Lamb Temporal Bone as a Surgical Training Model of Round Window Cochlear Implant Electrode Insertion
|
|
|
- Sydney Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Otology & Neurotology 37:52 56 ß 2015, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Lamb Temporal Bone as a Surgical Training Model of Round Window Cochlear Implant Electrode Insertion Georgios Mantokoudis, Markus E. Huth, ychristian Weisstanner, Hergen M. Friedrich, yclaude Nauer, Claudia Candreia, Marco D. Caversaccio, and Pascal Senn University Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery; and yuniversity Department of Neuroradiology and Interventional Radiology, Inselspital Bern, Switzerland Objective: The preservation of residual hearing in cochlear implantation opens the door for optimal functional results. This atraumatic surgical technique requires training; however, the traditional human cadaveric temporal bones have become less available or unattainable in some institutions. This study investigates the suitability of an alternative model, using cadaveric lamb temporal bone, for surgical training of atraumatic round window electrode insertion. Intervention: A total of 14 lamb temporal bones were dissected for cochlear implantation by four surgeons. After mastoidectomy, visualization, and drilling of the round window niche, an atraumatic round window insertion of a Medel Flex24 electrode was performed. Electrode insertion depth and position were verified by computed tomography scans. Main Outcome Measure: All cochleas were successfully implanted using the atraumatic round window approach; however, surgical access through the mastoid was substantially different when compared human anatomy. The mean number of intracochlear electrode contacts was 6.5 (range, 4 11) and the mean insertion depth 10.4 mm (range, 4 20 mm), which corresponds to a mean angular perimodiolar insertion depth of 229 degrees (range ). Full insertion of the electrode was not possible because of the smaller size of the lamb cochlea in comparison to that of the human. Conclusion: The lamb temporal bone model is well suited as a training model for atraumatic cochlear implantation at the level of the round window. The minimally pneumatized mastoid as well as the smaller cochlea can help prepare a surgeon for difficult cochlear implantations. Because of substantial differences to human anatomy, it is not an adequate training model for other surgical techniques such as mastoidectomy and posterior tympanotomy as well as full electrode insertion. Key Words: Animal model Cochlear implantation Electrode insertion Lamb Sheep Temporal bone. Otol Neurotol 37:52 56, Cochlear implantation (CI) with hearing preservation is a challenging low-volume procedure (1) and thus requires surgical training. The gold standard for CI training uses human cadaveric temporal bones (HTB) (2). As the most realistic model, HTBs provide the proper conditions for improving hand eye coordination, fine motor skills, and anatomical knowledge under microscopically magnified vision (2). However, the availability of HTBs is limited because of legal, economical, and ethical Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. med. Markus E. Huth, University Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Inselspital, 3010 Bern, Switzerland; markus.huth@ insel.ch Georgios Mantokoudis and Markus E. Huth equally contributed to this work. This work was financed by internal funding from the University Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery at Inselspital Bern. The authors disclose no conflicts of interest. reasons (2,3). Artificial temporal bones provide a three-dimensional training opportunity for anatomy visualization, but the tissue morphology is unnatural (4 6). Similarly, computer-based simulation models provide valuable anatomical training (7) and 3D virtual reality simulations are convincing but still cannot produce natural tissue morphology (8). This study defines the utilization of the lamb temporal bone (LTB) as a surgical training model for CI. This study particularly emphasizes the training of round window niche (RWN) preparation with 1) drill removal of the bone overhang without damaging the membrane, 2) removal of mucosal folds (pseudomembranes), and 3) vertical incision of the round window membrane (RWM). The overall training goal is to maximize electrode insertion while minimizing intracochlear trauma. Furthermore, the usability of the LTB as a model for training intracochlear electrode insertion is quantified and evaluated. 52
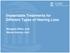
2 LAMB TEMPORAL BONE AS A SURGICAL TRAINING MODEL 53 INTERVENTION Preparations Seven lamb heads (9 12-mo-old) were acquired from a regional slaughterhouse. After skin removal, all heads were fixed in 4% formaldehyde (ph 7.4) for 2 weeks. For dissection the LTB were positioned in a drilling shell in the lateral position (Fig. 1). Soft tissues around the external auditory canal (EAC) and the retroauricular space were removed to expose the mastoidal plane. Landmarks such as the temporal line, the mastoid tip, and the zygoma were identified (Fig. 1, A, B, and E). Four otolaryngology (ENT) surgeons with no, low, moderate, and advanced experience levels participated in the study. Surgical Approach A canal-wall-down mastoidectomy of the nonpneumatized mastoid was performed (Fig. 1). The mastoid FIG. 1. Overview of surgical landmarks on the sheep skull (A, E), in the mastoid (C, G), and in the middle ear (D, H). The imaginary line between the occlusion plane of teeth and the lowest point of the bony external ear canal indicates the position of the round window (A, E). The round window niche is exposed after removal of the eminentia pyramidalis and part of the labyrinth block together with the facial nerve (D, H). The skull should be positioned in the lateral decubitus position with the mouth facing away from the surgeon (E). A conventional (human) temporal bone laboratory is well suited for the procedure, particularly if lamb heads are used (F). EAC indicates external auditory canal; H, hypotympanon; I, incus; LB, labyrinth block; M, malleus; S, stapes; TM, tympanic membrane.
3 54 G. MANTOKOUDIS ET AL. was drilled down to the osseous labyrinth block (LB) (Fig. 1, C and G). The bullous hypotympanon was opened inferiorly to the LB. The malleus and incus were readily identified (Fig. 1, D and H), whereas the stapes was only partially visible. The border of the LB toward the middle ear was drilled down until the stapedial muscle appeared. Further drilling of the eminentia pyramidalis with a smaller Rosen burr exposed the RWN completely. Understanding that this technique is not possible in humans, the facial nerve and the LB were partially removed to optimize the view into the RWN. The round window (RW) is situated in an extended imaginary line between the plane of teeth occlusion and the lowest point of the bony EAC (dotted line in Fig. 1A). Because of the different mastoid and middle ear anatomy compared with humans, a classical posterior tympanotomy could not be performed in the lamb. Round Window Approach and Electrode Array Insertion The overhanging bone of the RWN was completely removed using small diamond drills of 1 to 1.5 mm with a primary goal of preventing damage to the RWM. Any pseudomembranes covering the RWN were removed using microhooks. With particular emphasis on the atraumatic technique, the RWM was vertically incised using a small tympanotomy knife. Finally, the electrode array was inserted through the RWM using specially designed claws or alligator forceps (Fig. 2). Each of the surgeons was asked to insert the maximum number of electrode contacts possible, while aiming for minimal trauma of intracochlear structures. For all experiments, flex24 electrode arrays (MED-EL, Innsbruck, Austria) were used. These human-grade arrays had failed internal quality controls in the company and were shipped to us without the implant stimulator unit for research purposes. Each array with a length of 24 mm and a basal diameter of 0.8 mm features 12 electrode contacts, each with dimensions of 800 mm 500 mm, spaced 1.9 mm apart. This electrode was specifically designed for electro-acoustical stimulation with an emphasis on atraumatic implantation and hearing preservation (22). Control of Electrode Position by CT Scan All LTB were scanned immediately after implantation using a clinical spiral CT scanner (Lightspeed Ultra, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, U.S.A.). A high-resolution CT using a standard clinical protocol (coronal plane, field of view 10 cm) with 140 kv and 65 ma was performed. A standard bone plus reconstruction kernel (reconstruction algorithm) with 68% overlapping section thickness of mm was used. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE Surgical Evaluation The required dissection time was measured, and the surgical performance was self-evaluated by each surgeon regarding the mastoidectomy, round window approach, and electrode insertion. Radiologic Evaluation Electrode insertion was further objectified radiologically. The electrode position, the number of intracochlear electrode contacts, and angular insertion depths were evaluated by a senior staff radiologist on a standard workstation (Easyvision, Philips, Hamburg, Germany). RESULTS Mastoidectomy The exposure of the RW by canal-wall-down mastoidectomy was successful in all attempts, with a mean dissection time of 31 minutes (range, min). All surgeons demonstrated a decreased dissection time of 5 to 10 minutes with repeated procedures. The initial FIG. 2. Carefully prepared round window niche with flex24 electrode array atraumatically inserted through the incised round window membrane.
4 LAMB TEMPORAL BONE AS A SURGICAL TRAINING MODEL 55 FIG. 3. Examples of sheep temporal bone CT scans for angular insertion depths (A) and different intracochlear electrode positions: maximum insertion in scala tympani (B), incomplete insertion (C), malpositioned array in the utricle (D), and intracochlear folding (E). dissection of at least one LTB was required to learn the anatomy and surgical access technique via mastoidectomy. The lamb mastoid is minimally pneumatized and the sigmoid sinus is not in the vicinity to serve as a landmark. Usable anatomical landmarks are the posterior wall of the EAC and the suprameatal (Henle s) spine. The EAC diameter is smaller in the lamb but demonstrates the same axial orientation as in a human. The posterior wall of the lamb EAC has to be completely removed to allow for complete middle ear exposure. The LB was more difficult to identify because of the smaller size and the less pronounced yellowish bone color. Round Window Approach The RWN was always accessible through the proposed approach. The size of the niche was comparable to human anatomy. The three critical tasks of 1) drilling the RWN without damaging the membrane, 2) removal of pseudomembranes, and 3) vertical incision of the RWM were successfully achieved by all surgeons. There was no malformation or anatomical abnormality observed in any of the 14 dissected LTBs. Electrode Insertion The task of maximizing electrode insertion while minimizing intracochlear trauma was perceived as being challenging, particularly by the surgeons with little to no experience. The mean surgical insertion depth was 10.4 mm (range, 4 20 mm), and the mean radiological angular insertion depth was 229 degrees (range, ) around the modiolus. Figure 3A shows the angular definitions and Table 1 the electrode insertion depth for each LTB and for each surgeon. The mean number of electrode contacts inserted was 6.5 (range, 4 11); full insertion of 12 electrode contacts was never achieved. A correlation between insertion depths and the experience of the surgeon was observed; however, because of the limited number of insertions per surgeon, statistical relevance cannot be determined (Table 1). Furthermore, intracochlear array deformation occurred in a total of three (21%) implantations, of which one occurred in the hands of the most experienced surgeon. In addition, half of the trials did terminate in the scala tympani, as six electrodes deviated from the scala tympani to the scala vestibuli (scale shift); one electrode array ended up in the inner ear vestibule (Table 1, Fig. 3D). TABLE 1. Evaluation of CI electrode positions and insertion depths after implantation by four ENT surgeons with different levels of otologic surgical experience Insertion Depth Intracochlear Electrode Course Experience Level # Time (min) (mm) (8) Intracochlear Electrodes No experience Normal ST Misplaced U Normal ST Beginner Folded ST!SV Normal ST Scale shift ST!SV Normal ST Folded ST!SV Scale shift ST!SV Scale shift ST!SV Moderate Normal ST Normal ST Advanced Folded ST!SV Normal ST The implantations are ordered in sequence (#) for each surgeon to allow for assessing the learning effects. ST indicates scala tympani; SV, scala vestibuli; U, utricle.
5 56 G. MANTOKOUDIS ET AL. CONCLUSIONS The LTB is considerably different compared with human anatomy and is therefore unlikely to completely replace HTBs for ear surgery training. However, at the level of the RWN the wide visualization allows for training of the delicate drilling of the bony overhang of the niche, the removal of pseudomembranes without damaging the membrane, and the controlled incision of the RWM. Full electrode insertion could not be achieved and, even in the case of reasonable insertion depths, intracochlear array deformation and scale shifts were observed independently of the surgeon s experience. Therefore, the LTB provides an adequate model to train at the level of the RWN, whereas the minimally pneumatized mastoid as well as the smaller cochlea can help prepare a surgeon for difficult CIs. Acknowledgments: The authors thank the MEDEL corporation for providing the cochlear implant electrodes and Catherine Reid for language editing the manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Taylor F, Hine C. Cochlear implants: Informing commissioning decisions, based on need. J Laryngol Otol 2006;120: George AP, De R. Review of temporal bone dissection teaching: How it was, is and will be. J Laryngol Otol 2010;124: Campbell CS. Research on human tissue: religious perspectives. In: Commission NBA, editor. Research Involving Human Biological Materials: Ethical Issues and Policy Guidance Commisioned Papers. Rockland, MD: National Bioethics Advisory Commission; pp Mori K, Yamamoto T, Oyama K, et al. Modified three-dimensional skull base model with artificial dura mater, cranial nerves, and venous sinuses for training in skull base surgery: Technical note. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2008;48: Schwager K, Gilyoma JM. Ceramic model for temporal bone exercises: An alternative for human temporal bones? Laryngorhinootologie 2003;82: Suzuki M, Ogawa Y, Hagiwara A, et al. Rapidly prototyped temporal bone model for otological education. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 2004;66: Sorensen MS, Mosegaard J, Trier P. The visible ear simulator: A public PC application for GPU-accelerated haptic 3D simulation of ear surgery based on the visible ear data. Otol Neurotol 2009;30: Morris D, Sewell C, Barbagli F, et al. Visuohaptic simulation of bone surgery for training and evaluation. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 2006;26:48 57.
An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani
 An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani T. Just *a, E. Lankenau b, G. Hüttmann b, H.W. Pau a a Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University
An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani T. Just *a, E. Lankenau b, G. Hüttmann b, H.W. Pau a a Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
 COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: A SURGEON S PERSPECTIVE Ravi N. Samy, M.D., F.A.C.S. Ravi.Samy@UC.edu Director, Adult Cochlear Implant Program Program Director, Neurotology Fellowship CONFLICTS OF INTEREST RESEARCH
COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: A SURGEON S PERSPECTIVE Ravi N. Samy, M.D., F.A.C.S. Ravi.Samy@UC.edu Director, Adult Cochlear Implant Program Program Director, Neurotology Fellowship CONFLICTS OF INTEREST RESEARCH
Surgeon Oriented Preoperative Radiologic Evaluation in Cochlear Implantation - Our experience with a Proposed Checklist
 THIEME Original Research Surgeon Oriented Preoperative Radiologic Evaluation in Cochlear Implantation - Our experience with a Proposed Checklist Mahmoud Mandour 1 Mohammed Tomoum 1 Saad El Zayat 2 Hisham
THIEME Original Research Surgeon Oriented Preoperative Radiologic Evaluation in Cochlear Implantation - Our experience with a Proposed Checklist Mahmoud Mandour 1 Mohammed Tomoum 1 Saad El Zayat 2 Hisham
For Professionals. Electrode Arrays. Designed for Atraumatic Implantation Providing Superior Hearing Performance
 For Professionals Electrode Arrays Designed for Atraumatic Implantation Providing Superior Hearing Performance Electrode Arrays Designed for Atraumatic Implantation Providing Superior Hearing Performance,,,
For Professionals Electrode Arrays Designed for Atraumatic Implantation Providing Superior Hearing Performance Electrode Arrays Designed for Atraumatic Implantation Providing Superior Hearing Performance,,,
1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC.
 PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. new implantation method, the combined electric-acoustic stimulation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predicting Basal Cochlear Length for Electric-Acoustic Stimulation Oliver Adunka, MD; Marc H. Unkelbach, MD; Martin G. Mack, MD, PhD; Andreas Radeloff, MD; Wolfgang Gstoettner, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predicting Basal Cochlear Length for Electric-Acoustic Stimulation Oliver Adunka, MD; Marc H. Unkelbach, MD; Martin G. Mack, MD, PhD; Andreas Radeloff, MD; Wolfgang Gstoettner, MD, PhD
Scala Tympani Cochleostomy II: Topography and Histology
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2007 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Scala Tympani Cochleostomy II: Topography and Histology Oliver F. Adunka, MD;
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2007 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Scala Tympani Cochleostomy II: Topography and Histology Oliver F. Adunka, MD;
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual.
 The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
Current Standards in Cochlear Implantation. Preliminary Results of a Survey Among Politzer Society
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(3) 379-384 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Current Standards in Cochlear Implantation. Preliminary Results of a Survey Among Politzer Society Franco Trabalzini, Enrico Muzzi, Eva Orzan Department
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(3) 379-384 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Current Standards in Cochlear Implantation. Preliminary Results of a Survey Among Politzer Society Franco Trabalzini, Enrico Muzzi, Eva Orzan Department
STATE OF THE ART IN COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: CONCEPTS IN MINIMALLY TRAUMATIC SURGERY!
 STATE OF THE ART IN COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: CONCEPTS IN MINIMALLY TRAUMATIC SURGERY! Brendan P. O Connell MD! Assistant Professor! Otology and Neurotology- UNC Chapel Hill! EXPANDING INDICATIONS FOR CONVENTIONAL
STATE OF THE ART IN COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: CONCEPTS IN MINIMALLY TRAUMATIC SURGERY! Brendan P. O Connell MD! Assistant Professor! Otology and Neurotology- UNC Chapel Hill! EXPANDING INDICATIONS FOR CONVENTIONAL
A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study
 A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study By GRAEME M. CLARK (Melbourne) Introduction THERE is now increased interest in the possibility of restoring brain and nerve function by applying
A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study By GRAEME M. CLARK (Melbourne) Introduction THERE is now increased interest in the possibility of restoring brain and nerve function by applying
Our Experience with AB HiFocus MSE Cochlear Implant from Laboratory to OR: Electrode and Access Variables
 Our Experience with AB HiFocus MSE Cochlear Implant from Laboratory to OR: Electrode and Access Variables Sean O McMenomey, David R Friedmann MD, Ling Zhou MD, Stephen Rebscher,* J Thomas Roland, Jr. MD
Our Experience with AB HiFocus MSE Cochlear Implant from Laboratory to OR: Electrode and Access Variables Sean O McMenomey, David R Friedmann MD, Ling Zhou MD, Stephen Rebscher,* J Thomas Roland, Jr. MD
Clinical Workflow. White Paper No. 35 / 2016
 01 The mobile 3D C-arm Ziehm Vision RFD 3D A well-suited tool for intraoperative imaging in cochlear implantation More than 5 % of the world s population 360 million people suffer from hearing loss in
01 The mobile 3D C-arm Ziehm Vision RFD 3D A well-suited tool for intraoperative imaging in cochlear implantation More than 5 % of the world s population 360 million people suffer from hearing loss in
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Optimal electrode diameter in relation to volume of the cochlea
 Optimal electrode diameter in relation to volume of the cochlea Dan Gnansia, Thomas Demarcy, Clair Vandersteen, Charles Raffaelli, Nicolas Guevara, Hervé Delingette, Nicholas Ayache To cite this version:
Optimal electrode diameter in relation to volume of the cochlea Dan Gnansia, Thomas Demarcy, Clair Vandersteen, Charles Raffaelli, Nicolas Guevara, Hervé Delingette, Nicholas Ayache To cite this version:
Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
 Clinical Radiology (2003) 58: 288 293 doi:10.1016/s0009-9260(02)00523-8, available online at www.sciencedirect.com Pictorial Review Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
Clinical Radiology (2003) 58: 288 293 doi:10.1016/s0009-9260(02)00523-8, available online at www.sciencedirect.com Pictorial Review Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation
 Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation David S Haynes, MD FACS Fred F Telischi, MD MEE FACS Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Robert F Labadie, PhD MD Nikolas H Blevins, MD Matthew L. Carlson, MD
Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation David S Haynes, MD FACS Fred F Telischi, MD MEE FACS Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Robert F Labadie, PhD MD Nikolas H Blevins, MD Matthew L. Carlson, MD
Transcanal Endoscopic Approach to the Sinus Tympani: A Clinical Report
 Otology & Neurotology 30:758Y765 Ó 2009, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Transcanal Endoscopic Approach to the Sinus Tympani: A Clinical Report Daniele Marchioni, Francesco Mattioli, Matteo Alicandri-Ciufelli,
Otology & Neurotology 30:758Y765 Ó 2009, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Transcanal Endoscopic Approach to the Sinus Tympani: A Clinical Report Daniele Marchioni, Francesco Mattioli, Matteo Alicandri-Ciufelli,
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Exposure of facial nerve and endolymphatic sac
 Exposure of facial nerve and endolymphatic sac 1 7 4 2 3 5 6 8 1 Vertical part of the facial nerve exposed 1 Second genu of facial nerve. 2 Vertical part of facial nerve. 3 Horizontal part of facial nerve.
Exposure of facial nerve and endolymphatic sac 1 7 4 2 3 5 6 8 1 Vertical part of the facial nerve exposed 1 Second genu of facial nerve. 2 Vertical part of facial nerve. 3 Horizontal part of facial nerve.
Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy
 Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
TWO MEDICAL IMAGING PROCESSING TECHNIQUES FOR USE IN ACOUSTIC NEUROMA REMOVAL AND COCHLEAR PROSTHETIC IMPLANTATION. Kepra L McBrayer.
 TWO MEDICAL IMAGING PROCESSING TECHNIQUES FOR USE IN ACOUSTIC NEUROMA REMOVAL AND COCHLEAR PROSTHETIC IMPLANTATION By Kepra L McBrayer Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt
TWO MEDICAL IMAGING PROCESSING TECHNIQUES FOR USE IN ACOUSTIC NEUROMA REMOVAL AND COCHLEAR PROSTHETIC IMPLANTATION By Kepra L McBrayer Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt
Mi1000 CONCERTO PIN Surgical Guideline
 Cochlear Implants Mi1000 CONCERTO PIN Surgical Guideline AW7694_6.0 (English EU) Introduction The MED EL Cochlear Implant System serves to restore hearing sensations through electrical stimulation of the
Cochlear Implants Mi1000 CONCERTO PIN Surgical Guideline AW7694_6.0 (English EU) Introduction The MED EL Cochlear Implant System serves to restore hearing sensations through electrical stimulation of the
Insertion of electrode array using percutaneous cochlear implantation technique: a cadaveric study
 Insertion of electrode array using percutaneous cochlear implantation technique: a cadaveric study Ramya Balachandran 1, Jason E. Mitchell 2, Jack Noble 3, Daniel Schurzig 1, Grégoire Blachon 1, Theodore
Insertion of electrode array using percutaneous cochlear implantation technique: a cadaveric study Ramya Balachandran 1, Jason E. Mitchell 2, Jack Noble 3, Daniel Schurzig 1, Grégoire Blachon 1, Theodore
Mi1200 SYNCHRONY PIN Surgical Guideline
 Cochlear Implants Mi1200 SYNCHRONY PIN Surgical Guideline AW32150_1.0 (English EU) Introduction The MED EL Cochlear Implant System serves to restore hearing sensations through electrical stimulation of
Cochlear Implants Mi1200 SYNCHRONY PIN Surgical Guideline AW32150_1.0 (English EU) Introduction The MED EL Cochlear Implant System serves to restore hearing sensations through electrical stimulation of
87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE
 87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN November
87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN November
Narrowest segment of the ear canal. Limited microscopic. Wide endoscopic. field of view. field of view
 Endoscopic Transcanal Management of Cholesteatoma M. Tarabichi American Hospital-Dubai The Endoscope in Otology Mostly for documentation. Mostly diagnostic. Exploration of old mastoid cavities Endoscopic
Endoscopic Transcanal Management of Cholesteatoma M. Tarabichi American Hospital-Dubai The Endoscope in Otology Mostly for documentation. Mostly diagnostic. Exploration of old mastoid cavities Endoscopic
Clinical Study Imaging of Electrode Position after Cochlear Implantation with Flat Panel CT
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 728205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/728205 Clinical Study Imaging of Electrode Position after Cochlear Implantation with
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 728205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/728205 Clinical Study Imaging of Electrode Position after Cochlear Implantation with
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE
 84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN March 5-6,
84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN March 5-6,
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology
 3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
UC SF. Safe Surgery Rule #1. Cholesteatoma. It s hard to have a surgical complication when you are not operating
 UC SF Cholesteatoma Chronic Ear Surgery: Staying Out of Trouble! Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Department of Oto-HNS University of California San Francisco Ligaments and folds Spaces NU Epitympanic Cholesteatoma
UC SF Cholesteatoma Chronic Ear Surgery: Staying Out of Trouble! Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Department of Oto-HNS University of California San Francisco Ligaments and folds Spaces NU Epitympanic Cholesteatoma
Pediatric Temporal Bone
 Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
Surgery for Congenital Ear Malformations
 21 Surgery for Congenital Ear Malformations Robert A. Jahrsdoerfer and Bradley W. Kesser Classification Congenital malformations of the ear can be broadly classified into two categories: Minor malformations
21 Surgery for Congenital Ear Malformations Robert A. Jahrsdoerfer and Bradley W. Kesser Classification Congenital malformations of the ear can be broadly classified into two categories: Minor malformations
Residual Hearing Preservation After Cochlear Implantation via Round Window or Cochleostomy Approach
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Residual Hearing reservation After Cochlear Implantation via Round Window or Cochleostomy Approach Chuan-Hung
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Residual Hearing reservation After Cochlear Implantation via Round Window or Cochleostomy Approach Chuan-Hung
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Mi1000 CONCERTO Surgical Guideline
 Cochlear Implants ACHTUNG: U1, U2, U3 und U4 aus dem PDF für den DRUCK löschen (hier gibt es ein extra Coverfile für den Druck) Das WEB PDF soll U1-U4 beinhalten! Mi1000 CONCERTO Surgical Guideline AW7617_7.0
Cochlear Implants ACHTUNG: U1, U2, U3 und U4 aus dem PDF für den DRUCK löschen (hier gibt es ein extra Coverfile für den Druck) Das WEB PDF soll U1-U4 beinhalten! Mi1000 CONCERTO Surgical Guideline AW7617_7.0
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma. Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
SEMICIRCULAR CANAL ANATOMY AS SEEN IN MICRODISSECTION
 SUMMARY SEMICIRCULAR CANAL ANATOMY AS SEEN IN MICRODISSECTION Nguyen Thanh Vinh*; Tran Ngọc Anh** Nguyen Hoang Vu***; Le Gia Vinh****; Pham Ngoc Chat***** Objectives: To investigate semicircular canal
SUMMARY SEMICIRCULAR CANAL ANATOMY AS SEEN IN MICRODISSECTION Nguyen Thanh Vinh*; Tran Ngọc Anh** Nguyen Hoang Vu***; Le Gia Vinh****; Pham Ngoc Chat***** Objectives: To investigate semicircular canal
OTOLOGY. 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training.
 OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children
 CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children Michele H. Johnson, M. Suzanne Hasenstab, Michael A. Seicshnaydre, and George H. Williams PURPOSE: To
CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children Michele H. Johnson, M. Suzanne Hasenstab, Michael A. Seicshnaydre, and George H. Williams PURPOSE: To
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Preoperative Assessment for Cochlear Implant
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Preoperative Assessment for Cochlear Implant Eshrak Hassanein MD; Eman Geneidi MD; and Mohamed Taha MD From the Departments of Radiology (E.Hassanein), Otorhinolaryngology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Preoperative Assessment for Cochlear Implant Eshrak Hassanein MD; Eman Geneidi MD; and Mohamed Taha MD From the Departments of Radiology (E.Hassanein), Otorhinolaryngology
The fine anatomy of the round-window niche
 International Tinnitus Journal, Vol. 11, No.2, 158-162 (2005) Standardized Computed Tomographic Imaging and Dimensions of the Round-Window Niche David Cohen,1 George Blinder,2 Ronen Perez,! and David Raveh3
International Tinnitus Journal, Vol. 11, No.2, 158-162 (2005) Standardized Computed Tomographic Imaging and Dimensions of the Round-Window Niche David Cohen,1 George Blinder,2 Ronen Perez,! and David Raveh3
WHAT IS MANAGEMENT IN PDT?
 H. Skarżyński, ż ń ki A. Lorens, M. Porowski, PH P.H. Skarżyński, ż ń ki Ł. Olszewski IN WARSAW COCHLEAR IMPLANT PROGRAM (1992 2010) WHAT IS MANAGEMENT IN PDT? C. NEW INDICATIONS SELECTIONS OF CANDIDATES
H. Skarżyński, ż ń ki A. Lorens, M. Porowski, PH P.H. Skarżyński, ż ń ki Ł. Olszewski IN WARSAW COCHLEAR IMPLANT PROGRAM (1992 2010) WHAT IS MANAGEMENT IN PDT? C. NEW INDICATIONS SELECTIONS OF CANDIDATES
Electrode Trauma Assessed by Microdissection
 Electrode Trauma Assessed by Microdissection Peter S Roland MD C Gary Wright PhD University of Texas Medical Center Dallas, Texas Why worry about electrode trauma? Bilateral Implants Electro-acoustic implants
Electrode Trauma Assessed by Microdissection Peter S Roland MD C Gary Wright PhD University of Texas Medical Center Dallas, Texas Why worry about electrode trauma? Bilateral Implants Electro-acoustic implants
Research Article Semiautomatic Cochleostomy Target and Insertion Trajectory Planning for Minimally Invasive Cochlear Implantation
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research ternational Volume 2014, Article ID 596498, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/596498 Research Article Semiautomatic Cochleostomy Target and sertion Trajectory
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research ternational Volume 2014, Article ID 596498, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/596498 Research Article Semiautomatic Cochleostomy Target and sertion Trajectory
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Utku Aydil, Ali Koksal, Tuncay Ozcelik, Nuri Ozgirgin
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2010; 6:(3) 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Reformatted Two-Dimensional Images with Three-Dimensional Reconstructions Based on Images from Multi-Detector Computed Tomography of the
Int. Adv. Otol. 2010; 6:(3) 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Reformatted Two-Dimensional Images with Three-Dimensional Reconstructions Based on Images from Multi-Detector Computed Tomography of the
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
The number of cochlear implantations is increasing rapidly,
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Radiologic and Functional Evaluation of Electrode Dislocation from the Scala Tympani to the Scala Vestibuli in Patients with Cochlear Implants N. Fischer, L. Pinggera, V.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Radiologic and Functional Evaluation of Electrode Dislocation from the Scala Tympani to the Scala Vestibuli in Patients with Cochlear Implants N. Fischer, L. Pinggera, V.
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
MICROTIA. The condition is a complex mix of cosmetic, functional, and often psychological difficulties. Microtia: Not only the ear.
 MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
Physiologic Consequences of Intracochlear Electrode Placement. Oliver F. Adunka, MD, FACS Craig A. Buchman, MD, FACS Douglas C.
 Physiologic Consequences of Intracochlear Electrode Placement Oliver F. Adunka, MD, FACS Craig A. Buchman, MD, FACS Douglas C. Fitzpatrick, PhD Disclosures Advisory Board» MED-EL North America» Advanced
Physiologic Consequences of Intracochlear Electrode Placement Oliver F. Adunka, MD, FACS Craig A. Buchman, MD, FACS Douglas C. Fitzpatrick, PhD Disclosures Advisory Board» MED-EL North America» Advanced
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY
 NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
trauma? Bilateral Implants Electro-acoustic implants Preservation of ganglion cells?
 Electrode Trauma Assessed by Microdissection Peter S Roland MD C Gary Wright PhD University of Texas Medical Center Dallas, Texas Why worry about electrode trauma? Bilateral Implants Electro-acoustic implants
Electrode Trauma Assessed by Microdissection Peter S Roland MD C Gary Wright PhD University of Texas Medical Center Dallas, Texas Why worry about electrode trauma? Bilateral Implants Electro-acoustic implants
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Pediatric Ear Diseases
 Pediatric Ear Diseases Yasushi Naito Pediatric Ear Diseases Diagnostic Imaging Atlas and Case Reports 242 figures, 7 in color and 5 tables, 2013 Basel Freiburg Paris London New York New Delhi Bangkok
Pediatric Ear Diseases Yasushi Naito Pediatric Ear Diseases Diagnostic Imaging Atlas and Case Reports 242 figures, 7 in color and 5 tables, 2013 Basel Freiburg Paris London New York New Delhi Bangkok
ALESSANDRA RUSSO MD GRUPPO OTOLOGICO
 Gruppo Otologico Simultaneous Labyrinthectomy with Cochlear Implantation Cenacolo di Audiovestibologia, Chieti, 24-25/06/2016 ALESSANDRA RUSSO MD GRUPPO OTOLOGICO MENIERE DISEASE Therapeutic Steps 1 step
Gruppo Otologico Simultaneous Labyrinthectomy with Cochlear Implantation Cenacolo di Audiovestibologia, Chieti, 24-25/06/2016 ALESSANDRA RUSSO MD GRUPPO OTOLOGICO MENIERE DISEASE Therapeutic Steps 1 step
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Imaging in patients undergoing cochlear implant: CT and MR technique
 Imaging in patients undergoing cochlear implant: CT and MR technique Poster No.: C-0102 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Posillico Keywords: Ear / Nose / Throat, CT, MR, Comparative
Imaging in patients undergoing cochlear implant: CT and MR technique Poster No.: C-0102 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Posillico Keywords: Ear / Nose / Throat, CT, MR, Comparative
Cochlear Implantation through the Middle Fossa Approach: A Review of Related Temporal Bone Studies and Reported Cases
 102 Systematic Review THIEME Cochlear Implantation through the Middle Fossa Approach: A Review of Related Temporal Bone Studies and Reported Cases Juan Carlos Cisneros Lesser 1,2 Rubens Vuono de Brito
102 Systematic Review THIEME Cochlear Implantation through the Middle Fossa Approach: A Review of Related Temporal Bone Studies and Reported Cases Juan Carlos Cisneros Lesser 1,2 Rubens Vuono de Brito
Implantable Treatments for Different Types of Hearing Loss. Margaret Dillon, AuD Marcia Adunka, AuD
 Implantable Treatments for Different Types of Hearing Loss Margaret Dillon, AuD Marcia Adunka, AuD Implantable Technologies Types of hearing loss Bone-anchored devices Middle ear implantation Cochlear
Implantable Treatments for Different Types of Hearing Loss Margaret Dillon, AuD Marcia Adunka, AuD Implantable Technologies Types of hearing loss Bone-anchored devices Middle ear implantation Cochlear
CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY
 VolumeS Medicalloumal of the Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3,4 Payiz & Zemestan 1370 Fall & Winter 1991 CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY D. SAYIC, MD, DMS:
VolumeS Medicalloumal of the Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3,4 Payiz & Zemestan 1370 Fall & Winter 1991 CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY D. SAYIC, MD, DMS:
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Research Article The Construct Validity and Reliability of an Assessment Tool for Competency in Cochlear Implant Surgery
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 192741, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/192741 Research Article The Construct Validity and Reliability of an Assessment Tool for Competency in Cochlear
BioMed Research International, Article ID 192741, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/192741 Research Article The Construct Validity and Reliability of an Assessment Tool for Competency in Cochlear
Round window chamber and fustis: endoscopic anatomy and surgical implications
 Round window chamber and fustis: endoscopic anatomy and surgical implications Daniele Marchioni, Davide Soloperto, Elena Colleselli, Maria Fatima Tatti, Nirmal Patel & Nicholas Jufas Surgical and Radiologic
Round window chamber and fustis: endoscopic anatomy and surgical implications Daniele Marchioni, Davide Soloperto, Elena Colleselli, Maria Fatima Tatti, Nirmal Patel & Nicholas Jufas Surgical and Radiologic
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab
 Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
KEYHOLE COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION
 KEYHOLE COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION BRISBANE 1997- Site preparation, Lt. An adhesive drape is fixed around the site by close stapling to exclude hair from the site. A hair shave is unnecessary. A staple over
KEYHOLE COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION BRISBANE 1997- Site preparation, Lt. An adhesive drape is fixed around the site by close stapling to exclude hair from the site. A hair shave is unnecessary. A staple over
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the human middle ear and an application for clinics for tympanoplasty
 Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics XI 61 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the human middle ear and an application for clinics for tympanoplasty T. Higashimachi 1, Y. Shiratake 2, T. Maeda
Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics XI 61 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the human middle ear and an application for clinics for tympanoplasty T. Higashimachi 1, Y. Shiratake 2, T. Maeda
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
A COMPARISON OF IMPEDANCES, DYNAMIC RANGES AND NRTs FOR THE NUCLEUS 422 AND CONTOUR ELECTRODE ARRAYS
 A COMPARISON OF IMPEDANCES, DYNAMIC RANGES AND NRTs FOR THE NUCLEUS 422 AND CONTOUR ELECTRODE ARRAYS December 13, 2014! Sandra Velandia, AuD! Ear Institute, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami!
A COMPARISON OF IMPEDANCES, DYNAMIC RANGES AND NRTs FOR THE NUCLEUS 422 AND CONTOUR ELECTRODE ARRAYS December 13, 2014! Sandra Velandia, AuD! Ear Institute, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami!
Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear
 Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear Yanfei Lu 1,* 1 Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Institute of Mechanics and Printing, Department
Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear Yanfei Lu 1,* 1 Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Institute of Mechanics and Printing, Department
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 10 Page October 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Direct round window stimulation with the Med-El Vibrant Soundbridge: 5 years of experience using a technique without interposed fascia
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2014) 271:477 482 DOI 10.1007/s00405-013-2432-1 OTOLOGY Direct round window stimulation with the Med-El Vibrant Soundbridge: 5 years of experience using a technique without interposed
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2014) 271:477 482 DOI 10.1007/s00405-013-2432-1 OTOLOGY Direct round window stimulation with the Med-El Vibrant Soundbridge: 5 years of experience using a technique without interposed
Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery. Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery. Preoperative Considerations
 Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery David S. Haynes, MD, FACS The Otology Group of Vanderbilt Professor, Dept. of Otolaryngology, Professor Dept. of Neurosurgery Professor,
Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery Principles of Chronic Ear Surgery David S. Haynes, MD, FACS The Otology Group of Vanderbilt Professor, Dept. of Otolaryngology, Professor Dept. of Neurosurgery Professor,
The Vibrant Soundbridge
 REVIEW RTICLE IJOC Emeritus Professor, Padmashree Dr DY Patil Medical College, Honorary Consultant, Lilavati Hospital and Medical Research Center, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Correspondence:, Om partments,
REVIEW RTICLE IJOC Emeritus Professor, Padmashree Dr DY Patil Medical College, Honorary Consultant, Lilavati Hospital and Medical Research Center, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Correspondence:, Om partments,
Added Value of MDCT in Cochlear Parameters Assessment in Patients with Sensory Neural Hearing Loss Candidates for Cochlear Implantation
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(4): 33-39 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20180604.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Added Value of
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(4): 33-39 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20180604.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Added Value of
Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface
 Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface Christopher Wong 1, 4, Ian S. Curthoys 2, Stephen O Leary 3,4, Allan S. Jones 1 1 Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of
Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface Christopher Wong 1, 4, Ian S. Curthoys 2, Stephen O Leary 3,4, Allan S. Jones 1 1 Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of
Skull Base Course. Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads
 Skull Base Course Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads 711 November 2016 Gruppo Otologico Via Emmanueli 42 Piacenza 29122 t +39 0523 754 362 fax +39 0523 453 708 www.gruppootologico.com
Skull Base Course Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads 711 November 2016 Gruppo Otologico Via Emmanueli 42 Piacenza 29122 t +39 0523 754 362 fax +39 0523 453 708 www.gruppootologico.com
Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:322 327, February 2000 Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies Barbara Zeifer, Paul Sabini, and Jonathan Sonne BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:322 327, February 2000 Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies Barbara Zeifer, Paul Sabini, and Jonathan Sonne BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D.
 Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness. Bruce Black MD
 COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness Heterochromia iridis. Cases may be healthy or associated with a variety of conditions, e.g. Waardenburg syndrome. Waardenburg syndrome. Note the snowy lock of hair
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness Heterochromia iridis. Cases may be healthy or associated with a variety of conditions, e.g. Waardenburg syndrome. Waardenburg syndrome. Note the snowy lock of hair
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.66 Auditory Brainstem Implant Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 7.01.66 Auditory Brainstem Implant Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
CETACEAN EAR EXTRACTION AND FIXATION PROTOCOL
 CETACEAN EAR EXTRACTION AND FIXATION PROTOCOL Introduction There is an increasing concern about the impacts of anthropogenic underwater noise on cetacean populations. For this reason, the analysis of the
CETACEAN EAR EXTRACTION AND FIXATION PROTOCOL Introduction There is an increasing concern about the impacts of anthropogenic underwater noise on cetacean populations. For this reason, the analysis of the
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Research Article MRI-Based Estimation of Scalar Cochlear-Implant Electrode Position
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 6372704, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6372704 Research Article MRI-Based Estimation of Scalar Cochlear-Implant Electrode Position A.
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 6372704, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6372704 Research Article MRI-Based Estimation of Scalar Cochlear-Implant Electrode Position A.
Cochlear Implants and Electrodes Surgical Products Catalogue
 Cochlear Implants and Electrodes Surgical Products Catalogue A Sonova brand 028-M860-03 RevC US Surgical Products Catalogue.indd 1 14/11/2017 08:22:28 Table of Contents Implant and Electrode Portfolio...3
Cochlear Implants and Electrodes Surgical Products Catalogue A Sonova brand 028-M860-03 RevC US Surgical Products Catalogue.indd 1 14/11/2017 08:22:28 Table of Contents Implant and Electrode Portfolio...3
Finite Element Analysis of the Human Middle Ear and an Application for Clinics for Tympanoplasty (Static and Harmonic Vibration Analysis)
 2015 American Transactions on Engineering & Applied Sciences. American Transactions on Engineering & Applied Sciences http://tuengr.com/ateas Finite Element Analysis of the Human Middle Ear and an Application
2015 American Transactions on Engineering & Applied Sciences. American Transactions on Engineering & Applied Sciences http://tuengr.com/ateas Finite Element Analysis of the Human Middle Ear and an Application
Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss
 Arnold W, Häusler R (eds): Otosclerosis and Stapes Surgery. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 7, vol 65, pp 137 145 Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss Saumil
Arnold W, Häusler R (eds): Otosclerosis and Stapes Surgery. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 7, vol 65, pp 137 145 Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss Saumil
