Brazilian Portuguese transcultural adaptation of Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (BDEFS)
|
|
|
- Eustacia Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Portuguese transcultural adaptation of Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (BDEFS) Original article Victor Polignano Godoy¹, Fernanda Gomes da Mata 2, Bárbara Romaneli Conde 3, Caroline Antunes de Oliveira e Souza¹, Ana Luiza Guimarães Martins¹, Paulo Mattos 4, Débora Marques de Miranda 5, Leandro Fernandes Malloy- Diniz 5 1 Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG); Research Laboratory of Clinical Neuroscience (LINC) of UFMG, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. 2 Monash University, Melbourne, Australia. 3 Postgraduate Program in Neuroscience at UFMG, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. 4 Psychiatry Institute of Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ); CNA/D or Institute, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. 5 Department of Pediatrics of UFMG, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. Received: 7/5/2015 Accepted: 6/11/2015 DOI: / Abstract Background: Considering the importance of Executive Functions to clinical and nonclinical situations, Barkley proposed a new theory of executive functioning based on an evolutionary neuropsychological perspective and clinical research using large samples of clinical and community identified adults and children as well as children with ADHD followed to adulthood. Objective: The present study aims to adapt the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functions Scales (BDEFS) to Brazilian Portuguese and also assess its construct validity in a sample of normal Brazilian adults. Methods: The original version of scale was adapted to Brazilian Portuguese according to the guideline from the ISPOR Task Force. To assess the semantic equivalence between the original and adapted version, both of them were applied into a sample of 25 Brazilian bilingual adults. Finally, 60 Brazilian adults completed the BDEFS and the Brazilian versions of Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS-11) and Adult Self-Report Scale (ASRS-18) to assess convergent validity. Results: The BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese version has semantic correspondence with the original version indicating that the adaptation procedure was successful. The BDEFS correlated significantly with the impulsivity and attention scores from the BIS-11 and ASRS-18 supporting its construct validity. Cronbach s alpha (α = 0.961) indicated that the BDEFS translated version has satisfactory internal consistency. Discussion: Together, these findings indicate the successful adaptation of the BDEFS to Brazilian Portuguese and support its utility in that population. Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): Keywords: Executives functions, neuropsychology, psychometrics, assessment scales. Introduction Executive Functions (EF) are among the most important cognitive processes due to their role in complex cross-temporal behavior, adaptation to novel situations, problem solving, and decision-making. These cognitive processes are some of the most-studied constructs in neurosciences 1,2. Several theoretical models have tried to explain both the structure and functioning of EF 3. These models differ in terms of the number of processes thought to be involved (single or multiple processes) in the construct. Despite some divergence between different models of Executive Function, authors seem to agree that EF processes are pivotal for self-regulation and goal-directed behavior 4,5. Several psychopathologies are associated with impairments in EF processes, such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) 6, Bipolar Disorder 7, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder 8, and Schizophrenia 9. In clinical samples, as in ADHD, EF deficits are related to poor functional outcomes, such as educational fields 10. In non-psychiatric samples, EF seems to be related to others diseases and to everyday activities. Patients with increased severity of type 2 diabetes mellitus have lower performance in a working memory task and in a measure of general EF probably because chronic hyperglycemia may end in neural apoptosis and, as consequence, decreased the cognitive functioning. In addition, EF mediates the diabetes selfcare 11 (glucose monitoring, diet, medication administration, etc.). Moreover the executive functioning is related to driving behavior and the probability of traffic accidents 12 and to productivity at work 13. Considering the importance of EF to clinical and nonclinical situations, Barkley proposed a new theory of executive functioning based on an evolutionary neuropsychological perspective and clinical research using large samples of clinical and community identified adults and children as well as children with ADHD followed to adulthood. According to Barkley 14, executive functions could be understood by considering a hierarchic relationship between inhibitory control and other cognitive processes. Barkley argues that three inhibitory processes (a) inhibition of the prepotent response; (b) stopping of an ongoing response; and (c) interference control support higher abilities like working memory, internalization of speech, self-regulation of affect-motivation-arousal, reconstitution, and motor-control-fluency-syntax 15. These cognitive abilities operate as tools for the performance of major activities of daily life since the beginning of humanity. That is because EF is proposed to mediate complex behaviors such as reciprocity and social exchange, social cooperation, vicarious learning, mimesis, and self-regulation for self-defense that underlie the evolutionary process of the human species and the development of our culture 14. Despite the plethora of neuropsychological tests designed to assess EF, there is evidence that many of them do not have ecological validity considering their lack of correlation with daily-life activities or observations and ratings of EF in natural settings 6,16. In this context, Barkley created the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (BDEFS), which consists of a self-reported questionnaire that assesses different components of executive functioning related to daily-life impairments of psychiatric patients 16. Since the publication of BDEFS, this scale has accumulated evidence of validity 17,18, as well as utility in clinical practice for the assessment of psychiatric patients 19,20. The present work presents the adaptation of the BDEFS to Brazilian Portuguese, and provides evidence of its reliability and construct validity in a non-clinical community sample of Brazilian adults. Address for correspondence: Leandro Fernandes Malloy-Diniz. Av. Alfredo Balena, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. malloy@ufmg.br
2 148 Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): Materials and methods Samples Two convenience samples were recruited through local advertisements and the only exclusion criteria was age (less than 18 years old and more of 89 years old). For the translation phase, 25 bilingual Brazilian adults (n = 25; 17 women) answered the both versions of BDEFS. The participants had an average age of years old, with a minimum of 19 years old and a maximum of 41 (Standard Deviation = 5.515). All participants had at least 11 years of formal education. For the pilot study of psychometric properties of the Portuguese Brazilian version of BDEFS, 60 Brazilian individuals were recruited (n = 60; 21 men), all of whom had at least eight years of formal education. The participants in this phase had an average age of 27.3 years old, with a minimum age of 18 years old and a maximum of 55 years old (Standard Deviation = 12.3 years). Instruments Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (BDEFS) The self-report version of the BDEFS-LF is intended for adults ages 18 to 81. The patient completes the scale by indicating the frequency of certain behaviors and thoughts believed to reflect EF deficits. The ascertainment window for this self-assessment is the past six months, which should ensure a more stable measurement and representative sampling of the EF deficits over time than do typically short-duration cognitive tests. Answers to the 89 items comprise a four-point Likerttype scale, as follows: never or rarely (1), sometimes (2), often (3), and very often (4). The factor analysis of the BDEFS revealed a large, single factor along with four smaller factors. These became the five subscales that assess specific domains of EF in daily life: self-management of time (items 1 to 21), self-organization/problem solving (items 22 to 45), self-restraint (items 46 to 64), self-motivation (items 65 to 76), and self-regulation of emotion (items 77 to 89). The Scoring System involves the computing individual scores of the five subscales; the Total Score across all five subscales; the Executive Functioning Symptom Count which indicates clinical symptoms of deficits in executive functioning (items answered with 3 or 4 are added to obtain this score); and the ADHD-EF Index (items 1, 6, 14, 16, 24, 49, 50, 55, 60, 65 and 69 have their scores added). The ADHD-EF Index is only intended as a predictor of the risk of having ADHD and is not diagnostic of it per se. Barratt Impulsiveness Scale Eleventh edition, Brazilian version (BIS -11) The BIS-11 is a self-report instrument with 30 items for measure impulsivity of the Ernest Barratt model 21. The respondents have to select the best option based in a four-point Likert type-scale to describe the frequency of certain behaviors and situations linked with impulsivity. The BIS-11 has three subscales: attentional impulsivity (items 6, 5, 9, 11, 20, 24, 26, 28), motor impulsivity (items 2, 3, 4, 16, 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 30) and non-planning impulsivity (items 1, 7, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 18, 27, 29). Furthermore, the BIS-11 has a total score ranges from 30 to 120 points. Higher scores mean that the participant tends to behave impulsively. Adult Self-Report Scale, Brazilian version (ASRS-18) The ASRS-18 is a self-report measure of symptoms of the Attention- Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) based in the A diagnostic criteria of the Fourth Edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-4) adapted to adults 22. The scale was composed by 18 questions: 9 for evaluate the attention-deficit symptoms and 9 for measure the hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms. To be suspect of having ADHD is necessary at least 6 symptoms in one subscale or 12 symptoms in both (for the combined type). For clinical diagnosis is necessary fill the others criteria. Procedures There are two main phases of the present study: (1) the transcultural adaptation and (2) internal consistency and construct validity. First, the BDEFS was translated into and adapted to Brazilian Portuguese, following the principles and steps recommended by the ISPOR Task Force for Translation and Cultural Adaptation 21. The steps of translation and adaptation were (a) preparation: research design and obtaining authorization from Barkley and Guilford Press to translate and transculturally adapt the scale; (b) forward translation: translation for the Portuguese language; (c) reconciliation: comparison and synthesis of translations into Portuguese; (d) back translation: translation of the Portuguese version back into the English language; (e) review of back translation: comparison of the back-translated version with the original; (f) cognitive debriefing: testing of the translated version with a small sample; (g) review of cognitive debriefing results and finalization: interpretation of the results of cognitive debriefing; (h) proofreading: correction of any type of error; and (i) final report. Only the step of harmonization was not followed, because it is not applicable to this study. The comparison between the original version and the adapted version used the same procedure described in Malloy-Diniz et al. 22,23. Namely, both original and translated versions of the BDEFS were administered to the sample of 25 bilingual Brazilian participants. The original scale was administered first. After seven days, the translated version was administered, with the time between administrations decreasing the possibility that the participants would remember the order of and their responses to the items. In a second phase, relationships between the Brazilian versions of the BDEFS, the Adult Self Report Scale (ASRS ), and the Barrat Impulsiveness Scale (BIS ) were assessed. The three scales were applied in the sample of 60 Brazilian participants. Data analysis SPPS 21.0 software (Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 21.0) was used to analyze the distribution of each item of the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese version, finding that all the items did not follow normal distribution (p < 0.05) by the Shapiro-Wilk test (n < 50). This finding is typical of rating scales that assess symptoms or deficits. Accordingly, Spearman correlation was employed between the answers to the translated and the original instruments in order to verify the validity of the construct and the association between items. Finally, to assess the internal consistency of BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese version was calculated the inter-correlation among the items (the coefficient of Cronbach s Alpha). A Bland-Altman plot was constructed to analyze the agreement between the two versions of the BDEFS. This statistical method involves a scatter plot that has as the y-axis the difference between the two measures, with the x-axis representing the mean of the two measures. Upper and lower limits are established based on SD. If the bias has a normal distribution, 95% of the differences will be between the limits. A standard deviation of 1.96 is not clinically representative, so if the differences are within SD, the two measures correspond and may be used interchangeably. Results Thirty items of the scale showed a strong correlation index (0.70 < rho < 1), fifty-five items presented a moderate correlation (0.30 < rho < 0.70), and three items showed a weak correlation (0.1 < rho < 0.3). Only one item showed no correlation between the original and Brazilian versions. All five correlations were strong (0.7 < rho < 1) between the five subscale scores of the translated and the original versions. Finally, the total score, the FE Count Symptoms, and the ADHD Index showed strong correlations (0.7 < rho < 1). These results
3 Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): point to a good correspondence between the original and translated BDEFS. These correlations are presented in table 1. Cronbach s Alpha was calculated in order to measure the internal consistency of the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese Version for all scales and for each subscale, as done in the validity and normative study of the BDEFS English Version 15. For all scales, Cronbach s Alpha was (α = 0.961). For each subscale self-management of time, self-organization, self-restraint, self-motivation, and selfregulation of emotion the results of Cronbach s Alpha (α) were, respectively, 0.925, 0.920, 0.879, 0.790, and These results are quite satisfactory and are close to those Barkley found in 2011 (0.949, 0.958, 0.930, 0.914, and 0.946, respectively). These results indicate that the BDEFS translated version has satisfactory internal consistency. Table 1. Correlations between the items and indexes of the two versions of BDEFS Statements Rho P 1. Procrastinate or put off doing things until the last minute Poor sense of time Waste or mismanage my time Not prepared for work or assigned tasks Fail to meet deadlines for assignments Have trouble planning ahead or preparing for upcoming events Forget to do things I am supposed to do Can t seem to accomplish the goals I set for myself Late for work or scheduled appointments Can t seem to hold in mind things I need to remember to do Can t seem to get things done unless there is an immediate deadline Have difficulty judging how much time it will take to do something or get somewhere Have trouble motivating myself to start work Have difficulty motivating myself to stick with my work and get it done Not motivated to prepare in advance for things I know I am supposed to do Have trouble completing one activity before starting into a new one Have trouble doing what I tell myself to do Poor follow through on promises or commitments I may make to others Lack of self-discipline Have difficulty arranging or doing my work by its priority or importance; can t prioritize well Find it hard to get started or get going on things I need to get done I do not seem to anticipate the future as much or as well as others Can t seem to remember what I previously heard or read about I have trouble organizing my thoughts When I am shown something complicated to do, cannot keep the information in mind so as to imitate or do it correctly I have trouble considering various options for doing things and weighting their consequences Have difficulties saying what I want to say Unable to come up with or invent as many solutions to problems as others seem to do Find myself at a loss for words when I want to explain something to others Have trouble putting my thoughts down in writing as well or as quickly as others Feel I am not as creative or inventive as others of my level of intelligence In trying to accomplish goals or assignments, find I am not able to think of as many ways of doing things as others Have trouble learning new or complex activities as well as others Have difficulty explaining things in their proper order or sequence Can t seem to get to the point of my explanations as quickly as others Have trouble doing things in their proper order or sequence Unable to think on my feet or respond as effectively as others to unexpected events I am slower than others at solving problems I encounter in my daily life Easily distracted by irrelevant thoughts when I must concentrate on something Not able to comprehend what I read as well as I should be able to do; have to re-read material to get its meaning Cannot focus my attention on tasks or work as well as others Easily confused Can t seem to sustain my concentration on reading, paperwork, lectures, or work Find it hard to focus on what is important from what is not important when I do things I don t seem to process information as quickly or as accurately as others Find it difficult to tolerate waiting; impatient Make decisions impulsively Unable to inhibit my reactions or responses to events or others Have difficulty stopping my activities or behavior when I should do so (cont.)
4 150 Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): Statements Rho P 50. Have difficulty changing my behavior when I am given feedback about my mistakes Make impulsive comments to others Likely to do things without considering the consequences for doing them Change my plans at the last minute on a whim or last minute impulse Fail to consider past relevant events or past personal experiences before responding to situations (I act without thinking) Not aware of things I say or do Have difficulty being objective about things that affect me Find it hard to take other people s perspectives about a problem or situation Don t think about or talk things over with myself before doing something Trouble following the rules in a situation More likely to drive a motor vehicle much faster than others (Excessive speeding) Have a low tolerance for frustrating situations Cannot inhibit my emotions as well as others I don t look ahead and think about what the future outcomes will be before I do something (I don t use my foresight) I engage in risk taking activities more than others are likely to do Likely to take short cuts in my work and not do all that I am supposed to do Likely to skip out on work early if its boring or to do Do not put as much effort into my work as I should or than others are able to do Others tell me I am lazy or unmotivated Have to depend on others to help me get my work done Insignificant Insignificant 70. Things must have an immediate payoff for me or I do not seem to get them done Have difficulty resisting the urge to do something fun or more interesting when I am supposed to be working Inconsistent in the quality or quantity of my work performance Unable to work as well as others without supervision or frequent instruction I do not have the willpower or determination that others seem to have I am not able to work toward longer term or delayed rewards as well as others I cannot resist doing things that produce immediate rewards even if they are not good for me in the long run Quick to get angry or become upset Over act emotionally Easily excitable Unable to inhibit showing negative or positive emotions Have trouble calming myself down once I am emotionally upset Cannot seem to regain emotional control and become more reasonable once I am emotional Cannot seem to distract myself away from whatever is upsetting me emotionally to help calm me down. I can t refocus my mind to a more positive framework 84. Unable to manage my emotions in order to accomplish my goals successfully or get along well with others I remain emotional or upset longer than others Find it difficult to walk from emotionally upsetting encounters with others or leave situations in which I have become very emotional I cannot rechannel or redirect my emotions into more positive ways or outlets when I get upset I am not able to evaluate an emotionally upsetting event more objectively I cannot redefine negative events into more positive viewpoints when I feel strong emotions Total Score EF Count Symptom ADHD Index Self-management to time Self-organization Self-restraint Self-motivation Self-regulation of emotion EF: executive functioning; ADHD: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; Rho: Spearman Correlation; P: significance level. To build the Bland-Altman plot, the total score of both BDEFS were used to compute the differences and the means for each participant. Next, the standard deviation was calculated for the sample (SD = ). The mean of differences between the total scores on the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese Version and the total scores on the BDEFS English Version was (m = -0.16), and the maximum differences were and Finally, the SD was multiplied by , added to the mean of differences (-0.16), and the upper and down limits were thereby discovered. A strong relationship was expected between the scales because, in theory, they measure exactly the same construct. Based on this statistical information, the Brand-Altman plot (Figure 1) shows that all the results are within the 95% confidence range, indicating that the two versions have good clinical agreement.
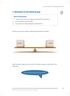
5 Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): Mean Difference Figure 1. The Bland-Altman Plot between the two versions of BDEFS. The next step was to correlate the five subscales, the indexes, and total score of BDEFS with the two factors (inhibition response and lack of planning) and the total score of BIS 11 and with the two factors (inattention and hyperactivity), the total score, and the total symptoms of ASRS 18. The results are shown in tables 2 and 3. Overall, the results of the Spearman correlations between the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese version, BIS 11, and ASRS 18 indicate satisfactory concurrent validity. Table 2. Correlations between subscales, indexes and total scores of ASRS 18, BIS 11 and BDEFS translated version ASRS 18 Brazilian Portuguese BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese Version TSc TSy II HI Rho Rho Rho Rho Total Score 0.523*** 0.499*** 0.528**** 0.333** EF Count Symptom 0.558*** 0.464*** 0.606*** 0.301* ADHD Index 0.57*** 0.511*** 0.645*** 0.276* Self-management to time 0.491*** 0.477*** 0.509*** 0.305* Self-organization 0.576*** 0.555*** 0.617** 0.344** Self-restraint 0.473*** 0.437*** 0.357* 0.394** Self-motivation 0.473*** 0.48*** 0.544** Self-regulation of emotion 0.386** 0.37** 0.321* 0.313** ASRS: Adult Self-Report Scale; BIS: Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BDEFS: Barkley Deficits in Executive Functions Scales; TSc: Total Score; TSy: Total Symptoms; II = Inattention Index; HI: Hyperactivity Index; IR: Inhibition Response; LP: Lack of Planning. Rho: Spearman Correlations; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < Table 3. Correlations between subscales, indexes and total scores of BIS 11 and BDEFS BIS 11 Brazilian Portuguese BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese Version TSc IR LP Rho Rho Rho Total Score 0.647*** 0.642*** 0.388** EF Count Symptom 0.556*** 0.583*** ADHD Index 0.694*** 0.696*** 0.440*** Self-management to time 0.62*** 0.601*** 0.385** Self-organization 0.546*** 0.602*** 0.264* Self-restraint 0.626*** 0.608*** 0.368** Self-motivation 0.641*** 0.625*** 0.471*** Self-regulation of emotion 0.453*** 0.436*** BIS: Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BDEFS: Barkley Deficits in Executive Functions Scales; TSc: Total Score; IR: Inhibition Response; LP: Lack of Planning; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < Discussion The present study reports evidence that our transcultural adaptation of the BDEFS to Brazilian Portuguese was quite satisfactory and successful. Furthermore, the adapted version of the BDEFS showed evidence of concurrent validity when compared with two other instruments (BIS 11 and ASRS 18), which measure different types of impulsive behavior, attention, and hyperactivity. The results also suggested that the internal consistency of the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese was not only satisfactory, but also straightforward in its relationship to the corresponding data for the BDEFS English version. The subscale self-regulation of emotion of the BDEFS Brazilian Portuguese has a Cronbach s Alpha higher than the same statistical procedure for the BDEFS English version. This is also strong evidence of the correspondence and validity between the versions. To validate the original scale, Barkley and colleagues did two studies (UMASS and Milwaukee Studies; Barkley 16 ) using several neuropsychological tests of executive and other functions. Those studies found a low correlation between the scores of the BDEFS English Version and the scores of these tests, consistent with many other studies. This absence of a strong correlation between ratings and tests reflects a lack of ecological validity of neuropsychological tests. Other studies using the BDEFS English Version have shown similar results 17-20,24,25. For example, as found by Vasconcelos et al. 26 the BIS 11 Brazilian Portuguese Version presents almost non-significant correlations with the Iowa Gambling Task, which support the theoretical and statistical difference between these types of neuropsychological methods. Due to the frequently reported weak correlation between neuropsychological tests and scales, in the present study we opted to use scales measuring similar constructs (i.e., ASRS-18 and BIS-11) and similar methods to assess the convergent validity of BDEFS. Even though the constructs measured by BIS-11 (impulsivity), ASRS-18 (ADHD s cardinal symptoms), and BDEFS (executive functioning) are not equivalent, they are hypothesized by Barkley to be substantially related to each other. Poor inhibition (self-restraint) is a major EF component in Barkley s and others theories of EF. Thus Barkley has argued that ADHD is primarily a disorder of EF beyond simply being one of inattention. Supporting these theoretical positions, we found significant correlations between the scores derived from those scales. This result suggests that the Brazilian adaptation of the BDEFS presents evidence of construct validity. Other studies using the BDEFS English Version have made important contributions regarding the validity and the potential for use of the scale. Dehili et al. 20 analyzed the capacity of BDEFS to predict symptoms of ADHD in comparison to a visual-search task in a college population. The results showed that the BDEFS is more predictive of ADHD than the task. Also, the relationship between the two measures was found to be low (just as in the studies of Barkley). Knouse 25 used the BDEFS successfully to examine the relationship of EF to understand and predict the mediation of self-regulation in academic performance. That study 19 also showed that the BDEFS could be used to predict depressive symptoms, especially using the self-management of time, self-organization, and problem-solving subscales, in a sample with symptoms of ADHD and depression. Future studies should address the relationship between the Brazilian adaptation of BDEFS and functional outcomes in a Brazilian context. The results of the present study should be interpreted in the context of its limitations. One such limitation was that we assumed that the factorial structure of the adapted BDEFS was the same as the original version and did not examine that factor structure directly. Because our sample was small, factor analysis could not be performed. This study was executed only for adapt the BDEFS for our culture and, for that objective, the sample could be small. Future studies should assess the factor structure of BDEFS in the Brazilian Population using both confirmatory and exploratory methods. These statistical analysis and the standardization of the BDEFS implies in a recruitment of a larger sample than the one used in the present study. The null correlation between the item 69 of the both versions of BDEFS probably can be explained for cultural differences. Although,
6 152 Godoy VP et al. / Arch Clin Psychiatry. 2015;42(6): in the future studies of the standardization of BDEFS Portuguese version, this result needs to be investigated more deeply. It is important to note that possible clinical use of this adaptation of BDEFS depends on future studies of criterion validity in clinical populations, as well as on factor analytical procedures, and the collection of additional norms for a Brazilian population that is representative of different regions, other important demographic factors, and socioeconomic levels. Yet the evidence found here suggests that such future studies could rely on this adaptation. Acknowledgments The authors wish to thank Russell Barkley, Ph.D. for his availability to serve as a consultant to this project, for his review of an earlier draft of this manuscript, and for authorization to translate his scale for use in this research. Conflict of interest None of the authors has any conflict of interest. This research doesn t have any financial support. References 1. Diamond A. Executive functions. Annu Rev Psychol. 2013;64: Verdejo-García A, Bechara A. Neuropsicología de las funciones ejecutivas. Psicothema. 2010;22(2): Barkley RA, editor. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a handbook for diagnosis and treatment. New York: Guilford Publications; Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Impairment in occupational functioning and adult ADHD: the predictive utility of executive function (EF) ratings versus EF tests. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2010;25(3): Fuster JM. The prefrontal cortex an update: time is of the essence. Neuron. 2001;30(2): Barkley RA, Murphy KR. The nature of executive function (EF) deficits in daily life activities in adults with ADHD and their relationship to performance on EF tests. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2011;33(2): Malloy-Diniz LF, Neves F, Corrêa H. Neuropsychological aspects of bipolar disorder. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2009;31(2): da Rocha FF, Alvarenga NB, Malloy-Diniz L, Corrêa H. Decision-making impairment in obsessive-compulsive disorder as measured by the Iowa Gambling Task. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011;69(4): Lepage M, Bodnar M, Bowie CR. Neurocognition: clinical and functional outcomes in schizophrenia. Can J Psychiatry. 2014;59(1): Biederman J, Monuteaux MC, Doyle AE, Seidman LJ, Wilens TE, Ferrero F, et al. Impact of executive function deficits and attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) on academic outcomes in children. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2004;72(5): Gatlin PK, Insel KC. Severity of type 2 diabetes, cognitive function, and self-care. Biol Res Nurs. 2015;17(5): Roca J, Crundall D, Moreno-Ríos S, Castro C, Lupiáñez J. The influence of differences in the functioning of the neurocognitive attentional networks on drivers performance. Accid Anal Prev. 2013;50: Ownsworth T, Shum D. Relationship between executive functions and productivity outcomes following stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(7): Barkley RA. The executive functions and self-regulation: an evolutionary neuropsychological perspective. Neuropsychol Rev. 2001;11(1): Barkley RA.Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull. 1997;121(1): Barkley RA. Barkley deficits in executive functioning scale (BDEFS). New York: Guilford Press; Coffman TP. The Psychometric Properties of the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (Bdefs) in a College Student Population. Florida State University; Kamradt JM, Ullsperger JM, Nikolas MA. Executive function assessment and adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: tasks versus ratings on the Barkley deficits in executive functioning scale. Psychol Assess. 2014;26(4): Knouse LE, Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Does executive functioning (EF) predict depression in clinic-referred adults? EF tests vs. rating scales. J Affect Disord. 2013;145(2): Dehili VM, Prevatt F, Coffman TP. An Analysis of the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale in a College Population: Does It Predict Symptoms of ADHD Better Than a Visual-Search Task? J Atten Disord Malloy-Diniz LF, Mattos P, Leite WB, Abreu N, Coutinho G, De Paula JJ, et al. Tradução e adaptação cultural da Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS- 11) para aplicação em adultos brasileiros. J Bras Psiquiatr. 2010;59(2): Mattos P, Segenreich D, Saboya E, Louzã M, Dias G, Romano M. Transcultural adaptation of the Adult Self-Report Scale into Portuguese for evaluation of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Rev Psiquiatr Clín. 2006;33(4): Wild D, Grove A, Martin M, Eremenco S, McElroy S, Verjee-Lorenz A, et al. ISPOR Task Force for Translation and Cultural Adaptation. Principles of good practice for the translation and cultural adaptation process for patient-reported outcomes (PRO) measures: report of the ISPOR Task Force for Translation and Cultural Adaptation. Value Health. 2005;8(2): Nogueira CYS, Carvalho AM, Gauer G, Tavares N, Santos RMM, Ginani G, et al. Translation and adaptation of Impulsive Behavior Scale (UPPS) to the Brazilian population. Clinical Neuropsychiatry. 2013;10(2): Knouse LE, Feldman G, Blevins EJ. Executive functioning difficulties as predictors of academic performance: examining the role of grade goals. Learn Individ Differ. 2014;36: Vasconcelos AG, Sergeant J, Corrêa H, Mattos P, Malloy-Diniz L. When self-report diverges from performance: the usage of BIS-11 along with neuropsychological tests. Psychiatry Res. 2014;218(1-2):
ADHD: MORE THAN ATTENTION PROBLEM JULIE STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP
 ADHD: MORE THAN ATTENTION PROBLEM JULIE STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP WWW.CHILDRENSRESOURCEGROUP.COM UNDERSTANDING THE NATURE OF ADHD IS CRITICAL TO TREATING THE DISORDER HYPERACTIVITY
ADHD: MORE THAN ATTENTION PROBLEM JULIE STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP WWW.CHILDRENSRESOURCEGROUP.COM UNDERSTANDING THE NATURE OF ADHD IS CRITICAL TO TREATING THE DISORDER HYPERACTIVITY
Adult ADHD-RS-IV* with Adult Prompts
 Adult ADHD-RS-IV* with Adult Prompts The ADHD-RS-IV with Adult Prompts is an 8-item scale based on the DSM-IV-TR criteria for ADHD that provides a rating of the severity of symptoms. The adult prompts
Adult ADHD-RS-IV* with Adult Prompts The ADHD-RS-IV with Adult Prompts is an 8-item scale based on the DSM-IV-TR criteria for ADHD that provides a rating of the severity of symptoms. The adult prompts
The Role of Executive Functions in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Learning Disabilities
 Journal April 2000 Volume 10, No. 2 (Reprinted with permission of Editor) Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) appears to be a disorder of self-control or executive functions. The executive
Journal April 2000 Volume 10, No. 2 (Reprinted with permission of Editor) Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) appears to be a disorder of self-control or executive functions. The executive
Executive Functions and ADHD
 Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in black type) or Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in white type) Executive Functions and ADHD: Theory Underlying the New Brown Executive Functions/Attention Scales
Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in black type) or Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in white type) Executive Functions and ADHD: Theory Underlying the New Brown Executive Functions/Attention Scales
For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive
 8 W H A T W E K N O W AD/HD Predominantly Inattentive Type For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive children have been recognized as having behavioral problems. In the 1970s, doctors recognized that
8 W H A T W E K N O W AD/HD Predominantly Inattentive Type For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive children have been recognized as having behavioral problems. In the 1970s, doctors recognized that
ADD / ADHD in Children
 ADD / ADHD in Children SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ATTENTION DEFICIT DISORDER It s normal for children to occasionally forget their homework, daydream during class, act without thinking, or get fidgety at the
ADD / ADHD in Children SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ATTENTION DEFICIT DISORDER It s normal for children to occasionally forget their homework, daydream during class, act without thinking, or get fidgety at the
ADHD Dan Shapiro, M.D. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics
 ADHD 2016 Dan Shapiro, M.D. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics drdanshapiro@gmail.com www.parentchildjourney.com Behavior is communication A riot is at bottom the language of the unheard. -Martin
ADHD 2016 Dan Shapiro, M.D. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics drdanshapiro@gmail.com www.parentchildjourney.com Behavior is communication A riot is at bottom the language of the unheard. -Martin
An Overview of The New Brown Executive Function/Attention Scales (Brown EF/A Scales) Presenter and Author. Change in Understanding ADHD
 Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in black type) or Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in white type) An Overview of The New Brown Executive Function/Attention Scales (Brown EF/A Scales) Presenter
Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in black type) or Image by Photographer s Name (Credit in white type) An Overview of The New Brown Executive Function/Attention Scales (Brown EF/A Scales) Presenter
Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorders (ADHD) definition
 Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorders (ADHD) definition: a pervasive pattern of inattention, impulsivity, and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that is more frequent and severe than is typically observed
Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorders (ADHD) definition: a pervasive pattern of inattention, impulsivity, and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that is more frequent and severe than is typically observed
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Test Based upon the DSM-5 criteria and other screening measures for ADD/ADHD Reviewed by John M. Grohol, Psy.D.
 Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Test Based upon the DSM-5 criteria and other screening measures for ADD/ADHD Reviewed by John M. Grohol, Psy.D. Use this quiz to help determine if you need to see
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Test Based upon the DSM-5 criteria and other screening measures for ADD/ADHD Reviewed by John M. Grohol, Psy.D. Use this quiz to help determine if you need to see
EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND GRADE POINT AVERAGE IN COLLEGE STUDENTS. Keli Fine
 EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND GRADE POINT AVERAGE IN COLLEGE STUDENTS by Keli Fine A Senior Honors Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The University of Utah In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND GRADE POINT AVERAGE IN COLLEGE STUDENTS by Keli Fine A Senior Honors Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The University of Utah In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That. Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens
 I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens AGENDA Behavioral Challenges Challenges and Diagnostic Categories New Ways of Understanding:
I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens AGENDA Behavioral Challenges Challenges and Diagnostic Categories New Ways of Understanding:
Accessibility and Disability Service. A Guide to Services for Students with
 Accessibility and Disability Service 4281 Chapel Lane ~ 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 adsfrontdesk@umd.edu www.counseling.umd.edu/ads A Guide to Services for Students with Attention-Deficit
Accessibility and Disability Service 4281 Chapel Lane ~ 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 adsfrontdesk@umd.edu www.counseling.umd.edu/ads A Guide to Services for Students with Attention-Deficit
A Look Inside. Executive Functioning Deficits. Wendy Kelly, M.A., C. Psych. Assoc. Psychological Services, Kawartha Pine Ridge DSB
 A Look Inside the ADHD Brain: Executive Functioning Deficits Wendy Kelly, M.A., C. Psych. Assoc. Psychological Services, Kawartha Pine Ridge DSB October 19, 2013 Parent Conference Nature of AD/HD Subtypes:
A Look Inside the ADHD Brain: Executive Functioning Deficits Wendy Kelly, M.A., C. Psych. Assoc. Psychological Services, Kawartha Pine Ridge DSB October 19, 2013 Parent Conference Nature of AD/HD Subtypes:
Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript
 Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript In class Tuesday we introduced learning disabilities and looked at a couple of different activities that are consistent and representative of
Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript In class Tuesday we introduced learning disabilities and looked at a couple of different activities that are consistent and representative of
Executive Functioning
 Executive Functioning What is executive functioning? Executive functioning is a process of higher brain functioning that is involved in goal directed activities. It is the part of the brain that enables
Executive Functioning What is executive functioning? Executive functioning is a process of higher brain functioning that is involved in goal directed activities. It is the part of the brain that enables
ADHD and social skills M. T. LAX-PERICALL CONSULTANT IN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY PRIORY HOSPITAL ROEHAMPTON
 ADHD and social skills M. T. LAX-PERICALL CONSULTANT IN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY PRIORY HOSPITAL ROEHAMPTON ADHD (DSM-5) persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes
ADHD and social skills M. T. LAX-PERICALL CONSULTANT IN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY PRIORY HOSPITAL ROEHAMPTON ADHD (DSM-5) persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes
EFFECTS OF ADHD ON EARLY LEARNING AND ACDEMIC PERFORMANCE 1
 EFFECTS OF ADHD ON EARLY LEARNING AND ACDEMIC PERFORMANCE 1 The Effects of ADHD on Learning and Academic Performance in the Pre- and Elementary School Years. Christopher Kalogeropoulos November 19, 2012
EFFECTS OF ADHD ON EARLY LEARNING AND ACDEMIC PERFORMANCE 1 The Effects of ADHD on Learning and Academic Performance in the Pre- and Elementary School Years. Christopher Kalogeropoulos November 19, 2012
Executive Function - Your Window to Understanding Cognitive Pathways
 Executive Function - Your Window to Understanding Cognitive Pathways Agenda 1. How does the brain learn? 2. What is executive function? How do executive weaknesses impact learning for all students? 3.
Executive Function - Your Window to Understanding Cognitive Pathways Agenda 1. How does the brain learn? 2. What is executive function? How do executive weaknesses impact learning for all students? 3.
More Accomplishment! Less Struggle. Bridging the Gaps in Executive Function to Empower our Children with ADHD to Succeed
 More Accomplishment! Less Struggle Bridging the Gaps in Executive Function to Empower our Children with ADHD to Succeed WELCOME Robin Nordmeyer Certified Life Coach and ADHD Coach Managing Director - Minnesota
More Accomplishment! Less Struggle Bridging the Gaps in Executive Function to Empower our Children with ADHD to Succeed WELCOME Robin Nordmeyer Certified Life Coach and ADHD Coach Managing Director - Minnesota
Background Information on ADHD
 Get to know ADHD Background Information on ADHD condition, which affects those parts of the brain which control attention, impulses and concentration (a neurobiological condition). It is thought to affect
Get to know ADHD Background Information on ADHD condition, which affects those parts of the brain which control attention, impulses and concentration (a neurobiological condition). It is thought to affect
SUPPORT INFORMATION ADVOCACY
 THE ASSESSMENT OF ADHD ADHD: Assessment and Diagnosis in Psychology ADHD in children is characterised by developmentally inappropriate overactivity, distractibility, inattention, and impulsive behaviour.
THE ASSESSMENT OF ADHD ADHD: Assessment and Diagnosis in Psychology ADHD in children is characterised by developmentally inappropriate overactivity, distractibility, inattention, and impulsive behaviour.
 alternate-form reliability The degree to which two or more versions of the same test correlate with one another. In clinical studies in which a given function is going to be tested more than once over
alternate-form reliability The degree to which two or more versions of the same test correlate with one another. In clinical studies in which a given function is going to be tested more than once over
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED YEARS
 CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPAIRMENTS
 SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPAIRMENTS Ellen Engstrom, M.A. Director of Education Groves Academy AGENDA Overview of AD/HD and executive functioning impairments and how
SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPAIRMENTS Ellen Engstrom, M.A. Director of Education Groves Academy AGENDA Overview of AD/HD and executive functioning impairments and how
Attention Disorders. By Donna Walker Tileston, Ed.D.
 Attention Disorders By Donna Walker Tileston, Ed.D. In This Session... The Characteristics of ADD and ADHD Diagnosis and Research Classroom Accommodations Paying Attention Involves three neural networks
Attention Disorders By Donna Walker Tileston, Ed.D. In This Session... The Characteristics of ADD and ADHD Diagnosis and Research Classroom Accommodations Paying Attention Involves three neural networks
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children.
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children. One of the leading authorities on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Russell Barkley, PhD., defines
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children. One of the leading authorities on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Russell Barkley, PhD., defines
Difference between ADHD and Executive Functioning. Dr. Josette Abdalla
 Difference between ADHD and Executive Functioning Dr. Josette Abdalla DSM-5 Definition of ADHD The DSM-5 diagnoses 3 types of ADHD: ADHD Predominantly Inattentive type ADHD Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive
Difference between ADHD and Executive Functioning Dr. Josette Abdalla DSM-5 Definition of ADHD The DSM-5 diagnoses 3 types of ADHD: ADHD Predominantly Inattentive type ADHD Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive
DEAF CHILDREN WITH ADHD AND LEARNING DIFFICULTIES
 DEAF CHILDREN WITH ADHD AND LEARNING DIFFICULTIES Scott R. Smith, MD, MPH Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrician University of Rochester Medical Center Common Complaints about Children with Problems Your
DEAF CHILDREN WITH ADHD AND LEARNING DIFFICULTIES Scott R. Smith, MD, MPH Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrician University of Rochester Medical Center Common Complaints about Children with Problems Your
Improving Attention and Learning in Children & Adolescents: The Role of Working Memory
 Improving Attention and Learning in Children & Adolescents: The Role of Working Memory Sophia S. Genone, Ph.D. Margaret J. Kay, Ed.D. Cogmed Working Memory Training: A Program for Improved Attention Sophia
Improving Attention and Learning in Children & Adolescents: The Role of Working Memory Sophia S. Genone, Ph.D. Margaret J. Kay, Ed.D. Cogmed Working Memory Training: A Program for Improved Attention Sophia
FACT SHEET. Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD or ADHD) General Overview (updated 2018)
 Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD or ADHD) General Overview (updated 2018) Attention deficit is a disorder that affects children from the first months of their lives through their school years, through adolescence,
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD or ADHD) General Overview (updated 2018) Attention deficit is a disorder that affects children from the first months of their lives through their school years, through adolescence,
Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes
 HO 4.1 Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes At the end of this session, participants should be able to: define Neuropsychology and the role of the Neuropsychologist (optional) recognise normal difficulties
HO 4.1 Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes At the end of this session, participants should be able to: define Neuropsychology and the role of the Neuropsychologist (optional) recognise normal difficulties
My ADHD Child Doesn t Seem Motivated to Get Good Grades Richard Lougy, LMFT/School Psychologist & David Rosenthal, MD, Psychiatrist
 My ADHD Child Doesn t Seem Motivated to Get Good Grades By Richard Lougy, LMFT/School Psychologist & David Rosenthal, MD, Psychiatrist All children at times find school work boring and not a high priority
My ADHD Child Doesn t Seem Motivated to Get Good Grades By Richard Lougy, LMFT/School Psychologist & David Rosenthal, MD, Psychiatrist All children at times find school work boring and not a high priority
ADD/ADHD AND EF. Attention Deficit Disorder/ Attention Deficit with Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function Difficulties
 Attention Deficit Disorder/ Attention Deficit with Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function Difficulties Dr. Danielle Morris Psy. D. - Clinical Psychologist Marybeth Fussa M.S.Ed. Special Educator/Social
Attention Deficit Disorder/ Attention Deficit with Hyperactivity Disorder and Executive Function Difficulties Dr. Danielle Morris Psy. D. - Clinical Psychologist Marybeth Fussa M.S.Ed. Special Educator/Social
Individuals wishing to seek an evaluation for ADHD
 9 WHAT WE KNOW Diagnosis of ADHD in Adults Individuals wishing to seek an evaluation for ADHD should use this information and resource sheet as a set of guidelines for what to expect from the clinician
9 WHAT WE KNOW Diagnosis of ADHD in Adults Individuals wishing to seek an evaluation for ADHD should use this information and resource sheet as a set of guidelines for what to expect from the clinician
Externalizing Disorders
 Externalizing Disorders Psychology 311 Abnormal Psychology Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides 1 Background Many types ADHD Oppositional Defiant Disorder Tourette Disorder Others Includes
Externalizing Disorders Psychology 311 Abnormal Psychology Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides 1 Background Many types ADHD Oppositional Defiant Disorder Tourette Disorder Others Includes
by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff
 by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client name : Sample Client Client ID : 321 Gender : Female Age : 27 Test date : Test form : BRIEF-A Informant Report
by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client name : Sample Client Client ID : 321 Gender : Female Age : 27 Test date : Test form : BRIEF-A Informant Report
Beyond Lazy and Unmotivated
 Beyond Lazy and Unmotivated Why Parents and Teachers Need to Know About Executive Skills Peg Dawson Center for Learning and Attention Disorders Portsmouth, NH dawson.peg@gmail.com smartbutscatteredkids.com
Beyond Lazy and Unmotivated Why Parents and Teachers Need to Know About Executive Skills Peg Dawson Center for Learning and Attention Disorders Portsmouth, NH dawson.peg@gmail.com smartbutscatteredkids.com
What You Need to Know About ADHD. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
 What You Need to Know About ADHD Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder 2 Table of Contents 1. What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? 3 2. What Does ADHD Look Like? 3 3. Examples of
What You Need to Know About ADHD Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder 2 Table of Contents 1. What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? 3 2. What Does ADHD Look Like? 3 3. Examples of
Russell Barkley, PhD. Internationally recognized authority on ADHD in children and adults
 Russell Barkley, PhD Internationally recognized authority on ADHD in children and adults Dr. Barkley has created a straightforward guide of best practices all educators should use with youth with ADHD.
Russell Barkley, PhD Internationally recognized authority on ADHD in children and adults Dr. Barkley has created a straightforward guide of best practices all educators should use with youth with ADHD.
Welcome to the ADHD group
 Welcome to the ADHD group Aims of this group 1. To help you make sense of your diagnosis and how ADHD has affected you 2. To learn strategies to cope with ADHD 3. To meet others with similar experiences
Welcome to the ADHD group Aims of this group 1. To help you make sense of your diagnosis and how ADHD has affected you 2. To learn strategies to cope with ADHD 3. To meet others with similar experiences
What is ADHD? DSM-5 Criteria
 Executive Functioning, Self-Regulation, and ADHD: Impact on Understanding and Treatment Russell A. Barkley, Ph.D. Clinical Professor of Psychiatry Virginia Treatment Center for Children Virginia Commonwealth
Executive Functioning, Self-Regulation, and ADHD: Impact on Understanding and Treatment Russell A. Barkley, Ph.D. Clinical Professor of Psychiatry Virginia Treatment Center for Children Virginia Commonwealth
Attention- Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Parent Talk. Presented by: Dr. Barbara Kennedy, R.Psych. Dr. Marei Perrin, R.Psych.
 Attention- Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Parent Talk Presented by: Dr. Barbara Kennedy, R.Psych. Dr. Marei Perrin, R.Psych. Agenda What is ADHD? What is ADHD s impact? What can we do about it?
Attention- Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Parent Talk Presented by: Dr. Barbara Kennedy, R.Psych. Dr. Marei Perrin, R.Psych. Agenda What is ADHD? What is ADHD s impact? What can we do about it?
Citation for published version (APA): Jónsdóttir, S. (2006). ADHD and its relationship to comorbidity and gender. s.n.
 University of Groningen ADHD and its relationship to comorbidity and gender Jónsdóttir, Sólveig IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen ADHD and its relationship to comorbidity and gender Jónsdóttir, Sólveig IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Executive Functioning in Gifted Students
 Executive Functioning in Gifted Students What is executive functioning? Executive Functioning Executive function is like the CEO of the brain. It s in charge of making sure things get done from the planning
Executive Functioning in Gifted Students What is executive functioning? Executive Functioning Executive function is like the CEO of the brain. It s in charge of making sure things get done from the planning
Objectives. Age of Onset. ASD: Communication Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision (2000)
 Autism and ADHD What Every Orthodontist Should Know! Heather Whitney Sesma, Ph.D., L.P. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Clinical Neuroscience Objectives Review the core features of autism
Autism and ADHD What Every Orthodontist Should Know! Heather Whitney Sesma, Ph.D., L.P. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Clinical Neuroscience Objectives Review the core features of autism
Consciously Counseling Adults with ADHD. A. Maren Tolley, MS Ed, LCPC
 Consciously Counseling Adults with ADHD A. Maren Tolley, MS Ed, LCPC Best Hopes I sure hope we talk about What is Adult ADHD? 3 core characteristics: Inattentive (trouble focusing) Hyperactive (restless)
Consciously Counseling Adults with ADHD A. Maren Tolley, MS Ed, LCPC Best Hopes I sure hope we talk about What is Adult ADHD? 3 core characteristics: Inattentive (trouble focusing) Hyperactive (restless)
3/10/14. Executive Functions
 Minimize the Madness- Taking the Mystery out of ADHD Medications Class #2 The Executive Function: The Source of ADHD Symptoms Presented by Laurie Dupar, Certified ADHD Coach and Nurse Practitioner Executive
Minimize the Madness- Taking the Mystery out of ADHD Medications Class #2 The Executive Function: The Source of ADHD Symptoms Presented by Laurie Dupar, Certified ADHD Coach and Nurse Practitioner Executive
Learning Styles Questionnaire
 This questionnaire is designed to find out your preferred learning style(s) Over the years you have probably developed learning habits that help you benefit from some experiences than from others Since
This questionnaire is designed to find out your preferred learning style(s) Over the years you have probably developed learning habits that help you benefit from some experiences than from others Since
1. Before starting the second session, quickly examine total on short form BDI; note
 SESSION #2: 10 1. Before starting the second session, quickly examine total on short form BDI; note increase or decrease. Recall that rating a core complaint was discussed earlier. For the purpose of continuity,
SESSION #2: 10 1. Before starting the second session, quickly examine total on short form BDI; note increase or decrease. Recall that rating a core complaint was discussed earlier. For the purpose of continuity,
Questionnaire Translation
 Dr Wan Nor Arifin Unit of Biostatistics and Research Methodology, Universiti Sains Malaysia. wnarifin@usm.my Wan Nor Arifin, 2017. by Wan Nor Arifin is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-
Dr Wan Nor Arifin Unit of Biostatistics and Research Methodology, Universiti Sains Malaysia. wnarifin@usm.my Wan Nor Arifin, 2017. by Wan Nor Arifin is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-
Neuropsychology of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
 Neuropsychology of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Ronna Fried, Ed.D. Director of Neuropsychology Clinical & Research Programs in Pediatric Psychopharmacology and Adult ADHD Massachusetts
Neuropsychology of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Ronna Fried, Ed.D. Director of Neuropsychology Clinical & Research Programs in Pediatric Psychopharmacology and Adult ADHD Massachusetts
MANAGEMENT OF ADHD IN ADULTS
 MANAGEMENT OF ADHD IN ADULTS RICHARD MOLDAWSKY, M.D. I Can t Focus on Anything Except Getting My Adderall 1 ASSUMPTIONS FOR TODAY Most of us don t work 2 W s without seeing a person with ADHD You are familiar
MANAGEMENT OF ADHD IN ADULTS RICHARD MOLDAWSKY, M.D. I Can t Focus on Anything Except Getting My Adderall 1 ASSUMPTIONS FOR TODAY Most of us don t work 2 W s without seeing a person with ADHD You are familiar
Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function BRIEF. Interpretive Report. Developed by SAMPLE
 Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function BRIEF Interpretive Report Developed by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client Information Client Name : Sample Client Client ID
Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function BRIEF Interpretive Report Developed by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client Information Client Name : Sample Client Client ID
Could I Have Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
 Could I Have Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)? Finding an Answer to ADHD as an Adult Do you feel that you have struggled throughout your life with poor concentration, inattention, impulsivity,
Could I Have Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)? Finding an Answer to ADHD as an Adult Do you feel that you have struggled throughout your life with poor concentration, inattention, impulsivity,
Impulsivity is Important
 Impulsivity is Important Involved in every major system of personality Vital role in the understanding & diagnosis of psychopathology: - DSM IV impulse control disorders - Criteria for BPD, ASPD, ADHD
Impulsivity is Important Involved in every major system of personality Vital role in the understanding & diagnosis of psychopathology: - DSM IV impulse control disorders - Criteria for BPD, ASPD, ADHD
Improving Reading Comprehension for Students with ADHD
 World Journal of Educational Research ISSN 2375-9771 (Print) ISSN 2333-5998 (Online) Vol. 2, No. 1, 2015 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/wjer Improving Reading Comprehension for Students with ADHD 1 College
World Journal of Educational Research ISSN 2375-9771 (Print) ISSN 2333-5998 (Online) Vol. 2, No. 1, 2015 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/wjer Improving Reading Comprehension for Students with ADHD 1 College
WEISS FUNCTIONAL IMPAIRMENT RATING SCALES (WFIRS) SELF REPORT RATING SCALE
 Page 1 of 5 DSM-5 criteria for the diagnosis of ADHD emphasize the importance of gathering behavioral information from multiple settings and multiple informants. To accomplish this, standardized ADHD rating
Page 1 of 5 DSM-5 criteria for the diagnosis of ADHD emphasize the importance of gathering behavioral information from multiple settings and multiple informants. To accomplish this, standardized ADHD rating
A guide to Getting an ADHD Assessment as an adult in Scotland
 A guide to Getting an ADHD Assessment as an adult in Scotland This is a guide for adults living in Scotland who think they may have ADHD and have not been diagnosed before. It explains: Things you may
A guide to Getting an ADHD Assessment as an adult in Scotland This is a guide for adults living in Scotland who think they may have ADHD and have not been diagnosed before. It explains: Things you may
Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1
 Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1 Please use the following citation when referencing this work: McGill, R. J. (2013). Test review: Children s Psychological Processing Scale (CPPS). Journal of Psychoeducational
Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1 Please use the following citation when referencing this work: McGill, R. J. (2013). Test review: Children s Psychological Processing Scale (CPPS). Journal of Psychoeducational
Tests/subtests that may capture this skill a,b. How it might look in school or in the home c Response inhibition
 Executive Skill How the skill may appear in testing situations Tests/subtests that may capture this skill a,b Where it might be seen on a behavior rating scale b How it might look in school or in the home
Executive Skill How the skill may appear in testing situations Tests/subtests that may capture this skill a,b Where it might be seen on a behavior rating scale b How it might look in school or in the home
2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction
 2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction 2.1 Introduction In our everyday life we try to achieve various goals through different activities, receive information from our environment, learn about many
2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction 2.1 Introduction In our everyday life we try to achieve various goals through different activities, receive information from our environment, learn about many
Adult ADHD. 1. Overview of ADHD 4. Principles for managing ADHD. 2. Common features of ADHD in adults. 3. General approaches to managing ADHD
 Adult ADHD 1. Overview of ADHD 4. Principles for managing ADHD 2. Common features of ADHD in adults 3. General approaches to managing ADHD Definition The name... 1. Overview of ADHD Definition Attention
Adult ADHD 1. Overview of ADHD 4. Principles for managing ADHD 2. Common features of ADHD in adults 3. General approaches to managing ADHD Definition The name... 1. Overview of ADHD Definition Attention
Making a psychometric. Dr Benjamin Cowan- Lecture 9
 Making a psychometric Dr Benjamin Cowan- Lecture 9 What this lecture will cover What is a questionnaire? Development of questionnaires Item development Scale options Scale reliability & validity Factor
Making a psychometric Dr Benjamin Cowan- Lecture 9 What this lecture will cover What is a questionnaire? Development of questionnaires Item development Scale options Scale reliability & validity Factor
1. *History of ADHD symptoms in childhood, such as distractibility, short attention span, impulsivity or restlessness. ADHD doesn't start at age 30.
 www.addresources.org Adult Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Checklist by Daniel G. Amen, M.D. back to graphic version Terms of Use: This educational material is made available courtesy of
www.addresources.org Adult Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Checklist by Daniel G. Amen, M.D. back to graphic version Terms of Use: This educational material is made available courtesy of
Undiagnosed ADHD Among Unionized Drivers in Ghana: Public Health and Policy Implications
 Undiagnosed ADHD Among Unionized Drivers in Ghana: Public Health and Policy Implications Thad Ulzen MD Professor and Chair, Dept. of Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Associate Dean for Academic Affairs
Undiagnosed ADHD Among Unionized Drivers in Ghana: Public Health and Policy Implications Thad Ulzen MD Professor and Chair, Dept. of Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Associate Dean for Academic Affairs
Managing ADHD. Strategies and Modifications for Counselors and Teachers
 Managing ADHD Strategies and Modifications for Counselors and Teachers F Russell Crites, Jr., M.S., L.P.C., L.M.F.T, L.S.S.P. Director Crites Psychoeducational Consultants www.critescounseling.com 972-506-7111
Managing ADHD Strategies and Modifications for Counselors and Teachers F Russell Crites, Jr., M.S., L.P.C., L.M.F.T, L.S.S.P. Director Crites Psychoeducational Consultants www.critescounseling.com 972-506-7111
TOOL KIT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT ATTENTION DEFICIT/ HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD)
 TOOL KIT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT ATTENTION DEFICIT/ HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) TOOL KIT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) The clinical tool kit is intended
TOOL KIT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT ATTENTION DEFICIT/ HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) TOOL KIT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) The clinical tool kit is intended
 http://www.kidshealth.org/teen/school_jobs/school/adhd.html ADHD stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. ADHD used to be known as attention deficit disorder, or ADD. In 1994, it was renamed
http://www.kidshealth.org/teen/school_jobs/school/adhd.html ADHD stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. ADHD used to be known as attention deficit disorder, or ADD. In 1994, it was renamed
Everyday Problem Solving and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living: Support for Domain Specificity
 Behav. Sci. 2013, 3, 170 191; doi:10.3390/bs3010170 Article OPEN ACCESS behavioral sciences ISSN 2076-328X www.mdpi.com/journal/behavsci Everyday Problem Solving and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living:
Behav. Sci. 2013, 3, 170 191; doi:10.3390/bs3010170 Article OPEN ACCESS behavioral sciences ISSN 2076-328X www.mdpi.com/journal/behavsci Everyday Problem Solving and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living:
Social Communication in young adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi
 Social Communication in young adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi We ll cover Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) ASD in young adults Social Communication (definition, components, importance,
Social Communication in young adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi We ll cover Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) ASD in young adults Social Communication (definition, components, importance,
Intro to Executive Functioning Across the Lifespan. Agenda. The Construct of Executive Functioning. Construct of Executive Functioning
 Intro to Executive Functioning Across the Lifespan Amy Dilworth Gabel, Ph.D. Anne-Marie Kimbell, Ph.D. Agenda Construct of Executive Functioning Conceptualizations Executive Functioning in Everyday Life
Intro to Executive Functioning Across the Lifespan Amy Dilworth Gabel, Ph.D. Anne-Marie Kimbell, Ph.D. Agenda Construct of Executive Functioning Conceptualizations Executive Functioning in Everyday Life
Update on the Treatment of ADHD 2019
 Update on the Treatment of ADHD 2019 James H. Beard, Jr., M.D, FAAP Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrician Division of Developmental Pediatrics The Rights of ADHD The right diagnosis of ADHD and co morbidities
Update on the Treatment of ADHD 2019 James H. Beard, Jr., M.D, FAAP Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrician Division of Developmental Pediatrics The Rights of ADHD The right diagnosis of ADHD and co morbidities
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)/Attention Deficit w/ Hyperactivity Self Test
 Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)/Attention Deficit w/ Hyperactivity Self Test The test physicians use to diagnose ADD/ADHD is subjective and rests on observing symptoms such as hyperactivity and attention
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)/Attention Deficit w/ Hyperactivity Self Test The test physicians use to diagnose ADD/ADHD is subjective and rests on observing symptoms such as hyperactivity and attention
TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from. Self-Perception Guide
 TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Self-Perception Guide Self-perception GUIDE Table of Contents Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM............................................. 1 Where Did Your Style
TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Self-Perception Guide Self-perception GUIDE Table of Contents Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM............................................. 1 Where Did Your Style
ADD/ADHD: REAL or IMAGINED?
 Author: Becky MacKenzie, 2006 ADD/ADHD: REAL or IMAGINED? Is ADD/ADHD a legitimate mental disorder? The subject of ADD/ADHD came up in class the other night. A student asked if ADD/ADHD was a real disorder
Author: Becky MacKenzie, 2006 ADD/ADHD: REAL or IMAGINED? Is ADD/ADHD a legitimate mental disorder? The subject of ADD/ADHD came up in class the other night. A student asked if ADD/ADHD was a real disorder
Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility
 CONCEPTS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility Concepts Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style
CONCEPTS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility Concepts Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style
Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Klijn, W. J. L. (2013).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Klijn, W. J. L. (2013).
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version
 Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Focus of Today s Presentation. Partners in Healing Model. Partners in Healing: Background. Data Collection Tools. Research Design
 Exploring the Impact of Delivering Mental Health Services in NYC After-School Programs Gerald Landsberg, DSW, MPA Stephanie-Smith Waterman, MSW, MS Ana Maria Pinter, M.A. Focus of Today s Presentation
Exploring the Impact of Delivering Mental Health Services in NYC After-School Programs Gerald Landsberg, DSW, MPA Stephanie-Smith Waterman, MSW, MS Ana Maria Pinter, M.A. Focus of Today s Presentation
Ask the Expert Educator Edition
 www.help4adhd.org (800) 233-4050 Help4ADHD@CHADD.org Ask the Expert Educator Edition How to Build Self-Motivation in Teens with ADHD Margaret Sibley, PhD Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine Florida International
www.help4adhd.org (800) 233-4050 Help4ADHD@CHADD.org Ask the Expert Educator Edition How to Build Self-Motivation in Teens with ADHD Margaret Sibley, PhD Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine Florida International
Understanding Students with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
 Understanding Students with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder At the end of this presentation you should be able to: Define and identify the characteristics of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity
Understanding Students with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder At the end of this presentation you should be able to: Define and identify the characteristics of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity
Departamento de Psicologia, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil. 2
 Clinical Neuropsychiatry (2014) 11 EPUB AHEAD OF PRINT THE FIVE DIGITS TEST ON THE ASSESSMENT OF PSYCHIATRIC PATIENTS WITH HETEROGENEOUS EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUNDS: EVIDENCES OF VALIDITY ON THE ASSESSMENT
Clinical Neuropsychiatry (2014) 11 EPUB AHEAD OF PRINT THE FIVE DIGITS TEST ON THE ASSESSMENT OF PSYCHIATRIC PATIENTS WITH HETEROGENEOUS EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUNDS: EVIDENCES OF VALIDITY ON THE ASSESSMENT
7/31/2017. Outline. What is mindfulness? What is complex ADHD? Mindful Awareness and ADHD Care. Complex ADHD & Mindfulness
 Outline Complex ADHD & Mindfulness What is mindfulness? What is complex ADHD? Mindful Awareness and ADHD Care Mark Bertin, MD Developmental Pediatrics Author, Mindful Parenting for ADHD What is mindfulness?
Outline Complex ADHD & Mindfulness What is mindfulness? What is complex ADHD? Mindful Awareness and ADHD Care Mark Bertin, MD Developmental Pediatrics Author, Mindful Parenting for ADHD What is mindfulness?
The ABCs of Dementia Diagnosis
 The ABCs of Dementia Diagnosis Dr. Robin Heinrichs, Ph.D., ABPP Board Certified Clinical Neuropsychologist Associate Professor, Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Director of Neuropsychology Training What
The ABCs of Dementia Diagnosis Dr. Robin Heinrichs, Ph.D., ABPP Board Certified Clinical Neuropsychologist Associate Professor, Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Director of Neuropsychology Training What
PRACTICE PARAMETERS FOR THE ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER
 PRACTICE PARAMETERS FOR THE ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). (2017, August 31). Retrieved April 06,
PRACTICE PARAMETERS FOR THE ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). (2017, August 31). Retrieved April 06,
A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems
 A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems 3 Facts Sheets: (1) Developmental Variations (2) Problems (3) Disorders The American Academy of Pediatrics has produced a manual for primary care providers
A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems 3 Facts Sheets: (1) Developmental Variations (2) Problems (3) Disorders The American Academy of Pediatrics has produced a manual for primary care providers
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The Impact of ADHD on Learning. Miranda Shields, PsyD
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The Impact of ADHD on Learning Miranda Shields, PsyD mshields@murrieta.k12.ca.us Definition DSM V Three types 1. Inattentive Type 2. Hyperactive Impulsive Type
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The Impact of ADHD on Learning Miranda Shields, PsyD mshields@murrieta.k12.ca.us Definition DSM V Three types 1. Inattentive Type 2. Hyperactive Impulsive Type
EMOTIONAL QUOTIENT ASSESSMENT RESULTS
 EMOTIONAL QUOTIENT ASSESSMENT RESULTS The Emotional Quotient (EQ) is a measure of your ability to sense, understand, and effectively apply the power and acumen of your emotions and the emotions of others
EMOTIONAL QUOTIENT ASSESSMENT RESULTS The Emotional Quotient (EQ) is a measure of your ability to sense, understand, and effectively apply the power and acumen of your emotions and the emotions of others
ADHD and Comorbid Conditions A Conceptual Model
 ADHD and Comorbid Conditions A Conceptual Model Thomas E. Brown PhD. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry, Yale University School of Medicine and Associate Director of the Yale Clinic for Attention
ADHD and Comorbid Conditions A Conceptual Model Thomas E. Brown PhD. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry, Yale University School of Medicine and Associate Director of the Yale Clinic for Attention
PLAN FOR TODAY. What is Emotional Intelligence/EQ? Why it Matters An Overview of the EQ Model Lots of ideas for improving your EQ
 PLAN FOR TODAY What is Emotional Intelligence/EQ? Why it Matters An Overview of the EQ Model Lots of ideas for improving your EQ EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IS NOT Being Emotional Always Agreeable Optimistic
PLAN FOR TODAY What is Emotional Intelligence/EQ? Why it Matters An Overview of the EQ Model Lots of ideas for improving your EQ EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IS NOT Being Emotional Always Agreeable Optimistic
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. ADHD and the Nature of Self-Control, Russell A. Barkley Copyright 2005.
 This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. ADHD and the Nature of Self-Control, Russell A. Barkley Copyright 2005 Afterword (2005) Afterword (2005) It is most gratifying to see the excellent
This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. ADHD and the Nature of Self-Control, Russell A. Barkley Copyright 2005 Afterword (2005) Afterword (2005) It is most gratifying to see the excellent
Stay Sane & More Satisfied in The Difference You Make 3/14/18. The Value CM Bring to all. 5.Re-igniting your spirit! Action Plan CMSNE 3/14/18
 Stay Sane & More Satisfied in 2018 1.The difference you make in so many lives 2. Managing yourself in stressful situations 3. Balancing your needs with others- connect with your strengths, self-talk &
Stay Sane & More Satisfied in 2018 1.The difference you make in so many lives 2. Managing yourself in stressful situations 3. Balancing your needs with others- connect with your strengths, self-talk &
Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders
 Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Introduction Attention deficit and disruptive behavior disorders are commonly known as child behavior disorders. A child behavior disorder is when a
Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Introduction Attention deficit and disruptive behavior disorders are commonly known as child behavior disorders. A child behavior disorder is when a
Attention-deficit hyperactive disorder in school-aged children in Saudi Arabia
 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1190-y ORIGINAL PAPER Attention-deficit hyperactive disorder in school-aged children in Saudi Arabia Mohammed M. J. Alqahtani Received: 31 December 2009 / Accepted: 9 March 2010
DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1190-y ORIGINAL PAPER Attention-deficit hyperactive disorder in school-aged children in Saudi Arabia Mohammed M. J. Alqahtani Received: 31 December 2009 / Accepted: 9 March 2010
SAFETY QUOTIENT. EMPLOYER REPORT For Hiring, Training & Coaching. June 20, Kelly Sample
 SAFETY QUOTIENT TM EMPLOYER REPORT For Hiring, Training & Coaching Kelly Sample support@talentclick.com June 20, 2017 PART A SAFETY RISK FACTORS Safety Personality Defined This section is a summary of
SAFETY QUOTIENT TM EMPLOYER REPORT For Hiring, Training & Coaching Kelly Sample support@talentclick.com June 20, 2017 PART A SAFETY RISK FACTORS Safety Personality Defined This section is a summary of
TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version
 TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version 2-2-2011 Scottsdale, Arizona INTRODUCTION The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version 2-2-2011 Scottsdale, Arizona INTRODUCTION The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
Adult ADHD and Its Impact on the Family System
 Adult ADHD and Its Impact on the Family System S T R O N G F A M I L I E S A Z C O N F E R E N C E S E P T E M B E R, 2 0 1 4 L I S A S T E R N E, M A, M A What is ADHD? Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
Adult ADHD and Its Impact on the Family System S T R O N G F A M I L I E S A Z C O N F E R E N C E S E P T E M B E R, 2 0 1 4 L I S A S T E R N E, M A, M A What is ADHD? Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
Everything DiSC Manual
 Everything DiSC Manual PRODUCTIVE CONFLICT ADDENDUM The most recently published version of the Everything DiSC Manual includes a new section, found in Chapter 6, The Everything DiSC Applications, for Everything
Everything DiSC Manual PRODUCTIVE CONFLICT ADDENDUM The most recently published version of the Everything DiSC Manual includes a new section, found in Chapter 6, The Everything DiSC Applications, for Everything
