A00.2 Office of the Medical Director
|
|
|
- Gladys Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A00.2 Office of the Medical Director Medications Individual license holders are responsible to hold and maintain the appropriate competencies (satisfactory knowledge and appropriate psychomotor skills) for the safe administration of these medications. Clinical care is to be provided in accordance with the protocols and procedures as established by the Provincial Medical Director and all patient care duties and functions must be performed in accordance with the EMS Protocols and Procedures as published by the Minister. A - Adult B - Adolescent C - Child D - Infant E - Neonatal 17 years & older 10 up to 17 years 1 up to 10 years 0 to 12 months Newly born VERSION M01 Adenosine M02 Simple Analgesics & Antipyretics M03.1 Opioid Analgesics M03.2 Nasal Fentanyl M04 Antiemetics M05.1 Epinephrine for Anaphylaxis revised M05.2 Epinephrine for Cardiopulmonary Arrest M06.1 Glucose M06.2 Dextrose revised M06.3 Glucagon revised M07.1 Intranasal Midazolam revised M07.2 Intramuscular Midazolam revised M07.3 Intravascular Midazolam revised M07.4 Diazepam revised M07.5 Lorazepam revised M08 Ranitidine NEW M09 Furosemide M10.1 Calcium for Hyperkalemia revised M10.2 Sodium Bicarbonate for Hyperkalemia revised M10.3 Insulin & Dextrose for Hyperkalemia revised M10.4 Salbutamol for Hyperkalemia NEW M11 Naloxone revised M12 Oxygen M13 Methlprednesolone NEW M14.1 Amiodarone for Cardiopulmonary Arrest M15 Bronchodilators revised M16 Oxytocin M17.1 Ketamine NEW M21A Nitroglycerin M24.1 Magnesium Sulfate for Cardiopulmonary Arrest M24.2 Magnesium Sulfate for Pregnancy Induced Hypertension M28A Tranexamic Acid M29 Intravenous Fluid (IVF) M30 Tetracaine NEW M33 Diphenhydramine M34 Haloperidol M36 Propofol pending M37.1A Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA) revised A00.2 Medications Page 1
2 M37.2A Ticagrelor M38 Toradol M39.1 Atropine for Unstable Bradycardia M43.1A Enoxaparin A00.2 Medications Page 2
3 M01 Medications Office of the Medical Director Adenosine ADULT DOSING (17 years & older): First dose: 6 mg rapid push, followed by fluid flush Second dose: 12 mg rapid push, followed by fluid flush INFANT, CHILD & ADOLESCENT DOSE (0 months up to 17 years): First dose: 0.1 mg / kg mg (max = 6 mg) rapid push, followed by fluid flush Second dose: 0.2 mg / kg (max = 12 mg) rapid push, followed by fluid flush Narrow complex tachycardia known or presumed to represent atrioventricular node re-entry tachycardia (AVNRT) also know as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT). Stable regular wide complex tachycardia known or suspected to be due to AVNRT with aberrant ventricular tachycardia. Unstable tachycardia requiring emergent DC cardioversion Adenosine must be given by rapid push into a well-running intravenous line, followed by a 30 ml normal saline flush. There should be evidence of central drug delivery such as bradycardia or asystole on the ECG monitor or patient s subjective sensation of dyspnea. Patients should be forewarned about the subjective sensations accompanying adenosine administration, such as dyspnea, lightheadedness, nausea and / or sense on impending doom. Do not exceed two doses even if tachycardia recurs. M01 Adenosine Page 1
4 M02 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Simple Analgesics & Antipyretics Primary ACETAMINOPHEN IBUPROFEN NAPROXEN ADULT (17 yr & older): - 10 to 15 mg/kg - Single max dose = 1000 mg - Repeat every 4 hr as required - 10 to 15 mg / kg - Single max dose = 650 mg - Repeat every 4 hr as required - 10 mg/kg - Single max dose = 800 mg - Repeat every 6 hr as required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): - 10 mg/kg - Single max dose = 400 mg - Repeat every 6 hr as required CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): to 500 mg - Repeat every 8 hr as required to 500 mg - Repeat every 8 hr as required - 10 to 15 mg/kg - Repeat every 4 hr as required - 10 mg/kg - Repeat every 6 hr as required N/A INFANT (0 up to 12 months): - 10 to 15 mg/kg - Repeat every 4 hr as necessary - 10 mg/kg - Repeat every 6 hr as necessary N/A M02 Simple Analgesia Page 1
5 Analgesia for mild to moderate pain Antipyretic for relief of fever True allergy to acetaminophen contraindicates acetaminophen administration True allergy to ibuprofen contraindicates both ibuprofen and naproxen administration True allergy to naproxen contraindicates both naproxen and ibuprofen administration Ibuprofen and naproxen administration are contraindicated by a history of aspirin (ASA) induced asthma Decreased LOC with inability to protect airway or risk of aspiration If patient may be going for surgery within 4 hours, consider intravenous analgesia. M02 Simple Analgesia Page 2
6 M03.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Opioid Analgesia FENTANYL: Age < 75 years: - 1 mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 50 mcg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 200 mcg Age > 75 years: mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 25 mcg - Repeat every 10 min as required - Hourly max = 100 mcg FENTANYL: Standard Dose: - 1 mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 50 mcg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 200 mcg Low Dose: mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 25 mcg - Repeat every 10 min as required - Hourly max = 100 mcg FENTANYL: Standard Dose: - 1 mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 25 mcg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 100 mcg Low Dose: mcg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 12.5 mcg - Repeat every 10 min as required - Hourly max = 50 mcg ADULT (17 yr & older): MORPHINE: Age < 75 years: mg/ kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 5 mg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 20 mg Age > 75 years: mg/kg IM / IO / IV - Max single dose = 2.5 mg - Repeat every 10 min as required - Hourly max = 10 mg ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): MORPHINE: mg/ g IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 5 mg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 20 mg CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): MORPHINE: mg/ kg IM / IO / IV - Single dose max = 2.5 mg - Repeat every 5 min as required - Hourly max = 10 mg HYDROMORPHONE: Age < 75 years: to 1 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 10 min as required - Hourly max = 4 mg Age > 75 years: to 0.5 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 15 min as required - Hourly max = 2 mg N/A N/A M03.1 Opioids Page 1
7 Moderate to severe pain from acute medical or traumatic conditions Systolic BP less than 100 mmhg in adults & adolescents; or systolic BP less than age-adjusted minimum in children ( x age) Presence of or potential for respiratory depression Decrease in LOC (GCS < 15) Presence or suspicion of head uinjury or raised intracranial pressure True allergy to codeine, morphine or hydromorphine contraindicates administration of morphine and hydromorphone a. Consider prophylactic use of an antiemetic as per M04 Antinauseant. b. If hypotension develops after opioid administration administer fluid bolus as per C07 Hypotension & Shock. c. If respiratory depression (hypoventilation, apnea) occurs after opioid administration, consider naloxone administration as per M11 Naloxone. d. Itching alone (absence of swelling or respiratory symptoms) with morphine or hydromorphone is not indicative of allergy. Slow rate of administration if itching develops. e. If patient is allergic to codeine or morphine or hydromorphine, consider administration of fentanyl. f. Morphine dosing is calculated in fractions of milligrams per kilogram. Round off to the nearest one milligram. Fentanyl is 100 times more potent as morphine. The dosing is calculated in micrograms per kilogram. Hydromorphone is 5 times more potent than morphine. The dosing is calculated in milligrams. M03.1 Opioids Page 2
8 M03.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intranasal Fentanyl (SUBLIMAZE) Primary Moderate to severe pain from acute medical or traumatic conditions, where IV administration is not otherwise available SBP less than 100 mmhg in adults & adolescents or less than age-adjusted minimum in children ( x age) Presence of or potential for respiratory depression Decrease in LOC (GCS < 15) Presence or suspicion of head injury or raised intracranial pressure True allergy to fentanyl Fentanyl is 100 times more potent as morphine. The dosing is calculated in micrograms per kilogram. ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) ABBREVIATIONS: GCS Glasgow coma score IV intravenous kg kilogram LOC level of consciousness max maximum mcg microgram min minute SBP systolic blood pressure Age < 75 years: 0.5 to 1 mcg/kg Single dose max = 50 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 200 mcg Standard Dose: 1 mcg/kg Single dose max = 50 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 200 mcg Standard Dose: 1 mcg/kg Single dose max = 25 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 100 mcg Age > 75 years: 0.25 to 0.5 mcg/kg Single dose max = 25 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 100 mcg Low Dose: 0.5 mcg/kg Single dose max = 25 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 100 mcg Low Dose: 0.5 mcg/kg Single dose max = 12.5 mcg Repeat every 10 min as required Hourly max = 50 mcg M03.2 IN Fentanyl Page 1
9 M04 Medications Office of the Medical Director Antiemetics (Antinauseants) Primary ADULT (17 yr & older): Dimenhydrinate (GRAVOL): - 50 mg IM / IO / IV / PO - Repeat as required - Max = 100 mg per 4 hr Dimenhydrinate (GRAVOL): - 25 to 50 mg IM / IO / IV / PO - Repeat as required - Max = 100 mg per 4 hr Dimenhydrinate (GRAVOL): to 25 mg IM / IO / IV / PO - Repeat as required - Max = 50 mg per 4 hr Metoclopramide (MAXERAN): - 5 to 10 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 6 hr as required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): Metoclopramide (MAXERAN): to 10 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 6 hr as required CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): Metoclopramide (MAXERAN): mg / kg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 6 hr as required - Max single dose = 5 mg Ondansetron (ZOFRAN): - 4 to 8 mg IV once only Ondansetron (ZOFRAN): - 4 mg IV once only Ondansetron (ZOFRAN): mg/kg IV once only - Max single dose = 4 mg Nausea and/or vomiting from acute medical, surgical, obstetrical or traumatic condition Known hypersensitivity Use dimenhydrinate in pregnant women. Do not administer PO dimenhydrinate if altered LOC. M04 Antiemetics Page 1
10 M05.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic year & older Epinephrine for Anaphylaxis Primary IM ADMINISTRATION ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 5 years) BASIC CARE: mg IM by autoinjector and repeat once as required BASIC CARE: mg IM by autoinjector and repeat once as required BASIC CARE: mg IM by autoinjector and repeat once as required PRIMARY CARE: mg IM by manual injection and repeat once as required PRIMARY CARE: mg IM by manual injection and repeat once as required IO/IV ADMINISTRATION (ACP only) PRIMARY CARE: mg IM by manual injection and repeat once as required CHILD (6 years & older) BASIC CARE: mg IM by autoinjector and repeat once as required PRIMARY CARE: mg IM by manual injection and repeat once as required mg IO / IV - Repeat as required mg IO / IV - Repeat as required Acute allergic reaction presenting with urticaria, angioedema, shock or bronchospasm Exposure to allergen with history of previous anaphylaxis None mg/kg IO / IV - Single maximum = 0.1 mg - Repeat as required If pediatric autoinjector is not available for children under age 5 years, use adult autoinjector once only. Epinephrine administration requires continuus cardiac monitoring. ABBREVIATIONS: IM = intramuscular IO = intraosseous IV = intravenous kg = kilogram mg/ kg = milligram per kilogram M05.1 Epinephrine / Anaphylaxis Page 1
11 M05.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Epinephrine for Cardiopulmonary Arrest ADULT (17 years & older): 1 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 3 to 5 minutes as required CHILD (1 up to 10 years): 0.01 mg/kg (maximum = 1 mg) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 3 to 5 min as required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years): 1 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 3 to 5 minutes as required INFANT (0 up to 12 months): 0.01 mg/kg (maximum = 1 mg) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 3 to 5 min as required Pulseless cardiopulmonary arrest that does not respond to initial defibrillation and/or first cycle CPR None REMINDER: Drug administration should not interrupt CPR or delay defibrillation. M05.2 Epinephrine / CPA Page 1
12 M06.1 Office of the Medical Director Basic Glucose Primary ADULT (17 yr & older): 25 to 50 gm PO Repeat once as required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): 25 to 50 gms PO Repeat once as required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): 12.5 to 25 gms PO Repeat once as required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia Suspected or confirmed hypoglycemia (glucose < 4 mmol / l) Decreased LOC is a relative contraindication (see (a) below) In patient with depressed LOC, with the patient in the recovery position, apply half dose of oral glucose paste to the dependent buccal mucosa. This can be repeated once, if there is no response to the initial application. If patient responds to buccal application of glucose paste, remainder of glucose dose may be swallowed and/or administered as solution. M06.1 Glucose Page 1
13 M06.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Dextrose Primary Suspected or confirmed hypoglycemia (glucose < 4 mmol / l) None D25W can be obtained by mixing 10 ml of D50W with 10 ml of sterile saline (1:1 dilution). ADULT (17 yr & older): 50 ml of D50W (25 gm) IV / IO Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): 25 ml of D50W (12.5 gm) IV / IO Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia CHILD (1 up to 10 yrs): 1 ml/kg of D25W (0.25 gm/kg) IV / IO Maximum single dose =10 gm Maximum single volume = 40 ml Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode Can be repeated as required for further confirmed hypoglycemia M06.2 Dextrose Page 1
14 APPENDIX A: CONCENTRATIONS & DILUTIONS OF DEXTROSE SOLUTIONS. SOLUTION Dextrose (gm) per 100 ml Dextrose (gm) per ml Dextrose (mg) per ml D50W D25W M06.2 Dextrose Page 2
15 M06.3 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Glucagon Primary 1 mg IM / IN / IO / IV Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode ADULT (17 yr & older): 1 mg IM / IN / IO / IV Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): 0.5 mg IM / IN / IO / IV Repeat once in 5 min if required for initial episode CHILD (1 up to 10 yrs): Suspected or confirmed hypoglycemia (glucose < 4 mmol / l) Refractory anaphylaxis in patients on beta blocker medications (adult only) None Glucagon may cause significant nausea. Consider antinauseant administration as per M04 Antinauseants. If vascular access is not available or delayed, glucagon can be administered prior to intravenous dextrose or oral glucose. Providers with appropriate delegation ( Care level) may administer up to 2 doses of glucagon for anaphylaxis not responding to multiple doses of epinephrine in patients known to be on beta blocker medications. M06.3 Glucagon Page 1
16 M07.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intranasal Midazolam (VERSED) Primary Active seizure(s) Known or suspected hypersensitivity DO NOT ADMINISTER IF SEIZURE(S) HAS/HAVE RESOLVED OR APPEAR(S) TO BE RESOLVING. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status: o Respiratory depression and hypotension are common in the post-seizure period, especially if benzodiazepines and/or other medications have been taken or administered to terminate the seizure(s). o Before administering providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. Use 5 mg / ml concentration. Alternate nostrils to facilitate maximum absorption. ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) INFANT (0 up to 12 months) 2 mg Repeat once in 5 minutes if required 1 to 2 mg Repeat once in 5 minutes if required 0.1 mg/kg Single maximum dose = 2 mg Repeat once in 5 minutes if required 0.1 mg/kg Single maximum dose = 1 mg Repeat once in 5 minutes if required M07.1 IN Midazolam Page 1
17 M07.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intranasal Midazolam (VERSED) Primary Active seizure Known or suspected hypersensitivity Respiratory depression or significant potential of same Hypotension ROUTE INTRANASAL ADULT (17 years & older) 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 10 mg Repeat half-dose once in 5 min if required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 10 mg Repeat half-dose once in 5 min if required CHILD (1 up to 10 years) ICP & ABOVE 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 5 mg Repeat half-dose once in 5 min if required INFANT (0 up to 12 months) ICP & ABOVE 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 2.5 mg Repeat half-dose once in 5 min if required DO NOT ADMINISTER IF SEIZURE(S) HAS/HAVE RESOLVED OR APPEAR(S) TO BE RESOLVING. Use 5 mg/ml concentration. Alternate nostrils to facilitate maximum absorption. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status. Providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. Respiratory depression and hypotension are especially common in the post-seizure period. ABBREVIATIONS: ICP = intermediate care provider max = maximum mg = milligram mg/kg = milligram per kilogram mg/ml=milligram per milliliter min = minute M07.1 IN Midazolam Page 1
18 M07.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intramuscular Midazolam (VERSED) Active seizure Significant alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal Known or suspected hypersensitivity Respiratory depression or significant potential of same Hypotension ROUTE ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) INFANT (0 up to 12 months) INTRAMUSCULAR 10 mg Repeat once in 15 min if required Wt > 40 kg - 10 mg Wt < 40 kg - 5 mg Repeat once in 15 min if required 2.5 mg Repeat once in 15 min if required N/A DO NOT ADMINISTER IF SEIZURE(S) HAS/HAVE RESOLVED OR APPEAR(S) TO BE RESOLVING. IM injection is only to be used when an alternate route of administration is not available or reasonably and safely obtained. Providers should switch to an alternative route or medication as soon as possible. Use 5 mg/ml concentration. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status. Providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. Respiratory depression and hypotension are especially common in the post-seizure period. ABBREVIATIONS: IM = intramuscular kg = kilogram mg = milligram mg/ml=milligram per milliliter min = minute wt = weight M07.2 IM Midazolam Page 1
19 M07.3 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intravenous Midazolam (VERSED) Active seizure Significant alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal Brief, conscious sedation for cardioversion or transcutaneous pacing Deep sedation for endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation Known or suspected hypersensitivity Respiratory depression or significant potential of same Hypotension ROUTE ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) INFANT (0 up to 12 months) INTRAVENOUS (seizures) 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 10 mg Repeat half-dose every 5 min as required 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 10 mg Repeat half-dose every 5 min as required 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 5 mg Repeat half-dose every 5 min as required 0.2 mg/kg Max dose = 2 mg Repeat half-dose every 5 min as required 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg Max dose = 1.25 mg Repeat every 5 min as required INTRAVENOUS (other indications) 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg Max dose = 5 mg Repeat every 5 min as required 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg Max dose = 5 mg Repeat every 5 min as required 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg Max dose = 2.5 mg Repeat every 5 min as required DO NOT ADMINISTER IF SEIZURE(S) HAS/HAVE RESOLVED OR APPEAR(S) TO BE RESOLVING. If IV access is not available, providers with appropriate delegation may administer by IO route. For IV administration, infuse over 30 to 60 sec. Titrate to desired effect. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status. Providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. Respiratory depression and hypotension are especially common in the post-seizure period. ABBREVIATIONS: IO = intraosseous IV = intravenous max = maximum mg = milligram mg/kg = milligram per kilogram min = minute M07.3 IV Midazolam Page 1
20 M07.4 Medications Office of the Medical Director years & older Diazepam (VALIUM) Primary Significant alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal Known or suspected hypersensitivity Respiratory depression or reasonably forseeable risk of same Hypotension If IV access is not available providers with appropriate delegation may administer by the IO route. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status. Providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. When administering IV, infuse over 30 to 60 sec. Titrate to desired effect. ROUTE ORAL (PCP & above) ADULT (17 years & older) 20 mg Repeat every 30 min as required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) 10 to 20 mg Repeat once in 30 min if required INTRAVENOUS (ICP & above) ABBREVIATIONS: 5 to 10 mg Repeat every 10 min as required ICP =intermediate care provider IO =intraosseous IV= intravenous max =maximum mg = milligram min =minute PCP=primary care provider sec = second 5 mg Repeat every 10 min as required (max 3 doses) M07.4 Diazepam Page 1
21 M07.5 Medications Office of the Medical Director years & older Lorazepam (ATIVAN) Primary Significant alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal Agitation or aggressionand patient / public / paramedic safety concerns Anxiety interfering with safe transport of patient (PO only) Known or suspected hypersensitivity Respiratory depression or reasonably forseeable risk of same Hypotension Administration by IM injection is only to be used when an alternate route of administration is not available or reasonably and safely obtained. Providers should switch to an alternative route or medication as soon as possible. If IV access is not available, providers with appropriate delegation may administer by IO route. For IV administration, infuse over 30 to 60 sec. Titrate to desired effect. Continuously monitor respiratory and cardiac status. Providers must be prepared to manage the airway, support ventilations and treat hypotension as required. When administering IV, infuse over 30 to 60 sec. Titrate to desired effect. ROUTE ORAL (PCP & above) INTRAMUSCULAR (ICP & above) INTRAVENOUS (ICP & above) ABBREVIATIONS: ADULT (17 years & older) 1 to 2 mg Repeat every 30 min as required 1 to 2 mg Repeat once in 15 min if required 1 to 2 mg Repeat every 10 min as required ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) 1 to 2 mg Repeat once in 30 min if required 1 to 2 mg Repeat once in 15 min if required 1 to 2 mg Repeat every 10 min as required (max 3 doses) ICP = intermediate care provider IM = Intramuscular IO = intraosseous IV - intravenous mg =milligram min = minute PCP =primaty care provider PO = per mouth sec = second M07.5 Lorazepam Page 1
22 M08 Medications Office of the Medical Director Ranitidine ADULT (17 yr & older): ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): 50 mg IO / IV once only 50 mg IO / IV once only 1 mg / kg IO / IV once only Acute allergic reaction presenting with urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm or shock Exposure to allergen with history of previous anaphylaxis None M08 Ranitdine Page 1
23 M09A Medications years & older Office of the Medical Director Furosemide (LASIX) - Adult Not currently taking furosemide: 20 mg IV once Acute heart failure True anaphylaxis to furosemide (rare) Hypotension Dehydration Currently taking furosemide: 40 mg IV once Known chronic renal failure: 80 mg IV once M09A Furosemide Page 1
24 M10.1Medications Office of the Medical Director Hyperkalemia Therapy: Calcium ADULT: (17 years & older) 10 ml 10 ml ADOLESCENT: (10 up to 17 years) CALCIUM CHLORIDE 10% IV 0.2 ml/kg (max dose = 10 ml at 50 kg) CALCIUM GLUCONATE 10% IV 0.6 ml/kg (max dose = 10 ml at 17 kg) CHILD: (1 up to 10 years) 0.2 ml/kg (max dose = 10 ml at 50 kg) 0.6 ml/kg (max dose = 10 ml at 17 kg) CPA in any dialysis-dependent patient Known or suspected significant hyperakalemia K greater than 5.5 in patient with ECG changes K greater than 6.0 in any patient without ECG changes Known or suspected digoxin toxicity (rare) Note that the dosages for calcium are calculated by volume. Calcium gluconate may be susbtsituted for calcium chloride in the ADVANCED RESUSCITATION care maps (but note that the volume dose in adolescent and child patients are different) because calcium chloride contains 3 times more elemental calcium than calcium gluconate (1.4 versus 0.5 meq). In an awake patient calcium chloride infusion may be irritating and painful to the vein; consider calcium gluconate. ABBREVIATIONS: CPA cardiopulmonary arrest ECG electrocardiogram IV - intravenous K - potassium kg - kilogram max maximum meq - millequivalent mg - milligram ml milliliter 10% = 100 mg / ml M10.1 Calcium (Hyperkalemia) Page 1
25 M10.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Hyperkalemia Therapy: 10 years & older Calcium CPA in any dialysis-dependent patient, or Known or suspected hyperkalemic CPA, or Dialysis-dependent patient having missed at least one scheduled dialysis treatment None CALCIUM GLUCONATE (10%): 1000 mg (10 ml) o Rapid IV push during CPA o Slow IV push over 2 min in non-cpa Repeat once in 5 min if findings suggestive of hyperkalemia on cardiac monitor or ECG do not resolve CALCIUM CHLORIDE (10%): 500 to 1000 mg (5 to 10 ml) o Rapid IV push during CPA o Slow IV push over 2 min in non-cpa Repeat once in 5 min if findings suggestive of hyperkalemia on cardiac monitor or ECG do not resolve Calcium gluconate may cause less pain and irritation at IV injection during administration, a consideration in conscious patients. During prolonged patient transport, repeat calcium administration once at 60 min if required. ABBREVIATIONS: CPA = cardiopulmonary arrest ECG = electrocardiogram IV = intravenous max = maximum mg = milligram min = minute ml = milliliter M10.1 Calcium (Hyperkalemia) Page 1
26 M10.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Hyperkalemia Therapy: 10 years & older Sodium Bicarbonate CPA in any dialysis-dependent patient, or Known or suspected hyperkalemic CPA None 1 ml/kg (1 meq/kg) Rapid IV push Max dose = 100 ml (2 ampules) NOTE: One ampule (50 ml) of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate contains 50 meq of buffer ABBREVIATIONS: CPA = cardiopulmonary arrest IV = intravenous max = maximum meq = millequivalent meq/kg = milliequivalents per kilogram ml/kg = milliliters per kilogram M10.2 Bicarbonate (Hyperkalemia) Page 1
27 M10.3 Medications Office of the Medicaol Director Hyperkalemia Therapy: 10 years & older Insulin & Dextrose Upon ROSC from CPA in any dialysis-dependent patient, or Dialysis-dependent patient having missed at least one scheduled dialysis treatment Hypoglycemia (serum glucose less than 4 mmol/l) ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) REGULAR INSULIN: 10 units Rapid IV push DEXTROSE (50%): 50 ml (1 ampule) Rapid IV push Check blood sugar at every 30 min after IV insulin administration. ABBREVIATIONS: CPA = cardiopulmonary arrest IV = intravenous kg = kilogram max = maximum ml = milliliter ml/kg = milliliter / kilogram mmol/l = millimole per liter ROSC = return of spontaneous circulation REGULAR INSULIN: 0.1 units/kg (max 10 units) Rapid IV push DEXTROSE (50%): 1 ml/kg (max 50 ml) Rapid IV push M10.3 Insulin/Dextrose (Hyperkalemia) Page 1
28 M10.4 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Hyperkalemia Therapy: 10 years & older Salbutamol Primary Dialysis-dependent patient having missed at least one scheduled dialysis treatment, where vascular access will be delayed or not available None 8 inhalations by MDI or 5 mg by NEB Repeat once in 5 min if findings suggestive of hyperkalemia on cardiac monitor or ECG do not resolve Repeat every 30 min during prolonged transport if this is the only agent given for treatment of hyperkalemia ABBREVIATIONS: ECG = electrocardiogram MDI = metered dose inhaler min = minute NEB = nebulizer M10.4 Salbutamol (Hyperkalemia) Page 1
29 M11 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Naloxone (NARCAN) Primary ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) INFANT 0 up to 12 months) STANDARD DOSING mg IM / IN / IO / IV - Repeat every 3 min as required - Cumulative max dose = 2 mg mg IM / IN / IO / IV - Repeat every 3 min as required - Cumulative max dose = 2 mg mg / kg - Single max dose = 0.4 mg - Repeat every 3 min as required - Cumulative max dose = 2 mg mg / kg - Single max dose = 0.4 mg - Repeat every 3 min as required - Cumulative max dose = 2 mg AUGMENTED DOSING - 2 mg IM / IN / IO / IV - Repeat as necessary - No cumulative max dose - 2 mg IM / IN / IO / IV - Repeat as necessary - No cumulative max dose -0.5 mg/kg IM / IN / IO / IV - Single max dose = 2 mg - Repeat as necessary - No cumulative max dose -0.5 mg/kg IM / IN / IO / IV - Single max dose = 2 mg - Repeat as necessary - No cumulative max dose Known or suspected opioid overdose causing respiratory depression Unknown overdose Promptly ensuring an open airway and adequate ventilation takes priority over naloxone administration in ALL cases. For known or suspected overdose with high potency opioids (fentanyl, sufentanil, carfentanil) use the augmented dose schedule. M11 Naloxone Page 1
30 M12 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Oxygen Primary Administer oxygen with appropriate device at fixed flow rate as specified in care map Providers with appropriate delegation may administer oxygen at sufficient flow rate & with appropriate device to achieve target saturation (commonly 92 to 94%) Dyspnea Respiratory distress Known or suspected hypoxemic respiratory failure (SaO2 < 90%) Known or suspected carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning None With severe respiratory distress or known / suspected respiratory failure, initiate treatment with O2 at 15 lpm flow rate by NRB mask or BVM apparatus. Providers with appropriate delegation may consider oxygen titration once the patient s condition has stabilized. For management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with known or suspected hypoxemic respiratory drive consider target saturation of 88 90%. If CO poisoning is known or suspected, administer O2 at 15 lpm flow rate by NRB mask or BVM apparatus. M16 Oxygen Page 1
31 M13 Medications Office of the Medical Director Methylprednisolone (SOLUMEDROL) ADULT (17 yr & older): ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 yr): CHILD (1 up to 10 yr): 40 mg IO / IV once only 125 mg IM once only 40 mg IO / IV once only 125 mg IM once only 2 mg / kg IO / IV once only Max dose = 40 mg Acute allergic reaction presenting with urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm or shock Exposure to allergen with history of previous anaphylaxis Known or suspected acute adrenal insufficiency None M13 Methylprednisolone Page 1
32 M14.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Amiodarone for Cardiopulmonary Arrest ADULT (17 years & older): 300 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat 150 mg once after 5 min Post arrest: 300 mg Infuse IV or IO over 30 min Hold if SBP < 100 mmhg CHILD (1 up to 10 years): 5 mg/kg (maximum = 150 mg) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 5 min up to twice as required (cumulative maximum dose = 15 mg/kg) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years): 5 mg/kg (maximum = 300 mg) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 5 min up to twice as required (cumulative maximum dose = 15 mg/kg) INFANT (0 up to 12 months): 5 mg/kg (maximum = 150 mg) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat every 5 min up to twice as required (cumulative maximum dose = 15 mg/kg) Pulseless cardiac arrest due to VT or VF Suspected or confirmed hypothermic cardiopulmonary arrest REMINDER: Drug administration should not interrupt CPR or delay defibrillation. May be given before or after shocks. Upon ROSC after VF or VT arrest (adults only) consider amiodarone by slow infusion if not yet given during arrest. If SBP decreases below 100 mmhg, omit or discontinue amiodarone administration. M14.1 Amiodarone / CPA Page 1
33 M15 Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Bronchodilators Primary Salbutamol (VENTOLIN): - 2 to 4 inhalations by inhaler, or by nebulizer - Repeat as required (no maximum) Salbutamol (VENTOLIN): - 2 to 4 inhalations by inhaler, or mg by nebulizer - Repeat as required (no maximum) Salbutamol (VENTOLIN): - 2 to 4 inhalations by inhaler, or mg by nebulizer - Repeat as required (no maximum) ADULT (17 years & older): Salbutamol & Ipratropium (COMBIVENT): - One ampule (2.5 mg salbutamol / 0.5 mg ipratropium) by nebulizer once ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) Salbutamol & Ipratropium COMBIVENT): - One ampule (2.5 mg salbutamol / 0.5 mg ipratropium) by nebulizer once CHILD (1 up to 10 years): Salbutamol & Ipratropium (COMBIVENT): - One ampule (2.5 mg salbutamol / 0.5 mg ipratropium) by nebulizer once Ipratropium (ATROVENT): - 2 inhalations by inhaler every 6 hours N/A N/A Salbutamol (VENTOLIN): mg by nebulizer - Repeat as required (no maximum) INFANT (0 up to 12 months): N/A N/A Acute excaerbation of known asthma Acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Dyspnea or respiratory distress where bronchospasm is known or suspected None If repeated administration of bronchodilators is required, use salbutamol only. Do not use Ipratropium as sole bronchodilator. For children under age 5, nebulizer administration or administration by an inhaler with an attached aerochamber will be preferable to inhaler administration. M15.1 Bronchodilators 1
34 M16 Medications Office of the Medical Director Oxytocin Primary DOSE: 10 units IM or IV after delivery of baby 10 units / hr IV by continuous infusion Greater than 20 weeks gestational age Patients experiencing significant blood loss after delivery Estimated blood loss greater than 500 ml SBP less than 100 mmhg, or suspicion of shock Incomplete deliver of baby, or muliple gestations where all babies have not delivered If significant bleeding continues after initial dose of oxytocin, providers may consider administration of additional oxytocin by continuous infusion. Mix 40 units of oxytocin in one liter of normal saline and infuse mechanically or by gravity at 250 mls per hour (10 units per hour). M16 Oxytocin Page 1
35 M17.1A Medications years & older Office of the Medical Director Ketamine (analgesic dose) Pre-reduction analgesia for extrication, and o shock is known or suspected, or o BP reading cannot be obtained Severe hypertension (BP greater than 185/110 mmhg) Severe tachycardia (HR greater than 120 bpm) Decreased LOC Acute delirium Intoxication with alcohol or drugs, or chronic alcoholism Acute eye injury or glaucoma Pregnancy Emergency reactions are more common in elderly patients (use with caution) DOSAGE: 0.2 mg/kg by slow IV push Single max dose = 20 mg ABBREVIATIONS: BP = blood pressure IO = intraosseous IV intravenous mg = milligrams mg/kg = milligrams per kilogram M17.1A Ketamine Page 1
36 M21A Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Primary years and older Nitroglycerin SUBLINGUAL DOSE: 0.4 mg sublingual Repeat every 5 minutes as required TOPICAL DOSE (Primary Care level & above): SBP > 100 mmhg 0.2 mg / hr SBP > 150 mmhg 0.4 mg / hr SBP > 200 mmhg 0.6 mg/hr INTRAVENOUS DOSE ( Care level only): Initiate infusion at 10 mcg / min Check the BP every 5 minutes; titrate up by 10 mcg every 5 minutes Maximum anianigianl dose is approximately 100 mcg / min Maximum antihypertensive dose is approximately 200 mcg / min Chest, back or upper abdominal pain, or dyspnea, known or suspected to be due to myocardial ischemia Known or suspected heart failure Severe hypertension with evidence of end-organ dysfunction or injury Systolic blood pressure < 100 mmhg Recent use of erectile dysfunction medication VIAGRA (sildefanil) within 24 hours CIALIS (tadalafil) within 72 hours LEVITRA (vardenafil) within 24 hours Known or suspected right ventricular infarct (relative) Providers with appropriate delegation should review ECG for evidence of right ventricular infarction prior to administering nitroglycerin. Providers without ECG interpretation delegation may administer nitroglycerin without ECG review. Providers with appropriate delegation may use IV nitroglycerin as per E21A Hypertensive Emergencies. M21A Nitroglycerin Page 1
37 M24.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Magnesium Sulfate 1 year & older for Cardiopulmonary Arrest ADULT (17 years & older): ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years): CHILD (1 up to 10 years): 2 gm IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat once as required 50 mg/kg (maximum = 2 gm) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat once as required 50 mg/kg (maximum = 1 gm) IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat once as required Pulseless cardiac arrest known or suspected to be due to polymorphic VT (torsades de pointes) Asystole REMINDER: Drug administration should not interrupt CPR or delay defibrillation. Magnesium sulfate may be given before or after shocks. M24.1 Magnesium Sulfate / CPA Page 1
38 M24.2 Medications Office of the Medical Director Magnesium Sulfate for 10 years & older Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) INTRAMUSCULAR INTRAVASCULAR 4 grams 2 grams (4 ml) once to each buttock (deep IM) 2 grams IV or IO Infuse over ten minutes Repeat once as required Symptoms and / or signs of preeclampsia in a woman at greater than 20 weeks estimated gestational age (EGA) Seizure in a woman at great than 20 weeks EGA until 6 wk post-partum Respiratory depression Do not administer IV or IO magnesium sulfate if IM dose has already been given. M24.2 Magnesium Sulfate / PIH Page 1
39 M28A Medications years & older Office of the Medical Director Tranexamic Acid (TXA) 1 gram IV or IO once only Exsanguinating external hemorrhage within 3 hours of injury Known hypersensitivity to TXA If exsanguinating external hemorrhage cannot otherwise be controlled by direct pressure or tourniquet application, providers may consider administration of tranexamic acid (TXA). With limited resources, do not interrupt direct pressure to obtain vascular access. Arterial or venous thrombosis is a recognized potential complication of TXA but is not a contraindication in the face of exsanguinating hemorrhage M28A TXA Page 1
40 M29 Medications Office of the Medical Director Intravenous Fluid (IVF) Primary ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) INFANT (0 up to 12 months) Normal saline Ringer s lactate Normal saline Ringer s lactate Normal saline Normal saline BOLUS THERAPY FOR NON-TRAUMATIC HYPOTENSION / SHOCK: 20 ml/kg Max = 1000 ml per bolus Repeat as required 20 ml/kg Max = 1000 ml per bolus Repeat as required 20 ml/kg Max = 500 ml per bolus Repeat as required 20 ml/kg Max = 250 ml per bolus Repeat as required BOLUS THERAPY FOR TRAUMATIC HEMORRHAGE / SHOCK & EXSANGUINATION: 20 ml/kg Max = 1000 ml per bolus Repeat as required 20 ml/kg Max = 1000 ml per bolus Repeat as required 20 ml/kg Max = 500 ml per bolus Repeat as required MAINTENANCE THERAPY: 50 ml/hr 50 ml/hr 0.5 ml / kg / hr 0.5 ml / kg / hr Non-traumatic hypotension and/or shock Traumatic hemorrhage and/or exsanguination Maintenance therapy Medication administration To maintain venous access (TKVO) None Consider smaller boluses (5 10 ml/kg) if age greater than 75 years or cardiac dysfunction is known / suspected Permissive hypotension is indicated only in the absence of head injury (see F02 TRAUMATIC HEMORRHAGE & SHOCK) NORMAL SALINE (NS): 0.9% sodium chloride 154 meq sodium per liter 154 meq chloride per liter Osmolarity = 308 mosm per liter RINGER S LACTATE (RL): 130 meq sodium per liter 110 meq chloride per liter 4 meq potassium per liter 2.5 meq calcium per liter Osmolarity = 273 mosm per liter M29 IVF Page 1
41 M30 Medications Office of the Medical Director Tetracaine (PONTOCAINE) Primary Thermal or chemical eye injury Corneal abrasion or foreign bodies Known or suspected open globe injury True allergy to benzocaine or procaine TETRACAINE 0.5%: Instill 1 to 3 drops to affected eye Repeat every ten minutes as required For patients with significant pain from any of the above injuries, consider also oral analgesic administration M30 Tetracaine Page 1
42 M33 Medications Office of the Medical Director Diphenhydramine (BENADRYL) Primary ADULT (17 years & older) ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years) CHILD (1 up to 10 years) - 50 mg PO once only - 25 to 50 mg PO once only to 25 mg PO once only - 25 to 50 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 15 min as required - Total max = 100 mg / 4 hr - 25 mg IM / IO / IV - Repeat every 15 min as required - Total max = 100 mg / 4 hr mg/kg IM / IO / IV - Single max dose = 25 mg - Repeat every 15 min as required - Total max = 50 mg / 4 hr Acute allergic reaction presenting with urticaria and / or angioedema, shock (epinephrine & dimenhydramine) or bronchospasm (all) Exposure to allergen with history of previous anaphylaxis Altered LOC Use of other CNS depressants True allergy to diphenhydramine Diphenhydramine can be used alone only when acute allergic reaction presents with itching or hives only. Acute allergic reactions with angioedema, shock or bronchospasm will require additional treatment with epinephrine and/or salbutamol. True allergy to antihistamines is exceedingly rare and is more likely an allergy to additive or preservative in oral preparations. Lower doses should be considered in patients > 75 years of age. M33 Diphenhydramine 1
43 M34 Medications years and older Office of the Medical Director Haloperidol (HALDOL) Age less than 75 years: 5 to 10 mg IM / IO / IV once Repeat once in 15 minutes as required Age greater than 75 years: 5 mg IM / IV / IO Repeat once in 15 minutes as required Acute agitation or combative behavior where the safety of the patient, health care providers and the public at large is or may be at risk Temperature > 38 degrees Celsius SBP < 100 mmhg Known or suspected prolonged QT syndrome Personal or family history of prior cardiac arrest or sudden death (relative) Known or suspected hypersensitivity to haloperidol or neuroleptics Active seizures or suspected or known post-ictal delirium Always treat correctable underlying causes of agitation or combative behavior, such as hypoglycemia or hypoxemia, before administering haloperidol. Attempt to achieve desired level of sedation / control with benzodiazepines alone, before haloperidol administration. Administration requires continuous monitoring of respiratory and cardiac functions. M34 Haloperidol Page 1
44 M37.1A Medications Office of the Medical Director Basic Antiplatelet: 17 years of age & older Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA) Primary DOSE: 160 mg PO (chew & swallow) Known or suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS) Active bleeding that cannot be controlled by basic measures (pressure, wound care) Known ASA allergy Known or suspected ASA-induced asthma (rare) Administer the above dose even if the patient is on a regular daily dose of ASA or has already taken ASA as advised by Emergency Medical dispatch EMS personnel will administer two chewable infant tablets (advise the patient to chew and swallow). If infant tablets are not available, one adult tablet (325 mg) may be administered (advise the patient to chew and swallow) Adverse effects to ASA such as stomach upset or easy bruising are not true allergic symptoms and are not contraindications to administration with potential ACS Administer ASA even if the patient is on anticoagulants or other antiplatelet agents M37.1A ASA Page 1
45 M37.2A Medications Office of the Medical Director Antiplatelet: 17 years of age & older Ticagrelor (Brillanta) Primary DOSE: 180 mg PO (2 x 90 mg) Known or suspected ST elevation myocardial infarction where primary percutaneous coronary angioplasty (PC is anticipated Active bleeding that cannot be controlled by basic measures (pressure, wound care) Known allergy to ticagrelor (rare) Ticagrelor administration requires consultation with on-line medical support or receiving cardiologist prior to administration. Administer the above dose even if the patient is on a regular daily dose of ASA or has already taken ASA as advised by Emergency Medical dispatch M37.2A Ticagrelor Page 1
46 M38 Medications year and older Office of the Medical Director Ketoroloac (TORADOL) Adult (17 years & older) Adolescent (10 up to years) Child (1 up to 10 years) 30 mg IM / IV once only 15 to 30 mg IM / IV once only 0.5 mg / kg IM / IV once only (single maximum dose = 15 mg) Analgesia for moderate to severe pain where opioid analgesics cannot be given or opioid dose has been maximized True allergy to ketorolac History of aspirin (ASA) induced asthma Known or presumed renal failure Providers may consider giving ketorolac prior to or instead of opioid analgesics in patients with pain from known or presumed kidney stones. M38 Toradol Page 1
47 M39.1 Medications Office of the Medical Director Atropine for Unstable Bradycardia ADULT (17 years & older): 0.5 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush May repeat to a cumulative dose of 3 mg ADOLESCENT (10 up to 17 years): 0.5 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush May cumulative to a total dose of 3 mg CHILD (1 up to 10 years): 0.02 mg / kg Minimum single dose = 0.1 mg Maximum single dose = 0.5 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat once as required to achieve a HR between 60 and 70 bpm INFANT (0 up to 12 months): 0.02 mg / kg Minimum single dose = 0.1 mg Maximum single dose = 0.5 mg IV or IO push, follow by 0.9% saline flush Repeat once as required to achieve a HR between 60 and 70 bpm Significant bradycardia known or suspected to be causing hypotension or poor perfusion None M39.1 Atropine / Bradycardia Page 1
48 M43.1A Medications years and older Office of the Medical director Enoxaparin (LOVENOX) Age less than 75 years: 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once only Age greater than 75 years: 0.75 mg/kg subcutaneously once only Known or suspected ST elevation myocardial infarction where primary percutaneous coronary angioplasty (PC is anticipated Active bleeding that cannot be controlled by basic measures (pressure, wound care) Patient is known or suspected to currently be on an anticoagulant Known allergy to enoxaparin (rare) Enoxaparin administration requires consultation with on-line medical support or receiving cardiologist prior to administration. M43.1A Enoxaparin Page 1
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV OBHG Education Subcommittee
 Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Z19.2 Cross Reference to Patient Care Maps & Clinical Care Procedures
 2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
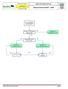 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
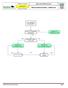 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS
 MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS
 THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Drug Profiles Professional Responder
 Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS
 EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
Title: Management of Allergic Reactions after IV Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ABSTRACT FOR SPS POSTER CASE PRESENTATION K Singer Title: Management of Allergic Reactions after IV Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction: Children undergoing radiologic imaging frequently
ABSTRACT FOR SPS POSTER CASE PRESENTATION K Singer Title: Management of Allergic Reactions after IV Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction: Children undergoing radiologic imaging frequently
Resuscitation Fluids
 Resuscitation Fluids Acceptable Fluids (also known as): Sodium Chloride Hartmann s Solution (Ringer-Lactate Solution, Compound Sodium Lactate) 4.5% Albumin Solution (PPS) Gelofusine 20ml/kg Bolus Can be
Resuscitation Fluids Acceptable Fluids (also known as): Sodium Chloride Hartmann s Solution (Ringer-Lactate Solution, Compound Sodium Lactate) 4.5% Albumin Solution (PPS) Gelofusine 20ml/kg Bolus Can be
Appendix A: Pharmacologic approaches to pain management during MVA
 Pain medication Though the medications shown below are commonly used for pain management during uterine evacuation, many other options exist. This table does not cover general anesthetic agents. Both anxiolytics
Pain medication Though the medications shown below are commonly used for pain management during uterine evacuation, many other options exist. This table does not cover general anesthetic agents. Both anxiolytics
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice
 Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Emergency Department Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set
 Form Title Form Number Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set 20746 2018, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0
Form Title Form Number Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set 20746 2018, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0
SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013
 8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
Pharmacology Drug Dosage Calculations
 Pharmacology Drug Dosage Calculations Overview Abbreviations Metric Conversions Desired Dose Concentrations Drip Rates Medications (Dopamine and Lidocaine) Abbreviations cc- cubic centimeter DD- Desired
Pharmacology Drug Dosage Calculations Overview Abbreviations Metric Conversions Desired Dose Concentrations Drip Rates Medications (Dopamine and Lidocaine) Abbreviations cc- cubic centimeter DD- Desired
North Carolina College of Emergency Physicians Standards for EMS Medications and Skills Use
 . The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
. The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
Management Of Medical Emergencies. Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS
 Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION
 POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION Name: Date: Instructions: Complete the Post-Test (an 85% is required to pass). If there are areas that you are unsure of, please review the relevant portions of the learning
POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION Name: Date: Instructions: Complete the Post-Test (an 85% is required to pass). If there are areas that you are unsure of, please review the relevant portions of the learning
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
Intermediate Medications. Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol
 Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Conscious Sedation Permit Evaluation. General Comments Emergency Algorithms
 General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
PM-03 PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS. Protocol SECTION: PM-03 PROTOCOL TITLE: PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS REVISED: 01MAY2018
 SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Table 3: Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults Last updated: July 2017
 Table 3: Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults Last updated: July 2017 HIVES (Urticaria) Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider:
Table 3: Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults Last updated: July 2017 HIVES (Urticaria) Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider:
PBCFR ALS/BLS Protocols 2009 ALS Pretest
 1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Naloxone Intranasal EMT OPTIONAL SKILL. Cell Phones and Pagers. Course Outline 09/2017
 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
** Note: second generation antihistamines cause less drowsiness; may be beneficial in patients that need to drive themselves home.
 Table 5 : Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults HIVES Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl )*
Table 5 : Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults HIVES Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl )*
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies):
 Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off.
 1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table
 2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS. S.I. No. 300 of 2014 MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (PRESCRIPTION AND CONTROL OF SUPPLY) (AMENDMENT) REGULATIONS 2014
 STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS. S.I. No. 300 of 2014 MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (PRESCRIPTION AND CONTROL OF SUPPLY) (AMENDMENT) REGULATIONS 2014 2 [300] S.I. No. 300 of 2014 MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (PRESCRIPTION AND CONTROL
STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS. S.I. No. 300 of 2014 MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (PRESCRIPTION AND CONTROL OF SUPPLY) (AMENDMENT) REGULATIONS 2014 2 [300] S.I. No. 300 of 2014 MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (PRESCRIPTION AND CONTROL
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
Addendum D. Procedural Sedation Test MERCY MEDICAL CENTER- SIOUX CITY. Procedural Sedation Questions
 Addendum D. Procedural Sedation Test MERCY MEDICAL CENTER- SIOUX CITY Procedural Sedation Questions Individuals applying for moderate sedation privileges must achieve a score of 80%. PRACTITIONER NAME
Addendum D. Procedural Sedation Test MERCY MEDICAL CENTER- SIOUX CITY Procedural Sedation Questions Individuals applying for moderate sedation privileges must achieve a score of 80%. PRACTITIONER NAME
ADENOSINE (Adenocard) VO = Intermediate Paramedic. ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT, EMT-IV, Intermediate Paramedic
 ADENOSINE (Adenocard) ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT,, AMIODARONE (Cordarone) -except in cardiac arrest ASPIRIN EMT, ATROPINE SULFATE -except in cardiac arrest 1 ST dose 6 mg IVP, 2 ND dose 12 mg IVP, 3 rd
ADENOSINE (Adenocard) ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT,, AMIODARONE (Cordarone) -except in cardiac arrest ASPIRIN EMT, ATROPINE SULFATE -except in cardiac arrest 1 ST dose 6 mg IVP, 2 ND dose 12 mg IVP, 3 rd
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
OSF NORTHERN REGION EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS ILS, ALS. SMO: Adult Pain Management
 OSF NORTHERN REGION EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS ILS, ALS SMO: Adult Pain Management Overview: Objective: Provide a reasonable relief of severe pain to make packaging and transport
OSF NORTHERN REGION EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS ILS, ALS SMO: Adult Pain Management Overview: Objective: Provide a reasonable relief of severe pain to make packaging and transport
The dose for paediatric patients may never exceed the adult dose.
 The medication formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice
The medication formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice
PAIN PODCAST SHOW NOTES:
 PAIN PODCAST SHOW NOTES: Dallas Holladay, DO Ultrasound Fellow Cook County Hospital Rush University Medical Center Jonathan D. Alterie, DO PGY-2, Emergency Medicine Midwestern University An overview of
PAIN PODCAST SHOW NOTES: Dallas Holladay, DO Ultrasound Fellow Cook County Hospital Rush University Medical Center Jonathan D. Alterie, DO PGY-2, Emergency Medicine Midwestern University An overview of
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information
 Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols
 Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016
 HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
2019 Protocol Roll - OUT
 2019 Protocol Roll - OUT Objectives Discuss participation in the Regional EMS Protocol Outline changes, and discuss how UH will implement Review changes from last year that carry over into this protocol
2019 Protocol Roll - OUT Objectives Discuss participation in the Regional EMS Protocol Outline changes, and discuss how UH will implement Review changes from last year that carry over into this protocol
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL
 PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
Administration and Supply of Emergency Medicines
 APPENDIX WHO CAN GIVE WHAT? Administration and Supply of Emergency Clinician Authorisation Key to Exemptions from legislation: NPP Non Parenteral POM. Can be given according to a protocol. 7 HMR 0, Schedule
APPENDIX WHO CAN GIVE WHAT? Administration and Supply of Emergency Clinician Authorisation Key to Exemptions from legislation: NPP Non Parenteral POM. Can be given according to a protocol. 7 HMR 0, Schedule
AT TRIAGE. Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway: Evidence based* recommendations For Emergency / Urgent Care
 1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
ILS Protocols Content Page
 Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Emergency Medical Services. Pharmacology Reference Guide
 The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas BioTel EMS System Emergency Medical Services Pharmacology Reference Guide January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2008 (subject to revision prior
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas BioTel EMS System Emergency Medical Services Pharmacology Reference Guide January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2008 (subject to revision prior
APPENDIX 1 - MEDICATION FORMULARY
 The medication formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to enable pre-hospital emergency care Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical
The medication formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to enable pre-hospital emergency care Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical
Clinical Practice Guidelines Edition (Updated February 2018)
 The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
Adrenaline 1mg in 10mL (1:10,000) Pre-filled syringe 3 Amiodarone 300mg/10mL Pre-filled syringe 5
 Quick Reference Guide for: Cardiac Arrest Medicines Box (BLUE) Please Note: Any medicines given must form part of an Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability and Exposure (ABCDE) Assessment (9)999 must
Quick Reference Guide for: Cardiac Arrest Medicines Box (BLUE) Please Note: Any medicines given must form part of an Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability and Exposure (ABCDE) Assessment (9)999 must
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013
 NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
Clinical Procedures and Guidelines
 Clinical Procedures and Guidelines Pocket Edition 2013-2015 2 foreword These are the Clinical Procedures and Guidelines (CPGs) for the New Zealand ambulance sector. This is the pocket edition of the Clinical
Clinical Procedures and Guidelines Pocket Edition 2013-2015 2 foreword These are the Clinical Procedures and Guidelines (CPGs) for the New Zealand ambulance sector. This is the pocket edition of the Clinical
disease or in clients who consume alcohol on a regular basis. bilirubin
 NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
ALBUTEROL. Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells
 ALBUTEROL Bronchodilator (Beta-2 specific) Actions: Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells Respiratory distress with wheezes/bronchospasm
ALBUTEROL Bronchodilator (Beta-2 specific) Actions: Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells Respiratory distress with wheezes/bronchospasm
