Haploidentical Transplantation Helen Heslop
|
|
|
- Gerald Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Haploidentical Transplantation Helen Heslop
2 Outline Haplodentical transplantation Indications Regimens Outcomes KIR mismatching and NK cells Reconstituting T cell immunity Allodepleted T cells Cytotoxic T cells
3 Haploidentical Transplants
4 Options for Patients without a Matched Sibling Donor Unrelated donor? Degree of mismatch accepted Cord blood donor? Degree of mismatch accepted Haploidentical donor
5 Haplotypes Father 4/6 Mother 4/6 A1 A2 A2 A1 B8 B44 B7 B57 DR3 DR4 DR2 DR11 A1 A2 A1 A1 A2 A2 A2 A1 B8 B7 B8 B57 B44 B7 B44 B57 DR3 DR2 DR3 DR11 DR4 DR2 DR4 DR11 Patient Sibling 3/6 Sibling 3/6 Sibling 2/6
6 Haplotypes Husband Patient A1 A2 A2 A1 B8 B44 B7 B57 DR3 DR4 DR2 DR11 A1 A2 A1 A1 A2 A2 A2 A1 B8 B7 B8 B57 B44 B7 B44 B57 DR3 DR2 DR3 DR11 DR4 DR2 DR4 DR11 Child 4/6 Child 3/6 Child 3/6 Child 4/6
7 Haploidentical versus Unrelated Donor Advantages More rapidly available Donor available for additional products More graft versus tumor effects Disadvantages Increased alloreactivity Increased risk rejection and GVHD Delayed immune reconstitution
8 Haploidentical versus Cord Donor Advantages Donor available for additional products More graft versus tumor effects Less issues with cell dose of product Disadvantages Increased alloreactivity Increased risk rejection and GVHD
9 Algorithm for Donor Choices Published data Dependent on center aspects Regimens Research interests Experience and results with specific products Should be regularly reviewed
10 Sample Algorithm for Donor Choices HLA identical sibling 6/6 relative 5/6 matched relative 6/6 matched MUD or cord 5/6 matched cord 5/6 matched MUD, 4/6 matched cord or 4/6 matched relative 3/6 matched relative 3/6 matched cord
11 Limitations of Haploidentical Transplant Increased alloreactivity Initial study at Marsden using unmanipulated marrow after TBI/Cytoxan 10/35 with graft failure 12/35 died of hyperacute GVHD
12 Limitations of Haploidentical Transplant Increased alloreactivity Seattle studies showed equivalent outcome for 5/6 donors Increased GVHD but also reduced relapse Poor outcomes for 3/6 and 4/6 donors with standard regimens
13 Haploidentical Regimens Intensive Immunosuppression T cell depletion Anergization Megadose CD34-selected cells
14 Intensive Immunosuppression 135 patients received busulfan, cytarabine, cyclophosphamide, rabbit ATG Unmanipulated bone marrow and/or PBSC transplantation. GVHD prophylaxis with MMF, cyclosporine, and methotrexate. Grades II to IV acute GVHD 40% Two year leukemia-free and overall survival probabilities were 64% and 71% Lu et al
15 Intensive Immunosuppression Low-dose TBI, fludarabine +/- cyclophosphamide conditioning, and high dose cyclophosphamide on day + 3 post-transplant. 54% Grade II-IV GVHD 38% DFS O Donnell et al
16 T Cell Depletion Partial antibody-mediated T-cell depletion and post-transplant cyclosporine T10B9 (anti-alpha beta T-cell receptor) OKT3 (anti-cd3) Engraftment in >90% Grade II-IV GVHD 13% Long term DFS 20% in high risk patients Henslee Downey et al
17 Anergized Haploidentical BMT Induction of alloantigen-specific anergy by the co-culturing of host and donor bone marrow mononuclear cells in the presence of CTLA-4-IG 3/12 patients developed GVHD 5/12 survived 5-29 months Guinan et al
18 Megadose CD34-selected cells GCSF stimulation donor followed by CD34 selection 3-4 log T cell depletion High engraftment (>95%) Low GVHD (<10%) 48% DFS Aversa et al
19 Haploidentical Nonmyeloablative HCT Conditioning with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and alemtuzumab followed by infusion of alemtuzumab treated PBSC. GVHD prophylaxis with MMF and cyclosporine. 16% developed grade II-IV acute GVHD 6% primary graft failure DFS at 1 year 31% Rizzieri et al
20 Outcome of CD34 Selected Haploidentical Transplants 100 Censored 100 Death/Relapse Survival % Years post transplant
21 Causes of Failure Relapse 21% Infection 21% Regimen related mortality 5%
22 Causes of Delayed Immune Recovery Degree of HLA disparity Low numbers of T-cells infused Use of T-cell depleting antibodies Intensity of the conditioning regimen Impaired thymic function
23 Current Research Strategies Reduce Alloreactivity T reg cells Mesenchymal cells Reconstitute Immunity NK cells T cells
24 NK Cells and KIR matching
25 NK Cells Natural killer cells are a unique CD56+CD3- cell population Innate antiviral and antitumor immune response Different cell subsets with distinct phenotypic and functional characteristics 90% are highly cytotoxic CD56dim cells 10% are immunoregulatory CD56 bright cells NK cells recover as early as 2 to 3 weeks post-transplant by rapid differentiation from engrafted CD34+ cells
26 NK Cell Subsets CD16 CD56 CD16 CD56 IL-2R αβγ IL-2R βγ c-kit CD56 bright NK cell L-selectin CD56 dim NK cell CD94/NKG2A IFN-γ, TNF-α, GM-CSF, IL-10 KIR ADCC Natural cytotoxicity Immunoregulatory function Cytolytic function
27 (Killer Ig-like Receptors)KIRs Means by which NK cells recognize self from non-self 15 KIRs currenlty identified on chromosome 19 Ligand specificity for HLA molecules particularly HLA-C Some are activating and some are inhibitory
28 (Killer Ig-like Receptors)KIRs NK cells are activated by the absence of self MHC class I molecules on the surface of target cells. Expression of self MHC molecules on target cells delivers an inhibitory signal to NK cells via inhibitory KIRs. killing is inhibited, Killing of target cells occurs when NK cell inhibitory receptors are not engaged due to the absence of MHC class I due to MHC mismatch.
29
30 Other NK Receptors Activating receptors such as NKG2D and NKp46 trigger NK cell alloreactivity when engaged by antigens on virally infected cells and tumor cells NK cell activity is regulated by quantitative differences in cumulative inhibitory and activating signals transmitted via KIRs. presence or absence of the respective ligands on recipient cells determines if NK cells will be primed to be alloreactive and kill the targets
31 NK Cytotoxicity Balance of activating and inhibitory signaling NK Cell NK Cell Activating receptor Inhibitory receptor Activating receptor Inhibitory receptor Activating ligand HLA class I ligand Activating ligand Target Cell Target Cell
32 KIR Mismatch If donor NK cells are not fully inhibited by recipient MHC class I ligands there is graft NK cell alloreactivity KIR ligand mismatching in the GVH direction following T-cell depleted haploidentical HCT y Reduced relapse in patients with AML Lower rate of graft rejection (donor NK-mediated lysis of host residual T-cells) Reduction in GVHD (donor NK-mediated depletion of host antigen presenting cells) Ruggieri et al
33 Killing with KIR Mismatch Resistance Susceptibility Donor NK Cell Donor NK Cell Activating receptor Inhibitory KIR2DL1 (group 2 specific) Activating receptor Inhibitory KIR2DL1 (group 2 specific) Activating ligand HLA-Cw4 (group2) Activating ligand HLA-Cw3 (group1) Host Leukemic Blast Host Leukemic Blast
34 NK Alloreactivity NK Cell No Lysis X Autologous Normal Cell NCR p30 p44 p46 NKG2D CD94/NKG2A KIRs + + HA? MICA, MICB, ULBPs HLA-E HLA-A, -B, -C Donor NK Lysis Allogeneic Leukemia NCR p30 p44 p46 NKG2D CD94/NKG2A KIRs + + v Stress ligands v MHC ligands v Incompatible MHC
35 Anti-AML effects of NK cells Haplo-identical SCT (Ruggeri et al) MUD SCT (Giebel et al) MSD SCT (Hsu et al) Non-SCT (Miller et al)
36 Relapse after Transplant for AML Ruggeri et al 2007 Perugia
37 DFS in patients with AML
38 Effects in ALL Not seen in Perugia series Seen in St Jude study (Leung et al) repertoire assessment for the four KIRs by genotyping vs phenotyping was not in complete agreement
39 Exploiting NK Alloreactivity Donor selection criteria to include KIR genotyping Ex vivo expansion of NK cells for adoptive transfer Antibody blockade of inhibitory receptors
40 Blocking Recognition of Self Donor NK Cell Donor NK Cell Activating receptor Activating ligand Inhibitory receptor HLA-C Activating receptor Activating ligand Y Inhibitory receptor Anti-KIR antibody HLA-C Host Leukemic Blast Host Leukemic Blast
41 Adoptive Transfer Of Haploidentical NK Cells NK cell infusions given to 43 patients with refractory or relapsed malignancies NK cells prepared by pheresis, CD3 depletion, and IL-2 activation 40% NK cells 25% monocytes 20% B cells 1% T cells Established safe NK dose --Escalated dose from 10 5 to 2 x 10 7 cells/kg --No infusion reactions and no GVHD Miller et al Blood 2005
42 Natural Killer Cell Infusions Donor cell Recipient Cell Reduced Risk of NK Dendritic cell GVHD T-cell Rejection Viral infected cell Infection Leukemia cell Relapse
43 Adoptive Transfer of Purified CD56+ Cells Feasible to obtain on immunomagnetic column with CD3 depletion followed by CD56 selection Retain proliferative capacity Trials underway to study safety and feasibility in HSCT and non-hsct areas Leung et al J Immunol 2005
44
45 Reconstituting T Cell Immunity
46 T cell Reconstitution Pathways Early reconstitution via homeostatic peripheral expansion expansion of mature T-cells that survive the conditioning Expansion of mature T cells in the allograft Late reconstitution via a thymicdependent pathway.
47 Approaches to Reconstituting Immunity T cell precursor frequencies in haploidentical transplantation: alloreactive > anti-viral > anti-tumor Options Virus Specific T cells Allodepleted T cells
48 Cytotoxic T cells Anti-viral CMV EBV Adenovirus Anti-tumor Viral antigens -LMP1 and 2 antigens Chimeric-antigen-receptor transduced CTLs targeting GD2 or CD19
49 Generating antigen specific cytotoxic T cells ex vivo Repeated stimulation with antigen expressed on antigen presenting cell Expand antigen specific T cells T cells with specificities for other antigens will nor survive
50 Generation Of Antigen-specific CTL Antigen APC CTL specific for target antigen PBMC IL2 After 3 rd or 4 th stimulation analyze CTL lines ---> Freeze & QA/QC
51 Requirements for Generation CTLs Good antigen presenting cell Dendritic cells Monocytes B cells Source of antigen Viral lysate Transduce with full length viral antigen(s) Pulse with peptides Helpful to have immune donor
52 Studies with EBV and CMV specific CTL Studies Transferred CTLs specific for latent virus expand and persist long term Efficacy in preventing and treating CMV and EBV infection But Only target 1 virus Time for generation
53 Extending EBV Immunotherapy Approach to CMV and Adenovirus Choosing optimal antigen presenting cell Monocyte LCL (includes EBV antigens) Source of CMV and adenovirus antigen? -Ad5f35 vector encoding pp65? Competition between viral antigens
54 Generation Of Adv-specific CTL Using Ad5f35 Vectors LMP1 LMP2 pp65 EBNA 3a,3b,3c LP EBNA-2 EBNA-1 Trivirus Bivirus CTL CTL lines lines (Adv/EBV/CMVpp65) (Adv/EBV) Lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL)
55 Generation Of Virus-specific CTL Ad5f35 vector PBMC Ad5f35 vector actmo LCL EBV-LCL + IL-2 O/N Adherence Activated monocytes + PBMC Virusspecific CTL After 3 rd or 4 th stimulation analyze CTL lines ---> Freeze & QA/QC
56 Analysis of CTL lines 34 CTL lines analyzed - 19 Bi-virus specific - 15 Tri-virus specific (CMV seropositive donors) Phenotypic analysis Specificity for viruses: - Cytotoxicity assay - ELISPOT assay for IFN-γ secretion - Pentamer analysis
57 CTL Phenotype % % cells % 80 80% 60 60% 40 40% 20 20% 0 0% CD4 CD8 CD56 CD19 CD14 CD4 CD8 CD56 CD19 CD14 Bi-virus specific CTL lines % CD4 CD8 CD56 CD19 CD14 Tri-virus specific CTL lines
58 CTL Specificity-Cytotoxicity CMV target EBV target Adv target Allo target Bivirus-specific CTL Mean of 19 lines Trivirus-specific CTL Mean of 15 lines
59 CTL Specificity-IFNγ ELISPOT Analysis CTL lines Adv EBV CMV CONTROL SFC / 1 x10 5 cells Bi-virus median (range) 558 ( ) 414 ( ) n/a 10 (1-32) Tri-virus median (range) 86 (20-350) 183 (46-351) 648 ( ) 14.5 (3-65) 19/19 Bi-virus & 14/15 Tri-virus specific CTL were Adv specific All CTL lines were EBV specific All Tri-virus-specific CTL were CMV specific
60 Antigenic competition Bivirus Trivirus Pool 1 (aa 1-100) Pool 2 (aa ) Pool 3 (aa ) Pool 4 (aa ) Pool 5 (aa ) Pool 6 (aa ) Pool 7 (aa ) Pool 8 (aa ) Pool 9 (aa ) Pool 10 (aa ) Hexon peptide pools Pool 11 (aa ) Pool 1 (aa 1-100) Pool 2 (aa ) Pool 3 (aa ) Pool 4 (aa ) Pool 5 (aa ) Pool 6 (aa ) Pool 7 (aa ) Pool 8 (aa ) Pool 9 (aa ) Pool 10 (aa ) Hexon peptide pools Pool 11 (aa ) CD8 epitope CD4 epitope Pt 14 Pt 15 Pt 16 Pt 17 Pt 18 Pt 19 Pt 20 Pt 21 Pt 22 Pt 23 Pt 24 Pt 25 Pt 26 Pt 1 Pt 2 Pt 3 Pt 4 Pt 5 Pt 6 Pt 7 Pt 8 Pt 9 Pt 10 Pt 11 Pt 12 Pt 13 Greather breadth of Adv reactivity in Bivirus-specific CTL lines
61 Eligibility Criteria CMV prophylaxis and Adenovirus prophylaxis and treatment studies Day +30 post HSCT GVHD <grade III at enrollment
62 Infused CTL lines 27 CTL lines infused -25 on-study -2 compassionate CTL dose range: 5x10 6 to 1.35x10 8 /m 2 12 patients received Bi-virus CTL 15 patients received Tri-virus CTL
63 Patient Characteristics Group Median age (range) Alternative donors Campath or ATG in vivo Median day CTL infused Off immune suppression Bivirus 4yr (1-13) 100% (13/13) 100% (13/13) +77 (22-150) 61% (8/13) Trivirus 10yr (1-62) 73% (11/15) 87% (13/15) +84 (35-164) 60% (9/15) 79% of patients received BMT for malignant disease 4 patients who received Bivirus CTL had Adv 5 patients who received Trivirus CTL had Adv
64 Toxicity No dose limiting toxicity
65 Efficacy of EBV and CMV -specific CTL Infusion After HSCT Mean SFC per 1x10e6 cells Nat Med. 2006;12(10): EBV and CMV-specific- T cells expanded after infusion and were protective in vivo SFC/1x10e6 cells 0 Infected Uninfected pre 1wk 2wk 4wk Pre weeks Adv Mean SFC per 2x10e5 cells Mean SFC per 2x10e5 cells Pre weeks Pre weeks EBV CMV
66 Clinical Outcome Summary-CMV 7/15 patients developed CMV reactivation immediately pre or post CTL infusion 6/7 had decrease in CMV viral load with corresponding elevation in CMV-specific CTL detected in PB 6/7 cleared virus long term (6-33mths) 1/7 resistant to antiviral Rx
67 Clinical Outcome Summary-EBV 8/28 patients had EBV reactivation All patients had decrease in EBV viral load with corresponding elevation in EBV-specific CTL detected in PB No antiviral therapy required
68 Resolution of Liver Lesion No Further Therapy Required Diagnosis of PTLD 2 months later
69 Reduced Adv load in blood and stool post- CTL Adv copies/ml blood Adv copies per ml blood Adv copies/gram stool x10e Adv copies/g stool 0 0 pre weeks 3yr old female; Improvement of diarrhea 2wks post-ctl
70 Patient with Adenovirus Disease Admitted for pneumonia/hypoxia Day +133 Day +138 BAL positive for adenovirus Required HFOV, inotropes, started Cidofovir
71 Resolution of Adenoviral Pneumonia after CTL Day x10 6 adenovirus-specific CTLs Day +166 extubated successfully
72 Reduction in Adv Load Post-CTL & Rise in Adv CTLp SFC per 1 x 10 6 cells Adv T cell Adv DNA (trachea) 1,400 1,200 1, Adv copies/ml 0 Pre CTL 2 wk 4 wk 6 wk 8 wk 0
73 Summary Bivirus-specific CTL routinely generated and have greater and broader adenovirus activity than trivirus specific CTL Ad-specific CTL expand only in presence of Ad infection Role of Ag in homeostatic expansion Expansion and clinical activity not related to dose level Leen et al Nat Med 2006
74 Future Directions Expand the number of antigens targeted Aspergillus RSV Influenza pp65 Parainfluenza BK virus Herpesvirues Combine immunotherapy with vaccination strategies
75 How Do We Extend Applicability? Simplify production patient specific product Modify APC Early selection Can we use bank of allogeneic matched CTLs
76 Alternative Rapid Selection Procedures Select low frequency antigen-specific CTLs Transfer small numbers selected cells Rely on expansion in vivo
77 Methods to Select T-cells tetramer CTL IFN-γ IFN-γ Tetramer selection Gamma interferon selection
78 Rapidly Available CTLs All have clinical activity Allogeneic banked cells Risk of rejection Tetramer selected cells Restricted specificity Gamma interferon capture selected cells Large volumes blood needed
79 Allodepletion Activated T cells express CD25, CD69, CD71 and HLA-DR If stimulate donor T-cells with host can remove responding T-cells with antibody
80 Selective Depletion Of Alloreactive Cells + 72 hours Murine IgG1 anti-cd25 conjugated to deglycosylated ricin A chain Donor PBMC Recipient EBVlymphoblastoid cell line (Irradiated) Alloreactive cells upregulate CD25 Allodepleted T-cells Amrolia at al Blood 2006
81 Patients 17 patients Median age 8 years (range 2-58) Median follow up 30 months Dose level 1 (9 patients): 10 4 /kg x3 Dose level 2: (8 patients) 10 5 /kg x3 6 not in remission 5 patients relapsed post previous transplant
82 CD3 Recovery Post HSCT Months post transplant Dose Level 2 -- Dose Level
83 Reconstitution Immunity to EBV SFC/10E6 PBM Dose Level 1 Dose Level Months Post HSCT
84 Recovery Of CD8 Response To CMV Donor A2-NLV 0.4% B8-ELR 0% Patient At 6 months 5.7% 3.9% Response larger and to additional epitopes compared to donor
85 Recovery From PML 14 year old with MDS 2 months post haplo SCT presented with tremor, inhibition and progressive LOC 2 months post HSCT CD3 and 4 = 0/mm 3 4months post HSCT CD3=630/mm 3, CD4=220/mm 3
86 GVHD Acute GVHD 2/17 1 grade 2 skin 1grade 4 skin Chronic GVHD 2/14 1 ext. skin/mouth 1 ext. liver
87 Clinical Status 6/14 Baylor patients alive in CR months post allodepleted cells 6 patients relapsed
88 Conclusions Adoptive immunotherapy with allo-depleted donor T-cells More rapid recovery of T-cells Effector memory phenotype Accelerated recovery of viral-specific immunity with clinical responses Low incidence of GVHD and viral deaths Significant relapse risk
89 Future Directions Dose escalate further to evaluate effect on risk of relapse Risk of GVHD Transition to allodepleted T cells modified with retroviral vector encoding icaspase9 and CD19
90 Can we extend approach to antitumor immunity? Antigens less well defined Antigens less immunogenic Other tumor evasion mechanisms
91 Extending CTL Therapy to Type II latency EBV tumors EBV infected B cell EBNA 2 EBNA 3 LMP1 EBNA 1 LMP2 BZLF1 T T T T T T Lytic EBNA 3 LMP 2 LP LMP 1 EBNA 2 EBNA1 Hodgkin s Or NPC tumor cell EBNA 1 LMP LMP1 1 LMP 2 Inhibitory cytokines
92 Making LMP2 an Immunodominant Antigen Ad5f35 LMP2 DC LCL IL-2 IL-2 IL-2 PBMC LMP2- specific CTL Gahn et al Int J Cancer 2002, Bollard et al, J Immunother 2004
93 LMP2-specificity of LMP2-CTL Line Generated From Patient With Relapsed Hodgkin Disease Tet-CLG Tet-FLY FC125Y CD8 FITC FC125Y % 13.5% % specific lysis Allo LCL Auto LCL PHA blasts Fibros GFP Fibros LMP CD8 FITC 0 40 to1 20 to 1 10 to 1 5 to 1
94 Clinical Results Relapsed Disease Arm No toxicity 1 progressive disease 1 very good partial response >18 months 4 complete responses Persisted 9 to 36+ months
95 Complete Radiological Response EBV+ve NK-T NHL Pre CTL Post CTL E B V c o p i e s / u g D N A Pre CTL 1 Pre CTL 2 Pre CTL 3 pre CT L1 1 wk 2 w ks/prectl 2 4 wk s 6wks prect L3 1wk 2 wk
96 Immunohistochemistry L Carytenoid Pre CTL Post CTL EBER 10x CD4 40x
97 Conclusions LMP2 specific CTLs have activity in EBV+ve Hodgkin s Disease and Type II latency NHL 4/6 CRs in patients with active disease (autologous) Bollard et al Blood 2007
98 Can We Extend Beyond Viral Antigens? Many express specific surface markers GD2 CD19 CD30 kappa Prepare chimeric T cells with antibody specificity See whole antigen on tumor surface
99 Improving T cell Therapies Grafting Additional Specificities α β TcR-complex γε εδ ζζ Fab v H v L Antibody C L C H1 C L C H1 v L v H v H v L
100 Overcoming limitations of CARs Dual-specific T cells -On EBV-CTL (Rossig et al, Blood 2002) -On Allo T cells (Kershaw et al, Nat Biotech 2002) -On MP-1-specific CTL (Cooper et al, Blood 2004) EBV-Infected B cell CD4+EBV CTL CD8+EBV CTL Cognate help for CTL activation and expansion tumor
101 Are CAR-CTL better than CAR-PTC in Neuroblastoma Patients? Transduce patient PTC and CTL with a vector encoding identical receptor but distinct oligonucleotide for each population 11 patients with relapsed neuroblastoma
102 Percent Transduced T cells in Blood % GD2 PTC 0 1 1Wk 2Wks 4Wks 6Wks Time post-infusion
103 Percent Transduced T cells in Blood % GD2 CTL GD2 PTC 0 1 1Wk 2Wks 4Wks 6Wks Time post-infusion
104 Dose 1 Complete Response Pre-Infusion 2 Months 4 Months
105 Engineering Haploidentical Grafts
Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant
 Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant Hanley PJ, Krance BR, Brenner MK, Leen AM, Rooney CM, Heslop HE, Shpall EJ, Bollard CM Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant Hanley PJ, Krance BR, Brenner MK, Leen AM, Rooney CM, Heslop HE, Shpall EJ, Bollard CM Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
The future of HSCT. John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD
 The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
Administration of Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Engineered to Resist TGF-ß to Patients with EBV-Associated Lymphomas
 Administration of Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Engineered to Resist TGF-ß to Patients with EBV-Associated Lymphomas CM. Bollard, G Dotti, S Gottschalk, E Liu, A Sheehan, M Mims, H Liu, AP. Gee,
Administration of Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Engineered to Resist TGF-ß to Patients with EBV-Associated Lymphomas CM. Bollard, G Dotti, S Gottschalk, E Liu, A Sheehan, M Mims, H Liu, AP. Gee,
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives
 Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Stem Cell Sources 2/22/13. Cellular Therapy Today and Tomorrow. Cellular Therapy in HCT. Bone Marrow
 2/22/13 Cellular Therapy Today and Tomorrow Robert S. Negrin, MD Division Chief, Stanford Bone and Marrow Transplant Program Professor of Medicine Cellular Therapy in Clinical Medicine Established Hematopoietic
2/22/13 Cellular Therapy Today and Tomorrow Robert S. Negrin, MD Division Chief, Stanford Bone and Marrow Transplant Program Professor of Medicine Cellular Therapy in Clinical Medicine Established Hematopoietic
The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells
 The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells CD34+ positive selection Negative Depletion of: CD3/CD19 TcRαβ/CD19 T-cell depletion: positive selection versus negative
The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells CD34+ positive selection Negative Depletion of: CD3/CD19 TcRαβ/CD19 T-cell depletion: positive selection versus negative
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology. Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases
 One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation. Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to Disclose
 Rupert Handgretinger Children s University Hospital, Tübingen, Germany Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to
Rupert Handgretinger Children s University Hospital, Tübingen, Germany Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Translating EBV Immunology from Bench to Bedside: Somnium Animadverto A Dream Realized
 Translating EBV Immunology from Bench to Bedside: Somnium Animadverto A Dream Realized Epstein-Barr Virus Human herpesvirus 90% population infected Associated with many other cancers latent infection.persists
Translating EBV Immunology from Bench to Bedside: Somnium Animadverto A Dream Realized Epstein-Barr Virus Human herpesvirus 90% population infected Associated with many other cancers latent infection.persists
Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology
 Advances in Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology April 12, 2014 Disclosures
Advances in Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology April 12, 2014 Disclosures
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
Does NK cell alloreactivity prevent relapse? Yes!!! Andrea Velardi Bone Marrow Transplant Program University of Perugia
 Does NK cell alloreactivity prevent relapse? Yes!!! Andrea Velardi Bone Marrow Transplant Program University of Perugia Recognition of missing self HLA triggers lysis NK Inhibitory receptor Activating
Does NK cell alloreactivity prevent relapse? Yes!!! Andrea Velardi Bone Marrow Transplant Program University of Perugia Recognition of missing self HLA triggers lysis NK Inhibitory receptor Activating
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients
 Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
Antiviral Adoptive Immunotherapy for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders. Speaker Disclosures
 3/27/218 Antiviral Adoptive Immunotherapy for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders Michael Keller, MD Program for Cell Enhancement & Technologies for Immunotherapy (CETI) Director: Dr. Catherine Bollard
3/27/218 Antiviral Adoptive Immunotherapy for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders Michael Keller, MD Program for Cell Enhancement & Technologies for Immunotherapy (CETI) Director: Dr. Catherine Bollard
Revista Cubana de Hematología, Inmunología y Hemoterapia. 2017; 36 (Suplemento).
 Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes
 T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
Evaluation of T Cell Products LMP-specific T cell therapies for Lymphoma
 Evaluation of T Cell Products LMP-specific T cell therapies for Lymphoma CM The Long Winding Road to Successful T cell Therapy Tumor specific T cells in the clinic (CAR modified) Multi-virus specific T
Evaluation of T Cell Products LMP-specific T cell therapies for Lymphoma CM The Long Winding Road to Successful T cell Therapy Tumor specific T cells in the clinic (CAR modified) Multi-virus specific T
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK. HCT in Children
 Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation
 Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
. TCR Alpha, Beta and CD19+ Cell Depleted Haploidentical Transplant for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders Feb 22 nd,2018
 . TCR Alpha, Beta and CD19+ Cell Depleted Haploidentical Transplant for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders Feb 22 nd,2018 Neena Kapoor Professor of Pediatrics Children s Hospital Los Angeles Keck School
. TCR Alpha, Beta and CD19+ Cell Depleted Haploidentical Transplant for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders Feb 22 nd,2018 Neena Kapoor Professor of Pediatrics Children s Hospital Los Angeles Keck School
T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG
 UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
MUD SCT. Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
 MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani, 2 Rajni Agarwal-Hashmi, 3 Melissa Aldinger, 4 Franco Locatelli 1
 Administration of Rivogenlecleucel (Rivo-cel, BPX-501) Following αβ T- and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT in Children With Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani,
Administration of Rivogenlecleucel (Rivo-cel, BPX-501) Following αβ T- and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT in Children With Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani,
Using Gene Transfer to Retarget Cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Malcolm Brenner
 Using Gene Transfer to Retarget Cytotoxic T lymphocytes Malcolm Brenner Epstein Barr Virus Infects >90% population Acute infection is followed by life-long latency Expression of limited array of viral
Using Gene Transfer to Retarget Cytotoxic T lymphocytes Malcolm Brenner Epstein Barr Virus Infects >90% population Acute infection is followed by life-long latency Expression of limited array of viral
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD
 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate
 3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
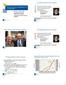 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect
 Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect All Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants Are Blind Doctor Donor Patient Genetic polymorphism gives rise to unique peptides in donor and recipient
Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect All Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants Are Blind Doctor Donor Patient Genetic polymorphism gives rise to unique peptides in donor and recipient
Adoptive Immunotherapy for Posttransplantation Viral Infections
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:143-155 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1003-0001$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2003.09.017 Adoptive Immunotherapy
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:143-155 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1003-0001$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2003.09.017 Adoptive Immunotherapy
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche
 Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche Massimo Fabrizio Martelli Ematologia ed Immunologia Clinica Università degli Studi di Perugia 41 Congresso Nazionale
Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche Massimo Fabrizio Martelli Ematologia ed Immunologia Clinica Università degli Studi di Perugia 41 Congresso Nazionale
Dr. Yi-chi M. Kong August 8, 2001 Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION
 Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION I. KINDS OF GRAFTS II. RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 2 of 10 II.GRAFT REJECTION IS IMMUNOLOGIC
Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION I. KINDS OF GRAFTS II. RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 2 of 10 II.GRAFT REJECTION IS IMMUNOLOGIC
Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia
 Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia Carmem Bonfim Director Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation Program HC Federal
Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia Carmem Bonfim Director Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation Program HC Federal
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
EBV Infection and Immunity. Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham
 EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH
 Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH Tzu-Ting Chen, Wen-Jyi Lo, Chiao-Lin Lin, Ching-Chan Lin, Li-Yuan Bai, Supeng Yeh, Chang-Fang Chiu Hematology and
Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH Tzu-Ting Chen, Wen-Jyi Lo, Chiao-Lin Lin, Ching-Chan Lin, Li-Yuan Bai, Supeng Yeh, Chang-Fang Chiu Hematology and
TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY. Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard
 TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard Outline MHC / HLA Direct vs indirect allorecognition Alloreactive cells: where do they come from? Rejection and Immunosuppression
TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard Outline MHC / HLA Direct vs indirect allorecognition Alloreactive cells: where do they come from? Rejection and Immunosuppression
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Using Mismatched/Haploidentical Donors
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 13:1249-1267 (2007) 2007 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/07/1311-0001$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.08.003 Allogeneic Hematopoietic
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 13:1249-1267 (2007) 2007 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/07/1311-0001$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.08.003 Allogeneic Hematopoietic
Allo CTL Protocol Page 1 of 43 Version 0.8 dated August 15th, 2008
 Page 1 of 43 Version 0.8 dated August 15th, 2008 Most Closely HLA Matched Allogeneic Virus Specific Cytotoxic T- Lymphocytes (CTL) to Treat Persistent Reactivation or Infection with Adenovirus, CMV and
Page 1 of 43 Version 0.8 dated August 15th, 2008 Most Closely HLA Matched Allogeneic Virus Specific Cytotoxic T- Lymphocytes (CTL) to Treat Persistent Reactivation or Infection with Adenovirus, CMV and
Transplantation. Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University
 Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 122-126 Suppl 1 (1986) Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum J. Kersey Bone Marrow Transplantation Program, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN,
International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 122-126 Suppl 1 (1986) Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum J. Kersey Bone Marrow Transplantation Program, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN,
T-cell Therapies for Hematologic Malignancies: Utilizing A Non-Gene Transfer Approach. Catherine Bollard
 T-cell Therapies for Hematologic Malignancies: Utilizing A Non-Gene Transfer Approach Catherine Bollard Rationale of Immunotherapy for EBV-positive Lymphoma Significant failure rate of therapy for advanced
T-cell Therapies for Hematologic Malignancies: Utilizing A Non-Gene Transfer Approach Catherine Bollard Rationale of Immunotherapy for EBV-positive Lymphoma Significant failure rate of therapy for advanced
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS
 ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS Didier Blaise, MD Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit (U2T) Department of Hematology Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie, Inserm U891
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS Didier Blaise, MD Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit (U2T) Department of Hematology Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie, Inserm U891
Exploiting NK-cell alloreactivity in AML
 1st CUNEO CITY IMMUNOTHERAPY CONFERENCE (CCITC) -May 17-19 2018- IMMUNOTHERAPY IN HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES 2018 Exploiting NK-cell alloreactivity in AML Antonio Curti Institute of Hematology L. and A.
1st CUNEO CITY IMMUNOTHERAPY CONFERENCE (CCITC) -May 17-19 2018- IMMUNOTHERAPY IN HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES 2018 Exploiting NK-cell alloreactivity in AML Antonio Curti Institute of Hematology L. and A.
Broad spectrum antiviral T cells for viral complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
 Editorial Page 1 of 5 Broad spectrum antiviral T cells for viral complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Britta Maecker-Kolhoff 1,2, Britta Eiz-Vesper 2,3 1 Department of Pediatric
Editorial Page 1 of 5 Broad spectrum antiviral T cells for viral complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Britta Maecker-Kolhoff 1,2, Britta Eiz-Vesper 2,3 1 Department of Pediatric
Improving the Outcome of Stem Cell Transplants for Cancer Treatment Using Multivirus-Specific T Cells (Viralym-M)
 OFF-THE-SHELF T CELL THERAPY FOR CANCER PATIENTS FOLLOWING STEM CELL TRANSPLANT Improving the Outcome of Stem Cell Transplants for Cancer Treatment Using Multivirus-Specific T Cells (Viralym-M) Ann M.
OFF-THE-SHELF T CELL THERAPY FOR CANCER PATIENTS FOLLOWING STEM CELL TRANSPLANT Improving the Outcome of Stem Cell Transplants for Cancer Treatment Using Multivirus-Specific T Cells (Viralym-M) Ann M.
Transplant Booklet D Page 1
 Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
New trends in donor selection in Europe: "best match" versus haploidentical. Prof Jakob R Passweg
 New trends in donor selection in Europe: "best match" versus haploidentical Prof Jakob R Passweg HSCT change in donor type: 1990-2015 9000 H S C T 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 HLA identical sibling/twin Haplo-identical
New trends in donor selection in Europe: "best match" versus haploidentical Prof Jakob R Passweg HSCT change in donor type: 1990-2015 9000 H S C T 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 HLA identical sibling/twin Haplo-identical
Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations. Tumor Immunology (Cancer)
 Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
UPDATE Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Lymphoma and Myeloma
 UPDATE Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Lymphoma and Myeloma Supported by a grant from Supported by a grant from UPDATE Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Lymphoma and Myeloma Jonathan W.
UPDATE Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Lymphoma and Myeloma Supported by a grant from Supported by a grant from UPDATE Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Lymphoma and Myeloma Jonathan W.
Haploidentical Donor Transplants: Outcomes and Comparison to Other. Paul V. O Donnell BSBMT Education Day London 12 October 2011
 Haploidentical Donor Transplants: Outcomes and Comparison to Other Donor Types Paul V. O Donnell BSBMT Education Day London 12 October 2011 Clinical Problem: Identification of a Donor for Allogeneic Transplantation
Haploidentical Donor Transplants: Outcomes and Comparison to Other Donor Types Paul V. O Donnell BSBMT Education Day London 12 October 2011 Clinical Problem: Identification of a Donor for Allogeneic Transplantation
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond
 PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, PhD Hematology and BMT Unit Hôpital Saint Antoine, Paris, France #EBMTITC16 www.ebmt.org Hematopoietic SCT
Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, PhD Hematology and BMT Unit Hôpital Saint Antoine, Paris, France #EBMTITC16 www.ebmt.org Hematopoietic SCT
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Cytotherapy. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 May 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cytotherapy. 2011 May ; 13(5): 518 522. doi:10.3109/14653249.2011.561983. Manufacture of GMP-grade Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes specific
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cytotherapy. 2011 May ; 13(5): 518 522. doi:10.3109/14653249.2011.561983. Manufacture of GMP-grade Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes specific
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON. Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells
 T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
Giornate Ematologiche Vicen1ne Vicenza,
 Giornate Ematologiche Vicen1ne Vicenza, 10-12 2016 Adop1ve immunotherapy with haploiden1cal alloreac1ve NK cells for the treatment of Minimal Residual Disease in elderly pa1ents with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Giornate Ematologiche Vicen1ne Vicenza, 10-12 2016 Adop1ve immunotherapy with haploiden1cal alloreac1ve NK cells for the treatment of Minimal Residual Disease in elderly pa1ents with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Clinical Translation of Immunotherapy using WT1 and CMV specific TCR Gene Transfer
 Clinical Translation of Immunotherapy using WT1 and CMV specific Gene Transfer Dr Emma C Morris Reader, Dept of Immunology, UCL Consultant Haematologist (BMT), UCLH and RFH ISCT, 2/5/211 Gene Transfer
Clinical Translation of Immunotherapy using WT1 and CMV specific Gene Transfer Dr Emma C Morris Reader, Dept of Immunology, UCL Consultant Haematologist (BMT), UCLH and RFH ISCT, 2/5/211 Gene Transfer
AIH, Marseille 30/09/06
 ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25)
 3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies. Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital
 Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital Survival by Cohort of Birth (N=977) 1.00 85-97 80-84 75-79 70-74 0.75 Survival Probability 0.50 0.25 P
Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital Survival by Cohort of Birth (N=977) 1.00 85-97 80-84 75-79 70-74 0.75 Survival Probability 0.50 0.25 P
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016
 What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
08/02/59. Tumor Immunotherapy. Development of Tumor Vaccines. Types of Tumor Vaccines. Immunotherapy w/ Cytokine Gene-Transfected Tumor Cells
 Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic
 Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic isbtc 10-13 November 2005 Valeria Milani, MD, PhD Munich Agenda 1. NK ligands
Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic isbtc 10-13 November 2005 Valeria Milani, MD, PhD Munich Agenda 1. NK ligands
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Cell-based immunotherapy products for the treatment of blood cancers and inherited blood disorders. Company Presentation June 2016
 Cell-based immunotherapy products for the treatment of blood cancers and inherited blood disorders Company Presentation June 2016 Disclaimer These slides and the accompanying oral presentation contain
Cell-based immunotherapy products for the treatment of blood cancers and inherited blood disorders Company Presentation June 2016 Disclaimer These slides and the accompanying oral presentation contain
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20898 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Jöris, Monique Maria Title: Challenges in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20898 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Jöris, Monique Maria Title: Challenges in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Cytotoxicity assays. Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1. Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
 Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/61077 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lugthart, G. Title: T and NK cell immunity after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/61077 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lugthart, G. Title: T and NK cell immunity after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Dedicated to Gordon. Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey
 Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma. Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy
 Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet, 1950s)
 TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
Histocompatibility Evaluations for HSCT at JHMI. M. Sue Leffell, PhD. Professor of Medicine Laboratory Director
 Histocompatibility Evaluations for HSCT at JHMI M. Sue Leffell, PhD Professor of Medicine Laboratory Director JHMI Patient Population Adults Peds NMDP data >20,000 HSCT JHMI HSCT Protocols Bone marrow
Histocompatibility Evaluations for HSCT at JHMI M. Sue Leffell, PhD Professor of Medicine Laboratory Director JHMI Patient Population Adults Peds NMDP data >20,000 HSCT JHMI HSCT Protocols Bone marrow
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Factors Influencing Haematopoietic Progenitor cell transplant outcome Optimising donor selection
 Factors Influencing Haematopoietic Progenitor cell transplant outcome Optimising donor selection Alison Logan Transplantation Laboratory Manchester Royal Infirmary Haematopoietic progenitor cell transplants
Factors Influencing Haematopoietic Progenitor cell transplant outcome Optimising donor selection Alison Logan Transplantation Laboratory Manchester Royal Infirmary Haematopoietic progenitor cell transplants
Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù, Rome, Italy, 2. Bellicum Pharmaceuticals Inc., Houston, United States
 Impact of Post-Transplant Infusion of Donor T-Cells Genetically Modified with Inducible Caspase 9 Suicide Gene (BPX-501 Cells) on Children with Leukemia Given αβ T-Cell and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT Pietro
Impact of Post-Transplant Infusion of Donor T-Cells Genetically Modified with Inducible Caspase 9 Suicide Gene (BPX-501 Cells) on Children with Leukemia Given αβ T-Cell and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT Pietro
Stem cells. -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA. Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT
 Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Tumor Immunology. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant
 Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Rapid and Robust CD4+ and CD8+ T-, NK-, BTitel and Monocyte Cell Reconstitution after Nicotinamide-Expanded Cord Blood (NiCord) Transplantation
 Rapid and Robust CD4+ and CD8+ T-, NK-, BTitel and Monocyte Cell Reconstitution after Nicotinamide-Expanded Cord Blood (NiCord) Subtitel Transplantation Boelens/Nierkens lab Jaap Jan Boelens, Central Immune
Rapid and Robust CD4+ and CD8+ T-, NK-, BTitel and Monocyte Cell Reconstitution after Nicotinamide-Expanded Cord Blood (NiCord) Subtitel Transplantation Boelens/Nierkens lab Jaap Jan Boelens, Central Immune
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
T lymphocytes targeting native receptors
 Cliona M. Rooney Ann M. Leen Juan F. Vera Helen E. Heslop T lymphocytes targeting native receptors Authors address Cliona M. Rooney 1, Ann M. Leen 1, Juan F. Vera 1, Helen E. Heslop 1 1 Center for Cell
Cliona M. Rooney Ann M. Leen Juan F. Vera Helen E. Heslop T lymphocytes targeting native receptors Authors address Cliona M. Rooney 1, Ann M. Leen 1, Juan F. Vera 1, Helen E. Heslop 1 1 Center for Cell
New Developments in Allotransplant Immunology
 New Developments in Allotransplant Immunology A. John Barrett, Katayoun Rezvani, Scott Solomon, Anne M. Dickinson, Xiao N. Wang, Gail Stark, Hannah Cullup, Mark Jarvis, Peter G. Middleton, and Nelson Chao
New Developments in Allotransplant Immunology A. John Barrett, Katayoun Rezvani, Scott Solomon, Anne M. Dickinson, Xiao N. Wang, Gail Stark, Hannah Cullup, Mark Jarvis, Peter G. Middleton, and Nelson Chao
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20522 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stevanović, Sanja Title: Exploiting HLA-class II disparity for anti-tumor immunity
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20522 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stevanović, Sanja Title: Exploiting HLA-class II disparity for anti-tumor immunity
