SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Carmel Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Text Results In vitro activation experiments established that treatment with anti-cd3 plus anti- CD28 was sufficient to promote EBI2 transcript on CD4 T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1d, e). CCR7 is slightly downregulated on activated T cells 4 and this change occurred normally on the EBI2 KO T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1k) indicating that the defective positioning was not due to altered regulation of CCR7 expression. WT and EBI2 KO T cells underwent equivalent amounts of proliferation to anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 in the presence or absence of 7α,25-OHC (Extended Data Fig. 2b, c). These data suggest that the oxysterol is most likely not directly promoting T cell proliferation in vivo, but rather is leading to enhanced proliferation due to effects on cell position. In addition to the findings in mixed transfer recipients, a defect in EBI2 KO Tfh cell induction was seen when control and EBI2-deficient OTII T cells were transferred to separate hosts indicating it was not dependent on competition (Extended Data Fig. 2g). To test whether the defect in Tfh cell induction extended to a different antigen type, the response to Listeria-OVA was measured. The EBI2 KO OTII Tfh cell response in mice immunized with Listeria-OVA was reduced (Extended Data Fig. 3a). Polyclonal Tfh cell development was analyzed by transferring control and EBI2 KO CD4 T cells into OTII recipients and immunizing with unconjugated SRBCs such that only the transferred T cells could participate in the response. Analysis at day 8 revealed a strong Tfh cell-induction defect for cells lacking EBI2 (Extended Data Fig. 3b, c). In accord with defective Tfh cell development, the day 12 GC response was 2-fold reduced (Extended Data Fig. 3d, e). The IgM and IgG plasma cell response was also 1
2 reduced (Extended Data Fig. 3f, g). The defective plasma cell response was associated with a reduced serum anti-srbc response (Extended Data Fig. 3h). To test the impact of T cell EBI2-deficiency on the B cell response to Listeria-OVA the OTII T cells were transferred into Cd28 -/- recipient mice that are defective in generating endogenous Tfh cells 1,2. At day 5 after transfer there was a 4-5-fold reduction in the GC and plasma cell response in recipients of EBI2 KO OTII T cells versus control OTII T cells (Extended Data Figs. 3i, j). Consistent with DCIR2 + DC movement to the outer T zone being important for early Tfh cell induction, when DCs lacked CCR7 the DCIR2 + cells failed to relocate to the outer T zone after SRBC immunization (Extended Data Fig. 4f) and few Tfh cells were induced (Extended Data Fig. 4g). Moreover, in Cd47 -/- mice that have a 4-5 fold deficiency in CD4 + DCIR2 + DCs but normal numbers of CD8 + DCs 18, 37,38, Tfh induction in response to SRBC-OVA was strongly impaired (Extended Data Fig. 4h). Irf4 f/f CD11c-Cre mice that had a 2-3-fold CD4 + DC deficiency (Extended Data Fig. 4i and 39 ) also showed a reduction in Tfh cell induction following SRBC immunization (Extended Data Fig. 4j). In contrast, in Batf3 -/- mice that are deficient in CD8 + DCs 39, Tfh cell induction by SRBC-OVA occurred normally and the response of EBI2- deficient T cells remained defective (Extended Data Fig. 4k). In addition to observing elevated ICOSL on DCs in mice where engagement with ICOS on activated T cells was blocked by anti-icos treatment, upregulation of surface ICOSL on CD4 + DCs was observed in SRBC-immunized Cd28 -/- mice that lack ICOS hi activated T cells (Extended Data Fig. 4m). Cd28 -/- recipients were therefore used for the experiments testing the activity of WT and EBI2 KO OTII T cells in causing DC ICOSL shedding to ensure that activated ICOS hi endogenous OVA- or SRBC-specific T cells did not contribute to ICOSL shedding. Il2 mrna was strongly induced in OTII T cells within 6-12 h of SRBC-OVA immunization and had declined by day 1 (Extended Data Fig.5g), similar to findings after other types of immunization 40,41. Intracellular staining showed IL2-expressing T cells were detectable at 12 hours and in increased frequency at day 1 (Extended 2
3 Data Fig. 5h). Il2 mrna and protein induction occurred to equivalent extents in EBI2 het and KO OTII T cells (Extended Data Fig. 5g, h). Induction of CD25 on the control and EBI2 KO OTII T cells also occurred to similar extents (Extended Data Fig. 5i). The higher pstat5 levels observed in EBI2 KO OTII T cells following immunization did not appear to be due to a direct inhibitory effect of EBI2 on IL2 signaling since incubation of WT T cells with 7α,25-OHC in vitro did not alter their sensitivity to IL2 (Extended Data Fig. 5k). Generation of mice lacking CD25 in DCs was achieved by reconstituting WT mice with an equal mixture of CD25 KO and Zbtb46-DTR BM and then treating the mice with DT at days -3, -1 and 2 of the experiment (Extended Data Fig. 6a). This treatment ablates the CD25 WT DCs (Extended Data Fig. 4b) leaving only CD25 KO DCs. Control mice included WT:Zbtb46-DTR chimeras treated with DT to control for the effects of DT-mediated DC ablation, and saline treated CD25 KO:Zbtb46 DTR chimeras to control for effects of having half CD25 KO non-dcs. In the DT-treated CD25 KO:Zbtb46-DTR chimeras the CD25 KO DCs were present in similar numbers to the WT DCs in DT-treated control chimeras, and they were activated comparably to WT DCs following SRBC immunization as assessed by CD86, CCR7 and MHCII expression and relocation to the outer T zone (Extended Data Fig. 6b-d). The numbers of endogenous FoxP3 + Treg cells in DT treated mixed chimeras were not altered by DC CD25-deficiency at the day 3 time point after SRBC-OVA immunization (Extended Data Fig. 6e). Discussion 7α,25-OHC is produced by lymphoid stromal cells and it is metabolized in both stromal cells and CD8 + DCs 31, and we speculate that it is more abundant in the outer T zone than the central T zone. We suggest that gradients of this oxysterol guide activated T cell positioning in the outer T zone. 3
4 Our studies do not rule out that the central T zone could serve as a site of Tfh cell induction under different immunization conditions, and some work has shown that antigen targeting to CD8 + DCs or monocyte-derived DCs can induce Tfh cell responses 42,43. The mode of scd25-mediated IL2 inhibition needs investigation, though one possibility is that it competes with target cell CD25 for IL2, a mechanism that may limit the negative effect to CD25-expressing IL2-responsive cells. Activated B cells upregulate CD25 and in vitro studies indicate they can respond to IL2 (ref. 44) making it possible that DC CD25 will have direct modulatory influences on IL2- driven B cell responses. Regulatory T cells can deplete IL2 through a mechanism involving IL2R-mediated internalization of the cytokine 45. Further work is needed to determine whether DCs inhibit IL2 function by CD25-mediated internalization and degradation as well as by releasing scd25. Certain CD25 disease susceptibility alleles have been correlated with increased levels of scd25 22,23. It will be important to see if these alleles increase scd25 production by activated DCs and if their presence is associated with increased generation of autoreactive Tfh cell responses. References 37 Van, V. Q., Lesage, S., Bouguermouh, S., Gautier, P., Rubio, M., Levesque, M., Nguyen, S., Galibert, L. & Sarfati, M. Expression of the self-marker CD47 on dendritic cells governs their trafficking to secondary lymphoid organs. EMBO J. 25, (2006). 38 Saito, Y., Iwamura, H., Kaneko, T., Ohnishi, H., Murata, Y., Okazawa, H., Kanazawa, Y., Sato-Hashimoto, M., Kobayashi, H., Oldenborg, P. A., Naito, M., Kaneko, Y., Nojima, Y. & Matozaki, T. Regulation by SIRPalpha of dendritic cell homeostasis in lymphoid tissues. Blood 116, (2010). 39 Murphy, K. M. Transcriptional control of dendritic cell development. Adv. Immunol. 120, (2013). 40 Khoruts, A., Mondino, A., Pape, K. A., Reiner, S. L. & Jenkins, M. K. A natural immunological adjuvant enhances T cell clonal expansion through a CD28- dependent, interleukin (IL)-2-independent mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 187, (1998). 4
5 41 O'Gorman, W. E., Dooms, H., Thorne, S. H., Kuswanto, W. F., Simonds, E. F., Krutzik, P. O., Nolan, G. P. & Abbas, A. K. The initial phase of an immune response functions to activate regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 183, (2009). 42 Kato, Y., Zaid, A., Davey, G. M., Mueller, S. N., Nutt, S. L., Zotos, D., Tarlinton, D. M., Shortman, K., Lahoud, M. H., Heath, W. R. & Caminschi, I. Targeting Antigen to Clec9A Primes Follicular Th Cell Memory Responses Capable of Robust Recall. J. Immunol. 195, (2015). 43 Chakarov, S. & Fazilleau, N. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells promote T follicular helper cell differentiation. EMBO molecular medicine 6, (2014). 44 Mingari, M. C., Gerosa, F., Carra, G., Accolla, R. S., Moretta, A., Zubler, R. H., Waldmann, T. A. & Moretta, L. Human interleukin-2 promotes proliferation of activated B cells via surface receptors similar to those of activated T cells. Nature 312, (1984). 45 Pandiyan, P., Zheng, L., Ishihara, S., Reed, J. & Lenardo, M. J. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, (2007). 5
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
How plasma cells develop. Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft
 How plasma cells develop Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft 1 Plasma cells develop from activated B cells Toll Like Receptor B Cell Receptor B cell B cell microbia
How plasma cells develop Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft 1 Plasma cells develop from activated B cells Toll Like Receptor B Cell Receptor B cell B cell microbia
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D.
 Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER
 Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Normal GC initiation then collapse; normal mutation and 10. Constitutive signalling leads to spontaneous GC in PP, even BCR -/- 19
 S1 Genetic modifications affecting germinal-centre formation and function Gene Compartment GC Phenotype Ref LTα, LTβ, TNF, Organ Disorganized lymphoid architecture in spleens; poor 1 TNFRI, LTβR architecture
S1 Genetic modifications affecting germinal-centre formation and function Gene Compartment GC Phenotype Ref LTα, LTβ, TNF, Organ Disorganized lymphoid architecture in spleens; poor 1 TNFRI, LTβR architecture
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Peer review correspondence
 OX40 controls effector CD4 + T-cell expansion, not follicular T helper cell generation in acute Listeria infection Clare L. Marriott, Emma C. Mackley, Cristina Ferreira, Marc Veldhoen, Hideo Yagita and
OX40 controls effector CD4 + T-cell expansion, not follicular T helper cell generation in acute Listeria infection Clare L. Marriott, Emma C. Mackley, Cristina Ferreira, Marc Veldhoen, Hideo Yagita and
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Adaptive (acquired) immunity. Professor Peter Delves University College London
 Adaptive (acquired) immunity Professor Peter Delves University College London p.delves@ucl.ac.uk Haematopoiesis Haematopoiesis Lymphocytes = adaptive response Recognition of pathogens by adaptive cells,
Adaptive (acquired) immunity Professor Peter Delves University College London p.delves@ucl.ac.uk Haematopoiesis Haematopoiesis Lymphocytes = adaptive response Recognition of pathogens by adaptive cells,
Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson
 Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson Center for Molecular Medicine Karolinska Institute Stockholm, Sweden DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Goran Hansson
Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson Center for Molecular Medicine Karolinska Institute Stockholm, Sweden DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Goran Hansson
Immune Tolerance. Kyeong Cheon Jung. Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. FOCiS. Lecture outline. Regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
FOCiS. Lecture outline. The immunological equilibrium: balancing lymphocyte activation and control. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
B220 CD4 CD8. Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN
 B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses
 Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
Circulating T follicular regulatory and helper cells have memory-like properties
 Circulating T follicular regulatory and helper cells have memory-like properties Peter T. Sage, 1,2 David Alvarez, 1 Jernej Godec, 1,2 Ulrich H. von Andrian, 1 and Arlene H. Sharpe 1,2,3 1 Department of
Circulating T follicular regulatory and helper cells have memory-like properties Peter T. Sage, 1,2 David Alvarez, 1 Jernej Godec, 1,2 Ulrich H. von Andrian, 1 and Arlene H. Sharpe 1,2,3 1 Department of
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses. Li Wang. Dartmouth Medical School
 VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma. Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate
 Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate Melanoma Melanoma is the 4 th most common cancer in Australia. Current treatment options are ineffective resulting
Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate Melanoma Melanoma is the 4 th most common cancer in Australia. Current treatment options are ineffective resulting
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Sensing Microbial Viability through Bacterial RNA Augments T Follicular Helper Cell and Antibody Responses
 Article Sensing Microbial Viability through Bacterial RNA Augments T Follicular Helper Cell and Antibody Responses Graphical Abstract Authors Gaetan Barbet, Leif E. Sander, Matthew Geswell, Irina Leonardi,
Article Sensing Microbial Viability through Bacterial RNA Augments T Follicular Helper Cell and Antibody Responses Graphical Abstract Authors Gaetan Barbet, Leif E. Sander, Matthew Geswell, Irina Leonardi,
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Supplemental Information. CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Regulatory T Cells Promote. Th17 Cells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance
 Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy
 Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
T cell memory Friday, February 10, 17
 T cell memory 2-10-2017 expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE 2 7-8 30 >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10
T cell memory 2-10-2017 expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE 2 7-8 30 >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10
Central tolerance. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance. Regulation of the T cell response
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
CD47 plays a role as a negative regulator in inducing protective immune responses to vaccination. against influenza virus
 JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 18 May 216 J. Virol. doi:1.1128/jvi.65-16 Copyright 216, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 CD47 plays a role as a negative regulator in
JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 18 May 216 J. Virol. doi:1.1128/jvi.65-16 Copyright 216, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 CD47 plays a role as a negative regulator in
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components
 Chapter 13 Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components Humoral imm 胞外 胞內 CMI: CD8 T Self Ag Self(Auto) antigen (encoded
Chapter 13 Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components Humoral imm 胞外 胞內 CMI: CD8 T Self Ag Self(Auto) antigen (encoded
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Harnessing tolerance mechanisms with monoclonal antibodies Prof. Herman Waldmann
 Harnessing tolerance mechanisms Herman Waldmann Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford University, UK 1 1. Transplantation 2 Lymphocyte depletion strategies to minimise drug immunosuppression in
Harnessing tolerance mechanisms Herman Waldmann Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford University, UK 1 1. Transplantation 2 Lymphocyte depletion strategies to minimise drug immunosuppression in
NFIL3/E4BP4 controls Type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression
 Manuscript EMBO-2010-75657 NFIL3/E4BP4 controls Type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression Masaki Kashiwada, Suzanne L. Cassel, John D. Colgan and Paul B. Rothman Corresponding author: Paul Rothman, University
Manuscript EMBO-2010-75657 NFIL3/E4BP4 controls Type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression Masaki Kashiwada, Suzanne L. Cassel, John D. Colgan and Paul B. Rothman Corresponding author: Paul Rothman, University
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity
 Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Canberra, Australia). CD11c-DTR-OVA-GFP (B6.CD11c-OVA), B6.luc + and. Cancer Research Center, Germany). B6 or BALB/c.FoxP3-DTR-GFP mice were
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Mice Female C57BL/6 (B6, I-E null, H-2 b ), BALB/c (H-2 d ) + ), FVB/N (H-2 q, I-E null, CD45.1 + ), and B6D2F1 (H-2 b/d ) mice were purchased from the Animal Resources
Supplemental Materials and Methods Mice Female C57BL/6 (B6, I-E null, H-2 b ), BALB/c (H-2 d ) + ), FVB/N (H-2 q, I-E null, CD45.1 + ), and B6D2F1 (H-2 b/d ) mice were purchased from the Animal Resources
Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology
 Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology The human microbiota The human gut harbors 10 11-10 12 bacteria per gram colonic content (>10 14 total bacteria) Total bacteria outnumber human cells
Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology The human microbiota The human gut harbors 10 11-10 12 bacteria per gram colonic content (>10 14 total bacteria) Total bacteria outnumber human cells
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Manipulating the Tumor Environment
 Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis
 ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-3493- OPEN Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis Dalia E. Gaddis 1, Lindsey E. Padgett 1, Runpei Wu 1, Chantel
ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-3493- OPEN Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis Dalia E. Gaddis 1, Lindsey E. Padgett 1, Runpei Wu 1, Chantel
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany
 How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
Practical Solution: presentation to cytotoxic T cells. How dendritic cells present antigen. How dendritic cells present antigen
 Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
Objectives. Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance. Question 1. Question 2. Question 3. Definitions
 Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were
 Supplementary Methods Mice. B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Real-time PCR Total cellular RNA was extracted from the
Supplementary Methods Mice. B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Real-time PCR Total cellular RNA was extracted from the
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Supplementary Information. Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania. through collective production of nitric oxide
 Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript by Zhuang and colleagues characterizes in depth the phenotype, origin and role of mononuclear phagocytes infiltrating murine cardiac
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript by Zhuang and colleagues characterizes in depth the phenotype, origin and role of mononuclear phagocytes infiltrating murine cardiac
Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center
 Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center Disclosure Research Funding from BMS. Learning Objectives -Define belatacept-resistant rejection
Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center Disclosure Research Funding from BMS. Learning Objectives -Define belatacept-resistant rejection
The g c Family of Cytokines Prof. Warren J. Leonard M.D.
 The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow
 Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX 77030
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout. Secondary lymphoid organs. Dr H Awad
 Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Biology of Immune Aging
 Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION. 1 hour between 8:30 a.m. - 10:00 a.m. McIntyre Medical Rm 504 (Martin Amphitheatre)
 GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
Basic Immunology. Immunological tolerance. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance. Lecture 23 rd
 Basic Immunology Lecture 23 rd Immunological tolerance Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance Tolerated skin grafts on MHC (H2) identical mice TOLERANCE & AUTOIMMUNITY Upon encountering
Basic Immunology Lecture 23 rd Immunological tolerance Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance Tolerated skin grafts on MHC (H2) identical mice TOLERANCE & AUTOIMMUNITY Upon encountering
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production
 The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c)
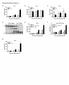 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
