CS 544 Human Abilities
|
|
|
- Harold Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 544 Human Abilities Human Information Processing Memory, Chunking & Phrasing, Modes Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul Greenberg (University of Calgary), Ravin Balakrishnan (University of Toronto), James Landay (University of California at Berkeley), monica schraefel (University of Toronto), and Colin Ware (University of New Hampshire). Used with the permission of the respective original authors. 1 Model Human (MHP) Developed by Card, Moran, & Newell The Psychology of Human-Computer Interaction, 1983 Long-term Memory (LTM) sensory buffers (Dix) Visual Image Working Memory (WM) Auditory Image Eyes Ears Perceptual Motor Cognitive 2 Fingers, etc.
2 MHP Basics sensory buffers (Dix) Visual Image Long-term Memory (LTM) Working Memory (WM) Auditory Image 3 Eyes Ears Perceptual Motor Process or Cognitive Based on empirical data Fingers, etc. Three interacting subsystems perceptual, motor, cognitive Sometimes serial, sometimes parallel serial in action & parallel in recognition pressing key in response to light driving, reading signs, & hearing at once Parameters processors have cycle time (T) ~ ms memories have capacity, decay time, & type (physical, acoustic, visual, semantic) Memory Working memory (short term) activated elements of LTM small capacity (7 ± 2 chunks ) vs. (617) Ears DECIBMGMC vs. DEC IBM GMC rapid access (~ 70ms) & decay (~200 ms) pass to LTM after a few seconds Long-term memory huge (if not unlimited ) slower access time (~100 ms) with little decay Eyes sensory buffers (Dix) Perceptual Visual Image Long-term Memory (LTM) Working Memory (WM) Auditory Image Motor Fingers, etc. Cognitive 4
3 MHP Principles of Operation Recognize-Act Cycle of the Cognitive (analogous to fetch-execute cycle in computers) on each cycle contents in WM initiate actions associatively linked to them in LTM ( recognize ) actions modify the contents of WM ( act ) Discrimination Principle retrieval is determined by candidates that exist in memory relative to retrieval cues interference: other memory chunks may be more strongly activated by the associations used as retrieval cues 5 Variable Cognitive Rate Principle CP cycle time T c is shorter when greater effort is induced by increased task demands/information also decreases with practice What s missing from MHP? Haptic memory for touch Moving from sensory memory to WM attention filters stimuli & passes to WM Moving from WM to LTM rehearsal Long-term Memory (LTM) Working Memory (WM) sensory buffers (Dix) Visual Image Auditory Image Eyes Ears Perceptual Motor Cognitive 6 Fingers, etc.
4 Perception Stimuli that occur within one PP cycle fuse into a single concept frame rate necessary for movies to look real? time for 1 frame < Tp (100 msec) -> 10 frame/sec. for some Tp < 100 msec -> 20 frame/sec max. morse code rate can be similarly calculated 7 Volumetric Display (fusing of 2D images to create 3D) 8
5 Perception Perceptual causality two distinct stimuli can fuse if the first event appears to cause the other events must occur in the same cycle 9 Perceptual Causality How soon must red ball move after cue ball collides with it? must move in < Tp (100 msec) 10
6 Simple experiment Volunteer Start saying colors you see in list of words when slide comes up as fast as you can Say done when finished Everyone else time it 11 Green White Yellow Red Black Blue 12
7 Simple Experiment Do it again 13 Paper Back Home Schedule Change Page 14
8 Simple Experiment Do it again 15 Blue Red Black White Green Yellow 16
9 Memory Interference two strong cues in working memory link to different chunks in long term memory Why learn about memory? know what s behind many HCI techniques helps you understand what users will get aging population of users 17 Stage Theory maintenance rehearsal Sensory Image Working Memory Long Term Memory decay decay, displacement chunking / elaboration decay? interference? Working memory is small temporary storage decay displacement Maintenance rehearsal rote repetition not enough to learn information well Answer to problem is organization Faith Age Cold Idea Value Past Large In a show of faith, the cold boy ran past the church 18
10 Elaboration Sensory Image Working Memory maintenance rehearsal Long Term Memory decay decay, displacement chunking / elaboration decay? interference? Attach meaning (make a story) e.g., sentences Visual imagery Organize (chunking) Link to existing knowledge, categories 19 Forgetting in Long Term Memory Causes for not remembering an item? 1) never stored: encoding failure 2) gone from storage: storage failure 3) can t get out of storage: retrieval failure Interference model of forgetting one item reduces ability to retrieve another proactive interference (3) earlier learning reduces ability to retrieve later info e.g., drive to your old house instead of the new one retroactive interference (3 & 2) later learning reduces the ability to retrieve earlier info e.g., change telephone numbers, can t remember the original 20
11 Recognition over Recall Recall info reproduced from memory Recognition presentation of info provides knowledge that info has been seen before easier because of cues to retrieval E.g., Command line (recall) vs. GUI (recognition) interfaces (remember Nielson s Heuristic #6) 21 Facilitating Retrieval: Cues Any stimulus that improves retrieval example: giving hints other examples in software? icons, labels, menu names, etc. Anything related to item or situation where it was learned Can facilitate memory in any system What are we taking advantage of? recognition over recall! 22
12 Attention Filter in brain Focus on certain things Ignore the rest sensory buffers (Dix) Visual Image Long-term Memory (LTM) Working Memory (WM) Auditory Image 3 types Selective Choose one thing to focus on Divided Try to focus on more than 1 thing at once Captured Eyes Ears Perceptual Stimuli that gets peoples attention Motor Fingers, etc. Cognitive 23 Selective Attention Pick one thing to focus on, amongst many possibilities Eye movement to item of interest Head movement to sounds of interest Cocktail party effect Ability to tune out numerous conversations in same vicinity and focus on just one Single locus of attention 24
13 Divided Attention Do multiple tasks Either simultaneous or time multiplexed (rapidly alternate) Can degrade performance If combined tasks exceed human abilities Interference between tasks 25 Chunking & UI Design Remember: 7±2 Create cognitive chunks: Progress from general to specific Menubar example from: 26
14 Chunking & UI Design Chunking menus: Not enough groups Too many groups Just right? Menubar example from: 27 Chunking & UI Design Visual separation Use whitespace to separate info into groups Visual differentiation Change visual characteristics of different groups to cause chunking Visual progression Rely on visual and cognitive cues to guide order in which users internalize information Button1 Button2 Button3 Button1 Button2 Button3 button example from: 28
15 Chunking & UI Design Visual separation Use whitespace to separate info into groups Visual differentiation Change visual characteristics of different groups to cause chunking Visual progression Rely on visual and cognitive cues to guide order in which users internalize information 29 Dialog box example from: Gestures Sequence of actions completed automatically once set in motion E.g., typing the word the Single gesture for experienced typist Three gestures for novice typist E.g., keying in phone numbers, passwords Haptic analogue to cognitive chunking UI guideline: facilitate gestures/phrases that result in haptic chunking 30
16 Modes Relates to how interfaces responds to a given gesture In a mode if interpretation of a gesture is constant In a different mode if gesture interpreted differently E.g., tapping Enter key Inserts return character into text in one mode executes a command in another mode Can be troublesome E.g., CapsLock key!@#$@#% Causes mode errors 31 Minimizing mode errors Do not have modes! Ensure modes distinctively marked Ensure commands required in different modes are different i.e., gesture issued in a wrong mode will not result in difficulty 32
17 Quasimodes Kinesthetically maintained modes e.g., holding shift key rather than CapsLock do not cause mode errors 33 The hunchback of Notre Dame (from Raskin, The Humane Interface, pg 55) Noun-Verb vs. Verb-Noun dialogues E.g., change font of a paragraph of text 2 ways to do it: Choose verb (change font) first Then select noun (paragraph) to which verb applies or Choose noun first, then apply verb What s the difference? 34
18 Noun-Verb interaction preferred (sometimes called Selection-Action) Error reduction Verb-noun is modal. Once command (verb) is selected, it effects next selection (noun). If there s a delay between actions, and wrong selection made, results can be surprising Noun-verb is non-modal Command (verb) executed immediately when issued 35 Noun-Verb interaction preferred Speed Attention remains on item of interest First on content/selection (noun), then on action (verb) (in verb-noun, attention moves from content to action and back to content again. Noun-verb uses one less attention switch) Simple & Reversible No escape/cancel operation needed (in verb-noun, if you issue a command and want to cancel it, have to explicitly issue cancel operation. In noun-verb, just select something else). 36 Is noun-verb always possible?
19 Readings Dix A., J. et al. (1993). Human-Computer Interaction, Second Edition. Sections 1.1 and 1.3. Buxton, W. (1986). Chunking and Phrasing and the design of human-computer dialogues (Reprinted in BGBG, ). 37
CS160: Sensori-motor Models. Prof Canny
 CS160: Sensori-motor Models Prof Canny 1 Why Model Human Performance? To test understanding of behavior To predict impact of new technology we can build a simulator to evaluate user interface designs 2
CS160: Sensori-motor Models Prof Canny 1 Why Model Human Performance? To test understanding of behavior To predict impact of new technology we can build a simulator to evaluate user interface designs 2
Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition. Hall of Shame! Hall of Fame or Shame? Hall of Shame! Outline
 Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington CSE 440 Winter 2012 2 Hall of Shame! Hall of Fame or Shame? Error Messages Where is error? What
Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington CSE 440 Winter 2012 2 Hall of Shame! Hall of Fame or Shame? Error Messages Where is error? What
Human Information Processing
 Human Information Processing CS160: User Interfaces John Canny. Topics The Model Human Processor Memory Fitt s law and Power Law of Practice Why Model Human Performance? Why Model Human Performance? To
Human Information Processing CS160: User Interfaces John Canny. Topics The Model Human Processor Memory Fitt s law and Power Law of Practice Why Model Human Performance? Why Model Human Performance? To
IPM 12/13 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system
 IPM 12/13 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Licenciatura em Ciência de Computadores Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by
IPM 12/13 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Licenciatura em Ciência de Computadores Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by
Human Information Processing. CS160: User Interfaces John Canny
 Human Information Processing CS160: User Interfaces John Canny Review Paper prototyping Key part of early design cycle Fast and cheap, allows more improvements early Formative user study Experimenters
Human Information Processing CS160: User Interfaces John Canny Review Paper prototyping Key part of early design cycle Fast and cheap, allows more improvements early Formative user study Experimenters
Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition. Hall of Shame! Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition. Outline. Video Prototype Review
 Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington Autumn 2008 October 21, 2008 2 Hall of Shame! Design based on a top retailer s site In study, user
Hall of Fame or Shame? Human Abilities: Vision & Cognition Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington Autumn 2008 October 21, 2008 2 Hall of Shame! Design based on a top retailer s site In study, user
SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system
 SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British
SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British
Optical Illusions 4/5. Optical Illusions 2/5. Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5. Reading. Reading. Fang Chen Spring 2004
 Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I. Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad
 Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad In the Last Lecture Vision Color Theory 3D Vision Reading Hearing Human Ear Processing Sound Touch (Haptic Perception)
Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad In the Last Lecture Vision Color Theory 3D Vision Reading Hearing Human Ear Processing Sound Touch (Haptic Perception)
Human cogition. Human Cognition. Optical Illusions. Human cognition. Optical Illusions. Optical Illusions
 Human Cognition Fang Chen Chalmers University of Technology Human cogition Perception and recognition Attention, emotion Learning Reading, speaking, and listening Problem solving, planning, reasoning,
Human Cognition Fang Chen Chalmers University of Technology Human cogition Perception and recognition Attention, emotion Learning Reading, speaking, and listening Problem solving, planning, reasoning,
Human Abilities: Vision, Memory and Cognition. Oct 14, 2016
 Human Abilities: Vision, Memory and Cognition Oct 14, 2016 Milestone I How many users? Depends Fall 2016 COMP 3020 2 Midterm True or false Multiple choice Short answer Fall 2016 COMP 3020 3 Midterm sample
Human Abilities: Vision, Memory and Cognition Oct 14, 2016 Milestone I How many users? Depends Fall 2016 COMP 3020 2 Midterm True or false Multiple choice Short answer Fall 2016 COMP 3020 3 Midterm sample
Cognition. Mid-term 1. Top topics for Mid Term 1. Heads up! Mid-term exam next week
 Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger Mid-term 1 Heads up! Mid-term exam next week Chapters 2, 3, of the textbook Perception, Attention, Short-term memory The lectures are to help you digest the chapters; exams
Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger Mid-term 1 Heads up! Mid-term exam next week Chapters 2, 3, of the textbook Perception, Attention, Short-term memory The lectures are to help you digest the chapters; exams
MEMORY. Announcements. Practice Question 2. Practice Question 1 10/3/2012. Next Quiz available Oct 11
 Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Human Abilities 2. How do people think? Universal Design
 Human Abilities 2 How do people think? Universal Design Agenda ØRevisit Brainstorming ØMemory ØCognitive Processes v Implications ØUniversal Design ØRecap ØHomework and Project Fall 2018 PSYCH / CS 6755
Human Abilities 2 How do people think? Universal Design Agenda ØRevisit Brainstorming ØMemory ØCognitive Processes v Implications ØUniversal Design ØRecap ØHomework and Project Fall 2018 PSYCH / CS 6755
HUMAN ABILITIES...and their implications for design
 Maya Cakmak, Matt Kay, Brad Jacobson, King Xia HUMAN ABILITIES...and their implications for design human-computer interaction CSE 440 WINTER 2015 JAN 29 - WEEK 4 - THURSDAY Today Re-cap for Assignment
Maya Cakmak, Matt Kay, Brad Jacobson, King Xia HUMAN ABILITIES...and their implications for design human-computer interaction CSE 440 WINTER 2015 JAN 29 - WEEK 4 - THURSDAY Today Re-cap for Assignment
Users. Perception and Cognition
 Users Perception and Cognition This lecture relies on Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson, The Humane Interface by Jef Raskin, and other sources. 1 Ergonomics and Human Factors Designing devices
Users Perception and Cognition This lecture relies on Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson, The Humane Interface by Jef Raskin, and other sources. 1 Ergonomics and Human Factors Designing devices
CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation
 CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation Human Computer Interaction Ute Schmid Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University last change May 22, 2007 CogSysIII Lecture
CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation Human Computer Interaction Ute Schmid Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University last change May 22, 2007 CogSysIII Lecture
Outline 3/14/2013. Practice question What are the two types of learning we discussed? Example: remembering our ATM PIN. PSYC 120 General Psychology
 Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
How should you study for Friday's exam?
 How should you study for Friday's exam? re-read textbook? re-read lecture slides? study guide? NO! these are passive. Use active study. Test yourself by Take the practice quizzes in Moodle Create your
How should you study for Friday's exam? re-read textbook? re-read lecture slides? study guide? NO! these are passive. Use active study. Test yourself by Take the practice quizzes in Moodle Create your
ASHI 712. The Neuroscience of Human Memory. Dr. Olave E. Krigolson LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory
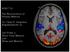 ASHI 712 The Neuroscience of Human Memory Dr. Olave E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory Working / Short Term Memory Sunglasses Chair Dress Earrings Boots Bed
ASHI 712 The Neuroscience of Human Memory Dr. Olave E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory Working / Short Term Memory Sunglasses Chair Dress Earrings Boots Bed
Memory 2/15/2017. The Three Systems Model of Memory. Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information
 Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Coding. The format in which information is stored in the various memory stores.
 Coding The format in which information is stored in the various memory stores. Coding The format in which information is stored in the various memory stores. Capacity The amount of information that can
Coding The format in which information is stored in the various memory stores. Coding The format in which information is stored in the various memory stores. Capacity The amount of information that can
Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory
 Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory Original Information Processing Model rehearsal transfer Sensory Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory input from the world attention retrieval Characterizing Memories
Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory Original Information Processing Model rehearsal transfer Sensory Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory input from the world attention retrieval Characterizing Memories
LECTURE 2 COGNITION, MEMORY, FOCUS MODELS & USER PSYCHOLOGY
 September 7 th 2017 LECTURE 2 COGNITION, MEMORY, FOCUS MODELS & USER PSYCHOLOGY 1 Recapitulation of Lecture 1 What is HCI? History Contributing disciplines CS, AI, Graphical Design Psychology Organizational/Management
September 7 th 2017 LECTURE 2 COGNITION, MEMORY, FOCUS MODELS & USER PSYCHOLOGY 1 Recapitulation of Lecture 1 What is HCI? History Contributing disciplines CS, AI, Graphical Design Psychology Organizational/Management
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
AQA A Level Psychology. Topic Companion. Memory. Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin
 AQA A Level Psychology Topic Companion Memory Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin AQA A LEVEL Psychology topic companion: MEMORY Page 2 Contents Memory The multi-store model 3 Types of long-term memory 9 The working
AQA A Level Psychology Topic Companion Memory Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin AQA A LEVEL Psychology topic companion: MEMORY Page 2 Contents Memory The multi-store model 3 Types of long-term memory 9 The working
IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization. Visual Attention. Lyn Bartram
 IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization Visual Attention Lyn Bartram Why we care in an information-rich world, the wealth of information means a dearth of something else: a scarcity of whatever it is that information
IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization Visual Attention Lyn Bartram Why we care in an information-rich world, the wealth of information means a dearth of something else: a scarcity of whatever it is that information
CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113 1) Which of the following sequences reflects the order in which the human brain processes
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113 1) Which of the following sequences reflects the order in which the human brain processes
Sensory Memory, Short-Term Memory & Working Memory
 Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Short-Term and Working Memory. Outline. What is memory? Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain. Chapter 5
 Short-Term and Working Memory Chapter 5 Outline Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain What is memory? The Persistence of Memory -Salvador Dali Intuitions about memory Memory for
Short-Term and Working Memory Chapter 5 Outline Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain What is memory? The Persistence of Memory -Salvador Dali Intuitions about memory Memory for
York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Chapter 1 The Human. York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering
 Chapter 1 The Human 1 The Human Information processed by humans I/O (input/output) Visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory Sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and
Chapter 1 The Human 1 The Human Information processed by humans I/O (input/output) Visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory Sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and
Intro to Cognitive Neuroscience. Working memory
 Intro to Cognitive Neuroscience Working memory 1 What is working memory? Brief, immediate memory for information we are currently processing. Closely related to attention: attending to something is often
Intro to Cognitive Neuroscience Working memory 1 What is working memory? Brief, immediate memory for information we are currently processing. Closely related to attention: attending to something is often
HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATION TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13
 HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATION TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony Includes slides from Karon
HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATION TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony Includes slides from Karon
(SAT). d) inhibiting automatized responses.
 Which of the following findings does NOT support the existence of task-specific mental resources? 1. a) It is more difficult to combine two verbal tasks than one verbal task and one spatial task. 2. b)
Which of the following findings does NOT support the existence of task-specific mental resources? 1. a) It is more difficult to combine two verbal tasks than one verbal task and one spatial task. 2. b)
HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATIONAL TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13
 HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATIONAL TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony Includes slides from
HUMAN ABILITIES CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATIONAL TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 7 CLASS 13 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony Includes slides from
MEMORY MODELS. CHAPTER 5: Memory models Practice questions - text book pages TOPIC 23
 TOPIC 23 CHAPTER 65 CHAPTER 5: Memory models Practice questions - text book pages 93-94 1) Identify the three main receptor systems used by a performer in sport. Where is the filtering mechanism found
TOPIC 23 CHAPTER 65 CHAPTER 5: Memory models Practice questions - text book pages 93-94 1) Identify the three main receptor systems used by a performer in sport. Where is the filtering mechanism found
Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology UNIT 1-2 MARKS
 UNIT 1-2 MARKS 1. What are the 5 major senses? Sight Hearing Touch Taste Smell 2. What are the effoectors? Limbs Fingers Eyes Head Vocal system. 3. What are the two stages of vision the physical reception
UNIT 1-2 MARKS 1. What are the 5 major senses? Sight Hearing Touch Taste Smell 2. What are the effoectors? Limbs Fingers Eyes Head Vocal system. 3. What are the two stages of vision the physical reception
Information Design. Information Design
 Information Design Goal: identify methods for representing and arranging the objects and actions possible in a system in a way that facilitates perception and understanding Information Design Define and
Information Design Goal: identify methods for representing and arranging the objects and actions possible in a system in a way that facilitates perception and understanding Information Design Define and
Today s Agenda. Human abilities Cognition Review for Exam1
 Today s Agenda Human abilities Cognition Review for Exam1 Announcement Exam 1 is scheduled Monday, Oct. 1 st, in class Cover materials until Sep. 24 Most of materials from class lecture notes You are allowed
Today s Agenda Human abilities Cognition Review for Exam1 Announcement Exam 1 is scheduled Monday, Oct. 1 st, in class Cover materials until Sep. 24 Most of materials from class lecture notes You are allowed
2/27/2017. Modal Model of Memory. Executive Attention & Working Memory. Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks)
 Executive Attention & Working Memory Memory 1 Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks) Why can we remember a telephone number long enough to place a call, but then we forget it almost immediately?
Executive Attention & Working Memory Memory 1 Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks) Why can we remember a telephone number long enough to place a call, but then we forget it almost immediately?
the human chapter 1 the human Vision Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term
 chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
the human chapter 1 the human Vision The Eye - physical reception Interpreting the signal (cont) Interpreting the signal
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
visual, auditory, haptic, movement sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving, skill, error
 chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs
 Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs Perception is the conscious experience of things and
Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs Perception is the conscious experience of things and
How Many Colors Can You Remember? Capacity is about Conscious vs unconscious memories
 Science B44 Lecture 18 Visual Memory Memory 1. Afterimage, persistence, iconic sensory memory 2. Conscious vs unconscious memories 3. Short and long term memories 4. Where are memories seen 5. Flashbulb
Science B44 Lecture 18 Visual Memory Memory 1. Afterimage, persistence, iconic sensory memory 2. Conscious vs unconscious memories 3. Short and long term memories 4. Where are memories seen 5. Flashbulb
Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk.
 chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY
 STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
Memory. Chapter 7 Outline. Human Memory: Basic Questions. Memory 10/2/ Prentice Hall 1. Chapter 7. How is pulled back out ( ) from memory?
 Memory Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Outline Basic Processing Encoding Retrieval Systems of Memory Physiology of Memory Your Memory Human Memory: Basic Questions How does get into memory? How is information in memory?
Memory Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Outline Basic Processing Encoding Retrieval Systems of Memory Physiology of Memory Your Memory Human Memory: Basic Questions How does get into memory? How is information in memory?
Users. Ergonomics vs. Cognetics
 Users 1 Ergonomics vs. Cognetics Ergonomics: The study of how people (physically) work Cognetics: The study of how people (mentally) work We must master an ergonomics of the mind if we want to design interfaces
Users 1 Ergonomics vs. Cognetics Ergonomics: The study of how people (physically) work Cognetics: The study of how people (mentally) work We must master an ergonomics of the mind if we want to design interfaces
ATTENTION! Learning Objective Topics. (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4. Selective Attention
 ATTENTION! (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4 Learning Objective Topics Selective Attention Visual Tasks Auditory Tasks Early vs. Late Selection Models Visual Search Divided Attention
ATTENTION! (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4 Learning Objective Topics Selective Attention Visual Tasks Auditory Tasks Early vs. Late Selection Models Visual Search Divided Attention
Chapter 3: Information Processing
 SENG 5334: Human Factors Engineering & INDH 5931: Research Topics in IH/Safety Chapter 3: Information Processing By: Magdy Akladios, PhD, PE, CSP, CPE, CSHM 1 A Model of Information Processing Def: A model
SENG 5334: Human Factors Engineering & INDH 5931: Research Topics in IH/Safety Chapter 3: Information Processing By: Magdy Akladios, PhD, PE, CSP, CPE, CSHM 1 A Model of Information Processing Def: A model
Running head: THE EFFECT OF STIMULUS LENGTH AND TYPE
 1 Running head: THE EFFECT OF STIMULUS LENGTH AND TYPE Stimuli Recognition: The Effect of Stimulus Length and Type Karla Roberts Hanover College 2 Stimuli Recognition: The Effect of Stimulus Length and
1 Running head: THE EFFECT OF STIMULUS LENGTH AND TYPE Stimuli Recognition: The Effect of Stimulus Length and Type Karla Roberts Hanover College 2 Stimuli Recognition: The Effect of Stimulus Length and
the human 1 of 3 Lecture 6 chapter 1 Remember to start on your paper prototyping
 Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
- Watson + Skinner: we aren t thinkers at all, no consciousness behaviour explained in terms of conditioning (positive/negative reinforcement)
 PSYC1002 Notes COGNITIVE PROCESSES BACKGROUND The history of cognitive psychology - - Cognitive psychology - mental processes - NOTE: cognitive psychology isn t about finding the perfect way of thinking
PSYC1002 Notes COGNITIVE PROCESSES BACKGROUND The history of cognitive psychology - - Cognitive psychology - mental processes - NOTE: cognitive psychology isn t about finding the perfect way of thinking
1960s Many models of memory proposed. Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model. Sensory Memory. Short-term Memory. Long-term Memory.
 1 1960s Many models of memory proposed Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model Sensory Memory Short-term Memory Long-term Memory 2 Primary Memory Secondary Memory 3 1 4 Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory
1 1960s Many models of memory proposed Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model Sensory Memory Short-term Memory Long-term Memory 2 Primary Memory Secondary Memory 3 1 4 Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory
Skills Center Psychology Practice Exam I Psychology The Adaptive Mind by Nairne
 1.) Psychology is defined as a. the scientific investigation of thought processes. b. the understanding of abnormal behavior. c. the scientific study of behavior and mind. d. the study of mental illness
1.) Psychology is defined as a. the scientific investigation of thought processes. b. the understanding of abnormal behavior. c. the scientific study of behavior and mind. d. the study of mental illness
Memory. Information Processing Approach
 Memory Information Processing Approach 5 Steps in Information ato Processing 1 Sensory Transduction Data first enters sensory register lasts 1 2secs C O N S O L I D A T I O N 5 Steps in Information ato
Memory Information Processing Approach 5 Steps in Information ato Processing 1 Sensory Transduction Data first enters sensory register lasts 1 2secs C O N S O L I D A T I O N 5 Steps in Information ato
Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Question bank (unit 1) UNIT 1-2 MARKS
 UNIT 1-2 MARKS 1. What are the 5 major senses? Sight Hearing Touch Taste Smell 2. What are the effectors? Limbs Fingers Eyes Head Vocal system. 3. What are the two stages of vision the physical reception
UNIT 1-2 MARKS 1. What are the 5 major senses? Sight Hearing Touch Taste Smell 2. What are the effectors? Limbs Fingers Eyes Head Vocal system. 3. What are the two stages of vision the physical reception
Psychology Perception
 Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
Chapter 8: Visual Imagery & Spatial Cognition
 1 Chapter 8: Visual Imagery & Spatial Cognition Intro Memory Empirical Studies Interf MR Scan LTM Codes DCT Imagery & Spatial Cognition Rel Org Principles ImplEnc SpatEq Neuro Imaging Critique StruEq Prop
1 Chapter 8: Visual Imagery & Spatial Cognition Intro Memory Empirical Studies Interf MR Scan LTM Codes DCT Imagery & Spatial Cognition Rel Org Principles ImplEnc SpatEq Neuro Imaging Critique StruEq Prop
Human Performance Model. Designing for Humans. The Human: The most complex of the three elements. The Activity
 Human Performance Model Designing for Humans People performing in systems have in common that they are each somebody, doing something, someplace (Bailey, 1996) Human limits and capabilities The Human:
Human Performance Model Designing for Humans People performing in systems have in common that they are each somebody, doing something, someplace (Bailey, 1996) Human limits and capabilities The Human:
Page # Perception and Action. Lecture 3: Perception & Action. ACT-R Cognitive Architecture. Another (older) view
 Perception and Action Lecture 3: Perception & Action Cognition is a lot, but not enough! We want models to perceive stimuli in the outside world respond by acting in the outside world This gives us a more
Perception and Action Lecture 3: Perception & Action Cognition is a lot, but not enough! We want models to perceive stimuli in the outside world respond by acting in the outside world This gives us a more
Prof. Greg Francis 5/23/08
 Prof. Greg Francis 5/3/8 Memory IIE 9: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Humans demonstrate memory when they behave in a way that could only be based upon previous experience Lecture does not necessarily
Prof. Greg Francis 5/3/8 Memory IIE 9: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Humans demonstrate memory when they behave in a way that could only be based upon previous experience Lecture does not necessarily
Human Perception and Cognition
 Human Perception and Cognition Textbook chapter 3.2, pp. 94 115. 1/50 Human perception: Information processing Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term,
Human Perception and Cognition Textbook chapter 3.2, pp. 94 115. 1/50 Human perception: Information processing Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term,
Perception and Memory. Higher Human Biology
 Perception and Memory Higher Human Biology SOMATIC MIX UP Put the statements in the correct order to show the pathway of nerves involved in a somatic response MOTOR NERVE SENSORY NERVE CNS EFFECTOR STIMULUS
Perception and Memory Higher Human Biology SOMATIC MIX UP Put the statements in the correct order to show the pathway of nerves involved in a somatic response MOTOR NERVE SENSORY NERVE CNS EFFECTOR STIMULUS
VISUAL PERCEPTION & COGNITIVE PROCESSES
 VISUAL PERCEPTION & COGNITIVE PROCESSES Prof. Rahul C. Basole CS4460 > March 31, 2016 How Are Graphics Used? Larkin & Simon (1987) investigated usefulness of graphical displays Graphical visualization
VISUAL PERCEPTION & COGNITIVE PROCESSES Prof. Rahul C. Basole CS4460 > March 31, 2016 How Are Graphics Used? Larkin & Simon (1987) investigated usefulness of graphical displays Graphical visualization
(Visual) Attention. October 3, PSY Visual Attention 1
 (Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
(Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
(In)Attention and Visual Awareness IAT814
 (In)Attention and Visual Awareness IAT814 Week 5 Lecture B 8.10.2009 Lyn Bartram lyn@sfu.ca SCHOOL OF INTERACTIVE ARTS + TECHNOLOGY [SIAT] WWW.SIAT.SFU.CA This is a useful topic Understand why you can
(In)Attention and Visual Awareness IAT814 Week 5 Lecture B 8.10.2009 Lyn Bartram lyn@sfu.ca SCHOOL OF INTERACTIVE ARTS + TECHNOLOGY [SIAT] WWW.SIAT.SFU.CA This is a useful topic Understand why you can
AS Module 1. Cognitive & Developmental Psychology. Cognitive Human Memory. The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types
 AS Module 1 Cognitive & Developmental Psychology Cognitive Human Memory The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types Sensory memory Short term memory Long term memory Short Term Memory
AS Module 1 Cognitive & Developmental Psychology Cognitive Human Memory The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types Sensory memory Short term memory Long term memory Short Term Memory
Introduction to Long-Term Memory
 Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding
 Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding Donna Bayliss Neurocognitive Development Unit School of Psychology University of Western Australia 1 Consolidation
Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding Donna Bayliss Neurocognitive Development Unit School of Psychology University of Western Australia 1 Consolidation
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind
 Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Cognitive Psychology. Mark Rafter Multiple Intelligences
 Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Multiple Intelligences Handouts: Please pick up a copy of today
Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Multiple Intelligences Handouts: Please pick up a copy of today
Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT)
 Avaya Vantage TM Basic for Avaya Vantage TM Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) Avaya Vantage TM Basic is a simple communications application for the Avaya Vantage TM device, offering basic
Avaya Vantage TM Basic for Avaya Vantage TM Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) Avaya Vantage TM Basic is a simple communications application for the Avaya Vantage TM device, offering basic
Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information:
 WORKING MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015 2016/2017
WORKING MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015 2016/2017
Study of the Brain. Notes
 Study of the Brain Notes 1. Three Components of the Brain Cerebrum. Most high-level brain functions take place in the cerebrum. It is divided into the left and right hemispheres. Many motor and sensory
Study of the Brain Notes 1. Three Components of the Brain Cerebrum. Most high-level brain functions take place in the cerebrum. It is divided into the left and right hemispheres. Many motor and sensory
Information is taken in by the senses (input) then encoded in the brain where it is processed; this processing is followed by an output.
 Define information processing Information is taken in by the senses (input) then encoded in the brain where it is processed; this processing is followed by an output. Define memory Memory is the encoding,
Define information processing Information is taken in by the senses (input) then encoded in the brain where it is processed; this processing is followed by an output. Define memory Memory is the encoding,
Cognitive Psychology. Mark Rafter Information Processing
 Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Photographs: I ll talk about these. Handouts: Please pick up a
Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Photographs: I ll talk about these. Handouts: Please pick up a
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University
 Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Chapter 5. Memory Structures and Processes. Chapter 5 Memory Processes
 Chapter 5 Memory Structures and Processes Chapter 5 Memory Processes 1 Memory The Man with the 30 Second Memory Chapter 5 Memory Processes 2 Are Some things Easier (Harder) to remember than others? Chapter
Chapter 5 Memory Structures and Processes Chapter 5 Memory Processes 1 Memory The Man with the 30 Second Memory Chapter 5 Memory Processes 2 Are Some things Easier (Harder) to remember than others? Chapter
Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information:
 EVALUATION OF THE MODAL MODEL OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
EVALUATION OF THE MODAL MODEL OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
MEMORY STORAGE. There are three major kinds of storage:
 MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
Mental Imagery. What is Imagery? What We Can Imagine 3/3/10. What is nature of the images? What is the nature of imagery for the other senses?
 Mental Imagery What is Imagery? What is nature of the images? Exact copy of original images? Represented in terms of meaning? If so, then how does the subjective sensation of an image arise? What is the
Mental Imagery What is Imagery? What is nature of the images? Exact copy of original images? Represented in terms of meaning? If so, then how does the subjective sensation of an image arise? What is the
Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction
 NPTEL Course on Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction Dr. Pradeep Yammiyavar Professor, Dept. of Design, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Dr. Samit Bhattacharya Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer
NPTEL Course on Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction Dr. Pradeep Yammiyavar Professor, Dept. of Design, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Dr. Samit Bhattacharya Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Psychological Tests that Examine Brain Functioning
 Psychological Tests that Examine Brain Functioning Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the video presentation available
Psychological Tests that Examine Brain Functioning Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the video presentation available
The Learning Process. Learning is a Process. Behavioral Learning Theories. Chapter 3 Learning and Memory. How many of these do you remind?
 Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
Chapter 3. Working Memory
 + Chapter 3 Working Memory + Atkinson and Shiffrin s (1971) Modal Model Environmental Input Sensory Registers Detect sensory input from the various modalities Visual, auditory, haptic, etc. Memories are
+ Chapter 3 Working Memory + Atkinson and Shiffrin s (1971) Modal Model Environmental Input Sensory Registers Detect sensory input from the various modalities Visual, auditory, haptic, etc. Memories are
Verbal Working Memory. The left temporoparietal junction in verbal working memory: Storage or attention. Baddelely s Multiple-Component Model
 Verbal Working Memory The left temporoparietal junction in verbal working memory: Storage or attention Susan Ravizza LTM vs WM Focusing on the storage component of WM Maintenance of words, pictures, goals
Verbal Working Memory The left temporoparietal junction in verbal working memory: Storage or attention Susan Ravizza LTM vs WM Focusing on the storage component of WM Maintenance of words, pictures, goals
Chapter 4. Two Types of Attention. Selective Listening 25/09/2012. Paying Attention. How does selective attention work?
 Chapter 4 Paying Attention Two Types of Attention How does selective attention work? How do we block out irrelevant information? What can t we block out? How much control do we have over our attention?
Chapter 4 Paying Attention Two Types of Attention How does selective attention work? How do we block out irrelevant information? What can t we block out? How much control do we have over our attention?
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues. Outline. Starting Points. Starting Points
 Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Memory Development. Cognitive Development
 Memory Development Cognitive Development Memory as information storage Memory Why does our memory sometimes fail us? Memory Schachter s Seven Sins of Memory 1. Transience 2. Absent-Mindedness 3. Blocking
Memory Development Cognitive Development Memory as information storage Memory Why does our memory sometimes fail us? Memory Schachter s Seven Sins of Memory 1. Transience 2. Absent-Mindedness 3. Blocking
IAT 355 Perception 1. Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get
 IAT 355 Perception 1 Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get Why we need to understand perception The ability of viewers to interpret visual (graphical) encodings of information and
IAT 355 Perception 1 Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get Why we need to understand perception The ability of viewers to interpret visual (graphical) encodings of information and
M P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist
 M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
MOVEMENT PREPARATION LAB. Name: Score: Activity I: Predictability of the correct response choice & Influence of Pre cueing
 MOVEMENT PREPARATION LAB Name: Score: Activity I: Predictability of the correct response choice & Influence of Pre cueing Introduction: Research evidence has consistently shown that as the predictability
MOVEMENT PREPARATION LAB Name: Score: Activity I: Predictability of the correct response choice & Influence of Pre cueing Introduction: Research evidence has consistently shown that as the predictability
Comment on McLeod and Hume, Overlapping Mental Operations in Serial Performance with Preview: Typing
 THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY, 1994, 47A (1) 201-205 Comment on McLeod and Hume, Overlapping Mental Operations in Serial Performance with Preview: Typing Harold Pashler University of
THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY, 1994, 47A (1) 201-205 Comment on McLeod and Hume, Overlapping Mental Operations in Serial Performance with Preview: Typing Harold Pashler University of
PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II
 PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II Session 4 Background of Object Recognition Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept., of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II Session 4 Background of Object Recognition Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept., of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education
MUSINGS ON ATTENTION. In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to?
 Part II -Attention MUSINGS ON ATTENTION In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to? How do we find meaningful information within a complex scene? What role does attention play
Part II -Attention MUSINGS ON ATTENTION In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to? How do we find meaningful information within a complex scene? What role does attention play
Memory (1) Visual Sensory Store. Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory
 Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
Attention. What is attention? Attention metaphors. Definitions of attention. Chapter 6. Attention as a mental process
 What is attention? Attention Chapter 6 To drive a car you Use effort Sustain attention Orient to several locations Restrict attention Select particular objects Search for particular objects Respond with
What is attention? Attention Chapter 6 To drive a car you Use effort Sustain attention Orient to several locations Restrict attention Select particular objects Search for particular objects Respond with
