well defined murine filariasis model of L. sigmodontis infection provide the first causal evidence to date for an antagonism between IL-4 and IL-10 in filariasis control. There are several potential pathways of IL-10 downregulation of parasite control mechanisms. While direct action of IL-10 on worm fertility can in principle not be excluded, there exist several other proven avenues of IL-10 downregulating the effector function of effector cells such as macrophages, eosinophils, and/or neutrophils (34, 38, 39, 42). Increasing evidence for an antagonism between IL-4 and IL-10 comes from the field of allergy. Thus, transfer of Tr-1 cells inhibited antigen-specific serum IgE responses in OVAimmunized mice (8). In humans, antigen-specific desensitization was associated with an increase of antigen-specific production of IL-10, suggesting that antigen-specific IL-10 induction is key to a novel concept of treatment of allergy and asthma. Given that protective immune mechanisms against helminths and allergic responses have a common evolutionary basis, it seems logical that the antagonistic downregulatory mechanisms also are similar. Thus, the genetic predisposition to allergy can be interpreted as an evolutionary advantage in the defense against helminths. Rather, the same genetic variants that are associated with atopy (11) are also linked to hyperreactivity against onchocerciasis, which is harmful to the host (14). The elucidation of antagonistic effects between IL-4 and IL-10 therefore improves our understanding of both helminth infection and allergy. Inasmuch as IL-10 induction may prevent allergy, neutralization of IL-10 may improve vaccination against helminths, as has been shown for schistosomiasis (16). The present study has given the first causal evidence of an antagonism of IL-4 and IL-10 in regard to parasite loads in a helminth infection. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank K. Fischer for expert technical assistance and B. Richter, Y. Richter, and A. Ali for maintaining the colonies of KO mice. We also thank H. Mossmann (MPI for Immunobiology, Freiburg, Germany) for the IL-10 KO strain. Financial support from the German Research Foundation (grant Ho/2009/1-1/3 and 1/4) is gratefully acknowledged.
7 VOL. 72, 2004 ANTAGONISM BETWEEN IL-10 AND IL REFERENCES 1. Al-Qaoud, K. M., E. Pearlman, J. Klukowski, T. Hartung, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf A new mechanism for IL-5 dependent helminth control: neutrophil accumulation and neutrophil-mediated worm encapsulation in murine filariasis are abolished in the absence of IL-5. Int. Immunol. 12: Al-Qaoud, K. M., A. Taubert, H. Zahner, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf Infection of BALB/c mice with the filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis: role of CD4 T cells in controlling larval development. Infect. Immun. 65: Babu, S., L. M. Ganley, T. R. Klei, L. D. Shultz, and T. V. Rajan Role of gamma interferon and interleukin-4 in host defense against the human filarial parasite Brugia malayi. Infect. Immun. 68: Brattig, N., C. Nietz, S. Hounkpatin, R. Lucius, F. Seeber, U. Pichlmeier, and T. Pogonka Differences in cytokine responses to Onchocerca volvulus extract and recombinant Ov33 and OvL3 1 proteins in exposed subjects with various parasitologic and clinical states. J. Infect. Dis. 176: Brattig, N. W., B. Lepping, C. Timmann, D. W. Büttner, Y. Marfo, C. Hamelmann, and R. D. Horstmann Onchocerca volvulus-exposed persons fail to produce interferon-gamma in response to O. volvulus antigen but mount proliferative responses with interleukin-5 and IL-13 production that decrease with increasing microfilarial density. J. Infect. Dis. 185: Chandrashekar, R., U. R. Rao, P. B. Parab, and D. Subrahmanyam Brugia malayi: rat cell interactions with infective larvae mediated by complement. Exp. Parasitol. 62: Chiaramonte, M. G., M. Mentink-Kane, B. A. Jacobson, A. W. Cheever, M. J. Whitters, M. E. Goad, A. Wong, M. Collins, D. D. Donaldson, M. J. Grusby, and T. A. Wynn Regulation and function of the interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 during a T helper cell type 2-dominant immune response. J. Exp. Med. 197: Cottrez, F., S. D. Hurst, R. L. Coffman, and H. Groux T regulatory cells 1 inhibit a Th2-specific response in vivo. J. Immunol. 165: Doetze, A., J. Satoguina, G. Burchard, T. Rau, C. Löliger, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf Antigen-specific cellular hyporesponsiveness in generalized onchocerciasis is mediated by Th3/Tr1-type cytokines IL-10 and TGFbeta but not by a Th1 to Th2 shift. Int. Immunol. 12: Groux, H An overview of regulatory T cells. Microbes Infect. 3: Heinzmann, A., X. Q. Mao, M. Akaiwa, R. T. Kreomer, P. S. Gao, K. Ohshima, R. Umeshita, Y. Abe, S. Braun, T. Yamashita, M. H. Roberts, R. Sugimoto, K. Arima, Y. Arinobu, B. Yu, S. Kruse, T. Enomoto, Y. Dake, M. Kawai, S. Shimazu, S. Sasaki, C. N. Adra, M. Kitaichi, H. Inoue, K. Yamauchi, N. Tomichi, F. Kurimoto, N. Hamasaki, J. M. Hopkin, K. Izuhara, T. Shirakawa, and K. A. Deichmann Genetic variants of IL-13 signalling and human asthma and atopy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9: Hoerauf, A Immune effectors important in protective resistance, p In T. Klei and T. V. Rajan (ed.), World class parasites: the filariae. Kluwer Academic Press, New York, N.Y. 13. Hoerauf, A., and N. Brattig Resistance and susceptibility in human onchocerciasis -beyond Th1 vs. Th2. Trends Parasitol. 18: Hoerauf, A., S. Kruse, N. W. Brattig, A. Heinzmann, B. Mueller-Myhsok, and K. A. Deichmann The variant Arg110Gln of human IL-13 is associated with an immunologically hyper-reactive form of onchocerciasis (sowda). Microbes Infect. 4: Hoffmann, K. F., A. W. Cheever, and T. A. Wynn IL-10 and the dangers of immune polarization: excessive type 1 and type 2 cytokine responses induce distinct forms of lethal immunopathology in murine schistosomiasis. J. Immunol. 164: Hoffmann, K. F., S. L. James, A. W. Cheever, and T. A. Wynn Studies with double cytokine-deficient mice reveal that highly polarized Th1- and Th2-type cytokine and antibody responses contribute equally to vaccineinduced immunity to Schistosoma mansoni. J. Immunol. 163: Hoffmann, W. H., A. W. Pfaff, H. Schulz-Key, and P. T. Soboslay Determinants for resistance and susceptibility to microfilaraemia in Litomosoides sigmodontis filariasis. Parasitology 122: King, C. L., S. Mahanty, V. Kumaraswami, J. S. Abrams, J. Regunathan, K. Jayaraman, E. A. Ottesen, and T. B. Nutman Cytokine control of parasite-specific anergy in human lymphatic filariasis. Preferential induction of a regulatory T helper type 2 lymphocyte subset. J. Clin. Investig. 92: Kuhn, R., J. Lohler, D. Rennick, K. Rajewsky, and W. Muller Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75: Lawrence, R. A., J. E. Allen, and C. A. Gray Requirements for in vivo IFN-gamma induction by live microfilariae of the parasitic nematode, Brugia malayi. Parasitology 120: Lawrence, R. A., J. E. Allen, J. Osborne, and R. A. Maizels Adult and microfilarial stages of the filarial parasite Brugia malayi stimulate contrasting cytokine and Ig isotype responses in BALB/c mice. J. Immunol. 153: Le Goff, L., T. J. Lamb, A. L. Graham, Y. Harcus, and J. E. Allen IL-4 is required to prevent filarial nematode development in resistant but not susceptible strains of mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 32: Mahanty, S., H. E. Luke, V. Kumaraswami, P. R. Narayanan, V. Vijayshekaran, and T. B. Nutman Stage-specific induction of cytokines regulates the immune response in lymphatic filariasis. Exp. Parasitol. 84: Martin, C., K. M. Al-Qaoud, O. Bain, K. Paehle, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf IL-5 is essential for protection after immunization against murine filariasis but not during primary infection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 189: Martin, C., L. Le Goff, M. N. Ungeheuer, P. N. Vuong, and O. Bain Drastic reduction of a filarial infection in eosinophilic interleukin-5 transgenic mice. Infect. Immun. 68: Martin, C., M. Saeftel, P. N. Vuong, S. Babayan, K. Fischer, O. Bain, and A. Hoerauf B-cell deficiency suppresses vaccine-induced protection against murine filariasis but does not increase the recovery rate for primary infection. Infect. Immun. 69: Osborne, J., S. J. Hunter, and E. Devaney Anti-interleukin-4 modulation of the Th2 polarized response to the parasitic nematode Brugia pahangi. Infect. Immun. 64: Pearlman, E., F. E. Hazlett, W. H. Boom, and J. W. Kazura Induction of murine T helper cell responses to the filarial nematode Brugia malayi. Infect. Immun. 61: Saeftel, M., L. Volkmann, S. Korten, N. Brattig, K. M. Al-Qaoud, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf Lack of IFN- confers impaired neutrophil granulocyte function and imparts prolonged survival of adult filarial worms in murine filariasis. Microbes Infect. 3: Sartono, E., Y. C. Kruize, A. Kurniawan, R. M. Maizels, and M. Yazdanbakhsh Depression of antigen-specific interleukin-5 and interferongamma responses in human lymphatic filariasis as a function of clinical status and age. J. Infect. Dis. 175: Satoguina, J., M. Mempel, J. Larbi, M. Badusche, C. Loliger, O. Adjei, G. Gachelin, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf Antigen-specific T regulatory-1 cells are associated with immunosuppression in a chronic helminth infection (onchocerciasis). Microbes Infect. 4: Schandene, L., C. Alonso-Vega, F. Willems, C. Gerard, A. Delvaux, T. Velu, R. Devos, M. de Boer, and M. Goldman B7/CD28-dependent IL-5 production by human resting T cells is inhibited by IL-10. J. Immunol. 152: Schopf, L. R., K. F. Hoffmann, A. W. Cheever, J. F. Urban, Jr., and T. A. Wynn IL-10 is critical for host resistance and survival during gastrointestinal helminth infection. J. Immunol. 168: Stampfli, M. R., M. Cwiartka, B. U. Gajewska, D. Alvarez, S. A. Ritz, M. D. Inman, Z. Xing, and M. Jordana Interleukin-10 gene transfer to the airway regulates allergic mucosal sensitization in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 21: Steel, C., and T. B. Nutman Ctla-4 in filarial infections: implications for a role in diminished T cell reactivity. J. Immunol. 170: Volkmann, L., O. Bain, M. Saeftel, S. Specht, K. Fischer, F. Brombacher, K. I. Matthaei, and A. Hoerauf Murine filariasis: interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 lead to containment of different worm developmental stages. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 192: Volkmann, L., M. Saeftel, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf Interleukin-4 is essential for the control of microfilariae in murine infection with the filaria Litomosoides sigmodontis. Infect. Immun. 69: Wang, P., P. Wu, M. I. Siegel, R. W. Egan, and M. M. Billah Interleukin (IL)-10 inhibits nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) activation in human monocytes. IL-10 and IL-4 suppress cytokine synthesis by different mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 270: Williams, L., L. Bradley, A. Smith, and B. Foxwell Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is the dominant mediator of the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 172: Wynn, T. A., and K. F. Hoffmann Defining a schistosomiasis vaccination strategy is it really Th1 versus Th2? Parasitol. Today 16: Zuany-Amorim, C., C. Creminon, M. C. Nevers, M. A. Nahori, B. B. Vargaftig, and M. Pretolani Modulation by IL-10 of antigen-induced IL-5 generation, and CD4 T lymphocyte and eosinophil infiltration into the mouse peritoneal cavity. J. Immunol. 157: Zuany-Amorim, C., S. Haile, D. Leduc, C. Dumarey, M. Huerre, B. B. Vargaftig, and M. Pretolani Interleukin-10 inhibits antigen-induced cellular recruitment into the airways of sensitized mice. J. Clin. Investig. 95: Editor: J. F. Urban, Jr.
B-Cell Deficiency Suppresses Vaccine-Induced Protection against Murine Filariasis but Does Not Increase the Recovery Rate for Primary Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 2001, p. 7067 7073 Vol. 69, No. 11 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7067 7073.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. B-Cell
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 2001, p. 7067 7073 Vol. 69, No. 11 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7067 7073.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. B-Cell
Transmission Intensity Affects Both Antigen-Specific and Nonspecific T-Cell Proliferative Responses in Loa loa Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2002, p. 1475 1480 Vol. 70, No. 3 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1475 1480.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Transmission
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2002, p. 1475 1480 Vol. 70, No. 3 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1475 1480.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Transmission
Regulatory Networks Induced by Live. in Patent Lymphatic Filariasis: Implications for Parasite Persistence
 This information is current as of April 13, 2017. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Regulatory Networks Induced by Live Parasites Impair Both Th1 and Th2 Pathways in Patent Lymphatic Filariasis:
This information is current as of April 13, 2017. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Regulatory Networks Induced by Live Parasites Impair Both Th1 and Th2 Pathways in Patent Lymphatic Filariasis:
Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma
 Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
Received 30 May 2003/Returned for modification 26 July 2003/Accepted 22 September 2003
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 2003, p. 6820 6829 Vol. 71, No. 12 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.6820 6829.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Resistance
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 2003, p. 6820 6829 Vol. 71, No. 12 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.6820 6829.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Resistance
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Page # Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology. Four Types of Hypersensitivity. Friend of Foe? Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency
 Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency Allergy and Asthma Graft rejection and Lupus Friend of Foe? Four Types of Hypersensitivity Allergic Responses - Type
Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency Allergy and Asthma Graft rejection and Lupus Friend of Foe? Four Types of Hypersensitivity Allergic Responses - Type
Th2 Cell-Intrinsic Hypo-Responsiveness Determines Susceptibility to Helminth Infection
 Th2 Cell-Intrinsic Hypo-Responsiveness Determines Susceptibility to Helminth Infection Nienke van der Werf 1, Stephen A. Redpath 2, Miyuki Azuma 3, Hideo Yagita 4, Matthew D. Taylor 5,6 * 1 Department
Th2 Cell-Intrinsic Hypo-Responsiveness Determines Susceptibility to Helminth Infection Nienke van der Werf 1, Stephen A. Redpath 2, Miyuki Azuma 3, Hideo Yagita 4, Matthew D. Taylor 5,6 * 1 Department
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20942 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wammes, Linda Judith Title: Immune regulation during parasitic infections : from
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20942 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wammes, Linda Judith Title: Immune regulation during parasitic infections : from
Drug discovery and development for the treatment and control of filariasis: repurposing emodepside
 Drug discovery and development for the treatment and control of filariasis: repurposing emodepside IMMIP, Bonn Sabine Specht, Achim Hoerauf DNDi Robert Don Ivan Scandale NPIMR, Northwick Park Simon Townson
Drug discovery and development for the treatment and control of filariasis: repurposing emodepside IMMIP, Bonn Sabine Specht, Achim Hoerauf DNDi Robert Don Ivan Scandale NPIMR, Northwick Park Simon Townson
Extracts of Ascaris suum egg and adult worm share similar immunosuppressive properties
 razilian Journal of Medical and iological Research (2002) 35: 81-89 ISSN 0100-879X 81 Extracts of scaris suum egg and adult worm share similar immunosuppressive properties V.M.O. Souza, E.L. Faquim-Mauro
razilian Journal of Medical and iological Research (2002) 35: 81-89 ISSN 0100-879X 81 Extracts of scaris suum egg and adult worm share similar immunosuppressive properties V.M.O. Souza, E.L. Faquim-Mauro
Received 21 February 1995/Returned for modification 13 April 1995/Accepted 21 July 1995
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 1995, p. 3772 3779 Vol. 63, No. 10 0019-9567/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Differential Antibody Isotype Reactivity to Specific Antigens in
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 1995, p. 3772 3779 Vol. 63, No. 10 0019-9567/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Differential Antibody Isotype Reactivity to Specific Antigens in
Killing filarial nematode parasites: role of treatment options and host immune response
 Kwarteng et al. Infectious Diseases of Poverty (2016) 5:86 DOI 10.1186/s40249-016-0183-0 SCOPING REVIEW Killing filarial nematode parasites: role of treatment options and host immune response Alexander
Kwarteng et al. Infectious Diseases of Poverty (2016) 5:86 DOI 10.1186/s40249-016-0183-0 SCOPING REVIEW Killing filarial nematode parasites: role of treatment options and host immune response Alexander
Cytokine production by spleen cells from mice with ovalbumin-specific, lge-selective unresponsiveness induced by ovalbumin-liposome conjugate
 Allergology International (1997) 46: 249-253 Original Article Cytokine production by spleen cells from mice with ovalbumin-specific, lge-selective unresponsiveness induced by ovalbumin-liposome conjugate
Allergology International (1997) 46: 249-253 Original Article Cytokine production by spleen cells from mice with ovalbumin-specific, lge-selective unresponsiveness induced by ovalbumin-liposome conjugate
Early Human Infection with Onchocerca volvulus Is Associated with an Enhanced Parasite-Specific Cellular Immune Response
 1662 Early Human Infection with Onchocerca volvulus Is Associated with an Enhanced Parasite-Specific Cellular Immune Response Philip J. Cooper, 1,a Tamara Mancero, 2 Mauricio Espinel, 2 Carlos Sandoval,
1662 Early Human Infection with Onchocerca volvulus Is Associated with an Enhanced Parasite-Specific Cellular Immune Response Philip J. Cooper, 1,a Tamara Mancero, 2 Mauricio Espinel, 2 Carlos Sandoval,
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection
 ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 236 240 Aboulghasem Ajami, Alireza Rafiei Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection Article Type: Research The Iranian Journal of Immunology
ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 236 240 Aboulghasem Ajami, Alireza Rafiei Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection Article Type: Research The Iranian Journal of Immunology
Down-regulation of T cell function resulting in immune
 CTLA-4 and CD4 CD25 Regulatory T Cells Inhibit Protective Immunity to Filarial Parasites In Vivo 1 Matthew D. Taylor, 2 * Anjanette Harris, Simon A. Babayan, Odile Bain, Abigail Culshaw, Judith E. Allen,
CTLA-4 and CD4 CD25 Regulatory T Cells Inhibit Protective Immunity to Filarial Parasites In Vivo 1 Matthew D. Taylor, 2 * Anjanette Harris, Simon A. Babayan, Odile Bain, Abigail Culshaw, Judith E. Allen,
T Regulatory-1 Cells Induce IgG4 Production by B Cells: Role of IL-10
 This information is current as of October 18, 2018. T Regulatory-1 Cells Induce IgG4 Production by B Cells: Role of IL-10 Judith S. Satoguina, Esther Weyand, John Larbi and Achim Hoerauf J Immunol 2005;
This information is current as of October 18, 2018. T Regulatory-1 Cells Induce IgG4 Production by B Cells: Role of IL-10 Judith S. Satoguina, Esther Weyand, John Larbi and Achim Hoerauf J Immunol 2005;
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Influence of Maternal Filariasis on Childhood Infection and Immunity to Wuchereria bancrofti in Kenya
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5231 5237 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5231 5237.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Influence
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5231 5237 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5231 5237.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Influence
Drastic Reduction of a Filarial Infection in Eosinophilic Interleukin-5 Transgenic Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2000, p. 3651 3656 Vol. 68, No. 6 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Drastic Reduction of a Filarial Infection in
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2000, p. 3651 3656 Vol. 68, No. 6 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Drastic Reduction of a Filarial Infection in
Of Mice, Cattle, and Humans: The Immunology and Treatment of River Blindness
 Review Of Mice, Cattle, and Humans: The Immunology and Treatment of River Blindness Judith E. Allen 1, Ohene Adjei 2, Odile Bain 3, Achim Hoerauf 4, Wolfgang H. Hoffmann 5, Benjamin L. Makepeace 6, Hartwig
Review Of Mice, Cattle, and Humans: The Immunology and Treatment of River Blindness Judith E. Allen 1, Ohene Adjei 2, Odile Bain 3, Achim Hoerauf 4, Wolfgang H. Hoffmann 5, Benjamin L. Makepeace 6, Hartwig
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
B1 B Lymphocytes Play a Critical Role in Host Protection against Lymphatic Filarial Parasites
 Published Online: 21 February, 2000 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.191.4.731 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 24, 2019 Brief Definitive Report B1 B Lymphocytes Play a Critical Role in
Published Online: 21 February, 2000 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.191.4.731 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 24, 2019 Brief Definitive Report B1 B Lymphocytes Play a Critical Role in
Peripheral Cytokine Responses to Trichuris muris Reflect Those Occurring Locally at the Site of Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 2000, p. 1815 1819 Vol. 68, No. 4 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Peripheral Cytokine Responses to Trichuris muris
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 2000, p. 1815 1819 Vol. 68, No. 4 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Peripheral Cytokine Responses to Trichuris muris
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Downloaded from:
 O Hara, GA; Elliott, AM (2016) HIV and Helminths - Not All Worms Created Equal? Trends in parasitology. ISSN 1471-4922 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/3327115/
O Hara, GA; Elliott, AM (2016) HIV and Helminths - Not All Worms Created Equal? Trends in parasitology. ISSN 1471-4922 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/3327115/
IMMUNO-EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BANCROFTIAN FILARIASIS : A 14-YEAR FOLLOW-UP STUDY IN ODISHA, INDIA
 IMMUNO-EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BANCROFTIAN FILARIASIS : A 14-YEAR FOLLOW-UP STUDY IN ODISHA, INDIA NN Mandal, KG Achary, SK Kar and MS Bal Division of Immunology, Regional Medical Research Centre, Indian Council
IMMUNO-EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BANCROFTIAN FILARIASIS : A 14-YEAR FOLLOW-UP STUDY IN ODISHA, INDIA NN Mandal, KG Achary, SK Kar and MS Bal Division of Immunology, Regional Medical Research Centre, Indian Council
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Immunobiology 7. The Humoral Immune Response
 Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE
 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Chapter IV - CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Sujatha, M. 2013. Evaluation of Immunological changes in Fish, Catla catla administered with bacterial pathogen, Aeromonas hydrophila,
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Chapter IV - CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Sujatha, M. 2013. Evaluation of Immunological changes in Fish, Catla catla administered with bacterial pathogen, Aeromonas hydrophila,
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #13 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #13 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) An epidemiologic survey was undertaken in a small town in Myanmar (Burma) endemic for lymphatic filariasis. Blood specimens were collected
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #13 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) An epidemiologic survey was undertaken in a small town in Myanmar (Burma) endemic for lymphatic filariasis. Blood specimens were collected
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Understanding basic immunology. Dr Mary Nowlan
 Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human IL5 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human IL5 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
Prospectus Trans-Atlantic Product Development Partnership for a River Blindness Vaccine
 Prospectus Trans-Atlantic Product Development Partnership for a River Blindness Vaccine The London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases of January 2012 called for sustained efforts to expand and
Prospectus Trans-Atlantic Product Development Partnership for a River Blindness Vaccine The London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases of January 2012 called for sustained efforts to expand and
Immunobiology, BIOL 537 Spring 2013
 Immunobiology, BIOL 537 Spring 2013 Instructor: Dr. Elliott Blumenthal Office: Science Building, # 390 Class Meets: 6:00-7:15 PM TR Phone: 481-6004 E-mail: Blumenth@ipfw.edu SB 168 481-6305 (Biology Office)
Immunobiology, BIOL 537 Spring 2013 Instructor: Dr. Elliott Blumenthal Office: Science Building, # 390 Class Meets: 6:00-7:15 PM TR Phone: 481-6004 E-mail: Blumenth@ipfw.edu SB 168 481-6305 (Biology Office)
District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide
 District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide Session 3: Diagnostic and laboratory tools for filarial worms, Soil- Transmitted Helminths and Schistosomiasis Key message addressed to communities: Community
District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide Session 3: Diagnostic and laboratory tools for filarial worms, Soil- Transmitted Helminths and Schistosomiasis Key message addressed to communities: Community
FOCiS. Lecture outline. The immunological equilibrium: balancing lymphocyte activation and control. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
Autoimmunity and Primary Immune Deficiency
 Autoimmunity and Primary Immune Deficiency Mark Ballow, MD Division of Allergy & Immunology USF Morsani School of Medicine Johns Hopkins All Children s Hospital St Petersburg, FL The Immune System What
Autoimmunity and Primary Immune Deficiency Mark Ballow, MD Division of Allergy & Immunology USF Morsani School of Medicine Johns Hopkins All Children s Hospital St Petersburg, FL The Immune System What
/01/$ DOI: /IAI Received 21 July 2000/Returned for modification 26 September 2000/Accepted 13 October 2000
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2001, p. 194 203 Vol. 69, No. 1 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.194 203.2001 Susceptibility to Secondary Francisella tularensis Live Vaccine Strain Infection in
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2001, p. 194 203 Vol. 69, No. 1 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.194 203.2001 Susceptibility to Secondary Francisella tularensis Live Vaccine Strain Infection in
A simple and quick method for enhanced detection of specific IgE in serum from lymphatic filariasis patients
 Acta Tropica 80 (2001) 51 57 www.parasitology-online.com A simple and quick method for enhanced detection of specific IgE in serum from lymphatic filariasis patients Walter G. Jaoko a, Mette Lund b, Edwin
Acta Tropica 80 (2001) 51 57 www.parasitology-online.com A simple and quick method for enhanced detection of specific IgE in serum from lymphatic filariasis patients Walter G. Jaoko a, Mette Lund b, Edwin
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
IMMUNOLOGY BIO 463 LABORATORY EXERCISE FALL 2015
 IMMUNOLOGY BIO 463 LABORATORY EXERCISE FALL 2015 IL-2 Production in mouse splenocytes INTRODUCTION Interleukin-2, or IL-2, is a potent cytokine produced by T-cells, stimulating their proliferation. As
IMMUNOLOGY BIO 463 LABORATORY EXERCISE FALL 2015 IL-2 Production in mouse splenocytes INTRODUCTION Interleukin-2, or IL-2, is a potent cytokine produced by T-cells, stimulating their proliferation. As
TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
GSI Canine IL-5 ELISA Kit-2 Plates DataSheet
 Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production activates T- and natural killer cells
 Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
Page 1 of 2. Standard curve of Human IFN gamma ELISA Ready- SET-Go! Product Information Contents: Human IFN gamma ELISA Ready- SET-Go!
 Page 1 of 2 Human IFN gamma ELISA Ready-SET-Go! Catalog Number: 88-7316 Also known as: Interferon-gamma, IFN-g, IFNg RUO: For. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Standard curve of Human IFN gamma ELISA
Page 1 of 2 Human IFN gamma ELISA Ready-SET-Go! Catalog Number: 88-7316 Also known as: Interferon-gamma, IFN-g, IFNg RUO: For. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Standard curve of Human IFN gamma ELISA
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Reciprocal Immunomodulatory Effects of Gamma Interferon and Interleukin-4 on Filaria-Induced Airway Hyperresponsiveness
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2001, p. 1463 1468 Vol. 69, No. 3 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.3.1463 1468.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Reciprocal
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2001, p. 1463 1468 Vol. 69, No. 3 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.3.1463 1468.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Reciprocal
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Cymax TM Mouse IL-4 ELISA
 Cymax TM Mouse IL-4 ELISA Catalog # LF-EK0268 (1 kit) Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Quantitative Detection of mouse IL-4 For research use only Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures
Cymax TM Mouse IL-4 ELISA Catalog # LF-EK0268 (1 kit) Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Quantitative Detection of mouse IL-4 For research use only Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures
Title: Oral administration of PPC enhances antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses while reducing IgE levels in sensitized mice.
 Author's response to reviews Title: Oral administration of PPC enhances antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses while reducing IgE levels in sensitized mice. Authors: Mike Burrows (mburrows@tampabayresearch.org)
Author's response to reviews Title: Oral administration of PPC enhances antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses while reducing IgE levels in sensitized mice. Authors: Mike Burrows (mburrows@tampabayresearch.org)
TNF-alpha ELISA. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
 TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
Critical Role for Alpha/Beta and Gamma Interferons in Persistence of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus by Clonal Exhaustion of Cytotoxic T Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2001, p. 8407 8423 Vol. 75, No. 18 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.18.8407 8423.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Critical
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2001, p. 8407 8423 Vol. 75, No. 18 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.18.8407 8423.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Critical
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for. Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David I Wilson,
 Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
What is the immune system? Types of Immunity. Pasteur and rabies vaccine. Historical Role of smallpox. Recognition Response
 Recognition Response Effector memory What is the immune system? Types of Immunity Innate Adaptive Anergy: : no response Harmful response: Autoimmunity Historical Role of smallpox Pasteur and rabies vaccine
Recognition Response Effector memory What is the immune system? Types of Immunity Innate Adaptive Anergy: : no response Harmful response: Autoimmunity Historical Role of smallpox Pasteur and rabies vaccine
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
Cytokine Regulation of Antigen-driven Immunoglobulin Production in Filarial Parasite Infections in Humans
 Cytokine Regulation of Antigen-driven Immunoglobulin Production in Filarial Parasite Infections in Humans C. L. King, E. A. Ottesen, and T. B. Nutman Laboratory ofparasitic Diseases, National Institutes
Cytokine Regulation of Antigen-driven Immunoglobulin Production in Filarial Parasite Infections in Humans C. L. King, E. A. Ottesen, and T. B. Nutman Laboratory ofparasitic Diseases, National Institutes
The Skinny of the Immune System
 The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
Regulatory T Cells Limit Induction of Protective Immunity and Promote Immune Pathology following Intestinal Helminth Infection
 This information is current as of July 19, 2018. Supplementary Material References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Regulatory T Cells Limit Induction of Protective Immunity and Promote Immune Pathology
This information is current as of July 19, 2018. Supplementary Material References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Regulatory T Cells Limit Induction of Protective Immunity and Promote Immune Pathology
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet
 Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Cytokine profiles of filarial granulomas in jirds infected with Brugia pahangi
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2006 Cytokine profiles of filarial granulomas in jirds infected with Brugia pahangi Ramakrishna U. Rao Washington
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2006 Cytokine profiles of filarial granulomas in jirds infected with Brugia pahangi Ramakrishna U. Rao Washington
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
Abstract. Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology and Immunology. Uniformed Services University of the Health Science
 Abstract Title of Dissertation: Evaluation of allergy effector cell function: suppression of basophils in chronic helminth infections David Larson, Doctor of Philosophy, 2011 Thesis directed by: Edward
Abstract Title of Dissertation: Evaluation of allergy effector cell function: suppression of basophils in chronic helminth infections David Larson, Doctor of Philosophy, 2011 Thesis directed by: Edward
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Wolbachia-Induced Neutrophil Activation in a Mouse Model of Ocular Onchocerciasis (River Blindness)
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2004, p. 5687 5692 Vol. 72, No. 10 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5687 5692.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Wolbachia-Induced
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2004, p. 5687 5692 Vol. 72, No. 10 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5687 5692.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Wolbachia-Induced
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Approved for public release; distribution unlimited
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
Immunology: an overview Lecture
 Slide #2: Immunology is sometimes regarded as part of microbiology department because it started there as an investigation of ways used to prevent against infectious agents (e.g. microorganisms ). However
Slide #2: Immunology is sometimes regarded as part of microbiology department because it started there as an investigation of ways used to prevent against infectious agents (e.g. microorganisms ). However
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
Functional Analysis of Effector and Regulatory T Cells in a Parasitic Nematode Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2008, p. 1908 1919 Vol. 76, No. 5 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01233-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Analysis
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2008, p. 1908 1919 Vol. 76, No. 5 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01233-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Analysis
Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host
 17 Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity, and humoral and cellular immunity. Define antigen, epitope, and hapten. Explain the function
17 Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity, and humoral and cellular immunity. Define antigen, epitope, and hapten. Explain the function
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c)
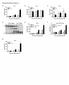 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
