Level of use and safety of botanical products for itching vulvar dermatoses. Are patch tests useful?
|
|
|
- Leo Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Level of use and safety of botanical products for itching vulvar dermatoses. Are patch tests useful? Monica Corazza, Annarosa Virgili, Giulia Toni, Sara Minghetti, Silvia Tiengo and Alessandro Borghi Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche Sezione di Dermatologia e Malattie Infettive, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy doi: /cod Summary Background. Topical remedies based on botanical ingredients are popular. Objectives. To assess: (i) the usage of botanical substances in subjects affected with itching and chronic vulvar complaints; (ii) the incidence of side-effects associated with their use and the frequency of contact allergy; (iii) the diagnostic usefulness of patch testing. Methods. Sixty-six patients were provided with a questionnaire to assess the prevalence and type of topical botanical preparations used and the occurrence of adverse reactions. Patients were patch tested with (i) the Italian baseline series, (ii) a topical medicament series, and (iii) a botanical series. Results. Forty-two patients (63.6%) reported the use of natural topical products on the vulva. Seven (16.7%) noted adverse reactions; 27 showed positive reactions with the baseline series; 14 (21.2%) had at least one relevant reaction, mainly to allergens in topical products and cosmetics; and 2 (3%) showed positive reactions to the botanical series. Of the 7 patients complaining of adverse effects of botanical products, 3 (42.8%) showed relevant sensitization. Conclusions. The use of natural topical products is widespread among women affected with itching vulvar diseases. Contact dermatitis is a possible adverse effect. Botanical series are of questionable usefulness, owing to the wide variety of botanical ingredients. Key words: botanical products; contact dermatitis; patch test; vulvar diseases. In recent years, the demand for topical products containing botanical extracts has increased, owing to their pleasing fragrance, purported therapeutic properties, and the widespread perception that these products are safer than their synthetic counterparts (1 4). A number of active herbal principles are used both in many cosmetic formulations and in curative topical products. Correspondence: Monica Corazza, Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche, Sezione di Dermatologia e Malattie Infettive, Università di Ferrara, via L. Ariosto 35, Ferrara, Italy. Tel: /205825; Fax: / czm@unife.it Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interests. Despite the popular belief in their harmlessness, several cases of adverse reactions to plant extracts have been reported, in particular cutaneous side-effects such as allergic contact dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis, phototoxic reactions, and contact urticaria (5 10). The aim of the present study was to assess the level of use of topical products containing herbal components in patients affected with itching vulvar inflammatory diseases, the reasons behind the choice of these non-conventional treatments, and the perceived safety of such remedies. The frequency of true contact allergy to topical natural products and the diagnostic usefulness of patch testing with both the baseline series and a specifically prepared botanical series were also assessed. Accepted for publication 24 January 2016 Contact Dermatitis, 74,
2 Materials and Methods The study population consisted of all outpatients aged >18 years consecutively presenting with itching vulvar inflammatory diseases in our department between September 2014 and April The patients included in the present observational study had received a clinical and, when available, histological diagnosis by us, and were either receiving treatment at the time of inclusion or had undergone previous treatments for their vulvar dermatoses. The vulvar diseases included were lichen sclerosus, lichen simplex chronicus, lichen planus, plasma cell vulvitis, psoriasis, vulvar itching without identified cause, and recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Women completed a self-administered questionnaire composed of two sections. The first section included items addressing the following: demographics; the use of topically applied botanical preparations (regular or occasional use; cosmetic and/or therapeutic aim) on the vulva; the reasons for choosing natural products; the characteristics of the treatment employed [formulation; natural active principle(s); perception of efficacy and tolerability]; adverse reactions [skin signs and symptoms; presumed causative compound(s)]. All of the included patients were patch tested with an extended Società Italiana Dermatologia Allergologica Professionale ed Ambientale (SIDAPA) baseline series (Lofarma, Milano, Italy) and two supplementary series: (i) a topical medicament series (FIRMA, Firenze, Italy), and (ii) a botanical series (FIRMA) (Table 1). When possible, the patients own products (ointments, creams, and oils) were also patch tested. Patients were excluded from the study in the presence of: no previous topical treatments for their vulvar disease; pregnancy or breastfeeding; refusal or inability to complete the questionnaire; and light exposure, application of topical corticosteroids to patch test sites or systemic treatment with immunosuppressive drugs during the 2 weeks before enrolment. Patch tests were performed with Finn Chambers (diameter 8 mm; SmartPractice, Phoenix, AZ, USA) on Scanpor tape (Norgesplaster, Vennesla, Norway); allergens were applied on the upper back, and removed after 2 days. The sites were examined on removal and on day (D)3 and D4, according to ICDRG guidelines (11). Reactions were interpreted as relevant on the basis of the identification of the allergen in a topical product or of a highly suggestive history of cutaneous adverse events after contact with topical products containing the allergen. Table 1. Allergens in the supplementary (a) drug series and (b) botanical series, with the concentrations and vehicles used for patch testing Allergen (a) Tetracaine hydrochloride Quinoline mix Clotrimazole Lidocaine Econazole nitrate Tocopherol (vitamin E) (b) Melaleuca alternifolia extract Compositae mix Aloe vera Peppermint oil Arnica montana extract Sesquiterpene lactone mix Achillea millefolium extract Results Concentration and vehicle 2% pet. 6% pet. 10% pet. 20% pet. 5% pet. 5% pet. 5% pet. 0.5% pet. 0. A total of 66 patients (mean age 59.4 ± 14.6 years) were enrolled in the study. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the enrolled population are shown in Table 2. Twenty-four patients (36.4%) denied using herbal remedies on their vulva. Of the 42 users of the natural products (63.6% of the study population), 7 (16.7% of users) reported use on a regular basis, and 35 (83.3%) sporadic use. The motivations for use were found to be as follows: perceived safety of botanical products with respect to synthetic preparations, 27 (64.3% of users); curiosity, 9 (21.4%); and search for an alternative treatment because conventional therapies had failed, 6 (14.3%). No patients reported mistrust of traditional topical products or the exclusive use of natural products. Overall, 71 herbal products for genital use were identified by the patients. The products used that contained botanical compounds were, in decreasing order: cleansers (30; 42.2% of the total); creams (21; 29.6%); vaginal suppositories and vaginal plugs (18; 25.3%); and perfumes and deodorants (2; 2.8%). Creams and vaginal suppositories and plugs were used mainly for therapeutic purposes. The natural active principles present in the used products are shown in Table 3. A total of 27 patients (64.3% of users) considered the botanical products to be well tolerated and efficacious; 7 (16.7%) considered them to be well tolerated, but with doubtful efficacy; 1 (2.4%) considered them to be inefficacious; 7 patients (16.7%) referred to cutaneous and/or mucosal adverse reactions resulting from botanical product application. The reported adverse effects 290 Contact Dermatitis, 74,
3 Table 2. Demographic and clinical data of the study population Vulvar diseases Previous topical therapies used for anogenital diseases Unspecified number (%) Anaesthetics, Sex hormones, Antibiotics, Antihaemorrhoidal, Antimycotics, Corticosteroids, RVC, n (%) VI, n (%) PCV, Psoriasis, Mean duration of vulvar disease (months), range(sd) LS, LSC, LP, Mean age (years), range (SD) Number of patients (%) 42 (63.6) 13 (19.7) 1 (1.5) 1 (1.5) 1 (1.5) 6 (9.1) 2 (3.0) 50 (75.8) 27 (40.9) 24 (36.4) 21 (31.8) 13 (19.7) 9 (13.6) 7 (10.6) 50.1 [3 240] (56.5) 66 (100) 59.4 [21 86] (14.6) LS, lichen sclerosus; LSC, lichen simplex chronicus; LP, lichen planus; PCV, plasma cell vulvitis; RVC, recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis; SD, standard deviation; VI, vulvar itching with unidentified cause. As patients could have undergone multiple treatments, the total of treatments was greater than the number of patients enrolled in the study. Table 3. Botanical active principles contained in topical products used by the study subjects Botanical topical products Number (%) Chamomile 22 (25) Aloe vera 12 (13.63) Calendula officinalis 12 (13.63) Arnica montana 8 (9.09) Mallow (Malva sylvestris) 4 (4.54) Tocopherol (vitamin E) 4 (4.54) Centella asiatica 3 (3.40) Propolis 2 (2.27) Almond oil 1 (1.13) Avocado 1 (1.13) Bergamot (Citrus bergamia) 1 (1.13) Cocoa butter 1 (1.13) Coconut oil 1 (1.13) Corn oil 1 (1.13) Echinacea purpurea 1 (1.13) Hypericum perforatum 1 (1.13) Liquorice 1 (1.13) Limonene 1 (1.13) Olive oil 1 (1.13) Rice starch 1 (1.13) Shea butter 1 (1.13) Soy 1 (1.13) Soy-isoflavone 1 (1.13) Tilia (lime) 1 (1.13) Verbena officinalis (dragon s claw) 1 (1.13) Not known/not remembered by patients 4 (4.54) Total 88 (100) were described as worsening of the clinical features of pre-existing dermatitis (2 patients), or worsening and/or occurrence of cutaneous symptoms and/or signs such as itching (7 cases), burning 6, erythema 3, swelling, and vesiculation 1. Some patients reported more than one adverse effect. All 7 patients with adverse effects discontinued the use of botanical products. Overall, 13 patients (19.7%) referred to local adverse effects resulting from application of topical products on the vulva; in addition to the 7 patients with adverse effects caused by botanical products, 10 patients referred to adverse effects of topical drugs. Four patients referred to local reactions to both drugs and botanical products. All of the study patients underwent patch testing with the SIDAPA and the supplementary series. A total of 47 positive reactions were observed in 27 patients (40.9%). Of the 47 positive reactions, 23 were considered to be relevant; 14 patients (21.2%) had at least one relevant reaction. Table 4 shows the positive reactions in detail. The most frequent allergens found to be positive in the SIDAPA series were nickel sulfate (11 reactions), fragrance mix Contact Dermatitis, 74,
4 I(5), Myroxylon pereirae resin (5), methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI)/methylisothiazolinone (MI) (4), and fragrance mix II (3). Concerning the supplementary topical medicament series, three positive reactions were found: two to tetracaine hydrochloride and one to quinoline mix. Three further patients reacted to corticosteroids included in the extended SIDAPA series. Two patients showed positive reactions to the botanical series, namely to Arnica montana and Compositae mix, respectively. All positive reactions to the supplementary series were considered to be relevant. Five patients were tested with their own products. One positive reaction (cream containing vitamin E) was detected, and judged to be relevant. Regarding the occurrence of relevant positive reactions in relation to the vulvar disease duration, we found that the risk of having at least one relevant sensitization among the patients with diseases that had lasted for >24 months was higher than in the patients whose disease had started more recently (odds ratio 5.87, 95%CI: , p = 0.041, Fisher s exact test). Regarding the occurrence of relevant sensitization related to vulvar disease, namely comparing patients affected with vulvar lichen sclerosus (42 subjects) with those affected with other diseases (24, of whom 13 were affected with lichen simplex chronicus), we did not find any difference (odds ratio 1.04, 95%CI: , p = 0.9, Fisher s exact test). Discussion The findings of the present study highlight the popularity of topical preparations containing botanical extracts among women affected with itching chronic vulvar diseases, as >60% of the patients questioned used natural topical products on their vulva. This percentage was higher than those found in previous observational studies (12 14). Cleansers were the most widely used topical herbal preparations, although creams and vaginal suppositories and plugs were also popular. The perception that herbal remedies are safer than synthetic alternatives was found to be the main reason for choosing natural products for the care of inflammatory vulvar disorders. This suggests that natural products are considered to be particularly suitable for this sensitive site. Indeed, the barrier function of vulvar skin is substantially weaker than that at other anatomical sites, and vulvar skin has been shown to react more intensely to irritants than other skin areas (15). Moreover, as compared with other areas, vulvar skin is exposed to many irritants, including occlusion, friction, sweating, vaginal secretions, and urine, which increase the susceptibility of the skin to contact dermatitis (16, 17). In subjects with chronic inflammatory diseases, the underlying conditions further enhance the degree of irritation. In addition, in the post-menopausal population, owing to the drop in oestrogen leading to tissue atrophy and decreased elasticity, the vulvar tissue becomes increasingly sensitive to injury (18). In the study population, the most widely used medicinal plants were chamomile, Aloe vera, and Calendula officinalis, but the list of botanical active principles is quite long (Table 3). Botanical compounds were judged to be both efficacious and well tolerated by the great majority of patients using these products. However, in spite of this belief, 16.7% of users referred one or more adverse mucosal and/or cutaneous reactions to herbal products. This percentage was higher than previously observed (12 14). The reported adverse effects were described mainly as the occurrence or worsening of distressing symptoms, mainly itching and burning. Erythema, swelling and vesiculation were also reported. Adverse effects led to herbal product discontinuation in all cases. In our study population, 41% of patients had one or more positive patch test reactions, which is generally in keeping with previous studies on vulvar contact dermatitis (15, 16, 19 21). However, only approximately half of the positive reactions were recognized as being clinically relevant. In the literature, the percentages of relevant reactions in patients with vulvar disorders range from 26% to 73% (22 24). Thus, our percentage was a little lower than those previously reported. Notably, we found that the risk of having at least one relevant sensitization was directly related to disease duration, but not to the underlying inflammatory disease. It can be supposed that disease duration can determine either progressive barrier function impairment at the vulvar level or protracted application of topical products, increasing the risk of contact dermatitis, or both. As reported by previous studies, nickel sulfate was found to be the most frequently positive allergen in this study, even though most of these positive reactions were considered not to be relevant (19, 24). With respect to the frequency of sensitization to the allergens typically found in cosmetics and topical medicaments and included in the SIDAPA series, such as fragrance mix, MCI/MI, M. pereirae, formaldehyde, paraben mix, hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde, colophonium, and lanolin alcohols, 25% of patients showed relevant positive sensitization. Sensitization to topical anaesthetics was found in 3% of our patients, in disagreement with data from the literature indicating that these molecules are the most frequent culprits in allergic contact dermatitis of the vulva (15, 17, 21, 25, 26). Sensitization to topical corticosteroids occurred in 4.5% of our patients, in line with previous reports (15, 19), even though, in other 292 Contact Dermatitis, 74,
5 Table 4. Positive reactions to the allergens of the SIDAPA series, integrative topical medicament series and integrative botanical series in the study population Patient no. Allergens of the SIDAPA series Allergens of the topical medicament series Allergens of the botanical series 4 Fragrance mix II 14% (R) 5 Myroxylon pereirae resin (R) 12 Nickel sulfate 5% 17 Nickel sulfate 5% 19 Nickel sulfate 5%, Myroxylon pereirae resin (R) 25 Nickel sulfate 5% 26 Nickel sulfate 5%, Myroxylon pereirae resin (R) 30 Fragrance mix II 14% 33 Fragrance mix I 8% (R), MCI/MI 0.01% (R) 38 Cocamidopropyl betaine 1% (R) Arnica montana 0.5% (R) 40 Myroxylon pereirae resin (R), MCI/MI 0.01% (R), Compositae mix 6% (R) methyldibromo glutaronitrile 0.3% 41 Nickel sulfate 5% 46 Quinoline mix 6% (R) 48 Tetracaine hydrochloride 2% (R) 49 Potassium dichromate 0.5%, MCI/MI 0.01% 50 Cocamidopropyl betaine 1% (R), fragrance mix I 8% (R) 51 Potassium dichromate 0.5% 53 Nickel sulfate 5% 54 Myroxylon pereirae resin, MCI/MI 0.01%, methyldibromo glutaronitrile 0.3% 56 Budesonide 0.01% (R), corticosteroid mix 2.1% (R), Quaternium-15 1% (R) 57 Nickel sulfate 5% 58 Hydrocortisone 21 acetate 1% (R) 60 Formaldehyde 1% (R), nickel sulfate 5% (R), cobalt chloride 1% 61 Fragrance mix I 8%, nickel sulfate 5% 62 Fragrance mix I 8% 63 Fragrance mix I 8%, fragrance mix II 14% (R), hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde 5% 65 Nickel sulfate 5%, cobalt chloride 1% Tetracaine hydrochloride 2% (R) MCI/MI, methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (3:1 mixture); R, relevant positivity. The reported numbers correspond to the consecutive ones given to the patients at enrolment. series, positive patch test rates as high as 10% have been reported (25). It is of interest that, among the 7 patients reporting cutaneous side-effects of botanical products, 4 (57.1%) showed at least one positive reaction, of whom 3 (42.8%) showed relevant sensitization. When the patients were tested with the botanical series as well, only two relevant positive reactions (28.7%) were found. Thus, a considerable proportion of the patients referring to cutaneous side-effects of natural products were not sensitized to natural active principles. This result may be explained in several ways. First, cosmetic ingredients, such as fragrances and preservatives, may be the main responsible allergens rather than plant ingredients as such (23). On the other hand, some of the cutaneous side-effects reported by our patients may not really be allergic dermatitis, but irritant dermatitis or worsening of the pre-existing inflammatory disorder resulting from contact with the natural products (15). Finally, it could be supposed that, as only a limited number of standardized botanical allergens are commercially available, they cannot be representative of the wide variety of botanical ingredients found in natural cosmetics. Moreover, as botanical extracts may greatly vary in composition, owing to origin and extraction, preservation and storage procedures, the commercial botanical allergens might be not representative of the actual sensitizing molecules. As a consequence, numerous cases of contact allergy may go unrecognized. The results reported herein should be viewed in the light of the limitations of the study. Both skin symptoms and causal relationships between exposure to herbal preparations and adverse skin reactions were retrospectively self-reported, and not corroborated by clinical Contact Dermatitis, 74,
6 assessment by a dermatologist. Because of the retrospective design of our analysis, we could not consider the clinical pattern of the skin reactions. As the natural products and herbal compounds used by the study patients were also self-reported, a memory bias in collecting data cannot be excluded. Possible risk factors for contact dermatitis, such as atopic background and previous, documented skin sensitization, were not investigated in our population. In spite of these limitations, this is the first study to specifically address both the level of use of topical products containing herbal components in the care of inflammatory vulvar diseases and the frequency of sensitization to such compounds. On the basis of our findings, there is widespread use of natural products among subjects affected with itching vulvar complaints. Despite their presumed harmlessness, natural products can cause contact dermatitis and adverse skin reactions at the vulvar level. Our results also suggest that the botanical integrative series may be of questionable diagnostic usefulness, as it scarcely improves the diagnostic accuracy of patch testing with standard series. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Ms Silvia Giari and Chiara Casaro for data management and technical assistance. References 1 Bedi M K, Shenefelt P D. Herbal therapy in dermatology. Arch Dermatol 2002: 138: Reuter J, Merfort I, Schempp C M. Botanicals in dermatology: an evidence-based review. Am J Clin Dermatol 2010: 11: Aburjai T, Natsheh F D. Plants used in cosmetics.phytother Res 2003: 17: Baumann L. Botanical ingredients in cosmeceuticals.j Drugs Dermatol 2007: 6: Ernst E. Adverse effects of herbal drugs in dermatology. Br J Dermatol 2000: 143: Bruynzeel D P, Van Ketel W G, Young E et al. Contact sensitization by alternative medical medications containing plant extracts. The Dutch Contact Dermatoses Group. Contact Dermatitis 1992: 27: Aberer W. Contact allergy and medicinal herbs. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2008: 6: Niggemann B, Grüber C. Side-effects of complementary and alternative medicine. Allergy 2003: 58: Thomson K F, Wilkinson S M. Allergic contact dermatitis to plant extracts in patients with cosmetic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 2000: 142: Simpson E L, Law S V, Storrs F J. Prevalence of botanical extract allergy in patients with contact dermatitis. Dermatitis 2004: 15: Wilkinson D S, Fregert S, Magnussen B et al. Terminology of contact dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol 1970: 50: Corazza M, Borghi A, Lauriola M M, Virgili A. Use of topical herbal remedies and cosmetics: a questionnaire-based investigation in dermatology out-patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009: 23: Corazza M, Borghi A, Gallo R et al. Topical botanically derived products: use, skin reactions, and usefulness of patch tests. A multicentre Italian study. Contact Dermatitis 2014: 70: Ventura M T, Viola M, Calogiuri G et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to complementary and alternative medicine products. Curr Pharm Desi 2006: 12: Margesson L J. Contact dermatitis of the vulva. Dermatol Ther 2004: 17: Al-Niaimi F, Felton S, Williams J. Patch testing for vulval symptoms: our experience with 282 patients. Clin Exp Dermatol 2014: 39: Bauer A, Rödiger C, Greif C et al. Vulvar dermatoses irritant and allergic contact dermatitis of the vulva. Dermatology 2005: 210: Summers P R, Hunn J. Unique dermatologic aspects of the postmenopausal vulva. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007: 50: Marren P, Wojnarowska F, Powell S. Allergic contact dermatitis and vulvar dermatoses. Br J Dermatol 1992: 126: Utaş S, Ferahbaş A, Yildiz S. Patients with vulval pruritus: patch test results. Contact Dermatitis 2008: 58: Lewis F M, Shah M, Gawkrodger D J. Contact sensitivity in pruritus vulvae: patch test results and clinical outcome. Am J Contact Dermat 1997: 8: Nunns D, Ferguson J, Beck M, Mandal D. Is patch testing necessary in vulval vestibulitis?contact Dermatitis 1997: 37: Haverhoek E, Reid C, Gordon L et al. Prospective study of patch testing in patients with vulval pruritus. Australas J Dermatol 2008: 49: Lucke T W, Fleming C J, McHenry P, Lever R. Patch testing in vulvar dermatoses: how relevant is nickel? Contact Dermatitis 1998: 38: Warshaw E M, Furda L M, Maibach H I et al. Anogenital dermatitis in patients referred for patch testing. Retrospective analysis of cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group, Arch Dermatol 2008: 144: Warshaw E M, Schram S E, Belsito D V et al. Patch-test reactions to topical anesthetics: retrospective analysis of cross-sectional data, 2001 to Dermatitis 2008: 19: Contact Dermatitis, 74,
Topical botanically derived products: use, skin reactions, and usefulness of patch tests. A multicentre Italian study
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Topical botanically derived products: use, skin reactions, and usefulness of patch tests. A multicentre Italian study Monica Corazza 1, Alessandro
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Topical botanically derived products: use, skin reactions, and usefulness of patch tests. A multicentre Italian study Monica Corazza 1, Alessandro
Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera?
 DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14516 JEADV SHORT REPORT Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera? A. Borghi,* A. Virgili, S. Minghetti, G. Toni, M. Corazza Dipartimento di Scienze
DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14516 JEADV SHORT REPORT Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera? A. Borghi,* A. Virgili, S. Minghetti, G. Toni, M. Corazza Dipartimento di Scienze
Tatiana A. Vogel, Rakita W. Heijnen, Pieter-Jan Coenraads and Marie-Louise A. Schuttelaar
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Two decades of p-phenylenediamine and toluene-2,5-diamine patch testing focus on co-sensitizations in the European baseline series and cross-reactions
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Two decades of p-phenylenediamine and toluene-2,5-diamine patch testing focus on co-sensitizations in the European baseline series and cross-reactions
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACD. See Allergic contact dermatitis. Acute and recurrent vesicular hand dermatitis, 337 353 Airborne contact dermatitis, 303 Allergen avoidance
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACD. See Allergic contact dermatitis. Acute and recurrent vesicular hand dermatitis, 337 353 Airborne contact dermatitis, 303 Allergen avoidance
ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS IN ATOPICS. Catalina Matiz MD Assistant Professor University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital San Diego
 ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS IN ATOPICS Catalina Matiz MD Assistant Professor University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital San Diego When to suspect Allergic contact dermatitis? Look for
ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS IN ATOPICS Catalina Matiz MD Assistant Professor University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital San Diego When to suspect Allergic contact dermatitis? Look for
Botanicals and Contact Allergy
 Botanicals and Contact Allergy Christen M. Mowad MD Geisinger Medical Center Danville, PA 17821 cmowad@geisinger.edu Botanicals plant extracts essential oils increasingly popular additives cosmetics cosmeceuticals
Botanicals and Contact Allergy Christen M. Mowad MD Geisinger Medical Center Danville, PA 17821 cmowad@geisinger.edu Botanicals plant extracts essential oils increasingly popular additives cosmetics cosmeceuticals
Kelly H. Tyler, MD, FACOG, FAAD S052 Gender Dermatology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital Skin Disorders Vulvar Dermatitis
 Vulvar Dermatitis Kelly H. Tyler, MD, FACOG, FAAD Assistant Professor The Ohio State University Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Dermatology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Center for
Vulvar Dermatitis Kelly H. Tyler, MD, FACOG, FAAD Assistant Professor The Ohio State University Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Dermatology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Center for
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Occupational dermatitis in hairdressers influence of individual and environmental factors
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Occupational dermatitis in hairdressers influence of individual and environmental factors Tanja K. Carøe 1, Niels E. Ebbehøj 1 and Tove Agner
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Occupational dermatitis in hairdressers influence of individual and environmental factors Tanja K. Carøe 1, Niels E. Ebbehøj 1 and Tove Agner
Conflicts of interest
 Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Pattern of contact sensitization in patients with and without atopic dermatitis in a hospital-based clinical database
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Pattern of contact sensitization in patients with and without atopic dermatitis in a hospital-based clinical database Kim Katrine Bjerring Clemmensen
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Pattern of contact sensitization in patients with and without atopic dermatitis in a hospital-based clinical database Kim Katrine Bjerring Clemmensen
This is a published version of a paper published in Acta Dermato-Venereologica. Access to the published version may require subscription.
 Umeå University This is a published version of a paper published in Acta Dermato-Venereologica. Citation for the published paper: Isaksson, M., Hansson, C., Inerot, A., Lidén, C., Matura, M. et al. (2011)
Umeå University This is a published version of a paper published in Acta Dermato-Venereologica. Citation for the published paper: Isaksson, M., Hansson, C., Inerot, A., Lidén, C., Matura, M. et al. (2011)
Contact allergy in the population of patients with chronic inflammatory dermatoses and contact hypersensitivity to corticosteroids
 Original paper Contact allergy in the population of patients with chronic inflammatory dermatoses and contact hypersensitivity Marek Kot 1, Jarosław Bogaczewicz 1, Beata Kręcisz 2, Anna Woźniacka 1 1 Department
Original paper Contact allergy in the population of patients with chronic inflammatory dermatoses and contact hypersensitivity Marek Kot 1, Jarosław Bogaczewicz 1, Beata Kręcisz 2, Anna Woźniacka 1 1 Department
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION
 OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus
 Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
METHYLDIBROMO GLUTARONITRILE
 OPINION OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON COSMETIC PRODUCTS AND NON-FOOD PRODUCTS INTENDED FOR CONSUMERS CONCERNING METHYLDIBROMO GLUTARONITRILE Colipa n P77 adopted by the SCCNFP during the 0 th plenary
OPINION OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON COSMETIC PRODUCTS AND NON-FOOD PRODUCTS INTENDED FOR CONSUMERS CONCERNING METHYLDIBROMO GLUTARONITRILE Colipa n P77 adopted by the SCCNFP during the 0 th plenary
Disorders of the vulva
 Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by cocamide diethanolamine
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Allergic contact dermatitis caused by cocamide diethanolamine Sarien Mertens, Liesbeth Gilissen and An Goossens Department of Dermatology, University
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Allergic contact dermatitis caused by cocamide diethanolamine Sarien Mertens, Liesbeth Gilissen and An Goossens Department of Dermatology, University
Access to the published version may require journal subscription. Published with permission from: Blackwell Synergy
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation
Self-Diagnosed Sensitive Skin in Women with Clinically Diagnosed Atopic Dermatitis
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPECIAL ISSUE Self-Diagnosed Sensitive Skin in Women with Clinically Diagnosed Atopic Dermatitis Miranda A. Farage 1, Philip Bowtell 2, and Alexandra Katsarou 3 1 Feminine Clinical Sciences,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPECIAL ISSUE Self-Diagnosed Sensitive Skin in Women with Clinically Diagnosed Atopic Dermatitis Miranda A. Farage 1, Philip Bowtell 2, and Alexandra Katsarou 3 1 Feminine Clinical Sciences,
6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema
 Acta Derm Venereol 2005; Suppl. 215: 28 32 6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema JOHN MCFADDEN Medicament allergy is a not uncommon problem both with antibiotics and topical corticosteroids.
Acta Derm Venereol 2005; Suppl. 215: 28 32 6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema JOHN MCFADDEN Medicament allergy is a not uncommon problem both with antibiotics and topical corticosteroids.
The Vulvar Lichen Disorders: Simplex, Sclerosus, Planus
 The Vulvar Lichen Disorders: Simplex, Sclerosus, Planus Paul Summers, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Utah School of Medicine Areas of Concern 1. Dermatopathology 2. Spongiotic
The Vulvar Lichen Disorders: Simplex, Sclerosus, Planus Paul Summers, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Utah School of Medicine Areas of Concern 1. Dermatopathology 2. Spongiotic
STUDY. Anogenital Dermatitis in Patients Referred for Patch Testing
 STUDY Anogenital Dermatitis in Referred for Patch Testing Retrospective Analysis of Cross-sectional Data From the North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 1994-2004 Erin M. Warshaw, MD, MS; Laura M. Furda,
STUDY Anogenital Dermatitis in Referred for Patch Testing Retrospective Analysis of Cross-sectional Data From the North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 1994-2004 Erin M. Warshaw, MD, MS; Laura M. Furda,
Practical Patch Testing and Chemical Allergens in Contact Dermatitis
 Practical Patch Testing and Chemical Allergens in Contact Dermatitis Sharon E. Jacob Elise M. Herro Practical Patch Testing and Chemical Allergens in Contact Dermatitis Sharon E. Jacob Division of Dermatology
Practical Patch Testing and Chemical Allergens in Contact Dermatitis Sharon E. Jacob Elise M. Herro Practical Patch Testing and Chemical Allergens in Contact Dermatitis Sharon E. Jacob Division of Dermatology
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients.
 Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
Dermatologists are trained to evaluate distribution
 The value of patch testing patients with a scattered generalized distribution of dermatitis: Retrospective cross-sectional analyses of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001 to 2004 Kathryn
The value of patch testing patients with a scattered generalized distribution of dermatitis: Retrospective cross-sectional analyses of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001 to 2004 Kathryn
CORTISPORIN Cream (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone acetate cream, USP)
 CORTISPORIN Cream (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone acetate cream, USP) DESCRIPTION CORTISPORIN Cream (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone acetate cream, USP) is a
CORTISPORIN Cream (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone acetate cream, USP) DESCRIPTION CORTISPORIN Cream (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone acetate cream, USP) is a
Contact allergy to local anaesthetics value of patch testing with a caine mix in the baseline series
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Contact allergy to local anaesthetics value of patch testing with a caine mix in the baseline series Ana Brinca, Rita Cabral and Margarida Gonçalo
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Contact allergy to local anaesthetics value of patch testing with a caine mix in the baseline series Ana Brinca, Rita Cabral and Margarida Gonçalo
Effectiveness of treating non-specific pruritus vulvae with topical steroids: A randomized controlled trial
 European Journal of General Practice. 2009; 15: 2933 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of treating non-specific pruritus vulvae with topical steroids: A randomized controlled trial ANTOINE L. M. LAGRO-JANSSEN
European Journal of General Practice. 2009; 15: 2933 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of treating non-specific pruritus vulvae with topical steroids: A randomized controlled trial ANTOINE L. M. LAGRO-JANSSEN
Cutaneous Immediate-Type Reactions to Textiles
 Elsner P, Hatch K, Wigger-Alberti W (eds): Textiles and the Skin. Curr Probl Dermatol. Basel, Karger, 2003, vol 31, pp 166 170 Cutaneous Immediate-Type Reactions to Textiles Andreas J. Bircher Allergy
Elsner P, Hatch K, Wigger-Alberti W (eds): Textiles and the Skin. Curr Probl Dermatol. Basel, Karger, 2003, vol 31, pp 166 170 Cutaneous Immediate-Type Reactions to Textiles Andreas J. Bircher Allergy
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Cream 0.025% Topical Corticosteroid
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Pr PROPADERM (beclomethasone dipropionate) Cream 0.025% Topical Corticosteroid Valeant Canada LP 2150 St-Elzear Blvd. West, Laval, Quebec, Canada H7L 4A8 Date of preparation: October
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Pr PROPADERM (beclomethasone dipropionate) Cream 0.025% Topical Corticosteroid Valeant Canada LP 2150 St-Elzear Blvd. West, Laval, Quebec, Canada H7L 4A8 Date of preparation: October
Diagnosis and Management of Vulvar Disorders
 Diagnosis and Management of Vulvar Disorders Kelly H. Tyler, MD, FACOG, FAAD Assistant Professor The Ohio State University Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Dermatology Department of Obstetrics
Diagnosis and Management of Vulvar Disorders Kelly H. Tyler, MD, FACOG, FAAD Assistant Professor The Ohio State University Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Dermatology Department of Obstetrics
Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/92/109955334.jpg) University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
4/3/2017 DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY OBJECTIVES
 DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS KELLY HODGES, MD (NO DISCLOSURES) OBJECTIVES REVIEW THE TWO MOST COMMON CAUSES OF RECURRENT ABNORMAL DISCHARGE (CANDIDA AND BV) REVIEW THE MOST
DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS KELLY HODGES, MD (NO DISCLOSURES) OBJECTIVES REVIEW THE TWO MOST COMMON CAUSES OF RECURRENT ABNORMAL DISCHARGE (CANDIDA AND BV) REVIEW THE MOST
STUDY. Changing Trends and Allergens in the Patch Test Standard Series
 STUDY Changing Trends and Allergens in the Patch Test Standard Series A Mayo Clinic 5-Year Retrospective Review, January 1, 2001, Through December 31, 2005 Mark D. P. Davis, MD; Leigh Ann Scalf, MD; James
STUDY Changing Trends and Allergens in the Patch Test Standard Series A Mayo Clinic 5-Year Retrospective Review, January 1, 2001, Through December 31, 2005 Mark D. P. Davis, MD; Leigh Ann Scalf, MD; James
Disclosures Dr. Lynette Margesson
 Management of Vulvar Pruritus 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and
Management of Vulvar Pruritus 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and
Vaginitis Lifestyle changes that may be helpful:
 Vaginitis Vaginitis, inflammation of the vagina, is responsible for an estimated 10% of all visits by women to their healthcare practitioners. The three general causes of vaginitis are hormonal imbalance,
Vaginitis Vaginitis, inflammation of the vagina, is responsible for an estimated 10% of all visits by women to their healthcare practitioners. The three general causes of vaginitis are hormonal imbalance,
Skin allergy to chemicals
 Skin allergy to chemicals clinical, epidemiological and public health perspectives Jeanne Duus Johansen National Allergy Research Centre Department of Dermato allergology Copenhagen University Hospital
Skin allergy to chemicals clinical, epidemiological and public health perspectives Jeanne Duus Johansen National Allergy Research Centre Department of Dermato allergology Copenhagen University Hospital
Prescribing Information
 Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
Occupational hand dermatitis among cement workers in Taiwan
 Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2011) 110, 775e779 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Occupational hand among cement workers in
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2011) 110, 775e779 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Occupational hand among cement workers in
Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus
 Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology) Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Lebanon, NH, USA Disclosures
Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology) Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Lebanon, NH, USA Disclosures
Anne Arundel Medical Center Informed Consent
 Informed Consent Title: Exploratory Trial of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Intradermal Injections for the Treatment of Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus Investigator: Andrew Goldstein, M.D. Telephone Study
Informed Consent Title: Exploratory Trial of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Intradermal Injections for the Treatment of Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus Investigator: Andrew Goldstein, M.D. Telephone Study
A Guide to Cutaneous Allergy. Dr David Orton Consultant Dermatologist The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
 A Guide to Cutaneous Allergy Dr David Orton Consultant Dermatologist The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Allergy inappropriate/exaggerated defence reaction to something that is not innately harmful
A Guide to Cutaneous Allergy Dr David Orton Consultant Dermatologist The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Allergy inappropriate/exaggerated defence reaction to something that is not innately harmful
Contact Allergy to Glucocorticosteroids in Patients with Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers, Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Allergy
 2008;16(2):72-78 CLINICAL ARTICLE Contact Allergy to Glucocorticosteroids in Patients with Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers, Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Allergy Maria Zmudzinska, Magdalena Czarnecka-Operacz,
2008;16(2):72-78 CLINICAL ARTICLE Contact Allergy to Glucocorticosteroids in Patients with Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers, Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Allergy Maria Zmudzinska, Magdalena Czarnecka-Operacz,
STUDY. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data,
 STUDY Contact Allergy in Children Referred for Patch Testing North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001-2004 Kathryn A. Zug, MD; Daniel McGinley-Smith, MD; Erin M. Warshaw, MD; James S. Taylor,
STUDY Contact Allergy in Children Referred for Patch Testing North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 2001-2004 Kathryn A. Zug, MD; Daniel McGinley-Smith, MD; Erin M. Warshaw, MD; James S. Taylor,
Cross-reactivity between citral and geraniol can it be attributed to oxidized geraniol?
 Contact Dermatitis riginal Article CD Contact Dermatitis Cross-reactivity between citral and geraniol can it be attributed to oxidized geraniol? Lina Hagvall 1 and Johanna Bråred Christensson 1,2 1 Department
Contact Dermatitis riginal Article CD Contact Dermatitis Cross-reactivity between citral and geraniol can it be attributed to oxidized geraniol? Lina Hagvall 1 and Johanna Bråred Christensson 1,2 1 Department
The relevance of chlorhexidine contact allergy
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis The relevance of chlorhexidine contact allergy Jussi Liippo 1,Päivi Kousa 2 and Kaija Lammintausta 1 1 Department of Dermatology, Turku University
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis The relevance of chlorhexidine contact allergy Jussi Liippo 1,Päivi Kousa 2 and Kaija Lammintausta 1 1 Department of Dermatology, Turku University
HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST. April, 2006
 HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST April, 2006 Protocol Number: Title: Objective: Human Phototoxicity and Photoallergenicity Test The objective of the test is to assess the potential of a
HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST April, 2006 Protocol Number: Title: Objective: Human Phototoxicity and Photoallergenicity Test The objective of the test is to assess the potential of a
Essentials of Contact Dermatitis 2018
 Essentials of Contact Dermatitis 2018 Joseph F. Fowler Jr. MD Clinical Professor of Dermatology U. Of Louisville Pres. No. American Contact Dermatitis Group Disclosures Consultant and speaker, SmartPractice
Essentials of Contact Dermatitis 2018 Joseph F. Fowler Jr. MD Clinical Professor of Dermatology U. Of Louisville Pres. No. American Contact Dermatitis Group Disclosures Consultant and speaker, SmartPractice
Access to the published version may require journal subscription. Published with permission from: Blackwell Synergy
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proofcorrections or journal pagination. Citation
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proofcorrections or journal pagination. Citation
Cobalt allergy: suitable test concentration, and concomitant reactivity to nickel and chromium
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Cobalt allergy: suitable test concentration, and concomitant reactivity to nickel and chromium Carola Lidén 1, Niklas Andersson 2, Anneli Julander
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Cobalt allergy: suitable test concentration, and concomitant reactivity to nickel and chromium Carola Lidén 1, Niklas Andersson 2, Anneli Julander
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Psoriasis (excluding widespread plaque psoriasis) Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disorder. Estimates of the prevalence (proportion
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Psoriasis (excluding widespread plaque psoriasis) Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disorder. Estimates of the prevalence (proportion
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
GROUP 15 TOPICAL PREPARATIONS
 - 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
- 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
Provide relief with Topicort 0.05% 1,2. For your patients with corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses... IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
 For your patients with corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses... SPREAD THE Provide relief with Topicort 0.05% 1,2 Group C molecule 3 Low allergenic potential 4-6 Available in cream and ointment 3,7 Topicort
For your patients with corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses... SPREAD THE Provide relief with Topicort 0.05% 1,2 Group C molecule 3 Low allergenic potential 4-6 Available in cream and ointment 3,7 Topicort
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist. Susan Nedorost, MD
 Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
Thoughts on how to improve the quality of multicentre patch test studies
 Contact Dermatitis Education & Debate COD Contact Dermatitis Thoughts on how to improve the quality of multicentre patch test studies Magnus Bruze Department of Occupational and Environmental Dermatology,
Contact Dermatitis Education & Debate COD Contact Dermatitis Thoughts on how to improve the quality of multicentre patch test studies Magnus Bruze Department of Occupational and Environmental Dermatology,
The Role of Low-Potency Topical Steroids in Day-to-Day Practice
 Supplement to the December 2009 & AGING Series: Relevance of Low-Potency Topical Steroids in Dermatology The Role of Low-Potency Topical Steroids in Day-to-Day Practice Supplement supported by HMP COMMUNICATIONS
Supplement to the December 2009 & AGING Series: Relevance of Low-Potency Topical Steroids in Dermatology The Role of Low-Potency Topical Steroids in Day-to-Day Practice Supplement supported by HMP COMMUNICATIONS
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
Result of Standard Patch Test in Patients Suspected of Having Allergic Contact Dermatitis
 Result of Standard Patch Test in Patients Suspected of Having Allergic Contact Dermatitis Jongkonnee Wongpiyabovorn MD, PhD*, Porntip Puvabanditsin MD** * Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine,
Result of Standard Patch Test in Patients Suspected of Having Allergic Contact Dermatitis Jongkonnee Wongpiyabovorn MD, PhD*, Porntip Puvabanditsin MD** * Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine,
WHITE PAPER SmartXide 2 V 2 LR. MonaLisa Touch Dual Probe Therapy for the Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus and Vaginal Atrophy
 WHITE PAPER SmartXide 2 V 2 LR MonaLisa Touch Dual Probe Therapy for the Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus and Vaginal Atrophy DEKA White Paper SMARTXIDE 2 V 2 LR November 2015 MonaLisa Touch Dual Probe Therapy
WHITE PAPER SmartXide 2 V 2 LR MonaLisa Touch Dual Probe Therapy for the Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus and Vaginal Atrophy DEKA White Paper SMARTXIDE 2 V 2 LR November 2015 MonaLisa Touch Dual Probe Therapy
Ethylhexylglycerin: a low-risk, but highly relevant, sensitizer in hypo-allergenic cosmetics
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Ethylhexylglycerin: a low-risk, but highly relevant, sensitizer in hypo-allergenic cosmetics Olivier Aerts 1, Lien Verhulst 2 and An Goossens
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Ethylhexylglycerin: a low-risk, but highly relevant, sensitizer in hypo-allergenic cosmetics Olivier Aerts 1, Lien Verhulst 2 and An Goossens
Contact Hypersensitivity to European Baseline Series and Corticosteroid Series Haptens in a Population of Adult Patients with Contact Eczema
 2016;24(1):29-36 CLINICAL ARTICLE Contact Hypersensitivity to European Baseline Series and Corticosteroid Series Haptens in a Population of Adult Patients with Contact Eczema Marek Kot 1, Jarosław Bogaczewicz
2016;24(1):29-36 CLINICAL ARTICLE Contact Hypersensitivity to European Baseline Series and Corticosteroid Series Haptens in a Population of Adult Patients with Contact Eczema Marek Kot 1, Jarosław Bogaczewicz
Annex III: Tabular summary of dose-elicitation studies in sensitised patients
 Annex III: Tabular summary of dose-elicitation studies in sensitised patients Contents Chloroatranol... 2 Cinnamal... 4 Hydroxycitronellal... 6 Hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexenecarboxaldehyde (HICC)... 8 Isoeugenol...
Annex III: Tabular summary of dose-elicitation studies in sensitised patients Contents Chloroatranol... 2 Cinnamal... 4 Hydroxycitronellal... 6 Hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexenecarboxaldehyde (HICC)... 8 Isoeugenol...
Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu
 Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu Hand dermatitis is the most frequently recognized occupational skin disease. Comprehensive
Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu Hand dermatitis is the most frequently recognized occupational skin disease. Comprehensive
PRURITOCEPTIVE AND PSYCHOGENIC PRURITUS IN LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES PRURITOCEPTIVE AND PSYCHOGENIC PRURITUS IN LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS Department of Dermatology and Venerology, ABSTRACT Pruritus is a diagnostic hallmark for Lichen Simplex Chronicus (LSC).
ORIGINAL ARTICLES PRURITOCEPTIVE AND PSYCHOGENIC PRURITUS IN LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS Department of Dermatology and Venerology, ABSTRACT Pruritus is a diagnostic hallmark for Lichen Simplex Chronicus (LSC).
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Contact Dermatitis Susan Nedorost, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Environmental Health Science Case Reserve University School of Medicine University Hospitals Case Medical Center Cleveland,
Contact Dermatitis Susan Nedorost, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Environmental Health Science Case Reserve University School of Medicine University Hospitals Case Medical Center Cleveland,
Etiology of Allergic Contact Dermatitis based on Patch Test
 AMJ. 2017;4(4):541 5 541 Etiology of Allergic Contact Dermatitis based on Patch Test Dita Maulida Anggraini, 1 Endang Sutedja, 2 Achadiyani 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department
AMJ. 2017;4(4):541 5 541 Etiology of Allergic Contact Dermatitis based on Patch Test Dita Maulida Anggraini, 1 Endang Sutedja, 2 Achadiyani 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department
COD. Summary. Contact Dermatitis. Magnus Bruze 1, An Goossens 2 and Marléne Isaksson 1
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Recommendation to increase the test concentration of methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone in the European baseline patch test series
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Recommendation to increase the test concentration of methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone in the European baseline patch test series
Prescribing Information. Taro-Clobetasol. Taro-Clobetasol
 Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology is intended for the treatment of: Steroid responsive dermatoses such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis of the hairy regions,
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology is intended for the treatment of: Steroid responsive dermatoses such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis of the hairy regions,
The Prevention and Management of Acute Skin Reactions Related to Radiation Therapy
 Evidence-Based Series 13-7 IN REVIEW A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) The Prevention and Management of Acute Skin Reactions Related to Radiation
Evidence-Based Series 13-7 IN REVIEW A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) The Prevention and Management of Acute Skin Reactions Related to Radiation
What are the symptoms of a vulval skin condition?
 Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Allergic contact dermatitis to shoes: contribution of a specific series to the diagnosis *
 Vitamin 696 D levels in actinic keratosis: a preliminary study Investigation 696 s Allergic contact dermatitis to shoes: contribution of a specific series to the diagnosis * Rosana Lazzarini 1, Rodolfo
Vitamin 696 D levels in actinic keratosis: a preliminary study Investigation 696 s Allergic contact dermatitis to shoes: contribution of a specific series to the diagnosis * Rosana Lazzarini 1, Rodolfo
Syddansk Universitet. Published in: Acta Dermato-Venereologica DOI: / Publication date: 2016
 Syddansk Universitet Contact Allergy in Danish Healthcare Workers A Retrospective Matched Case-control Study Schwensen, Jakob F; Menné, Torkil; Sommerlund, Mette; Andersen, Klaus Ejner; Mørtz, Charlotte
Syddansk Universitet Contact Allergy in Danish Healthcare Workers A Retrospective Matched Case-control Study Schwensen, Jakob F; Menné, Torkil; Sommerlund, Mette; Andersen, Klaus Ejner; Mørtz, Charlotte
Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients
 Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients Jenny Murase, MD Palo Alto Foundation Medical Group Director of Patch Testing University of California, San Francisco Associate Clinical Professor Disclosures Consultant
Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients Jenny Murase, MD Palo Alto Foundation Medical Group Director of Patch Testing University of California, San Francisco Associate Clinical Professor Disclosures Consultant
TOPCORT Cream/Ointment (Mometasone furoate 0.1%)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 TOPCORT Cream/Ointment (Mometasone furoate 0.1%) Composition TOPCORT Cream Mometasone Furoate, IP... 0.1% w/w In a cream base... q.s. TOPCORT Ointment Mometasone Furoate, IP...
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 TOPCORT Cream/Ointment (Mometasone furoate 0.1%) Composition TOPCORT Cream Mometasone Furoate, IP... 0.1% w/w In a cream base... q.s. TOPCORT Ointment Mometasone Furoate, IP...
Fragrance and Cosmetic Contact Allergy in Children Martine Vigan, PhD * Florence Castelain, PhD
 Current Treatment Options in Allergy (2014) 1:310 316 DOI 10.1007/s40521-014-0027-8 Pediatric Allergy (A Giménez-Arnau, Section Editor) Fragrance and Cosmetic Contact Allergy in Children Martine Vigan,
Current Treatment Options in Allergy (2014) 1:310 316 DOI 10.1007/s40521-014-0027-8 Pediatric Allergy (A Giménez-Arnau, Section Editor) Fragrance and Cosmetic Contact Allergy in Children Martine Vigan,
DAILY CARE FOR DRY, IRRITATED AND REACTIVE SKIN. Physiogel A.I. Help your patients restore skin balance and well-being
 DAILY CARE FOR DRY, IRRITATED AND REACTIVE SKIN Help your patients restore skin balance and well-being Dry, irritated and reactive skin a question of balance Changes in the lipid barrier (1) Neurological
DAILY CARE FOR DRY, IRRITATED AND REACTIVE SKIN Help your patients restore skin balance and well-being Dry, irritated and reactive skin a question of balance Changes in the lipid barrier (1) Neurological
Hand contact dermatitis in hairdressers: clinical and causative allergens, experience in Bangkok
 Original article Hand contact dermatitis in hairdressers: clinical and causative allergens, experience in Bangkok Poohglin Tresukosol and Chanutta Swasdivanich Summary Background: Hand dermatitis in hairdressers
Original article Hand contact dermatitis in hairdressers: clinical and causative allergens, experience in Bangkok Poohglin Tresukosol and Chanutta Swasdivanich Summary Background: Hand dermatitis in hairdressers
Informed Consent And Authorization To Disclose Health Information
 Gynecologic Cancer Research Foundation Page 1 of 11 Informed Consent And Authorization To Disclose Health Information Sponsor / Study Title: Principal Investigator: (Study Doctor) Gynecologic Cancer Research
Gynecologic Cancer Research Foundation Page 1 of 11 Informed Consent And Authorization To Disclose Health Information Sponsor / Study Title: Principal Investigator: (Study Doctor) Gynecologic Cancer Research
Patch Testing interactive workshop. Susan Nedorost, MD
 Patch Testing interactive workshop Susan Nedorost, MD Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant financial interest or other relationships with a commercial entity producing health-care
Patch Testing interactive workshop Susan Nedorost, MD Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant financial interest or other relationships with a commercial entity producing health-care
CORTISPORIN Ointment (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates, bacitracin zinc, and. hydrocortisone ointment, USP)
 CORTISPORIN Ointment (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates, bacitracin zinc, and hydrocortisone ointment, USP) DESCRIPTION CORTISPORIN Ointment (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates, bacitracin zinc, and hydrocortisone
CORTISPORIN Ointment (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates, bacitracin zinc, and hydrocortisone ointment, USP) DESCRIPTION CORTISPORIN Ointment (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates, bacitracin zinc, and hydrocortisone
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to the 26 EU-labelled fragrances van Oosten, Eleonoor J; Schuttelaar, Maria; Coenraads, Pieter
 University of Groningen Clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to the 26 EU-labelled fragrances van Oosten, Eleonoor J; Schuttelaar, Maria; Coenraads, Pieter Published in: CONTACT DERMATITIS
University of Groningen Clinical relevance of positive patch test reactions to the 26 EU-labelled fragrances van Oosten, Eleonoor J; Schuttelaar, Maria; Coenraads, Pieter Published in: CONTACT DERMATITIS
The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus
 The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus Dr. Christina Kuhler-Obbarius, Elisabeth Kunkel, Dr. Matthias Theden-Schow, Hamburg, Germany Our clinical center located in Hamburg includes eight
The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus Dr. Christina Kuhler-Obbarius, Elisabeth Kunkel, Dr. Matthias Theden-Schow, Hamburg, Germany Our clinical center located in Hamburg includes eight
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley
 Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE SHAMPOO IN THERAPY OF PSORIASIS OF THE SCALP
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Platonova et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 4, Issue 04, 238-246. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Platonova et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 4, Issue 04, 238-246. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE
The role of allergy in oral mucosal diseases
 Q J Med 2000; 93:507±511 The role of allergy in oral mucosal diseases D.WRAY,S.R.REES,J.GIBSONandA.FORSYTH 1 From the Department of Oral Medicine, Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, and 1 Contact Dermatitis
Q J Med 2000; 93:507±511 The role of allergy in oral mucosal diseases D.WRAY,S.R.REES,J.GIBSONandA.FORSYTH 1 From the Department of Oral Medicine, Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, and 1 Contact Dermatitis
The Evaluation of Contact Sensitivity with Standard and Cosmetic Patch Test Series in Rosacea Patients
 HK Erdogan, et al pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 30, No. 3, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.290 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Evaluation of Contact Sensitivity with Standard and Cosmetic
HK Erdogan, et al pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 30, No. 3, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.290 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Evaluation of Contact Sensitivity with Standard and Cosmetic
Treating GSM without Estrogens. Lubrication and Vaginal Dilators
 Treating GSM without Estrogens Lubrication and Vaginal Dilators Hope K. Haefner, MD Michigan Medicine Ann Arbor, MI USA Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest Hope Haefner, MD has no disclosures or conflicts
Treating GSM without Estrogens Lubrication and Vaginal Dilators Hope K. Haefner, MD Michigan Medicine Ann Arbor, MI USA Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest Hope Haefner, MD has no disclosures or conflicts
CLINICAL EFFICACY OF TWO TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROIDS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HAND ECZEMA
 INDEXED BY INDEX MEDICUS (MEDLINE) SCIENCE CITATION INDEX EXPANDED (ISI) OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETÀ ITALIANA DI DERMATOLOGIA MEDICA, CHIRURGICA, ESTETICA E DELLE MALATTIE SESSUALMENTE TRASMESSE (SIDeMaST)
INDEXED BY INDEX MEDICUS (MEDLINE) SCIENCE CITATION INDEX EXPANDED (ISI) OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETÀ ITALIANA DI DERMATOLOGIA MEDICA, CHIRURGICA, ESTETICA E DELLE MALATTIE SESSUALMENTE TRASMESSE (SIDeMaST)
PROCTOSEDYL. Anorectal Therapy. Version Date: 85 Enterprise Blvd., Suite 500 August 10, 2018 Markham, Ontario Canada L6G 0B
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Including Patient Medication Information PROCTOSEDYL (Hydrocortisone BP - Framycetin sulfate BP - Cinchocaine hydrochloride BP - Aesculin) Anorectal Therapy APTALIS PHARMA CANADA
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Including Patient Medication Information PROCTOSEDYL (Hydrocortisone BP - Framycetin sulfate BP - Cinchocaine hydrochloride BP - Aesculin) Anorectal Therapy APTALIS PHARMA CANADA
An Everyday Guide to Eczema
 An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
11/1/18. Age and Vulvar Pathology ANATOMY. Prepuce Clitoris Vestibule Hart line. Labia. minora. Labia. majora. Fourchette.
 Age and Vulvar Pathology Maria Angelica Selim, MD Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Director Dermatopathology Unit Duke University Medical Center Labia minora Labia majora Bartholin s duct Prepuce
Age and Vulvar Pathology Maria Angelica Selim, MD Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Director Dermatopathology Unit Duke University Medical Center Labia minora Labia majora Bartholin s duct Prepuce
Patching the Gaps in Our Diagnostic Knowledge. By Tyler Hooton MS3 UWSOM
 Patching the Gaps in Our Diagnostic Knowledge By Tyler Hooton MS3 UWSOM Disclosures The author has no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest The following patient has given permission for this
Patching the Gaps in Our Diagnostic Knowledge By Tyler Hooton MS3 UWSOM Disclosures The author has no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest The following patient has given permission for this
GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH
 GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH INTRODUCTION Skin conditions caused by chemical, physical or biological agents in the workplace are common among disposable glove wearers in the industrial sector. Understanding
GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH INTRODUCTION Skin conditions caused by chemical, physical or biological agents in the workplace are common among disposable glove wearers in the industrial sector. Understanding
Management of benign vulval dermatoses in primary care
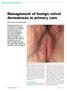 PRESCRIBING IN PRACTICE Management of benign vulval dermatoses in primary care MITESH PATEL AND DAVID NUNNS SPL Vulval dermatoses can be difficult to manage in primary care, and GPs need to be aware of
PRESCRIBING IN PRACTICE Management of benign vulval dermatoses in primary care MITESH PATEL AND DAVID NUNNS SPL Vulval dermatoses can be difficult to manage in primary care, and GPs need to be aware of
Wahlberg Elsner Kanerva Maibach Management of Positive Patch Test Reactions
 Wahlberg Elsner Kanerva Maibach Management of Positive Patch Test Reactions Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH J.E. Wahlberg P. Elsner L. Kanerva H.I. Maibach (Eds.) Management of Positive Patch Test
Wahlberg Elsner Kanerva Maibach Management of Positive Patch Test Reactions Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH J.E. Wahlberg P. Elsner L. Kanerva H.I. Maibach (Eds.) Management of Positive Patch Test
OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
 JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Female Sexual Arousal
JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Female Sexual Arousal
