Summary of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (II) January 12, 2010
|
|
|
- Peregrine Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summary of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (II) January 12, 2010 The Sixteenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 8:30am to 3:30pm on January 12, 2010 to discuss tuberculosis. The Task Force Members are: Sir George Alleyne, Johns Hopkins University; Mr. Ekkehard Betsch, The World Bank; Dr. Stephen Blount, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Dr. Mickey Chopra, UNICEF; Dr. Donald Hopkins, The Carter Center (Chair); Dr. Adetokunbo Lucas, Harvard University; Professor David Molyneux, Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine (Rtd.); Dr. Mark Rosenberg, Task Force for Global Health; Dr. Lorenzo Savioli, World Health Organization (WHO); Dr. Harrison Spencer, Association of Schools of Public Health; Dr. Dyann Wirth, Harvard School of Public Health; and Dr. Yoichi Yamagata, Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Eight Task Force members (Alleyne, Betsch, Blount, Hopkins, Lucas, Rosenberg, Spencer, Wirth) attended this meeting, and one was represented by an alternate (Dr. Mario Raviglione for Savioli). The presenters on tuberculosis were Dr. Jose Becerra and Dr. Kevin Cain of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Megan Murray of the Harvard School of Public Health, and Dr. Mario Raviglione of the World Health Organization. A representative from the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) was unable to attend. Tuberculosis In 2008, there were an estimated 9.4 million cases of tuberculosis globally, including 1.4 million cases of HIV-associated tuberculosis, and 1.8 million deaths, including 0.52 million deaths in HIV-infected patients. In the same year, there were an estimated 0.5 million cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB: strains resistant to, at least, the two most important first-line drugs isoniazid and rifampicin) with at least 0.15 million associated deaths, as well as about 50,000 cases of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB: resistant to first- and second-line drugs) and at least 30,000 associated deaths. Drug-resistant tuberculosis strains, including XDR-TB, have been found in every country where they have been sought. Approximately 85% of all tuberculosis cases are located in the South East Asian (34%), African (31%) and Western Pacific (20%) Regions of WHO, with the remainder in the Eastern Mediterranean (7%), European (5%) and American (3%) Regions. Cases of MDR-TB are especially numerous in nations of the former Soviet Union, India and China, while 80% of TB/HIV cases are found in Africa, especially in southern and southeastern Africa. The DOTS strategy, launched by WHO in 1995, calls for government commitment to tuberculosis control; bacteriological diagnosis of cases detected among symptomatic
2 patients; use of standard short-course chemotherapy regimen under supervision in all patients; assurance of a regular supply of drugs; and a system for surveillance and monitoring of the program performance. Specific targets were set by the World Health Assembly in 1991: to detect at least 70% of estimated cases and cure at least 85% of those detected. The Stop TB Strategy, launched by WHO in 2006, calls for enhancing the DOTS strategy to address new challenges and to expand access to the most vulnerable populations. It targets achievement of the TB-related Millennium Development Goal 6, target 6c: "to have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence of tuberculosis". Other elements of the Stop TB Strategy require addressing TB/HIV, MDR-TB and the needs of the poor and vulnerable; contributing to strengthening health systems; engaging all healthcare providers; empowering people with tuberculosis and their communities; and promoting research. The Stop TB Partnership, established in 2001 and housed by WHO, defined the goals of reducing overall prevalence and deaths from tuberculosis by 50% by 2015 (compared to 1990), and achieving elimination (defined as an incidence of <1 case per million population) by 2050 (global incidence is about 1,400 per million population now). Major achievements between 1995 and 2008 include 36 million patients cured, more than 6 million deaths averted compared to non-dots treatment, reduction of case fatality rate from 7.6% to 4%, and attainment of highest-ever cure rates of 87% in Incidence rates are declining globally and in all sub-regions except in certain African countries since 2004, but not as rapidly as predicted (less than 1% per year) or as necessary in order to reach the program s quantitative targets. However, the absolute number of cases is still increasing, due to population growth off-setting per capita rate reductions, and limited reduction in transmission. Funding for tuberculosis programs has increased substantially in recent years, from US$2.7 billion in 2006 to US$4.1 billion in 2010, including near doubling of government funding to almost US$2.5 billion. However, the funding gap remains substantial compared to funding needs estimated by the Global Plan to Stop TB. Overall, about 61% (5.5 million) of estimated tuberculosis cases were reported as of 2008, while less than 10% of MDR-TB cases are detected. Overall case detection has been stagnating globally since This is partly linked to the failure to report cases detected within the non-state sector. For example, between 1999 and 2005, the program in Bangalore, India increased reporting of tuberculosis cases nearly five-fold by involving health providers among NGOs, private, corporate, medical college and other government entities outside of the designated services of the national program. Delayed detection of infectious cases is also a problem, especially where access to services is seriously impaired. Few laboratories in the African Region can test for resistant strains of tuberculosis. In 2008, about 45% of TB patients in Africa were tested for HIV infection, while about 4% of HIV positive persons were screened for tuberculosis infection. Coverage with some key interventions to address HIV-associated tuberculosis has been scaled up in recent years: an estimated 73% of TB/HIV infected Africans were on cotrimoxazole preventive therapy (CPT) for treatment of concomitant bacterial infections in 2008; 31% were placed on anti-retroviral therapy (ART) for treatment of their HIV infection. 2
3 In the syndemic of dual TB/HIV infection, the two diseases act synergistically to cause excess morbidity and mortality. Tuberculosis is common and deadly in persons with HIV infection, with up to 25-50% dying within months. Persons with such dual infections comprise about 30% of all deaths from tuberculosis. In the African subregion, where this syndemic is most prevalent, HIV prevalence in the general population rose to a peak in about 2000, and in turn triggered an explosion of tuberculosis, which attained peak incidence in about Persons with either disease should be screened or tested for the other infection. While the evidence strongly supports the need for TB screening in people with HIV, there is currently no internationally accepted, evidence-based approach to doing so. Persons infected with HIV may lack classic signs and symptoms of tuberculosis, and tests that are routinely used to diagnose TB (sputum smear microscopy and chest radiography) are relatively insensitive in people with HIV. A study by CDC has determined that chronic cough, which is commonly used for TB screening, is very insensitive in people with HIV and should not be used alone for TB screening in this group. The best combination of symptoms/signs to predict likely tuberculosis in HIV infected persons, based on this analysis, is night sweats for at least 3 weeks, or cough or fever of any duration. Patients who lack all of these symptoms are unlikely to have TB. Isoniazid preventive therapy (IPT), if indicated, can be safely started in most cases. Patients who do have one or more of these symptoms require diagnostic evaluation (including sputum smears, chest radiography, and CD4 testing). Most patients with negative sputum smears will require liquid culture of sputum specimens to accurately diagnose TB. Implementing the preferred diagnostic procedures would require scaling up of laboratory capacity to conduct liquid cultures for tuberculosis, especially in the African countries of greatest concern. It is important to start anti-retroviral therapy (ART) as early as possible in coinfected tuberculosis patients, as it can substantially reduce mortality. In people with HIV who do not yet have TB, ART can reduce the incidence of active tuberculosis by about 50%. IPT can also reduce incidence of active tuberculosis in co-infected persons whose tuberculin skin test is positive. Note is also made of examples where behavioral change brought about a significant reduction in the prevalence of HIV infection. 12 Tuberculosis has had a long association with poverty and low socio-economic status throughout history, and deaths from the disease began declining sharply in wealthier countries long before the advent of anti-tuberculosis drugs. In modern times documented surges in tuberculosis incidence have been associated with adverse economic developments in several countries, reflecting complex and inadequately understood interactions among people, their environment, health services, and tubercle bacilli. Some studies have found an inverse correlation between the risk of tuberculosis and the number and kind of material goods possessed by individuals or their families. The poor suffer by having less access to proper care, by spending a higher proportion of their income on 1 Lugalla J, Emmelin M, Mutembei A, Sima M, Kwesigabo G, Killewo J, Dahlgren L, Social, cultural and sexual behavioral determinants of observed decline in HIV infection trends: Lessons from the Kagera Region, Tanzania. Soc Sci Med 59(1): Kirby D, Changes in sexual behaviour leading to the decline in the prevalence of HIV in Uganda: Confirmation from multiple sources of evidence. Sex Transm Infect 84(Suppl II):ii35 ii41. 3
4 health care, and in numerous other poorly understood ways. Other studies suggest significant population attributable fraction of risk of tuberculosis in association with malnutrition, indoor air pollution, cigarette smoking, HIV infection, alcohol abuse, and diabetes. Education is also an important determinant of risk of tuberculosis, apart from level of income. Some such factors (e.g., HIV and diabetes) that are associated with increased risk of tuberculosis must be addressed by other health programs (e.g., HIV/AIDS programs or primary care services) while other determinants (e.g., over crowding, indoor air pollution, malnutrition) by agencies outside of the health sector altogether. Mathematical modeling of tuberculosis transmission highlights the current overwhelming importance of latent infections in foreign-born residents as the major source of new tuberculosis disease in the United States. Immigrants from a few countries account for a large share of the emerging cases. If current control measures are sustained, preventing progression of latent tuberculosis infection towards active disease will be the most important determinant to stop transmission in the U.S. New tools for preventing, diagnosing, and to provide shorter and safer treatment, particularly among foreign-born persons with latent infections, will be required in order to eliminate tuberculosis from the U.S. in this century. Task Force members noted the importance of improving the quality and extending the coverage of interventions to all populations at risk for tuberculosis urgently, in order to make better use of existing tools, and to help reduce the spread of TB, MDR-TB, XDR- TB, and reduce the incidence of HIV-associated tuberculosis. Tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS programs need to work together to mutual benefit, in order to ensure that patients with either disease are screened or tested promptly for the other disease and begun on appropriate measures immediately if indicated. Prevention and treatment of HIV infections are powerful weapons for preventing tuberculosis. In this and other areas, tuberculosis programs should aggressively seek synergies with other appropriate programs, including outside of the health sector, by emphasizing to the other programs the benefit of an additional impact on tuberculosis. Given the multiple, disparate risk factors for tuberculosis, control of the disease and, any possibility of elimination will require a multi-dimensional approach. Besides the core interventions against tuberculosis that are part of the Stop TB Strategy, bold policies across the health system, intensified research, and action on the risk factors and the determinants of the disease will be necessary. Vigorous advocacy on behalf of tuberculosis programs is needed in order to engage other relevant health programs as well as relevant potential allies outside of the health sector. Tuberculosis programs cannot bear the entire burden of such advocacy, but should solicit the help of other members of the government, including the minister of health, and through the minister of health, other ministers, the head of government and the head of state, where necessary. The tuberculosis program should have in hand cogent data on the burden of tuberculosis, the progress and effectiveness of tuberculosis interventions, and the costs of not intervening, as ammunition to help recruit other allies. It was mentioned during the discussion that a study by The World Bank estimated that investment of $1 in 4
5 tuberculosis control yields an average of about $10 in benefits. The need to develop and publicize more such data, including the potential numbers of Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYS) that could be saved by tuberculosis interventions was also emphasized in the discussion. Control of tuberculosis can be presented as a way to combat poverty, and as a driver of improved services to vulnerable, deprived, marginalized groups. More can be accomplished using the tools that we already have to combat tuberculosis. There was not a separate presentation on the status of tuberculosis research, as planned, due to unforeseen circumstances. It was evident, however, that the existing tools for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of tuberculosis are very old, increasingly outdated, and in the case of available drugs, of diminishing effectiveness. Thanks largely to recent investments by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, some potential new diagnostics, drugs, and a better tuberculosis vaccine are or may be in the pipeline, but the most optimistic time to possible delivery of any successful new tools is still several years away, and their improvement over existing tools may only be marginal. Some knowledgeable members of the Task Force therefore suggested that the current situation calls for a radical re-thinking in the direction of higher risk basic research on tuberculosis and tubercle bacilli in the hope of a possible substantial success in the longer term, while making batter use of currently available tools for the foreseeable future. Tuberculosis is a chronic disease, and delivering effective health care to prevent and treat it could provide the basis for combating other chronic conditions. In the case of tuberculosis, however, stigma against persons suffering from the disease varies in different cultures, but must be addressed where it occurs. It was pointed out that volunteer or compensated community health workers have proven very effective in some programs, as has the kinship strategy 3, and those approaches might be useful to help extend the reach of interventions against tuberculosis and make detection of cases and follow-up of the long 6-month treatment easier. The need for better surveillance and reporting of tuberculosis cases and for focusing on a limited set of key indicators of coverage (process) and impact (outcome) of tuberculosis programs was discussed extensively. The value of using absolute numbers of cases reported instead of prevalence or incidence rates in order to appreciate priorities for reducing the global burden of the disease was also mentioned. Judicious use of computers to help process reports of cases and the status of interventions as revealed by key indices would help leverage the surveillance data to guide programs. Leaders of the global program were strongly urged to gather whatever reports are available into an annual surveillance summary for publication in the World Health Organization s Weekly Epidemiological Record. Experience of other programs has shown the effectiveness of such publications to stimulate improved reporting of cases and of other program data. Members of the Task Force agreed that it is in the self-interest of the US to provide more support for tuberculosis research (operational, laboratory, epidemiologic, health systems) 3 Katabarwa MN, Habomugisha P, Agunyo S, McKelvey AC, Ogweng N, Kwebiiha S, Byenume F, Male B, McFarland D (2010). Traditional kinship system enhanced classic community-directed treatment with ivermectin (CDTI) for onchocerciasis control in Uganda. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. [in press] 5
6 and control, similar to the greatly enhanced support for control of HIV/AIDS and malaria. Conclusions and Recommendations 1. Implementation of the World Health Organization-led DOTS strategy since 1995 and the enhanced Stop TB Strategy beginning in 2006 has advanced control of tuberculosis significantly. The global Stop TB Partnership, established in 2001 and hosted by WHO, may serve as a model for coordinating collaborative efforts among several stakeholders. 2. Although tuberculosis cannot be eradicated in the foreseeable future with currently available tools, progress towards better control and reduction in transmission rates can and should be accelerated urgently. 3. The neglect of tuberculosis research over several decades has taken a large toll in additional illness and deaths, in increased resistance to available therapeutic drugs, and in lack of new tools for diagnosis, prevention and treatment, but funding by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and others has stimulated important new research in recent years. Much more research is needed however, and increase more support by public and private agencies, especially in Europe, is encouraged. 4. The ITFDE emphasized the need for more vigorous political advocacy in support of tuberculosis control, including among potential allies within and outside of the health sector; for significant increase in access and coverage among the poorest and most vulnerable population, using available interventions; and for radical re-thinking of basic, research related to tuberculosis. 5. In order to intervene on the socio-economic determinants of tuberculosis and prevent infection and disease, other sectors must be targeted with proper advocacy strategies. These should be based on the possibility and feasibility to implement pragmatic interventions that would link tuberculosis control efforts with those of the relevant sectors. 6. Tuberculosis control and elimination depend ultimately also on establishing and enforcing policies across the health system which would benefit disease control in general. These include removing financial barriers to diagnosis and care, ensuring availability of quality drugs and regulating the use of all anti-tuberculosis drugs, establishing a network of laboratories where rapid tests are also available, ensuring well-trained and sufficient human resources, etc. 7. The emergence of tuberculosis strains that are resistant to multiple anti-tuberculosis drugs, and the synergy between tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS in co-infected persons are two major challenges to tuberculosis control. Combating the first requires pursuit of the proper strategy of TB control to prevent its emergence and monitoring of use of available drugs and of drug resistance. For the latter, preventing HIV/AIDS infections is one of the most important ways to prevent death from either or both diseases in areas where prevalence of HIV/AIDS is high. For now, TB incidence and 6
7 mortality in people with HIV can be reduced through early HIV testing of TB patients, high quality TB screening in people with HIV, increased use of ART and IPT, and scale-up of TB culture capacity. 8. The WHO's Stop TB Tuberculosis Department should publish annual summaries of global surveillance and interventions data, including key indices of programmatic operations, in WHO s Weekly Epidemiological Record. 9. Successful expansion of current interventions requires greatly accelerated improvements and extension of laboratory services that can support accurate and rapid diagnosis and treatment, including assessment of drug resistance. With additional support, such improved tuberculosis laboratories could form the base for upgrading laboratory services for other diseases 10. Successful expansion of current interventions also requires effective supervision of long-term treatment, a service that can be a model for addressing other chronic conditions, and which would benefit from existing or newly established effective primary health care services and community care schemes. 11. Most new cases of tuberculosis in the United States are in persons who were born in other countries. Interruption of tuberculosis transmission in the United States therefore would benefit greatly from increased assistance for improved control and research of tuberculosis in selected other countries. 7
MODULE SIX. Global TB Institutions and Policy Framework. Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit
 MODULE SIX Global TB Institutions and Policy Framework Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit 1 Topics to be Covered Global TB policy and coordinating structures The Stop TB Strategy TB/HIV collaborative
MODULE SIX Global TB Institutions and Policy Framework Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit 1 Topics to be Covered Global TB policy and coordinating structures The Stop TB Strategy TB/HIV collaborative
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response. Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director
 TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE CONTROL OF A DUAL EPIDEMIC IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Regional Director.
 30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
The WHO END-TB Strategy
 ENDING TB and MDR-TB The WHO END-TB Strategy Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Joint GDI/GLI Partners Forum WHO Geneva, 27 April 2015 This talk will deal with TB Burden Progress, Challenges Way Forward Who
ENDING TB and MDR-TB The WHO END-TB Strategy Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Joint GDI/GLI Partners Forum WHO Geneva, 27 April 2015 This talk will deal with TB Burden Progress, Challenges Way Forward Who
2010 global TB trends, goals How DOTS happens at country level - an exercise New strategies to address impediments Local challenges
 Outline of what it will take Tuberculosis Elimination 25: Global and Local Challenges Anne Fanning, MD November 9, 211 21 global TB trends, goals How DOTS happens at country level - an exercise New strategies
Outline of what it will take Tuberculosis Elimination 25: Global and Local Challenges Anne Fanning, MD November 9, 211 21 global TB trends, goals How DOTS happens at country level - an exercise New strategies
Kenya Perspectives. Post-2015 Development Agenda. Tuberculosis
 Kenya Perspectives Post-2015 Development Agenda Tuberculosis SPEAKERS Anna Vassall Anna Vassall is Senior Lecturer in Health Economics at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. She is a health
Kenya Perspectives Post-2015 Development Agenda Tuberculosis SPEAKERS Anna Vassall Anna Vassall is Senior Lecturer in Health Economics at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. She is a health
Summary of the Twelfth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 6, 2008
 Summary of the Twelfth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 6, 2008 The Twelfth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 8:30am to 4:00pm
Summary of the Twelfth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 6, 2008 The Twelfth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 8:30am to 4:00pm
Questions and Answers Press conference - Press Centre Room 3 Wednesday 16 August 2006, 14.00hrs
 Questions and Answers Press conference - Press Centre Room 3 Wednesday 16 August 2006, 14.00hrs What causes TB? TB is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Although it can cause disease in
Questions and Answers Press conference - Press Centre Room 3 Wednesday 16 August 2006, 14.00hrs What causes TB? TB is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Although it can cause disease in
Global, National, Regional
 Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
The United Nations flag outside the Secretariat building of the United Nations, New York City, United States of America
 The United Nations flag outside the Secretariat building of the United Nations, New York City, United States of America Mike Segar / Reuters Executive Summary Context On 26 September 2018, the United Nations
The United Nations flag outside the Secretariat building of the United Nations, New York City, United States of America Mike Segar / Reuters Executive Summary Context On 26 September 2018, the United Nations
RAPID DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF MDR-TB
 RAPID DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF MDR-TB FORMING PARTNERSHIPS TO STRENGTHEN THE GLOBAL RESPONSE TO MDR-TB - WHERE IT MATTERS MOST I am delighted that this initiative will improve both the technology needed
RAPID DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF MDR-TB FORMING PARTNERSHIPS TO STRENGTHEN THE GLOBAL RESPONSE TO MDR-TB - WHERE IT MATTERS MOST I am delighted that this initiative will improve both the technology needed
Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals
 SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA63.15 Agenda item 11.4 21 May 2010 Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals The Sixty-third World Health Assembly, Having considered
SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA63.15 Agenda item 11.4 21 May 2010 Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals The Sixty-third World Health Assembly, Having considered
TB EPIDEMIOLOGY: IMPACT ON CHILDREN. Anneke C. Hesseling Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department Paediatrics and Child Health Stellenbosch University
 TB EPIDEMIOLOGY: IMPACT ON CHILDREN Anneke C. Hesseling Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department Paediatrics and Child Health Stellenbosch University Robert Koch 1843-1910 Discovered M. tuberculosis 1882 TB deaths
TB EPIDEMIOLOGY: IMPACT ON CHILDREN Anneke C. Hesseling Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department Paediatrics and Child Health Stellenbosch University Robert Koch 1843-1910 Discovered M. tuberculosis 1882 TB deaths
The Western Pacific Region faces significant
 COMBATING COMMUNICABLE DISEASES A medical technician draws blood for HIV screening in Manila. AFP elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and congenital syphilis was piloted in Malaysia and
COMBATING COMMUNICABLE DISEASES A medical technician draws blood for HIV screening in Manila. AFP elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and congenital syphilis was piloted in Malaysia and
10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan,
 10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan, 2006 2015 Introduction A significant scaling-up of advocacy, communication and social mobilization for TB will
10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan, 2006 2015 Introduction A significant scaling-up of advocacy, communication and social mobilization for TB will
Global, National, Regional
 Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Controlling TB in the era of HIV
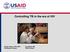 Controlling TB in the era of HIV Christy Hanson, PhD, MPH TB Research Advisor Amy Bloom, MD TB/HIV Advisor TB Incidence rates highest in Africa Estimated new TB cases (all forms) per 100 000 population
Controlling TB in the era of HIV Christy Hanson, PhD, MPH TB Research Advisor Amy Bloom, MD TB/HIV Advisor TB Incidence rates highest in Africa Estimated new TB cases (all forms) per 100 000 population
Summary of the Ninth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 12, 2006 (revised)
 Summary of the Ninth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 12, 2006 (revised) The Ninth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to
Summary of the Ninth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) May 12, 2006 (revised) The Ninth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to
Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group -
 Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group - 8 July 2008 This report is the recommendation from the G8 Health Experts Group to the G8 leaders. I Introduction 1.
Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group - 8 July 2008 This report is the recommendation from the G8 Health Experts Group to the G8 leaders. I Introduction 1.
TB IN EMERGENCIES. Disease Control in Humanitarian Emergencies (DCE)
 TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
Background. Proposed to develop a framework for action. Address by Foreign Minister Koumura
 July 2008 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan Background Address by Foreign Minister Koumura Global Health and Japan s Foreign Policy From Okinawa to Toyako (25 November 2007) Special Address by Prime
July 2008 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan Background Address by Foreign Minister Koumura Global Health and Japan s Foreign Policy From Okinawa to Toyako (25 November 2007) Special Address by Prime
7.5 South-East Asian Region: summary of planned activities, impact and costs
 PART II: GLOBAL AND REGIONAL SCENARIOS FOR TB CONTROL 26 215 7.5 South-East Asian Region: summary of planned activities, impact and costs Achievements DOTS expanded rapidly in the South-East Asian Region
PART II: GLOBAL AND REGIONAL SCENARIOS FOR TB CONTROL 26 215 7.5 South-East Asian Region: summary of planned activities, impact and costs Achievements DOTS expanded rapidly in the South-East Asian Region
Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development
 Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development Prof. Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria United Nations University, Tokyo,
Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development Prof. Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria United Nations University, Tokyo,
Children and AIDS Fourth Stocktaking Report 2009
 Children and AIDS Fourth Stocktaking Report 2009 The The Fourth Fourth Stocktaking Stocktaking Report, Report, produced produced by by UNICEF, UNICEF, in in partnership partnership with with UNAIDS, UNAIDS,
Children and AIDS Fourth Stocktaking Report 2009 The The Fourth Fourth Stocktaking Stocktaking Report, Report, produced produced by by UNICEF, UNICEF, in in partnership partnership with with UNAIDS, UNAIDS,
Towards universal access
 Key messages Towards universal access Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector September 2009 Progress report Towards universal access provides a comprehensive global update on progress
Key messages Towards universal access Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector September 2009 Progress report Towards universal access provides a comprehensive global update on progress
La Lotta alla Tubercolosi. Matteo Zignol and Mario C. Raviglione Stop TB Department WHO, Geneva, Switzerland. Geneva March 2012
 La Lotta alla Tubercolosi Matteo Zignol and Mario C. Raviglione Stop TB Department WHO, Geneva, Switzerland Geneva 19-20 March 2012 Overview of the presentation The global burden of tuberculosis The WHO
La Lotta alla Tubercolosi Matteo Zignol and Mario C. Raviglione Stop TB Department WHO, Geneva, Switzerland Geneva 19-20 March 2012 Overview of the presentation The global burden of tuberculosis The WHO
The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership
 The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership Prof Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director UNICEF Executive Board February 9 th, 2011 The Global Fund Millennium Development Goals 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and
The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership Prof Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director UNICEF Executive Board February 9 th, 2011 The Global Fund Millennium Development Goals 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and
Principle of Tuberculosis Control. CHIANG Chen-Yuan MD, MPH, DrPhilos
 Principle of Tuberculosis Control CHIANG Chen-Yuan MD, MPH, DrPhilos Estimated global tuberculosis burden 2015 an estimated 10.4 million incident cases of TB (range, 8.7 million 12.2 million) 142 cases
Principle of Tuberculosis Control CHIANG Chen-Yuan MD, MPH, DrPhilos Estimated global tuberculosis burden 2015 an estimated 10.4 million incident cases of TB (range, 8.7 million 12.2 million) 142 cases
Copenhagen, Denmark, September August Malaria
 Regional Committee for Europe 64th session EUR/RC64/Inf.Doc./5 Copenhagen, Denmark, 15 18 September 2014 21 August 2014 140602 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Malaria Following the support
Regional Committee for Europe 64th session EUR/RC64/Inf.Doc./5 Copenhagen, Denmark, 15 18 September 2014 21 August 2014 140602 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Malaria Following the support
Investing for Impact
 Global Fund Strategic Framework: Investing for Impact M&E: Capturing data to improve services Workshop to Scale Up the Implementation of Collaborative TB/HIV Activities in Africa 10-11 April, 2013; Maputo,
Global Fund Strategic Framework: Investing for Impact M&E: Capturing data to improve services Workshop to Scale Up the Implementation of Collaborative TB/HIV Activities in Africa 10-11 April, 2013; Maputo,
Summary of the Eighth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) October 4, 2005
 Summary of the Eighth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) October 4, 2005 The Eighth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 4:00pm
Summary of the Eighth Meeting of the ITFDE (II) October 4, 2005 The Eighth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 4:00pm
DEVELOPMENT. The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis. A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION
 DEVELOPMENT The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION DE 121 FEB 2004 A global challenge Every minute, 11 people
DEVELOPMENT The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION DE 121 FEB 2004 A global challenge Every minute, 11 people
Post-2015 TB Elimination Strategy and Targets
 Photo: Riccardo Venturi Vision and proposed framework for a Post-2015 TB Elimination Strategy and Targets Consultation on Eliminating the catastrophic economic burden of TB" Universal Health Coverage and
Photo: Riccardo Venturi Vision and proposed framework for a Post-2015 TB Elimination Strategy and Targets Consultation on Eliminating the catastrophic economic burden of TB" Universal Health Coverage and
Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005
 Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005 The Seventh Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 3:30pm
Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005 The Seventh Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 3:30pm
Guidance on Matching Funds: Tuberculosis Finding the Missing People with TB
 February 2017 Guidance on Matching Funds: Tuberculosis Finding the Missing People with TB 1. Background TB is the leading cause of death by infectious disease, killing 1.8 million people in 2015. Each
February 2017 Guidance on Matching Funds: Tuberculosis Finding the Missing People with TB 1. Background TB is the leading cause of death by infectious disease, killing 1.8 million people in 2015. Each
CMH Working Paper Series
 CMH Working Paper Series Paper No. WG5 : 8 Title Interventions to reduce tuberculosis mortality and transmission in low and middle-income countries: effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and constraints to
CMH Working Paper Series Paper No. WG5 : 8 Title Interventions to reduce tuberculosis mortality and transmission in low and middle-income countries: effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and constraints to
CARE S PERSPECTIVE ON THE MDGs Building on success to accelerate progress towards 2015 MDG Summit, September 2010
 CARE S PERSPECTIVE ON THE MDGs Building on success to accelerate progress towards 2015 MDG Summit, 20-22 September 2010 MDG Goal 5: Improve Maternal Health Target 1: Reduce by three-quarters, between 1990
CARE S PERSPECTIVE ON THE MDGs Building on success to accelerate progress towards 2015 MDG Summit, 20-22 September 2010 MDG Goal 5: Improve Maternal Health Target 1: Reduce by three-quarters, between 1990
International Standards for Tuberculosis Care Barbara J. Seaworth, MD August 22, 2007
 TB Along the US/Mexico Border El Paso, Texas August 22-23, 2007 International Standards for Tuberculosis Care Barbara J. Seaworth, MD August 22, 2007 Barbara J Seaworth MD Medical Director Heartland National
TB Along the US/Mexico Border El Paso, Texas August 22-23, 2007 International Standards for Tuberculosis Care Barbara J. Seaworth, MD August 22, 2007 Barbara J Seaworth MD Medical Director Heartland National
WHERE DO WE GO FROM HERE?
 WHERE DO WE GO FROM HERE? WHAT WILL BE REQUIRED TO ACHIEVE ZERO DEATHS FROM TUBERCULOSIS? SALMAAN KESHAVJEE, MD, PHD, SCM HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL PARTNERS IN HEALTH INTERNATIONAL
WHERE DO WE GO FROM HERE? WHAT WILL BE REQUIRED TO ACHIEVE ZERO DEATHS FROM TUBERCULOSIS? SALMAAN KESHAVJEE, MD, PHD, SCM HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL PARTNERS IN HEALTH INTERNATIONAL
WHO Consultation on universal access to core malaria interventions in high burden countries: main conclusions and recommendations
 WHO Consultation on universal access to core malaria interventions in high burden countries: main conclusions and recommendations 12-15 February 2018 Salle XI, ILO Building, Geneva, Switzerland Country
WHO Consultation on universal access to core malaria interventions in high burden countries: main conclusions and recommendations 12-15 February 2018 Salle XI, ILO Building, Geneva, Switzerland Country
Stop TB Working Group on DOTS-Plus for MDR-TB Strategic Plan
 Stop TB Working Group on DOTS-Plus for MDR-TB Strategic Plan 2006-2015 Background Current threat and status of the global epidemic of multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) Along with HIV/AIDS, MDR-TB
Stop TB Working Group on DOTS-Plus for MDR-TB Strategic Plan 2006-2015 Background Current threat and status of the global epidemic of multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) Along with HIV/AIDS, MDR-TB
Drug-resistant Tuberculosis
 page 1/6 Scientific Facts on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Source document: WHO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that affects a growing number of
page 1/6 Scientific Facts on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Source document: WHO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that affects a growing number of
Technology and innovation: Changing dynamics of TB control. Karin Weyer
 Technology and innovation: Changing dynamics of TB control Karin Weyer Latest news 1. New tools finally a reality 2. Universal access for all affected from TB 3. Emphasis on early case detection and treatment
Technology and innovation: Changing dynamics of TB control Karin Weyer Latest news 1. New tools finally a reality 2. Universal access for all affected from TB 3. Emphasis on early case detection and treatment
Developing a Rights-Based Approach to Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis in India
 University of Chicago Center in Delhi Developing a Rights-Based Approach to Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis in India Organizers United States: Evan Lyon, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Department
University of Chicago Center in Delhi Developing a Rights-Based Approach to Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis in India Organizers United States: Evan Lyon, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Department
Japan's Role in Global Health and Human Security
 Japan's Role in Global Health and Human Security Prof.Keizo TAKEMI Senior Fellow, Japan Center for Interantional Exchange, Research Fellow, Harvard School of Public Health Professor, Tokai University Why
Japan's Role in Global Health and Human Security Prof.Keizo TAKEMI Senior Fellow, Japan Center for Interantional Exchange, Research Fellow, Harvard School of Public Health Professor, Tokai University Why
Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite
 Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite Riga East Clinical hospital, Centre for tuberculosis and lung diseases. Head of outpatient department.
Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite Riga East Clinical hospital, Centre for tuberculosis and lung diseases. Head of outpatient department.
The Global Fight Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria. Current Status and Future Perspectives
 Maputo Conference / Fighting HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria The Global Fight Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Current Status and Future Perspectives Marco Vitoria, MD, 1 Reuben Granich,
Maputo Conference / Fighting HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria The Global Fight Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Current Status and Future Perspectives Marco Vitoria, MD, 1 Reuben Granich,
Resolutions of the 50 th East, Central and Southern African Health Ministers Conference
 50 th ECSA HMC East, Central and Southern African Health Community ECSA-HC February 2010 Resolutions of the 50 th East, Central and Southern African Health Ministers Conference Serena Hotel, Kampala Uganda
50 th ECSA HMC East, Central and Southern African Health Community ECSA-HC February 2010 Resolutions of the 50 th East, Central and Southern African Health Ministers Conference Serena Hotel, Kampala Uganda
THE Price of a Pandemic 2017
 THE Price of a Pandemic 2017 From 2000-2015: 33 million people died because of TB at a global economic cost of $617bn This report was produced the Global TB Caucus, an international network of over 2,000
THE Price of a Pandemic 2017 From 2000-2015: 33 million people died because of TB at a global economic cost of $617bn This report was produced the Global TB Caucus, an international network of over 2,000
Innovation, Access and Delivery for Universal Health Coverage
 A side event at the UHC Forum Co-hosted by UNDP and the GHIT Fund Tokyo, Japan 12 December 2017 Innovation, Access and Delivery for Universal Health Coverage From Innovation & Inequality, a UNDP-supported
A side event at the UHC Forum Co-hosted by UNDP and the GHIT Fund Tokyo, Japan 12 December 2017 Innovation, Access and Delivery for Universal Health Coverage From Innovation & Inequality, a UNDP-supported
2. Treatment coverage: 3. Quality of care: 1. Access to diagnostic services:
 The theme for World TB Day 2014 is Reach the missed 3 million. Every year 3 million people who fall ill with TB are missed by health systems and do not always get the TB services that they need and deserve.
The theme for World TB Day 2014 is Reach the missed 3 million. Every year 3 million people who fall ill with TB are missed by health systems and do not always get the TB services that they need and deserve.
1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review
 1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review 1.1 The new World Bank Group strategy makes a strong case for an expanded World Bank Group role in global and regional dialogue and collective
1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review 1.1 The new World Bank Group strategy makes a strong case for an expanded World Bank Group role in global and regional dialogue and collective
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations E/CN.6/2010/L.6 Economic and Social Council Distr.: Limited 9 March 2010 Original: English ADOPTED 12 March 2010 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION Commission on the Status of Women Fifty-fourth session
United Nations E/CN.6/2010/L.6 Economic and Social Council Distr.: Limited 9 March 2010 Original: English ADOPTED 12 March 2010 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION Commission on the Status of Women Fifty-fourth session
GIVING BIRTH SHOULD NOT BE A MATTER OF LIFE AND DEATH
 GIVING BIRTH SHOULD NOT BE A MATTER OF LIFE AND DEATH Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Every day, almost 800 women die in pregnancy or childbirth Almost all of these women 99 per cent live
GIVING BIRTH SHOULD NOT BE A MATTER OF LIFE AND DEATH Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Every day, almost 800 women die in pregnancy or childbirth Almost all of these women 99 per cent live
World Health Organization HIV/TB Facts 2011
 World Health Organization HIV/TB Facts 20 Note: The facts and figures of the HIV/TB Facts 20 are drawn from WHO HIV and TB surveillance data from 200 and 2009, as referenced below. Why is tuberculosis
World Health Organization HIV/TB Facts 20 Note: The facts and figures of the HIV/TB Facts 20 are drawn from WHO HIV and TB surveillance data from 200 and 2009, as referenced below. Why is tuberculosis
The Strategy Development Process. Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015
 The Strategy Development Process Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015 Structure of the current 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy The 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy.. States a forward
The Strategy Development Process Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015 Structure of the current 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy The 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy.. States a forward
REPRODUCTIVE, MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (RMNCH) GLOBAL AND REGIONAL INITIATIVES
 Information Brief: REPRODUCTIVE, MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (RMNCH) GLOBAL AND REGIONAL INITIATIVES Family Care International (FCI) developed this information brief as part of the Mobilising Advocates
Information Brief: REPRODUCTIVE, MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (RMNCH) GLOBAL AND REGIONAL INITIATIVES Family Care International (FCI) developed this information brief as part of the Mobilising Advocates
128th Session 25 November 2010 Provisional agenda item Malaria. Prevention and control: sustaining the gains and reducing transmission
 EXECUTIVE BOARD 128th Session 25 November 2010 Provisional agenda item 4.11 Malaria Prevention and control: sustaining the gains and reducing transmission Report by the Secretariat 1. Millennium Development
EXECUTIVE BOARD 128th Session 25 November 2010 Provisional agenda item 4.11 Malaria Prevention and control: sustaining the gains and reducing transmission Report by the Secretariat 1. Millennium Development
OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK. for the Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents Health
 OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK for the Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents Health Every Woman Every Child 2016 OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK for the Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents
OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK for the Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents Health Every Woman Every Child 2016 OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK for the Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents
ADVANCE UNEDITED E/CN.6/2008/L.5/REV.1. Women, the girl child and HIV/AIDS * *
 E/CN.6/2008/L.5/REV.1 ADVANCE UNEDITED Women, the girl child and HIV/AIDS The Commission on the Status of Women, Reaffirming the Beijing Declaration 1 and Platform for Action, 2 the outcome documents of
E/CN.6/2008/L.5/REV.1 ADVANCE UNEDITED Women, the girl child and HIV/AIDS The Commission on the Status of Women, Reaffirming the Beijing Declaration 1 and Platform for Action, 2 the outcome documents of
DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL. A GLOBAL AND INDIAN SITUATION
 JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE MEDICINE 2008; 16(3-4): 3-9 Inviting Editorial DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL. A GLOBAL AND INDIAN SITUATION Harshad Thakur Centre for Health Policy, Planning and Management,
JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE MEDICINE 2008; 16(3-4): 3-9 Inviting Editorial DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL. A GLOBAL AND INDIAN SITUATION Harshad Thakur Centre for Health Policy, Planning and Management,
International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June Rotary s financial contribution to the polio eradication effort:
 International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June 2018 1. The goal of the PolioPlus program: The goal of the PolioPlus program is the global certification of polio eradication. By eradication,
International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June 2018 1. The goal of the PolioPlus program: The goal of the PolioPlus program is the global certification of polio eradication. By eradication,
Accelerating progress towards the health-related Millennium Development Goals
 Accelerating progress towards the health-related Millennium Development Goals The critical role of the national health policy & strategy in strengthening health systems and delivering effective interventions
Accelerating progress towards the health-related Millennium Development Goals The critical role of the national health policy & strategy in strengthening health systems and delivering effective interventions
Ram Sharan Gopali (MPH) Executive Director
 Ram Sharan Gopali (MPH) Executive Director Basic Facts of Nepal Nepal is a landlocked country located in the WHO Asian region at the edge of the Himalaya between India and the Peoples Republic of China
Ram Sharan Gopali (MPH) Executive Director Basic Facts of Nepal Nepal is a landlocked country located in the WHO Asian region at the edge of the Himalaya between India and the Peoples Republic of China
~Health and Development Initiative~
 ~Health and Development Initiative~ Global Issues Division International Cooperation Bureau Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Japan March 2007 More than 10 million children
~Health and Development Initiative~ Global Issues Division International Cooperation Bureau Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Japan March 2007 More than 10 million children
Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response
 Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response 20 th International AIDS Conference Melbourne, Australia J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in Asia and the Pacific 21 July
Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response 20 th International AIDS Conference Melbourne, Australia J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in Asia and the Pacific 21 July
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 12 July 2011 Original:
Change the Game. An agenda for action on childhood tuberculosis
 Change the Game An agenda for action on childhood tuberculosis Four-year-old Nyajime Guet was suffering from severe acute malnutrition (SAM) when she was admitted to a UNICEF-supported clinic a in Juba,
Change the Game An agenda for action on childhood tuberculosis Four-year-old Nyajime Guet was suffering from severe acute malnutrition (SAM) when she was admitted to a UNICEF-supported clinic a in Juba,
A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection
 Human Journals Review Article May 2015 Vol.:1, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Jyoti P. Waghmode et al. A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection Keywords: tuberculosis, HIV, co-infection, prevalence
Human Journals Review Article May 2015 Vol.:1, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Jyoti P. Waghmode et al. A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection Keywords: tuberculosis, HIV, co-infection, prevalence
Monitoring the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals
 SIXTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A66/13 Provisional agenda item 14.1 14 May 2013 Monitoring the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals Report by the Secretariat 1. In response
SIXTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A66/13 Provisional agenda item 14.1 14 May 2013 Monitoring the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals Report by the Secretariat 1. In response
Overview of the Presentation
 Overview of the Presentation Definitions(TBCase, MDR-TB & XDR-TB) Global Tuberculosis (TB,HIV/TB,MDR & XDR)Scenario & Trend Risk factor for TB Natural history of TB Types of TB & Trends of Extra Pulmonary
Overview of the Presentation Definitions(TBCase, MDR-TB & XDR-TB) Global Tuberculosis (TB,HIV/TB,MDR & XDR)Scenario & Trend Risk factor for TB Natural history of TB Types of TB & Trends of Extra Pulmonary
2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030
 S T A T E M E N T 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030 World leaders commit to reach three goals and 20 new Fast-Track Targets
S T A T E M E N T 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030 World leaders commit to reach three goals and 20 new Fast-Track Targets
In the Name of God, the Compassionate, the Merciful. Address by DR HUSSEIN A. GEZAIRY REGIONAL DIRECTOR WHO EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION.
 In the Name of God, the Compassionate, the Merciful Address by DR HUSSEIN A. GEZAIRY REGIONAL DIRECTOR WHO EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION on the FIRST EMIRATES INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON VACCINATION Dubai,
In the Name of God, the Compassionate, the Merciful Address by DR HUSSEIN A. GEZAIRY REGIONAL DIRECTOR WHO EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION on the FIRST EMIRATES INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON VACCINATION Dubai,
Countdown to 2015: tracking progress, fostering accountability
 Countdown to 2015: tracking progress, fostering accountability Countdown to 2015 is a global movement to track, stimulate and support country progress towards achieving the health-related Millennium Development
Countdown to 2015: tracking progress, fostering accountability Countdown to 2015 is a global movement to track, stimulate and support country progress towards achieving the health-related Millennium Development
World Health Organization. A Sustainable Health Sector
 World Health Organization A Sustainable Health Sector Response to HIV Global Health Sector Strategy for HIV/AIDS 2011-2015 (DRAFT OUTLINE FOR CONSULTATION) Version 2.1 15 July 2010 15 July 2010 1 GLOBAL
World Health Organization A Sustainable Health Sector Response to HIV Global Health Sector Strategy for HIV/AIDS 2011-2015 (DRAFT OUTLINE FOR CONSULTATION) Version 2.1 15 July 2010 15 July 2010 1 GLOBAL
Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States
 Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 1 Progress Toward TB Elimination in the United States... 3 TB Disease Trends in the United
Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 1 Progress Toward TB Elimination in the United States... 3 TB Disease Trends in the United
WFP and the Nutrition Decade
 WFP and the Nutrition Decade WFP s strategic plan focuses on ending hunger and contributing to a revitalized global partnership, key components to implement and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
WFP and the Nutrition Decade WFP s strategic plan focuses on ending hunger and contributing to a revitalized global partnership, key components to implement and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
Progress on the targets of Millennium Development Goal 6 in central and eastern Europe and central Asia
 Progress on the targets of Millennium Development Goal 6 in central and eastern Europe and central Asia 11 October 2011 Moscow, Russian Federation Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe Millennium
Progress on the targets of Millennium Development Goal 6 in central and eastern Europe and central Asia 11 October 2011 Moscow, Russian Federation Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe Millennium
aids in asia and the pacific
 HIV AIDS AND DEVELOPMENT IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC a lengthening shadow aids in asia and the pacific World Health Organization Regional Offices for South East Asia and the Western Pacific Region 9 10 OCTOBER
HIV AIDS AND DEVELOPMENT IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC a lengthening shadow aids in asia and the pacific World Health Organization Regional Offices for South East Asia and the Western Pacific Region 9 10 OCTOBER
XDR-TB Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. What, Where, How and Action Steps
 XDR-TB Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis What, Where, How and Action Steps The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever
XDR-TB Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis What, Where, How and Action Steps The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever
combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
 MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOAL #6 scic comic saskatchewan council for international cooperation combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases series IN THIS ISSUE - MOSHUMS SADDEST STORY Millennium Development
MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOAL #6 scic comic saskatchewan council for international cooperation combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases series IN THIS ISSUE - MOSHUMS SADDEST STORY Millennium Development
IFMSA Policy Statement Ending AIDS by 2030
 IFMSA Policy Statement Ending AIDS by 2030 Proposed by IFMSA Team of Officials Puebla, Mexico, August 2016 Summary IFMSA currently acknowledges the HIV epidemic as a major threat, which needs to be tackled
IFMSA Policy Statement Ending AIDS by 2030 Proposed by IFMSA Team of Officials Puebla, Mexico, August 2016 Summary IFMSA currently acknowledges the HIV epidemic as a major threat, which needs to be tackled
Renewing Momentum in the fight against HIV/AIDS
 2011 marks 30 years since the first cases of AIDS were documented and the world has made incredible progress in its efforts to understand, prevent and treat this pandemic. Progress has been particularly
2011 marks 30 years since the first cases of AIDS were documented and the world has made incredible progress in its efforts to understand, prevent and treat this pandemic. Progress has been particularly
Drug-resistant Tuberculosis
 page 1/15 Scientific Facts on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Source document: WHO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Level 2 - Details on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis 1. What is tuberculosis and why is it
page 1/15 Scientific Facts on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Source document: WHO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Level 2 - Details on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis 1. What is tuberculosis and why is it
Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group, U.S. and Global Health Policy Director. On behalf of the Tuberculosis Roundtable
 United States House of Representatives Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on State and Foreign Operations and Related Programs Fiscal Year 2020 Written Testimony Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group,
United States House of Representatives Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on State and Foreign Operations and Related Programs Fiscal Year 2020 Written Testimony Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group,
Millennium Development Goals: Past and Future. Andrew Park, M1 15 December 2014
 Millennium Development Goals: Past and Future Andrew Park, M1 15 December 2014 What are the MDGs 8 international development goals created by the United Nations in 2000 set to be met by 2015. 21 measurement
Millennium Development Goals: Past and Future Andrew Park, M1 15 December 2014 What are the MDGs 8 international development goals created by the United Nations in 2000 set to be met by 2015. 21 measurement
Global health sector strategies on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections ( )
 Regional Committee for Europe 65th session EUR/RC65/Inf.Doc./3 Vilnius, Lithuania, 14 17 September 2015 2 September 2015 150680 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Global health sector strategies
Regional Committee for Europe 65th session EUR/RC65/Inf.Doc./3 Vilnius, Lithuania, 14 17 September 2015 2 September 2015 150680 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Global health sector strategies
Finding the missing TB cases
 Finding the missing TB cases Optimizing strategies to enhance case detection in high HIV burden settings Dr Malgosia Grzemska Global TB Programme, WHO/HQ, Geneva SWITZERLAND Child and Adolescent TB Working
Finding the missing TB cases Optimizing strategies to enhance case detection in high HIV burden settings Dr Malgosia Grzemska Global TB Programme, WHO/HQ, Geneva SWITZERLAND Child and Adolescent TB Working
Assessment of G8 Commitments on Maternal, Newborn and Child Health
 Assessment of G8 Commitments on Maternal, Newborn and Child Health Robin Lennox Researcher, G8 Research Group June 13, 2010 In January 2010, Canadian prime minister Stephen Harper announced that maternal,
Assessment of G8 Commitments on Maternal, Newborn and Child Health Robin Lennox Researcher, G8 Research Group June 13, 2010 In January 2010, Canadian prime minister Stephen Harper announced that maternal,
Annex A: Impact, Outcome and Coverage Indicators (including Glossary of Terms)
 IMPACT INDICATORS (INDICATORS PER GOAL) HIV/AIDS TUBERCULOSIS MALARIA Reduced HIV prevalence among sexually active population Reduced HIV prevalence in specific groups (sex workers, clients of sex workers,
IMPACT INDICATORS (INDICATORS PER GOAL) HIV/AIDS TUBERCULOSIS MALARIA Reduced HIV prevalence among sexually active population Reduced HIV prevalence in specific groups (sex workers, clients of sex workers,
THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR WOMEN S, CHILDREN S AND ADOLESCENTS HEALTH ( )
 THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR WOMEN S, CHILDREN S AND ADOLESCENTS HEALTH (2016-2030) SURVIVE THRIVE TRANSFORM AT A GLANCE SURVIVE THRIVE TRANSFORM The Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents
THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR WOMEN S, CHILDREN S AND ADOLESCENTS HEALTH (2016-2030) SURVIVE THRIVE TRANSFORM AT A GLANCE SURVIVE THRIVE TRANSFORM The Global Strategy for Women s, Children s and Adolescents
Achieve universal primary education
 GOAL 2 Achieve universal primary education TARGET Ensure that, by 2015, children everywhere, boys and girls alike, will be able to complete a full course of primary schooling Considerable progress has
GOAL 2 Achieve universal primary education TARGET Ensure that, by 2015, children everywhere, boys and girls alike, will be able to complete a full course of primary schooling Considerable progress has
SPECIAL EVENT ON PHILANTHROPY AND THE GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH AGENDA. 23 February 2009, United Nations, New York Conference Room 2, 3:00 p.m. 6:00 p.m.
 SPECIAL EVENT ON PHILANTHROPY AND THE GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH AGENDA 23 February 2009, United Nations, New York Conference Room 2, 3:00 p.m. 6:00 p.m. ISSUES NOTE Improving the Health Outcomes of Women and
SPECIAL EVENT ON PHILANTHROPY AND THE GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH AGENDA 23 February 2009, United Nations, New York Conference Room 2, 3:00 p.m. 6:00 p.m. ISSUES NOTE Improving the Health Outcomes of Women and
Costing of the Sierra Leone National Strategic Plan for TB
 Costing of the Sierra Leone National Strategic Plan for TB 2016-2020 Introduction The Government of Sierra Leone established the National Leprosy Control Programme in 1973 with support from the German
Costing of the Sierra Leone National Strategic Plan for TB 2016-2020 Introduction The Government of Sierra Leone established the National Leprosy Control Programme in 1973 with support from the German
Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007
 Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007 National Surveillance Data for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a major public
Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007 National Surveillance Data for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a major public
the africa we want Why adolescent sexual and reproductive health is key for Africa s development
 the africa we want Why adolescent sexual and reproductive health is key for Africa s development what unfpa strives for: Imagine a world where all adolescents and young people are healthy, productive and
the africa we want Why adolescent sexual and reproductive health is key for Africa s development what unfpa strives for: Imagine a world where all adolescents and young people are healthy, productive and
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 November 2014 Original: English Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Asia-Pacific Intergovernmental Meeting on HIV and AIDS
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 November 2014 Original: English Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Asia-Pacific Intergovernmental Meeting on HIV and AIDS
Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector
 TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS? Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector Yves Souteyrand, WHO October 2011 Towards universal access targets UN General Assembly High level Meeting June
TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS? Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector Yves Souteyrand, WHO October 2011 Towards universal access targets UN General Assembly High level Meeting June
ACHAP LESSONS LEARNED IN BOTSWANA KEY INITIATIVES
 ACHAP Together with our company s foundation, a U.S.-based, private foundation, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, we established the African Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Partnerships (ACHAP) in 2000 to
ACHAP Together with our company s foundation, a U.S.-based, private foundation, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, we established the African Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Partnerships (ACHAP) in 2000 to
Submitted electronically to:
 Submitted electronically to: ODOARRFI19@nih.gov Maureen Goodenow, PhD Associate Director of AIDS Research, NIH Director, Office of AIDS Research (OAR) National Institutes of Health 5601 Fishers Lane. Room
Submitted electronically to: ODOARRFI19@nih.gov Maureen Goodenow, PhD Associate Director of AIDS Research, NIH Director, Office of AIDS Research (OAR) National Institutes of Health 5601 Fishers Lane. Room
