A Glomerella species phylogenetically related to Colletotrichum acutatum on Norway maple in Massachusetts
|
|
|
- Ilene Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mycologia, 100(5), 2008, pp DOI: / # 2008 by The Mycological Society of America, Lawrence, KS A Glomerella species phylogenetically related to Colletotrichum acutatum on Norway maple in Massachusetts Katherine F. LoBuglio 1 Donald H. Pfister Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, Massachusetts Abstract: A fungus isolated from Norway maple (Acer platanoides) in the Boston, Massachusetts, area was determined to be a species of Glomerella, the teleomorph of Colletotrichum acutatum. Pure cultures of the fungus were obtained from discharged ascospores from perithecia in leaf tissue. This fungus was determined to be homothallic based on the observation of perithecial development in cultures of single-spore isolates grown on minimal salts media and with sterile toothpicks. A morphological and molecular analysis was conducted to determine the taxonomic position of this fungus. Parsimony analyses of a combined nucleotide dataset of the ITS and LSU rdna region, and of the D1 D2 LSU rdna region, indicated that this species has phylogenetic affinities with Colletotrichum acutatum, C. acutatum f. sp. pineum, C. lupini, C. phormii and G. miyabeana. These results are significant because C. acutatum has not been reported on Acer platanoides. In addition the consistent presence of perithecia on leaf tissue and in culture is unusual for Colletotrichum, suggesting that the teleomorphic state is important in the life cycle of this fungus. Key words: Acer, anamorph, Ascomycota, phylogeny, ribosomal DNA, teleomorph INTRODUCTION During fall 2006 leaves of Norway maple (Acer platanoides) in the Boston area exhibited symptoms of an anthracnose disease. Symptoms included irregularly shaped, brown, necrotic lesions with reddish margins. The lesions often were delimited by veins. From August to November perithecia with mature asci were found in the lesions on leaves still attached to trees and on leaves that had fallen prematurely. This study was undertaken to determine the identity and phylogenetic relationships of the fungus associated with the lesions as well as the mating system of the fungus. Accepted for publication 16 May Corresponding author. klobuglio@oeb.harvard.ed MATERIALS AND METHODS Isolation. Symptomatic leaves were collected from A. platanoides trees Aug Nov 2006 (FIG. 1a). Leaves were examined under a dissecting microscope (FIG. 1a) for the presence of perithecia (FIG. 1b). Petri plates containing malt-yeast-extract agar (MEYE, 3.0 g yeast extract, 3.0 g malt extract, 5.0 g peptone, 10.0 g glucose and 1 L H 2 0) medium were inverted over leaves with perithecia. Discharged ascospores were observed on the agar medium with a dissecting microscope within 1 h and transferred to fresh medium. Cultures were incubated at room temperature (approximately 23 C) and ambient light. Cultures also were established by placing surface-sterilized, symptomatic leaf pieces on MEYE media and incubating them under the conditions above. Colony morphology was observed from cultures grown on potato-dextrose agar (PDA, Difco, Becton Dickinson & Co., Sparks, Maryland) incubated at 23 C in the dark as well as at room temperature with ambient light. Development and morphology of appressoria was observed examining the underside of glass cover slips that had been placed on the margin of developing cultures from which a block of agar had been removed. Single-spore isolation. To determine the compatibility systemofthisfungussingle-sporeisolateswereestablishedfrom ascospores produced in cultures obtained from maple leaf tissue. Mature perithecia were removed from a culture and placed on the inside surface of a Petri plate lid. The Petri plate was turned upside down so that the perithecia would discharge spores upward onto the surface of water agar. Isolated perithecia also were placed in Petri plates, crushed and flooded with sterile water. The water with ascospores was spread on the surface of water agar. Petri plates were examined with a compound microscope for germinating ascospores that were not in contact with other spores. Individual germinating ascospores were transferred to the surface of PDA, incubated at 23 C with constant light from a 10-watt fluorescent bulb and examined every other day for growth. Thirty-three single-spore isolates obtained as described above were grown on PDA and on a minimal salts medium with autoclaved flat toothpicks on the agar surface (Guerber and Correll 2001). Inoculum on the minimal salts medium was placed close to the toothpicks, which provide a surface for perithecial development (Guerber and Correll 2001). These cultures were grown at 23 C under constant light provided by a 10-watt fluorescent bulb and were examined every other day for perithecial development. DNA isolation, amplification and sequencing. Three of the five original A. platanoides isolates were selected for DNA isolation. The isolates were grown on sterile dialysis membrane (Bel-Art Products, Pequannock, New Jersey, No ) placed on the surface of PDA. Mycelium (equivalent to a volume of 250 ml) from each isolate was 710
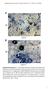
2 LOBUGLIO AND PFISTER: GLOMERELLA AND COLLETOTRICHUM ACUTATUM 711 FIG. 1. Glomerella sp. on Acer platanoides. A. Irregularly shaped lesions on leaf of Acer platanoides. B. Close-up of perithecia observed on lesions. Bar mm. scraped from the membrane into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube. The mycelium was ground with pestles (Kontes Glass Co., Vineland, New Jersey, No ) and sterile sand. A total of 500 ml of SDS lysis buffer (1% SDS; 200 mmtris, ph 7.5; 250 mm NaCL; 25 mm EDTA) was added next, followed by additional grinding. The three samples were incubated at 70 C on a heating block with occasional grinding. This solution was extracted with phenol-chloroform and precipitated as described in Lee et al (1988). A 1/ 100 dilution of the DNA was used for PCR amplification of the ITS and LSU rdna regions. These rdna regions were amplified with rdna primers ITS1 and ITS4 (White et al 1990) and LROR and LR5 (Moncalvo et al 2000). PCR amplification, purification and sequencing were carried out as described in Hansen et al (2005). Sequence analyses. The program Sequencher 4.6 (Gene- Codes, Ann Arbor, Michigan) was used to edit nucleotide sequences. Comparison of Glomerella sequences to Colletotrichum species was done with the program Se-Al v 2.0a8 (Rambaut 1996). A total of 44 Colletotrichum sequences were compared in this analysis, 42 of which were provided by M.C. Aime (now at Louisiana State University) from a recent study of this genus (Farr et al 2006). Plectosphaerella cucumerina was chosen as the outgroup (Farr et al 2006). Maximum parsimony analysis of the ITS-LSU combined dataset was performed with PAUP 4.0b10 (Swofford 2002). Heuristic searches consisted of 1000 random sequence addition replicates with tree bisection-reconnection branch swapping. The strength of the internal branches from the resulting trees was tested statistically by bootstrap analysis from 500 bootstrap replications. The relationship of this fungus from maple to two species known to infect other tree hosts, C. acutatum f. sp. pineum and G. miyabeana, was examined by phylogenetic analysis of the D1 D2 LSU region (209 nucleotides) of taxa used in the present study and the D1 D2 LSU sequences of C. acutatum subgroups A, B and C, C. acutatum f. sp. pineum and G. miyabeana (EMBL No. U79691 U79700 and U79710 U79713, Johnston and Jones 1997). RESULTS Morphology and compatibility. Five isolates (MP1 MP5) were established from either ascospores or leaf tissue. Colonies were initially white, becoming gray, green/gray, or dark gray, initially in the center but then coloring throughout. Some isolates were slightly salmon on the upper and lower surface, each with a distinct white margin. Other cultures remained white/cream to gray with or without a dark center, and some became dark olive green as viewed from the top or the under surface. Dense, elevated, aerial mycelium was characteristic of the colonies, the center often appearing green/gray velvety. Colony growth was respectively cm diam after 5 and 14 d on PDA in the dark at 23 C. Dark structures, which resembled perithecia but did not produce asci, often were observed throughout. Limited production of conidia was observed after 1 mo at room temperature under ambient light. Conidia also formed in orange gelatinous masses throughout cultures more than 1 mo old. Conidia were hyaline, aseptate, narrow to broadly oblong, straight to irregular in outline, with one end tapered. Conidia were mm. Perithecia were produced regularly in MEYE and were single or clustered and superficially embedded in the mycelium (FIG. 2a). Mature ascospores were variable at mm (FIG. 2b, c). Ascospores were hyaline, aseptate, narrowly to broadly oblong and straight to slightly curved.
3 712 MYCOLOGIA FIG. 2. Glomerella sp. from Acer platanoides. A. Longitudinal section of perithecia with asci. Bar 5 50 mm. B. Ascus showing spore arrangement (lactophenol cotton blue). Bar 5 20 mm. C. Young ascus. Bar 5 20 mm. D. Appressoria produced in slide culture. Bar 5 10 mm. Appressoria were observed on the underside of sterile covers slips arising from vegetative hyphae (FIG. 2d). They were smooth, simple, obovate to clavate (instead of lobed and/or in chains) and varied from light to dark brown. In all single-spore cultures perithecia containing asci with ascospores were observed after 1 wk on inoculum plugs and on toothpicks on minimal salts medium. This observation suggests that this fungus is homothallic. Perithecia were not observed in cultures grown on PDA under the same conditions. Phylogenetic analysis. The ITS and LSU DNA sequences obtained for the three isolates (MP1, MP2 and MP3) were identical for both rdna regions. The ITS-LSU dataset included 1273 nucleotide characters of which 87 were excluded due to questionable alignment. Of the remaining characters 974 were constant, 114 of the variable characters were parsimony uninformative and 98 were parsimony informative. The strict consensus of equally parsimonious trees (tree length 369, CI and RI ) is provided (FIG. 3). Bootstrap values are included on branches. Our analyses showed that the fungus on maple is related phylogenetically to Colletotrichum species in the clade comprising Colletotrichum acutatum, C. lupini and C. phormii with 100% bootstrap support (FIG. 3). Phylogenetic resolution within this clade was not achieved due to the high sequence similarity among members of this group. Phylogenetic analysis of the D1 D2 LSU rdna region placed the fungus from maple in the C. acutatum clade, which included C. acutatum f. sp. pineum and G. miyabeana with 92% bootstrap support (1000 bootstrap replications, data not shown). Phylogenetic relationships within this clade were not resolved due to the high sequence similarity among isolates (98 100% similarity). DISCUSSION Molecular analyses indicated that the Glomerella species on Acer platanoides in the Boston area is phylogenetically related to species in the C. acutatum clade, which include C. acutatum, C. lupini, C. phormii (FIG. 3), C. acutatum f. sp. pineum and G. miyabeana. Glomerella miyabeana is a pathogen of willow and was found to be related phylogenetically to C. acutatum by Johnston and Jones (1997) using the D1 D2 LSU rdna region. Colletotrichum acutatum has not been reported on A. platanoides, to our knowledge. Stipes and Clement (1978) reported an anthracnose on Acer platanoides in Virginia caused by Glomerella cingulata, which is considered a causal agent of anthracnose leaf spot on maple species (Sinclair and Lyons 2005). We could not find reference to G. acutata or C. acutatum as a pathogen of Acer platanoides, however C. acutatum has been reported to cause a disease of Japanese maple (Acer palmatum) in Connecticut (Smith 1993). Smith (1993) noted that perithecia never were observed on diseased plant material or in isolates from Japanese maple leaves grown either alone or in paired combinations. Some of the morphological characters in culture of the Glomerella from Norway maple are similar to those of C. acutatum. For example the dark structures resembling perithecia that often were observed
4 LOBUGLIO AND PFISTER: GLOMERELLA AND COLLETOTRICHUM ACUTATUM 713 FIG. 3. Strict Consensus of equally parsimonious trees based on 1186 nucleotide characters from combined ITS and LSU DNA sequences (tree length 369, CI and RI ). Values from 500 bootstrap replications are shown above tree branches. Asterisk indicates the type culture of Colletotrichum acutatum. Numbers after scientific names are GenBank. throughout cultures also were observed for C. acutatum Group D as has been described by Lardner et al (1999). In addition few conidia were produced in culture. Production of conidia by C. acutatum has been shown to vary significantly among isolates, and loss of the ability to produce conidia in culture is not uncommon (Fernando et al 2000, Du et al 2005). Conidia were mm, which is longer than those reported by Simmonds (1965) in the original description of C. acutatum ( mm) but overlaps with the morphological subgroups of C. acutatum described by Lardner et al (1999) and with
5 714 MYCOLOGIA C. phormii, C. acutatum f. sp. pineum and G. miyabeana (Farr et al 2006, Lardner et al 1999). Many of the characters of this Glomerella differ from those of C. acutatum. These isolates lack the intense red pigment described for some isolates of C. acutatum (Simmonds 1965, Sutton 1992, Lardner et al 1999, Du et al 2005). Concentric rings, described in cultures for some isolates of C. acutatum (Lardner et al 1999, Du et al 2005) were not observed. Ascospores of the Glomerella from Norway maple were mm. This is longer than G. acutata ascospores reported from highbush blueberry ( mm) by Talgø et al (2007) and from the teleomorphs established in laboratory crosses by Guerber and Corell (2001) ( mm). The teleomorph generally is considered to have a minor role in the life history of C. acutatum, occurring rarely if at all in nature (Bryson et al 1992, Peres et al 2005). C. acutatum typically predominates on its host in the anamorphic state producing acervuli with abundant conidia during the growing season, which are dispersed by water (Peres et al 2005, Sinclair and Lyons 2005). In the present study the teleomorph was the dominant state in the life cycle both in vivo and in vitro. Guerber and Correll (2001) were the first to observe the teleomorph of C. acutatum, Glomerella acutata, from laboratory crosses of single-spore isolates. Glomerella acutata has been detected for the first time in nature on fruits from highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) (Talgø et al 2007). The phylogenetic placement of the Glomerella from maple in the Colletotrichum acutatum clade, which includes other Glomerella species capable of producing perithecia in nature, suggests that the sexual state might have a larger role in the life history of this group than previously considered. The fungus in this study was widespread in 2006 in eastern Massachusetts on Norway maple leaves exhibiting early defoliation in We found no evidence of this fungus on Norway maple leaves in The significantly less precipitation in Massachusetts during summer and fall 2007 compared to 2006 (www. bluehill.org) might account for the absence of this fungus on Norway maple leaves in Nonetheless no collections of this fungus could be located in the Farlow Herbarium, which house many specimens collected locally over the past 150 y. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Amy Y. Rossman, James C. Correll and an anonymous reviewer for helpful comments on this manuscript. LITERATURE CITED Bryson RJ, Caten CE, Hollomon DW, Bailey JA Sexuality and genetics of Colletotrichum. In: Bailey JA, Jeger MJ, eds. Colletotrichum. Biology, pathology and control. Wallingford, UK: CAB International. p Du M, Schardl CL, Nuckles EM, Vaillancourt LJ Using mating-type gene sequences for improved phylogenetic resolution of Colletotrichum species complexes. Mycologia 97: Farr DF, Aime MC, Rossman AY, Palm ME Species of Colletotrichum on Agavaceae. Mycol Res 110: Fernando THP, Jayasinghe CK, Wijesundera RLC Factors affecting spore production, germination and viability of Colletotrichum acutatum isolates from Hevea brasiliensis. Mycol Res 104: Guerber JC, Correll JC Characterization of Glomerella acutata, the teleomorph of Colletotrichum acutatum. Mycologia 93: Hansen K, LoBuglio KL, Pfister DH Evolutionary relationships of the cup-fungus genus Peziza and Pezizaceae inferred from multiple nuclear genes: RPB2, b-tublin and LSU rdna. Mol Phylogenet Evol 36:1 23. Johnston PR, Jones D Relationships among Colletotrichum isolates from fruit-rots assessed using rdna sequences. Mycologia 89: Lardner R, Johnston PR, Plummer KM, Pearson MN Morphological and molecular analysis of Colletotrichum acutatum sensu lato. Mycol Res 103: Lee SB, Milgroom MG, Taylor JW A rapid high yield mini-prep method for isolation of total genomic DNA from fungi. Fungal Genet Newslett 35: Moncalvo J-M, Lutzoni FM, Rehner SA, Johnson J, Vilgalys R Phylogenetic relationships of agaric fungi based on nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Sys Biol 49: Peres NA, Timmer LW, Adaskaveg JE, Correll JC Lifestyles of Colletotrichum acutatum. Plant Dis 89: Rambaut A Se-Al. Sequence alignment editor. Version 1.0 alpha. Oxford, UK: Univ Oxford. evolve.zoo.ox.ac.uk/se-al/se-al.html Simmonds JH A study of the species of Colletotrichum causing ripe fruit rots in Queensland. Queensland J Ag Sc 22: Sinclair WA, Lyons HH Diseases of trees and shrubs. 2nd ed. Ithaca, New York: Cornell Univ Press. 110 p. Smith VL Canker of Japanese maple caused by Colletotrichum acutatum. Plant Dis 77: Stipes RJ, Clement GL Anthracnose of Acer platanoides in Virginia. Virginia J Sc 29:76. Sutton BC The genus Glomerella and its anamorph Colletotrichum. In: Bailey JA, Jeger MJ, eds. Colletotrichum. Biology, pathology and control. Wallingford, UK: CAB International. p Swofford DL PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates. Talgø V, Aamot HU, Stromeng GM, Klemsdal SS, Stensvand
6 LOBUGLIO AND PFISTER: GLOMERELLA AND COLLETOTRICHUM ACUTATUM 715 A Glomerella acutata on Highbush Blueberry (Vaccinium corymosum L.) in Norway. Plant Health Prog. DOI: /PHP RS. White T, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, eds. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego: Academic Press. p
First Report of Penicillium adametzioides from Decayed Grapes (Vitis vinifera) in Pakistan
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 316-320 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.034
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 316-320 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.034
report on PLANT DISEASE FUNGAL LEAF SPOTS OF BLACK WALNUT
 report on PLANT DISEASE RPD No. 600 1987 DEPARTMENT OF CROP SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN FUNGAL LEAF SPOTS OF BLACK WALNUT Several important fungal leaf spot diseases of black walnut
report on PLANT DISEASE RPD No. 600 1987 DEPARTMENT OF CROP SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN FUNGAL LEAF SPOTS OF BLACK WALNUT Several important fungal leaf spot diseases of black walnut
The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(6): 2016, Page: Javaidet al., The J. Anim. Plant Sci. 26(6):2016
 The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(6): 2016, Page: 1894-1898 Javaidet al., The J. Anim. Plant Sci. 26(6):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 Short Communication NEW HOST RECORD OF ALTERNARIA BRASSICICOLA INFECTING
The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(6): 2016, Page: 1894-1898 Javaidet al., The J. Anim. Plant Sci. 26(6):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 Short Communication NEW HOST RECORD OF ALTERNARIA BRASSICICOLA INFECTING
Sexual reproduction of
 Sexual reproduction of Phyllosticta citricarpa, the causal agent of citrus black spot Nga Tran, Andrew Miles, Ralf Dietzgen, and André Drenth Centre for Plant Science, Queensland Alliance for Agriculture
Sexual reproduction of Phyllosticta citricarpa, the causal agent of citrus black spot Nga Tran, Andrew Miles, Ralf Dietzgen, and André Drenth Centre for Plant Science, Queensland Alliance for Agriculture
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, the causal agent of citrus anthracnose in Guizhou Province
 Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, the causal agent of citrus anthracnose in Guizhou Province Jiang YL, Tan P, Zhou XY, Hou XL and Wang Y* Department of Plant Pathology, Guizhou University, Guiyang, Guizhou,
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, the causal agent of citrus anthracnose in Guizhou Province Jiang YL, Tan P, Zhou XY, Hou XL and Wang Y* Department of Plant Pathology, Guizhou University, Guiyang, Guizhou,
Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin. Objective
 Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin Objective Rationale The continuing objective of this research is to investigate the environmental factors that influence
Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin Objective Rationale The continuing objective of this research is to investigate the environmental factors that influence
Tree and Shrub Disease
 n t h r a A n t h r a c n o s e A number of different trees are affected by anthracnose disease. This fungal disease can cause severe leaf blighting and deformation, but in many cases the damage to the
n t h r a A n t h r a c n o s e A number of different trees are affected by anthracnose disease. This fungal disease can cause severe leaf blighting and deformation, but in many cases the damage to the
Identification of Yeasts. Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital
 Identification of Yeasts Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital Definition of Yeasts Eukaryote cells have defined nucleus
Identification of Yeasts Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital Definition of Yeasts Eukaryote cells have defined nucleus
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Introduction to Medical Mycology. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Introduction to Medical Mycology. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-7. TASKS OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Select the statement
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Introduction to Medical Mycology. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-7. TASKS OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Select the statement
Molecular Phylogenetic and Morphological Analysis of a Powdery Mildew Found on Dalbergia lanceolaria in Thailand
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017; 44(2) 350 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017; 44(2) : 350-357 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Molecular Phylogenetic and Morphological Analysis of a Powdery Mildew
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017; 44(2) 350 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017; 44(2) : 350-357 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Molecular Phylogenetic and Morphological Analysis of a Powdery Mildew
Diagnosing Strawberry Root and Crown Diseases. Heather Scheck, Plant Pathologist, Santa Barbara County Ag Commissioner s Office
 Diagnosing Strawberry Root and Crown Diseases?? Heather Scheck, Plant Pathologist, Santa Barbara County Ag Commissioner s Office Soil Borne Pathogens Symptoms are not diagnostic not even to separate biotic
Diagnosing Strawberry Root and Crown Diseases?? Heather Scheck, Plant Pathologist, Santa Barbara County Ag Commissioner s Office Soil Borne Pathogens Symptoms are not diagnostic not even to separate biotic
Phytophthora cactorum
 4 2012 Phytophthora cactorum A symptom of Phytophthora rot caused by Phytophthora cactorum on strawberry petioles and stolons NAO Masahiro 2011 6 Glomerella cingulata Phytophthora cactorum 3 22 21 3 835
4 2012 Phytophthora cactorum A symptom of Phytophthora rot caused by Phytophthora cactorum on strawberry petioles and stolons NAO Masahiro 2011 6 Glomerella cingulata Phytophthora cactorum 3 22 21 3 835
Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species
 Research Article Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species Abstract M H Wijedasa 1, L V C Liyanapathirana 1. Sri Lanka Journal of Infectious
Research Article Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species Abstract M H Wijedasa 1, L V C Liyanapathirana 1. Sri Lanka Journal of Infectious
Molecular approach to clarify taxonomy of powdery mildew on Chilli plants caused by Oidiopsis sicula in Thailand
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2011 Vol. 7(6): 1801-1808 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2011, Vol. 7(6): 1801-1808 ISSN 1686-9141 Molecular approach
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2011 Vol. 7(6): 1801-1808 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2011, Vol. 7(6): 1801-1808 ISSN 1686-9141 Molecular approach
Genetic diversity in the fungal pathogen Dothistroma septosporum. Angie Dale Masters of Science, NRES Supervisor: Kathy Lewis
 Genetic diversity in the fungal pathogen Dothistroma septosporum Angie Dale Masters of Science, NRES Supervisor: Kathy Lewis 1 Outline Introduction Research Questions Methods Results to date Implications
Genetic diversity in the fungal pathogen Dothistroma septosporum Angie Dale Masters of Science, NRES Supervisor: Kathy Lewis 1 Outline Introduction Research Questions Methods Results to date Implications
Study of wilt producing Fusarium sp. from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill)
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 8 (2014) pp. 854-858 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Study of wilt producing Fusarium sp. from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) Patel Harikrushana 1,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 8 (2014) pp. 854-858 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Study of wilt producing Fusarium sp. from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) Patel Harikrushana 1,
7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
RESEARCH REPOSITORY.
 RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is available
RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is available
Mycosphaerella leaf spot and other fungal diseases in organic black currant production in Norway
 Mycosphaerella leaf spot and other fungal diseases in organic black currant production in Norway Black currant diseases in Norway Black currant reversion virus Anthracnose (Drepanopeziza ribis) Mycosphaerella
Mycosphaerella leaf spot and other fungal diseases in organic black currant production in Norway Black currant diseases in Norway Black currant reversion virus Anthracnose (Drepanopeziza ribis) Mycosphaerella
Hands-on identification of vegetable diseases: Roses
 Hands-on identification of vegetable diseases: Roses Theme: How to diagnose a specific disease from diseases or disorders with similar symptoms. Mathews Paret, Susannah Da Silva, Binoy Babu, Fanny Iriarte,
Hands-on identification of vegetable diseases: Roses Theme: How to diagnose a specific disease from diseases or disorders with similar symptoms. Mathews Paret, Susannah Da Silva, Binoy Babu, Fanny Iriarte,
Biological control of Tradescantia fluminensis with pathogens report August 2011
 Biological control of Tradescantia fluminensis with pathogens report August 2011 Robert W. Barreto 1 Davi M. Macedo 1 1 Departamento de Fitopatologia, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, MG, 3657-000,
Biological control of Tradescantia fluminensis with pathogens report August 2011 Robert W. Barreto 1 Davi M. Macedo 1 1 Departamento de Fitopatologia, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, MG, 3657-000,
First Report of Banana Septoria Leaf Spot Disease Caused by Septoria eumusae in Iran
 International Journal of Farming and Allied Sciences Available online at www.ijfas.com 2014 IJFAS Journal-2014-3-11/1140-1144/ 30 November, 2014 ISSN 2322-4134 2014 IJFAS First Report of Banana Septoria
International Journal of Farming and Allied Sciences Available online at www.ijfas.com 2014 IJFAS Journal-2014-3-11/1140-1144/ 30 November, 2014 ISSN 2322-4134 2014 IJFAS First Report of Banana Septoria
Pathogen Information and Management
 Pathogen Information and Management K.A. Cochran Assistant Professor & Extension Specialist Texas A&M University AgriLife Extension Dept. Plant Pathology & Microbiology What is plant disease? A disruption
Pathogen Information and Management K.A. Cochran Assistant Professor & Extension Specialist Texas A&M University AgriLife Extension Dept. Plant Pathology & Microbiology What is plant disease? A disruption
7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
7-007: Detection of Alternaria linicola, Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum lini on Linum usitatissimum (flax) seed
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-007: Detection of Alternaria linicola, Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum lini on Linum usitatissimum (flax) seed
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-007: Detection of Alternaria linicola, Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum lini on Linum usitatissimum (flax) seed
7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus
 A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus By M. Muntanjola-Cvetkovic & J. Bata Institute for Biological Research Botanicki Zavod, Takovska 43, Belgrade, Yugoslavia Summary. A spontaneous
A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus By M. Muntanjola-Cvetkovic & J. Bata Institute for Biological Research Botanicki Zavod, Takovska 43, Belgrade, Yugoslavia Summary. A spontaneous
Research & Reviews: Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology
 e-issn:2320-3528 Research & Reviews: Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology Two Novel Eupenicillium Species Isolated from Soil in China Hong-Kai Wang, Yi-Chen Cao, Fu-Cheng Lin* State Key Laboratory
e-issn:2320-3528 Research & Reviews: Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology Two Novel Eupenicillium Species Isolated from Soil in China Hong-Kai Wang, Yi-Chen Cao, Fu-Cheng Lin* State Key Laboratory
Principles of phylogenetic analysis
 Principles of phylogenetic analysis Arne Holst-Jensen, NVI, Norway. Fusarium course, Ås, Norway, June 22 nd 2008 Distance based methods Compare C OTUs and characters X A + D = Pairwise: A and B; X characters
Principles of phylogenetic analysis Arne Holst-Jensen, NVI, Norway. Fusarium course, Ås, Norway, June 22 nd 2008 Distance based methods Compare C OTUs and characters X A + D = Pairwise: A and B; X characters
7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
Mango Dieback and Gummosis in Sindh, Pakistan Caused by Lasiodiplodia theobromae
 2004 Plant Management Network. Accepted for publication 16 January 2004. Published 2 March 2004. Mango Dieback and Gummosis in Sindh, Pakistan Caused by Lasiodiplodia theobromae Muhammad Ali Khanzada,
2004 Plant Management Network. Accepted for publication 16 January 2004. Published 2 March 2004. Mango Dieback and Gummosis in Sindh, Pakistan Caused by Lasiodiplodia theobromae Muhammad Ali Khanzada,
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Observations on Erysiphe platani in Germany
 Observations on Erysiphe platani in Germany Kirschner R* Department of Life Sciences, National Central University, Jhongli City, 320 Taoyuan County, Taiwan R.O.C. Kirschner R. 2011 Observations on Erysiphe
Observations on Erysiphe platani in Germany Kirschner R* Department of Life Sciences, National Central University, Jhongli City, 320 Taoyuan County, Taiwan R.O.C. Kirschner R. 2011 Observations on Erysiphe
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics
 This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories hot topics. These presentations provide short discussion
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories hot topics. These presentations provide short discussion
Dactylella shizishanna sp. nov., from Shizi Mountain, China
 Dactylella shizishanna sp. nov., from Shizi Mountain, China XueFeng Liu 1,2 and KeQin Zhang 1 * 1 Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-resource, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan 650091,
Dactylella shizishanna sp. nov., from Shizi Mountain, China XueFeng Liu 1,2 and KeQin Zhang 1 * 1 Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-resource, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan 650091,
Supplemental Data. Hiruma et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc Col-0. pen2-1
 A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
Investigation into the etiology of decline of Raywood ash in Northern California
 Investigation into the etiology of decline of Raywood ash in Northern California Principal Investigator: Thomas R. Gordon Department of Plant Pathology, UC Davis, One Shields Ave., Davis, CA 95616 Report
Investigation into the etiology of decline of Raywood ash in Northern California Principal Investigator: Thomas R. Gordon Department of Plant Pathology, UC Davis, One Shields Ave., Davis, CA 95616 Report
Cultural and Physiological Variation Between Isolates of Stemphylium botryosum the Causal of Stemphylium Blight Disease of Lentil (Lens culinaris)
 World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 5 (): 94-98, 2009 ISSN 87-3047 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Cultural and Physiological Variation Between Isolates of Stemphylium botryosum the Causal of Stemphylium Blight
World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 5 (): 94-98, 2009 ISSN 87-3047 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Cultural and Physiological Variation Between Isolates of Stemphylium botryosum the Causal of Stemphylium Blight
Recipes for Media and Solution Preparation SC-ura/Glucose Agar Dishes (20mL/dish, enough for 8 clones)
 Protocol: 300 ml Yeast culture preparation Equipment and Reagents needed: Autoclaved toothpicks Shaker Incubator set at 30 C Incubator set at 30 C 60 mm 2 sterile petri dishes Autoclaved glass test tubes
Protocol: 300 ml Yeast culture preparation Equipment and Reagents needed: Autoclaved toothpicks Shaker Incubator set at 30 C Incubator set at 30 C 60 mm 2 sterile petri dishes Autoclaved glass test tubes
Update on Black Leg Disease of Canola John Damicone, Extension Plant Pathologist
 Entomology and Plant Pathology, Oklahoma State University 127 Noble Research Center, Stillwater, OK74078 405.744.5527 Vol. 10, No. 3 http://entoplp.okstate.edu/pddl/ Mar 3, 2011 Update on Black Leg Disease
Entomology and Plant Pathology, Oklahoma State University 127 Noble Research Center, Stillwater, OK74078 405.744.5527 Vol. 10, No. 3 http://entoplp.okstate.edu/pddl/ Mar 3, 2011 Update on Black Leg Disease
Research Update Meeting Upright Dieback 2005
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Cranberry Station Extension meetings Cranberry Station Outreach and Public Service Activities 2005 Research Update Meeting 2005 - Upright
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Cranberry Station Extension meetings Cranberry Station Outreach and Public Service Activities 2005 Research Update Meeting 2005 - Upright
Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
A new race of Diplocarpon rosae capable of causing severe black spot on Rosa rugosa hybrids
 I 38 lnventaire des maladies des plantes au Canada 59:2, 1979 A new race of Diplocarpon rosae capable of causing severe black spot on Rosa rugosa hybrids A. T. Bolton and F. J. Svejda In 1977, severe black
I 38 lnventaire des maladies des plantes au Canada 59:2, 1979 A new race of Diplocarpon rosae capable of causing severe black spot on Rosa rugosa hybrids A. T. Bolton and F. J. Svejda In 1977, severe black
Colonial and Morphological Characteristics of various fungi Species Isolated from soil in Bangalore city
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6[1] December 2016: 17-21 2016 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6[1] December 2016: 17-21 2016 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Geoffrey J. Thomas, Bevan J. Buirchell & Ken G. Adcock
 Re-emergence of grey leaf spot caused by Stemphylium botryosum and its implications for Western Australian lupins Geoffrey J. Thomas, Bevan J. Buirchell & Ken G. Adcock Australasian Plant Pathology Journal
Re-emergence of grey leaf spot caused by Stemphylium botryosum and its implications for Western Australian lupins Geoffrey J. Thomas, Bevan J. Buirchell & Ken G. Adcock Australasian Plant Pathology Journal
Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
Goosiomyces bambusicola - A new cheirosporous anamorphic species from Western Ghats, India.
 Current Research in Environmental & Applied Mycology 4 (2): 211 216 (2014) ISSN 2229-2225 www.creamjournal.org Article CREAM Copyright 2014 Doi 10.5943/cream/4/2/8 Online Edition Goosiomyces bambusicola
Current Research in Environmental & Applied Mycology 4 (2): 211 216 (2014) ISSN 2229-2225 www.creamjournal.org Article CREAM Copyright 2014 Doi 10.5943/cream/4/2/8 Online Edition Goosiomyces bambusicola
Pear Scab in Oregon Symptoms, disease cycle and management
 Pear Scab in Oregon Symptoms, disease cycle and management R.A. Spotts and S. Castagnoli EM 9003 May 2010 Introduction Pear scab is a disease of European and Asian pear. It has been an economic problem
Pear Scab in Oregon Symptoms, disease cycle and management R.A. Spotts and S. Castagnoli EM 9003 May 2010 Introduction Pear scab is a disease of European and Asian pear. It has been an economic problem
California Leafy Greens Research Program April 1, 2014 to March 31, 2015
 California Leafy Greens Research Program April 1, 2014 to March 31, 2015 Project Title: Development of management strategies for Bacterial Leaf Spot of Lettuce. Principle investigator: Carolee Bull, USDA/ARS,
California Leafy Greens Research Program April 1, 2014 to March 31, 2015 Project Title: Development of management strategies for Bacterial Leaf Spot of Lettuce. Principle investigator: Carolee Bull, USDA/ARS,
Forest Pathology in New Zealand No. 19 (Second Edition 2007) Poplar anthracnose. A.G. Spiers (Revised by M.A. Dick)
 Forest Pathology in New Zealand No. 19 (Second Edition 2007) Poplar anthracnose A.G. Spiers (Revised by M.A. Dick) Causal organisms Marssonina brunnea (Ellis & Everhart) Magnus Marssonina castagnei (Desmazières
Forest Pathology in New Zealand No. 19 (Second Edition 2007) Poplar anthracnose A.G. Spiers (Revised by M.A. Dick) Causal organisms Marssonina brunnea (Ellis & Everhart) Magnus Marssonina castagnei (Desmazières
Fusarium root rot of soybean occurrence, impact, and relationship with soybean cyst nematode
 Proceedings of the Integrated Crop Management Conference Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Integrated Crop Management Conference Dec 1st, 12:00 AM Fusarium root rot of soybean occurrence, impact, and relationship
Proceedings of the Integrated Crop Management Conference Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Integrated Crop Management Conference Dec 1st, 12:00 AM Fusarium root rot of soybean occurrence, impact, and relationship
Epidemiological Research on Botrytis Diseases of Tulip Plants Caused by B. tulipae and B. cinerea
 Epidemiological Research on Botrytis Diseases of Tulip Plants Caused by and B. cinerea Kie Yamada, Takeharu Aoki, Chiharu Ikeda, Yukari Ichiman, Yuji Kanno, Tomohiro Suzuki, Hirotaka Nagashima, Masami
Epidemiological Research on Botrytis Diseases of Tulip Plants Caused by and B. cinerea Kie Yamada, Takeharu Aoki, Chiharu Ikeda, Yukari Ichiman, Yuji Kanno, Tomohiro Suzuki, Hirotaka Nagashima, Masami
Biological control of aquatic weeds by Plectosporium alismatis
 Biological control of aquatic weeds by Plectosporium alismatis, a potential mycoherbicide in Australian rice crops: comparison of liquid culture media for their ability to produce high yields of desiccation-tolerant
Biological control of aquatic weeds by Plectosporium alismatis, a potential mycoherbicide in Australian rice crops: comparison of liquid culture media for their ability to produce high yields of desiccation-tolerant
Tropentag 2012, Göttingen, Germany September 19-21, 2012
 Tropentag 2012, Göttingen, Germany September 19-21, 2012 Conference on International Research on Food Security, Natural Resource Management and Rural Development organised by: Georg-August Universität
Tropentag 2012, Göttingen, Germany September 19-21, 2012 Conference on International Research on Food Security, Natural Resource Management and Rural Development organised by: Georg-August Universität
STEM-END ROTS: THE INFECTION PORTAL
 STEM-END ROTS: THE INFECTION PORTAL W.F.T. HARTILL 1, K.R. EVERETT 1 and H.A. PAK 2. 1) The Horticulture and Food Research Institute of New Zealand Ltd Private Bag 92 169, Mt Albert, Auckland 2) Avocado
STEM-END ROTS: THE INFECTION PORTAL W.F.T. HARTILL 1, K.R. EVERETT 1 and H.A. PAK 2. 1) The Horticulture and Food Research Institute of New Zealand Ltd Private Bag 92 169, Mt Albert, Auckland 2) Avocado
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Forest Pest Management SD14 M CI Report 87-12
 Forest Pest Management SD14 M CI Report 87-12 A-3 27._ 3450 December 1987 MI)RTALITY OF BAREROOT COLORADO BLUE SPRUCE SEEDLINGS MONTANA STATE NURSERY, MISSOULA by R. L. James, Plant Pathologist INTRODUCTION
Forest Pest Management SD14 M CI Report 87-12 A-3 27._ 3450 December 1987 MI)RTALITY OF BAREROOT COLORADO BLUE SPRUCE SEEDLINGS MONTANA STATE NURSERY, MISSOULA by R. L. James, Plant Pathologist INTRODUCTION
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2017 Tues/Thurs. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2017 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Aug. 29 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Aug. 31 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2017 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Aug. 29 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Aug. 31 Orientation with Pathogen
CHAPTER II THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE AND CULTURE MEDIUM ON THE GROWTH AND SPORULATION OF DRECHSLERA CATENARIA
 CHAPTER II THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE AND CULTURE MEDIUM ON THE GROWTH AND SPORULATION OF DRECHSLERA CATENARIA 61 \ INTRODUCTION Sporulation and growth of fungi are affected by light, temperature, relative
CHAPTER II THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE AND CULTURE MEDIUM ON THE GROWTH AND SPORULATION OF DRECHSLERA CATENARIA 61 \ INTRODUCTION Sporulation and growth of fungi are affected by light, temperature, relative
REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI
 REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp. 265 270 (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI MIEN A. RIFAI, KARTINI KRAMADIBRATA Herbarium Bogorievnc LBN, Bogor,
REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp. 265 270 (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI MIEN A. RIFAI, KARTINI KRAMADIBRATA Herbarium Bogorievnc LBN, Bogor,
Data Sheets on Quarantine Pests. Diaporthe vaccinii
 EPPO quarantine pest Prepared by CABI and EPPO for the EU under Contract 90/399003 Data Sheets on Quarantine Pests Diaporthe vaccinii IDENTITY Name: Diaporthe vaccinii Shear Anamorph: Phomopsis vaccinii
EPPO quarantine pest Prepared by CABI and EPPO for the EU under Contract 90/399003 Data Sheets on Quarantine Pests Diaporthe vaccinii IDENTITY Name: Diaporthe vaccinii Shear Anamorph: Phomopsis vaccinii
Microscopic Observation and Pathogenicity Determination of Common Molds on Postharvest Longan Fruit cv. Daw
 Biology Research in Thailand Microscopic Observation and Pathogenicity Determination of Common Molds on Postharvest Longan Fruit cv. Daw Pitchayaporn SUWANAKOOD 1 *, Vicha SARDSUD 2, Somsiri SANGCHOTE
Biology Research in Thailand Microscopic Observation and Pathogenicity Determination of Common Molds on Postharvest Longan Fruit cv. Daw Pitchayaporn SUWANAKOOD 1 *, Vicha SARDSUD 2, Somsiri SANGCHOTE
Control of Dieback, Caused by Eutypa lata, in Red Currant (Ribes rubrum) and Gooseberry (Ribes uva-crispa) in the Netherlands
 Control of Dieback, Caused by Eutypa lata, in Red Currant (Ribes rubrum) and Gooseberry (Ribes uva-crispa) in the Netherlands M. Wenneker 1, P.A.H. van der Steeg 1, P. Vink 2, I.R. van Brouwershaven 3
Control of Dieback, Caused by Eutypa lata, in Red Currant (Ribes rubrum) and Gooseberry (Ribes uva-crispa) in the Netherlands M. Wenneker 1, P.A.H. van der Steeg 1, P. Vink 2, I.R. van Brouwershaven 3
Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species
 Medical Mycology May 2006, 44, 227231 Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species TAKAMASA KANEKO*$,
Medical Mycology May 2006, 44, 227231 Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species TAKAMASA KANEKO*$,
Key words wild passion-fruit, Mycosphaerellaceae, tropical fruits, cercosporoid fungi
 A NEW FUNGAL DISEASE CAUSED BY A PSEUDOCERCOSPORA SPECIES ON PASSIFLORA SETACEA IN PLANALTINA-DF, BRAZIL Alexei C. Dianese 1, Ana M. Costa 1 & José C. Dianese 2 ( 1 Embrapa Cerrados, Br-020, Km 18, 73310-970
A NEW FUNGAL DISEASE CAUSED BY A PSEUDOCERCOSPORA SPECIES ON PASSIFLORA SETACEA IN PLANALTINA-DF, BRAZIL Alexei C. Dianese 1, Ana M. Costa 1 & José C. Dianese 2 ( 1 Embrapa Cerrados, Br-020, Km 18, 73310-970
Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato. David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest
 Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest Background Sporothrix schenckii causes a cutaneous mycosis Sporotrichosis (aka rose
Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest Background Sporothrix schenckii causes a cutaneous mycosis Sporotrichosis (aka rose
BALLISTICS IN CERTAIN ASCOMYCETES
 BALLISTICS IN CERTAIN ASCOMYCETES BY C. T. INGOLD Birkbeck College, University of London (Received 5 January 1961) (With 3 figures in the te.xt) SUMMARY Horizontal spore discharge has been studied in the
BALLISTICS IN CERTAIN ASCOMYCETES BY C. T. INGOLD Birkbeck College, University of London (Received 5 January 1961) (With 3 figures in the te.xt) SUMMARY Horizontal spore discharge has been studied in the
STUDIES ON CULTURAL, MORPHOLOGICAL AND PATHOGENIC VARIABILITY AMONG THE ISOLATES OF FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM F. SP. CICERI CAUSING WILT OF CHICKPEA
 Volume-7, Issue-1 Jan-Mar-2017 Coden: IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2015ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 1 st Oct-2016 Revised: 26 th Nov-2016 Accepted: 27 th Nov-2016 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Volume-7, Issue-1 Jan-Mar-2017 Coden: IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2015ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 1 st Oct-2016 Revised: 26 th Nov-2016 Accepted: 27 th Nov-2016 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Progress in Biological Sciences Mahdieh S. Hosseini-Moghaddam ; Jalal Soltani ABSTRACT Key Words
 Progress in Biological Sciences Vol. 3, Number 2, Summer/Fall 2013/135-143 An investigation on the effects of photoperiod, aging and culture media on vegetative growth and sporulation of rice blast pathogen
Progress in Biological Sciences Vol. 3, Number 2, Summer/Fall 2013/135-143 An investigation on the effects of photoperiod, aging and culture media on vegetative growth and sporulation of rice blast pathogen
MSES consultants, inc.
 MSES consultants, inc. 609 West Main Street P.O. Drawer 190 Clarksburg, WV 26302-0190 304.624.9700 304.622.0981 304.842.3325 http://www.msesinc.com Office September 13, 2012 Project Number: 12-437 Mr.
MSES consultants, inc. 609 West Main Street P.O. Drawer 190 Clarksburg, WV 26302-0190 304.624.9700 304.622.0981 304.842.3325 http://www.msesinc.com Office September 13, 2012 Project Number: 12-437 Mr.
Weds. Date. Aug. 26. Sept. 2
 Mt.SanAntonioCollege Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2015 Mon./ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk. Mon. 1 Aug. 24 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations 2 Aug. 31 Exercise #1: The Microscope
Mt.SanAntonioCollege Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2015 Mon./ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk. Mon. 1 Aug. 24 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations 2 Aug. 31 Exercise #1: The Microscope
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Case Study: As the Worm Turns Speciation and the Apple Fly Maggot Introduction: Task: Final Product:
 Name: Period: AP/FLCC Biology Due Date: Case Study: As the Worm Turns Speciation and the Apple Fly Maggot Introduction: Hawthorn trees grow throughout North America and they produce a small fruit which
Name: Period: AP/FLCC Biology Due Date: Case Study: As the Worm Turns Speciation and the Apple Fly Maggot Introduction: Hawthorn trees grow throughout North America and they produce a small fruit which
Studies on cherry leaf spot at Dresden- Pillnitz
 Studies on cherry leaf spot at Dresden- Pillnitz Mirko Schuster Institute for Breeding Research on Fruit Crops Cherry breeding Disease resistance Cherry leaf spot (Blumeriella jaapii) Leaf spot on sweet
Studies on cherry leaf spot at Dresden- Pillnitz Mirko Schuster Institute for Breeding Research on Fruit Crops Cherry breeding Disease resistance Cherry leaf spot (Blumeriella jaapii) Leaf spot on sweet
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet
 Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-139 Cylindrocladium Black Rot (CBR) of Peanut, Soybean, and Forage Legumes in Florida Tom Kucharek, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Plant Pathology Department,
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-139 Cylindrocladium Black Rot (CBR) of Peanut, Soybean, and Forage Legumes in Florida Tom Kucharek, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Plant Pathology Department,
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides on Adhatoda vasica in India
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2013 Vol. 9(3): 581-587 Journal of Agricultural Available online Technology http://www.ijat-aatsea.com 2013, Vol. 9(3): 581-587 ISSN 1686-9141 Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2013 Vol. 9(3): 581-587 Journal of Agricultural Available online Technology http://www.ijat-aatsea.com 2013, Vol. 9(3): 581-587 ISSN 1686-9141 Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
C E R T I F I C A T E O F M O L D A N A L Y S I S
 C E R T I F I C A T E O F M O L D A N A L Y S I S PREPARED FOR: A Plus Inspections of Texas Phone Number: (713) 249-2618 Email: paul@inspec4.net Test Location: Phil Homebuyer 123 Mold City Dr Houston,
C E R T I F I C A T E O F M O L D A N A L Y S I S PREPARED FOR: A Plus Inspections of Texas Phone Number: (713) 249-2618 Email: paul@inspec4.net Test Location: Phil Homebuyer 123 Mold City Dr Houston,
AP BIOLOGY. Investigation #7 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis. Slide 1 / 35. Slide 2 / 35. Slide 3 / 35. Investigation #1: Artificial Selection
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 35 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 35 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN : Research Article
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN : 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Research Article First Report of Penicillium digitatum (Pers. ex Fr.) Sacc. causing a postharvest green
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN : 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Research Article First Report of Penicillium digitatum (Pers. ex Fr.) Sacc. causing a postharvest green
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(8):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 8 (2016) pp. 381-386 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.508.040
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 8 (2016) pp. 381-386 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.508.040
THE OCCURRENCE AND EFFECTS OF CEPHALOTHECIUM ROSEUM ON AVOCADO
 California Avocado Society 1951 Yearbook 36: 179-185 THE OCCURRENCE AND EFFECTS OF CEPHALOTHECIUM ROSEUM ON AVOCADO John Wesley Yale, Jr. and George R. Johnstone John Wesley Yale, Jr. (at the time of writing)
California Avocado Society 1951 Yearbook 36: 179-185 THE OCCURRENCE AND EFFECTS OF CEPHALOTHECIUM ROSEUM ON AVOCADO John Wesley Yale, Jr. and George R. Johnstone John Wesley Yale, Jr. (at the time of writing)
Asian Journal of Food and Agro-Industry ISSN Available online at
 As. J. Food Ag-Ind. 2009, Special Issue, S24-S30 Research Article Asian Journal of Food and Agro-Industry ISSN 1906-3040 Available online at www.ajofai.info Antifungal properties of essential oils from
As. J. Food Ag-Ind. 2009, Special Issue, S24-S30 Research Article Asian Journal of Food and Agro-Industry ISSN 1906-3040 Available online at www.ajofai.info Antifungal properties of essential oils from
INFLUENCE OF SOME GROWTH FACTORS ON IN-VITRO GROWTH OF FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM F. SP. PHASEOLI CAUSING SEEDLING MORTALITY OF BUSH BEAN
 INFLUENCE OF SOME GROWTH FACTORS ON IN-VITRO GROWTH OF FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM F. SP. PHASEOLI CAUSING SEEDLING MORTALITY OF BUSH BEAN S. Sharmin Siddique 1, M. K. A. Bhuiyan 2, M. R. Uddin 3 and M. B. Anwar
INFLUENCE OF SOME GROWTH FACTORS ON IN-VITRO GROWTH OF FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM F. SP. PHASEOLI CAUSING SEEDLING MORTALITY OF BUSH BEAN S. Sharmin Siddique 1, M. K. A. Bhuiyan 2, M. R. Uddin 3 and M. B. Anwar
Fusarium thapsinum is the dominant species associated with sorghum stalk rot in Queensland and northern New South Wales
 Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation Fusarium thapsinum is the dominant species associated with sorghum stalk rot in Queensland and northern New South Wales Lisa Kelly, Malcolm
Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation Fusarium thapsinum is the dominant species associated with sorghum stalk rot in Queensland and northern New South Wales Lisa Kelly, Malcolm
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/Thurs. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/Weds. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
MYCOTAXON. Volume 91, pp January March Dactylella coccinella sp. nov., an anamorphic species. 1
 MYCOTAXON Volume 91, pp. 127 132 January March 2005 Dactylella coccinella sp. nov., an anamorphic species YING YANG 1,2 & XING ZHONG LIU 1 liuxz@sun.im.ac.cn 1 Key Laboratory of Systematic Mycology & Lichenology
MYCOTAXON Volume 91, pp. 127 132 January March 2005 Dactylella coccinella sp. nov., an anamorphic species YING YANG 1,2 & XING ZHONG LIU 1 liuxz@sun.im.ac.cn 1 Key Laboratory of Systematic Mycology & Lichenology
Tape Lift and Swab Sampling of Items found at Glenwood Middle School Project #J15-876
 October 21, 2015 Mr. Jeff Klenk Howard County Public School System 10910 Route 108 Ellicott City, MD 21043 RE: Tape Lift and Swab Sampling of Items found at Glenwood Middle School Project #J15-876 Dear
October 21, 2015 Mr. Jeff Klenk Howard County Public School System 10910 Route 108 Ellicott City, MD 21043 RE: Tape Lift and Swab Sampling of Items found at Glenwood Middle School Project #J15-876 Dear
Effect of Environmental Factors on the Growth of Aspergillus Species Associated with Stored Millet Grains in Sokoto.
 Available online at http://www.ajol.info/index.php/njbas/index Nigerian Journal of Basic and Applied Science (2011), 19(2):218-223 ISSN 0794-5698 ffect of nvironmental Factors on the Growth of Aspergillus
Available online at http://www.ajol.info/index.php/njbas/index Nigerian Journal of Basic and Applied Science (2011), 19(2):218-223 ISSN 0794-5698 ffect of nvironmental Factors on the Growth of Aspergillus
L. R. BEUCHAT. Department of Food Science, University of Georgia Agricultural Experiment Station, Experiment, Georgia 30212
 512 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 47, No. 7, Pages 512-519 (July 1984) Copyright*', International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Comparison of Aspergillus Differential Medium
512 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 47, No. 7, Pages 512-519 (July 1984) Copyright*', International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Comparison of Aspergillus Differential Medium
PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY
 18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
The Effects of Alcohol and Nicotine on Microbial Flora. Jeff Van Kooten Grade 11 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School
 The Effects of Alcohol and Nicotine on Microbial Flora Jeff Van Kooten Grade 11 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Microbial Flora The internal and external flora has eukaryotic fungi, protists, and
The Effects of Alcohol and Nicotine on Microbial Flora Jeff Van Kooten Grade 11 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Microbial Flora The internal and external flora has eukaryotic fungi, protists, and
MIDHILA PADMAN and JANARDHANA G R*
 Inhibitory effect of essential oils on the growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. & Sacc. the causal organism of leaf spot disease of Murraya koenigii L MIDHILA PADMAN and JANARDHANA G
Inhibitory effect of essential oils on the growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. & Sacc. the causal organism of leaf spot disease of Murraya koenigii L MIDHILA PADMAN and JANARDHANA G
History of the Vacutainer Tube. Coagulant Blood Tests
 History of the Vacutainer Tube The different tubes are known as a vacutainer and were developed by Joseph Kleiner in 1947. The vacutainer is currently being manufactured by Becton, Dickinson and Company
History of the Vacutainer Tube The different tubes are known as a vacutainer and were developed by Joseph Kleiner in 1947. The vacutainer is currently being manufactured by Becton, Dickinson and Company
Topic 21. The Non-Vascular Plants
 Topic 21. The Non-Vascular Plants Plants are eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms with chlorophylls a and b, xanthophylls and carotenoids. they have cell walls with cellulose, and store food as starch
Topic 21. The Non-Vascular Plants Plants are eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms with chlorophylls a and b, xanthophylls and carotenoids. they have cell walls with cellulose, and store food as starch
To produce its kind is a
 12 Reproduction in Plants To produce its kind is a characteristic of all living organisms. You have already learnt this in Class VI. The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
12 Reproduction in Plants To produce its kind is a characteristic of all living organisms. You have already learnt this in Class VI. The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp , September, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX
 World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp. 013-016, September, 2014. www.premierpublishers.org, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX WJM Research Article Study of Fungal Genus Gyrothrix Corda from the forest flora of Indian
World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp. 013-016, September, 2014. www.premierpublishers.org, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX WJM Research Article Study of Fungal Genus Gyrothrix Corda from the forest flora of Indian
The role of climate and topography in the development of Dothistroma septosporum. Crystal Braun, Kathy Lewis and Alex Woods.
 The role of climate and topography in the development of Dothistroma septosporum. Crystal Braun, Kathy Lewis and Alex Woods February 8, 2008 Outline Introduction Study 1: Effects of Climate Study 2: Effects
The role of climate and topography in the development of Dothistroma septosporum. Crystal Braun, Kathy Lewis and Alex Woods February 8, 2008 Outline Introduction Study 1: Effects of Climate Study 2: Effects
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
