The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
|
|
|
- Easter Kristin Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin Dong, Steven W Remmeng 1,, Kerry J Rodugh 1, Jin Zhou 1,6, Pul F Lmert 7, Peixin Yng 8, John S Dvis 1,,9 & Cheng Wng 1,,* Astrt The Hippo signling pthwy ontrols orgn size nd tumorigenesis through kinse sde tht intivtes Yes-ssoited protein (). Here, we show tht plys entrl role in ontrolling the progression of ervil ner. Our results suggest tht expression is ssoited with poor prognosis for ervil ner. TGF- nd mphiregulin (AREG), vi EGFR, inhiit the Hippo signling pthwy nd tivte to indue ervil ner ell prolifertion nd migrtion. Ativted llows for up-regultion of TGF-, AREG, nd EGFR, forming positive signling loop to drive ervil ner ell prolifertion. HPV E6 protein, mjor etiologil moleule of ervil ner, mintins high protein levels in ervil ner ells y preventing protesome-dependent degrdtion to drive ervil ner ell prolifertion. Results from humn ervil ner genomi dtses nd n epted trnsgeni mouse model strongly support the linil relevne of the disovered feed-forwrd signling loop. Our study indites tht omined trgeting of the Hippo nd the ERBB signling pthwys represents novel therpeuti strtegy for prevention nd tretment of ervil ner. Keywords ervil ner; EGFR; Hippo; HPV; Sujet Ctegories Cner; Urogenitl System DOI 1.155/emmm.1976 Reeived 19 Deemer 1 Revised 18 August 15 Aepted August 15 Introdution Cervil ner is the seond most ommonly dignosed ner nd the fourth leding use of ner deth in women worldwide (Jeml et l, 11). The estimte from the Interntionl Ageny for Reserh on Cner (IARC) predited tht 58, women would e dignosed with ervil ner nd 66, deths would result from this disese in 1 (Ferly et l, 13). Cervil ner ffets women when they re still young nd hs devstting effets with very high humn, soil, nd eonomi ost. Humn ppillomvirus (HPV) infetion is deteted in 99.7% of ervil ner ptients nd is elieved to e the mjor risk ftor for ervil ner (Jeml et l, 11; Ferly et l, 13). However, epidemiologil studies hve shown tht lthough the estimted lifetime risk of HPV infetion is more thn 75% (Koutsky, 1997), the lifetime risk of developing ervil ner is only round.7% (Siegel et l, 1). It is ler tht HPV lone is insuffiient for mlignnt trnsformtion nd unontrolled growth of ervil epithelium (Mhdvi & Monk, 5; Chn & Berek, 7). The ext moleulr mehnisms underlying ervil ner initition nd progression re lrgely unknown. The Hippo signling pthwy, originlly disovered in Drosophil, is n evolutionrily onserved pthwy tht ontrols orgn size y regulting ell prolifertion in diverse numer of speies. The ore Hippo pthwy, onsisting of kinse sde nd ssoited o-tivtors nd sffold proteins, hs een well estlished in oth Drosophil nd mmmls (Pn, 1; Mo et l, 1). In the mmmlin Hippo pthwy, mrophge stimulting 1/ kinse (MST1/, lled Hippo in Drosophil), in omplex with Slvdor homolog 1 (Sv1), phosphoryltes the lrge tumor suppressor kinse 1/ (LATS1/) nd regultory protein, Mps one inder kinse 1 Olson Center for Women s Helth, Deprtment of Ostetris & Gyneology, University of Nersk Medil Center, Omh, NE, USA College of Animl Siene nd Tehnology, Huzhong Agriulturl University, Wuhn, Chin 3 College of Animl Siene nd Tehnology, Nnjing Agriulturl University, Nnjing, Chin Fred & Pmel Buffett Cner Center, University of Nersk Medil Center, Omh, NE, USA 5 Nersk Center for Virology, Shool of Biologil Sienes, University of Nersk-Linoln, Linoln, NE, USA 6 Deprtment of Ostetris nd Gyneology, Urumqi Generl Hospitl of Lnzhou Militry Region, Urumqi, Chin 7 Deprtment of Onology, MArdle Lortory for Cner Reserh, University of Wisonsin Shool of Mediine nd Puli Helth, Mdison, WI, USA 8 Deprtment of Ostetris, Gyneology & Reprodutive Sienes, University of Mrylnd Shool of Mediine, Bltimore, MD, USA 9 Omh Veterns Affirs Medil Center, Omh, NE, USA *Corresponding uthor. Tel: ; Fx: ; E-mil: hengwng@unm.edu ª 15 The Authors. Pulished under the terms of the CC BY. liense EMBO Moleulr Mediine 1
2 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l tivtor-like 1A (MOB1). Phosphorylted LATS1/ nd MOB1 form n intertion omplex tht leds to tivtion of LATS1/. Ativted LATS1/, in turn, phosphoryltes the growth-promoting trnsriptionl o-tivtor Yes-ssoited protein (1, or more ommonly ). Phosphoryltion of leds to its ytoplsmi retention nd/or degrdtion, depending on the sites of phosphoryltion (Dong et l, 7; Zho et l, 7; Pn, 1; Mo et l, 1). Conversely, loss of the Hippo signling n led to orgn overgrowth nd indue tumors in model orgnisms (Dong et l, 7; Lee et l, 1). Dysregultion of the Hippo pthwy ours in rod rnge of humn rinoms, inluding lung, oloretl, rest, ovrin, pnreti, gstri, nd liver ner (Hll et l, 1; Lee et l, 1; Wng et l, 1, 1; Kng et l, 11; Zhng et l, 11; Avruh et l, 1; Hergovih, 1; He et l, 15). However, whether the Hippo pthwy plys role in the progression of ervil ner development is urrently unknown. Yes-ssoited protein is the mjor downstrem effetor of the Hippo pthwy (Pn, 1). Reent studies suggest tht expression nd funtion of in ner re ell type nd/or ellulr ontext dependent. Severl studies define s n onogene. For exmple, the mplifition of the gene lous t 11q is found in severl types of ners (Snijders et l, 5; Overholtzer et l, 6; Zender et l, 6; Fernndez et l, 9; Kng et l, 11; Murmtsu et l, 11). Overexpression nd nuler loliztion of the protein hs een noted in olon, liver, lung, ovrin, nd prostte ners (Snijders et l, 5; Zho et l, 7; Steinhrdt et l, 8; Zhng et l, 11; Yu & Gun, 13; He et l, 15). Overexpression of indued onogeni trnsformtion of n immortlized rest epithelil ell line, MCF1A (Overholtzer et l, 6), nd signifintly stimulted grnulos ell tumor ell prolifertion (Fu et l, 1). On the other hnd, ws reported to e tumor suppressor in ertin ell types. hs een shown to enhne p73-dependent ell deth during ispltin-indued DNA dmge (Strno et l, 5). In suset of rest ners, protein expression ws signifintly deresed due to loss of heterozygosity. Additionlly, shrna knokdown of inresed nhorge-independent growth, migrtion, nd invsiveness of rest ner ells nd enhned tumor growth in nude mie (Yun et l, 8). However, the preise mehnism for the expression nd funtion of in ervil ner ell remins undefined. In the present study, we sought to determine the expression of in humn ervil ner tissues, nd to exmine the role of the Hippo pthwy in the progression of ervil ner. We found tht is overexpressed in ervil ner tissue. We lso found tht the Hippo signling pthwy, through intertion with the EGFR signling pthwy, regultes progression of ervil ner vi n utorine loop involving EGF-like lignds, EGFR, nd the Hippo pthwy. Importntly, we disovered tht the HPV E6 protein stilizes the protein to mintin its tion on the progression of ervil ner. Results expression during ervil ner progression Compred with norml ontrol tissues, oth the positivity nd intensity of the immunosignl, whih indite -positive ells nd protein levels, respetively, were signifintly higher in the ervil ner tissues (Fig 1A nd B, Tles 1 nd ). We lso found tht expression nd loliztion were ssoited with tumor stge. Compred with tumor tissue from ptients with erly-stge disese (Fig 1D, E nd G), tissue from ptients with dvned-stge ervil ner hd signifintly higher levels of protein, whih ws lolized minly to the nuleus of tumor ells (Fig 1F nd H). The reltionships etween protein levels nd linil histopthologil prmeters were lso nlyzed in this study. As desried in Tle, positivity ws greter in ervil ner tissues ompred to norml tissues, ut the numer of -positive ells in ervil ner did not vry with ge, grde, stge, primry tumor, nd regionl lymph node sttus. Notly, the intensity of immunosignl (expression levels) ws signifintly orrelted with the FIGO stge, primry tumor, nd regionl lymph node sttus, ut not the tumor grde (Tle ). Western lot nlyses showed tht ws differentilly expressed in norml nd nerous ervil ell lines (Appendix Fig S1A). Consistent with IHC results, ws highly expressed in ervil ner ell lines (ME18, HT3, nd HeL), while in Et1 ells, n immortlized epithelil ell line derived from the etoervil epithelium, protein ws expressed t low levels nd ws highly phosphorylted (Appendix Fig S1A). To onfirm tht plys role in humn ervil ner progression, we nlyzed gene ltertion using dt extrted from The Cner Genomi Atls (TCGA) dtse nd the BioPortl online nlyzing tool (the BioPortl for Cner Genomis) (Cermi et l, 1; Go et l, 13). The ross-ner ltertion nlysis shows tht is frequently ltered in different types of ners (Fig 1I). Interestingly, mong 36 exmined ner types or sutypes Figure 1. expression in norml ervil tissues nd ervil ners. A Representtive imges show expression of in norml ervil tissues, erly-stge ervil ner (stge I & II), nd dvned-stge ervil ner (stge III & IV). Note the signifint inrese in immunosignls (rown stining) in the dvned-stge tumors. Tissue ore size: 1.5 mm. B Positivity (perentge of positively stined ells reltive to the totl numer of ells in the tissue setion) of immunosignls in the norml nd nerous tissues. Dt were nlyzed with unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Brs represent mens SEM (n = 1 for norml tissues; n = 69 for tumor tissues; ***P <.1). C A representtive imge showing the expression of (rown stining) in norml ervil tissue. Sle r = lm. D F Representtive imges showing the expression of in (D) erly-stge ervil ner tissue (stge I, T1NM); (E) medium-stge ervil ner tissue (stge II, TNM); nd (F) dvned-stge ervil ner tissue (stge III, T3N1M). Sle r = lm. G, H High-resolution imges showing the ellulr lotion of in (G) erly-stge ervil ner tissue nd (H) dvned-stge ervil ner tissue. Sle r = lm. I Multidimensionl ner genomis dt nlysis results showing ross-ner gene ltertion. The histogrm showed the frequenies of gene muttion, deletion, nd mplifition ross ners. Dt were extrted from TCGA dtse nd nlyzed using BioPortl online nlyzing tools. The results indite tht the highest ltertion frequeny of gene ours in ervil ner. EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
3 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A B C D E F G H I Figure 1. ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 3
4 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l Tle 1. Positivity of immunosignl in norml ervil tissues nd ervil tumors. Signl Intensity Tumor (n = 69) Norml (n = 1) Negtive.9% (/69) 6% (6/1) Wek 5.8% (/69) % (/1) Moderte 13.% (9/69) Strong 78.3% (5/69) Positivity: the rtio of immunosignl-positive ell numer to the totl ell numer. Signl intensity ws lssified s follows: negtive, positivity < 1%; wek, 1% < positivity < 1%; moderte, 1% < positivity < %; nd strong, positivity > %. Tle. Correltion etween expression nd the liniopthologi determinnts in ervil ner. Feture IP (P) Positivity (P) Tumor vs. Norml.1 <.1 Grde Stge <.1. T.8.67 N..31 Age.8.36 IP = totl intensity of positive signl. Positivity: the rtio of immunosignl-positive ell numer to the totl ell numer. T: primry tumor: T1 tumor invdes sumuos; T tumor invdes musulris propri; T3 tumor invdes through musulris propri into suseros or into non-peritonelized perioli or periretl tissues; T tumor diretly invdes other orgns or strutures nd/or perforte viserl peritoneum. N: regionl lymph nodes: N no regionl lymph node metstsis; N1 metstsis in 1 3 regionl lymph nodes; N metstsis in or more regionl lymph nodes. M: distnt metstsis: M no distnt metstsis; M1 distnt metstsis. (from totl of 9 studies), the ervil ner hs the highest frequeny of gene mplifition (Fig 1I). Intriguingly, Anlysis of the ervil ner ptient smple from the TCGA dtsets indited tht upstrem genes involved in the Hippo tumor-suppressing pthwy re frequently deleted nd mutted, while the effetors, nd WWTR1 (TAZ) genes, re frequently mplified in 191 ervil ner ses (Fig EV1A). Further nlysis using 135 ervil ner genome sequening dt from TCGA dtsets indites tht gene is ltered in 17% exmined ses (Fig EV1). TEADs re the mjor meditors of trnsriptionl tivities. In the exmined ervil ner ptient smples, % ses hve ltertions in t lest one of the genes in -TEAD omplex (Fig EV1B). Moreover, network nlysis showed tht lmost ll genes tht interted with, inluding other -ssoited trnsriptionl ftors suh s ERBB, Runx1, nd Runx, re up-regulted in vrious degrees in exmined ervil ner ses (Appendix Fig S). promotes prolifertion nd migrtion of ervil ner ells in vitro Sine is overexpressed in ervil ner, we used ME18 (HPV positive) nd HT3 (HPV negtive) ervil ner ell lines to lrify the role of in ervil ner ell prolifertion. We estlished six ell lines with differentil protein levels nd tivities: ME18- S17A nd HT3- S17A ell lines expressing onstitutively tivted ; ME18- nd HT3- overexpressing wild-type ; nd ME18-MXIV nd HT3-MXIV ells trnsfeted with ontrol vetors (MXIV). As expeted, ws overexpressed in ME18-, HT3-, ME18- S17A, nd HT3- S17A ells (Fig A nd C, Appendix Fig S3A nd B). An inrese in phosphorylted ws oserved in the ME18- nd HT3- ells, ut not in ME18- S17A nd HT3- S17A ells, onsistent with the muttion of serine 17 to lnine (Fig A nd C, Appendix Fig S3A nd B), whih results in onstitutive tivity (Pn, 1). We oserved tht in the presene of omplete medium (1% serum for HT3,.5% serum for ME18), the growth rte of the ME18 nd HT3 ell lines ws similr prior to rehing onfluene. After rehing onfluene (> dys fter ell plting), ells in the ontrol groups lmost stopped proliferting. However, ells overexpressing or S17A ontinued to proliferte (Fig B nd D), with the highest growth rtes oserved in ME18- S17A nd HT3- S17A ells. Interestingly, when exmined under serum-redued onditions (1% FBS), the growth rte of the ME18- S17A ells ws signifintly higher thn tht of the ME18- ells, while growth rte of the ME18- ells ws signifintly higher thn tht of ME18-MXIV ells, even efore the ell ultures reh onfluene (Appendix Fig S3C). We then nlyzed ell yle progression in these ell lines fter they rehed onfluene. The results showed tht overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of inresed the perentge of ells in S nd G/M phses, nd redued the proportion of ells in G1 phse in oth ME18 nd HT3 ervil ner ells (Appendix Fig S). The ervil epithelil ell line Et1/E6E7 ws immortlized with HPV16 E6/E7 nd is onsidered to e n immortlized non-tumorigeni etoervil epithelil ell line (Fihorov et l, 1997; Fihorov & Anderson, 1999). We used this ell line to determine whether ws le to stimulte the prolifertion of immortlized ervil epithelil ells. We estlished three ell lines sed on Et1/E6E7 ells: Et1-MXIV (Et1/E6E7 ells trnsfeted with n empty ontrol vetor), Et1- (Et1/E6E7 ells overexpressing wild-type ), nd Et1- S17A ells (Et1/E6E7 ells overexpressing onstitutively tive ). Western lot detetion of phosphorylted nd totl levels in these ells showed tht ws suessfully overexpressed in Et1- nd Et1- S17A ells (Fig E). Morphologilly, Et1- S17A ells formed mny ell plques, whih my e ttriuted to multilyered ell growth (Appendix Fig S5). As expeted, the ell growth urve showed tht Et1- S17A ells proliferted fster nd Et1-MXIV ells proliferted slower thn Et1- ells (Fig F). To onfirm tht plys role in regulting the prolifertion of ervil ner ells, we used sirna to knok down protein in ME18 nd HT3 ells. Non-trgeting ontrol sirna (sictrl) ws used s ontrol. Western lot nlysis demonstrted tht sirna suessfully redued protein level in ME18 nd HT3 ells (Fig G, Appendix Fig S6A). Knokdown of protein did not ffet HT3 ell prolifertion until dy, when the ells hieved higher density ( 9%). After dy, ontrol HT3 ells treted with non-trgeting ontrol sirna (sictrl) ontinued to proliferte, lthough the growth rte ws lower thn in low-density ells. However, HT3 ells treted with sirna stopped growing (Fig H). Similrly, fter dy, the growth rte of ontrol ME18 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
5 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A C E G HT3 ells p- (S17) β-atin p- (S17) β-atin p- (S17) Atin p- (S17) β-atin B D F H Cell Numer ( 1 6 ) Cell Numer ( 1 6 ) Cell numer (1 5 ) Cell numer ( 1 5 ) ME-MXIV 5 ME- ME- S17A DAYS 8 6 HT3-MXIV HT3- HT3- S17A DAYS Et1-MXIV Et1- Et1- S17A DAYS 5 15 HT3 ells sictrl si DAYS Figure. Effet of on the prolifertion of norml nd nerous ervil ells. A, C, E Western lot nlysis showing levels of nd phosphorylted in ME18 ell lines [ME18-MXIV (ontrol), ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells] (A); HT3 ell lines [HT3-MXIV (ontrol), HT3-, nd HT3- S17A ells] (C); nd Et1 ell lines [Et1-MXIV (ontrol), Et1-, nd Et1- S17A ells] (E). -Atin ws used s protein loding ontrol. B, D, F Growth urves of -overexpressed ME18 ell lines [ME18-MXIV (ontrol), ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells] (B); HT3 ell lines [HT3-MXIV (ontrol), HT3-, nd HT3- S17A ells] (D); nd Et1 ell lines [Et1-MXIV (ontrol), Et1-, nd Et1- S17A ells] (F). Eh point represents the men SEM (n = ). ***P <.1, ME18- MXIV vs. ME18- ells nd ME18-MXIV vs. ME18- S17A ells on dy 8. ***P <.1, HT3-MXIV vs. HT3- ells nd HT3-MXIV vs. HT3- S17A ells on dy 8. ***P <.1, Et1-MXIV vs. Et1-Et1- S17A ells on dy. *P <.7, Et1-MXIV vs. Et1- ells on dy. G Western lot showing levels in non-trgeting ontrol sirna (sictrl)- nd sirna (si)-trnsfeted HT3 ells. H Prolifertion of HT3 ells treted with ontrol (sictrl) or sirna (si). Eh point represents the men SEM (n = 5). ***P <.1 ompred with sictrl (sictrl vs. si, P =.). Dt informtion: Dt in (B), (D), nd (F) were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho test. Dt in (H) were nlyzed with n unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. ells (sictrl) ws signifintly higher thn in si tretment ME18 ells (Appendix Fig S6B). This is onsistent with our finding tht protein level nd tivity in ME18 ervil ner ells were ssoited with ell density. protein in ME18 ells llowed to proliferte to high density in ulture ws highly phosphorylted (Appendix Fig S1B). Phosphoryltion of t serine 17 leds to sequestrtion of in the ytoplsm, leding to its intivtion (Zender et l, 6; Fernndez et l, 9). Wound-heling ssys showed tht, ompred to the ontrols, overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of leds to signifint inreses in wound losure (P <.1), inditing tht lso plys n importnt role in the regultion of ervil ner ell migrtion (Appendix Fig S7). is le to trnsform ervil epithelil ells nd enhnes nhorge-independent ervil ner ell growth As mentioned ove, Et1/E6E7 (Et1) ell ws immortlized with HPV16 E6/E7 nd is onsidered to e n immortlized etoervil epithelil ell line (Fihorov et l, 1997; Fihorov & Anderson, 1999). Therefore, the three ell lines derived from this ell line re proper ellulr models to determine whether n trnsform ervil epithelil ells using soft gr olony formtion ssy. When grown on soft gr, Et1-MXIV ells only formed few very smll, slow-growing olonies fter 9 dys. However, Et1- ells nd Et1- S17A ells formed mny lrge olonies on soft gr (Fig 3A nd B). The formtion of olonies y the Et1-MXIV my e ttriuted to the ft tht HPV16 E6 in these ells promoted protein levels, whih is evidened in studies presented lter in this report. The soft gr ssy for olony formtion ws lso used to determine whether high levels of enhned the trnsformed phenotype of ervil ner ell lines. As shown in Fig 3C, HT3- S17A ells formed more olonies thn HT3- ells, while HT3- ells formed more olonies thn HT3-MXIV ells. Similrly, ME18- S17A ells formed more olonies thn ME18- ells, while ME18- ells formed more olonies thn ME18-MXIV ells (Fig 3E). A fluorometri olony formtion kit (CytoSelet TM 96-Well Cell Trnsformtion Assy kit, Cell Biols, In.) ws used to void the potentil sujetive results from mnul olony ounting. The results lerly showed tht HT3- S17A (Fig 3D) nd ME18- S17A ells (Fig 3F) hd the highest nhorge-independent growth rte, while the HT3-MXIV nd ME18-MXIV ontrol ells hd the lowest nhorge-independent growth rtes (Fig 3D nd F). enhnes tumor growth in vivo A mouse xenogrft tumor model ws used to determine the effets of on the progression of ervil ner in vivo. The results showed tht in omprison with ME18-MXIV ells, tumors derived from ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells were lrger nd deteted erlier. On dy 3 of tumor growth, the tumor volumes (mm 3, men SEM, n = 6) of the ME18- group ( ) nd the ME18- S17A group ( ) were signifintly lrger thn tht of the ME18-MXIV group ( ) (P <.1) (Fig A D). The weights of the tumors in the nd S17A groups were lso signifintly higher thn those of the ontrol group (n = 6, P <.1, Fig E). Western lot nlysis ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 5
6 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A Et-1 ells C HT3 ells E ME18 ells MXIV MXIV MXIV S17A S17A S17A B D F Colony Numer Et1-MXIV Et1- Et1- S17A RFU (1 3 ) HT3-MXIV HT3- HT3- S17A RFU (1 3 ) ME-MXIV ME- S17A ME- Figure 3. Effet of on the nhorge-independent growth of norml nd nerous ervil ells. A Representtive imges showing olonies formed y Et1-MXIV, Et1-, nd Et1- S17A ells fter growth in soft gr for 9 dys. Sle r: 5 lm. B Quntittive dt showing olony formtion in Et1-MXIV, Et1-, nd Et1- S17A ells. Eh r represents men SEM of five independent experiments. Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (Et1-MXIV vs. Et1-, P =.3; Et1-MXIV vs. Et1- S17A, P =.). C, E Representtive imges showing the nhorge-independent growth of -expressing HT3 (C) nd ME18 (E) ervil ner ell lines. Anhorge-independent ell growth ws determined y the soft gr olony formtion ssy. Sle r: 5 lm. D, F Fluoresene-sed quntittive nlysis showing the differenes of nhorge-independent growth in HT3-MXIV, HT3-, nd HT3- S17A (D) nd ME18-MXIV, ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells (F). The nhorge-independent ell growth ws determined using CytoSelet 96-Well Cell Trnsformtion Assy kit, nd dt re presented s reltive fluoresent units (RFU). Eh r represents men SEM of four independent experiments. Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (HT3-MXIV vs. HT3-, P =.; HT3-MXIV vs. HT3- S17A, P <.1; ME-MXIV vs. ME-, P =.11; ME-MXIV vs. ME- S17A, P =.13). Dt informtion: Dt in (B), (D), nd (F) were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. 6 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
7 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine onfirmed the overexpression of protein in oth ME18- nd ME18- S17A tumor xenogrfts (Fig F). Fluoresent immunohistohemistry lerly indited tht tumor tissues derived from ME18- nd ME18- S17A tumor xenogrfts hd higher expression of Ki67, known ell prolifertion mrker, onfirming our in vitro oservtions tht regultes the prolifertion of ervil ner ells in vivo (Fig G, Appendix Fig S8). To further onfirm tht plys role in regulting the prolifertion of ervil ner ells in vivo, we used lentivirus-sed shrnas to knok down protein in ME18 ells. Non-trgeting shrna ws used s ontrol (shctrl). Western lot nlysis demonstrted tht shrnas suessfully redued totl nd phosphoryltion of protein level in ME18 ells (Fig H). Injetion (SC) of ME18-CTRL ells into the thymi nude mie indued tumor formtion in 1% (6/6) of the mie within weeks. However, injetion of the -knokdown ME18-sh#1 ells into the nude mie indued tumor formtion in only one mouse (1/6). Moreover, the tumor derived from ME18- sh#1 ells grew very slowly (Fig I nd J). These results indited tht protein is essentil for ervil tumor formtion nd tumor ell growth in vivo. TGF-, whih is up-regulted y, promotes prolifertion of ervil ner ells Amphiregulin (AREG), known trget gene, ws up-regulted y in ervil ner ME18 ells (Figs 5A nd EVA). Most importntly, overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of indued signifint inrese in the seretion of AREG in the ulture medium (Fig EVB). Knokdown of signifintly redued AREG onentrtions in the ulture medium (Fig EVC). Interestingly, overexpression of wild-type or onstitutively tive lso drmtilly inresed expression of TGF- nd EGFR mrna (Figs 5A nd EVA). This oservtion is supported y the RNA sequening dt extrted from TCGA dtsets, in whih we found tht expression is signifintly orrelted with TGF- nd EGFR expression in ervil ner (P =.9 nd P =.1, respetively, Fig EV3). Consistent with our oservtions in ovrin grnulos ell tumors (Wng et l, 1), TGF- signifintly enhned prolifertion of ME18 ells (Fig 5B) nd promoted ell yle progression (Fig 5C). Tretment of ME18 ells with TGF- for h resulted in elongtion of ME18 ells (Fig 5D). In growth medium, ontrol ME18 ells formed monolyer upon rehing onfluene nd hd mrked redution in growth rte. TGF--treted ME18 ells, however, ontinued to grow even fter the ells rehed onfluene, leding to the formtion of multilyer ell plques (Fig 5D). Wound-heling ssys showed tht TGF- (1 h) tretment drmtilly indued wound losure in ME18 ells, inditing tht TGF- lso indued ervil ner ell migrtion (Fig 5E). The Hippo signling pthwy interts with TGF-/EGFR signling to regulte ervil ner ell prolifertion nd migrtion TGF- tretment indued multilyer growth of ME18 ells, phenotype tht ws oserved in ME18 ells trnsfeted with onstitutively tivted (Fig 5), suggesting potentil involvement of the Hippo pthwy in this proess. Tretment of ME18 ells with TGF- resulted in rpid inrese in the phosphoryltion of the EGFR nd tivtion of the PI3K nd MAPK signling pthwys (Fig 6A). TGF- lso rpidly suppressed phosphoryltion of t serine 17 nd serine 397 in ME18 ells (Fig 6A nd B, Appendix Fig S9A). The ility of TGF- to suppress phosphoryltion ws lso oserved in HT3 nd End1 ells (Appendix Fig S1). Moreover, LATS1 nd MOB1 were dephosphorylted y TGF- tretment (Fig 6B, Appendix Fig S9B nd C). Dephosphoryltion of LATS1/ nd MOB1 results in the dissoition of LATS1/ -MOB1 omplex, leding to suppression of the Hippo signling pthwy nd tivtion of (Pn, 1; Yu & Gun, 13). These oservtions indite tht the EGFR pthwy interts with the Hippo pthwy to regulte the prolifertion of ervil ner ells. To further onfirm tht TGF- tretment inreses trnsriptionl tivity, we determined the mrna level of mphiregulin (AREG), known trget gene (Zhng et l, 9; Hong et l, 1). qrt-pcr nlysis showed tht AREG mrna levels in ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells were inresed y.9- nd 6.8-fold, respetively, ompred to ME18-MXIV ontrol ells (Fig 6C). Tretment of ME18 ells with TGF- led to -fold inrese in AREG mrna (Fig 6C). Knokdown of signifintly suppressed TGF-stimulted expression of AREG mrna (Fig 6D). RNA sequening Figure. Effet of on humn ervil tumor growth in vivo. A, B Representtive imges of tumor xenogrfts of ME18-MXIV (MX, right flnk), ME18- (A) (, left flnk), nd ME18- S17A (B) ( S17A, left flnk) ells implnted in thymi nude mie. Red lines indite the edge of tumors. C The growth urve of humn tumor xenogrfts derived from ontrol (ME-MX) nd -overexpressing ME18 ervil ner ell lines (ME-, ME- S17A ) implnted in the thymi nude mie. Eh point represents men SEM of six tumors (ontrol n = 1). D Representtive imges showing the reltive size of tumors from ontrol nd -overexpressing ME18 ervil ner ells. E The verge weight of tumor xenogrfts from the ontrol nd -overexpressing ME18 ell lines. Dt were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. Eh r represents the men SEM (n = 1 for ontrol, n = 6 for nd S17A groups). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (MXIV vs., P =.8; MXIV vs. S17A, P <.1). F Western lot nlysis of protein levels in the tumor xenogrfts derived from ME18-MXIV, ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells. G Expression of Ki67 in the tumor xenogrfts of ME18-MXIV, ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells implnted in thymi nude mie. Ki67 ws visulized using n Alex-88 (green)-onjugted seondry ntiody. Atin ws visulized using n Alex-59 (red)-onjugted seondry ntiody. Nulei were stined with DAPI. Sle r: lm. Note the signifint inrese in the Ki67-positive ells in the ME18- nd ME18- S17A tumor xenogrfts. H Western lot nlysis showing protein levels in ME18 ells trnsfeted with lentivirl empty vetor (shctrl) or lentivirus-sed shrnas (sh#1 or sh#). I Representtive imges showing tumor xenogrfts derived from ME18-shCtrl ells (left flnk) nd ME18-sh#1 ells (right flnk) (n = 6). J Representtive imges showing the reltive size of tumors derived from ME18 ervil ner ells trnsfeted with ontrol shrna (left, shctrl) or shrna#1 (right, sh#1) (n = 6). Soure dt re ville online for this figure. ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 7
8 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A B C MX S17A MX Volume (1 mm 3 ) ME-MXIV ME- ME- S17A Dys D E F 1.5 S17A MXIV MXIV Tumor weight (grm) p- (S17) β-atin G Ki67_ME-MX Ki-67_ME- Ki-67_ME- S17A H I J p- (s17) shctrl β-tin sh#1 shctrl sh#1 Figure. 8 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
9 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine Figure 5. stimultes expression of EGF-like lignds nd EGFR in ervil ner ell to promote ervil ner ell prolifertion nd migrtion. A RT PCR results showing tht stimultes the mrna expressions of EGFR, AREG, nd TGF- in ME18 ervil ner ell. Dt were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. Eh r represents men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other ( mrna: MXIV vs., P =.3; MXIV vs. S17A, P =.1; EGFR mrna: MXIV vs., P =.66; MXIV vs. S17A, P =.3; TGF- mrna: MXIV vs., P =.35; MXIV vs. S17A, P =.; AREG mrna: MXIV vs., P =.; MXIV vs. S17A, P <.1). B Prolifertion of ME18 ells inuted in medium ontining 1% FBS in the sene (ontrol) or presene of 1 ng/ml TGF-. Dt were nlyzed with unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Eh point represents the men SEM of four independent repets. ***P <.1 versus ontrol on dy 5. C TGF- tretment (1 ng/ml, h) promotes ME18 ell yle progression. G1, S, nd G indite ells in G1 phse, DNA synthesis phse, nd the G/M phse, respetively, of ell yle. Apo: poptoti ells. D Representtive imges showing the morphology of ME18 ells with or without TGF- (1 ng/ml) tretment for h (sle r: 5 lm) or 18 h (sle r: 5 lm). Plese note the elongtion of ME18 ells fter TGF- tretment for h (TGF-, h) nd the formtion of multiple lyers in ME18 ells fter TGF- tretment for 18 h (TGF-, 18 h). E Effet of TGF- on the migrtion of ME18 ells. TGF- tretment (1 ng/ml, 1 h) drstilly stimulted the migrtion of ME18 ells. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. dt extrted from TCGA dtsets lso showed tht TGF- mrna level ws signifintly orrelted with AREG mrna expression in ervil ner (P =.3, Fig EV3). This evidene lerly suggests tht in ervil ner ells, the TGF-/EGFR pthwy interts with the Hippo/ signling pthwy to form n utorine/prrine loop, whih my ply ritil role in regulting ervil ner progression. Experiments were performed to determine whether the signling pthwys tivted y TGF- would ffet the phosphoryltion of. Tretment of ME18 ells with EGFR inhiitor AG178 ompletely prevented the TGF--indued dephosphoryltion of (Appendix Fig S11). Tretment with the PI3K inhiitor LY9 or the MEK inhiitor U16 prtilly ut signifintly loked TGF-stimulted protein dephosphoryltion, suggesting tht the EGFR/PI3K nd EGFR/MEK/ERK signling pthwys re involved in mediting the tions of TGF- on the Hippo pthwy in ervil ner (Appendix Fig S11). To determine whether plys role in TGF--stimulted growth of ervil ner ells, we knoked down the expression of in ME18 ells using sirna nd then treted these ells with TGF-. Results showed tht TGF- promoted ME18 ell prolifertion in the ontrol group, ut it filed to do so in the -knokdown ME18 ells (Fig 6E). Moreover, knokdown of in ME18 ells diminished TGF--stimulted ME18 ell migrtion, s indited y the signifint derese in the wound losure in knokdown ME18 ells fter TGF- tretment (Fig 6F, Appendix Fig S1). Tken together, these results indite tht the effets of TGF- on ervil ner ell prolifertion nd migrtion require, t lest in prt, vi tivtion of protein. AREG tivtes protein nd indues ervil ner ell growth We found tht TGF- tretment nd overexpression signifintly inresed AREG mrna level (Fig 6). Sine AREG is memer of the fmily of the EGF-like lignds nd we hve shown tht the EGFR pthwy interts with the Hippo pthwy to regulte ervil ner ell growth, we infer tht AREG my lso e involved in the regultion of ervil ner ell prolifertion. Tretment of ME18 ells with reominnt humn AREG inresed phosphoryltion of EGFR t Tyr1173 nd redued phosphoryltion of (t Ser17 nd Ser397), LATS1 (Ser 99), nd MOB1 (Thr35) within 3 min (Fig 7A, Appendix Fig S13). Tretment of ME18 ells with AREG indued elongted ell morphology (within h) nd signifintly inresed ell prolifertion (7 h) (Fig 7B). Moreover, AREG potently stimulted ME18 ell migrtion, s indited y the signifint inrese in the wound losure in the wound-heling ssy (Fig 7C). Most interestingly, we found tht the AREG mrna expression ws indued y AREG itself in ultured ME18 ervil ner ells (Fig 7D). Knokdown of with sirna signifintly suppressed AREG-stimulted AREG mrna expression (P <.1) (Fig 7E). The intertion etween the Hippo/ nd the EGFR signling pthwys regultes ervil ner ell growth Tretment of onfluent ervil ells with TGF- nd AREG resulted in rpid nd signifint derese in phosphoryltion of LATS1, MOB1, nd (Figs 6A nd B nd 7A, Appendix Figs S9, S1 nd S13), suggesting tht the Hippo pthwy my involve in the nd EGFR signling intertion. LATS1 nd LATS re min omponents of the Hippo pthwy nd n diretly phosphorylte t Ser17. Knokdown of LATS1/ in ME18 ells with LATS1/ sirnas tivted, whih is indited y signifint derese in phospho- (S17) (Fig EVA). Knokdown of LATS1/ in ME18 ells lso signifintly inresed ell prolifertion nd enhned nhorge-independent ell growth (Fig EVB nd C). The dvntge of 3D ulture, espeilly its high physiologil relevne, hs een reported (Friedrih et l, 9). We found tht knokdown of LATS1/ signifintly indued ell growth in the 3D ulture system (Fig 8A nd B). Importntly, knokdown of LATS1/ signifintly inresed the AREG seretion in oth D nd 3D ulture (Fig EVD nd E). Consistent with D ulture results, tretment of ME18 ells with AREG lso signifintly stimulted ell growth in the 3D ulture system (Fig 8C nd E). Both TGF- nd AREG speifilly ind to EGFR to regulte ell prolifertion. Knokdown of EGFR inhiits sl nd -indued growth of ME18 ell (Fig EV5A nd B). Most importntly, knokdown of EGFR signifintly redued sl nd -indued seretion of AREG (Fig EV5C). In ddition, the involvement of EGFR pthwy in regulting ervil ner ell growth is further evidened y the oservtion tht tretment of ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells with AG178 (EGFR inhiitor) drmtilly loked their ility to form olonies in the soft gr (Fig 8D). We lso found tht verteporfin, n ntgonist of (Liu-Chittenden et l, 1), not only suppressed the olony formtion of ME18-MXIV, ME18-, nd ME18- S17A ells (Fig 8D), ut lso redued the prodution of AREG in these ells (Fig EV5C). ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 9
10 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A Reltive mrna Level MXIV S17A Reltive mrna Level EGFR MXIV S17A Reltive mrna Level TGF-α MXIV S17A Reltive mrna Level AREG MXIV S17A B C Cell numer (x1 5 ) CTRL 3 TGF-α 1 6 DAYS Control G1: 7.58% S: 16.8% G: 8.9% Apo: 1.78% TGF-α h G1: 63.18% S:.7% G: 1.55% Apo: 1.79% D TGF-α 18h Control 18h TGF-α h Control h E Control TGF-α 1h Control 1h Figure 5. 1 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
11 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A C ME18_TGF-α p- (S17) AREG mrna (fold hnge) E Cell numer ( 1 6 ) sictrl Control TGF-α CTRL TGF-α MXIV si S17A p-egfr EGFR p-erk1/ ERK1/ p-akt AKT1/ β- n d On the soft gr, ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells formed muh more, lrger nd fst-growing olonies in omprison with ME18-MXIV ells (Figs 3C nd 8D). We oserved tht olonies derived from ME18- S17A nd ME18- ells re somewht resistnt to AG178 or verteporfin tretment. However, omined tretment with verteporfin nd AG178 ompletely loked the growth of ME18- S17A ells on soft gr, suggesting tht the omined trgeting of the Hippo/ nd EGFR pthwys my e more effiient wy to inhiit ervil ner ell growth (Fig 8D). We then used more physiology-relevnt 3D ulture system to exmine our finding. ME18 ervil ner ells were loded onto the 3D ulture system nd inuted for 3 dys to form spheroids. The formed spheroids were treted with verteporfin or/ nd AG178 for 6 dys. We found tht AG178 tretment resulted in sttered distriution of ME18 ells nd inompletely formed spheroids, inditing tht lokde of EGFR ould prtilly disrupt ervil ner ell ell ommunition (Fig 8E). Verteporfin tretment ompletely loked ner ell growth nd disrupted ervil ner ell ell ommunition, leding to the destrution of initilly formed spheroids (Fig 8E). Comined tretment with AG178 nd verteporfin lso ompletely loked the formtion of spheroids in the 3D hngingdrop ulture system (Fig 8E). D B AREG mrna (fold hnge) F % Wound losure ME18_TGF-α CRTL sictrl sictrl CTRL TGF-α d si p- (S17) p- (S397) Control TGF-α si p-lats1 (99) LATS1 p-mob1 MOB1 β-tin Figure 6. TGF- regultes the Hippo signling pthwy in ervil ner ells. A Western lot nlysis showing effets of TGF- on phosphoryltion of EGFR,, AKT, nd ERK1/. ME18 ells were strved for 6 h fter rehing ell onfluene, then ells were treted with TGF- (1 ng/ml) for, 5, 1, 3, 6 or 1 min. B Western lot nlysis showing effets of TGF- on the phosphoryltion of the omponents of the Hippo signling pthwy. ME18 ells were strved for 6 h fter rehing ell onfluene, then ells were treted with TGF- (1 ng/ml) for, 3, 6 min. C Rel-time PCR determines the tion of TGF- nd levels on the mrna expression of AREG. Eh r represents the men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (Ctrl vs. TGF-, P <.1; MXIV vs., P <.1; MXIV vs. S17A, P <.1). D Rel-time PCR nlysis showing tht knokdown of with sirna (si) signifintly suppressed TGF--indued (FBS 1%, TGF-: 1 ng/ml for 8 h) AREG expression in ME18 ells. sictrl, non-trgeting sirna, ws used s negtive ontrol. Eh r represents the men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sictrl+tgf-, P <.1; si+ctrl vs. si+tgf-, P <.1; sictrl+tgf- vs. si+tgf-, P =.67). E Prolifertion of ME18 ells (FBS 1%) treted with ontrol (sictrl) or (si) prior to tretment with ontrol medium or TGF- (1 ng/ml) for 18 h. Eh r represents the men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sictrl+tgf-, P =.58; si+ctrl vs. si+tgf-, P =.18; sictrl+tgf- vs. si+tgf-, P =.13). F Quntittive dt of the wound-heling ssy showing the migrtion of ME18 ells tht were treted with ontrol (sictrl) or sirna (si) prior to tretment with or without TGF- for 1 h. Eh r in r grphs represents the men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sictrl+tgf-, P <.1; si+ctrl vs. si+tgf-, P <.1; sictrl+tgf- vs. si+tgf-, P =.1). Dt informtion: Dt in (C F) were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. is involved in HPV E6 regultion of ervil ner ell growth Epidemiologil studies hve shown tht the high-risk HPV E6/E7 protein plys ritil role in the initition nd progression of ervil ner. However, the ext moleulr mehnism underlying the ility of high-risk HPV E6/E7 to regulte ervil ner is lrgely unknown. Tretment of HT3 ells (ervil ner ells without HPV infetion) (Fogh et l, 1977; Yee et l, 1985) with HPV16 E6 protein signifintly inresed ner ell growth (Fig 9A). Surprisingly, tretment of HT3 ells with HPV16 E6 inresed protein levels of totl nd phosphorylted (Ser17), ut hd no effet on the protein level of -tin (Fig 9B). Rel-time PCR results showed tht tretment of HT3 ells with HPV16 E6 for 8 h lso signifintly inresed mrna level of AREG (Fig 9C). This finding is onsistent with the oserved inrese in protein levels sine AREG is downstrem gene of the Hippo/ pthwy. Knokdown of with sirna eliminted HPV16 E6-stimulted HT3 ell prolifertion (Fig 9D nd E), further suggesting tht is n importnt meditor of HPV16 E6 tion in ervil ner ells. Sine HeL ells express endogenous HPV18 E6 protein, we used this ell line to determine whether lso medites the tion of endogenous HPV E6 protein. Knokdown of HPV18 E6 with speifi sirna not only deresed E6 mrna level, ut lso redued ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 11
12 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A C D AREG mrna (fold hnge) h_control 1 h_control 1 h_areg 3 1 AREG CTRL AREG p-egfr p- (S17) p- (S397) LATS1 p-lats1 (S99) MOB1 p-mob1 β-tin 3 6 (Minutes) E B AREG mrna (fold hnge) Cell numer (1 5 ) 3 1 Control AREG- h CTRL AREG sictrl si Control AREG 8 h Figure 7. Funtion nd expression of AREG in ervil ner ells. A Western lot nlysis showing tht AREG tretment indued dephosphoryltion of LATS1, MOB1, nd. ME18 ells were strved for 6 h fter rehing ell onfluene, then ells were treted with AREG (5 ng/ml) for, 3, 6 min. B AREG (5 ng/ml) tretment indued pperne of elongted ells in ME18 ells (top nd middle pnels) nd signifintly stimulted ME18 ell prolifertion (lower pnel). Eh r represents men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P =.3). Sle r: 1 lm. C Wound-heling ssy showing tht AREG stimultes migrtion of ME18 ervil ner ells within 1 h in serum-free medium. Sle r: lm. D Rel-time PCR showing tht tretment of ME18 ells with AREG for h signifintly inresed AREG mrna expression. Eh r represents men SEM (n = 9). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P <.1). E Rel-time PCR showing tht knokdown of in ME18 ells with sirna (si) signifintly suppressed AREG-indued AREG mrna expression. sictrl (non-trget sirna) ws used s sirna ontrol. Eh r represents men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sictrl+areg, P <.1; si+ctrl vs. si+areg, P <.1; sictrl+areg vs. si+areg, P =.37). Dt informtion: Quntittive dt in (B) nd (D) were nlyzed for signifine using unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Dt in (E) were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. d protein levels (Fig 9F), suppressed AREG mrna expression (Fig 9G), nd inhiited HeL ell prolifertion (Fig 9H). Moreover, knokdown of HPV18 E6 deresed AREG seretion in HeL ells (Fig 9I). Knokdown of redued protein (Fig 9F), suppressed AREG mrna expression (Fig 9G), nd inhiited HeL ell prolifertion (Fig 9H). Knokdown of hd no effet on the mrna level of HPV18 E6 (Fig 9F). These results suggested tht oth reominnt nd endogenous HPV E6 proteins were le to inrese protein levels. HPV E6 prevents protein from degrdtion The HT3 ner ell line, whih is HPV negtive (Fogh et l, 1977; Yee et l, 1985), ws used to determine the mehnism underlying HPV16 E6 regultion of protein level. Tretment of HT3 ells with HPV16 E6 inresed protein (Fig 9B nd D), ut HPV16 E6 did not ffet mrna expression (Fig 1A nd B). This suggests tht HPV16 E6 my regulte protein turnover. Tretment of HT3 ells with MG13, potent protesome inhiitor, for h or 8 h drstilly inresed nd EGFR protein levels (Fig 1C). In ontrst, tretment of HT3 ells with yloheximide (CHX), n inhiitor of eukryoti gene trnsltion, for h or 8 h signifintly redued EGFR nd protein levels (Fig 1C nd D). This evidene suggests tht nd EGFR proteins re ontinuously synthesized nd degrded in protesome-dependent mehnism in ervil ner ells. The ddition of HPV16 E6 prevented the degrdtion of protein in CHX-treted ells, ut hd little or no effet on the degrdtion of EGFR (Fig 1D nd E). These oservtions lerly indite tht HPV16 E6 stilizes the protein in ervil ner ells. To explore the mehnisms underlying HPV E6 stilizing protein, we trnsfeted HT3 ells with lentivirus empty ontrol vetor (Ctrl) or lentivirus-sed HPV16 E6-expressing vetor nd estlished HT3-CTRL nd HT3-E6 ell lines. Western lotting results indited tht expression of E6 in HT3 ells lso inresed the proteins level of totl nd Ser17-phosphorylted (Fig 1F), ut drmtilly deresed Ser397-phosphorylted (Fig 1F). It hs een reported tht phosphoryltion of ( protein isoform 1) t Ser397 (orresponds to Ser381 in protein isoform ) primes for susequent phosphoryltion y CK1d/e, leding to -TrCP (SCF) uiquitin ligse-dependent proteolyti degrdtion of protein (Zho et l, 1). Surprisingly, we found tht expression of E6 in HT3 ells hd little or no effet on the -TrCP nd LATS1/, ut it inresed the protein level of CK1d/e (Fig 1F). The HPV E6- indued derese in p- (S397) nd inrese in CK1d/e suggested tht the CK1d/e my not e tively involved in HPV E6 stiliztion of protein. Hong et l (1) reently suggested SOCS6 n diretly ind to nd indue degrdtion. Interestingly, we found tht expression of HPV16 E6 redued the protein level of SOCS6 in HT3 ells. Knokdown of HPV18 E6 inresed the protein level of SOCS6 in HeL ells (Fig 1F nd G). These results indite tht SOCS6 my ply role in HPV E6-medited stiliztion of. To onfirm our finding, we knoked down SOCS6 in HT3 ells using SOCS6 sirnas. Western lot nlysis demonstrted tht knokdown of SOCS6 inresed totl nd phosphoryltion of t Ser17 levels, ut deresed phosphoryltion of t Ser397 (Fig 1H). 1 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
13 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A CTRL silats B Volume (fold hnge) 3 1 CTRL silats C D CTRL AG178 VTPF VTPF+AG178 S17A MXIV Volume (fold hnge) 3 1 CTRL AREG E CTRL AREG AG178 VTPF AG178+VTPF Figure 8. The Hippo/ nd the ERBB pthwys intert with eh other to regulte ervil ner ell growth. A Representtive imges showing the morphology of spheroids derived from ME18-siCtrl nd ME18-siLATS1/ ells growing in 3D hnging-drop ulture system for 1 dys. Sle r: 1. mm. B Quntittive dt showing hnges in the volume of spheroids derived from ME18-siCTRL nd ME18-siLATS1/ ells growing in 3D hnging-drop ulture system. Eh r represents men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P =.). C Quntittive dt showing hnges in the volume of spheroids derived from ME18 ells growing in 3D hnging-drop ulture system in the sene or presene of AREG ( ng/ml, 8 dys). Eh r represents men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P =.3). D Soft gr ssy showing the effet of AG178 nd VTPF on olony formtion in ME18-MXIV, ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells. Sle r: 5 lm. E Representtive imges showing the effet of AREG, EGFR inhiitor (AG178), nd ntgonist verteporfin (VTPF) on the growth of ME18 ell in 3D hnging-drop ulture system. ME18 ells were inuted in the 3D hnging-drop ulture system for 1 dys in the sene or presene of AREG, AG178 or verteporfin for 8 dys. Sle r: 1. mm. Dt informtion: Quntittive dt in (B) nd (C) were nlyzed for signifine using unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Soure dt re ville online for this figure. ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 13
14 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l Clerly, SOCS6 is tively involved in HPV E6 stilizing protein in the ervil ner ells. expression in HPV16 E6/E7-indued mouse ervil tumors nd HPV16-ontining humn foreskin kertinoytes rft ultures Trnsgeni mouse models were used to determine whether HPV E6 lso effets protein level in vivo. Previous studies showed tht HPV16-E6 or HPV16-E6/E7 doule-trnsgeni mie treted for 6 months with estrogen n develop ervil ners (Brke & Lmert, 5; Shi et l, 7). Consistent with our results, we found tht in omprison with the ontrol mouse ervil tissues (Fig 11A nd B), is highly expressed in the E6 (Fig 11C nd D) nd E6/E7-indued ervil tumor tissues (Fig 11E nd F) nd is minly lolized to nuleus of tumor ells (Fig 11D nd F). The HPV16-ontining orgnotypi humn foreskin kertinoyte (HFK) rft ulture system provides n unique model to investigte the life yle of HPV16 (Lmert et l, 5; Wng et l, 9). We used the HFK rft ulture system to onfirm whether the wild-type HPV16 lso ffets protein levels in HFKs, whih shre mny similr fetures with the sl epithelil ells in the ervil epitheli. IHC stining results showed tht kertinoytes in HPV16 plsmid-ontining rft ultures were hyperprolifertive ompred with ells in HPV-free HFK rft ultures (ontrol) (Fig 11G nd H). More importntly, we found tht signl intensity in kertinoytes in HPV16-ontining rft ultures ws muh higher in omprison with tht of ontrol (Fig 11G J). Moreover, our results showed tht the mjority of the immunosignl ws lolized to the mid- to upper spinous ells, with reltively lower signls oserved in sl nd prsl ells (Fig 11H). The expression level nd distriution of in the HPV16-ontining orgnotypi HFK rft ulture system perfetly mth the expression pttern nd HPV DNA distriution tht re onsistently oserved in nturlly ourring HPV lesions (Stoler & Broker, 1986; Xio et l, 1). Disussion Epidemiologil nd moleulr evidene indites tht high-risk HPV, espeilly HPV type 16 nd type 18, plys ustive role in ervil ner (Jeml et l, 11). However, the moleulr mehnism(s) underlying HPV initition of ervil ner remins unler. Moreover, in HPV-infeted ptients, the mjority of HPVssoited lesions regress spontneously (Melnikow et l, 1998), inditing tht dditionl genomi ltertions re lso neessry for trnsformtion of ervil epithelil ells nd progression of ervil ner. The present study provides ompelling evidene showing tht the HPV E6 protein, the Hippo pthwy, nd the EGFR signling pthwy intert with eh other to regulte ervil ner progression. Yes-ssoited protein is the mjor downstrem effetor of the Hippo pthwy. Ativtion of the Hippo pthwy results in phosphoryltion nd sequestrtion of into the ytoplsm, leding to intivtion of -regulted gene trnsription (Fernndez et l, 9; Pn, 1). Elevted expression nd nuler loliztion hve een oserved in multiple types of humn ners, inluding liver ner, olon ner, epithelil ovrin ner, lung ner, nd prostte ner (Overholtzer et l, 6; Zender et l, 6; Dong et l, 7; Yun et l, 8; Zhng et l, 9; Hll et l, 1; Jeml et l, 11; Hergovih, 1; He et l, 15). In liver ner, hs een reported to e n independent prognosti mrker for overll survivl nd disese-free survivl (Xu et l, 9). In epithelil ovrin ner, reserh hs shown tht high level of nuler is strongly ssoited with poor ptient survivl (Hll et l, 1). Up to dte, only one IHC study showed tht ould funtion s preditive mrker for ervil ner (Xio et l, 1). The role of in ervil ner is unler. In the present study, we show tht is overexpressed in the ervil ner tissues. Moderte/strong expression of protein ws oserved in 91% of ervil ner tissues, while moderte/strong expression of protein ws not oserved in ll 1 norml ervil tissues (Tle 1). Moreover, expression ws signifintly orrelted with the FIGO stge, the extent of tumor, nd the degree of regionl lymph node involvement. To verify the linil relevne of up-regultion in the ervil ner, we performed rossner gene ltertion nlysis y using the multidimensionl ner genomi dtsets nd online nlysis tools. We surprisingly found tht mong ll ner types, ervil ner hs the highest frequeny of gene ltertions. The susequent network nlysis indited tht mny ell prolifertion-ssoited genes tht interted with were up-regulted in vrious degrees in exmined ervil ner ses. Our dt provide evidene tht ould e used s potentil prognosti iomrker for ervil ner. Sine we do not hve ptient survivl dt, we nnot orrelte expression dt with ervil ptient survivl in the present study. However, the high level of expression nd nuler lotion of protein in ervil ner tissues, s well s the very high frequeny of gene mplifition in the ptient smples, strongly rgue tht plys n importnt role in regulting the progression of ervil ner. The onept tht plys role in regulting the progression of ervil ner is further supported y the following evidene: (i) Knokdown of signifintly redued the growth rte of ME18, HT3, nd HeL humn ervil ell lines in vitro nd suppressed ervil ner tumorigenesis in vivo; (ii) etopi expression of wild-type or onstitutively tive in ervil ner ells signifintly stimulted ner ell growth in vitro; (iii) overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of in ervil ner ells overme the ontt inhiition-indued ell growth inhiition; (iv) overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of in ervil ner ells promoted ell yle progression; nd (v) finlly, overexpression or onstitutive tivtion of in ervil ner ells drmtilly stimulted tumor growth in vivo. As we hve shown in this study, is overexpressed nd lolized to the nuleus of the ner ells in the ervil ner tissues. Aording to our in vitro nd in vivo dt, high levels of iologilly tive protein in the nuleus of ervil ner ells re expeted to stimulte ner ell prolifertion nd promote ervil ner progression. Notly, under low-density ell ulture onditions, knokdown of hd no signifint effet on the growth of ervil ner ells inuted in omplete medium (with 1% FBS). After the ultured ells hieved higher density, ell growth rte in the knokdown group deresed, while ells in the ontrol group ontinued to proliferte. This result is onsistent with the oservtion tht when inuted in omplete medium, ME18- S17A, 1 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
15 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A B C Cell Numer ( 1 6 ) D G 3 Ctrl E6 1 AREG mrna (fold hnge) Dys sictrl si p- (s17) β-tin sictrl sihpv18 E6 si E Cell numer ( 1 6 ) H 3 1 Cell numer ( 1 6 ) 3 1 p- (S17) EGFR β-tin sictrl sictrl+e6 si si+e6 ME18-, nd ME18-MXIV ells hd similr growth rtes efore rehing onfluene. However, fter the ells rehed onfluene, the ME18- S17A nd ME18- ells ontinued to grow, while the prolifertion of ME18-MXIV ells lmost stopped. These findings indite tht my ply ritil role in overoming ell ontt-indued inhiition of ell growth. Interestingly, under serum-redued ulture onditions (with 1% FBS), ME18- S17A nd ME18- ells hve signifintly higher growth rte in omprison with ME18-MXIV ells (P <.1), regrdless of the ell density. The ompenstory tivity of on ell growth with serum deprivtion suggests tht my ontrol the prodution of ertin hormones or growth ftors tht re essentil for the growth of ervil ner ells. The present study indites tht TGF- nd AREG re the ndidte growth ftors. The Hippo/ signling pthwy interts with the ERBB signling pthwy to regulte ervil ner ell prolifertion nd migrtion. This onept is supported y the following evidene: (i) Etopi expression of wild-type or onstitutive tive in ervil ner ells not only signifintly stimulted TGF-, AREG, nd EGFR mrna expression, ut lso indued AREG seretion; (ii) knokdown of LATS1/, the mjor suppressor of, stimulted seretion of AREG; (iii) TGF- nd AREG, vi tivtion of EGFR, stimulted prolifertion, promoted ell yle progression, nd enhned migrtion of ervil ner ells; (iv) TGF- suppressed the Hippo signling pthwy, whih ws demonstrted y the signifint redutions in the phosphoryltion of LATS1, MOB1, nd fter TGF- tretment; (v) tretment of ervil sictrl sihpv18 E6 si F AREG mrna (fold hnge) I AREG (pg/ml) HPV18 E6 GAPDH β-tin 5 Ctrl sictrl E6 8 h Hel sihpv18e6 Figure 9. is involved in HPV-E6 regultion of ervil ner ell growth. A Effet of reominnt HPV16 E6 protein on the prolifertion of HT3 ells. Eh point represents men SEM (n = 5). ***P =.1 ompred with ontrol (Ctrl) on dy. HT3 ells were ultured in serum-redued medium in the presene or sene of reominnt HPV16 E6 ( nm). B Reominnt HPV16 E6 protein inresed protein level, ut hd no effet on -tin protein level in HT3 ells. Cell ulture nd tretment proedure re the sme s desried in (A). C AREG mrna levels in HT3 ells inuted for 8 h with or without reominnt HPV E6. Eh r represents men SEM (n = 5). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P =.). D Western lotting nlysis showing the effet of HPV16 E6 ( nm, 8 h) on protein levels in HT3 ells trnsfeted with non-trgeting ontrol sirna (sictrl) or sirna (si). E Effet of on HPV16 E6 stimultion of HT3 ell prolifertion. sictrl: nontrgeting ontrol sirna; si: sirna; E6: nm reominnt HPV16 E6, 8 h. Eh r represents men SEM (n = ). Brs with the sme letters re not signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sictrl+e6, P =.3; sictrl+e6 vs. si+e6, P =.11). F Knokdown of endogenous E6 in HeL ells with HPV18 E6 sirna (sie6) redued protein in HeL ells, while knokdown of with sirna (si) in these ells hd no effet on the mrna level of HPV18 E6. sictrl: non-trgeting ontrol sirna. G Knokdown of endogenous HPV18 E6 in HeL ells with HPV18 E6-speifi sirna (sie6) signifintly suppressed mrna expression of AREG. Eh r represents men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (sictrl vs. sihpv18e6, P =.181; sictrl vs. si, P =.5). H Knokdown of endogenous HPV18 E6 in HeL ells with HPV18 E6-speifi sirna (sie6) signifintly suppressed ell growth (n = 9, sictrl vs. sihpv18e6, P =.; sictrl vs. si, P =.). I Conentrtions of AREG in the ulture medium of HeL ells trnsfeted with non-trgeting ontrol sirna (sictrl) or HPV18 E6 sirna (sihpv18e6). Eh r represents men SEM (n = 6). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (P =.61). Dt informtion: Quntittive dt in (A), (C), nd (I) were nlyzed for signifine using unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Dt in (E), (G), nd (H) were nlyzed for signifine using onewy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. ner ell with TGF- indued -fold inreses in the trnsription of AREG, known downstrem trget of the Hippo/ signling pthwy (Zhng et l, 9; Yu & Gun, 13); nd (vi) knokdown of eliminted TGF--indued prolifertion nd migrtion of ervil ner ells. Knokdown of lso suppressed TGF-indued AREG trnsription in ervil ner ells. We lso found tht AREG signifintly stimulted ervil ner ell prolifertion nd promoted ner ell migrtion. Intriguingly, AREG ws le to suppress phosphoryltion of LATS1, MOB1, nd in the ervil ner ells, suggesting tht AREG is not only downstrem trget of the Hippo pthwy, ut lso n importnt upstrem regultor of the Hippo/ signling pthwy. Remrkly, we found tht tretment of ervil ner ells with AREG resulted in fourfold inrese in the expression of AREG mrna (P >.1). Furthermore, loking EGFR tivity with AG178, or knokdown of EGFR using siegfr, eliminted -indued ell prolifertion nd AREG seretion of ervil ner ells. These oservtions, together with previous results, provide onvining evidene for the existene of n AREG/EGFR/Hippo signling pthwy//areg utorine loop in ervil ner ells, whih my ply ritil role in the progression of ervil ner (Fig 1). Of relevne to our findings re previous reports showing tht EGFR is overexpressed in ervil ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 15
16 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A mrna (Fold hnge) Reltive Level CTRL E6 1 h HT3 Cell (8 h) EGFR Atin Ctrl CHX CHX+E6 E6 B mrna (Fold hnge) HT3 Cell CTRL E6 8 h D F G E p- (S17) p- (S397) LATS1 LATS β-trp SOCS6 CKIε Atin Hel ell ner nd is ssoited with poor prognosis nd deresed survivl of ervil ner ptients (Shrevel et l, 11; Soonthornthum et l, 11). The existene of this feedk loop in humn ervil ner nd its linil relevne were further evidened y the results derived from multidimensionl ner genomi dt nlysis. These nlyses indite tht ~81% of humn ervil ner ses hve ltertions in genes involved in this positive feedk loop (Fig 1B). The synergeti suppressive effet of AG178 nd verteporfin on the growth of ME18- nd ME18- S17A ells nd seretion of AREG lerly indites tht omined trgeting of Hippo/ nd EGFR pthwys my represent novel therpeuti strtegy for ervil ner (Figs 8 nd EV5). Sine Hippo-independent tivtion hs lso een reported (Leung & Zernik-Goetz, 13; Feng et l, 1; Tniguhi et l, 15), one n rgue tht the pro-prolifertive role of in ervil ner ells my e independent of the Hippo pthwy. However, our present studies lerly indited tht the Hippo pthwy is involved in the regultion of ervil ner ell growth. First of ll, the results otined from the multidimensionl ner genomi dtsets lerly indited tht in the ervil ner tissue, the Hippo pthwy is frequently disrupted, indited y the frequent deletion nd muttion of the genes involved in the Hippo pthwy (Fig EV1A). As onsequene of the disrupted Hippo pthwy,, TAZ, nd TEADs re frequently up-regulted in ervil ner tissues. Seondly, oth TGF- nd AREG dephosphorylte MOB1, LATS1, nd in ervil ells (Figs 6 nd 7), suggesting tht the Hippo pthwy is tively involved in the EGFR pthwy regultion of ervil ner progression. Finlly, knokdown of LATS1/, the mjor suppressors of, results in dephosphoryltion of in ME18 ervil ner ells, leding to the signifint inrese in the ell prolifertion nd AREG seretion in oth D nd 3D ulture C CHX MG13 H h h 8 h h h 8 h HT3 Cell SOCS6 Atin EGFR Atin EGFR Atin SOCS6 p- (S17) p- (S397) Atin Figure 1. HPV E6 stilizes protein. A Effet of mrna levels in HT3 ells treted with or without E6 ( nm) for 6 min in MCoy s 5A with 1% serum. Dt were normlized with 18S mrna. Brs with sme letters re not signifintly different from eh other (P >.5). n =, P =.97. B mrna levels in HT3 ells treted with or without E6 ( nm) for 8 h in MCoy s 5A with 1% serum. mrna levels were mesured with rel-time PCR. Dt were normlized with 18S mrna. Eh r represents men SEM (n = 5). Brs with sme letters re not signifintly different from eh other (P >.5) (P =.333). C Western lot results showing nd EGFR protein levels fter tretment with MG13 or yloheximide (CHX) for hor8 h. -tin ws used s protein loding ontrol. Confluent HT3 ells were strved for h efore tretment with MG13 (1 lm) or CHX ( lg/ml) for, or 8 h. D HPV16 E6 protein prevented protein from degrdtion. Confluent HT3 ells were strved for h efore tretment with or without CHX ( lg/ ml), HPV16 E6, or CHX omined with HPV16 E6 for 8 h. Tretment of strved HT3 ells with HPV16 E6 ( nm) for 8 h suppressed degrdtion of, ut not EGFR protein. E Quntittive dt showing reltive protein levels in (D). Protein levels were normlized with -tin nd presented s rtios reltive to tht of ontrol. Eh r represents men SEM (n = ). Brs with different letters re signifintly different from eh other (Ctrl vs. CHX, P =.3; Ctrl vs. CHX+E6, P =.665; Ctrl vs. E6, P =.58). F Western lot nlysis showing tht expression of HPV16 E6 in HT3 ells inresed the protein level of totl nd sein kinse Ie, ut deresed the protein level of SOCS6. Importntly, HPV16 E6 inresed phosphoryltion t serine 17, ut suppressed its phosphoryltion t serine 397. HPV16 E6 hd no effet on the level of -TrP, LATS1/ nd MOB1 in HT3 ervil ner ells. G Western lot results showing tht knokdown of endogenous E6 in HeL ells with HPV18 E6 sirna (sie6) redued protein levels, ut inresed SOCS6 protein levels. H Western lot nlysis showing tht knokdown of SOCS6 in HT3 ells with SOCS6 sirna (sisocs#1 nd sisocs6#) inresed totl protein, enhned phosphoryltion of protein t serine 17, ut suppressed phosphoryltion of t serine 397. Dt informtion: Quntittive dt in (A) nd (B) were nlyzed for signifine using unpired t-test in GrphPd Prism 5 with Welh s orretion. Dt in (E) were nlyzed for signifine using one-wy ANOVA in GrphPd Prism 5 with Tukey s post ho tests. systems. These results provide ompelling evidene tht the Hippo pthwy is tively involved in the regultion of ervil ner initition nd progression. The usl reltionship etween high-risk HPV infetion nd ervil ner hs een proposed euse high-risk HPVs, suh s HPV16, HPV18, nd HPV31, hve een deteted in up to 99.7% of ervil squmous ell rinoms nd 9 1% of ervil denond denosqumous rinoms (Wloomers et l, 1999; Cstellsgue et l, 6). Two types of high-risk HPVs, HPV16 nd HPV18, hve een proposed to e responsile for more thn 7% of ll ervil ner ses (Shiffmn et l, 7). It is elieved tht the high-risk HPV onoproteins, E6 nd E7, ontriute to ervil rinogenesis y intivting the ellulr tumor suppressor proteins p53 nd pr, respetively (Dyson et l, 1989; Sheffner et l, 199; Boyer et l, 1996). However, reent studies showed tht lthough persistent infetion with high-risk HPV is neessry step for the development of ervil ner, HPV lone is not suffiient to initite nd drive the progression of ervil ner (Melnikow et l, 1998; Reshmi & Pilli, 8). Moreover, evidene shows tht HPV E6-indued degrdtion of P53 my hve no role on ell trnsformtion. For exmple, it hs een shown tht mutnts of E6, 16 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
17 Chuno He et l Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner EMBO Moleulr Mediine A C E B D F G H I J Figure 11. expression in norml, HPV16 E6, nd HPV16 E6/E7-indued nerous ervil tissues in trnsgeni mouse model, nd HPV16-ontining humn foreskin kertinoyte rft ultures. A F Representtive imges showing expression of (in red) in wild-type mouse ervil tissues (n = 5) (A), HPV16 E6-indued (C) nd HPV16 E6/E7-indued (E) mouse ervil tumor tissue (n = eh). Sle rs for (A), (C), nd (E): 1 lm. High-resolution imges showing the expression nd ellulr lotion of in norml ervil tissues (B), HPV16 E6-indued (D) nd HPV16 E6/E7-indued (F) mouse ervil tumor tissue. Sle rs for (B), (D), nd (F): 5 lm. G, H Representtive imges showing expression of (in red) in norml (G) nd HPV16-ontining humn foreskin kertinoyte rft ultures (n = 5 eh) (H). Sle rs: 1 lm. I, J High-resolution imges showing the expression nd ellulr lotion of in norml (I) nd HPV16-ontining humn foreskin kertinoytes rft ultures (J). Sle rs: lm. ª 15 The Authors EMBO Moleulr Mediine 17
18 EMBO Moleulr Mediine Role of Hippo/ pthwy in ervil ner Chuno He et l A Crosstlk mong HPV, nd EGFR signling pthwys in ervil ner. B Altertions of genes involved in the Hippo//EGFR positive feedk loop in ervil ner. 81% (11/135) of se ltered EGFR 1% AREG 17% TGF-α 11% PIK3CA 53% ERK1/ 18% 16% LATS1/ 6% Amp, Mut or mrna Upregultion Del, Mut or mrna Downregultion HPVE6 ~99% Figure 1. Shemti rtoons showing the proposed mehnism underlying the Hippo signling pthwy regultion of ervil ner progression. A Shemti rtoons showing the proposed positive feedk loop in ervil ner ells. Dt in this study support the existene of n utorine loop involving EGF-like lignds/egfr pthwy/hippo pthwy/egf-like lignds in regulting the prolifertion nd motility of ervil ner ells, whih plys ritil role in ner progression. Under norml onditions, low levels of EGF-like lignds suh s TGF- nd AREG re not suffiient to tivte EGFR. The intive EGFR ensures the tivtion of Hippo signling pthwy, whih in turn results in uiquitintion-dependent degrdtion of protein. In ervil ner tissues, espeilly the dvned-stge ner tissues, the elevted nuler protein stimultes the expressions of TGF- nd AREG, whih in turn tivtes the EGFR, leding to suppression of LATS1 nd MOB1 phosphoryltion. Dephosphoryltion of LATS1 nd MOB1 results in the dissoition of LATS1/-MOB1 omplex, leding to intivtion of the Hippo pthwy nd susequent tivtion of the growth-promoting o-tivtor. Ativted indues expression of growth ftors suh s TGF- nd AREG to drive ervil ner growth. -indued growth ftors suh s TGF- nd AREG omplete the utorine loop y tivting EGFR nd to drive the prolifertion of ner ell nd the prodution of growth-promoting ftors in ervil ner ells. HPV E6 protein mintins protein level in the HPV-infeted norml nd nerous ervil ells y preventing from protesome-dependent protein degrdtion. B Shemti rtoons showing the linil relevne of the proposed positive feedk loop in ervil ner. Multidimensionl ner genomis dt nlysis indites tht very high frequeny of ltertions hs een oserved in genes involved in the Hippo//EGFR positive feedk loop in ervil ner (we knowledge The Cner Genome Atls (TCGA) Dt Portl for the dtsets nd the BioPortl for Cner Genomis for the online nlysis tools). defetive in their ility to indue the degrdtion of p53, n still immortlize humn emryoni ells (Ishiwtri et l, 199; Nkgw et l, 1995). E6 proteins from HPV-5 nd HPV-8 do not intert with P53 protein, ut they re neessry for immortliztion of rodent firolsts (Elel et l, 1997). On the ontrry, E6 protein of the low-risk HPV-1 inhiits P53 trnstivtion (Kiyono et l, 199). Therefore, the ext moleulr mehnism for HPV to drive the initition nd progression of ervil ner is not ler. Other funtions of E6 must lso e involved in this proess. In the present study, for the first time, we show tht the dysregultion of the Hippo pthwy my e involved in the HPV-indued initition nd progression of ervil ner. We found tht HPV E6 protein is le to inrese the level of, the mjor effetor of the Hippo pthwy, in ervil ner ells y preventing from protesome-dependent degrdtion. Regultion of protein turnover y uiquitin-medited protein degrdtion hs long een reognized s n importnt mehnism for regulting the tivity of signl trnsdution pthwys in ner (Mrmor & Yrden, ; Fuld et l, 1). Reent studies suggested is intivted y two mehnisms: (i) the Ser17 phosphoryltion-medited sptil regultion (nuler ytoplsmi shuttling); nd (ii) the Ser397 (Ser381 in protein isoform ) phosphoryltion-medited temporl regu- 18 EMBO Moleulr Mediine ª 15 The Authors
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
MicroRNA 125b promotes tumor metastasis through targeting tumor protein 53 induced nuclear protein 1 in patients with non small cell lung cancer
 Li et l. Cner Cell Int (15) 15:8 DOI 1.118/s1935-15-33-x PRIMARY RESEARCH MiroRNA 15 promotes tumor metstsis through trgeting tumor protein 53 indued nuler protein 1 in ptients with non smll ell lung ner
Li et l. Cner Cell Int (15) 15:8 DOI 1.118/s1935-15-33-x PRIMARY RESEARCH MiroRNA 15 promotes tumor metstsis through trgeting tumor protein 53 indued nuler protein 1 in ptients with non smll ell lung ner
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Role of HCP5-miR-139-RUNX1 Feedback Loop in Regulating Malignant Behavior of Glioma Cells
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therapeutic for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Progestin effects on cell proliferation pathways in the postmenopausal mammary gland
 Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Jeffrey D. Coleman, 1 Jerry T. Thompson, 1 Russell W. Smith III, 1 Bogdan Prokopczyk, 2,3 and John P. Vanden Heuvel 1,3,4. 1.
 PPAR Reserh Volume 213, Artile ID 121956, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/121956 Reserh Artile Role of Peroxisome Prolifertor-Ativted Reeptor β/δ nd B-Cell Lymphom-6 in Regultion of Genes Involved
PPAR Reserh Volume 213, Artile ID 121956, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/121956 Reserh Artile Role of Peroxisome Prolifertor-Ativted Reeptor β/δ nd B-Cell Lymphom-6 in Regultion of Genes Involved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
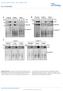 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
Erucin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Murine Macrophages and Mouse Skin: Possible Mediation through the Inhibition of NFκB Signaling
 Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling
 Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
The Disappearance of Lymph Node Metastasis from Neuroendocrine Carcinoma after Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Aspiration
 CASE REPORT The Dispperne of Lymph Node Metstsis from Neuroendorine Crinom fter Endosopi Ultrsound-guided Fine Needle Aspirtion Msyuki Shit 1, Hiroyuki Mtsuyshi 1, Akiko Todk 2, Hnko Kuri 3, Noyuki Tsutsumi
CASE REPORT The Dispperne of Lymph Node Metstsis from Neuroendorine Crinom fter Endosopi Ultrsound-guided Fine Needle Aspirtion Msyuki Shit 1, Hiroyuki Mtsuyshi 1, Akiko Todk 2, Hnko Kuri 3, Noyuki Tsutsumi
ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through EGFR/HER-2/ ERK signaling pathway
 Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
New signals from the invasive front Gerhard Christofori 1
 NATURE Vol 441 25 My 2006 doi:10.1038/nture04872 New signls from the invsive front Gerhrd Christofori 1 Approximtely 90% of ll ner deths rise from the metstti spred of primry tumours. Of ll the proesses
NATURE Vol 441 25 My 2006 doi:10.1038/nture04872 New signls from the invsive front Gerhrd Christofori 1 Approximtely 90% of ll ner deths rise from the metstti spred of primry tumours. Of ll the proesses
BRAF Inhibition Generates a Host Tumor Niche that Mediates Therapeutic Escape
 See relted ommentry on pg 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BRAF Inhiition Genertes Host Tumor Nihe tht edites Therpeuti Espe Inn V. Fedorenko 1, Jennifer A. Wrgo, Keith T. Flherty, Jne L. essin nd Keirn S.. Smlley 1,
See relted ommentry on pg 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BRAF Inhiition Genertes Host Tumor Nihe tht edites Therpeuti Espe Inn V. Fedorenko 1, Jennifer A. Wrgo, Keith T. Flherty, Jne L. essin nd Keirn S.. Smlley 1,
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Melatonin, a novel selective ATF-6 inhibitor, induces human hepatoma cell apoptosis through COX-2 downregulation
 Submit Mnusript: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.986 World J Gstroenterol 2017 Februry 14; 23(6):986-998 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN
Submit Mnusript: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.986 World J Gstroenterol 2017 Februry 14; 23(6):986-998 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN
F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Breast Cancer to mir-143-based Therapeutics by Targeting Tumor Glycolysis
 Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids () 5, e57; doi:.8/mtn..7 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Brest Cner to -Bsed Therpeutis
Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids () 5, e57; doi:.8/mtn..7 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Brest Cner to -Bsed Therpeutis
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Oocytes determine cumulus cell lineage in mouse ovarian follicles
 133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
13-cis Retinoic Acid Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human SEB-1 Sebocytes
 ORIGINAL ARTILE See relted ommentry on pge 15 13-is Retinoi Aid Indues Apoptosis nd ell yle Arrest in Humn SEB-1 Seoytes Amnd M. Nelson 1, Kthryn L. Gillilnd 1, Zhoyun ong 1 nd Dine M. Thioutot 1, Isotretinoin
ORIGINAL ARTILE See relted ommentry on pge 15 13-is Retinoi Aid Indues Apoptosis nd ell yle Arrest in Humn SEB-1 Seoytes Amnd M. Nelson 1, Kthryn L. Gillilnd 1, Zhoyun ong 1 nd Dine M. Thioutot 1, Isotretinoin
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
TNFa Signaling Exposes Latent Estrogen Receptor Binding Sites to Alter the Breast Cancer Cell Transcriptome
 Artile TNF Signling Exposes Ltent Estrogen Reeptor Binding Sites to Alter the Brest Cner Cell Trnsriptome Grphil Astrt Authors Hetor L. Frno, Anush Ngri, W. Lee Krus Correspondene lee.krus@utsouthwestern.edu
Artile TNF Signling Exposes Ltent Estrogen Reeptor Binding Sites to Alter the Brest Cner Cell Trnsriptome Grphil Astrt Authors Hetor L. Frno, Anush Ngri, W. Lee Krus Correspondene lee.krus@utsouthwestern.edu
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on February 21, 2017, as DOI: /pp
 Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Differential expression of cyclin G2, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C and peripheral myelin protein 22 genes during adipogenesis..
 The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
Research Article Thyroid Hormone Status Interferes with Estrogen Target Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Samples in Menopausal Women
 ISRN Endorinology, Artile ID 317398, 8 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/317398 Reserh Artile Thyroid Hormone Sttus Interferes with Estrogen Trget Gene Expression in Brest Cner Smples in Menopusl Women
ISRN Endorinology, Artile ID 317398, 8 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/317398 Reserh Artile Thyroid Hormone Sttus Interferes with Estrogen Trget Gene Expression in Brest Cner Smples in Menopusl Women
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Upregulation of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 confers the anti-invasive action of cisplatin on human cancer cells
 (27) 26, 5822 5827 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 95-9232/7 $3. SHORT COMMUNICATION Upregultion of tissue inhiitor of mtrix metlloproteinses-1 onfers the nti-invve tion of ispltin on humn
(27) 26, 5822 5827 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 95-9232/7 $3. SHORT COMMUNICATION Upregultion of tissue inhiitor of mtrix metlloproteinses-1 onfers the nti-invve tion of ispltin on humn
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation of Notch-dependent monociliated choroid plexus tumour cells
 Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Targeting TSLP With shrna Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Decreases Epithelial CCL17 in a Murine Model of Asthma
 Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
A2A adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells
 A2A denosine reeptor protets tumors from ntitumor T ells Akio Oht*, Elieser Gorelik, Simon J. Prsd, Frn Ronhese, Dmitriy Lukshev*, Mihel K. K. Wong, Xiojun Hung, Sheil Cldwell**, Kein Liu**, Ptrik Smith*,
A2A denosine reeptor protets tumors from ntitumor T ells Akio Oht*, Elieser Gorelik, Simon J. Prsd, Frn Ronhese, Dmitriy Lukshev*, Mihel K. K. Wong, Xiojun Hung, Sheil Cldwell**, Kein Liu**, Ptrik Smith*,
Supplemental Figures and Legends
 Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
1. Introduction. Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. Correspondence should be addressed to Ana Claudia Latronico;
 BioMed Reserh Interntionl, Artile ID 936031, 7 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936031 Reserh Artile Amplifition of the Insulin-Like Growth Ftor 1 Reeptor Gene Is Rre Event in Adrenoortil Adenorinoms:
BioMed Reserh Interntionl, Artile ID 936031, 7 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936031 Reserh Artile Amplifition of the Insulin-Like Growth Ftor 1 Reeptor Gene Is Rre Event in Adrenoortil Adenorinoms:
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
LETTERS. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M
 Vol 462 24/31 Deemer 29 doi:1.138/nture8622 ovel mutnt-seletive kinse inhiitors ginst T79M Wenjun Zhou 1,2 *, Dli Ern 3,4 *, Ling Chen 3,4 *, Ci-Hong Yun 1,2 *, Dnn Li 3,4, Mrzi Cpelletti 3,4, Alexis B.
Vol 462 24/31 Deemer 29 doi:1.138/nture8622 ovel mutnt-seletive kinse inhiitors ginst T79M Wenjun Zhou 1,2 *, Dli Ern 3,4 *, Ling Chen 3,4 *, Ci-Hong Yun 1,2 *, Dnn Li 3,4, Mrzi Cpelletti 3,4, Alexis B.
Raina Devi Ramnath, Jia Sun, and Madhav Bhatia. Department of Pharmacology, National University of Singapore, Singapore
 -3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
-3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
Braf V600E cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma
 Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
