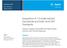
ESI-MS of chondroitin oligosaccharides Possible ions (charge) m/z ( 1) ( 2) ( 3) ( 4) ( 5) ( 6) ( 7) ( 8) Chondroitin oligomers
|
|
|
- Leslie Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008; 22: Published online in Wiley InterScience ( Mass spectrometry for the characterization of unsulfated chondroitin oligosaccharides from 2-mers to 16-mers. Comparison with hyaluronic acid oligomers Nicola Volpi 1 *, Zhenqing Zhang 2 and Robert J. Linhardt 2 1 Department of Biologia Animale, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy 2 Departments of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Chemical and Biological Engineering and Biology, Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA Received 27 June 2008; Revised 5 September 2008; Accepted 11 September 2008 This study reports for the first time the complete liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) analyses performed in negative ion mode of saturated unsulfated chondroitin oligosaccharides up to 16-mers and comparison with hyaluronic acid (HA) oligomers differing only in the nature of the hexosamine residue. MS/MS of the chondroitin disaccharide on the singly charged precursor at m/z afforded a glycosidic cleavage C 1 product ion at m/z In the tetrasaccharide, C 2 (m/z 396.0) and C 3 (m/z 572.0) product anions were generated by glycosidic cleavage. A C 5 [M 2H] 2S product ion at m/z was generated by the glycosidic cleavage of the hexasaccharide, and a C 7 ion (m/z 664.6, charge state of S2) was produced from the octasaccharide. The same fragmentation pattern of deprotonated oligomers was observed for the largest oligosaccharides, from 10- to 16-mers. There has been no previous report of MS/MS spectra for unsulfated chondroitin oligomers of these sizes. Unsulfated saturated chondroitin oligosaccharides with x-mer units and larger than a tetrasaccharide dissociate to almost exclusively form C X 1 -type ions. Saturated HA oligomers also afforded the same fragmentation pattern as deprotonated oligomers by ESI-MS and MS/MS analyses. Thus, under the experimental conditions used in the current study, we were unable to distinguish between unsulfated chondroitin and HA. Copyright # 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Escherichia coli K4 bacteria (05:K4:H4) produces a polysaccharide composed of repeating disaccharides [GlcA (b1! 3) GalNAc (b1! 4)] n to which b-fructofuranose units are linked to C-3 of D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) residues. 1,2 D-Fructose is easily and rapidly removed by acid hydrolysis 3 5 to produce an unsulfated chondroitin backbone. This uncommon unsulfated polymer has a very similar structure to the more common nonsulfated hyaluronic acid or hyaluronan (HA) formed of repeating disaccharides [GlcA (b1! 3) GlcNAc (b1! 4)] n differing only in the nature of the hexosamine residue. Oligosaccharides prepared from glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) by controlled enzymatic depolymerization are often studied to define the structural requirements for biological activity 6,7 and electrospray ionization/tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) coupled online with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) is particularly useful for characterizing the structure of these GAG-derived oligomers, such as N-acetylheparosan, 8,9 heparin, 10 Escherichia coli K4 polysaccharide, 2 and HA. 9,11 Isobaric oligosaccharides enzymatically prepared from HA and N-acetylheparosan, differing from each other only in the *Correspondence to: N. Volpi, Department of Biologia Animale, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Via Campi 213/d, Modena, Italy. volpi@unimo.it position of the linkage between GlcA and GlcNAc, have been distinguished using MS/MS. 9 Although the ESI-MS spectra of unsaturated chondroitin disaccharide 12 and tetrasaccharide 13 are known, this work examines the ESI-MS and ESI-MS/MS analyses of saturated unsulfated chondroitin oligosaccharides as large as 16-mers (hexadecasaccharides). Furthermore, MS/MS analyses were performed to evaluate differences and similarities between the isobaric saturated oligosaccharides derived from chondroitin and HA. EXPERIMENTAL E. coli strain K4 U1-41, serotype O5:K4(L):H4, was from the American Type Culture Collection (LGC Promochem s.r.l., Milan, Italy). HA sodium salt from rooster comb and hyaluronidase from bovine testes [E.C , 300 units/ mg solid] were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Acetonitrile, MS-grade, and all other reagents, of the purest grade available, were from Sigma Aldrich. K4 polysaccharide was produced and purified as previously reported 2 and totally defructosylated by acid treatment 3 5 to produce the chondroitin polymer. This unsulfated polysaccharide (and HA) was partially degraded by using bovine testicular hyaluronidase to produce saturated oligosaccharides of various lengths, up to 16-mers. To a Copyright # 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
2 ESI-MS of chondroitin oligosaccharides 3527 solution containing 20 mg of polysaccharide in 2 ml of 100 mm Na acetate buffer adjusted to ph 5.2 with acetic acid containing 150 mm NaCl were added 5000 units of hyaluronidase, and enzymatic digestion was performed at 378C for 1 8 h. The incubation time of the hyaluronidase varied according to the size of oligosaccharides to be obtained, assessed at various time points by running 5 ml of the reaction mixture by strong anion exchange (SAX)-HPLC. 3 The reactions were stopped by boiling for 20 min. The sample was centrifuged at rpm for 30 min at 58C, and the supernatant was studied by HPLC/ESI-MS as previously reported 2,11 on a 3-mm Gemini C Å column ( mm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA). Eluent A was water/acetonitrile (80:20) and eluent B was water/ acetonitrile (35:65). Tributylamine (15 mm) and ammonium acetate (50 mm) were added to both eluents. 10 The ph of the mobile phase was adjusted to 7.0 with acetic acid. The sample (20 ml, approx. 200 mg) was injected, and a linear gradient (from 0 to 100% eluent B in 90 min) at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/ min was used for elution. Samples were directly on-line injected at 0.3 ml/min into the ESI source of an Agilent Technologies LC/MSD Trap VL ion trap mass spectrometer fitted with an ESI interface with an orthogonal nebulizer (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The oligosaccharides were detected in the negative ion mode using the following parameters: capillary voltage 3500 V (to obtain the Figure 1. Total ion chromatograms (TICs) of unsulfated saturated chondroitin oligosaccharides up to 16-mers in negative ion mode separated by reversed-phase ion-pairing (RPIP)-HPLC. According to Thanawiroon and Linhardt, 17 the presence of tributylamine may result in peak doubling, presumably through the resolution of the a and b anomeric forms of the individual oligosaccharides. Table 1. Calculated monoisotopic m/z values for anions derived from fully saturated unsulfated chondroitin oligomer species separated by means of reversed-phase ion pairing (RPIP)-HPLC, and calculated MS/MS C 1 product ions derived from precursor ions by glycosidic cleavage (according to the nomenclature of Domon and Costello 14 ). The main ions detected for each oligosaccharide are highlighted in bold. m.m. ¼ molecular mass. RT ¼retention time Possible ions (charge) m/z Chondroitin oligomers m.m. ( 1) ( 2) ( 3) ( 4) ( 5) ( 6) ( 7) ( 8) 2-mers (RT ¼ 6.3 min) GlcA-GalNAc C1 product mers (RT ¼ 7.8 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C3 product mers (RT ¼ 10.2 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C5 product mers (RT ¼ 13.6 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C7 product mers (RT ¼ 18.6 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C9 product mers (RT ¼ 23.2 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C11 product mers (RT ¼ 26.5 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C13 product mers (RT ¼ 29.2 min) [GlcA-GalNAc] C15 product
3 3528 N. Volpi, Z. Zhang and R. J. Linhardt maximum value of signal-to-noise ratio), nebulizer gas pressure 40 psi ( N/m 2 ), trap drive 47.2 V, skimmer one 43.2 V, capillary exit offset 77.2 V. Nitrogen was used as the drying gas at a flow rate of 9 L/min and temperature of 3508C. The scan range used was m/z , with a maximum accumulation time of 300 ms, and a ion charge control (ICC) target of Auto MS/MS, a procedure for performing MS n analyses to analyze multiple precursor ions, was turned on in these experiments giving an estimated cycle time of 0.1 min. The collision energy was optimized in order to obtain all structurally informative product ions. The isolation Software versions were LC/MSD trap control version 4.2 and Data Analysis version 2.2 (Agilent Technologies). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION After removal of fructose, the chondroitin polysaccharide was depolymerized by partial controlled digestion with testicular hyaluronidase, and separated into fully saturated Figure 2. ESI-MS spectra recorded in negative ion mode of various single unsulfated saturated chondroitin oligosaccharide species, in particular tetrasaccharide (A), octasaccharide (B), dodecasaccharide (C), and the 16-mer oligomer (D), separated by RPIP-HPLC.
4 ESI-MS of chondroitin oligosaccharides 3529 oligosaccharides from 2- to 16-mers, having the general structure [GlcA (1! 3) GalNAc (1 > 4)] n with n from 1 to 8 (identified by ESI-MS), by HPLC in approx. 30 min. (Figure 1 shows the total ion chromatogram (TIC) of the chondroitin oligosaccharides in negative ion mode.) According to Thanawiroon et al., 10 the choice of a volatile ion-pairing reagent represents a compromise between low alkyl chain length affording high volatility, required for compatibility with on-line MS, and longer alkyl chain length affording higher on-column retention of oligosaccharides associated with enhanced resolution. Tributylamine provided optimal retention with MS compatibility and good detection sensitivity. The choice of a small analytical RP-C18 column with a particle size of 3 mm and a pore size of 110 Å enabled the separation and analysis of discrete amounts of chondroitin (or HA) digest mixture, about 200 mg sample size suitable for ESI-MS detection, by maintaining the capacity to resolve each single oligosaccharide species in a relatively short time. Calculated and experimentally derived m/z values for oligomers are shown in Table 1 (the ESI-MS spectra of several oligomers are shown in Fig. 2 as examples). More highly charged molecules were produced with the increasing length of the oligosaccharides. The ESI-MS/MS spectrum of the [M H] 1 precursor ion at m/z of the disaccharide (2-mer) from chondroitin (Fig. 3(A) and Table 1) afforded a glycosidic cleavage C 1 product ion (according to the nomenclature of Domon and Costello 14 )atm/z and the same ion was found for the smallest saturated HA oligomer, 2-mers (not shown). C 2 (m/z 396.0) and C 3 (m/z 572.0) product ions 14 were generated by the glycosidic cleavage of the 4-mer oligosaccharide ([M H] 1 ion at m/z 775.2) (Fig. 3(B)). A C 5 [M 2H] 2 ion at m/z was produced by the glycosidic cleavage of the 6-mer oligosaccharide (ion [M 2H] 2 ion at m/z 576.7) (Fig. 3(C)), a C 7 ion (m/z 664.6, charge state of 2) was generated from the octasaccharide ([M 2H] 2 ion at m/z 766.2) (Fig. 3(D)), and a C 9 [M 3H] 3 ion (m/z 568.8) was produced from the decasaccharide [M 3H] 3 ion at m/z 636.8) (not shown). The same fragmentation of the deprotonated oligomers was observed for larger oligomers. In fact, MS/MS on the [M 3H] 3 ion (m/z 763.2) of the 12-mer oligosaccharide afforded the C 11 [M 3H] 3 ion (m/z 695.7) (Fig. 3(E)). MS/MS on the [M 3H] 3 ion (m/z 889.6) of the 14-mer species produced a C 13 [M 3H] 3 ion (m/z 821.8) " Figure 3. ESI-MS/MS spectra recorded in negative ion mode of various single unsulfated saturated chondroitin oligosaccharide species, in particular disaccharide (A), tetrasaccharide (B), hexasaccharide (C), octasaccharide (D), dodecasaccharide (E), and 16-mer oligomer (F), separated by means of RPIP-HPLC. See also Table 1 for the calculated MS/MS C 1 product ions derived from specific precursor ions. The inset in (A) shows the nomenclature for disaccharide fragmentation proposed by Domon and Costello. 14 Ions that contain a non-reducing terminus are labeled with uppercase letters from the beginning of the alphabet (A, B, C), and those that contain the reducing end of the oligosaccharide are labeled with letters from the end of the alphabet (X, Y, Z). Subscripts indicate the cleaved ions. The A and X ions are produced by cleavage across the glycosidic ring, and are labeled by assigning each ring bond a number and counting clockwise. Ions produced from cleavage of successive residues are labeled A m,b m, and C m, with m ¼ 1 for the non-reducing end, and X n,y n, and Z n, with n ¼ 1 for the reducing-end residue.
5 3530 N. Volpi, Z. Zhang and R. J. Linhardt (not shown), and a C 15 [M 3H] 3 product ion (m/z 948.4) was generated from the 16-mer [M 3H] 3 precursor ion (m/z ) (Fig. 3(F)). The MS/MS spectra of unsulfated chondroitin oligomers of sizes as large as 16-mers have not previously been reported. It is noteworthy that the same fragmentation pattern was found for the saturated HA oligomers (not shown). This study provides MS/MS analyses of unsulfated chondroitins, composed of repeating [GlcA (b1! 3) GalNAc (b1! 4)] n disaccharidesaslargeas16-mers.zaia et al. 13 found that the [M H] 1 ion of an unsulfated unsaturated chondroitin tetrasaccharide dissociated to form an abundant series of C-type product ions. The same product ions have been observed in this study for the saturated chondroitin 4-mer oligomer, in particular the formation of the C 3 and C 2 anions. Furthermore, we found that unsulfated saturated chondroitin oligosaccharides, formed of x-mer units and larger than a tetrasaccharide, dissociate to form C X 1 -type ions almost exclusively. According to Zaia et al., 13 C-type ions are favored in the negative ion mode when either sulfate or carboxylate groups are present in the oligomer structure. In contrast, the formation of B- and Y-type ion pairs is favored in the presence of both sulfate and carboxylate groups. These data should be useful for the structural characterization of oligosaccharides having the previously reported disaccharide sequences, as for example for the enzymatic synthesis of chondroitin by using chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. 15 Furthermore, a comparison was made of the isobaric HA saturated oligosaccharides and no differences were observed in the spectra of these two polymers, despite differences in the nature of the hexosamine residue. Thus, other MS approaches are needed to differentiate between these two isobars. Studies are in progress to evaluate the possibility to distinguish unsulfated chondroitin and HA oligosaccharides by using MS n experiments. CONCLUSIONS The current study reports for the first time the complete MS and MS/MS spectra of saturated unsulfated chondroitin oligosaccharides up to 16-mers. Several studies 15,16 have been undertaken to enzymatically produce and elongate chondroitin with specific transferases. As a consequence, chondroitin oligosaccharides of various sizes are being generated. The rapid analytical methodology presented here for the characterization of saturated unsulfated chondroitin oligosaccharides up to 16-mers may be useful for the understanding of their fine structure and related properties of such enzymatically synthesized chondroitins. REFERENCES 1. Rodriguez ML, Jann B, Jann K. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988; 177: Volpi N. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 21: Volpi N. Glycobiology 2003; 13: Volpi N. Electrophoresis 2003; 24: Volpi N. Electrophoresis 2004; 25: Seyfried NT, McVey GF, Almond A, Mahoney DJ, Dudhia J, Day AJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2005; 280: Blundell CD, Mahoney DJ, Almond A, DeAngelis PL, Kahmann JD, Teriete P, Pickford AR, Campbell ID, Day AJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2003; 278: Kuberan B, Lech M, Zhang L, Wu ZL, Beeler DL, Rosenberg RD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002; 124: Zhang Z, Xie J, Liu J, Linhardt RJ. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2008; 19: Thanawiroon C, Rice KG, Toida T, Linhardt RJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2004; 279: Volpi N. Anal. Chem. 2007; 79: Ii T, Okuda S, Hirano T, Ohashi M. Glycoconjugate J. 1994; 11: Zaia J, Miller MJ, Seymour JL, Costello CE. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 18: Domon B, Costello CE. Glycoconjugate J. 1988; 5: Gotoh M, Sato T, Akashima T, Iwasaki H, Kameyama A, Mochizuki H, Yada T, Inaba N, Zhang Y, Kikuchi N, Kwon YD, Togayachi A, Kudo T, Nishihara S, Watanabe H, Kimata K, Narimatsu H. J. Biol. Chem. 2002; 277: Sato T, Gotoh M, Kiyohara K, Akashima T, Iwasaki H, Kameyama A, Mochizuki H, Yada T, Inaba N, Togayachi A, Kudo T, Asada M, Watanabe H, Imamura T, Kimata K, Narimatsu H. J. Biol. Chem. 2003; 278: Thanawiroon C, Linhardt RJ. J. Chromatogr. A 2003; 1014: 215.
High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for mapping and sequencing glycosaminoglycan-derived oligosaccharides
 High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for mapping and sequencing glycosaminoglycan-derived oligosaccharides Nicola Volpi 1 & Robert J Linhardt 2 PRTCL 1 Department of Biology, University
High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for mapping and sequencing glycosaminoglycan-derived oligosaccharides Nicola Volpi 1 & Robert J Linhardt 2 PRTCL 1 Department of Biology, University
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities by LC/MS. Application Note. Christine Miller Agilent Technologies.
 Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry. Supporting Information
 Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application
 Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column
 High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column Application Note BioPharma Authors James Martosella, Phu Duong, and Alex Zhu Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
High Resolution Glycopeptide Mapping of EPO Using an Agilent AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping Column Application Note BioPharma Authors James Martosella, Phu Duong, and Alex Zhu Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis
 2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
Application Note. Author. Abstract. Introduction. Food Safety
 Determination of β2-agonists in Pork with SPE eanup and LC-MS/MS Detection Using Agilent BondElut PCX Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges, Agilent Poroshell 120 column and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass
Determination of β2-agonists in Pork with SPE eanup and LC-MS/MS Detection Using Agilent BondElut PCX Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges, Agilent Poroshell 120 column and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass
Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
PHOTOCATALYTIC DECONTAMINATION OF CHLORANTRANILIPROLE RESIDUES IN WATER USING ZnO NANOPARTICLES. DR. A. RAMESH, Ph.D, D.Sc.,
 PHOTOCATALYTIC DECONTAMINATION OF CHLORANTRANILIPROLE RESIDUES IN WATER USING ZnO NANOPARTICLES DR. A. RAMESH, Ph.D, D.Sc., raamesh_a@yahoo.co.in 1 OBJECTIVES Determination of persistence and photolysis
PHOTOCATALYTIC DECONTAMINATION OF CHLORANTRANILIPROLE RESIDUES IN WATER USING ZnO NANOPARTICLES DR. A. RAMESH, Ph.D, D.Sc., raamesh_a@yahoo.co.in 1 OBJECTIVES Determination of persistence and photolysis
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium. Application. Authors. Abstract.
 Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS
 New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS Subhra Bhattacharya, Deva H. Puranam, and Stephen C. Roemer Thermo Fisher Scientific Fisher Chemical, One Reagent Lane, Fair Lawn, NJ Material
New Solvent Grade Targeted for Trace Analysis by UHPLC-MS Subhra Bhattacharya, Deva H. Puranam, and Stephen C. Roemer Thermo Fisher Scientific Fisher Chemical, One Reagent Lane, Fair Lawn, NJ Material
Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme
 P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification
 22 SEPARATION SCIENCE REDEFINED MAY 2005 Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification In the drug discovery process the detection and
22 SEPARATION SCIENCE REDEFINED MAY 2005 Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification In the drug discovery process the detection and
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008
 Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis
 Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS
Applying a Novel Glycan Tagging Reagent, RapiFluor-MS, and an Integrated UPLC-FLR/QTof MS System for Low Abundant N-Glycan Analysis Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS
Detection of Low Level of Chloramphenicol in Milk and Honey with MIP SPE and LC-MS-MS
 Detection of Low Level of Chloramphenicol in Milk and Honey with MIP SPE and LC-MS-MS Olga Shimelis, An Trinh, and Michael Ye Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte, PA T407125 Introduction Molecularly
Detection of Low Level of Chloramphenicol in Milk and Honey with MIP SPE and LC-MS-MS Olga Shimelis, An Trinh, and Michael Ye Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte, PA T407125 Introduction Molecularly
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear, acidic
 Tandem MS Can Distinguish Hyaluronic Acid from NAcetylheparosan Zhenqing Zhang, a Jin Xie, a Jian Liu, b and Robert J. Linhardt a a Departments of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Chemical and Biological
Tandem MS Can Distinguish Hyaluronic Acid from NAcetylheparosan Zhenqing Zhang, a Jin Xie, a Jian Liu, b and Robert J. Linhardt a a Departments of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Chemical and Biological
Targeted and untargeted metabolic profiling by incorporating scanning FAIMS into LC-MS. Kayleigh Arthur
 Targeted and untargeted metabolic profiling by incorporating scanning FAIMS into LC-MS Kayleigh Arthur K.Arthur@lboro.ac.uk Introduction LC-MS is a highly used technique for untargeted profiling analyses
Targeted and untargeted metabolic profiling by incorporating scanning FAIMS into LC-MS Kayleigh Arthur K.Arthur@lboro.ac.uk Introduction LC-MS is a highly used technique for untargeted profiling analyses
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Materials and Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
Lecture 3. Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing
 Lecture 3 Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing Nancy Allbritton, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biophysics 824-9137 (office) nlallbri@uci.edu Office- Rm D349 Medical Science D Bldg. Tandem MS Steps:
Lecture 3 Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing Nancy Allbritton, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biophysics 824-9137 (office) nlallbri@uci.edu Office- Rm D349 Medical Science D Bldg. Tandem MS Steps:
Rapid, Simple Impurity Characterization with the Xevo TQ Mass Spectrometer
 Robert Plumb, Michael D. Jones, and Marian Twohig Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION The detection and characterization of impurities and degradation products of an active pharmaceutical
Robert Plumb, Michael D. Jones, and Marian Twohig Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION The detection and characterization of impurities and degradation products of an active pharmaceutical
Preparation and structural determination of large oligosaccharides derived from acharan sulfate
 Carbohydrate Research 341 (2006) 864 869 Preparation and structural determination of large oligosaccharides derived from acharan sulfate Lianli Chi, a Eva M. Munoz, a Hyung Seok Choi, b Young Wan Ha, b
Carbohydrate Research 341 (2006) 864 869 Preparation and structural determination of large oligosaccharides derived from acharan sulfate Lianli Chi, a Eva M. Munoz, a Hyung Seok Choi, b Young Wan Ha, b
LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 EC C18 Column
 Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids
 Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
Introduction to LC/MS/MS
 Trends in 2006 Introduction to LC/MS/MS By Crystal Holt, LC/MS Product Specialist, Varian Inc. Toxicology laboratories Increased use of LC/MS Excellent LD Cheaper (still expensive) Much more robust Solves
Trends in 2006 Introduction to LC/MS/MS By Crystal Holt, LC/MS Product Specialist, Varian Inc. Toxicology laboratories Increased use of LC/MS Excellent LD Cheaper (still expensive) Much more robust Solves
SEPARATION OF BRANCHED PFOS ISOMERS BY UPLC WITH MS/MS DETECTION
 SEPARATION OF BRANCHED PFOS ISOMERS BY UPLC WITH MS/MS DETECTION Marian Twohig 1, Nicholas Ellor 1, Keith Worrall 2, Tim Jenkins 2, Gordon Kearney 2 1 Waters Corporation, 1 Cummings Center, Beverly, MA
SEPARATION OF BRANCHED PFOS ISOMERS BY UPLC WITH MS/MS DETECTION Marian Twohig 1, Nicholas Ellor 1, Keith Worrall 2, Tim Jenkins 2, Gordon Kearney 2 1 Waters Corporation, 1 Cummings Center, Beverly, MA
Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ Orbitrap
 Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ rbitrap Donald Daley, Russell Scammell, Argenta Discovery Limited, 8/9 Spire Green Centre, Flex Meadow, Harlow, Essex, CM19 5TR, UK bjectives unknown
Characterization of an Unknown Compound Using the LTQ rbitrap Donald Daley, Russell Scammell, Argenta Discovery Limited, 8/9 Spire Green Centre, Flex Meadow, Harlow, Essex, CM19 5TR, UK bjectives unknown
GlycanPac AXR-1 Columns
 CHRMATGRAPHY GlycanPac AXR- Columns For High Resolution Glycan Analysis Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXR- columns are highperformance, silica-based HPLC columns for simultaneous
CHRMATGRAPHY GlycanPac AXR- Columns For High Resolution Glycan Analysis Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXR- columns are highperformance, silica-based HPLC columns for simultaneous
Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography
 Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography Application Note Metabolomics Author Yuqin Dai Agilent Technologies, Inc. 31 Stevens Creek Blvd,
Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography Application Note Metabolomics Author Yuqin Dai Agilent Technologies, Inc. 31 Stevens Creek Blvd,
Quantitation of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring
 Quantitation of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Application Note Authors Ning Tang, Christine A. Miller and Keith Waddell Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA This
Quantitation of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Application Note Authors Ning Tang, Christine A. Miller and Keith Waddell Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA This
A Robustness Study for the Agilent 6470 LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
 A Robustness Study for the Agilent 7 LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometer Application Note Clinical Research Authors Linda Côté, Siji Joseph, Sreelakshmy Menon, and Kevin McCann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
A Robustness Study for the Agilent 7 LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometer Application Note Clinical Research Authors Linda Côté, Siji Joseph, Sreelakshmy Menon, and Kevin McCann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract
Identification & Confirmation of Structurally Related Degradation Products of Simvastatin
 Identification & Confirmation of Structurally Related Degradation Products of Simvastatin Power of QTRAP Systems for Identification and Confirmation of Degradation Products Dilip Reddy 1, Chandra Sekar
Identification & Confirmation of Structurally Related Degradation Products of Simvastatin Power of QTRAP Systems for Identification and Confirmation of Degradation Products Dilip Reddy 1, Chandra Sekar
Analyze Barbiturates in Urine with Agilent 6430 LC/MS/MS and Poroshell 120 EC-C18
 Analyze Barbiturates in Urine with Agilent 6 LC/MS/MS and Poroshell EC-C8 Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors Elijah Steinbauer and Pat Friel Toxicology Laboratory at the Veterans Administration
Analyze Barbiturates in Urine with Agilent 6 LC/MS/MS and Poroshell EC-C8 Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors Elijah Steinbauer and Pat Friel Toxicology Laboratory at the Veterans Administration
Determination of β2-agonists in Pork Using Agilent SampliQ SCX Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Determination of β2-agonists in Pork Using Agilent SampliQ SCX Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Application Note Food Safety Authors Chenhao Zhai Agilent
Determination of β2-agonists in Pork Using Agilent SampliQ SCX Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Application Note Food Safety Authors Chenhao Zhai Agilent
Edgar Naegele. Abstract
 Simultaneous determination of metabolic stability and identification of buspirone metabolites using multiple column fast LC/TOF mass spectrometry Application ote Edgar aegele Abstract A recent trend in
Simultaneous determination of metabolic stability and identification of buspirone metabolites using multiple column fast LC/TOF mass spectrometry Application ote Edgar aegele Abstract A recent trend in
Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms
 Supporting Information for Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms Submitted by Yong Feng, Deli
Supporting Information for Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms Submitted by Yong Feng, Deli
Supporting information
 Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
Designer Cannabinoids
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-010 Designer Cannabinoids LCMS-8030 Summary A rapid LC-MS-MS method for determination of designer cannabinoids in smokeable herbs was developed. Background
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-010 Designer Cannabinoids LCMS-8030 Summary A rapid LC-MS-MS method for determination of designer cannabinoids in smokeable herbs was developed. Background
Analysis of anti-epileptic drugs in human serum using an Agilent Ultivo LC/TQ
 Application Note Clinical Research Analysis of anti-epileptic drugs in human serum using an Agilent Ultivo LC/TQ Authors Jennifer Hitchcock 1, Lauren Frick 2, Peter Stone 1, and Vaughn Miller 2 1 Agilent
Application Note Clinical Research Analysis of anti-epileptic drugs in human serum using an Agilent Ultivo LC/TQ Authors Jennifer Hitchcock 1, Lauren Frick 2, Peter Stone 1, and Vaughn Miller 2 1 Agilent
About bioassay of Oximes:? New isolation alternatives from biomatrices? Chromatographic separation issues? Reserve on using MS or MS/MS detection
 State of the art: xime-type AChE Reactivators: Wide use as antidotes in organo phosphorous compounds poisoning; Synthesis of new congeners; Intense studies on their transfer through BBB; Intense studies
State of the art: xime-type AChE Reactivators: Wide use as antidotes in organo phosphorous compounds poisoning; Synthesis of new congeners; Intense studies on their transfer through BBB; Intense studies
Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards]
![Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] Neosolaniol. [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards]](/thumbs/86/94003482.jpg) Neosolaniol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of mycotoxins by liquid chromatography/ tandem mass spectrometry [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter 5, Section 1 9.1 ]
Neosolaniol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of mycotoxins by liquid chromatography/ tandem mass spectrometry [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter 5, Section 1 9.1 ]
Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS
 Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors audimir Lucio do Lago Department of Fundamental Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry University of São Paulo,
Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors audimir Lucio do Lago Department of Fundamental Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry University of São Paulo,
application Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS
 application LC/MS Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS Introduction Many kinds of natural colors are used in beverages,
application LC/MS Natural Food Colorants Analysis of Natural Food Colorants by Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization LC/MS Introduction Many kinds of natural colors are used in beverages,
Detection, Confirmation, and Quantification of Chloramphenicol in Honey, Shrimp and Chicken Using the Agilent 6410 LC/MS Triple Quadrupole
 Detection, Confirmation, and Quantification of Chloramphenicol in Honey, Shrimp and Chicken Using the Agilent LC/MS Triple Quadrupole Application Food Safety Authors Yanyan Fang Agilent Technologies (Shanghai),
Detection, Confirmation, and Quantification of Chloramphenicol in Honey, Shrimp and Chicken Using the Agilent LC/MS Triple Quadrupole Application Food Safety Authors Yanyan Fang Agilent Technologies (Shanghai),
Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas decomposition products of irradiated DMC.
 200000 C 2 CH 3 CH 3 DMC 180000 160000 140000 Intensity 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 C 2 H 6 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CCH 3 EMC DEC 20000 C 3 H 8 HCCH 3 5 10 15 20 25 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas
200000 C 2 CH 3 CH 3 DMC 180000 160000 140000 Intensity 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 C 2 H 6 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CCH 3 EMC DEC 20000 C 3 H 8 HCCH 3 5 10 15 20 25 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1: Gas
Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Sequencing Approach for Highly Sulfated Heparin-derived Oligosaccharides*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 4, Issue of January 23, pp. 2608 2615, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Liquid Chromatography/Mass
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 4, Issue of January 23, pp. 2608 2615, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Liquid Chromatography/Mass
Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS
 The Open Analytical Chemistry Journal, 2011, 5, 27-36 27 Open Access Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS Viorica Lopez-Avila * and George Yefchak
The Open Analytical Chemistry Journal, 2011, 5, 27-36 27 Open Access Mass Spectral Fragmentation Studies of Coumarin-Type Compounds Using GC High-Resolution MS Viorica Lopez-Avila * and George Yefchak
Sample Preparation is Key
 PLOS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117232 February 6, 2015 Presented by Katie Gibbs Sample Preparation is Key Sample extraction and instrumental analysis methods are well documented in metabolomics. Understanding
PLOS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117232 February 6, 2015 Presented by Katie Gibbs Sample Preparation is Key Sample extraction and instrumental analysis methods are well documented in metabolomics. Understanding
Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood
 Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood Application Note Forensics/Doping Control Author Stephan Baumann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara CA 95051 USA Abstract A robust method
Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood Application Note Forensics/Doping Control Author Stephan Baumann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara CA 95051 USA Abstract A robust method
Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
 Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Michael McCullagh, 1 Kieran Neeson, 2 and Antonietta Gledhill 1 Waters Corporation,
Profiling Flavonoid Isomers in Highly Complex Citrus Juice Samples Using UPLC Ion Mobility Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Michael McCullagh, 1 Kieran Neeson, 2 and Antonietta Gledhill 1 Waters Corporation,
Shotgun Proteomics MS/MS. Protein Mixture. proteolysis. Peptide Mixture. Time. Abundance. Abundance. m/z. Abundance. m/z 2. Abundance.
 Abundance Abundance Abundance Abundance Abundance Shotgun Proteomics Protein Mixture 1 2 3 MS/MS proteolysis m/z 2 3 Time µlc m/z MS 1 m/z Peptide Mixture m/z Block Diagram of a Mass Spectrometer Sample
Abundance Abundance Abundance Abundance Abundance Shotgun Proteomics Protein Mixture 1 2 3 MS/MS proteolysis m/z 2 3 Time µlc m/z MS 1 m/z Peptide Mixture m/z Block Diagram of a Mass Spectrometer Sample
Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them. Cyclopropylfentanyl
 Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them Cyclopropylfentanyl Science for a safer world The in vitro metabolism of cyclopropylfentanyl Simon Hudson & Charlotte Cutler, Sport and Specialised
Designer Fentanyls Drugs that kill and how to detect them Cyclopropylfentanyl Science for a safer world The in vitro metabolism of cyclopropylfentanyl Simon Hudson & Charlotte Cutler, Sport and Specialised
SimGlycan. A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows.
 PREMIER Biosoft SimGlycan A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows SimGlycan software processes and interprets the MS/MS and higher
PREMIER Biosoft SimGlycan A high-throughput glycan and glycopeptide data analysis tool for LC-, MALDI-, ESI- Mass Spectrometry workflows SimGlycan software processes and interprets the MS/MS and higher
Extended Mass Range Triple Quadrupole for Routine Analysis of High Mass-to-charge Peptide Ions
 Extended Mass Range Triple Quadrupole for Routine Analysis of High Mass-to-charge Peptide Ions Application Note Targeted Proteomics Authors Linfeng Wu, Christine A. Miller, Jordy Hsiao, Te-wei Chu, Behrooz
Extended Mass Range Triple Quadrupole for Routine Analysis of High Mass-to-charge Peptide Ions Application Note Targeted Proteomics Authors Linfeng Wu, Christine A. Miller, Jordy Hsiao, Te-wei Chu, Behrooz
Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA)
 Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA) Elisabeth A. Kast and Elizabeth A. Higgins GlycoSolutions Corporation, Worcester, MA Data originally presented
Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA) Elisabeth A. Kast and Elizabeth A. Higgins GlycoSolutions Corporation, Worcester, MA Data originally presented
Accumulation and transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic in rice and role of
 Supplementary Information: Accumulation and transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic in rice and role of thiol-complexation to restrict their translocation to shoot Seema Mishra 1,2 *, Jürgen Mattusch
Supplementary Information: Accumulation and transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic in rice and role of thiol-complexation to restrict their translocation to shoot Seema Mishra 1,2 *, Jürgen Mattusch
Standardization of a LC/MS/MS Method for the Determination of Acyl Glucuronides and Their Isomers
 1 1 2 2 3 3 2 1 S.Bolze,.Lacombe, G.Durand, P.Chaimbault, F.Massière, C.Gay-Feutry,.Bromet * and T.Hulot 1. LIPHA, 115, avenue Lacassagne, 69003 Lyon, France 2. BITEC CETRE, 10 avenue aude Guillemin, 45071
1 1 2 2 3 3 2 1 S.Bolze,.Lacombe, G.Durand, P.Chaimbault, F.Massière, C.Gay-Feutry,.Bromet * and T.Hulot 1. LIPHA, 115, avenue Lacassagne, 69003 Lyon, France 2. BITEC CETRE, 10 avenue aude Guillemin, 45071
LC-MS/MS analysis of Chlorates in Milk and Whey Powder using the Agilent 6470 QQQ
 LC-MS/MS analysis of Chlorates in Milk and Whey Powder using the Agilent 6470 QQQ Anthony Sullivan, LC/MS Product Specialist Melanie Mülek and Christoph Müller LC-MS Applications Specialists Hewlett-Packard-Str.
LC-MS/MS analysis of Chlorates in Milk and Whey Powder using the Agilent 6470 QQQ Anthony Sullivan, LC/MS Product Specialist Melanie Mülek and Christoph Müller LC-MS Applications Specialists Hewlett-Packard-Str.
LC/MS/MS Analysis of Metabolites of Synthetic Cannabinoids JWH-018 and JWH-073 in Urine
 Abstract A liquid chromatographic method was developed to resolve a comprehensive set of metabolites of JWH-018 and JWH-073. In addition to the chromatographic analysis method, an extraction method was
Abstract A liquid chromatographic method was developed to resolve a comprehensive set of metabolites of JWH-018 and JWH-073. In addition to the chromatographic analysis method, an extraction method was
Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with LC/MS Detection
 Application Note Food Testing, Metabolomics, Agricultural Chemistry, Environmental Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with
Application Note Food Testing, Metabolomics, Agricultural Chemistry, Environmental Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with
Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices
 Application ote #LCMS-2 esquire series Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices Introduction The simple monitoring
Application ote #LCMS-2 esquire series Application of LC/Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Quantification of Pesticides in Complex Matrices Introduction The simple monitoring
O O H. Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL. LC /MS conditions
 Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
The Raptor HILIC-Si Column
 The Raptor HILIC-Si Column With Raptor LC columns, Restek chemists became the first to combine the speed of superficially porous particles (also known as SPP or core-shell particles) with the resolution
The Raptor HILIC-Si Column With Raptor LC columns, Restek chemists became the first to combine the speed of superficially porous particles (also known as SPP or core-shell particles) with the resolution
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS. Application. Authors. Abstract. Experimental. Introduction. Food Safety
 Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
Determination of Amphetamine and Derivatives in Urine
 Determination of Amphetamine and Derivatives in Urine Using a Modified QuEChERS and Capillary Electrophoresis Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis Application Note Authors Vagner B. dos Santos and Claudimir
Determination of Amphetamine and Derivatives in Urine Using a Modified QuEChERS and Capillary Electrophoresis Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis Application Note Authors Vagner B. dos Santos and Claudimir
Author. Introduction. Abstract
 Simultaneous Measurement of Sirolimus and Tacrolimus Concentrations in Blood by Semi-Automated Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Application Author Gary L.
Simultaneous Measurement of Sirolimus and Tacrolimus Concentrations in Blood by Semi-Automated Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Application Author Gary L.
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D
 LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma Lipids
 Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
4.5 Minute Analysis of Benzodiazepines in Urine and Whole Blood Using LC/MS/MS and an Ultra Biphenyl Column
 Clinical, Forensic & Toxicology Applications 4.5 Minute Analysis of Benzodiazepines in Urine and Whole Blood Using LC/MS/MS and an Ultra Biphenyl Column By Amanda Rigdon Abstract A rapid, sensitive method
Clinical, Forensic & Toxicology Applications 4.5 Minute Analysis of Benzodiazepines in Urine and Whole Blood Using LC/MS/MS and an Ultra Biphenyl Column By Amanda Rigdon Abstract A rapid, sensitive method
Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI
 Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI Kate Yu, Eric Block LC/MS Waters Corporation Introduction to polymer additive analysis by LC/MS. Electron Ionization (EI) Advantages Classical spectra Library searchable
Polymer Additive Analysis by EI and APCI Kate Yu, Eric Block LC/MS Waters Corporation Introduction to polymer additive analysis by LC/MS. Electron Ionization (EI) Advantages Classical spectra Library searchable
Analysis of N-Linked Glycans from Coagulation Factor IX, Recombinant and Plasma Derived, Using HILIC UPLC/FLR/QTof MS
 Analysis of N-Linked Glycans from Coagulation Factor IX, Recombinant and Plasma Derived, Using HILIC UPLC/FLR/QTof MS Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F I T
Analysis of N-Linked Glycans from Coagulation Factor IX, Recombinant and Plasma Derived, Using HILIC UPLC/FLR/QTof MS Ying Qing Yu Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F I T
Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco
 JTI-Ökolab Vienna, Austria Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco Madeleine Werneth, Jutta Pani, Bernhard Mayer-Helm 2014 CORESTA CONGRESS - ST46 Québec City, Canada 12-16 October 2014 Background
JTI-Ökolab Vienna, Austria Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco Madeleine Werneth, Jutta Pani, Bernhard Mayer-Helm 2014 CORESTA CONGRESS - ST46 Québec City, Canada 12-16 October 2014 Background
Improved matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric detection of glycosaminoglycan disaccharides as cesium salts
 RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 21: 1315 1320 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2964 Improved matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 21: 1315 1320 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2964 Improved matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
Qualitative and quantitative determination of cannabinoid profiles and potency in CBD hemp oil using LC/UV and Mass Selective Detection
 Application Note Cannabis Qualitative and quantitative determination of cannabinoid profiles and potency in CBD hemp oil using LC/UV and Mass Selective Detection Authors Mike Adams, Annette Roth, Sue D
Application Note Cannabis Qualitative and quantitative determination of cannabinoid profiles and potency in CBD hemp oil using LC/UV and Mass Selective Detection Authors Mike Adams, Annette Roth, Sue D
4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group
 4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group MDLC for Shotgun Proteomics Introduction General concepts Advantages Challenges
4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group MDLC for Shotgun Proteomics Introduction General concepts Advantages Challenges
Separation of 15 Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards
 Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether
 Supplemental Material Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether species by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry James G. Bollinger *, Hiromi Ii*, Martin
Supplemental Material Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether species by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry James G. Bollinger *, Hiromi Ii*, Martin
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/e1500678/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Chemical synthesis of erythropoietin glycoforms for insights into the relationship between glycosylation pattern and
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/e1500678/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Chemical synthesis of erythropoietin glycoforms for insights into the relationship between glycosylation pattern and
High-throughput lipidomic analysis of fatty acid derived eicosanoids and N-acylethanolamines
 High-throughput lipidomic analysis of fatty acid derived eicosanoids and N-acylethanolamines Darren S. Dumlao, Matthew W. Buczynski, Paul C. Norris, Richard Harkewicz and Edward A. Dennis. Biochimica et
High-throughput lipidomic analysis of fatty acid derived eicosanoids and N-acylethanolamines Darren S. Dumlao, Matthew W. Buczynski, Paul C. Norris, Richard Harkewicz and Edward A. Dennis. Biochimica et
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
Agilent Anion-Exchange Media for Proteins - Loading vs Resolution - Effect of Flow Rate and Example Protein Separations
 Agilent Anion-Exchange Media for Proteins - Loading vs Resolution - Effect of Flow Rate and Example Protein Separations Technical Overview Introduction PL-SAX is a hydrophilic strong anion-exchange chromatographic
Agilent Anion-Exchange Media for Proteins - Loading vs Resolution - Effect of Flow Rate and Example Protein Separations Technical Overview Introduction PL-SAX is a hydrophilic strong anion-exchange chromatographic
[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector
![[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector [ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector](/thumbs/83/88757464.jpg) Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
An Alternative Approach: Top-Down Bioanalysis of Intact Large Molecules Can this be part of the future? Lecture 8, Page 27
 An Alternative Approach: Top-Down Bioanalysis of Intact Large Molecules Can this be part of the future? Lecture 8, Page 27 Top-down HRAM Bioanalysis of Native Proteins/Molecules Relative Abundance 100
An Alternative Approach: Top-Down Bioanalysis of Intact Large Molecules Can this be part of the future? Lecture 8, Page 27 Top-down HRAM Bioanalysis of Native Proteins/Molecules Relative Abundance 100
REDOX PROTEOMICS. Roman Zubarev.
 REDOX PROTEOMICS Roman Zubarev Roman.Zubarev@ki.se Physiological Chemistry I, Department for Medical Biochemistry & Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm What is (RedOx) Proteomics? Proteomics -
REDOX PROTEOMICS Roman Zubarev Roman.Zubarev@ki.se Physiological Chemistry I, Department for Medical Biochemistry & Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm What is (RedOx) Proteomics? Proteomics -
Application of mass spectrometry to determine the activity and specificity of pectin lyase A
 Carbohydrate Research 337 (2002) 1217 1227 www.elsevier.com/locate/carres Application of mass spectrometry to determine the activity and specificity of pectin lyase A Kudzai E. Mutenda, a Roman Körner,
Carbohydrate Research 337 (2002) 1217 1227 www.elsevier.com/locate/carres Application of mass spectrometry to determine the activity and specificity of pectin lyase A Kudzai E. Mutenda, a Roman Körner,
1. Sample Introduction to MS Systems:
 MS Overview: 9.10.08 1. Sample Introduction to MS Systems:...2 1.1. Chromatography Interfaces:...3 1.2. Electron impact: Used mainly in Protein MS hard ionization source...4 1.3. Electrospray Ioniztion:
MS Overview: 9.10.08 1. Sample Introduction to MS Systems:...2 1.1. Chromatography Interfaces:...3 1.2. Electron impact: Used mainly in Protein MS hard ionization source...4 1.3. Electrospray Ioniztion:
Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
 CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2012, 28(1), 31 36 Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS ZHANG Yu-chi 1,2, PI Zi-feng 1*, LIU Chun-ming 2, SONG
CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2012, 28(1), 31 36 Analysis of Low-polar Ginsenosides in Steamed Panax Ginseng at High-temperature by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS ZHANG Yu-chi 1,2, PI Zi-feng 1*, LIU Chun-ming 2, SONG
Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni
 0 out of 21 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni This monograph
0 out of 21 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni This monograph
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit
 Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass Spectrometry
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass
Quantification of lovastatin in human plasma by LC/ESI/MS/MS using the Agilent 6410 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS system
 Quantification of lovastatin in human plasma by LC/ESI/MS/MS using the Agilent 641 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS system Application Note Clinical Research Author Siji Joseph Agilent Technologies Bangalore, India
Quantification of lovastatin in human plasma by LC/ESI/MS/MS using the Agilent 641 Triple Quadrupole LC/MS system Application Note Clinical Research Author Siji Joseph Agilent Technologies Bangalore, India
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C18 MM & FLARE C18+ Columns
 Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents
 No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
Choosing the metabolomics platform
 Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology University of Alabama at Birmingham sbarnes@uab.edu Challenges Unlike DNA, RNA and proteins, the metabolome
Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology University of Alabama at Birmingham sbarnes@uab.edu Challenges Unlike DNA, RNA and proteins, the metabolome
Available online Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(12):519-523 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CDEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Characterization of cyanidin 3-(6-acetylglucoside)-5-(3
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(12):519-523 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CDEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Characterization of cyanidin 3-(6-acetylglucoside)-5-(3
High-yield novel leech hyaluronidase to expedite the. preparation of specific hyaluronan oligomers
 High-yield novel leech hyaluronidase to expedite the preparation of specific hyaluronan oligomers Peng Jin 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3,6, Na Zhang 1,2,3, Guocheng Du 1,3,5,6 & Jian Chen 1,3,4,6 1 Synergetic
High-yield novel leech hyaluronidase to expedite the preparation of specific hyaluronan oligomers Peng Jin 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3,6, Na Zhang 1,2,3, Guocheng Du 1,3,5,6 & Jian Chen 1,3,4,6 1 Synergetic
Advantages of Ion Mobility Q-TOF for Characterization of Diverse Biological Molecules
 Advantages of Ion Mobility Q-TOF for Characterization of Diverse Biological Molecules Add a New Dimension to your Research Capability with Agilent s New Drift Ion Mobility Q-TOF System Overview: 6560 IM
Advantages of Ion Mobility Q-TOF for Characterization of Diverse Biological Molecules Add a New Dimension to your Research Capability with Agilent s New Drift Ion Mobility Q-TOF System Overview: 6560 IM
