Citation for published version (APA): Meijer, M. (2015). Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty. [Groningen]: University of Groningen.
|
|
|
- Oswin Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty Meijer, Marrigje IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 015 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): Meijer, M. (015). Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty. [Groningen]: University of Groningen. Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty Chapter Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty M. F. Meijer I. H. F. Reininga A. L. Boerboom M. Stevens S. K. Bulstra International Orthopaedics 013;37:
3
4 Abstract Purpose: Revision total knee arthroplasty (rtka) is a complex procedure. Depending on the degree of ligament and bone damage, either primary or revision implants are used. The purpose of this study was to compare survival rates of primary implants with revision implants when implanted during rtka. Methods: A retrospective comparative study was conducted between 1998 and 009 during which 69 rtkas were performed on 65 patients. Most common indications for revision were infection (30%), aseptic loosening (5%) and wear/ osteolysis (5%). During rtka, a primary implant was used in nine knees and a revision implant in 60. Results: Survival of primary implants was 100% at one year, 73% (95% CI: %) at two years and 44% (95% CI: 7-81%) at five years. Survival of revision implants was 95% (95% CI: %) at one year, 9% (95% CI: 84-99%) at two years and 9% (95% CI: 84-99%) at five years. Primary implants had a significantly worse survival rate compared to revision implants when implanted during rtka (P=.039; hazard ratio= % CI: ). Conclusions: Based on the results, it has to be considered whether primary implants are even an option during rtka. 7
5 Introduction Over the past two decades there has been an increase in the number of primary total knee arthroplasties (TKAs) performed. 1, Despite good results of primary TKA, the number of revision TKAs (rtkas) is rising 3 and a further increase in revision procedures in the future is predicted. 4 The demand for revision TKA is expected to double by 015 and a growth of 601% is predicted for the United States between 005 and A similar trend is expected for other Western countries. Primary implants differ from revision implants in type of insert (constraint) and in the absence of stems and augmentations. During rtka the surgeon faces greater bone loss and more ligament damage, which may lead to instability of the knee joint. 5,6 To overcome these problems, an implant with more constraint is recommended, and augmentations are commonly used to compensate for bone defects. 7 Although a posterior cruciate retaining (PCR) or a posterior stabilized (PS) prosthesis is generally implanted during primary TKA, 8 most of the time, an rtka requires a PS type. 9 Condylar-constrained knee (CCK) and rotating-hinge knee (RHK) types are also commonly used in rtka When all ligaments are intact and of good quality and bone defects are limited, use of a PCR prosthesis will be sufficient. When only the posterior cruciate is damaged, a PS type is needed. A CCK is chosen when one or both collateral ligaments are inadequate. If medial and/or lateral collaterals and cruciate ligaments are compromised or when a severe deformity exists, a RHK is required. 7,8,11,1 The consequence of using one of these types of revision prosthesis, however, is greater constraint. Higher constraint has negative effects on implant interfaces and is usually counteracted by press-fit stems. 8,13 Hence, the choice of implant type is based on accurate assessment of ligament quality, bone loss and component fixation; the least degree of constraint necessary is recommended. 8,10,14-16 In handling bone defects, the classification of the Anderson Orthopaedic Research Institute is a useful guide. 17 In type 1 defects, primary prostheses may be used, whereas type or 3 defects necessitate revision 8
6 Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty implants. Reasons to opt for a primary implant may also be greater surgeon experience and availability of revision components during the operation when encountering defects and the costs. However, theoretical advantages of using primary implants, such as ease of use, less time and cost savings, may be lost when inadequate reconstruction leads to early loosening. Previous research has shown that compared with primary TKA, survival following rtka is poorer The objective of this study was to investigate whether there are differences in survival rates between primary and revision implants when implanted during rtka. Materials and methods Study design and data collection A retrospective comparative study was conducted. Data on 171 rtkas performed between January 1998 and December 009 at our institution were collected retrospectively. The cases were divided into two groups: knees that received a primary implant and knees that received a revision implant. Primary implants were defined as PCR and PS types without the use of stems or augmentations. Revision implants were defined as PS types with the use of stems or augmentations and CCK and RHK types. Survivorship and reason for any reoperation were documented. A telephone call to obtain this information was made to the patients, or to their general practitioner or surviving relative when a patient had died. The study was conducted in accordance with the regulations of the local medical ethical committee. Study population Patients with a primary total knee implant who underwent a total revision or reimplantation were included in the study. Excluded were partial revisions, insert replacements, conversions from a unicompartimental prosthesis to a total knee prosthesis and patients who received a tumour prosthesis during revision surgery. Eventually, 69 knees (65 patients) were available for final analysis (Fig. 1). The patient population consisted of 7 9
7 men and 38 women, with a mean age of 64.3 (range 30-85) years. Mean time between primary TKA and rtka was (range -76) months. The most common reasons for revision were infection (30%), aseptic loosening of one or more components (5%) and wear/osteolysis (5%). During rtka, nine knees received a primary implant and 60 knees received a revision implant. Of the nine knees receiving a primary implant, three received a NexGen Legacy posterior stabilized (NexGen PS; Zimmer, Warsaw, IN, USA), five an AGC PCR prosthesis (Biomet Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA) and one an LCS rotating platform (PS) prosthesis (Depuy Johnson & Johnson, Warsaw, IN, USA). Sixty revisions were performed with a NexGen revision implant with stems and augmentation. In 37 knees a PS insert was used, in 0 a semiconstrained insert (Legacy Condylar Constrained Knee, LCCK) and in three a rotating-hinge knee (NexGen RHK; Zimmer, Warsaw, IN, USA). Surgical procedure Revision TKA was performed by two senior orthopaedic surgeons (SKB and ALB) working at our institution. During rtka all components were removed and replaced by a primary or revision implant. The medial parapatellar approach was used in all procedures, and all femoral, tibial and patellar components were cemented. Stems were routinely uncemented but a press-fit was used. Infections were treated by two-stage revision. Postoperatively, all patients followed the same protocol with early weight bearing mobilisation permitted in cases with repair of contained defects. Otherwise, this was postponed to six to 1 weeks postoperatively, depending on individual situations. Statistical analysis Survival of primary implants used during rtka was compared with survival of revision implants. The patient who was lost to follow-up was censored using the date of last contact at our hospital. Deceased patients were censored using the date of death. Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were performed to assess the survival of the two types of implant at one, two and five years. To study differences between groups and to adjust for potential confounders 30
8 POOReR SuRvIvAL AFteR A PRIMARy IMPLAnt during RevISIOn total Knee ARtHROPLASty such as age, indication, sex and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, the Cox regression analysis was performed. 1 Additionally, the variables of age, indication (septic or aseptic), sex and ASA classification were assessed for confounding. When the variable was a significant confounder, it was added to the Cox regression. The endpoint for survival following rtka was defined as repeat revision when one or more of the components was removed or exchanged. Statistical analyses were performed using the PASW software package (version 18, SPSS, Chicago). A p-value of <.05 was considered to be statistically significant. 171 revision TKAs performed between January 1998 and December knees were excluded according to the exclusion criteria Reasons for exclusion (number of knees): - A tumor prosthesis was implanted (3) - Partial revisions, insert replacements or conversions from unicompartimental knee prosthesis to total knee prosthesis (70) 69 knees (65 patients) were available for final analysis Figure 1. Flow chart of exclusion procedure. 31
9 Results Mean survival of all rtkas was 58.6 (range 1-161) months. Overall survival of both primary and revision implants was 96% (95% CI: %) at one year, 89% (95% CI: 8-97%) at two years and 85% (95% CI: 75-94%) at five years. Survival of primary implants was 100% at one year, 73% (95% CI: %) at two years and 44% (95% CI: 7-81%) at five years. Survival of revision implants was 95% (95% CI: %) at one year, 9% (95% CI: 84-99%) at two years and 9% (95% CI: 84-99%) at five years. The use of a revision implant during revision surgery had a significantly better survival rate than the primary implant (P=.008; hazard ratio (HR) = 5.87, 95% CI: ). 1,0 Cumulative survival 0,8 0,6 0,4 0, 0, Follow-up time (months) Figure. Survival of revision implants. Implants were divided into two groups: primary implants and revision implants. Covariate septic or aseptic indication for revision was added in this Cox regression analysis. 3
10 Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty The variables of age, ASA classification and sex were not significant confounders. The variable of indication for rtka because of sepsis appeared to be a significant confounder. After adding this confounder into the Cox regression analysis, use of a revision implant during rtka retained a significantly better survival rate than implantation of a primary implant (P=.039; HR=4.56, 95% CI: ) (Fig. ). A total of nine re-operations were assessed in this study. Four primary implants underwent a re-rtka. Indications were aseptic loosening in two cases and infection in two cases. Five revision implants underwent a re-operation. Three re-rtkas, one amputation and one arthrodesis were performed. Indications for re-rtka were aseptic loosening, infection and instability in one case each. Indication for amputation was chronic pain, and infection was the reason for arthrodesis. Discussion To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate survival of primary and revision implants. Over the past two decades, there has been an increase in rtkas 3 performed, and a further increase is predicted. 4 This has heightened the interest in rtka and factors that influence the outcome of this procedure. During rtka, primary and revision implants are used to restore the knee joint. However, little is known about the survival rate of both types of implants following rtka and whether implanting a primary implant during rtka is a good option. This study was conducted to compare survival rates of primary implants with revision implants when implanted during rtka. Our results show that a primary implant used during rtka suffers a significantly worse survival rate compared with a revision implant during the revision operation. Overall survival of implants, with repeat rtka defined as the endpoint, was 96% at one year, 89% at two years and 85% at five years in this study. These results are comparable with rtka survival in Finland between 1990 and 00, which showed rates of 95% at two years, 89% at five years and 79% at ten years. 18 Other, generally older, studies report failure rates or poor results of 19-63% for follow-up periods of five years or less
11 In this study, five of the 60 revision implants and four of the nine primary implants underwent a re-rtka. For revision implants, one of the five re-rtkas was performed for aseptic loosening. For primary implants, two of the four rertkas were performed because of aseptic loosening. Several clinical studies suggest that more constraint leads to earlier aseptic loosening because of more implant-cement-bone stress. 8,13 A characteristic of a revision implant is more constraint; hence, one might expect a higher rate of aseptic loosening. However, in this study, the frequency of aseptic loosening was significantly higher in the group that received a primary implant. Indications for using a primary implant in rtka are minimal ligament and bone damage. It is possible that these two factors are underestimated in this group of patients. When a primary implant is implanted and more constraint and augmentations are required, this may lead to diminished fixation of prosthesis components to bone, earlier aseptic loosening and thus re-revision. Therefore, it may be questionable whether using a primary implant should be even an option in rtka, as bone and ligament damage are usually extensive. Which type of revision implant should be advised for what degree of bone and ligament damage is a subject for further study. Several investigators report that results of septic rtkas are inferior to aseptic revision In five of the nine revisions where primary implants were used, the reason for revision was infection. In the group of revision implants in our study, 16 of the 60 were done because of an infection; therefore, corrections were made during the survival analysis for septic or aseptic indication. A strong point of this study is that it adds new knowledge to the scarce literature on survival of primary implants in revision arthroplasty. However, this study also has some limitations. Firstly, a selection bias must be present. Restoration of a knee joint with major ligamental damage and bone loss is a complex procedure. In these cases, a revision implant is always performed. When bone loss and ligamental damage are limited, i.e. cases of Anderson Orthopaedic Research Institute (AORI) type I defects, 31 the surgical procedure is less complex, and one can choose between either a primary or revision implant. Consequently, primary implants are always used in less complex 34
12 Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty revision operations, whereas revision implants are also commonly used in more difficult procedures. Secondly, with respect to Cox regression analyses, it is assumed that observations are independent of each other. However, four patients in this study underwent bilateral rtka, and survival analyses were carried out without taking bilaterality into account. Robertsson et al. reported that the effect of not accounting for bilaterality in knee revision surgery is minute, and that the risk of revision of knee implants can be analysed without consideration for subject dependency. 3 Finally, it can be argued that a limited number of patients was available. Revision surgery is a difficult procedure, and this type of surgery is only performed in specialised centres. Therefore, survival of implants at one, two and five years has a wide confidence interval. Because a growing number of rtkas is expected, future studies with larger series are necessary to gain more insight into long-term survival and the factors that influence rtka outcome. Overall, it can be concluded that despite the relatively small number of patients in this study, primary implants implanted during rtka have a significantly worse survival rate than revision implants. Choosing the right type of implant in rtka is a challenging task. Based on results of this study, it has to be considered whether primary implants are even an option during rtka. Conflict of interest Drs. A.L. Boerboom is a paid consultant for Zimmer (Warsaw, IN, USA) for training in knee arthroplasty and computer-assisted surgery. The department receives research institutional support from Stryker (Kalamazoo, Mich., USA) and Zimmer (Warsaw, IN, USA). The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. 35
13 References 1. Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K, Chan N, Lau E, Halpern M. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 00. J Bone Joint Surg Am 005;87: Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, Widmer M, Maravic M, Gomez-Barrena E, et al. International survey of primary and revision total knee replacement. Int Orthop 011;35: Nevalainen J, Keinonen A, Mäkelä A, Pentti A. The implant yearbook on orthopaedic endoprostheses: Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Helsinki, Finland: National Agency for Medicines; julkaisut/orthopaedic_endoprostheses_003_v.pdf. 4. Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 005 to 030. J Bone Joint Surg Am 007;89: Bryan RS, Rand JA. Revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 198;170: Whiteside LA. Cementless revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;86: Hwang SC, Kong JY, Nam DC, Kim DH, Park HB, Jeong ST, et al. Revision total knee arthroplasty with a cemented posterior stabilized, condylar constrained or fully constrained prosthesis: a minimum -year follow-up analysis. Clin Orthop Surg 010;: Morgan H, Battista V, Leopold SS. Constraint in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 005;13: Peters CL, Hennessey R, Barden RM, Galante JO, Rosenberg AG. Revision total knee arthroplasty with a cemented posterior-stabilized or constrained condylar prosthesis: a minimum 3-year and average 5-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 1997;1: Scuderi GR. Revision total knee arthroplasty: how much constraint is enough? Clin Orthop Relat Res 001;39: Pour AE, Parvizi J, Slenker N, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF. Rotating hinged total knee replacement: use with caution. J Bone Joint Surg Am 007;89: Sculco TP. The role of constraint in total knee arthoplasty. J Arthroplasty 36
14 Poorer survival after a primary implant during revision total knee arthroplasty 006;1: Hartford JM, Goodman SB, Schurman DJ, Knoblick G. Complex primary and revision total knee arthroplasty using the condylar constrained prosthesis: an average 5-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 1998;13: Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Liu SS. The role of implant constraint in revision total knee arthroplasty: not too little, not too much. J Arthroplasty 005;0: Cuckler JM. Revision total knee arthroplasty: how much constraint is necessary? Orthopedics 1995;18:93,3, Gustke KA. Preoperative planning for revision total knee arthroplasty:avoiding chaos. J Arthroplasty 005;0: Mulhall KJ, Ghomrawi HM, Engh GA, Clark CR, Lotke P, Saleh KJ. Radiographic prediction of intraoperative bone loss in knee arthroplasty revision. Clin Orthop Relat Res 006;446: Sheng PY, Konttinen L, Lehto M, Ogino D, Jamsen E, Nevalainen J, et al. Revision total knee arthroplasty: 1990 through 00. A review of the Finnish arthroplasty registry. J Bone Joint Surg Am 006;88: Meding JB, Wing JT, Ritter MA. Does high tibial osteotomy affect the success or survival of a total knee replacement? Clin Orthop Relat Res 011;469: Ranawat CS, Flynn WF,Jr, Deshmukh RG. Impact of modern technique on long-term results of total condylar knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1994;309: Cox DR. Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc Series B 197;34: Rand JA, Bryan RS. Revision after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 198;13: Goldberg VM, Figgie MP, Figgie HE,3rd, Sobel M. The results of revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1988;6: Cameron HU, Hunter GA. Failure in total knee arthroplasty: mechanisms, revisions, and results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 198;170: Hanssen AD, Rand JA. A comparison of primary and revision total knee arthroplasty using the kinematic stabilizer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1988;70:
15 6. Barrack RL, Engh G, Rorabeck C, Sawhney J, Woolfrey M. Patient satisfaction and outcome after septic versus aseptic revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 000;15: Deehan DJ, Murray JD, Birdsall PD, Pinder IM. Quality of life after knee revision arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 006;77: Wang CJ, Hsieh MC, Huang TW, Wang JW, Chen HS, Liu CY. Clinical outcome and patient satisfaction in aseptic and septic revision total knee arthroplasty. Knee 004;11: Mortazavi SM, Molligan J, Austin MS, Purtill JJ, Hozack WJ, Parvizi J. Failure following revision total knee arthroplasty: infection is the major cause. Int Orthop 011;35: Zywiel MG, Johnson AJ, Stroh DA, Martin J, Marker DR, Mont MA. Prophylactic oral antibiotics reduce reinfection rates following two-stage revision total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 011;35: Engh GA, Ammeen DJ. Bone loss with revision total knee arthroplasty: defect classification and alternatives for reconstruction. Instr Course Lect 1999;48: Robertsson O, Ranstam J. No bias of ignored bilaterality when analysing the revision risk of knee prostheses: analysis of a population based sample of 44,590 patients with 55,98 knee prostheses from the national Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 003;4:1. 38
2- to 9-year outcome of stemmed total knee arthroplasty
 Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (6): 609 613 609 2- to 9-year outcome of stemmed total knee arthroplasty Similar failure rates in patients when used primary or as a revision Rüdiger J Weiss 1,2, Martin Thorsell
Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (6): 609 613 609 2- to 9-year outcome of stemmed total knee arthroplasty Similar failure rates in patients when used primary or as a revision Rüdiger J Weiss 1,2, Martin Thorsell
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes
 178 Revision TKA: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay et al Original Article Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay, 1 MBBS, Ngai Nung Lo, 1 MMed (Surg), FRCS (Edin), FAMS, Seng
178 Revision TKA: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay et al Original Article Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay, 1 MBBS, Ngai Nung Lo, 1 MMed (Surg), FRCS (Edin), FAMS, Seng
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up
 Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up Ronald Huang, MD; Gustavo Barrazueta, BS; Alvin Ong, MD; Fabio Orozco, MD; Mehdi Jafari, MD; Catelyn Coyle, BS; Matthew
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up Ronald Huang, MD; Gustavo Barrazueta, BS; Alvin Ong, MD; Fabio Orozco, MD; Mehdi Jafari, MD; Catelyn Coyle, BS; Matthew
Knee Revision. Portfolio
 Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
INTEROBSERVER CORRELATION IN CLASSIFICATION OF BONE LOSS IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 Original Article INTEROBSERVER CORRELATION IN CLASSIFICATION OF BONE LOSS IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY José Ricardo Pécora, Betina Bremer Hinckel, Marco Kawamura Demange, Riccardo Gomes Gobbi, Luis Eduardo
Original Article INTEROBSERVER CORRELATION IN CLASSIFICATION OF BONE LOSS IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY José Ricardo Pécora, Betina Bremer Hinckel, Marco Kawamura Demange, Riccardo Gomes Gobbi, Luis Eduardo
Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review
 Original Article Page 1 of 5 Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review Luigi Sabatini 1, Salvatore Risitano 1, Lorenzo Rissolio 1, Andrea Bonani
Original Article Page 1 of 5 Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review Luigi Sabatini 1, Salvatore Risitano 1, Lorenzo Rissolio 1, Andrea Bonani
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
Results of Revision Surgery and Causes of Unstable Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:165-172 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.165 Results of Revision Surgery and Causes of Unstable Total Knee Arthroplasty In-Soo Song, MD, Doo-Hoon
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:165-172 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.165 Results of Revision Surgery and Causes of Unstable Total Knee Arthroplasty In-Soo Song, MD, Doo-Hoon
Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis
 Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis Jung-Ro Yoon M.D 1., In-Wook Seo M.D 1., Young-Soo Shin M.D 2. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis Jung-Ro Yoon M.D 1., In-Wook Seo M.D 1., Young-Soo Shin M.D 2. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Appendix E-1 (Figures and Tables) Fig. E-1
 Page 1 Appendix E-1 (Figures and Tables) Fig. E-1 Survival curves (Kaplan-Meier) for revised knees (failed primary TKAs revised to TKAs [TKA TKA] and failed primary UKAs revised to TKAs [UKA TKA]) according
Page 1 Appendix E-1 (Figures and Tables) Fig. E-1 Survival curves (Kaplan-Meier) for revised knees (failed primary TKAs revised to TKAs [TKA TKA] and failed primary UKAs revised to TKAs [UKA TKA]) according
The fate of augments to treat type-2 bone defects in revision knee arthroplasty
 Knee The fate of augments to treat type-2 bone defects in revision knee arthroplasty J. V. Patel, J. L. Masonis, J. Guerin, R. B. Bourne, C. H. Rorabeck From the University of Western Ontario, London,
Knee The fate of augments to treat type-2 bone defects in revision knee arthroplasty J. V. Patel, J. L. Masonis, J. Guerin, R. B. Bourne, C. H. Rorabeck From the University of Western Ontario, London,
Title of the article: the epidemiology of revision knee arthroplasty at a tertiary care center in india.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. VII (May. 2016), PP 124-128 www.iosrjournals.org Title of the article: the epidemiology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. VII (May. 2016), PP 124-128 www.iosrjournals.org Title of the article: the epidemiology
THE PERSONALIZED KNEE
 THE PERSONALIZED KNEE REDEFINING PERSONALIZATION Total knee replacement has long ranked among the most successful procedures in modern medicine. While you can expect excellent implant survivorship with
THE PERSONALIZED KNEE REDEFINING PERSONALIZATION Total knee replacement has long ranked among the most successful procedures in modern medicine. While you can expect excellent implant survivorship with
Sequential soft tissue release and unconstrained TKA implants in severe varus deformity- Prospective study in 75 knees
 2017; 3(3): 15-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 15-20 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 04-05-2017 Accepted: 05-06-2017 Dr. Ranganatha B Thimmegowda MS, DNB, Assistant Professor, ESIC Medical College,
2017; 3(3): 15-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 15-20 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 04-05-2017 Accepted: 05-06-2017 Dr. Ranganatha B Thimmegowda MS, DNB, Assistant Professor, ESIC Medical College,
Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects Jun Sung Park,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects Jun Sung Park,
Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 61-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses Ashok RAJGOpAl, Attique VASDEV, Asit S. CHIDGUpKAR, Vivek DAHIyA, Vipin C. TyAGI From the Medanta Bone
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 61-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses Ashok RAJGOpAl, Attique VASDEV, Asit S. CHIDGUpKAR, Vivek DAHIyA, Vipin C. TyAGI From the Medanta Bone
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Sun-Chul Hwang, MD, Jae-Yeon Kong, MD, Dae-Cheol Nam, MD, Dong-Hee Kim, MD, Hyung-Bin Park, MD, Soon-Taek Jeong, MD, Se-Hyun Cho, MD
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:112-120 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.112 Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Cemented Posterior Stabilized, Condylar Constrained or Fully Constrained
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:112-120 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.112 Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Cemented Posterior Stabilized, Condylar Constrained or Fully Constrained
Current Etiologies and Modes of Failure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 446, pp. 45 50 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Current Etiologies and Modes of Failure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision Kevin J. Mulhall, MB, MCh,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 446, pp. 45 50 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Current Etiologies and Modes of Failure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision Kevin J. Mulhall, MB, MCh,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1599-1603 Elsherbiny Ali Elsherbiny *, Ismail Ahmed Yaseen *, and Hisham Mohamed Safwat * Department of Orthopedic surgery, Faculty
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1599-1603 Elsherbiny Ali Elsherbiny *, Ismail Ahmed Yaseen *, and Hisham Mohamed Safwat * Department of Orthopedic surgery, Faculty
Low rate of infected knee replacements in a nationwide series is it an underestimate?
 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 205 212 205 Low rate of infected knee replacements in a nationwide series is it an underestimate? Review of the Finnish Arthroplasty Register on 38,676 operations performed
Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 205 212 205 Low rate of infected knee replacements in a nationwide series is it an underestimate? Review of the Finnish Arthroplasty Register on 38,676 operations performed
Successful outcomes with total. Constraint in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Constraint in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Hannah Morgan, MD, Vincent Battista, MD, and Seth S. Leopold, MD Dr. Morgan is Acting Instructor, Department of Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine, University
Constraint in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Hannah Morgan, MD, Vincent Battista, MD, and Seth S. Leopold, MD Dr. Morgan is Acting Instructor, Department of Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine, University
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Bilateral Total Knee Replacements using Two Different Implant Designs - Preliminary Report
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 1, March 2005 Bilateral Total Knee Replacements using Two Different Implant Designs - Preliminary Report Ali Redha, MD* Abdalla A Malki FRCS Ed, MD Orth** Faisal
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 1, March 2005 Bilateral Total Knee Replacements using Two Different Implant Designs - Preliminary Report Ali Redha, MD* Abdalla A Malki FRCS Ed, MD Orth** Faisal
Revision TKA with a condylar constrained prosthesis using metaphyseal and surface cementation: a minimum 6-year follow-up analysis
 Sanz-Ruiz et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:39 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0485-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Revision TKA with a condylar constrained prosthesis using metaphyseal and surface
Sanz-Ruiz et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:39 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0485-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Revision TKA with a condylar constrained prosthesis using metaphyseal and surface
The Epidemiology of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in the United States
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2010) 468:45 51 DOI 10.1007/s11999-009-0945-0 SYMPOSIUM: PAPERS PRESENTED AT THE ANNUAL MEETINGS OF THE KNEE SOCIETY The Epidemiology of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in the United
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2010) 468:45 51 DOI 10.1007/s11999-009-0945-0 SYMPOSIUM: PAPERS PRESENTED AT THE ANNUAL MEETINGS OF THE KNEE SOCIETY The Epidemiology of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in the United
Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 699-705 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments Zeeshan Khan, Syed Z. Nawaz, Steven
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 699-705 ORIGINAL STUDY Conversion of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty : The challenges and need for augments Zeeshan Khan, Syed Z. Nawaz, Steven
Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications
 DOI: 10.2478/v10163-012-0036-2 ACTA CHIRURGICA LATVIENSIS 2011 (11) CASE REPORT Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications Silvestris Zebolds*/***,
DOI: 10.2478/v10163-012-0036-2 ACTA CHIRURGICA LATVIENSIS 2011 (11) CASE REPORT Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications Silvestris Zebolds*/***,
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Analysis of factors affecting range of motion after Total Knee Arthroplasty
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk?
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 6-1-2012 Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk? S Mehdi Jafari The
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 6-1-2012 Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk? S Mehdi Jafari The
Is there a difference in joint line restoration in revision Total knee arthroplasty according to prosthesis type?
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:382 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2295-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is there a difference in joint line restoration in revision Total knee arthroplasty
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:382 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2295-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is there a difference in joint line restoration in revision Total knee arthroplasty
Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
A Systematic Review on Performance of the Vanguard Complete Knee System
 A Systematic Review on Performance of the Vanguard Complete Knee System Author: Jing Xie, Ph.D. June 30, 2011 Abstract A systematic review was conducted to evaluate the clinical performance of the Vanguard
A Systematic Review on Performance of the Vanguard Complete Knee System Author: Jing Xie, Ph.D. June 30, 2011 Abstract A systematic review was conducted to evaluate the clinical performance of the Vanguard
University of Groningen. Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke
 University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
Over the past 3 decades, total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
 Points on Outcomes and A Survivorship of Total Knee Arthroplasty Jeffrey J. Cherian, DO, Anil Bhave, PT, Steven F. Harwin, MD, and Michael A. Mont, MD Over the past 3 decades, total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
Points on Outcomes and A Survivorship of Total Knee Arthroplasty Jeffrey J. Cherian, DO, Anil Bhave, PT, Steven F. Harwin, MD, and Michael A. Mont, MD Over the past 3 decades, total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
Factors Associated with a Short-Term Revision of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Journal of Surgery 2018; 6(6): 162-166 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20180606.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Factors Associated with a Short-Term Revision
Journal of Surgery 2018; 6(6): 162-166 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20180606.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Factors Associated with a Short-Term Revision
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT
 ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
Value of preoperative radiographic evaluations on knee bone defects for
 original article Value of preoperative radiographic evaluations on knee bone defects for revision arthroplasty Mauricio Masasi Iamaguchi 1, Camilo Partezani Helito 2, Riccardo Gomes Gobbi 3, Marco Kawamura
original article Value of preoperative radiographic evaluations on knee bone defects for revision arthroplasty Mauricio Masasi Iamaguchi 1, Camilo Partezani Helito 2, Riccardo Gomes Gobbi 3, Marco Kawamura
Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface
 Original Article 435 Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface Peter M. Bonutti, MD 1 Anton Khlopas, MD 2 Morad Chughtai,
Original Article 435 Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface Peter M. Bonutti, MD 1 Anton Khlopas, MD 2 Morad Chughtai,
Citation for published version (APA): Gerritsma-Bleeker, C. L. E. (2005). Long-term follow-up of the SKI knee prosthesis s.n.
 University of Groningen Long-term follow-up of the SKI knee prosthesis Gerritsma-Bleeker, Catharina Louise Emilie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen Long-term follow-up of the SKI knee prosthesis Gerritsma-Bleeker, Catharina Louise Emilie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
There has been speculation as to how the outcome
 Early patient outcomes after primary and revision total knee arthroplasty A PROSPECTIVE STUDY R. C. Hartley, N. G. Barton-Hanson, R. Finley, R. W. Parkinson From Arrowe Park Hospital, Upton, England There
Early patient outcomes after primary and revision total knee arthroplasty A PROSPECTIVE STUDY R. C. Hartley, N. G. Barton-Hanson, R. Finley, R. W. Parkinson From Arrowe Park Hospital, Upton, England There
Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist
 Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success. Zimmer Natural-Knee II System
 Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
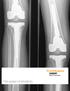
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Mid- to long-term outcomes of a medialpivot system for primary total knee replacement
 KNEE Mid- to long-term outcomes of a medialpivot system for primary total knee replacement A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS Freely available online D. A. Fitch, K. Sedacki, Y. Yang From MicroPort
KNEE Mid- to long-term outcomes of a medialpivot system for primary total knee replacement A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS Freely available online D. A. Fitch, K. Sedacki, Y. Yang From MicroPort
Revision of Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty: Two-Stage Reimplantation Using an Antibiotic-Impregnated Static Spacer
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:180-187 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.180 Revision of Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty: Two-Stage Reimplantation Using an Antibiotic-Impregnated
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:180-187 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.180 Revision of Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty: Two-Stage Reimplantation Using an Antibiotic-Impregnated
Outcome After Isolated Polyethylene Tibial Insert Exchange in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 28 No. 1 2013 Outcome After Isolated Polyethylene Tibial Insert Exchange in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Richard P. Baker, MSc, MBChB, FRCS, Bassam A. Masri, MD, FRCSC,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 28 No. 1 2013 Outcome After Isolated Polyethylene Tibial Insert Exchange in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Richard P. Baker, MSc, MBChB, FRCS, Bassam A. Masri, MD, FRCSC,
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement
 ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases Katrina F. Franke, Iulian Nusem, Gaugin Gamboa, David A.F. Morgan From Queensland
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases Katrina F. Franke, Iulian Nusem, Gaugin Gamboa, David A.F. Morgan From Queensland
Bicruciate-Retaining or Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis Pritchett 225 Fig. 3. The MP total knee prosthesis. Fig. 1. An anteroposterior radiograph o
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties
 Acta Orthopaedica 2013; 84 (4): 387 391 387 10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties A follow-up of a previous report
Acta Orthopaedica 2013; 84 (4): 387 391 387 10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties A follow-up of a previous report
SUMMIT and DURALOC. Clinical Summary
 SUMMIT and DURALOC Clinical Summary Ten-year results of a press-fit, porous-coated acetabular component Grobler G.P. Learmonth I.D. Bernstein B.P. Dower B.J. (2005) The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery;
SUMMIT and DURALOC Clinical Summary Ten-year results of a press-fit, porous-coated acetabular component Grobler G.P. Learmonth I.D. Bernstein B.P. Dower B.J. (2005) The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery;
Instrumentation Options
 Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis
 Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
No Difference Between Trabecular Metal Cones and Femoral Head Allografts in Revision TKA: Minimum 5-year Followup
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:118 124 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4898-9 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2016 KNEE SOCIETY
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:118 124 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4898-9 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2016 KNEE SOCIETY
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEARING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTRAINT
 CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
A systematic literature review of the Profix in primary total knee arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 55-60 ORIGINAL STUDY A systematic literature review of the Profix in primary total knee arthroplasty Roberto VIGAnò, Luca MAREGA, Eric BREEMAnS, Rafael Llopis MIRó From Azienda
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 55-60 ORIGINAL STUDY A systematic literature review of the Profix in primary total knee arthroplasty Roberto VIGAnò, Luca MAREGA, Eric BREEMAnS, Rafael Llopis MIRó From Azienda
Evolution. Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee. Key Aspects
 Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
A randomised controlled trial of cemented versus cementless press-fit condylar total knee replacement
 A randomised controlled trial of cemented versus cementless press-fit condylar total knee replacement 15-YEAR SURVIVAL ANALYSIS P. N. Baker, F. M. Khaw, L. M. G. Kirk, C. N. A. Esler, P. J. Gregg From
A randomised controlled trial of cemented versus cementless press-fit condylar total knee replacement 15-YEAR SURVIVAL ANALYSIS P. N. Baker, F. M. Khaw, L. M. G. Kirk, C. N. A. Esler, P. J. Gregg From
Patellar Fractures After Total Knee Replacement
 Patellar Fractures fter Total Knee Replacement Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kyung h Chun 1,2 Kenjirou Ohashi 1 D. Lee ennett 1 Georges Y. El-Khoury 1 Chun K, Ohashi K, ennett DL, El-Khoury
Patellar Fractures fter Total Knee Replacement Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kyung h Chun 1,2 Kenjirou Ohashi 1 D. Lee ennett 1 Georges Y. El-Khoury 1 Chun K, Ohashi K, ennett DL, El-Khoury
Isolated Polyethylene Exchange versus Acetabular Revision for Polyethylene Wear
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-1-2009 Isolated Polyethylene Exchange versus Acetabular Revision
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-1-2009 Isolated Polyethylene Exchange versus Acetabular Revision
Modularity in tibial components for total knee
 CHAPTER 22 Insert Exchange Rahul V. Deshmukh and Richard D. Scott Modularity in tibial components for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is controversial. Advantages of insert modularity include component inventory
CHAPTER 22 Insert Exchange Rahul V. Deshmukh and Richard D. Scott Modularity in tibial components for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is controversial. Advantages of insert modularity include component inventory
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Revision total knee arthroplasty: hybrid vs standard cemented fixation
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-018-0494-y Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Revision total knee arthroplasty: hybrid vs standard cemented fixation Jesús Gómez Vallejo
https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-018-0494-y Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Revision total knee arthroplasty: hybrid vs standard cemented fixation Jesús Gómez Vallejo
Multiple joint reconstructions in one patient: computer-assisted simultaneous procedures
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Multiple joint reconstructions in one patient: computer-assisted simultaneous procedures Mahmoud Hafez, Hosamuddin Hamza, Raid Aumran Essa The Orthopaedic Department, October 6
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Multiple joint reconstructions in one patient: computer-assisted simultaneous procedures Mahmoud Hafez, Hosamuddin Hamza, Raid Aumran Essa The Orthopaedic Department, October 6
An Optimum Prosthesis Combination of Low Risk TKR Options in All Five Primary Categories of Design Results in a 60% Reduction in Revision Risk
 An Optimum Prosthesis Combination of Low Risk TKR Options in All Five Primary Categories of Design Results in a 60% Reduction in Revision Risk Christopher Vertullo Andrea Peng Stephen Graves Peter Lewis
An Optimum Prosthesis Combination of Low Risk TKR Options in All Five Primary Categories of Design Results in a 60% Reduction in Revision Risk Christopher Vertullo Andrea Peng Stephen Graves Peter Lewis
Automated Industry Report 824 Depuy Synthes Australia Attune PS Total Knee
 Automated Industry Report 824 Depuy Synthes Australia Total Knee Report Generated: 9 January 2019 This report has been prepared by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry
Automated Industry Report 824 Depuy Synthes Australia Total Knee Report Generated: 9 January 2019 This report has been prepared by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Gender Solutions Patello-Femoral Joint System
 Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
Triathlon Tritanium Knee System
 Triathlon Tritanium Knee System Table of Contents Cementless TKA... 4 Why Cementless TKA?... 4 Cementless TKA - Clinical History... 4 Published RSA Results Comparing Fixation Methods... 5 Biologic Fixation...
Triathlon Tritanium Knee System Table of Contents Cementless TKA... 4 Why Cementless TKA?... 4 Cementless TKA - Clinical History... 4 Published RSA Results Comparing Fixation Methods... 5 Biologic Fixation...
Higher revision risk for unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in low-volume hospitals
 Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (4): x x 1 Higher revision risk for unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in low-volume hospitals Data from 5,791 cases in the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register Mona Badawy 1, Birgitte
Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (4): x x 1 Higher revision risk for unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in low-volume hospitals Data from 5,791 cases in the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register Mona Badawy 1, Birgitte
DePuy Attune CR and Attune PS. Contents Recorded Usage in NJR Patient and Procedure Details Revision and Survivorship APPENDIX A Component List
 Implant Summary Report for: DePuy Comprising PRIMARY knees implanted up to: 31 May 2018 NJR Database extract: 30 July 2018 Produced on: Licenced for use until: 11 August 2018 11 December 2018 Contents
Implant Summary Report for: DePuy Comprising PRIMARY knees implanted up to: 31 May 2018 NJR Database extract: 30 July 2018 Produced on: Licenced for use until: 11 August 2018 11 December 2018 Contents
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
KEY CHOICES AND TECHNIQUES IN REVISION THA AND TKA Step-by-Step Decisions
 KEY CHOICES AND TECHNIQUES IN REVISION THA AND TKA Step-by-Step Decisions Moderator: Panelists: Daniel J Berry, Mayo Clinic John J Callaghan William L Griffin Thomas P Vail Michael P Bolognesi Presenter
KEY CHOICES AND TECHNIQUES IN REVISION THA AND TKA Step-by-Step Decisions Moderator: Panelists: Daniel J Berry, Mayo Clinic John J Callaghan William L Griffin Thomas P Vail Michael P Bolognesi Presenter
Formosan Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Formosan Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders 3 (2012) 83e87 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Formosan Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders journal homepage: www.e-fjmd.com Original Article
Formosan Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders 3 (2012) 83e87 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Formosan Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders journal homepage: www.e-fjmd.com Original Article
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 392, pp. 56 61 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty James B. Stiehl, MD*; Richard
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 392, pp. 56 61 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty James B. Stiehl, MD*; Richard
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques. Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018
 Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with Paprosky III or IV Acetabular Bone Defects: A Minimum 2-year Follow Up Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 98-103, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.98 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 98-103, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.98 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with
Gold standard of a TKA. Conflicting goals? POLYETHYLENE WEAR THE SOLUTION: MOBILE BEARING KNEES. MOBILE BEARING A totally new approach (1977)
 Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
Automated Industry Report 823 Depuy Synthes Australia Attune CR Total Knee
 Automated Industry Report 823 Depuy Synthes Australia Total Knee Report Generated: 9 January 2019 This report has been prepared by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry
Automated Industry Report 823 Depuy Synthes Australia Total Knee Report Generated: 9 January 2019 This report has been prepared by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA
 Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
Sung-Hyun Lee 1, Sung-Hyun Noh 1, Keun-Churl Chun 1, Joung-Kyue Han 2 and Churl-Hong Chun 1*
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:69 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1981-2 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of bilateral revision total knee arthroplasty using distal femoral allograft
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:69 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1981-2 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of bilateral revision total knee arthroplasty using distal femoral allograft
Jae Ang Sim, MD, Yong Seuk Lee, MD, Ji Hoon Kwak, MD, Sang Hoon Yang, MD, Kwang Hui Kim, MD, Beom Koo Lee, MD
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:287-291 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.287 Comparison of Complete Distal Release of the Medial Collateral Ligament and Medial Epicondylar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:287-291 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.287 Comparison of Complete Distal Release of the Medial Collateral Ligament and Medial Epicondylar
Revision surgery for failed unicompartmental knee replacement : Technical aspects and clinical outcome
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 312-317 ORIGINAL STUDY Revision surgery for failed unicompartmental knee replacement : Technical aspects and clinical outcome Curtis A. Robb, Gulraj S. Matharu, Khalid Baloch,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 312-317 ORIGINAL STUDY Revision surgery for failed unicompartmental knee replacement : Technical aspects and clinical outcome Curtis A. Robb, Gulraj S. Matharu, Khalid Baloch,
Total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthrosis in younger patients in the Finnish arthroplasty register
 Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthrosis in younger patients in the Finnish
Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthrosis in younger patients in the Finnish
PARTIALS?1 SHOULD BE AT LEAST 20% DID YOU KNOW OF KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 PARTIAL KNEE DID YOU KNOW AT LEAST 20% OF KNEE REPLACEMENTS SHOULD BE PARTIALS?1 Research shows that surgeons utilizing Partial Knee Arthroplasty (PKA) for at least 20% of their annual knee arthroplasties
PARTIAL KNEE DID YOU KNOW AT LEAST 20% OF KNEE REPLACEMENTS SHOULD BE PARTIALS?1 Research shows that surgeons utilizing Partial Knee Arthroplasty (PKA) for at least 20% of their annual knee arthroplasties
The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J.
 University of Groningen The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J. Published in: Knee surgery
University of Groningen The Oxford phase III unicompartmental knee replacement in patients less than 60 years of age Kort, Nanne P.; van Raay, Jos J. A. M.; van Horn, Jim J. Published in: Knee surgery
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer A technique of predicting radiographic joint line and posterior femoral condylar offset of the knee Citation for published version: Clement, ND, Hamilton, DF & Burnett, R 2014,
Edinburgh Research Explorer A technique of predicting radiographic joint line and posterior femoral condylar offset of the knee Citation for published version: Clement, ND, Hamilton, DF & Burnett, R 2014,
Knee Failure Mechanisms After Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Techniques in Knee Surgery 3(1):55 59, 2004 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia T E C H N I Q U E Knee Failure Mechanisms After Total Knee Arthroplasty Matthew S. Austin, MD, Peter F.
Techniques in Knee Surgery 3(1):55 59, 2004 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia T E C H N I Q U E Knee Failure Mechanisms After Total Knee Arthroplasty Matthew S. Austin, MD, Peter F.
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World. Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation
 Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
