하부위장관비종양성질환의 감별진단 주미인제의대일산백병원
|
|
|
- Samuel Powers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 하부위장관비종양성질환의 감별진단 주미인제의대일산백병원
2 Solutions for diagnostic problems in Colitis : Please ask yourself five questions Normal or Inflamed? Acute or Chronic? IBD or Other chronic colitis? Ulcerative colitis or Crohn s disease? Another form of inflammation? Guidelines for the initial biopsy diagnosis of suspected chronic idiopathic IBD J Clin Pathol. 1997;50(2):
3 Ulcerative colitis Colon Bx Inflammation Chronic (idiopathic) IBD Acute (infective) Crohn s disease Indeterminate colitis Acute self-limited colitis Pseudomembranous colitis Enterohemorrhagic E.coli Ischemic colitis Normal Specific (Unclassified) Collagenous colitis Lymphocytic colitis Eosinophilic colitis Others Focal active colitis Drug-induced colitis Guidelines for the initial biopsy diagnosis of suspected chronic idiopathic IBD J Clin Pathol. 1997;50(2):
4 Normal versus Abnormal It is important to understand normal variations and preparation effects
5 Normal colonic mucosa Architecture of crypts - Rack of Test Tube or Daisy flower - Mild architectural distortion Epithelial cells - Colonocytes : Goblet cell = 5:1 (Rt), 3:1 (Lt) - Paneth cells: Normal in Rt colon Paneth cell metaplasia in Lt colon Lamina propria inflammatory cells - Normal: 30%~50% of free lamina propria - Normal gradient
6 Normal colonic mucosa Architecture (Surface), Lamina propria
7 Histology for Pathologists, 3rd Edition Mills, Stacey E.
8 Preparation effects or Artifact Focal active colitis Surface neutrophilic infiltration Stromal edema & Fresh hemorrhages Pseudolipomatosis (Gas effect, No fat)
9 병리진단에 Normal 이라고써도될까? Some pathologists may argue that such comments is unnecessary, even insulting, to clinician. Biopsy Pathology in Colorectal disease 2 nd Ed. Pathologists should not be afraid to render a diagnosis of normal colon. Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas 3 rd Ed. Colonic mucosa with no significant pathologic changes
10 Significance of the normal biopsy Stating This is a normal biopsy help to Highlight other more important diagnoses Make a differential diagnosis : UC vs CD (skip lesion) Determine the extent of disease : Left sided UC with cecal patchy Evaluate treatment effects (Normalization) : Rectal sparing of UC
11 Abnormal.. So, what s the diagnosis?
12 Q: What is it? A: It s a kind of Q: IBD? A: Moderate chronic active colitis Q: What disease, specifically? A: Pattern of injury, at best
13 Pattern of injury 에의한진단은어떻게? Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract & Pancreas 3 rd Ed. Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Preserved Architecture Abnormal Architecture Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
14 Look for a pattern of injury One of the biggest challenges in mucosal biopsy pathology is to recognize a specific morphologic pattern of injury, which is often best performed at low magnification. Archtecture & Lamina propria
15 Guidelines for biopsy diagnosis of chronic colitis (IBD) (J Clin Pathol 1997;50:93 105)
16 필수요건, 적어도둘중하나는있어야.. Activity 와관련.. 필수적이지않음 있으면도움이되는소견..
17 Active (Acute) Colitis Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Neutrophils only Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Abnormal Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture Architecture: Abnormal Lamina propria: Abnormal Chronic Injury Pattern Architecture: Abnormal Lamina propria: nearly Normal
18 Active (Acute) Colitis
19 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Acitve colitis only + ischemia/ hemorrhage Preserved Architecture Abnormal Architecture Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
20 Acute (Active) Colitis only Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Normal Neutrophilic infiltration: Superficial-predominant pattern Epitheliotropic (Cryptitis, Crypt abscess) Most often caused by infections >>> drugs or IBD Acute self-limited colitis: Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter & Yersinia
21 Useful information Acute (Active) colitis (1) Drug-associated Colitis: NSAID : Can mimic almost any type or pattern of colitis, including infectious colitis, IBD, ischemic colitis, microscopic colitis, and even eosinophilic colitis. Older individuals, Stool culture (-) History of NSAID consumption for a period of at least 1 months before illness (or 1 to 2 weeks after high dose NSAID) Erythema, friability, erosions or ulcer (Right > Left) Bleeding, diarrhea, IDA or rarely perforation Microscopic findings Typical features of active colitis ± mild cryptal apoptosis, some eosinophilic infiltration, mild intraepithelial lymphocytosis
22 Acute (Active) colitis (2) Rarely IBD, mild form or early phase of disease Endoscopic impression: R/O IBD, R/O UC Microscopic findings: Active colitis without well established features of chronicity Diagnosis: Colon, endoscopic biopsy: - Active colitis - No features of chronicity is seen (see Note) Note: Definite features of chronicity are not identified. However, an early phase of IBD cannot be excluded. Clinical correlation and follow-up are needed.
23 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Acitve colitis only + ischemia/ hemorrhage Ischemic Radiation Preserved Architecture Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections Abnormal Architecture DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
24 Acute Ischemic/Hemorrhagic Colitis Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Normal Neutrophilic infiltration: Usually not prominent, Pseudomembrane Fibrohyalinized lamina propria, withering crypts, hemorrhages, regenerating epithelial changes, with or without intravascular thrombi Most often caused by ischemia, infections (E.coli O157:H7 and Clostridium difficile), radiation injury, and drug reactions. From Diagnostic Pathology Gastrointestinal, Amirsys
25 From Diagnostic Pathology Gastrointestinal ( Histologically indistinguishable colitis: Enterohemorrhagic E. coli colitis versus Acute ischemic colitis DDx points - Patient age, anatomic distribution, Clinical history
26 Differential Diagnosis of Active (Acute) ischemic/hemorrhagic colitis Feature Ischemia Infection (E. coli) Radiation Anatomic distribution Watershed Right > Left Left > Right Edema/hemorrhage Withered crypts ++ ± ± Fibrin thrombi ± + ± Neutrophils ± ++ ± Atypical cells ± Dilated blood vessels ± ++ LP hyalinization ++ ± ±
27 Chronic colitis
28 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Preserved Architecture Abnormal Architecture Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
29 Chronic colitis with preserved architecture Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Abnormal (basal plasmacytosis, lymphoid aggregates) Neutrophilic infiltration: Diffuse pattern Predominantly Neutrophilic Predominantly Lymphoplasmacytic Infectious colitis (Delayed resolution) Early phase IBD (NSAIDs) Microscopic colitis Resolving IBD Diverticulosis Some infections (Shigella)
30 Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture Predominantly neutrophilic Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Increased cellularity, Mild basal plasmacytosis Neutrophilic infiltration: Prominent, Diffuse pattern Differential diagnoses include delayed resolution of infectious colitis >> early phase of IBD or drug reactions ( 감별어려움 ) Colon, endoscopic biopsy: - Colonic mucosa with diffuse neutrophilic infiltration & mild basal lymphoplasmacytosis, but no architectural abnormality (see Note) Note: Differential diagnoses include delayed resolution of infectious colitis, early phase IBD & drug-induced colitis. Clinical correlation & F/U are needed.
31 Chronic colitis with preserved architecture Predominantly lymphoplasmacytic Architecture: Normal Lamina propria: Abnormal, dense lymphoplsamacytic infiltration basal plasmacytosis, basal lymphoid aggregates Neutrophilic infiltration: Not prominent - Microscopic colitis? Lymphocytic colitis, Collagenous colitis - Others? Resolving IBD, Diverticulitis, Drugs, Infections.. The major difficulties in this category of inflammatory disorders involves differentiating microscopic colitis from IBD.
32 Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture predominantly lymphoplasmacytic (1) Lymphocytic colitis Chronic watery, nonbloody diarrhea Normal endoscopy (sometimes minor changes, rarely ulceration) Intraepithelial lymphocytosis ( 20/100 epithelial cells) Surface epithelial injury (flattening, regeneration, mucin depletion) + Increased cellularity (lymphoplasmacytosis) in lamina propria
33 Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture predominantly lymphoplasmacytic (2) Collagenous colitis Chronic watery, nonbloody diarrhea Normal endoscopy (sometimes minor changes, rarely ulceration) Immunologic response to intraluminal dietary or bacterial elements Presence of irregular thickened subepithelial collagen layer (Type IV collagen, >10 μm, usually 20 to 60 μm) Entrapment of inflammatory cells and vessels + Increased cellularity (lymphoplasmacytosis) in lamina propria
34 The IBD-like features are seen in 30% of collagenous colitis, usually focal & mild. Typical histologic features are readily seen in the majority of the serial biopsies. Focal IBD-like changes should not alter the diagnosis if all other features are C/W collagenous colitis.
35 Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture predominantly lymphoplasmacytic (3) Longstanding infectious colitis - 40-year-old man - Abdominal pain & diarrhea lasting > 1 year - No response to UC medication Dx: Amebic colitis mistaken for UC 소화기병리연구회삼성서울병원제출 case
36 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Architecture preserved Abnormal Architecture Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
37 Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture Architecture: Abnormal Lamina propria: Abnormal + Neutrophils: Chronic active colitis (mild, moderate, severe) With lamina propria fibrosis or hyaline-like material Without lamina propria fibrosis or hyaline-like material Chronic ischemia Chronic radiation colitis Mucosal prolapse Posttreatment IBD Inflammatory bowel disease Diverticular diseaseassociated colitis (DDAC)
38 Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture With lamina propria fibrosis or hyaline-like material Architecture: Abnormal (loss or atrophy of crypt) Lamina propria: Abnormal Neutrophlic infiltration: Not prominent Vascular ectasia, thrombi formation
39 Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture with Lamina Propria Fibrosis or Hyaline-like Material (1) Chronic radiation colitis History of Radiation Frequent rectal involvement Predominantly hyalinization & fibrosis Vascular ectasia with hyalinization Atypical stromal cells From Diagnostic Pathology Gastrointestinal, Amirsys
40 Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture with Lamina Propria Fibrosis or Hyaline-like Material (2) Rectal mucosal prolapse (solitary rectal ulcer syndrome) Rectal Mucosal prolapse with or without ulcer Common in younger adults or older than 60 yo Chronic constipation & strenuous defecation Hyalinization in LP & Fibromuscular hyperplasia Crypt elongation with Glandular hyperplasia
41 Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Crypt Architecture and Lamina Propria Fibrosis or Hyaline-like Material Feature Radiation Prolapse Chronic Ischemia Polyp/mass formation Rare + Rare Primarily rectal involvement Rare IBD-like mucosal inflammation ± ++ Withering crypts ± ± ± Pseudomembrane ± Hyalinization Fibromuscular hyperplasia ++ ± Vascular dilatation/proliferation ++ ± Atypical stromal/epithelial cells ++ Hyperplastic changes ++ Thrombi ± ± ++
42 Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture Without lamina propria fibrosis or hyaline-like material Architecture: Abnormal Lamina propria: Abnormal (basal plasmacytosis, lymphoid aggregates) + Neutrophils: Chronic active colitis (mild, moderate, severe) Inflammatory bowel disease Diverticular disease-associated colitis Generally, two diseases are histologically indistinguishable. - DDx points: Presence of diverticulosis, Involvement of rectum
43 Inflammatory Bowel Disease
44 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Preserved Architecture Abnormal Architecture Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
45 Biopsy pathology of IBD Index (First) biopsy - Early phase of IBD - Typical IBD Follow up biopsy - Resolving IBD (Healing period) - Posttreatment IBD (Resolution period) - Flare up - CMV infection UC versus Crohn s disease
46 Index (First) biopsy Early phase of IBD (DDx Acute colitis) Active(Acute) Colitis Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture Typical IBD Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture
47 Follow up biopsy Resolving IBD (Less activity and crypt injury) Chronic Colitis with Preserved Architecture predominantly lymphoplasmacytic Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture Less inflammatory activity Posttreatment IBD Chronic Inactive Colitis Abnormal Architectural only Chronic Colitis with Abnormal Architecture + Fibrosis Normal (Normalization)
48 Microscopic features of untreated UC and Crohn s disease Ulcerative Colitis Diffuse, continuous disease Rectal involvement Disease worse distally No fissures No transmural aggregates No ileal involvement (except in backwash ileitis) Upper GI tract involvement less common Crypt-rupture (mucin) granulomas Crohn's Disease Segmental disease, skip lesion Variable rectal involvement Variable disease severity Fissures, sinuses, fistulous tracts Transmural lymphoid aggregates Ileal involvement Upper GI tract involvement common Epithelioid granulomas unrelated to ruptured crypts The distinction may be impossible on biopsies & always requires clinical correlation.
49 Diffuse colitis seen in every Bx: Favor Ulcerative colitis Left-sided UC Subtotal UC Total (Pan) UC Left-sided UC with cecal patch Backwash ileitis Patchy colitis + Normal (Skip) Favor Crohn s disease Chronic ileitis: ileocolic type
50 Terminal ileal biopsy Normal Active ileitis ( Active colitis): infection, nonspecific Chronic ileitis ( Chronic colitis): Crohn s disease, Tuberculosis, rarely UC Aphthous (incidental) ulcer (Erosion with active ileitis): Drugs, CD Colonic disease Site of ileitis Length involvement Histology Pyloric metaplasia, a histologic marker of chronicity Backwash ileitis in UC Severe pancolitis, Usually cecal involvement Distal few (1 2cm) of terminal ileum Short, patchy, discontinuous Mostly active ileitis Sometimes chronic ileitis May be present Ileal involvement in CD Segmental disease, CD-like features > 3cm proximal from IC valve Long (> 5cm) Frequently chronic ileitis Sometimes granuloma Usually present
51 Colon biopsy shows CC versus UC Biopsy from ileum (> 3cm proximal from IC valve) Endoscopy: Large healing ulcer - Widening of lamina propria with villous blunting, Architectural distortion, Pyloric metaplasia (Chronic ileitis) Favor ileal involvement of CD than BWI of UC
52 Granulomas in Crohn s disease, Ulcertive colitis, and intestinal tuberculosis True granuloma Crohn s disease Crypt rupture granuloma (pseudo) Ulcerative colitis True granuloma Intestinal Tuberculosis Histologic features Crohn s disease Intestinal tuberculosis Granuloma size < 100μm > 200μm Mean No. of granulomas 1 > 5/section Shape of granuloma Small, pericryptal Confluent Other helpful findings Aphthous ulcer Focally enhanced colitis Necrosis, Lymphocytic cuffing around granuloma Ulcer lined by histiocytes Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105(3):642-51
53 Feautures of typical IBD But, No granuloma, No chronic ileitis NOTE for UC versus Crohn s colitis These findings are consistent with idiopathic IBD. Distinction between ulcerative colitis & crohn's disease cannot be made on the basis of these biopsies. Clinical correlation is advised.
54 Others Eosinophilic, Paucicellular colitis
55 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Architecture preserved Architecture NOT preserved Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis DDAC Some infections IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis GVHD Systemic dx
56 Eosinophil-Predominant Colitis Architecture: Usually normal Lamina propria: Usually normal Eosinophilic infiltration: Prominent Differential diagnoses include Allergic colitis, Eosinophilic GE Parasitic infection, and Mast cell disorder. From Diagnostic Pathology Gastrointestinal, Amirsys Eosinophilic infiltration in all compartment including muscularis mucosa Usually localized to lower third of the mucosa 6 ~ 20 Eos/HPF, up to 60/10HPFs Cryptitis, Crypt abscess (Eosinophilic microabcess), degranulation No features of chronicity
57 A 32-year-old man with abdominal pain & diarrhea Mastocytosis CD117 Lamina propria infiltration by round cells with metachromic cytoplasm & eosinophils Colonic involvement of systemic mastocytosis or Mastocytic enterocolitis Positive for CD117 & mast cell tryptase, CD25 (+) only in systemic mastocytosis
58 Inflammatory Disorders of Colon Acute Chronic Eosinophilic Paucicellular Ischemic/ hemorrhagic Non-ischemic/ Non-hemorrhagic Architecture preserved Architecture NOT preserved Ischemic Radiation Microscopic colitis Early IBD DDAC Some infections DDAC Chronic ischemia Radiation Tuberculosis Healed injury GVHD Systemic dx IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; DDAC, Diverticular disease-associated colitis Allergic Eosinophilic gastroenteritis Mastocytosis
59 Paucicellular Colitis Architecture: Variable, dilated crypt Lamina propria: Minimal infiltrates Commonly associated with increased apoptosis (Apoptotic colonopathy) Differential diagnoses include Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD), & Drug reactions (Chemotherapy, Mycophenolate mofetil). Increased epithelial apoptosis Dilated damaged crypt
60 Take home message Don't be afraid of diagnosing Normal Colon Look for a pattern of injury Identify specific features Otherwise, put a descriptive diagnosis (+ Note)
11/1/2017. Tetyana Mettler, MD Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota. Cerilli & Greenson
 Tetyana Mettler, MD Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Acute infectious (self-limited) colitis Focal active colitis Pseudomembranous colitis Ischemic colitis Collagenous
Tetyana Mettler, MD Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Acute infectious (self-limited) colitis Focal active colitis Pseudomembranous colitis Ischemic colitis Collagenous
BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF COLITIS Common and Unusual Forms of Inflammatory Bowel disease
 BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF COLITIS Common and Unusual Forms of Inflammatory Bowel disease David A Owen University of British Columbia CAUSES OF DIARRHEA DIARRHEA COLITIS PRESENT COLITIS ABSENT INFECTIOUS NON-INFECTIOUS
BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF COLITIS Common and Unusual Forms of Inflammatory Bowel disease David A Owen University of British Columbia CAUSES OF DIARRHEA DIARRHEA COLITIS PRESENT COLITIS ABSENT INFECTIOUS NON-INFECTIOUS
IBD. Crohn s. Outline. Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? UC vs. Crohn s? Is it easy? Biopsy settings 21/07/2017 IBD
 Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
GUIDELINES FOR THE INITIAL BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE A STRUCTURED APPROACH TO COLORECTAL BIOPSY ASSESSMENT
 Guidelines for the Initial Biopsy Diagnosis of Chronic Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease 1 GUIDELINES FOR THE INITIAL BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE A STRUCTURED
Guidelines for the Initial Biopsy Diagnosis of Chronic Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease 1 GUIDELINES FOR THE INITIAL BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE A STRUCTURED
Biopsy Evaluation of Non- Neoplastic Diseases of the Large Bowel: an algorithmic approach
 Biopsy Evaluation of Non- Neoplastic Diseases of the Large Bowel: an algorithmic approach Laura W. Lamps, M.D. Godfrey D. Stobbe Professor and Director of GI Pathology University of Michigan Health System
Biopsy Evaluation of Non- Neoplastic Diseases of the Large Bowel: an algorithmic approach Laura W. Lamps, M.D. Godfrey D. Stobbe Professor and Director of GI Pathology University of Michigan Health System
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Jürg Vosbeck Pathology
 Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Case History B Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment
 Case History B-1325945 Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment Case History B-1325945 Pathology Submucosa & Muscularis Endometriosis
Case History B-1325945 Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment Case History B-1325945 Pathology Submucosa & Muscularis Endometriosis
Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Robert H Riddell MD Mt Sinai Hospital Toronto Prof of Lab. Medicine and Pathobiology University of Toronto Atypical gross / endoscopic distribution
Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Robert H Riddell MD Mt Sinai Hospital Toronto Prof of Lab. Medicine and Pathobiology University of Toronto Atypical gross / endoscopic distribution
A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue
 A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue UCSF Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update Sept. 4, 2009 How to Go Wrong When Evaluating Small Bowel Biopsies, Based on
A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue UCSF Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update Sept. 4, 2009 How to Go Wrong When Evaluating Small Bowel Biopsies, Based on
What is your diagnosis? a. Lymphocytic colitis. b. Collagenous colitis. c. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) associated colitis
 Case History A 24 year old male presented with fatigue, fever, watery diarrhea, and a cough with sputum production for the past three weeks. His past medical history was significant for recurrent bouts
Case History A 24 year old male presented with fatigue, fever, watery diarrhea, and a cough with sputum production for the past three weeks. His past medical history was significant for recurrent bouts
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST QUESTIONS. Ver. #
 SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
Oncologist-induced Disease of the GI tract: New Developments
 Oncologist-induced Disease of the GI tract: New Developments Jeffrey D Goldsmith, MD Children s Hospital Boston, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Everyone s on drugs
Oncologist-induced Disease of the GI tract: New Developments Jeffrey D Goldsmith, MD Children s Hospital Boston, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Everyone s on drugs
Interpretation of inflammatory colorectal biopsies has
 The of Colitis in Endoscopic Biopsy Specimens A Review Article Lisa A. Cerilli, MD; Joel K. Greenson, MD Context. A variety of inflammatory disorders may affect the colon, with widely differing clinical
The of Colitis in Endoscopic Biopsy Specimens A Review Article Lisa A. Cerilli, MD; Joel K. Greenson, MD Context. A variety of inflammatory disorders may affect the colon, with widely differing clinical
Kids Like to Break the Rules: Gastrointestinal Pathology in Children
 Kids Like to Break the Rules: Gastrointestinal Pathology in Children Jeffrey Goldsmith MD Director of Surgical Pathology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center; Consultant in Gastrointestinal Pathology,
Kids Like to Break the Rules: Gastrointestinal Pathology in Children Jeffrey Goldsmith MD Director of Surgical Pathology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center; Consultant in Gastrointestinal Pathology,
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea?
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
The pathology of IBD and its modification by liver disease. Roger Feakins ESP/H-ECCO
 The pathology of IBD and its modification by liver disease Roger Feakins ESP/H-ECCO Enterprise Interest None IBD UC [IBDU] Crohn s IBD: distribution of disease Ulcerative colitis continuous Crohn s colitis
The pathology of IBD and its modification by liver disease Roger Feakins ESP/H-ECCO Enterprise Interest None IBD UC [IBDU] Crohn s IBD: distribution of disease Ulcerative colitis continuous Crohn s colitis
Normal small intestine Variations
 THE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM BIOPSY K. Geboes, MD, PhD, AGAF, dr. H.C. Belgium Normal small intestine Variations Duodenum Ileum 1 Proliferative compartment Normal variations 2
THE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM BIOPSY K. Geboes, MD, PhD, AGAF, dr. H.C. Belgium Normal small intestine Variations Duodenum Ileum 1 Proliferative compartment Normal variations 2
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Original Article. Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis. Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT
 Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(2):107 111 Original Article Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT Department
Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(2):107 111 Original Article Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT Department
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD
 What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
Diagnostic difficulties in inflammatory bowel disease pathology
 Histopathology 2006, 48, 116 132. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02248.x REVIEW Diagnostic difficulties in inflammatory bowel disease pathology R K Yantiss & R D Odze 1 Departments of Pathology, Weill Medical
Histopathology 2006, 48, 116 132. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02248.x REVIEW Diagnostic difficulties in inflammatory bowel disease pathology R K Yantiss & R D Odze 1 Departments of Pathology, Weill Medical
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ischemic bowel disease
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ischemic bowel disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease The two disorders that comprise IBD are: ulcerative colitis Crohn disease The distinction between ulcerative colitis and Crohn
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ischemic bowel disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease The two disorders that comprise IBD are: ulcerative colitis Crohn disease The distinction between ulcerative colitis and Crohn
IATROGENIC AND DRUG INDUCED PATHOLOGY IN THE SMALL INTESTINE. Claude Cuvelier N. Goormaghtigh Institute of Pathology
 IATROGENIC AND DRUG INDUCED PATHOLOGY IN THE SMALL INTESTINE Claude Cuvelier N. Goormaghtigh Institute of Pathology Content Iatrogenic pathology Radiation Chemotherapy Graft-Versus-Host disease Changes
IATROGENIC AND DRUG INDUCED PATHOLOGY IN THE SMALL INTESTINE Claude Cuvelier N. Goormaghtigh Institute of Pathology Content Iatrogenic pathology Radiation Chemotherapy Graft-Versus-Host disease Changes
HDF Case CRYPTOSPORIDIOSE
 HDF Case 986949 CRYPTOSPORIDIOSE 45 yo male with severe diarrhea. Known HIV positive. Endoscopic biopsy of duodenum, the colon and ileum. EXUDATIVE CHANGES GRANULAR BASOPHILIC BODIES Colonic biopsy shows
HDF Case 986949 CRYPTOSPORIDIOSE 45 yo male with severe diarrhea. Known HIV positive. Endoscopic biopsy of duodenum, the colon and ileum. EXUDATIVE CHANGES GRANULAR BASOPHILIC BODIES Colonic biopsy shows
Histological and immunological characteristics of colitis associated with anti-ctla 4 antibody therapy
 Histological and immunological characteristics of colitis associated with anti-ctla 4 antibody therapy M. Perdiki 2, G. Bamias 1, D. Pouloudi 2, H. Gogas 3, I. Delladetsima 2 1 Academic Dpt. of Gastroenterology,
Histological and immunological characteristics of colitis associated with anti-ctla 4 antibody therapy M. Perdiki 2, G. Bamias 1, D. Pouloudi 2, H. Gogas 3, I. Delladetsima 2 1 Academic Dpt. of Gastroenterology,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
Chapter 8 Ischemic Colitis
 Chapter 8 Ischemic Colitis Peter Van Eyken, Daniela Fanni, and Clara Gerosa Abstract The large bowel accounts for roughly half of all episodes of gastrointestinal ischemia. Three major manifestations of
Chapter 8 Ischemic Colitis Peter Van Eyken, Daniela Fanni, and Clara Gerosa Abstract The large bowel accounts for roughly half of all episodes of gastrointestinal ischemia. Three major manifestations of
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects
 Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects Patient Group Macroscopic examination Ileum Histology Colon/rectum Histology 1 INR Normal Acute and chronic
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Endoscopic and histolological findings in INR and FR study subjects Patient Group Macroscopic examination Ileum Histology Colon/rectum Histology 1 INR Normal Acute and chronic
12/7/2011. Patterns of mucosal damage=dx. Non IBD-Colitis: How to communicate with the clinicians. Chronic colitis
 Non IBD-Colitis: How to communicate with the clinicians Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Vice Chairman Department of Pathology Director, Gastrointesinal Pathology Service Massachusetts General Hospital Professor
Non IBD-Colitis: How to communicate with the clinicians Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Vice Chairman Department of Pathology Director, Gastrointesinal Pathology Service Massachusetts General Hospital Professor
INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014
 INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014 Endoscopic biopsy samples of naïve colitides patients: Role of basal
INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014 Endoscopic biopsy samples of naïve colitides patients: Role of basal
The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series
 OPEN ACCESS CASE REPORT The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series Maria Lourdes Tilbe, Francia Victoria De Los
OPEN ACCESS CASE REPORT The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series Maria Lourdes Tilbe, Francia Victoria De Los
T he distinction between ulcerative colitis
 1233 REVIEW Indeterminate colitis M Guindi, R H Riddell... Indeterminate colitis (IC) originally referred to those 10 15% of cases of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in which there was difficulty distinguishing
1233 REVIEW Indeterminate colitis M Guindi, R H Riddell... Indeterminate colitis (IC) originally referred to those 10 15% of cases of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in which there was difficulty distinguishing
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening. Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University.
 CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening By Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University. The CT findings of bowel wall thickening includes 1 Degree of thickening.
CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening By Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University. The CT findings of bowel wall thickening includes 1 Degree of thickening.
... Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment.
 Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Patterns of Colonic Involvement at Initial Presentation in Ulcerative Colitis A Retrospective Study of 46 Newly Diagnosed Cases
 Anatomic Pathology / PATTERNS OF INVOLVEMENT IN ULCERATIVE COLITIS Patterns of Colonic Involvement at Initial Presentation in Ulcerative Colitis A Retrospective Study of 46 Newly Diagnosed Cases Marie
Anatomic Pathology / PATTERNS OF INVOLVEMENT IN ULCERATIVE COLITIS Patterns of Colonic Involvement at Initial Presentation in Ulcerative Colitis A Retrospective Study of 46 Newly Diagnosed Cases Marie
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you)
 What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you) Jonathan N. Glickman MD PhD Director, GI Pathology, Caris Diagnostics, Newton, MA Associate Professor of Pathology,
What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you) Jonathan N. Glickman MD PhD Director, GI Pathology, Caris Diagnostics, Newton, MA Associate Professor of Pathology,
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
The Spectrum of IBD. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Symptoms. Epidemiology. Tests for IBD. CD or UC? Inflamatory Bowel Disease. Fernando Vega, M.D.
 The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
Review Histological evaluation in ulcerative colitis
 Gastroenterology Report 2 (2014) 178 192, doi:10.1093/gastro/gou031 Advance access publication 18 June 2014 Review Histological evaluation in ulcerative colitis Tom C. DeRoche 1, Shu-Yuan Xiao 2 and Xiuli
Gastroenterology Report 2 (2014) 178 192, doi:10.1093/gastro/gou031 Advance access publication 18 June 2014 Review Histological evaluation in ulcerative colitis Tom C. DeRoche 1, Shu-Yuan Xiao 2 and Xiuli
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases?
 How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
CLINICAL PATHOLOGY. Diagnosis of Colitis: Making the Initial Diagnosis. Case History. Clinical Evaluation of New Onset Colitis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:295 301 CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Diagnosis of Colitis: Making the Initial Diagnosis MARIA T. ABREU* and NOAM HARPAZ*, *Division of Gastroenterology and the Inflammatory
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:295 301 CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Diagnosis of Colitis: Making the Initial Diagnosis MARIA T. ABREU* and NOAM HARPAZ*, *Division of Gastroenterology and the Inflammatory
ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article
 ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Histology of the Mucosa in Sigmoid Colon Specimens With Diverticular Disease Observations for the Interpretation of Sigmoid Colonoscopic Biopsy Specimens NEAL S. GOLDSTEIN,
ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Histology of the Mucosa in Sigmoid Colon Specimens With Diverticular Disease Observations for the Interpretation of Sigmoid Colonoscopic Biopsy Specimens NEAL S. GOLDSTEIN,
Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX
 Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX Appendix Occurrence of lesions (%) Acute appendicitis 72 Normal 16 Fibrosis 3 (Cyst-)Adenoma 3 Diverticulitis
Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX Appendix Occurrence of lesions (%) Acute appendicitis 72 Normal 16 Fibrosis 3 (Cyst-)Adenoma 3 Diverticulitis
TRICHURIASIS : LOCALIZED INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES IN THE COLON
 TRICHURIASIS : LOCALIZED INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES IN THE COLON Gurjeet Kaur 1, S Mahendra Raj 2 and Nyi Nyi Naing 3 Departments of 1 Pathology and 2 Medicine and the 3 Epidemiology and Medical Statistics
TRICHURIASIS : LOCALIZED INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES IN THE COLON Gurjeet Kaur 1, S Mahendra Raj 2 and Nyi Nyi Naing 3 Departments of 1 Pathology and 2 Medicine and the 3 Epidemiology and Medical Statistics
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia
 Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia ianbrown@envoi.com.au Topics for discussion Classification of gastritis Minimal diagnostic criteria for gastritis H.pylori negative
Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia ianbrown@envoi.com.au Topics for discussion Classification of gastritis Minimal diagnostic criteria for gastritis H.pylori negative
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
Unexpected Findings at Endoscopy
 The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
MANAGEMENT OF IMMUNOTHERAPY RELATED GI AND HEPATIC ADVERSE EVENTS
 MANAGEMENT OF IMMUNOTHERAPY RELATED GI AND HEPATIC ADVERSE EVENTS Wai K. Leung Li Shu Fan Medical Foundation Professor in Gastroenterology Associate Dean (Human Capital), LKS Faculty of Medicine, University
MANAGEMENT OF IMMUNOTHERAPY RELATED GI AND HEPATIC ADVERSE EVENTS Wai K. Leung Li Shu Fan Medical Foundation Professor in Gastroenterology Associate Dean (Human Capital), LKS Faculty of Medicine, University
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies
 How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle, Washington, March 12, 2016
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle, Washington, March 12, 2016
Chapter 12: Training in Pathology. DDSEP Chapter 13: Question 19
 DDSEP Chapter 13: Question 19 A 70 year-old male with a history of celiac disease diagnosed in his forties reports abdominal pain, dark stools, and 20-pound weight loss. He reports complete compliance
DDSEP Chapter 13: Question 19 A 70 year-old male with a history of celiac disease diagnosed in his forties reports abdominal pain, dark stools, and 20-pound weight loss. He reports complete compliance
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies
 How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Mayo Clinic Scottsdale, AZ Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle,
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Mayo Clinic Scottsdale, AZ Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle,
Small Bowel Cases. Introduction. Introduction, Continued 12/7/2011. Lesions Found on endoscopic biopsies Just Like Signing Out
 Small Bowel Cases Lesions Found on endoscopic biopsies Just Like Signing Out Introduction Small intestinal biopsies have a few special pitfalls, for example: Neuroendocrine tumors are readily mistaken
Small Bowel Cases Lesions Found on endoscopic biopsies Just Like Signing Out Introduction Small intestinal biopsies have a few special pitfalls, for example: Neuroendocrine tumors are readily mistaken
Non-Neoplastic Disorders. of the Intestines. Laura W. Lamps, M.D. University of Arkansas Little Rock, AR
 Non-Neoplastic Disorders Laura W. Lamps, M.D. University of Arkansas Little Rock, AR Audrey J. Lazenby, M.D. University of Alabama Birmingham, AL Joel K. Greenson, M.D. University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Non-Neoplastic Disorders Laura W. Lamps, M.D. University of Arkansas Little Rock, AR Audrey J. Lazenby, M.D. University of Alabama Birmingham, AL Joel K. Greenson, M.D. University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
2015 복영증례 51/M C.C. Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl) 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 APCT (HAD #1) APCT (HAD#1) APCT (HAD #15)
 Case 1 2015 복영증례 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 51/M C.C Abdominal pain and chilling (1 week ago) Diarrhea (a month ago) Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Alcoholic liver disease (2008) Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl)
Case 1 2015 복영증례 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 51/M C.C Abdominal pain and chilling (1 week ago) Diarrhea (a month ago) Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Alcoholic liver disease (2008) Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl)
Endoscopy in IBD. F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M.
 F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
Allergic Colitis Clinical and Endoscopic Aspects of Infants. with Rectal Bleeding
 Allergic Colitis Clinical and Endoscopic Aspects of Infants. with Rectal Bleeding Allergic Colitis is an inflammatory disorder of the colon which occurs mainly in preschool children. It is caused by an
Allergic Colitis Clinical and Endoscopic Aspects of Infants. with Rectal Bleeding Allergic Colitis is an inflammatory disorder of the colon which occurs mainly in preschool children. It is caused by an
Frequency and Distribution of Microscopic Findings in Patients with Chronic Non-Bloody Diarrhea and Normal Colonoscopy
 IJMS Vol 33, No 2, June 2008 Original Article Frequency and Distribution of Microscopic Findings in Patients with Chronic Non-Bloody Diarrhea and Normal Colonoscopy H. Tabrizchie, M.J. Zahedie 1, M. Hayatbakhsh
IJMS Vol 33, No 2, June 2008 Original Article Frequency and Distribution of Microscopic Findings in Patients with Chronic Non-Bloody Diarrhea and Normal Colonoscopy H. Tabrizchie, M.J. Zahedie 1, M. Hayatbakhsh
For the past 40 years, it has been standard practice to obtain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Good Agreement Between Endoscopic Findings and Biopsy Reports Supports Limited Tissue Sampling During Pediatric Colonoscopy Michael A. Manfredi, Hongyu Jiang, Lawrence
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Good Agreement Between Endoscopic Findings and Biopsy Reports Supports Limited Tissue Sampling During Pediatric Colonoscopy Michael A. Manfredi, Hongyu Jiang, Lawrence
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
Diseases of the Colon. Jack Bragg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I.
 Diseases of the Colon Jack Bragg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I. I have no disclosures I work for the Curators of the University of Missouri Inflammatory Bowel Disease ULCERATIVE COLITIS CROHN S DISEASE Transmural Inflammation
Diseases of the Colon Jack Bragg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I. I have no disclosures I work for the Curators of the University of Missouri Inflammatory Bowel Disease ULCERATIVE COLITIS CROHN S DISEASE Transmural Inflammation
Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Focally Enhanced Gastritis in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה
 ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה Presentaion: S.A is 38 years old. Referred for rectal bleeding investigation. Describes several occasions of bleeding and abdominal pain.
ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה Presentaion: S.A is 38 years old. Referred for rectal bleeding investigation. Describes several occasions of bleeding and abdominal pain.
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Simple objective criteria for diagnosis of causes of
 5808 JClin Pathol 1997;50:580-585 Simple objective criteria for diagnosis of causes of acute diarrhoea on rectal biopsy Division of Pathology, Queen's Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK D Jenkins Department
5808 JClin Pathol 1997;50:580-585 Simple objective criteria for diagnosis of causes of acute diarrhoea on rectal biopsy Division of Pathology, Queen's Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK D Jenkins Department
Segmental colonoscopic biopsies in the differentiation of ileocolic tuberculosis from Crohn s disease
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJGHJournal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology0815-93192005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMay 2005205688696Original ArticleSegmental biopsies in and Crohn s diseaseab
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJGHJournal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology0815-93192005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMay 2005205688696Original ArticleSegmental biopsies in and Crohn s diseaseab
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
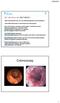 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
The revised Porto criteria for diagnosing
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Long-term Outcome of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unclassified in Children SIBA PROSAD PAUL AND BHUPINDER KAUR SANDHU From Bristol Royal Hospital for Children, Upper Maudlin Street,
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Long-term Outcome of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unclassified in Children SIBA PROSAD PAUL AND BHUPINDER KAUR SANDHU From Bristol Royal Hospital for Children, Upper Maudlin Street,
A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1607-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis Rumiko Tsuboi,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1607-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis Rumiko Tsuboi,
Endoscopic mucosal biopsies are useful in distinguishing granulomatous colitis due to Crohn s disease from tuberculosis
 Gut 1999;45:537 541 537 Wellcome Research Unit, Department of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore 632 004, Tamilnadu, India A B Pulimood B S Ramakrishna G Kurian
Gut 1999;45:537 541 537 Wellcome Research Unit, Department of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore 632 004, Tamilnadu, India A B Pulimood B S Ramakrishna G Kurian
Crohn s Disease. Resident Lecture 1/17/19
 Crohn s Disease Resident Lecture 1/17/19 Objectives Features/Classification of Crohn s Disease Medical Treatment Surgical Indications Surgical Considerations 2 Case 25 yo F presents to your office with
Crohn s Disease Resident Lecture 1/17/19 Objectives Features/Classification of Crohn s Disease Medical Treatment Surgical Indications Surgical Considerations 2 Case 25 yo F presents to your office with
Murine Models of. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Outline. Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center
 Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center September 19, 2017 Outline Review of IBD in humans Murine models of IBD Tissue
Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center September 19, 2017 Outline Review of IBD in humans Murine models of IBD Tissue
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Collagenous colitis presenting as spontaneous perforation in an 80 year old woman: Report of a Case
 Mitchell and Dugas BMC Gastroenterology (2016) 16:124 DOI 10.1186/s12876-016-0533-1 CASE REPORT Open Access Collagenous colitis presenting as spontaneous perforation in an 80 year old woman: Report of
Mitchell and Dugas BMC Gastroenterology (2016) 16:124 DOI 10.1186/s12876-016-0533-1 CASE REPORT Open Access Collagenous colitis presenting as spontaneous perforation in an 80 year old woman: Report of
children Crohn s disease in MR enterography for GI Complications Microscopy Characterization Primary sclerosing cholangitis Anorectal fistulae
 MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Diagnostic difficulty arising from rectal recovery
 J Clin Pathol 1996;49:319-323 319 Cellular Pathology, Northwick Park and St Mark's NHS Trust, Harrow T S Levine A B Price Gastroenterology S Mitchell Histopathology, Heraklion University General Hospital,
J Clin Pathol 1996;49:319-323 319 Cellular Pathology, Northwick Park and St Mark's NHS Trust, Harrow T S Levine A B Price Gastroenterology S Mitchell Histopathology, Heraklion University General Hospital,
Imaging Evaluation of Polyps. CT Colonography: Sessile Adenoma. Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon Objectives
 Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Terminal ileitis is not always Crohn s disease
 INVITED REVIEW Annals of Gastroenterology (2011) 24, 271-275 Terminal ileitis is not always Crohn s disease Daniela Bojic a, Srdjan Markovic b University of Belgrade, Serbia Abstract Chronic inflammation
INVITED REVIEW Annals of Gastroenterology (2011) 24, 271-275 Terminal ileitis is not always Crohn s disease Daniela Bojic a, Srdjan Markovic b University of Belgrade, Serbia Abstract Chronic inflammation
Diarrhoea on the AMU. Dr Chris Roseveare
 Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Chronic Colitis Pattern Christina A. Arnold, M.D. The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Columbus, Ohio
 Chronic Colitis Pattern Christina A. Arnold, M.D. The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Columbus, Ohio Identify this medication resin: A. Bile Acid Sequestrant B. Kayexalate C. Sevelamer D. Renvela
Chronic Colitis Pattern Christina A. Arnold, M.D. The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Columbus, Ohio Identify this medication resin: A. Bile Acid Sequestrant B. Kayexalate C. Sevelamer D. Renvela
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Restorative proctocolectomy with ileal reservoir: pathological and histochemical study of mucosal biopsy specimens
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:601-607 Restorative proctocolectomy with ileal reservoir: pathological and histochemical study of mucosal biopsy specimens N A SHEPHERD,* J R JASS,*t I DUVAL,T R L MOSKOWITZ,t R J
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:601-607 Restorative proctocolectomy with ileal reservoir: pathological and histochemical study of mucosal biopsy specimens N A SHEPHERD,* J R JASS,*t I DUVAL,T R L MOSKOWITZ,t R J
Keep microscopic colitis in mind!
 Keep microscopic in mind! Information for gastroenterologists and pathologists D. Aust (Dresden), S. Miehlke (Hamburg) An initiative of the EUROPEAN MICROSCOPIC COLITIS GROUP Microscopic is a chronic inflammatory
Keep microscopic in mind! Information for gastroenterologists and pathologists D. Aust (Dresden), S. Miehlke (Hamburg) An initiative of the EUROPEAN MICROSCOPIC COLITIS GROUP Microscopic is a chronic inflammatory
Colon ischemia. Bible class 12 September Stefan Christen. ACG Clinical Guideline: Am J Gastroenterol 2015
 Colon ischemia Bible class 12 September 2018 Stefan Christen ACG Clinical Guideline: Am J Gastroenterol 2015 Definition Definition Imbalance between blood supply and metabolic demands of the colonocytes
Colon ischemia Bible class 12 September 2018 Stefan Christen ACG Clinical Guideline: Am J Gastroenterol 2015 Definition Definition Imbalance between blood supply and metabolic demands of the colonocytes
Hompes Method. Practitioner Training Level II. Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation
 Hompes Method Practitioner Training Level II Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Hompes Method is a trading name of
Hompes Method Practitioner Training Level II Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Hompes Method is a trading name of
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma
 Gut, 1988, 29, 1607-1612 Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma P J SMART, S SASTRY, AND S WELLS From the Departments of Histopathology and Surgery, Bolton General Hospital, Fan
Gut, 1988, 29, 1607-1612 Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma P J SMART, S SASTRY, AND S WELLS From the Departments of Histopathology and Surgery, Bolton General Hospital, Fan
Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease
 Gut, 1979, 20, 141-148 Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease R. J. DICKINSON, H. M. GILMOUR, AND D. B. L. McCLELLAND' From the Department of Infectious
Gut, 1979, 20, 141-148 Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease R. J. DICKINSON, H. M. GILMOUR, AND D. B. L. McCLELLAND' From the Department of Infectious
Clinico-pathological study of colonoscopic biopsies in patients with chronic diarrhea
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Bhagyalakshmi A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jul;4(7):2738-2744 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161942
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Bhagyalakshmi A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jul;4(7):2738-2744 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161942
Case discussions. Case 1
 Case discussions Arzu Ensari 12 year old teen Case 1 Progressive cough and dysphagia following flu-like symptoms Family history of asthma Erythema in lower oesophagus 1 40 eos/hpf 2 What is Eosinophilic
Case discussions Arzu Ensari 12 year old teen Case 1 Progressive cough and dysphagia following flu-like symptoms Family history of asthma Erythema in lower oesophagus 1 40 eos/hpf 2 What is Eosinophilic
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Chapter 5 Dilemmas and Pitfalls in Diagnostic Evaluation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review on the Available Armamentarium for Diagnosis Gunjan S Desai MS, MRCS, FMAS 2 *; Ujwala Sitaram Chavan MD
Chapter 5 Dilemmas and Pitfalls in Diagnostic Evaluation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review on the Available Armamentarium for Diagnosis Gunjan S Desai MS, MRCS, FMAS 2 *; Ujwala Sitaram Chavan MD
Plan. Sarcoidosis 21/07/2017. Sarcoidosis Liver involvement. Sarcoidosis GI involvement. Sarcoidosis Diagnosis
 Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
