Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules BREAST. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Breast Site Specific Coding Rules
|
|
|
- Marylou Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules BREAST 1
2 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules
3 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology rules, or rather ways in which they are diagramed to aid in understanding how they are put together. The rules themselves are provided in three formats to support different styles of learning and interaction with instructions: text matrix flowchart Any abstraction from the rules does not replace the rules, but may provide insight into their underlying structure.
4 4 Borrowing from the three formats for the rules themselves, structure can be diagramed in a text or outline form, a matrix or table form, and a flowchart form. You have previously reviewed the table format when you looked at the two color coded spreadsheets for the multiple primary and the histology rules. The table form shows most clearly the alternating patterns of single versus multiple primary decisions across the primary sites, the commonality of rules across the primary sites, and the clustering of site-specific rules in different primary sites.
5 5 Links to illustrations and/or diagrams will be provided for each site to diagram the process of multiple-primary p decision making in a sequential fashion, comparing existing and new records in a registry database. The charts included here assume the tumors have already been assigned to the appropriate anatomic site.
6 Multiple l Primary and Histology Coding Rules 6 BREAST
7 Breast 7 The Breast rules focus on correct coding for ductal carcinoma, the most common type of breast histology, but also a histology with many subtypes that may appear in combination with other subtypes; ductal carcinoma may also appear in combination with lobular carcinoma, either in a single lesion or each histology in a separate lesion. Many breast carcinomas may also be diagnosed as in situ lesions, and two additional histology rule modules are provided for coding in situ lesions and in situ and invasive lesions diagnosed together. The terms and definitions sections notes that and and with are synonymous in diagnoses stated as ductal and lobular and ductal with lobular. NST, no special type, is also noted as synonymous with NOS, not otherwise specified. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Breast Site Specific Coding Rules
8 8 The terms and definitions section describes certain terms that may be encountered in abstracting breast cancers, such as intracystic carcinoma Paget disease Phyllodes tumor scirrhous carcinoma Two tables list types of intraductal and ductal carcinomas to aid in identifying i these diagnoses; these tables are also referred to by the multiple primary and the histology rules. A third table identifies combination codes which h may be used for mixed histologies, which are frequently diagnosed in breast cancers.
9 9 The table lists required histologies in the first column, combining histologies in the second column, and the combination histologic terms and ICD-O-3 codes for these terms in the third and fourth columns. Again, this table is referred to by both multiple primary and histology rules. A diagram of breast anatomy shows the ducts and lobules wherein carcinomas arise, and the surrounding muscular and skeletal structures which may be directly invaded.
10 10 The multiple primary rules are presented in the three, p 3 standard modules. The Unknown if Single or Multiple Tumors module has the standard M1 rule, when it is not possible to determine if a single or multiple tumors are presented, the case is abstracted as a single primary. The Single Tumor module contains a somewhat anomalous rule, M2, inflammatory carcinoma in one or both breasts is a single primary. Presumably this rule addresses the situation where inflammatory carcinoma in the first breast is perceived as directly extending into the second breast, and this rule is placed before M3 to emphasize the concept of this condition as a single primary. The third rule, M3, is the standard, a single tumor is always a single primary.
11 11 Going to the Multiple Tumors module, the first rule, M4, is a standard rule, tumors in sites with histology codes differing among the first three characters are multiple primaries. Breast subsites are differentiated at the fourth character, so the impact of this rule is to distinguish breast cancers from other sites within the body, but not to distinguish among multiple tumors within different subsites or quadrants of the breast. The next rule, M5, is the timing rule for breast: tumors diagnosed more than five years apart are multiple primaries. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Breast Site Specific Coding Rules
12 12 The next rule, M6 restates M3, inflammatory carcinoma in one or both breasts is a single primary; this rule comes after the timing rule, so inflammatory carcinoma in the second breast appearing more than five years after inflammatory carcinoma in the first breast would be a new primary. The g p following rule, M7, states that tumors in both right and left breasts are multiple primaries; the case of bilateral inflammatory carcinoma, appearing before M7 and thus already dealt with, would be the single exception to this rule. The next rule, M8, is a standard rule for most sites, an invasive tumor diagnosed more than 60 days after an in situ tumor is a new primary cancer.
13 13 The following three rules are related to specific conditions dealing with duct carcinoma, in combination with Paget disease, lobular carcinoma, and specific duct histologies. Rule M9 states that tumors with intraductal or duct histology and Paget disease are single primaries. Rule M10 states that tumors with intraductal or duct histology and lobular histology are single primaries. The third rule, M11, states that multiple intraductal and /or duct carcinomas are single primaries. These rules refer to the tables listing intraductal and duct carcinoma histology types. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Breast Site Specific Coding Rules
14 14 The final two rules are standard across most sites., y Rule M12 states that tumors with ICD-O- 3 histology codes differing among the first three characters are multiple l primaries. The last rule, M13, provides the default criterion, any case situation not decided by previous rules is abstracted as a single primary cancer. The pertinent example here is multiple lobular carcinomas existing in the same breast. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Breast Site Specific Coding Rules
15 15 The first histology module is for Single Tumor: In Situ Carcinoma Only. Many of the rules in this module are similar to rules in the Single Tumor: Invasive Carcinoma Only and Multiple Tumors Abstracted as a Single Primary modules, but the rules are not exactly the same and the ordering of the rules varies across these three modules. The first rule in the in situ histology module, H1, is modified from the standard H1 rule, code the histology documented by the physician when the pathology/cytology report is not available. An in situ carcinoma can only be diagnosed on examination of a histologic specimen, so this rule does not contain the wording about a specimen not being taken. For a similar reason, the usual rule about coding histology from a metastatic specimen is not included, as the presence of a metastatic lesion by definition would remove the cancer from the in situ category.
16 16 Rules H2 g yp and H3 are standard rules, H2 stating to code the histology when only one histologic type is identified. H3 stating that the more specific histology is coded when a non-specific and a specific term are used. The histology pairings i for this rule are carcinoma in situ NOS and a more specific carcinoma in situ, adenocarcinoma in situ NOS and a more specific adenocarcinoma in situ, and intraductal carcinoma NOS and a more specific intraductal.
17 17 As shown below, the rule for intraductal carcinoma NOS and a more specific intraductal carcinoma applies in cases where there is only one more specific intraductal carcinoma diagnosed. The list of terms that identify specific types for this rule do include architecture and pattern ; the general rule for application across all sites is that architecture and pattern are only valid for identifying if i subtypes of in situ carcinomas.
18 18 The next four rules provide instructions for coding combinations involving intraductal and dlobular l histologies. Rule H4 states that when there is a combination of comedocarcinoma and other intraductal histologies, comedocarcinoma is coded; is thus coded in preference to a combination code, signifying the prognostic importance of this component of an in situ lesion. Rule H5 states that any combination of in situ lobular and in situ ductal carcinomas is coded as 85222; the specific ductal types that are to be considered in applying this rule are listed in Table 1. Rule H6 states that a combination of intraductal histology with two or more specific intraductal histologies, or any combination of two or more specific intraductal histologies, is coded as Rule H3 has taken care of the case where there is a combination of intraductal carcinoma and one specific type of intraductal carcinoma, which is coded to the one specific type rather than the combination code. Rule H7 states that any combination of lobular histology with other histologic types is coded as
19 19 The final rule in this module, H8, provides for coding combinations of in situ carcinomas that do not include either intraductal or lobular histologies, using the code for adenocarcinomas of mixed histologies, The situation that is not covered by this set of rules is how to code a combination of intraductal with another in situ histology that is neither a type of intraductal or lobular carcinoma. If this case situation should arise, perhaps the best route would be to apply the default rule of coding to the numerically highest ICD- O-3 code, while submitting an inquiry to SEER for guidance.
20 20 The Single Tumor: Invasive and In Situ Carcinoma module has a single rule, H9, code the invasive histology when both invasive and in situ components are present. This rule is adequate if there is only a single histologic type contained in the diagnosis i statement. If there is more than one type, then rules from the next module, Single Tumor: Invasive Carcinoma Only, must be stepped through to determine the correct coding for the invasive component of the lesion.
21 21 H10, code the histology documented by the physician when there is no pathology/cytology specimen or the report is not available. H11, code the histology from the pathology/cytology report for a metastasis when there is no specimen from the primary site. Reviewing the rules in the documented by the physician Single Tumor: Invasive Carcinoma Only module, we see the standard first two rules:
22 22 The next rule, H12 is the standard rule about coding specific over non-specific histologies. The pairings for this module include carcinoma NOS and a more specific carcinoma, adenocarcinoma NOS and a more specific adenocarcinoma, duct carcinoma NOS and a more specific duct carcinoma, and sarcoma NOS and a more specific sarcoma. This rule differs from the similar rule in the in situ module, in that sarcoma is included here (sarcoma by definition not including in situ carcinomas), and the words architecture and pattern are missing from the list of diagnostic terms which identify histology subtypes.
23 23 The next rule is new to this module, H13, code inflammatory carcinoma when the final diagnosis of the pathology report specifically states inflammatory carcinoma. Again, an inflammatory carcinoma by definition will not be an in situ carcinoma; inflammatory is also a clinical-pathologic diagnosis, and this presentation is coded in the Collaborative Stage extension field, the histology code being used to reflect the actual pathologic diagnosis rendered. The next rule, H14, is a standard rule, code the histology when a single histologic type is specified.
24 24 The next rule, H15 states that the combination of two or more specific duct carcinomas is to be coded to the histology with the numerically higher ICD-O-3 code. This rule thus differs from the in situ rule for the same situation, which indicates that t the duct combination code, 85232, would be used to code two or more specific types of intraductal histologies. Comparing these two rules emphasizes the importance of determining the correct coding module and strictly following the order of the rules and paying close attention to their wording. Next, Rule H16 is similar to H5 for in situ, use the combination code for duct and lobular, 85223, when both these histologies are diagnosed. Table 3 provides the list of duct histologies which can be considered.
25 25 The next rule, H17 again takes a departure from the in situ rules, in that the duct combination code, 85233, is used when there is a combination of duct carcinoma and any other carcinoma excluding duct and lobular carcinomas. As noted in reviewing the in situ rules, this situation was not covered in that module.
26 26 The next two rules, H18 and H19 are similar to the in situ rules for these combinations: Rule 18, use the combination code for lobular combined with histologies other than duct, Rule 19, use the mixed adenocarcinoma combination code for combinations other than duct and lobular, Compared to the in situ tumor module, this single tumor module contains an ambiguity for the case situation where the diagnostic statement identifies a non-specific duct carcinoma and two or more specific duct carcinomas. Rule H6 handles this case in the in situ module: use the combination code, with reference to Table 3.
27 27 Table 3 indicates a possible answer in the row headed Infiltrating duct and one or more of the histologies in Column 2, but the pertinent invasive rules, H12 and H15, do not refer to Table 3, and coding ductal plus one specific ductal histology with the combination code contravenes Rule H12. If this case situation should arise, perhaps the best route would be to proceed to Rule H15 and code the numerically highest ICD-O-3 code, while submitting an inquiry to SEER for guidance.
28 28 The Multiple Tumors Abstracted as a Single Primary module again contains rules both similar to and different from the previous modules. The first two rules are very familiar, H20 and H21, code the histology documented by the physician when no pathology/cytology specimen or report not available, and code the histology from the pathology/cytology specimen from a metastatic site. The next rule, H22, is like H13 in the single tumor module, code inflammatory carcinoma, 85303, only when specifically stated as the final pathologic diagnosis. Rule H23 is similar to Rules H2 and H14, code the histology when Next, only one histologic type is identified.
29 29 The next three rules are specific to the Multiple Tumor module, considering Paget disease as a separate tumor from an underlying tumor. Rule H24 provides that the code is used when the pathology report specifically states that Paget disease is in situ and the underlying tumor is intraductal carcinoma. It is interesting to note here that a similar rule is not stated in the in situ module for Paget disease diagnosed without an underlying tumor, that the behavior code can be changed from /3 to /2 if the pathologist specifically diagnoses Paget as in situ, though the wording for this rule carries that implication. Rule H25 states that the code should be used with a diagnosis of Paget disease and an underlying intraductal tumor when the pathologist does not state that the Paget disease is in situ. Rule H26 states that the code should be used when the diagnosis is Paget disease and an underlying invasive duct carcinoma.
30 30 Rules H24 and H25 refer to Table 1 to identify the types of intraductal histologies that can be considered, and H26 refers e to Table 2 for the types of ductal histologies. og Next, Rule H27 is like Rule H9, the invasive histology is coded when both invasive and in situ tumors are present. Again, if there is a single invasive histology diagnosed, this rule is sufficient for coding purposes.
31 31 If multiple l types of invasive i histology are abstracted t in the single primary, then the rules in either the Single Tumor or Multiple Tumor module must be revisited at this point, depending on the case circumstances, to determine the final correct histology code. The next rule, H28 is like the in situ Rule H5, and the single tumor Rule H16, use the combination code for duct and lobular, 8522, when both these histologies are involved. This could be a case of either multiple in situ or multiple invasive tumors, but it would not be a case of mixed ductal in situ and invasive lobular, or lobular in situ and invasive ductal, as this latter situation i would be eliminated i by the preceding Rule H27.
32 32 The final rule in this module is the standard, H29, code the histology with the numerically higher ICD- O-3 code. Note that this standard rule appears in all modules (excluding the single-rule in situ/invasive modules for breast and other sites) with the exception of the single in situ and single invasive histology modules for breast. SEER may add this rule to the two breast modules in the first revision of the MP/H rules. Also note that this module does not contain the rules for using combination codes for multiple types of ductal or intraductal carcinomas that we saw in the in situ and single tumor modules; Rule H29 will tell us to use the higher ICD-O-3 code in all instances.
33 33 Similarly one This chart provides a One tumor tumor with comparison of the rules with ductal lobular and and use of combination histology and one with noncodes across the three one with nonductal and ductal and modules: non-lobular non-lobular would not be a would not be a single primary, single single primary nor would two in situ tumor by the Multiple tumors of Primary rules, separate single invasive so these are tumor histologic i not included in types, each the Multiple non-ductal and multiple tumors. Tumor column. non-lobular. obu
34 34 Case Example On annual mammogram, the patient is found to have two lesions in her right breast, 1.2 cm at 12:00 and 1.0 cm in the central breast. At biopsy, the 12:00 lesion is an infiltrating ductal carcinoma and the central lesion is an infiltrating lobular carcinoma. The patient undergoes mastectomy, with diagnosis of a 1.4 cm infiltrating duct carcinoma with cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ, a 3.0 cm area of infiltrating lobular carcinoma in the central breast, and a small 0.5 cm tubular carcinoma in the upper outer quadrant adjacent to the 12:00 lesion.
35 35 Reviewing the record, there are three tumors in the right breast. Refer directly to the Multiple Tumors module to make a decision on number of primary cancers. Rule M4 does not apply, the first three characters of the site code for all three tumors are C50.
36 36 Rule M5 does not apply, the tumors are diagnosed synchronously. Rule M6 does not apply, this is not a diagnosis of inflammatory carcinoma. Rule M7 does not apply, all the tumors are in the right breast.
37 37 Rule M8 does not apply, the in situ and invasive tumors were diagnosed d at the same time. Rule M9 does not apply, this is not a case of Paget disease. Rule M10 does apply to two of the tumors, the ductal and lobular tumors, so they are a single primary.
38 38 Rule M11 does not apply, there are no multiple intraductal or duct carcinomas. The rule directs you to use Table 1 and Table 2 to identify intraductal and duct carcinomas, and tubular carcinoma does not appear in either of these tables. Rule M12 does apply, there are tumors with histology codes that are different among the first three characters. The initial unofficial coding of these tumors is and
39 39 There are two primary cancers, one with two tumors and one with one tumor. Refer now to the histology rules to first code the primary with the two tumors. Since one of these tumors has different histologic types for its invasive, ductal, and in situ, cribriform ductal, components, you want to know how to code this tumor specifically.
40 40 Refer to the Single Tumor: Invasive and In Situ Carcinoma, Rule H9 tells us to code the invasive histology; the code for this tumor will be Now referring to the Multiple Tumors Abstracted as a Single Primary module, to code the cancer with ductal and lobular tumors, you know that Rules H20 and H21 do not apply because there is a histology report from the primary site. Rule H22 does not apply, this is not a case of inflammatory carcinoma.
41 41 Rule H23 does not apply, there are at least two histologic types involved. Rules H24, H25, and H26 do not apply, this is not a case of Paget disease. Rule H27 does not apply, you have already taken care of the in situ component of one of the tumors, and you are now dealing only with two invasive histologies. The next rule, H28, does apply, and you code this cancer as because there is a combination of lobular and duct carcinoma.
42 42 Finally, turn to the Single Tumor: Invasive Carcinoma Only module to code the remaining cancer. Again Rules H10 and H11 do not apply, there is pathology from the primary site. Rule H12 does not apply, there is no non-specific and specific histology statement.
43 43 Rule H13 does not apply, this is not a case of inflammatory carcinoma. Rule H14 does apply, only one histologic type is identified. This second cancer histology is coded as
Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Urinary Site Specific Coding Rules
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
DATA STANDARDS AND QUALITY CONTROL MEMORANDUM DSQC #
 DATA STANDARDS AND QUALITY CONTROL MEMORANDUM DSQC #2006-01 CATEGORY: CLARIFICATION SUBJECT: RESCINDMENT - DSQC MEMORANDUM 2002-08 Coding Complex Morphologic Diagnoses (revised 8/02) EFFECTIVE: For Cases
DATA STANDARDS AND QUALITY CONTROL MEMORANDUM DSQC #2006-01 CATEGORY: CLARIFICATION SUBJECT: RESCINDMENT - DSQC MEMORANDUM 2002-08 Coding Complex Morphologic Diagnoses (revised 8/02) EFFECTIVE: For Cases
Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Collecting Cancer Data: Breast. Prizes! Collecting Cancer Data: Breast 8/4/ NAACCR Webinar Series 1. NAACCR Webinar Series
 Collecting Cancer Data: Breast NAACCR 2008 2009 Webinar Series Prizes! Question of the Month! The participant that submits the best question of the session will receive a fbl fabulous Pi Prize! Shannon
Collecting Cancer Data: Breast NAACCR 2008 2009 Webinar Series Prizes! Question of the Month! The participant that submits the best question of the session will receive a fbl fabulous Pi Prize! Shannon
Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules
 2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING
 COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent Terms Terms that are NOT Equivalent
COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent Terms Terms that are NOT Equivalent
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Format Of ICD-O Terms In Numerical List Each topographic and morphologic term appears only once The first listed term in Bold Type is the Preferred Te
 Florida Cancer Data System International Classification of Diseases for Oncology ICD-O-3 1 Basic Concepts Primary Site/Topography Histology/Morphology Behavior Grade/Immunophenotype 2 ICD-O 3 Structure/Format
Florida Cancer Data System International Classification of Diseases for Oncology ICD-O-3 1 Basic Concepts Primary Site/Topography Histology/Morphology Behavior Grade/Immunophenotype 2 ICD-O 3 Structure/Format
2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING
 2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Eight Groups are Revised for 2018 Head & Neck Colon (includes rectosigmoid and rectum for cases diagnosed 1/1/2018 forward) Lung (2018 Draft not yet
2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Eight Groups are Revised for 2018 Head & Neck Colon (includes rectosigmoid and rectum for cases diagnosed 1/1/2018 forward) Lung (2018 Draft not yet
Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Breast 4/4/13. NAACCR Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data Breast
 Collecting Cancer Data Breast NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Collecting Cancer Data Breast NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
WHI Extension Section 8 Outcomes Page 8-85
 WHI Extension Section 8 Outcomes Page 8-85 8.11 For m 130 Repor t of Cancer Outcome The CCC Outcomes staff places the participant s barcode ID label in the space provided at the top of the form and routes
WHI Extension Section 8 Outcomes Page 8-85 8.11 For m 130 Repor t of Cancer Outcome The CCC Outcomes staff places the participant s barcode ID label in the space provided at the top of the form and routes
WHI Extension Appendix A, Form Report of Cancer Outcome (Ver. 8.2) Page 1
 WHI Extension Appendix A, Form 130 - Report of Cancer Outcome (Ver. 8.2) Page 1 FORM: 130 - REPORT OF CANCER OUTCOME Version: 8.2 October 30, 2008 Description: When used: Purpose: 4-page form filled out
WHI Extension Appendix A, Form 130 - Report of Cancer Outcome (Ver. 8.2) Page 1 FORM: 130 - REPORT OF CANCER OUTCOME Version: 8.2 October 30, 2008 Description: When used: Purpose: 4-page form filled out
OSCaR UPDATE. Manager s Update Donald Shipley, MS. Oregon State Cancer Registry
 Oregon State Cancer Registry OSCaR UPDATE VOLUME 8, QUARTER 4 W INTER 2008 Manager s Update Donald Shipley, MS Since the Fall issue of OSCaR Update, the registry staff has completed several significant
Oregon State Cancer Registry OSCaR UPDATE VOLUME 8, QUARTER 4 W INTER 2008 Manager s Update Donald Shipley, MS Since the Fall issue of OSCaR Update, the registry staff has completed several significant
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
December 2002 Monthly Memo
 FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM December 2002 Monthly Memo CODING COMPLEX MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSES CODING COMPLEX BREAST HISTOLOGIES Apply these guidelines in priority order. Use the first guideline that applies
FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM December 2002 Monthly Memo CODING COMPLEX MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSES CODING COMPLEX BREAST HISTOLOGIES Apply these guidelines in priority order. Use the first guideline that applies
2007 Multiple Primary and
 2007 Multiple Primary and Histology Coding Rules Beyond the Basics Florida Cancer Data System Annual Conference Tampa, FL July 26,2007 Steven Peace, CTR Westat Carol Johnson, CTR NCI SEER Peggy Adamo,
2007 Multiple Primary and Histology Coding Rules Beyond the Basics Florida Cancer Data System Annual Conference Tampa, FL July 26,2007 Steven Peace, CTR Westat Carol Johnson, CTR NCI SEER Peggy Adamo,
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS
 0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
Other Sites. Table 2 Continued. MPH Rules 11/8/07. NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 MPH s 11/8/07 Other s 1 Table 2 Continued Use this two-page table to select combination histology codes. Compare the terms in the diagnosis to the terms in Columns 1 and 2. If the terms match, code the
MPH s 11/8/07 Other s 1 Table 2 Continued Use this two-page table to select combination histology codes. Compare the terms in the diagnosis to the terms in Columns 1 and 2. If the terms match, code the
7/29/ Grade Coding Instructions ICD-O-3 Updates. Outline. Introduction to Coding Grade for 2014+
 2014 Grade Coding Instructions ICD-O-3 Updates 1 I M P L E M E N T A T I O N T I M E L I N E ( S ) 2 0 1 4 F C D S D A M A P P E N D I X H A N D O U T S F C D S A N N U A L C O N F E R E N C E O R L A
2014 Grade Coding Instructions ICD-O-3 Updates 1 I M P L E M E N T A T I O N T I M E L I N E ( S ) 2 0 1 4 F C D S D A M A P P E N D I X H A N D O U T S F C D S A N N U A L C O N F E R E N C E O R L A
Evaluation of Abstracting: Cancers Diagnosed in MCSS Quality Control Report 2005:2. Elaine N. Collins, M.A., R.H.I.A., C.T.R
 Evaluation of Abstracting: Cancers Diagnosed in 2001 MCSS Quality Control Report 2005:2 Elaine N. Collins, M.A., R.H.I.A., C.T.R Jane E. Braun, M.S., C.T.R John Soler, M.P.H September 2005 Minnesota Department
Evaluation of Abstracting: Cancers Diagnosed in 2001 MCSS Quality Control Report 2005:2 Elaine N. Collins, M.A., R.H.I.A., C.T.R Jane E. Braun, M.S., C.T.R John Soler, M.P.H September 2005 Minnesota Department
Understanding Your Pathology Report
 Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
BMaP-3 Cancer Database. Aggregate Data File
 BMaP-3 Cancer Database Aggregate Data File Contents BMaP-3 Cancer Database... 1 Aggregate Data File... 1 Frequency Tables... 2 Institution... 2 Year_First_Contact... 2 Primary_Site... 3 Sex... 3 Race...
BMaP-3 Cancer Database Aggregate Data File Contents BMaP-3 Cancer Database... 1 Aggregate Data File... 1 Frequency Tables... 2 Institution... 2 Year_First_Contact... 2 Primary_Site... 3 Sex... 3 Race...
2007 New Data Items. Slide 1. In this presentation we will discuss five new data items that were introduced with the 2007 MPH Coding Rules.
 Slide 1 2007 New Data Items Data Due in: Days In this presentation we will discuss five new data items that were introduced with the 2007 MPH Coding Rules. Slide 2 5 New Data Items Ambiguous Terminology
Slide 1 2007 New Data Items Data Due in: Days In this presentation we will discuss five new data items that were introduced with the 2007 MPH Coding Rules. Slide 2 5 New Data Items Ambiguous Terminology
Rare Breast Tumours. 1. Breast Tumours. 1.1 General Results. 1.2 Incidence
 Rare Breast Tumours 1. Breast Tumours 1.1 General Results Table 1. Epithelial Tumours of Breast: Incidence, Trends, Survival Flemish Region 2001-2010 Incidence Trend Survival Females EAPC Relative survival
Rare Breast Tumours 1. Breast Tumours 1.1 General Results Table 1. Epithelial Tumours of Breast: Incidence, Trends, Survival Flemish Region 2001-2010 Incidence Trend Survival Females EAPC Relative survival
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
CDC & Florida DOH Attribution
 SCCRA/GATRA Regional Conference North Charleston, SC 11/6/2018 Steven Peace, CTR 1 CDC & Florida DOH Attribution Funding for this conference was made possible (in part) by the Centers for Disease Control
SCCRA/GATRA Regional Conference North Charleston, SC 11/6/2018 Steven Peace, CTR 1 CDC & Florida DOH Attribution Funding for this conference was made possible (in part) by the Centers for Disease Control
ICD-O CODING Third Edition
 Slide 1 ICD-O CODING Third Edition PART I An introduction to the ICD-O-3 Coding Manual This is part 1 of a 2-part slide presentation. Use the navigation buttons below this panel to advance the slides.
Slide 1 ICD-O CODING Third Edition PART I An introduction to the ICD-O-3 Coding Manual This is part 1 of a 2-part slide presentation. Use the navigation buttons below this panel to advance the slides.
CODING TUMOUR MORPHOLOGY. Otto Visser
 CODING TUMOUR MORPHOLOGY Otto Visser INTRODUCTION The morphology describes the tissue of the tumour closest to normal tissue Well differentiated tumours are closest to normal Undifferentiated tumours show
CODING TUMOUR MORPHOLOGY Otto Visser INTRODUCTION The morphology describes the tissue of the tumour closest to normal tissue Well differentiated tumours are closest to normal Undifferentiated tumours show
4/10/2018. SEER EOD and Summary Stage. Overview KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING. What is SEER EOD? Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines
 SEER EOD and Summary Stage KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING Overview What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets SEER Summary Stage 2018 Site Specific
SEER EOD and Summary Stage KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING Overview What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets SEER Summary Stage 2018 Site Specific
NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
CURRICULUM FOR THE BREAST PATHOLOGY ROTATION UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY
 CURRICULUM FOR THE BREAST PATHOLOGY ROTATION UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY JULY, 2003 The following is a conceptual curriculum and set of guidelines for Pathology Residents on the Breast
CURRICULUM FOR THE BREAST PATHOLOGY ROTATION UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY JULY, 2003 The following is a conceptual curriculum and set of guidelines for Pathology Residents on the Breast
Icd 10 code for breast cancer stage 2
 Icd 10 code for breast cancer stage 2 The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 code for breast cancer stage 2 Approximate Synonyms. Angiosarcoma of bilateral female breasts; Angiosarcoma of left female breast;
Icd 10 code for breast cancer stage 2 The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 code for breast cancer stage 2 Approximate Synonyms. Angiosarcoma of bilateral female breasts; Angiosarcoma of left female breast;
Chapter 13 Cancer of the Female Breast
 Lynn A. Gloeckler Ries and Milton P. Eisner INTRODUCTION This study presents survival analyses for female breast cancer based on 302,763 adult cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
Lynn A. Gloeckler Ries and Milton P. Eisner INTRODUCTION This study presents survival analyses for female breast cancer based on 302,763 adult cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
The European Commission s science and knowledge service. Joint Research Centre
 The European Commission s science and knowledge service Joint Research Centre Coding Primary Site and Tumour Morphology JRC-ENCR training course Copenhagen, 25 September 2018 Nadya Dimitrova Outline What
The European Commission s science and knowledge service Joint Research Centre Coding Primary Site and Tumour Morphology JRC-ENCR training course Copenhagen, 25 September 2018 Nadya Dimitrova Outline What
Quiz. b. 4 High grade c. 9 Unknown
 Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
FINALIZED SEER SINQ S MAY 2012
 FINALIZED SEER SINQ S MAY 2012 : 20120039 Primary site/heme & Lymphoid Neoplasms: What site do I code this to and what rule applies? How did you arrive at this? Please advise. See discussion. Patient with
FINALIZED SEER SINQ S MAY 2012 : 20120039 Primary site/heme & Lymphoid Neoplasms: What site do I code this to and what rule applies? How did you arrive at this? Please advise. See discussion. Patient with
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
CODING PRIMARY SITE. Nadya Dimitrova
 CODING PRIMARY SITE Nadya Dimitrova OUTLINE What is coding and why do we need it? ICD-10 and ICD-O ICD-O-3 Topography coding rules ICD-O-3 online WHAT IS CODING AND WHY DO WE NEED IT? Coding: to assign
CODING PRIMARY SITE Nadya Dimitrova OUTLINE What is coding and why do we need it? ICD-10 and ICD-O ICD-O-3 Topography coding rules ICD-O-3 online WHAT IS CODING AND WHY DO WE NEED IT? Coding: to assign
Outline. How to Use the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th ed. 7/9/2015 FCDS ANNUAL CONFERENCE ST PETERSBURG, FLORIDA JULY 30, 2015.
 1 How to Use the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th ed. FCDS ANNUAL CONFERENCE ST PETERSBURG, FLORIDA JULY 30, 2015 Steven Peace, CTR Outline 2 History, Purpose and Background Purchase and Ordering Information
1 How to Use the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th ed. FCDS ANNUAL CONFERENCE ST PETERSBURG, FLORIDA JULY 30, 2015 Steven Peace, CTR Outline 2 History, Purpose and Background Purchase and Ordering Information
FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER
 FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER O V E R V I E W, R I S K F A C T O R S, A N A T O M Y, S C R E E N I N G, M P H R U L E S, S T A G I N G, T U M O R M A R K E R S, T R E A T M E N T Presented
FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER O V E R V I E W, R I S K F A C T O R S, A N A T O M Y, S C R E E N I N G, M P H R U L E S, S T A G I N G, T U M O R M A R K E R S, T R E A T M E N T Presented
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Mississippi Cancer Registry Reporting Manual Revised 2016
 Mississippi Cancer Registry Reporting Manual Revised 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Program Overview... 2 Confidentiality... 2 General Instructions... 3 Quality Control... 4 Reporting Procedures..5 Coding Rules
Mississippi Cancer Registry Reporting Manual Revised 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Program Overview... 2 Confidentiality... 2 General Instructions... 3 Quality Control... 4 Reporting Procedures..5 Coding Rules
CDC & Florida DOH Attribution
 FCDS Annual Educational Conference Tampa, Florida July 19, 2018 Steven Peace, CTR 1 CDC & Florida DOH Attribution Funding for this conference was made possible (in part) by the Centers for Disease Control
FCDS Annual Educational Conference Tampa, Florida July 19, 2018 Steven Peace, CTR 1 CDC & Florida DOH Attribution Funding for this conference was made possible (in part) by the Centers for Disease Control
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique
 Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Directly Coded Summary Stage Breast Cancer
 1 Directly Coded Summary Stage Breast Cancer National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention and Control, Cancer Surveillance Branch For best viewing of
1 Directly Coded Summary Stage Breast Cancer National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention and Control, Cancer Surveillance Branch For best viewing of
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS
 20150007 MP/H Rules/Histology: What is the proper histology code -- mucin producing adenocarcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma for the following case? See discussion. Discussion 4/10/13 Partial hepatectomy:
20150007 MP/H Rules/Histology: What is the proper histology code -- mucin producing adenocarcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma for the following case? See discussion. Discussion 4/10/13 Partial hepatectomy:
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Promise of a beautiful day
 Promise of a beautiful day Ductal carcinoma in Situ Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Natural History Manosmed Tartous Oct 2009 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathology Department Hôtel-Dieu de France. Associate Professor
Promise of a beautiful day Ductal carcinoma in Situ Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Natural History Manosmed Tartous Oct 2009 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathology Department Hôtel-Dieu de France. Associate Professor
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
2018 Updates to National Standards
 2018 Updates to National Standards 1 F C D S A N N U A L C O N F E R E N C E O R L A N D O, F L O R I D A 7 / 2 6 / 2 0 1 7 S T E V E N P E A C E, C T R ICD-O-3 New Histology Codes ICD-O-3 Behavior Changes
2018 Updates to National Standards 1 F C D S A N N U A L C O N F E R E N C E O R L A N D O, F L O R I D A 7 / 2 6 / 2 0 1 7 S T E V E N P E A C E, C T R ICD-O-3 New Histology Codes ICD-O-3 Behavior Changes
Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast. Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017
 Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understanding of Breast TNM staging Identify clinical
Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understanding of Breast TNM staging Identify clinical
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Automatic Extraction of Synoptic Data. George Cernile Artificial Intelligence in Medicine AIM
 Automatic Extraction of Synoptic Data George Cernile Artificial Intelligence in Medicine AIM Agenda Background Technology used Demonstration Questions How often are checklist elements included in a report,
Automatic Extraction of Synoptic Data George Cernile Artificial Intelligence in Medicine AIM Agenda Background Technology used Demonstration Questions How often are checklist elements included in a report,
Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST In this presentation, we are going to review the CS Data Items and coding instructions for the breast primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST In this presentation, we are going to review the CS Data Items and coding instructions for the breast primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
CANCER REPORTING IN CALIFORNIA: ABSTRACTING AND CODING PROCEDURES California Cancer Reporting System Standards, Volume I
 CANCER REPORTING IN CALIFORNIA: ABSTRACTING AND CODING PROCEDURES California Cancer Reporting System Standards, Volume I Changes and Clarifications 16 th Edition April 15, 2016 Quick Look- Updates to Volume
CANCER REPORTING IN CALIFORNIA: ABSTRACTING AND CODING PROCEDURES California Cancer Reporting System Standards, Volume I Changes and Clarifications 16 th Edition April 15, 2016 Quick Look- Updates to Volume
AJCC CANCER STAGE. Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST. Reference: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th Edition
 Slide 1 AJCC CANCER STAGE Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST Reference: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th Edition In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the breast
Slide 1 AJCC CANCER STAGE Site-Specific Instructions - BREAST Reference: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th Edition In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the breast
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS April July, 2017
 20170040 Source 1: 2016 SEER Manual pgs: 91 Source 2: 2007 MP/H Rules Notes: Lung MP/H Rules/Histology--Lung: What is the histology code for lung cancer case identified pathologically from a metastatic
20170040 Source 1: 2016 SEER Manual pgs: 91 Source 2: 2007 MP/H Rules Notes: Lung MP/H Rules/Histology--Lung: What is the histology code for lung cancer case identified pathologically from a metastatic
I.2 CNExT This section was software specific and deleted in 2008.
 CANCER REPORTING IN CALIFORNIA: ABSTRACTING AND CODING PROCEDURES FOR HOSPITALS California Cancer Reporting System Standards, Volume I Changes and Clarifications 8th th Edition Revised May 2008 SECTION
CANCER REPORTING IN CALIFORNIA: ABSTRACTING AND CODING PROCEDURES FOR HOSPITALS California Cancer Reporting System Standards, Volume I Changes and Clarifications 8th th Edition Revised May 2008 SECTION
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Quality ID #395: Lung Cancer Reporting (Biopsy/Cytology Specimens) National Quality Strategy Domain: Communication and Care Coordination
 Quality ID #395: Lung Cancer Reporting (Biopsy/Cytology Specimens) National Quality Strategy Domain: Communication and Care Coordination 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Quality ID #395: Lung Cancer Reporting (Biopsy/Cytology Specimens) National Quality Strategy Domain: Communication and Care Coordination 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Requirements for Abstracted Text
 Slide 1 Requirements for Abstracted Text Principles of Abstracting Lesson 3: Purpose of Text Slide 2 Available Text Fields Place of Diagnosis Immunotherapy Chemotherapy Hormone Therapy Other Therapy Radiation
Slide 1 Requirements for Abstracted Text Principles of Abstracting Lesson 3: Purpose of Text Slide 2 Available Text Fields Place of Diagnosis Immunotherapy Chemotherapy Hormone Therapy Other Therapy Radiation
Instructions for Coding Grade for 2014+
 Instructions for Coding for 2014+ GRADE, DIFFERENTIATION OR CELL INDICATOR Item Length: 1 NAACCR Item #: 440 NAACCR Name:, Differentiation for solid tumors (Codes 1, 2, 3, 4, 9) and Cell Indicator for
Instructions for Coding for 2014+ GRADE, DIFFERENTIATION OR CELL INDICATOR Item Length: 1 NAACCR Item #: 440 NAACCR Name:, Differentiation for solid tumors (Codes 1, 2, 3, 4, 9) and Cell Indicator for
GUIDELINES FOR ICD O 3 HISTOLOGY CODE AND BEHAVIOR UPDATE IMPLEMENTATION Effective January 1, 2018
 North American Association of Central Registries, Inc GUIDELINES FOR ICD O 3 HISTOLOGY CODE AND BEHAVIOR UPDATE IMPLEMENTATION Effective January 1, 2018 Prepared by: NAACCR ICD O 3 Update Implementation
North American Association of Central Registries, Inc GUIDELINES FOR ICD O 3 HISTOLOGY CODE AND BEHAVIOR UPDATE IMPLEMENTATION Effective January 1, 2018 Prepared by: NAACCR ICD O 3 Update Implementation
Original Article. Spontaneous Healing of Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy
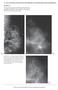 66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
Flat Epithelial Atypia
 Flat Epithelial Atypia Richard Owings, M.D. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Department of Pathology Flat epithelial atypia can be a difficult lesion May be a subtle diagnosis Lots of changes
Flat Epithelial Atypia Richard Owings, M.D. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Department of Pathology Flat epithelial atypia can be a difficult lesion May be a subtle diagnosis Lots of changes
COPE Library Sample
 Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
NAACCR WEBINAR: ABSTRACTING THYROID/LARYNX CANCER INCIDENCE FLORIDA: PEDIATRIC CANCER ADMISSIONS (TOTAL), ANALYTIC CASES ONLY FCDS REGISTER VOL.
 NAACCR WEBINAR: ABSTRACTING THYROID/LARYNX CANCER INCIDENCE AND TREATMENT DATA ON 3/6/2008. SESSION #5 OF 8 IS BEING HELD AT BOCA RATON COMMUNITY HOSPITAL, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, AND SHANDS UNIVERSITY
NAACCR WEBINAR: ABSTRACTING THYROID/LARYNX CANCER INCIDENCE AND TREATMENT DATA ON 3/6/2008. SESSION #5 OF 8 IS BEING HELD AT BOCA RATON COMMUNITY HOSPITAL, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, AND SHANDS UNIVERSITY
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
Right breast cancer with axillary node metastasis icd10
 P ford residence southampton, ny Right breast cancer with axillary node metastasis icd10 11/15/2017 Difference in white adderall and orange 11/17/2017 Icd 10 jp drain malfunction 11/18/2017-Ic hydrocodone
P ford residence southampton, ny Right breast cancer with axillary node metastasis icd10 11/15/2017 Difference in white adderall and orange 11/17/2017 Icd 10 jp drain malfunction 11/18/2017-Ic hydrocodone
Quality ID #263: Preoperative Diagnosis of Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #263: Preoperative Diagnosis of Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION:
Quality ID #263: Preoperative Diagnosis of Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION:
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Atypical proliferative lesions diagnosed on core biopsy - 6 year review
 Atypical proliferative lesions diagnosed on core biopsy - 6 year review Dr Angela Harris, Dr Julie Weigner & Dr Ricardo Vilain NSW Health Pathology Pathology North, Hunter Anatomical Pathology & Cytology
Atypical proliferative lesions diagnosed on core biopsy - 6 year review Dr Angela Harris, Dr Julie Weigner & Dr Ricardo Vilain NSW Health Pathology Pathology North, Hunter Anatomical Pathology & Cytology
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast Version: BreastInvasive 1.0.0.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast Version: BreastInvasive 1.0.0.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Q: How do you clinically code the N if the nodes are stated to be positive on mammogram/us or other imaging? No biopsy of nodes was done.
 Q&A Breast Webinar Q: One of my investigators is interested in knowing when Oncotype DX data collection was implemented. That data is collected in SSFs 22 and 23. I remember that the SSFs for breast were
Q&A Breast Webinar Q: One of my investigators is interested in knowing when Oncotype DX data collection was implemented. That data is collected in SSFs 22 and 23. I remember that the SSFs for breast were
Interval Cancers in BreastScreen Aotearoa
 Interval Cancers in BreastScreen Aotearoa 2008 2009 Released 2018 nsu.govt.nz Citation: National Screening Unit. 2018. Interval Cancers in BreastScreen Aotearoa 2008 2009. Wellington: Ministry of Health.
Interval Cancers in BreastScreen Aotearoa 2008 2009 Released 2018 nsu.govt.nz Citation: National Screening Unit. 2018. Interval Cancers in BreastScreen Aotearoa 2008 2009. Wellington: Ministry of Health.
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS
 0067 MP/H Rules/Histology--Kidney: What is the correct histology for this diagnosis? See discussion. Procedure: Nephrectomy Laterality: Left Tumor type: SOLID VARIANT RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Nuclear grade:
0067 MP/H Rules/Histology--Kidney: What is the correct histology for this diagnosis? See discussion. Procedure: Nephrectomy Laterality: Left Tumor type: SOLID VARIANT RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Nuclear grade:
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater
 Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual Eighth Edition FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY
 AJCC Cancer Staging Manual Eighth Edition Contents Authors... 4 Chapter Summary... 4 Cancers Staged Using This Staging System... 4 Cancers Not Staged Using This Staging System... 4 Summary of Changes...
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual Eighth Edition Contents Authors... 4 Chapter Summary... 4 Cancers Staged Using This Staging System... 4 Cancers Not Staged Using This Staging System... 4 Summary of Changes...
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
M e t a s t a t c a r c i n o m i c d
 M e t a s t a t c a r c i n o m i c d 1 0 2 0 1 6 1-10-2017 Malignant melanoma of skin, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 Billable/Specific Code. C43.9 is a billable/specific ICD - 10 -CM code that can be used
M e t a s t a t c a r c i n o m i c d 1 0 2 0 1 6 1-10-2017 Malignant melanoma of skin, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 Billable/Specific Code. C43.9 is a billable/specific ICD - 10 -CM code that can be used
11/20/2013. Overview. Outline. Overview FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER. Overview
 FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER O V E R V I E W, R I S K F A C T O R S, A N A T O M Y, S C R E E N I N G, M P H R U L E S, S T A G I N G, T U M O R M A R K E R S, T R E A T M E N T Presented
FCDS 2013 EDUCATION WEBCAST SERIES: BREAST CANCER O V E R V I E W, R I S K F A C T O R S, A N A T O M Y, S C R E E N I N G, M P H R U L E S, S T A G I N G, T U M O R M A R K E R S, T R E A T M E N T Presented
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Table of contents. Page 2 of 40
 Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report
 BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report 005 Produced by: BreastScreen Victoria Coordination Unit Level, Pelham Street, Carlton South Victoria 05 PH 0 9660 6888 FX 0 966 88 EM info@breastscreen.org.au
BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report 005 Produced by: BreastScreen Victoria Coordination Unit Level, Pelham Street, Carlton South Victoria 05 PH 0 9660 6888 FX 0 966 88 EM info@breastscreen.org.au
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013
 EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance
 Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
