Minimally Invasive Surgery by Angular Stability Systems in Proximal Tibia Fractures Biomechanical Characteristics and Preliminary Results
|
|
|
- Jennifer Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Minimally Invasive Surgery by Angular Stability Systems in Proximal Tibia Fractures Biomechanical Characteristics and Preliminary Results P.D. Sirbu 1, E. Carata 2, T. Petreus 1, F. Munteanu 1, C. Popescu 3, R. Asaftei 1, and P. Botez 1 1 Gr.T.Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Iasi, Romania 2 Gh. Asachi Technical University, Iasi, Romania 3 Prof. Dr. Nicolae Oblu Emergency Clinical Hospital, Iasi, Romania Abstract Complex fractures of the proximal tibia are difficult to treat. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) has determined the result improvement while the angular stability plate type Less Invasive Stabilization System proximal lateral tibia (LISS-PLT) or Locked Compression plate (LCP-PLT) were specially created for this kind of fractures. The purpose of this study was to emphasize the design and biomechanical characteristics of these systems as well as to evaluate the results following the treatment of the complex fractures on the proximal tibia by MIPO with these plates with angular stability. The authors emphasize the design of the plate, the concept of the internal fixator and the importance of the aiming device for percutaneous insertion. There were investigated 8 fractures of the proximal tibia in 8 patients, with a mean age of 39.5 years. Fractures were classified according to AO/ASIF in 2 type A3, 2 type C1, 2 type C2 and 2 type C3). There were three open fractures (1 type I and 2 type II) according to Gustilo. In all 8 cases we have performed minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, using a LISS-PLT system in 5 cases or a LCP-PLT in 3 cases. All fractures healed after a mean time of 13 weeks and the knee mobility was considered as good (mean flexion of 105 ). Due to major biomechanical and biological advantages, the authors consider that, despite the high prices, the internal fixator type LISS-PLT or LCP-PLT represent the ideal implants for the complex fractures of proximal tibia. Keywords LISS-PLT, proximal tibia fractures, internal fixator, aiming device, angular stability. I. INTRODUCTION Complex fractures of the proximal tibia represent severe lesions that raise treatment problems. In displaced or unstable complex fractures (with/without articular involvement) the main indication is represented by the plate osteosynthesis [1]. The incidence of tegumentary necrosis, nonunions and infections is increased especially for the extended external and medial approach. These complications induce a decrease of the local blood flow due to excessive deperiostation and fragment devitalization. The disadvantages of the external placed plates determined authors as Krettek [2] to introduce MIPPO (minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis) technique by medial approach. The main advantages are represented by the ease of molding technique and the subcutaneous placement, without deperiostation or blood flow limitations [3]. However, fixation with classic plates and screws has some limitations regarding immediate and secondary displacements as well as periosteal compression with blood flow reduction. The combination of four requirements for complex meta- and epiphyseal fractures (anatomical reduction, stable internal fixation, preservation of the blood supply and early active and painfree mobilization) has led to the development of a new generation of locked plates and instruments type LISS (Less Invasive Stabilization System). These systems were created mainly for MIPPO in distal femoral fractures [4] and recently for proximal tibia (LISS-PLT) [5,6] II. PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to emphasize the design and biomechanical characteristics of the locked plates type LISS-PLT and LCP-PLT (locked compression plate) as well as to evaluate the results following the treatment of the complex fractures on the proximal tibia by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with these plates with angular stability. III. MATERIAL AND METHODS A. Biomechanical Characteristics The LISS-PLT plate has the properties of an internal fixator (screws with threaded head that are locked in the round threaded holed in the plate). This determines the stability increase and eliminates the risks of the secondary displacement, due to an accidental lag between the screw and the plate. This plate differs totally from the classic one where the screws are tightened to fix and compress the plate onto the bone; the stability is due to the friction between the plate and the bone (Fig. 1A). For LISS-PLT, there is no contact between the bone and the internal fixator, so the periosteal blood supply is preserved. (Fig. 1B). S. Vlad, R.V. Ciupa, and A.I. Nicu (Eds.): MEDITECH 2009, IFMBE Proceedings 26, pp ,
3 414 P.D. Sirbu et al. Fig. 3 (A) LCP-PLT with combi-holes. (B) The concept of LCP with classical screw and locked screw Fig. 1 Distribution differences for the biomechanical load for standard plates (A) by comparison to LISS with unicortical screws (B) and boneimplant interface (adapted from Frigg R, Injury, 32, 2001) [4] By comparison with LISS-PLT with round threaded holes (Fig. 2) the introduction of Locked Compression Plates (LCP) with combi-hole [7] represented the next step in the evolution of the internal fixators by the possible placement of the classic screws (that brings the bone to the plate) or of the locked screws (in the threaded half of the hole) (fig.3). In order to increase the construct stability (bone-liss or LCP), a very complex pattern for the position and angulation of the proximal screws was developed in order to maximize the anchorage and purchase of the screws in proximal tibia (Fig.4). Fig. 4 (A-D) Position and angulation of the proximal screws in the LCP- PLT system Fig. 2 LISS-PLT plate with round threaded holes For optimal stability and for preserving the soft tissues, the internal fixator has to be placed very close to the bone. The plates are therefore preshaped (Fig. 5) and the midshaft is twisted to insure optimal position and fixation (Fig. 6). IFMBE Proceedings Vol. 26
4 1 Minimally invasive surgery by angular stability systems in proximal tibia fractures. Biomechanical characteristics and preliminary results. P.D. Sirbu 1, E. Carata 2, T. Petreus 1, Fl. Munteanu 1, C. Popescu 3, R. Asaftei 1, P. Botez 1 1 Gr.T.Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Iasi, Romania 2 Gh. Asachi Technical University, Iasi, Romania 3 Prof. Dr. Nicolae Oblu Emergency Clinical Hospital, Iasi, Romania Abstract Complex fractures of the proximal tibia are difficult to treat. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) has determined the result improvement while the angular stability plate type Less Invasive Stabilization System proximal lateral tibia (LISS-PLT) or Locked Compression plate (LCP-PLT) were specially created for this kind of fractures. The purpose of this study was to emphasize the design and biomechanical characteristics of these systems as well as to evaluate the results following the treatment of the complex fractures on the proximal tibia by MIPO with these plates with angular stability. The authors emphasize the design of the plate, the concept of the internal fixator and the importance of the aiming device for percutaneous insertion. There were investigated 8 fractures of the proximal tibia in 8 patients, with a mean age of 39.5 years. Fractures were classified according to AO/ASIF in 2 type A3, 2 type C1, 2 type C2 and 2 type C3). There were three open fractures (1 type I and 2 type II) according to Gustilo. In all 8 cases we have performed minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, using a LISS-PLT system in 5 cases or a LCP-PLT in 3 cases. All fractures healed after a mean time of 13 weeks and the knee mobility was considered as good (mean flexion of 105 ). Due to major biomechanical and biological advantages, the authors consider that, despite the high prices, the internal fixator type LISS-PLT or LCP-PLT represent the ideal implants for the complex fractures of proximal tibia. Keywords LISS-PLT, proximal tibia fractures, internal fixator, aiming device, angular stability. I. INTRODUCTION Complex fractures of the proximal tibia represent severe lesions that raise treatment problems. In displaced or unstable complex fractures (with/without articular involvement) the main indication is represented by the plate osteosynthesis [1]. The incidence of tegumentary necrosis, nonunions and infections is increased especially for the extended external and medial approach. These complications induce a decrease of the local blood flow due to excessive deperiostation and fragment devitalization. The disadvantages of the external placed plates determined authors as Krettek [2] to introduce MIPPO (minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis) technique by medial approach. The main advantages are represented by the ease of molding technique and the subcutaneous placement, without deperiostation or blood flow limitations [3]. However, fixation with classic plates and screws has some limitations regarding immediate and secondary displacements as well as periosteal compression with blood flow reduction. The combination of four requirements for complex meta- and epiphyseal fractures (anatomical reduction, stable internal fixation, preservation of the blood supply and early active and painfree mobilization) has led to the development of a new generation of locked plates and instruments type LISS (Less Invasive Stabilization System). These systems were created mainly for MIPPO in distal femoral fractures [4] and recently for proximal tibia (LISS-PLT) [5,6] II. PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to emphasize the design and biomechanical characteristics of the locked plates type LISS-PLT and LCP-PLT (locked compression plate) as well as to evaluate the results following the treatment of the complex fractures on the proximal tibia by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with these plates with angular stability. III. MATERIAL AND METHODS The LISS-PLT plate has the properties of an internal fixator (screws with threaded head that are locked in the round threaded holed in the plate). This determines the stability increase and eliminates the risks of the secondary displacement, due to an accidental lag between the screw and the plate. There is no contact between the bone and the internal fixator, so the periosteal blood supply is preserved. (Fig. 1). This plate differs totally from the classic one where the screws are tightened to fix and compress the plate onto the bone; the stability is due to the friction between the plate and the bone (Fig. 1A).
5 2 Fig. 3 (A) LCP-PLT with combi-holes. (B) The concept of LCP with classical screw and locked screw. Fig. 1 Distribution differences for the biomechanical load for standard plates (A) by comparison to LISS (B) and bone-implant interface (adapted from Frigg R, Injury, 32, 2001) [10] By comparison with LISS-PLT with round threaded holes (Fig. 2) the introduction of Locked Compression Plates (LCP) with combi-hole [7] represented the next step in the evolution of the internal fixators by the possible placement of the classic screws (that brings the bone to the plate) or of the locked screws (in the threaded half of the hole) (fig.3). In order to increase the construct stability (bone-liss or LCP), a very complex pattern for the position and angulation of the proximal screws was developed in order to maximize the anchorage and purchase of the screws in proximal tibia (Fig.4). Fig. 4 (A-D) Position and angulation of the proximal screws in the LCP-PLT system. Fig. 2 LISS-PLT plate with round threaded holes. For optimal stability and for preserving the soft tissues, the internal fixator has to be placed very close to the bone. The plates are therefore preshaped (Fig. 5) and the midshaft is twisted to insure optimal position and fixation (Fig. 6).
6 3 Special instruments and insertion guides allow the plates to slide under the muscle in a percutaneous minimally invasive manner (Fig. 8). Fig. 5 Molded LCP plate placement, at distance from tibial bone Fig. 8 (A) LISS-PLT with aiming device, made of carbon reinforced PEEK (B) LISS insertion through a limited curved approach, beneath the anterior tibial muscle. We have investigated 8 fractures of the proximal tibia in 8 patients, with a mean age of 39.5 years. Fractures were classified according to AO/ASIF in 2 type A3, 2 type C1, 2 type C2 and 2 type C3). There were three open fractures (1 type I and 2 type II) according to Gustilo. In all 8 cases we have performed minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, using a LISS-PLT system in 5 cases (Fig. 9) or a LCP-PLT in 3 cases. Fig. 6 The twisted midshaft of the LCP-PLT. The ideal anatomical location for LISS or for LCP-PLT is a more anterior placement on the anterolateral tibial wall, just posterior to the crest. (Fig. 7A). Thus, the diaphyseal screws are angled slightly posteriorly in order to be directed toward the center of the tibial canal for optimal fixation into the bone (Fig. 7B) Fig. 9 (A,B) Proximal tibia fracture C1/AO (C,D) MIPPO with LISS PLT. Fig. 7 (A) Ideal anatomical location for LISS or for LCP-PLT (B) the diaphyseal screws, angled slightly posteriorly Superficial thread of the locked screws differs from the classic screws with sharp edges and does not cut through the bone substrate when a perpendicular load is applied. Moreover, the superficial thread insures a wider diameter of the core that allows a larger bending force. We have used either a curved incision or a strait incision from the Gerdy tubercle about 50 mm in distal direction. The anterior tibial muscle was detached 1 cm from the tibial ridge, allowing the LISS plate insertion between periosteum and bone. For complex intraarticular fractures we have performed first an indirect reduction and the bone defect was filled with bone substitute. The aiming device allowed the percutaneous insertion of the self-drilling, self-taping screws (Fig. 10). This was possible by using a special water-cooled drill sleeve which connects to a standard syringe and infu-
7 4 sion set for directing cooling sterile saline to the screw/bone interface and prevent heating. reestablish the length, axis and rotation during minimally invasive techniques [8] VI. CONCLUSIONS Even if our study is limited, our experience with MIPO with classic plates in proximal tibia and the present results with MIPPO with LISS-PLT and LCP-PLT allows us to consider the internal fixators as ideal for these difficult lesions. REFERENCES Fig. 10 The insertion of the locked screws in diaphysis using aiming device, drill sleeve and saline solution for preventing heating. IV. RESULTS All fractures healed after a mean time of 13 weeks without bone grafting. At the most recent follow-up, all patients were walking without crutches with a good knee mobility (mean knee flexion 105 ) V. DISCUSSIONS The system with angular stability type LISS-PLT and LCP-PLT have revolutionized MIPO techniques in proximal tibia fractures due to the biomechanical and biological advantages. Beside important benefits in direct high-energy injuries, the clinical and biomechanical studies have demonstrated that the features of LISS-PLT and LCP-PLT became particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone, periprosthetic fractures and open fractures [4,5,6]. In the future, the real time photogrammetry and triangulation techniques by top-performance software will allow the trauma surgeon to obtain accurate images in order to 1. White R.R., Babikian G.M. (2000) Tibia: shaft, in AO Principles of Fractures Management, Thieme, Stuttgart Eds. Rüedi T.P., Murphy W.M., Dell Oca A.F., Holz U., Kellam J.F., Ochsner P.E., New York, Krettek C, Gerich F.T., Miclau T.H. (2001) A minimally invasive medial approach for proximal tibia, Injury, 2001, vol. 32, suppl. 1, Sirbu P., Mihaila R., Ghionoiu G., Bruja R., Asaftei R. (2006) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in proximal and distal fractures of tibia. in Smrkolj Vl., (ed.) 7th European Trauma Congress, Ljubljana (Slovenia), May 14-17, Ed. Medimond Italia, pp , ISBN Frigg R., Appenzeller A, Christensen R., Frenk A, Gilbert S., Schavan R. The development of the distal femur. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS), Injury, Int. J. Care Injured, 2001, 32, Goesling T., Frenk A., Appenzeller A., Garapati R., Marti A., Krettek C., LISS PLT: Design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics, Injury, Int. Care Injured, 2003, S-A11-S-A15 6. Sîrbu P., (2007) Osteosinteza minim invazivă cu plăci în fracturile femurului distal, Casa de Editură Venus, Iaşi 7. Frigg R., Frenk A., Haas N.P., Regazzoni P.- The Locking Compression Plate System. Dialogue (AO International), 2001,14, I, Ip David Orthopedic Traumatology A Resident s Guide; Springer Berlin-Heidelberg 2006 Use macro [author address] to enter the address of the corresponding author: Author: Paul Dan Sîrbu Institute: Gr.T.Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iasi Street: 16, Universitatii City: Iasi Country: Romania pdsirbu@yahoo.com
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
AO / Synthes Proximal Posterior Medial Tibia Plate. Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis
 Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES
 NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES Dr.eng. Comşa Stanca, sing. Gheorghiu Doina, eng. Ciobota Dan National Institute of Research & Development for fine
NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES Dr.eng. Comşa Stanca, sing. Gheorghiu Doina, eng. Ciobota Dan National Institute of Research & Development for fine
Locked Plating: Biomechanics and Biology
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(4):E1 E6 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Biomechanics and Biology Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John W. Munz, M.D. Summary: Since the early ideas
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(4):E1 E6 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Biomechanics and Biology Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John W. Munz, M.D. Summary: Since the early ideas
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures.
 LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
Locked Plating: Clinical Indications
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
LCP Metaphyseal Plate for distal medial tibia. Anatomically precontoured metaphyseal plate.
 Indications The LCP Metaphyseal Plate for distal medial tibia is a preshaped plate that allows optimal treatment of juxta-articular fractures of the distal tibia extending into the shaft area. This plate
Indications The LCP Metaphyseal Plate for distal medial tibia is a preshaped plate that allows optimal treatment of juxta-articular fractures of the distal tibia extending into the shaft area. This plate
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
Long Volar Plates for Diaphyseal-Metaphyseal Radius Fractures LCP. Dia-Meta Volar Distal Radius Plates. Surgical Technique
 Long Volar Plates for Diaphyseal-Metaphyseal Radius Fractures LCP Dia-Meta Volar Distal Radius Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction LCP Dia-Meta Volar Distal Radius Plates 2 AO Principles
Long Volar Plates for Diaphyseal-Metaphyseal Radius Fractures LCP Dia-Meta Volar Distal Radius Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction LCP Dia-Meta Volar Distal Radius Plates 2 AO Principles
3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures.
 Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
LCP DISTAL TIBIA PLATE
 LCP DISTAL TIBIA PLATE Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Image intensifier control This description
LCP DISTAL TIBIA PLATE Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Image intensifier control This description
3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Technique Guide. LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system.
 Technique Guide LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Allows percutaneous plate insertion and targeting of screws in the proximal tibia.
 Technique Guide Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Allows percutaneous plate insertion and targeting of screws in the proximal tibia. Table of Contents Introduction Less Invasive Stabilization
Technique Guide Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Allows percutaneous plate insertion and targeting of screws in the proximal tibia. Table of Contents Introduction Less Invasive Stabilization
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
LCP Metaphyseal Plates. For extra-articular fractures.
 LCP Metaphyseal Plates. For extra-articular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
LCP Metaphyseal Plates. For extra-articular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments
 Part of the 3.5 mm LCP 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate 2 Aiming Instruments
Part of the 3.5 mm LCP 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate 2 Aiming Instruments
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Technique Guide. Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures.
 Technique Guide Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Patient Positioning 5 Preparation
Technique Guide Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Patient Positioning 5 Preparation
3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates
 Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended
Low Bend Distal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
Technique Guide. TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee.
 Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
 LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended
LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended
VA-LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System.
 VA-LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
VA-LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System
 Stainless Steel and Titanium Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System 2 AO Principles
Stainless Steel and Titanium Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System 2 AO Principles
2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System.
 2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System. Technique Guide Instruments and Implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Radial
2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System. Technique Guide Instruments and Implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Radial
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 Technique Guide LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Superior Clavicle
Technique Guide LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Superior Clavicle
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System. 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO
LCP Distal Femur Plates. Shape based on Distal Femur LISS Plate design.
 LCP Distal Femur Plates. Shape based on Distal Femur LISS Plate design. Preshaped plate Round threaded holes in plate head Combi holes in plate shaft LCP Distal Femur Plates Plates The LCP Distal Femur
LCP Distal Femur Plates. Shape based on Distal Femur LISS Plate design. Preshaped plate Round threaded holes in plate head Combi holes in plate shaft LCP Distal Femur Plates Plates The LCP Distal Femur
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate
 For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant
LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Variable Angle LCP Volar Rim Distal Radius Plate 2.4. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide Variable Angle LCP Volar Rim Distal Radius Plate 2.4. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Image intensifier control Warning This description
Technique Guide Variable Angle LCP Volar Rim Distal Radius Plate 2.4. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Image intensifier control Warning This description
PROXIMAL TIBIAL PLATE
 SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP. Ankle Trauma System
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Ordering information. LCP Locking Compression Plate. Combine without compromise.
 Ordering information LCP Locking Compression Plate. Combine without compromise. Table of Contents Small Fragment System Large Fragment System LCP Instruments Emergency Instruments Implants Humerus Plates,
Ordering information LCP Locking Compression Plate. Combine without compromise. Table of Contents Small Fragment System Large Fragment System LCP Instruments Emergency Instruments Implants Humerus Plates,
NCB Large Fragment System. Surgical Technique
 NCB Large Fragment System Surgical Technique NCB Large Fragment System Surgical Technique 3 Table of Contents Introduction 4 System Features 7 Indications and Contraindications 10 NCB Large Fragment Plate
NCB Large Fragment System Surgical Technique NCB Large Fragment System Surgical Technique 3 Table of Contents Introduction 4 System Features 7 Indications and Contraindications 10 NCB Large Fragment Plate
2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plate
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture
 Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture Jansri Janpanya Product specialist The Bangkok Unitrade Co,.ltd. Objectives Type of LCP for distal radius Fx. The new LCP design for distal radius Fx. Have knowledge
Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture Jansri Janpanya Product specialist The Bangkok Unitrade Co,.ltd. Objectives Type of LCP for distal radius Fx. The new LCP design for distal radius Fx. Have knowledge
Technique Guide. Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Stainless steel and titanium.
 Technique Guide Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Stainless steel and titanium. Table of Contents Introduction Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Stainless steel and titanium. Table of Contents Introduction Small Fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System 2 AO Principles
Provision of Rotational Stability: Prevention of Collapse: Closed Fracture Reduction: Minimally Invasive Surgery with no Exposure of the Fracture:
 INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
4.5 mm VA-LCP. Part of the Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System
 4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved Condylar Plate Part of the Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved Condylar Plates 2 4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved
4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved Condylar Plate Part of the Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved Condylar Plates 2 4.5 mm VA-LCP Curved
Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large).
 Technique Guide Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Image intensifier control Warning This description
Technique Guide Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Image intensifier control Warning This description
Technique Guide. LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
OBSOLETED. LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Surgical Technique LCP Small Fragment System This publication
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Surgical Technique LCP Small Fragment System This publication
LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0 with Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments
 LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0 with Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO
LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0 with Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
LCP Periprosthetic System. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
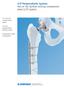 LCP Periprosthetic System. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. 4.5 mm LCP curved broad plates 5.0 mm periprosthetic locking screws Orthopaedic cable components LCP Periprosthetic
LCP Periprosthetic System. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. 4.5 mm LCP curved broad plates 5.0 mm periprosthetic locking screws Orthopaedic cable components LCP Periprosthetic
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes LCP Periarticular Plating System 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO Principles
Part of the DePuy Synthes LCP Periarticular Plating System 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO Principles
Clinical. Solutions. Synthes Solutions. Foot and Ankle.
 Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Experience with a Macroporous Synthetic Bone Substitute (Eurocer ) in the Treatment of the Patients with Bone Defects
 Clinical Experience with a Macroporous Synthetic Bone Substitute (Eurocer ) in the Treatment of the Patients with Bone Defects P.D. Sirbu, T. Petreus, Fl. Munteanu, M. Pertea, S. Lunca, V. Poroch, and
Clinical Experience with a Macroporous Synthetic Bone Substitute (Eurocer ) in the Treatment of the Patients with Bone Defects P.D. Sirbu, T. Petreus, Fl. Munteanu, M. Pertea, S. Lunca, V. Poroch, and
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement.
 LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
3.5 mm LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plates
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plates
LCP Locking Compression Plate. Surgical Technique
 LCP Locking Compression Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon
LCP Locking Compression Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon
LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate.
 Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
2.4 mm LCP Volar Column Distal Radius Plates. Part of the 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System.
 2.4 mm LCP Volar Column Distal Radius Plates. Part of the 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. 12 anatomically shaped volar plates Multiple screw options for fixedangle support to articular surface Combi holes
2.4 mm LCP Volar Column Distal Radius Plates. Part of the 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. 12 anatomically shaped volar plates Multiple screw options for fixedangle support to articular surface Combi holes
LCP Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 LCP Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for
LCP Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for
Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large).
 Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
Large Distractor Femur
 Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Olecranon Locking Plate II
 INDEX Indications Patient Position Fracture Reduction and Fixation Surgical Technique Step 1 Surgical Approach Step 2 Implantation Step 3 Proximal Locking Screw Insertion Step 4 Distal Screw Insertion
INDEX Indications Patient Position Fracture Reduction and Fixation Surgical Technique Step 1 Surgical Approach Step 2 Implantation Step 3 Proximal Locking Screw Insertion Step 4 Distal Screw Insertion
Surgical Technique. Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates
 Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article To Study the Functional Outcome of Locking Compression Plate in Metaphyseal Fractures Saraf
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article To Study the Functional Outcome of Locking Compression Plate in Metaphyseal Fractures Saraf
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
LISS PLT. The less invasive stabilization system for proximal tibia fractures.
 LISS PLT. The less invasive stabilization system for proximal tibia fractures. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO
LISS PLT. The less invasive stabilization system for proximal tibia fractures. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO
NCB Distal Femur System. Surgical Technique
 NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
3.5 mm LCP Hook Plate
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Hook Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Hook Plate 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Clinical
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Hook Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Hook Plate 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Clinical
WINSTA-C. Clavicle Plating System
 Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
3.5 mm Clavicle Hook Plates
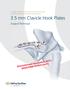 A Single Solution for Lateral Clavicle Fractures and Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations 3.5 mm Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/1016/1126(1) Table of Contents
A Single Solution for Lateral Clavicle Fractures and Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations 3.5 mm Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/1016/1126(1) Table of Contents
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
4.5 mm LCP Condylar Plate Aiming Instruments
 Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Instrument System (Large) 4.5 mm LCP Condylar Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Condylar Plate Aiming Instruments
Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Instrument System (Large) 4.5 mm LCP Condylar Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Condylar Plate Aiming Instruments
