The LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System in patients with limited access
|
|
|
- Felix Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery The LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System in patients with limited access Sunil S. Rayan, MD, Thomas T. Terramani, MD, Victor J. Weiss, MD, and Elliot L. Chaikof, MD, PhD, Atlanta, Ga Objective: The LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System was recently introduced as a completely subcutaneous device with reported advantages of improved patient comfort and reduced catheter-related infection. The performance of the LifeSite catheter at a single, tertiary-care university medical center was reviewed. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all patients who underwent placement of the LifeSite catheter between February 2001 and March Kaplan Meier analysis was used to determine the probability of patient survival, freedom from catheter-related infection, and freedom from device failure necessitating catheter removal. Results: Thirty-six patients who had previously received dialysis for an average of 6.1 years underwent placement of 37 LifeSite catheters. Most patients (95%) were referred for LifeSite placement because they had exhausted all available arteriovenous fistula and graft sites. Mean follow-up was 6.8 months, with a patient survival rate of 81% at 8 months. Primary and secondary patency rates were 62% and 87% at 8 months, respectively. Two patients died from infectious device-related complications. Twelve of 17 patients (71%) with device-related infection did not manifest any signs or symptoms at the valve site. There were 2.4 catheter-related infections and 2.6 device failures requiring removal per 1000 patient-catheter days. Freedom from infection and device removal at 8 months was 46% and 49%, respectively. Conclusions: The LifeSite demonstrated acceptable patency, infection, and device failure rates; however, in patients with limited access, unrecognized infection and death may occur. The LifeSite should not be used as a substitute for a more permanent form of hemodialysis access. (J Vasc Surg 2003;38:714-8.) According to the United States Renal Data System ( the prevalence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in the United States has grown from 195,000 in 1991 to over 350,000 in Consequently, rising costs associated with vascular access have approached $200 million. Complications associated with vascular access account for much of the problem. The USRDS reports that hemodialysis access failure is the most frequent cause of hospitalization among ESRD patients, and in some centers, it accounts for the largest number of hospital days. 1 Arteriovenous fistulae and grafts are the means by which most patients are dialyzed in the United States. Tunneled dialysis catheters (TDC), however, provide a temporary solution until more permanent access is achieved. Until now, all TDC have been at least partially external and have been prone to such problems as patient discomfort, infection, diminished flow rates, and venous thrombosis. 2 The LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System (Vasca Inc., Tewksbury, Mass) was specifically designed to correct some of the problems inherent in existing TDC. From the Division of Vascular Surgery, Emory University School of Medicine. Competition of interest: none Presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery, Miami, Fla, Mar 5 9, Reprint requests: Elliot L. Chaikof, MD, PhD, 1639 Pierce Drive, Room 5105, Emory University, Atlanta, GA ( echaiko@emory.edu). Copyright 2003 by The Society for Vascular Surgery /2003/$ doi: /s (03) The LifeSite, as described elsewhere, uses two separate entirely subcutaneous cannulas to provide hemodialysis access. 3 Each cannula is connected to a separate titanium alloy valve that uses a pinch-clamp mechanism to allow needle access under the skin. One valve is for blood draw, and the other is for blood return. The system must be disinfected with antimicrobial solution (70% isopropyl alcohol) after each use. Tissue hydrostatic pressure keeps the valves closed when they are not being used. Since its first description in 1997, the LifeSite catheter has had moderate clinical success. Most investigators have found the device superior to conventional hemodialysis catheters, as would be expected. 4-6 However, some authors noted high infection rates. 7 We set out to review our results at a single tertiary-care university hospital with the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System. METHODS The individual records of all patients who underwent placement of a LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System at our institution were retrospectively reviewed. Data regarding demographics, duration of hemodialysis-dependent ESRD, history of prior vascular access, operative details, and postoperative follow-up were recorded. Significant time points were dates of occlusion, infection, removal, and death. Occlusion was defined as malfunction requiring thrombolysis or port exchange. Infection was defined as positive cultures from the catheter, catheter tract, or catheter tip that were not regarded as contaminant and were in concordance with the clinical picture of catheter infection. Device failure was characterized as thrombosis or infection neces-
2 JOURNAL OF VASCULAR SURGERY Volume 38, Number 4 Rayan et al 715 sitating catheter removal. All dates of death were either obtained from or confirmed with the online Social Security Death Index ( vital/ssdi/main.htm). LifeSite catheter insertion was performed in the operating room by a vascular surgeon with the aid of fluoroscopy. One catheter was placed directly into the inferior vena cava via translumbar puncture by an interventional radiologist. The technique for catheter placement has been reported elsewhere. 8 Statistics were performed using Statview software (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC). Kaplan Meier analysis was used to analyze device patency, patient survival, freedom from infection, and freedom from device failure. Events were also reported per 1000 patient-catheter days for purposes of comparison. RESULTS A total of 37 LifeSite catheters were placed in 36 patients at our institution from February 2001 to March The average age of our cohort was years and 44% were males. There were 20 females and 16 males. Our patients had been receiving hemodialysis for an average of years prior to LifeSite insertion. Etiologies of ESRD included hypertension (76%), diabetes (46%), systemic lupus erythematosus (8%), and other (16%). Some patients had more than one contributing factor. Access target veins included femoral (54%), internal jugular (41%), and iliac (3%). One patient had direct translumbar insertion of the LifeSite into the vena cava, as all conventional access sites were unusable. Almost all patients were referred to our institution because of difficult access. Twenty-five patients (68%) had at least three separate failed extremity arteriovenous fistulas or grafts. This is in addition to countless graft revisions, thrombectomies, and angioplasties. Femoral Lifesite placement was only attempted if upper extremity sites were exhausted. In the fraction of patients (68%) who underwent perioperative ultrasonography or venography to evaluate central venous patency, 40% showed occlusion of two central veins or more. Patient survival was 90%, 86%, and 81% at 3, 6, and 8 months, respectively (Fig 1). A total of 7 patients died during follow-up. Two patients died perioperatively in the hospital. One patient died from causes unrelated to catheter placement (complications arising from upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage). The other patient died from septic shock 3 weeks after a femoral-popliteal bypass with saphenous vein and LifeSite catheter insertion. The cause of death was thought to be catheter-related sepsis due to persistent coagulase-negative Staphylococcus bacteremia. One patient died at 2.5 months from catheter-related sepsis and another at 8.3 months from sepsis (exact etiology unknown). The cause of the remaining three deaths is unknown. There were 2.4 device infections and 1.4 initial device occlusions per 1000 days. Freedom from catheter infection was 80%, 57%, and 46% at 3, 6, and 8 months, respectively (Fig 2). Of the 14 patients who demonstrated positive blood or catheter cultures, the overwhelming majority were Fig 1. Survival rates by Kaplan Meier analysis. Standard error exceeds 10% at 9.2 months. Two of the first three deaths were from catheter-related sepsis. Fig 2. Freedom from infection by Kaplan Meier analysis. Standard error exceeds 10% at 7.8 months. infected with gram-positive organisms (93%). Bacterial resistance to methicillin (36%) and vancomycin (7%) was not uncommon in our population. Two patients with exposed LifeSite valves were not counted as infections as they were successfully treated by revision and did not manifest other signs of clinical infection. Twelve of the 17 patients (71%) with device infection did not present with symptoms relating to the valve site; rather, they manifested signs of systemic sepsis such as fever, leukocytosis, and bacteremia. Often, other sources of infection were ruled out before the Lifesite was suspected. Femoral catheter infection occurred in 12 of 18 patients (67%). Femoral LifeSite placement was not statistically associated with death or infection, however. Diabetes did not correlate with device infection by the generalized Wilcoxon rank sum test. Primary and secondary patency were 86% and 92%, 73% and 92%, and 62% and 87% at 3, 6, and 8 months, respec-
3 716 Rayan et al JOURNAL OF VASCULAR SURGERY October 2003 Fig 3. Primary and secondary patency rates by Kaplan Meier analysis. Standard error 10% for both curves. Only catheter occlusions requiring operative intervention were recorded in our database, so actual patency rates may be lower. Fig 4. Freedom from device failure by Kaplan Meier analysis. Standard error exceeds 10% at 7.1 months. Device failure was defined as catheter occlusions or infections requiring device removal. tively (Fig 3). There were 2.6 device failures per 1000 days. Freedom from device failure was 93%, 81%, and 49% at 3, 6, and 8 months, respectively (Fig 4). Eighteen patients (49%) underwent LifeSite catheter removal due to infection or thrombosis. Two patients had the LifeSite removed after successful cadaveric renal transplant, and access was lost inadvertently during cannula exchange for thrombosis in another. These three patients were not considered device failures. DISCUSSION Infections have plagued TDC with catheter-related bacteremia rates ranging from 3.4 to 9.8 events per 1000 patient-catheter days These complications have resulted in rising costs associated with vascular access. 2 The LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System was introduced as the next logical step to combat the high complication rate of cuffed catheters. Reports of the LifeSite have been generally favorable in regard to infection and device failure although no report has focused on patients with difficult access. Several series in the literature document an infection rate of 1.3 to 2.5 per 1000 patient-catheter days. 4-6 In an early study of 23 patients, Beathard and Posen 4 found the LifeSite to have a device failure rate of 2.5 per 1000 patient-catheter days solely due to infection. Neither catheter thrombosis events nor device-related deaths occurred in their series; however, the infection rate was 52%. A multicenter study evaluating 45 patients found an infection rate of 1.9 per 1000 patient-catheter days. Interestingly, all the device-related infections (12 in 6 patients) occurred in patients with a history of prior dialysis access. Patients in this study had a history of prior TDC (71%), and 29% underwent femoral vein implantation of the LifeSite. 5 Finally, a multicenter prospective randomized trial evaluated the LifeSite compared with the Tesio-Cath Hemodialysis Catheter (Med Comp, Harleysville, Pa) and discovered a low infection rate of 1.3 per 1000 patient-catheter days when 70% isopropyl alcohol was used as the disinfecting agent. 6 One report cites an alarmingly high infection rate of 4.8 per 1000 patient-catheter days. 7 This study describes seven
4 JOURNAL OF VASCULAR SURGERY Volume 38, Number 4 Rayan et al 717 patients who all have a history of access failure and limited options for dialysis, similar to our own. Five patients (71%) developed device-related infection, necessitating removal in four patients. There were no deaths or thrombosis events associated with the LifeSite in this review. Our study describes a patient population that is truly end-stage. More than two thirds of our patients had at least three failed arteriovenous fistulas or grafts in addition to multiple operations for TDC insertion and graft salvage. Our patient population is chronically ill and debilitated, typical of a tertiary-care university setting. This is reflected in the reduced survival rate of only 66% of our patients surviving at 12 months. Essentially all of our patients exhausted conventional access sites, which was why our femoral insertion rate for the LifeSite system is so high (54%). The paucity of central venous access in these patients also indicates that they have had ESRD for some time and are likely preterminal. Our results show that the infection rate with the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System is in concordance with the rest of the literature at 2.6 per 1000 patient-catheter days. Although this rate is superior compared with TDC, the device clearly cannot be used as a substitute for more permanent dialysis access such as arteriovenous fistulas and grafts. National Kidney Foundation Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative guidelines 12 recommend that dialysis catheters have infection rates of less than 10% at 3 months and 50% at 1 year. Our results show that the LifeSite system does not meet those expectations in patients with limited access. Perhaps using this device in other patient subgroups as primary dialysis access may produce more favorable results. The relatively high rate of device-related mortality in this study probably reflects a desire to salvage any form of dialysis access in this patient population. Most infections were initially treated with antibiotics, but ultimately, LifeSite infection usually required removal of the device for definitive management. At least 2 patients died from catheter-related sepsis and another died from sepsis of unknown etiology. Our study is the only one published to date that relates mortality to LifeSite infection. Of concern is that only 5 of 17 patients who presented with infection manifested symptoms at the valve site. Most patients with catheter infection presented with signs of systemic sepsis: fever, bacteremia, and leukocytosis. This suggests that the subcutaneous nature of the device may mask any early signs of device-related infection. Our primary and secondary patency rates are quite favorable. However, catheter thrombosis was referred to us only when it required operative intervention. Our rates of catheter thrombosis are most likely underreported, as we did not take into account thrombolytic therapy initiated by the nephrologists for partial occlusions. In 2001, the Food and Drug Administration reviewed Vasca s policies regarding the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System. 13 According the administration s report, The majority of reported deaths and many reported injuries occurred in patients that were not candidates for permanent access placement....many affected patients had a history of multiple access failures and access infections and would not be candidates for further permanent access placement. Moreover, several centers reported patient deaths for individuals that had been considered last resort patients by their healthcare providers, in that they were not candidates for permanent access, were very ill, and had limited options for dialysis access. Several reported deaths and many reported injuries occurred in patients that underwent access placement procedures (femoral or direct thoracotomy implantation) for which the device is not currently labeled. Although Vasca does not describe femoral insertion in its indications for use, femoral insertion of the LifeSite has been reported. 14 TDC in the femoral location have been associated with higher infection rates. 10 Indeed, the K/DOQI guidelines recommend against femoral vein cannulation if other sites are available. 12 In our study, there was no statistical association between femoral LifeSite placement and infection or death. In summary, our results with the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System in patients with limited access revealed infection and device failure rates comparable to tunneled dialysis catheters. The femoral location was not statistically associated with an increased rate of adverse events. The LifeSite s subcutaneous nature may conceal the development of infection until sepsis develops. In patients with limited access and a relatively long history of ESRD, Lifesite catheter infection may result in death. REFERENCES 1. Mayers JD, Markell MS, Cohen LS, Hong J, Lundin P, Friedman EA. Vascular access surgery for maintenance hemodialysis: variables in hospital stay. ASAIO J 1992;38: Schwab SJ, Beathard G. The hemodialysis catheter conundrum: hate living with them, but can t live without them. Kidney Int 1999;56: Moran JE. Subcutaneous vascular access devices. Semin Dial 2001;14: Beathard GA, Posen GA. Initial clinical results with the LifeSite hemodialysis access system. Kidney Int 2000;58: Lamarche MB, Zeik JC, Clark RV. High performance and low complication rates of a subcutaneous vascular access device: the LifeSite hemodialysis access system. Dial Transplant 2002;31: Schwab SJ, Weiss MA, Rushton F, Ross JP, Jackson J, Kapoian T, et al. Multicenter clinical trial results with the LifeSite hemodialysis access system. Kidney Int 2002;62: Ross JJ, Narayan G, Bergeron EK, Worthington MG, Strom JA. Infections associated with use of the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System. Clin Infect Dis 2002;35: Ross JR. Clinical outcomes of four hemodialysis patients implanted with the LifeSite Hemodialysis Access System: a novel approach for vascular access. In: Henry ML, editor. Vascular access for hemodialysis-vii. Chicago: W.L. Gore and Precept Press; p Saad TF. Central venous dialysis catheters: catheter-associated infection. Semin Dial 2001;14: Oliver MJ, Callery SM, Thorpe KE, Schwab SJ, Churchill DN. Risk of bacteremia from temporary hemodialysis catheters by site of insertion and duration of use: a prospective study. Kidney Int 2000;58:
5 718 Rayan et al JOURNAL OF VASCULAR SURGERY October Almirall J, Gonzalez J, Rello J, Campistol JM, Montoliu J, Puig de la Bellacasa J, et al. Infection of hemodialysis catheters: incidence and mechanisms. Am J Nephrol 1989;9: NKF-K/DOQI. Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access: update Am J Kidney Dis 2001;37(Suppl 1):S Department of Health and Human Services, US Food and Drug Administration. Warning Letter Number NWE-04-02W. Available from: URL: pdf. 14. Ross J. Subcutaneous implantation of the LifeSite hemodialysis access system in the femoral vein. J Vasc Access 2001;2:91-6. Submitted Mar 10, 2003; accepted Jun 2, PREVIEW UPCOMING ARTICLES ON THE WEB Articles that have been accepted for publication and copyedited can often be read on the Journal Web site 1 or 2 months before publication in print. The full text of the article with all figures, references, and reference links to PubMed are available. The articles can be printed in their final format using the PDF link.
HeRO. Jeffrey H. Lawson, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Surgery and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina
 HeRO Jeffrey H. Lawson, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Surgery and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina Disclosures Consulting, Clinical Trials and Opinion Hemosphere Ark Therapeutics
HeRO Jeffrey H. Lawson, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Surgery and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina Disclosures Consulting, Clinical Trials and Opinion Hemosphere Ark Therapeutics
Nephrology. ABC Fax Marie Philipneri Ziyad Al Aly Kamal Amin Mary E. Gellens Bahar Bastani
 American Journal of Nephrology Original Article: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2003;23:202 207 DOI: 10.1159/000071479 Received: April 1, 2003 Accepted: April 9, 2003 Published online:
American Journal of Nephrology Original Article: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2003;23:202 207 DOI: 10.1159/000071479 Received: April 1, 2003 Accepted: April 9, 2003 Published online:
The HeRO Graft. Shawn M. Gage, PA Division of Vascular Surgery Duke University Medical Center
 The HeRO Graft Shawn M. Gage, PA Division of Vascular Surgery Duke University Medical Center Faculty Disclosure I disclose the following financial relationships: CryoLife/Hemosphere, Inc. & W.L. Gore and
The HeRO Graft Shawn M. Gage, PA Division of Vascular Surgery Duke University Medical Center Faculty Disclosure I disclose the following financial relationships: CryoLife/Hemosphere, Inc. & W.L. Gore and
Dialysis Event Protocol
 Dialysis Event Protocol Introduction In 2009, more than 370,000 patients were treated with maintenance hemodialysis in the United States. 1 Hemodialysis patients require a vascular access, which can be
Dialysis Event Protocol Introduction In 2009, more than 370,000 patients were treated with maintenance hemodialysis in the United States. 1 Hemodialysis patients require a vascular access, which can be
What s on the Horizon in Dialysis Access? Libby Watch, MD, FACS Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
 What s on the Horizon in Dialysis Access? Libby Watch, MD, FACS Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Disclosures No relevant disclosures Employee Advanced Access Care Dialysis Work 5 operating surgeons 3
What s on the Horizon in Dialysis Access? Libby Watch, MD, FACS Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Disclosures No relevant disclosures Employee Advanced Access Care Dialysis Work 5 operating surgeons 3
Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP)
 Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP) Considerations: Age Sex Body Composition Hydration Status Chemotherapy Use Access History Considerations: Immunosuppression Use Chemotherapy Frequency of plasma exchanges
Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP) Considerations: Age Sex Body Composition Hydration Status Chemotherapy Use Access History Considerations: Immunosuppression Use Chemotherapy Frequency of plasma exchanges
Novel solutions for access challenges
 Novel solutions for access challenges Mr James Gilbert Consultant Transplant & Vascular Access Surgeon Disclosures I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: I currently hold a consultancy
Novel solutions for access challenges Mr James Gilbert Consultant Transplant & Vascular Access Surgeon Disclosures I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: I currently hold a consultancy
Preservation of Veins and Timing for Vascular Access
 Preservation of Veins and Timing for Vascular Access Vassilis Liakopoulos, MD, PhD Department of Nephrology School of Medicine University of Thessaly Greece Hemodialysis VA A sound long-term dialysis access
Preservation of Veins and Timing for Vascular Access Vassilis Liakopoulos, MD, PhD Department of Nephrology School of Medicine University of Thessaly Greece Hemodialysis VA A sound long-term dialysis access
Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses.
 Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses. Poster No.: C-1038 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Ferrer-Puchol, R. Ramiro, E. Garcia-Oliver,
Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses. Poster No.: C-1038 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Ferrer-Puchol, R. Ramiro, E. Garcia-Oliver,
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE
 2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion. Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW
 Title Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion Author(s) Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW Citation Nephrology, 2010, v. 15 n.
Title Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion Author(s) Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW Citation Nephrology, 2010, v. 15 n.
Managing the Failing Dialysis Permacath: Results from a 5-year Retrospective Analysis
 Interventional Original Article Managing the Failing Dialysis Permacath: Results from a 5-year Retrospective Analysis Panagiotis M. Kitrou 1, Panagiotis Papadimatos 1, Konstantinos Katsanos 1, Stavros
Interventional Original Article Managing the Failing Dialysis Permacath: Results from a 5-year Retrospective Analysis Panagiotis M. Kitrou 1, Panagiotis Papadimatos 1, Konstantinos Katsanos 1, Stavros
CATHETER REDUCTION. Angelo N. Makris, M.D. Medical Director Chicago Access Care
 CATHETER REDUCTION Angelo N. Makris, M.D. Medical Director Chicago Access Care Objectives Discuss tools/techniques proven to improve AVF rates & decrease catheter rates Implement a change process in your
CATHETER REDUCTION Angelo N. Makris, M.D. Medical Director Chicago Access Care Objectives Discuss tools/techniques proven to improve AVF rates & decrease catheter rates Implement a change process in your
Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face
 Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th 2018 Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face Disclosures Dialysis Background Why is it important? Outline National
Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th 2018 Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face Disclosures Dialysis Background Why is it important? Outline National
Decreased Incidence of Clotted AV Access in Hemodialysis Patients after the Implementation of Follow up Program
 Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 8, No. 10; 2016 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Decreased Incidence of Clotted AV Access in Hemodialysis Patients
Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 8, No. 10; 2016 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Decreased Incidence of Clotted AV Access in Hemodialysis Patients
Outcomes Of Combined Rheolytic And Rotational Mechanical Thrombectomy For Total Access Circuit Thrombosis In Hemodialysis Patients
 Outcomes Of Combined Rheolytic And Rotational Mechanical Thrombectomy For Total Access Circuit Thrombosis In Hemodialysis Patients Nicholas Petruzzi, MD Raphael Cohen, MD Mark Mantell, MD Timothy W. Clark,
Outcomes Of Combined Rheolytic And Rotational Mechanical Thrombectomy For Total Access Circuit Thrombosis In Hemodialysis Patients Nicholas Petruzzi, MD Raphael Cohen, MD Mark Mantell, MD Timothy W. Clark,
ASDIN 7th Annual Scientific Meeting
 Strategies for Decreasing the Use of Hemodialysis Catheters ASDIN 7 th Annual Scientific Meeting Outline Late referral Primary failure Why Not PD? Summary Micah Chan MD MPH FACP Assistant Professor of
Strategies for Decreasing the Use of Hemodialysis Catheters ASDIN 7 th Annual Scientific Meeting Outline Late referral Primary failure Why Not PD? Summary Micah Chan MD MPH FACP Assistant Professor of
Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Leads & Arteriovenous Hemodialysis Access
 Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Leads & Arteriovenous Hemodialysis Access Theodore F. Saad, MD Nephrology Associates, PA Christiana Care Health System Newark, Delaware Cardiovascular Implantable
Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Leads & Arteriovenous Hemodialysis Access Theodore F. Saad, MD Nephrology Associates, PA Christiana Care Health System Newark, Delaware Cardiovascular Implantable
Sample page. POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com.
 2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
Primary to non-coronary IVUS
 codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
Measure #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES REGISTRY ONLY This is
Measure #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES REGISTRY ONLY This is
Technical and Clinical Barriers to Implementing an Optimal Case Mix of Vascular Access
 Technical and Clinical Barriers to Implementing an Optimal Case Mix of Vascular Access Louise Moist Associate Professor Lead Vascular Access Ontario Renal Network Schulich School of Medicine University
Technical and Clinical Barriers to Implementing an Optimal Case Mix of Vascular Access Louise Moist Associate Professor Lead Vascular Access Ontario Renal Network Schulich School of Medicine University
MIHÁLY TAPOLYAI, MD, FASN, FACP Associate Professor, Louisiana State University; Shreveport, Louisiana, USA Associate Professor; University of Hawai
 MIHÁLY TAPOLYAI, MD, FASN, FACP Associate Professor, Louisiana State University; Shreveport, Louisiana, USA Associate Professor; University of Hawai i Postgraduate Training Program at Chubu Hospital, Okinawa,
MIHÁLY TAPOLYAI, MD, FASN, FACP Associate Professor, Louisiana State University; Shreveport, Louisiana, USA Associate Professor; University of Hawai i Postgraduate Training Program at Chubu Hospital, Okinawa,
PROVINCIAL STANDARDS & GUIDELINES
 PROVINCIAL STANDARDS & GUIDELINES Insertion and Removal of Tunneled Hemodialysis Catheters Reviewed May 2017 Developed by the BCPRA Hemodialysis Committee Table of Contents 1.0 Scope... 1 2.0 Recommendations...
PROVINCIAL STANDARDS & GUIDELINES Insertion and Removal of Tunneled Hemodialysis Catheters Reviewed May 2017 Developed by the BCPRA Hemodialysis Committee Table of Contents 1.0 Scope... 1 2.0 Recommendations...
Quality ID #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Quality ID #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE:
Selection of Permanent Hemodialysis Vascular Access
 Selection of Permanent Hemodialysis Vascular Access TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Scope...1 2.0 Recommendations & Rationale... 2 3.0 References... 3 4.0 Sponsors... 9 5.0 Effective Date... 10 Appendix 1: Key Elements
Selection of Permanent Hemodialysis Vascular Access TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Scope...1 2.0 Recommendations & Rationale... 2 3.0 References... 3 4.0 Sponsors... 9 5.0 Effective Date... 10 Appendix 1: Key Elements
Regardless of whether you are a vascular surgeon,
 C A S E R E P O R T The Versatility of the GORE VIABAHN Endoprosthesis Several case reports highlighting its unique design and why it is a valuable tool for the interventionist. BY PETER WAYNE, MD Regardless
C A S E R E P O R T The Versatility of the GORE VIABAHN Endoprosthesis Several case reports highlighting its unique design and why it is a valuable tool for the interventionist. BY PETER WAYNE, MD Regardless
Thrombectomy, open, arteriovenous fistula without revision, autogenous or nonautogenous dialysis graft (separate procedure)
 Dialysis Vascular Access Coverage, Coding and Reimbursement Overview Hospital Outpatient 2019 Edition All Reimbursement Amounts are Listed at ational Unadjusted Medicare Rates and Do ot Include the 2%
Dialysis Vascular Access Coverage, Coding and Reimbursement Overview Hospital Outpatient 2019 Edition All Reimbursement Amounts are Listed at ational Unadjusted Medicare Rates and Do ot Include the 2%
NYU School of Medicine Department of Radiology Rotation-Specific House Staff Evaluation
 Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Dedicated outpatient vascular access center decreases hospitalization and missed outpatient dialysis treatments
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Dedicated outpatient vascular access center decreases hospitalization and missed outpatient dialysis treatments
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Dedicated outpatient vascular access center decreases hospitalization and missed outpatient dialysis treatments
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access
 Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
4/29/2012. Management of Central Vein Stenoses. Central Venous Stenoses and Occlusions
 Central Venous Stenoses and Occlusions Management of Central Vein Stenoses Robert K. Kerlan Jr. M.D. Professor of Clinical Radiology and Surgery University of California San Francisco Key Questions What
Central Venous Stenoses and Occlusions Management of Central Vein Stenoses Robert K. Kerlan Jr. M.D. Professor of Clinical Radiology and Surgery University of California San Francisco Key Questions What
JVA ISSN Hemodialysis vascular access management in the Netherlands. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 JVA ISSN 1129-7298 J Vasc Access 2015; 16 (Suppl 9): S11-S15 DOI: 10.5301/jva.5000366 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hemodialysis vascular access management in the Netherlands Jan H.M. Tordoir 1, Magda M. van Loon 1,
JVA ISSN 1129-7298 J Vasc Access 2015; 16 (Suppl 9): S11-S15 DOI: 10.5301/jva.5000366 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hemodialysis vascular access management in the Netherlands Jan H.M. Tordoir 1, Magda M. van Loon 1,
SCIENTIFIC LETTERS. Haemodialysis access by inferior vena cava catheterisation. Background. Methods. Results
 SCIENTIFIC LETTERS Haemodialysis access by inferior vena cava catheterisation A G H Assounga, M A Conrads, T M Han, S V Ramdial To the Editor: Progress in haemodialysis (HD) has made it increasingly accessible
SCIENTIFIC LETTERS Haemodialysis access by inferior vena cava catheterisation A G H Assounga, M A Conrads, T M Han, S V Ramdial To the Editor: Progress in haemodialysis (HD) has made it increasingly accessible
K/DOQI Guidelines: What Should an Interventionalist Know?
 K/DOQI Guidelines: What Should an Interventionalist Know? Aalpen A. Patel, M.D., 1,3 Catherine M. Tuite, M.D., 1,3 and Scott O. Trerotola, M.D. 2,3 ABSTRACT The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
K/DOQI Guidelines: What Should an Interventionalist Know? Aalpen A. Patel, M.D., 1,3 Catherine M. Tuite, M.D., 1,3 and Scott O. Trerotola, M.D. 2,3 ABSTRACT The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital
 Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital Button hole or Ladder?? Vascular Access Cannulation It s a Life Line of Hemodialysis patient Arterio-venous fistula(avf) is the K/DOQI
Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital Button hole or Ladder?? Vascular Access Cannulation It s a Life Line of Hemodialysis patient Arterio-venous fistula(avf) is the K/DOQI
COVERA Vascular Covered Stents in the Management of Dysfunctional AV Access
 COVERA Vascular Covered Stents in the Management of Dysfunctional AV Access Bart L. Dolmatch, M.D., FSIR Palo Alto Medical Foundation Mountain View, CA USA This presentation is being made on behalf of
COVERA Vascular Covered Stents in the Management of Dysfunctional AV Access Bart L. Dolmatch, M.D., FSIR Palo Alto Medical Foundation Mountain View, CA USA This presentation is being made on behalf of
Vascular Access Options for Apheresis Medicine
 Vascular Access Options for Apheresis Medicine Josh King, MD Divisions of Nephrology and Medical Toxicology University of Virginia September 21, 2018 Disclosure I have no personal or professional financial
Vascular Access Options for Apheresis Medicine Josh King, MD Divisions of Nephrology and Medical Toxicology University of Virginia September 21, 2018 Disclosure I have no personal or professional financial
Safety of arteriovenous fistulae and grafts for continuous renal replacement therapy: The Michigan experience
 Hemodialysis International 2018; 22:50 55 Original Article Access Safety of arteriovenous fistulae and grafts for continuous renal replacement therapy: The Michigan experience Anas AL RIFAI, 1,2 Nidhi
Hemodialysis International 2018; 22:50 55 Original Article Access Safety of arteriovenous fistulae and grafts for continuous renal replacement therapy: The Michigan experience Anas AL RIFAI, 1,2 Nidhi
( GFR 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) [2] (Tunneled cuffed catheter) [1] [3]
![( GFR 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) [2] (Tunneled cuffed catheter) [1] [3] ( GFR 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) [2] (Tunneled cuffed catheter) [1] [3]](/thumbs/92/109141024.jpg) [1] 07-3422121-2045 E-mail: cyhsu@vghks.gov.tw ( GFR 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) [2] (fistula) (graft) (Tunneled cuffed catheter) [3] 97 20 2 63 Allen s test (Duplex doppler ultrasound) [4] 2.0 mm2.5 mm [5] ()
[1] 07-3422121-2045 E-mail: cyhsu@vghks.gov.tw ( GFR 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) [2] (fistula) (graft) (Tunneled cuffed catheter) [3] 97 20 2 63 Allen s test (Duplex doppler ultrasound) [4] 2.0 mm2.5 mm [5] ()
Renal Physicians Association Kidney Quality Improvement Registry, Powered by Premier, Inc non-mips Measure Specifications
 Renal Physicians Association Kidney Quality Improvement Registry, Powered by Premier, Inc. 2018 non-mips Measure Specifications Last updated January 2, 2018 RPAQIR1: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)
Renal Physicians Association Kidney Quality Improvement Registry, Powered by Premier, Inc. 2018 non-mips Measure Specifications Last updated January 2, 2018 RPAQIR1: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)
Measure #330: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use for Greater Than or Equal to 90 Days National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety
 Measure #330: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use for Greater Than or Equal to 90 Days National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES REGISTRY ONLY This is a
Measure #330: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use for Greater Than or Equal to 90 Days National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES REGISTRY ONLY This is a
Salvaging prosthetic dialysis fistulas with stents: Forearm versus upper arm grafts
 From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery Salvaging prosthetic dialysis fistulas with stents: Forearm versus upper arm grafts Stephen Kolakowski, Jr, MD, Matthew J. Dougherty, MD, and Keith D. Calligaro,
From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery Salvaging prosthetic dialysis fistulas with stents: Forearm versus upper arm grafts Stephen Kolakowski, Jr, MD, Matthew J. Dougherty, MD, and Keith D. Calligaro,
Case #1. Case #1- Possible codes. Unraveling the -59 modifier. Principles of Interventional. CASE 1: Simple angioplasty
 Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio
 Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Central Line Care and Management
 Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Percutaneous and Surgical Treatments
 AVG Pseudoaneurysms Percutaneous and Surgical Treatments Marius Florescu M.D. Feb. 2015 ASDIN DEFINITION AVG Pseudoaneurysm Formation Incidence AVG Pseudoaneurysm incidence rate ranges between 2% and 10%
AVG Pseudoaneurysms Percutaneous and Surgical Treatments Marius Florescu M.D. Feb. 2015 ASDIN DEFINITION AVG Pseudoaneurysm Formation Incidence AVG Pseudoaneurysm incidence rate ranges between 2% and 10%
NKF K/DOQI GUIDELINES
 NKF K/DOQI GUIDELINES Executive Summaries Anemia Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis Vascular Access Nutrition CKD 2002 Dyslipidemias Bone Metabolism Hypertension and Antihypertensive Agents Cardiovascular
NKF K/DOQI GUIDELINES Executive Summaries Anemia Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis Vascular Access Nutrition CKD 2002 Dyslipidemias Bone Metabolism Hypertension and Antihypertensive Agents Cardiovascular
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related. Iliocaval Thrombosis
 Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
UC SF. End Stage Renal Disease. National Kidney Foundation Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI) BUT-- No Cephalic Vein What s Next
 No Cephalic Vein What s Next End Stage Renal Disease Charles Eichler MD Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery UCSF April 5, 2014 Population of patients with ESRD growing rapidly -
No Cephalic Vein What s Next End Stage Renal Disease Charles Eichler MD Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery UCSF April 5, 2014 Population of patients with ESRD growing rapidly -
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
Why Can't I Cannulate This Fistula? Fistula Immaturity: The Simple But Critical Steps for a Functioning (Mature) AVF
 Why Can t I Cannulate This Access? Steven J. Bander M.D. Adjunct Professor of Nephrology St. Louis University Director, Vascular Access Center, St. Luke s Hospital Saint Louis, MO Why Can't I Cannulate
Why Can t I Cannulate This Access? Steven J. Bander M.D. Adjunct Professor of Nephrology St. Louis University Director, Vascular Access Center, St. Luke s Hospital Saint Louis, MO Why Can't I Cannulate
Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 137-142 137 Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases SHE-MENG CHENG SUK-PING NG FEI-SHIH YANG SHIN-LIN SHIH Department
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 137-142 137 Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases SHE-MENG CHENG SUK-PING NG FEI-SHIH YANG SHIN-LIN SHIH Department
Port Design. Page 1. Port Placement, Removal, and Management. Selecting a Vascular Access Device. Thomas M. Vesely, MD
 Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
The University of Toledo Medical Center and its Medical Staff
 Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Vascular Access for Patients affected by non Renal Disorders. Eric S Chemla St George s vascular Institute London UK
 Vascular Access for Patients affected by non Renal Disorders Eric S Chemla St George s vascular Institute London UK Disclosures Gore Covidien Maquet Proteon Therapeutics INTRODUCTION I First fistula in
Vascular Access for Patients affected by non Renal Disorders Eric S Chemla St George s vascular Institute London UK Disclosures Gore Covidien Maquet Proteon Therapeutics INTRODUCTION I First fistula in
morbidity & mortality
 morbidity & mortality esrd introduction of ESRD treatment. We examine these concerns throughout the ADR, particularly in Chapter One. This year we focus on infectious complications, especially those related
morbidity & mortality esrd introduction of ESRD treatment. We examine these concerns throughout the ADR, particularly in Chapter One. This year we focus on infectious complications, especially those related
Malfunctioning and Infected Tunneled Infusion Catheters: Over-the-Wire Catheter Exchange versus Catheter Removal and Replacement
 CLINICAL STUDY Malfunctioning and Infected Tunneled Infusion Catheters: Over-the-Wire Catheter versus Catheter Removal and David M. Guttmann, BS, Scott O. Trerotola, MD, Timothy W. Clark, MD, Mandeep Dagli,
CLINICAL STUDY Malfunctioning and Infected Tunneled Infusion Catheters: Over-the-Wire Catheter versus Catheter Removal and David M. Guttmann, BS, Scott O. Trerotola, MD, Timothy W. Clark, MD, Mandeep Dagli,
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular
 Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Understanding the Dialysis Event Protocol and Avoiding Common Reporting Mistakes Alicia Shugart, MA
 Understanding the Dialysis Event Protocol and Avoiding Common Reporting Mistakes Alicia Shugart, MA Public Health Analyst Topics Dialysis Event Protocol Collecting data Reporting a numerator and denominator
Understanding the Dialysis Event Protocol and Avoiding Common Reporting Mistakes Alicia Shugart, MA Public Health Analyst Topics Dialysis Event Protocol Collecting data Reporting a numerator and denominator
Disclosure. Tunneled Catheters: How to Get Unstuck. ASDIN 10th Annual Scientific Meeting Final. Thomas Vesely, M.D.
 Tunneled Catheters: How to Get Unstuck Thomas Vesely, M.D. Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Caymus Medical Cylerus, Inc. Phase One Medical W.L. Gore & Associates Definition : Stuck Catheter A tunneled
Tunneled Catheters: How to Get Unstuck Thomas Vesely, M.D. Saint Louis, Missouri Disclosure Caymus Medical Cylerus, Inc. Phase One Medical W.L. Gore & Associates Definition : Stuck Catheter A tunneled
Chapter six Outcomes: hospitalization & mortality. There is an element of death in life, and I am astonished
 INTRODUCTION 1 OVERALL HOSPITALIZATION & MORTALITY 1 hospital admissions & days, by primary diagnosis & patient vintage five-year survival mortality rates, by patient vintage expected remaining lifetimes
INTRODUCTION 1 OVERALL HOSPITALIZATION & MORTALITY 1 hospital admissions & days, by primary diagnosis & patient vintage five-year survival mortality rates, by patient vintage expected remaining lifetimes
Current treatment status and medical costs for hemodialysis vascular access based on analysis of the Korean Health Insurance Database
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 218;33:116-1168 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.218.17 Current treatment status and medical costs for hemodialysis vascular access based on analysis of the Korean Health
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 218;33:116-1168 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.218.17 Current treatment status and medical costs for hemodialysis vascular access based on analysis of the Korean Health
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health
 Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health The painter who draws merely by practice and by eye, without any reason, is like a mirror which copies every thing placed in front of it without being
Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health The painter who draws merely by practice and by eye, without any reason, is like a mirror which copies every thing placed in front of it without being
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in the treatment of stenosis of hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulae: our experience
 Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in the treatment of stenosis of hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulae: our experience Poster No.: C-3355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in the treatment of stenosis of hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulae: our experience Poster No.: C-3355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional
Lysis-Assisted Balloon (LAB) Thrombectomy
 Lysis-Assisted Balloon (LAB) Thrombectomy Panagiotis M. Kitrou MD, MSc, PhD, EBIR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Interventional Radiology Dpt. Patras University Hospital Greece Facts & Figures Thrombosis:
Lysis-Assisted Balloon (LAB) Thrombectomy Panagiotis M. Kitrou MD, MSc, PhD, EBIR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Interventional Radiology Dpt. Patras University Hospital Greece Facts & Figures Thrombosis:
03/20/2019. Thank you for the invitation to speak. I have no conflicts of interest
 Raj Munshi, MD Annual Dialysis Conference 2019 Thank you for the invitation to speak I have no conflicts of interest Expected remaining lifetime in years of prevalent patients by initial ESRD modality,
Raj Munshi, MD Annual Dialysis Conference 2019 Thank you for the invitation to speak I have no conflicts of interest Expected remaining lifetime in years of prevalent patients by initial ESRD modality,
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents
 Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
Reviews in Infection
 Reviews in Infection RIF 1(1):1-6 (2010) RIF ISSN:1837-6746 Original Research Infection related processes during haemodialysis: A study in General Hospital Haemodialysis unit Naser Hussain 1, *Mona F.
Reviews in Infection RIF 1(1):1-6 (2010) RIF ISSN:1837-6746 Original Research Infection related processes during haemodialysis: A study in General Hospital Haemodialysis unit Naser Hussain 1, *Mona F.
Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU
 Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU Jer-Ming Chang. M.D., Ph.D. 1 Professor, Attending physician, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital; 2 Secretary General, Taiwan Society
Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU Jer-Ming Chang. M.D., Ph.D. 1 Professor, Attending physician, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital; 2 Secretary General, Taiwan Society
Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy
 Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Stuck dialysis catheters. ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond
 Stuck dialysis catheters ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond NT 39 yr old CI Maori - ESKD 2 o to cortical necrosis HD August 2002 R IJ tunneled Tesio catheter Oct 2002 Failed L RC AVF Feb 2004 Failed
Stuck dialysis catheters ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond NT 39 yr old CI Maori - ESKD 2 o to cortical necrosis HD August 2002 R IJ tunneled Tesio catheter Oct 2002 Failed L RC AVF Feb 2004 Failed
Hemodialysis catheters - from placement to complications: Our experience
 Hemodialysis catheters - from placement to complications: Our experience Poster No.: C-2048 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional Radiology - Vascular Authors: E. T. H. Liu,
Hemodialysis catheters - from placement to complications: Our experience Poster No.: C-2048 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional Radiology - Vascular Authors: E. T. H. Liu,
COVERA Vascular Covered Stents Innovation in AV Access
 IL0118 Rev.0 1 COVERA Vascular Covered Stents Innovation in AV Access Dheeraj Rajan, MD, FRCPC, FSIR Head and Associate Professor, Division of Vascular & Interventional Radiology Department of Medical
IL0118 Rev.0 1 COVERA Vascular Covered Stents Innovation in AV Access Dheeraj Rajan, MD, FRCPC, FSIR Head and Associate Professor, Division of Vascular & Interventional Radiology Department of Medical
Fistula/Graft Protection. Leslie Dork Renal Medicine Associates
 + Fistula/Graft Protection Leslie Dork Renal Medicine Associates + Disclaimer Renal Medicine Associates employee I have no conflicts of interest. + Access failure Infections Infiltrations Stenoses/Thrombosis
+ Fistula/Graft Protection Leslie Dork Renal Medicine Associates + Disclaimer Renal Medicine Associates employee I have no conflicts of interest. + Access failure Infections Infiltrations Stenoses/Thrombosis
RESTORING PATENCY TO CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES
 RESTORING PATENCY TO CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES Indications Venous access is poor Intravenous therapy involves venous sclerosants Ambulatory chemotherapy given as an outpatient Repeated sampling, or
RESTORING PATENCY TO CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES Indications Venous access is poor Intravenous therapy involves venous sclerosants Ambulatory chemotherapy given as an outpatient Repeated sampling, or
2019 ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule
 ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule This document and the information contained herein is for general information purposes only and is not intended and does not constitute legal, reimbursement,
ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule This document and the information contained herein is for general information purposes only and is not intended and does not constitute legal, reimbursement,
CHAPTER 3 ARTERIOVENOUS ACCESS: INFECTION, NEUROPATHY AND OTHER COMPLICATIONS
 CHAPTER 3 ARTERIOVENOUS ACCESS: INFECTION, NEUROPATHY AND OTHER COMPLICATIONS AUTHORS: Jennifer MacRae MSc MD, Christine Dipchand MD MSc, Matthew Oliver MD MSc, Louise Moist MD MSc, Serdar Yilmaz MD Phd,
CHAPTER 3 ARTERIOVENOUS ACCESS: INFECTION, NEUROPATHY AND OTHER COMPLICATIONS AUTHORS: Jennifer MacRae MSc MD, Christine Dipchand MD MSc, Matthew Oliver MD MSc, Louise Moist MD MSc, Serdar Yilmaz MD Phd,
Access Preservation: Recurrent Central Venous Stenosis, Pacemaker Wires and other Nightmares. Who am I? Disclosures
 Access Preservation: Recurrent Central Venous Stenosis, Pacemaker Wires and other Nightmares Jason Burgess, MD RVT Surgical Specialists of Charlotte CMC-Mercy Charlotte, NC Disclosures Gore Vascular- Consultant
Access Preservation: Recurrent Central Venous Stenosis, Pacemaker Wires and other Nightmares Jason Burgess, MD RVT Surgical Specialists of Charlotte CMC-Mercy Charlotte, NC Disclosures Gore Vascular- Consultant
III. NKF-K/DOQI CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR VASCULAR ACCESS: UPDATE 2000
 III. NKF-K/DOQI CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR VASCULAR ACCESS: UPDATE 2000 NOTE: The citation for these guidelines should read as follows: National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines
III. NKF-K/DOQI CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR VASCULAR ACCESS: UPDATE 2000 NOTE: The citation for these guidelines should read as follows: National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines
Long-term complications of cuffed tunneled central
 IMAGING TEACHING CASE Epistaxis as a Rare Complication of Catheter-Related Central Venous Stenosis Jin-Ju Tsai, MD, 1 Ching-Chih Hsia, MD, 1,2 Dong-Ming Tsai, MD, 1 Wei-Tsung Chen, MD, 3 and Yung-Hsuen
IMAGING TEACHING CASE Epistaxis as a Rare Complication of Catheter-Related Central Venous Stenosis Jin-Ju Tsai, MD, 1 Ching-Chih Hsia, MD, 1,2 Dong-Ming Tsai, MD, 1 Wei-Tsung Chen, MD, 3 and Yung-Hsuen
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
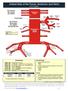 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS. Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas
 AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports
 Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
Since the initiation of hemodialysis, multiple inventions
 Special Feature Stent Graft for Nephrologists: Concerns and Consensus Loay Salman and Arif Asif Division of Nephrology, Section of Interventional Nephrology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine,
Special Feature Stent Graft for Nephrologists: Concerns and Consensus Loay Salman and Arif Asif Division of Nephrology, Section of Interventional Nephrology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine,
Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD**
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient. Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN
 Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN Understand principles of hemodialysis Recognize different access ports Identify side effects and complications Discuss nursing care for pre and
Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN Understand principles of hemodialysis Recognize different access ports Identify side effects and complications Discuss nursing care for pre and
Dr. Murty Mantha MD FRACP Cairns Base Hospital Cairns. DNT 2011 Hunter Valley
 Dr. Murty Mantha MD FRACP Cairns Base Hospital Cairns DNT 2011 Hunter Valley Approximately 45% of AVF are functional without intervention after creation The procedure rate is 1.45-3.3 procedures/avf
Dr. Murty Mantha MD FRACP Cairns Base Hospital Cairns DNT 2011 Hunter Valley Approximately 45% of AVF are functional without intervention after creation The procedure rate is 1.45-3.3 procedures/avf
Alberta Health Services Infection Prevention and Control - Initiatives and Services. Surveillance Protocol January 12, 2010 Rev.
 Alberta Health Services Infection Prevention and Control - Initiatives and Services Hospital Acquired Bloodstream Infections (HABSI) Hospital Wide- in Acute Care and Acute Rehabilitation Facilities Surveillance
Alberta Health Services Infection Prevention and Control - Initiatives and Services Hospital Acquired Bloodstream Infections (HABSI) Hospital Wide- in Acute Care and Acute Rehabilitation Facilities Surveillance
Conversion of tunneled hemodialysis catheter consigned patients to arteriovenous fistula
 Kidney International, Vol. 67 (2005), pp. 2399 2406 Conversion of tunneled hemodialysis catheter consigned patients to arteriovenous fistula ARIFASIF, GAUTAM CHERLA, DONNA MERRILL, CRISTIAN D. CIPLEU,
Kidney International, Vol. 67 (2005), pp. 2399 2406 Conversion of tunneled hemodialysis catheter consigned patients to arteriovenous fistula ARIFASIF, GAUTAM CHERLA, DONNA MERRILL, CRISTIAN D. CIPLEU,
Prevention of Hemodialysis Catheter- Related Bloodstream Infection Using an Antimicrobial Lock
 Blood Purif 2002;20:87 92 Prevention of Hemodialysis Catheter- Related Bloodstream Infection Using an Antimicrobial Lock Francesco Quarello Giacomo Forneris Nephrology and Dialysis Unit, San Giovanni Bosco
Blood Purif 2002;20:87 92 Prevention of Hemodialysis Catheter- Related Bloodstream Infection Using an Antimicrobial Lock Francesco Quarello Giacomo Forneris Nephrology and Dialysis Unit, San Giovanni Bosco
Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2018
 Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2018 Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street, Suite 514 St. Paul, MN 55101 1-800-252-1578 medlearnmedia.com
Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2018 Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street, Suite 514 St. Paul, MN 55101 1-800-252-1578 medlearnmedia.com
Original Article. Adam E. Frampton, Nicos Kessaris, Mohammad Hossain, Mohamed Morsy and Eric S. Chemla. Introduction. Patients and methods
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 24: 913 918 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn582 Advance Access publication 24 October 2008 Original Article Use of the femoral artery route for placement of temporary catheters for emergency
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 24: 913 918 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn582 Advance Access publication 24 October 2008 Original Article Use of the femoral artery route for placement of temporary catheters for emergency
Endovascular therapy of central vein stenosis in hemodialysis patients. Venous chimney graft to preserve residual jugular vein
 Endovascular therapy of central vein stenosis in hemodialysis patients. Venous chimney graft to preserve residual jugular vein Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R.
Endovascular therapy of central vein stenosis in hemodialysis patients. Venous chimney graft to preserve residual jugular vein Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R.
Intravenous Catheter Complications
 Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Balloon angioplasty for arteriovenous graft stenosis Anain P, Shenoy S, O'Brien M, Harris L M, Dryjski M
 Balloon angioplasty for arteriovenous graft stenosis Anain P, Shenoy S, O'Brien M, Harris L M, Dryjski M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for
Balloon angioplasty for arteriovenous graft stenosis Anain P, Shenoy S, O'Brien M, Harris L M, Dryjski M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for
FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 92 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access
 INTRODUCTION ANEMIA TREATMENT hemoglobin levels epo treatment iron treatment FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 2 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access EPO DOSING PATTERNS 4 epo dosing per kg
INTRODUCTION ANEMIA TREATMENT hemoglobin levels epo treatment iron treatment FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 2 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access EPO DOSING PATTERNS 4 epo dosing per kg
