Cover Image: Courtesy of Historical Collections & Services, Claude Moore Health Sciences Library, University of Virginia.
|
|
|
- Cameron Hodge
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M a r g a r e t S t e r l i n g, c s t, l p n, m a With their belief in the healing power of gods combined with the influence of the Greeks in finding empirical evidence of the origins of diseases, ancient Romans made significant contributions to the history of medicine. Cover Image: Healthy lifestyle Daily life in Rome was generally harsh by today s standards. Besides the many hazards of simply surviving daily life, physical illness and injury were significant concerns. How did the Romans deal with these challenges? They stayed fit. The Romans believed that a healthy mind equaled a healthy body. They also observed that a fit body could fight diseases more effectively than an unfit one. Rather than spend money on doctors, Romans spent their income on staying fit. Celsus, a Roman writer generally believed to have lived circa 175 or 180 CE, is credited with saying, A person should put aside some part of the day for the care of his body. He should always make sure that he gets enough exercise, especially before a meal. 9 All eight volumes of Celsus s De Medicina (On Medicine) have been discovered intact. From his writings, historians concluded that Celsus knew the difference between fresh wounds and ulcers that were slow to heal. He also knew how to prevent hemorrhages by clamping blood vessels. Complex surgical procedures, such as goiter and cataract removal, were described in his works, as well as plastic surgical procedures, including countercircumcision and gynaemastia (breast reduction). 3 11
2 272 AUGUST CE CREDIT Ancient beliefs The Romans maintained that diseases and catastrophic natural occurrences were caused by gods. Prayers, sacrifices, and pagan rites were considered the only ways for healing to occur. Prior to the Christian era, there were temples, such as the Aesculapium on the Tiber Island, where the sick spent the night in prayer to the gods hoping to receive a cure, and doctors made rounds doing what little they could. And there were establishments to house the dying or sick, essentially to keep them off the streets. The concept was not to cure or even care, but to keep the wretched and sickly poor off the streets. Out of sight, out of mind, so to speak. 11 Thanks to the influence of the Greeks, the Romans were also starting to discover at this time, that there were often explanations for many seemingly unexplainable phenomena. For example, the Romans noticed an increase in disease among people who lived near malariainfested swamps and in areas with bad sewage problems. This led them to conclude that illnesses could have a natural cause, which resulted in their creating a system of aqueducts and sewer pipes to improve the public health of all Roman citizens. In this sense, the Romans were the first civilization to introduce a program of public health for everyone regardless of wealth. 9 The Romans also took great care in where they built their cities, homes, and military encampments: When building a house or farm, special care should be taken to place it at the foot of a wooded hill where it is exposed to health-giving winds. Care should be taken where there are swamps in the neighborhood, because certain tiny creatures which cannot be seen by the eyes breed there. These float through the air and enter the body by the mouth and nose and cause serious disease. Marcus Varro 9 There should be no marshes near buildings, for marshes give off poisonous vapors during the hot period of the summer. At this time, they give birth to animals with mischief-making stings which fly at us in thick swarms. Columella 9 Clean water was also very important in Roman society. Towns, military camps, and villas were almost always built near springs, so that a ready supply of moving water was available. FIGURE 1: Scalpels The Surgical Technologist AUGUST
3 But as the cities grew in population, the need for water increased. The lead pipes of the time were not sturdy enough to handle the large amount of water needed to flush waste out of an expanding city, and bronze although available was too expensive for such a massive undertaking. The techniques for manufacturing cast iron pipes were not known to the ancient Romans, so they instead invented a system of conduits that moved water overland. When the water needed to cross valleys or rivers, the Romans built aqueducts that served as bridges for the water to cross. As the water neared the cities, it was directed into smaller bronze or ceramic pipes, which slowed the water s speed and allowed the Romans to direct water into homes and buildings. By 97 CE, an estimated one billion liters of water were pumped into Rome each day. Good personal hygiene, which was important to the Romans, could be achieved with this system of clean water, and Romans eventually became famous for their baths used by both rich and poor citizens. Even the sick were encouraged to bathe regularly, because it was believed that cleanliness would speed the healing process. Most Roman households had toilets, as did all military forts. By 315 CE, it is said that the city of Rome had 144 public toilets, which were flushed clean by running water. 9 To flush this vast system of wastewater out of the cities, Romans invented and created highly efficient sewers, considered by some to be one of the Roman empire s greatest achievements. Lack of hospitals Hospitals, as they are known today, did not exist in ancient Rome. Medical facilities were only available in military camps. Some of the wealthier families had buildings called valetudinaria on the grounds of their estates, but these were built primarily to deal with sick or injured slaves and to isolate them from the rest of the staff and family. 11 The concept of the modern hospital did not come into existence in Europe until well after the time of Constantine and the rise of Christianity. While these early Christian hospitals were grossly inadequate in terms of medical capabilities (they essentially served as last stops for the dying or quarantine centers), the concept of providing care to the public was the actual intent. 11 FIGURE 2: Bone levers 13
4 FIGURE 3: Surgical scissors Roman physicians The medical profession in ancient Rome was not highly regarded. It was considered a low social position, fit for slaves, freedmen and non-latin citizens, mainly Greeks. While there were some who were respected, most were considered just as they were cheaters, liars and quacks. The majority of doctors, at least early on, were selftaught or apprenticed practitioners who simply claimed to be healers, with little basis in scientific, medical knowledge. Many doctors did try to find effective treatments and perform valuable services for the community, but even more were simply engaging in ways to con and cheat their patients. Since there were no licensing boards, no formal requirements or education for entrance to the profession, anyone could call himself a doctor. If his methods were successful, he attracted more patients; if not, they simply moved on to another career. 2 With their less-than-spectacular success rates, Roman physicians were viewed with suspicion and scorn by the rest of society. Some of the wealthier physicians established practices that resemble those of today, with an office and staff. Others simply advertised their services on the streets, going so far as to perform simple surgeries in front of crowds to increase their notoriety. 2 Beauty supplies and cosmetics were commonly sold by doctors, and most were willing to treat any ailment, if the price was right. This was despite their recognition that their treatments were usually ineffective. There are even reports of doctors being hired as assassins and poisoning their patients. 2 With the establishment of a medical school around the first century in the Common Era, the field of ancient medicine became more uniform and practical. Surgeons grew more skilled and valued. The largest gains in knowledge, though, continued to originate from procedures and observations performed by the medical corps of the Roman military. These advances formed the basis for the entire field of medicine for the next two millenia. 2 Galen By far the most famous and important physician of the Roman world was Galen, who was born in 129 CE. Galen served as a physician for the gladiator school in his hometown of Pergamum, in modern-day Turkey. The knowledge and experi- The Surgical Technologist AUGUST
5 FIGURE 4: Cupping vessels for bloodletting ence he gained in trauma and wound treatment had an enormous impact on the history of medicine and led him to regard wounds as windows into the body. 6 After leaving the gladiator school, Galen moved to Rome and became personal physician to the Emperor Marcus Aurelius. As part of his royal duties, Galen performed many surgeries that were not replicated for almost 2,000 years, including brain and eye surgery. 6 To perform cataract surgery, Galen would insert a long, needle-like instrument into the eye behind the lens. He would then pull it back slightly and remove the cataract. The slightest slip could cause permanent blindness. 6 Galen continued to do experimental surgeries throughout his life, including public vivisections of animals to study the anatomy and function of the kidneys and spinal cord. In one of these public displays, Galen dissected a live pig, cutting its nerve bundles one at a time and ending with the laryngeal nerve (now also known as Galen s nerve), which ended the pig s squealing. In other demonstrations, he tied the ureters of live animals to prove that urine is produced in the kidneys, and he severed spinal cords to study paralysis. 6 His public dissections were very valuable in debating the biological theories of the time and were one of the primary means of academic learning in Rome for citizens as well as for medical students. So significant were the findings of his research that his writings were still used as manuals for physicians in the early 1800s, and Galen together with Hippocrates is considered one of the earliest and most significant contributors to the history of medicine. 6 Surgical procedures In ancient Rome, it was commonly recognized that blood moved through the body via a system of arteries and veins. Surgeons knew how to stop the flow of blood by using tourniquets, arterial clamps, and ligatures. They also knew how to prevent deadly gangrene by performing amputation of the infected limbs. Historians have learned that Roman surgeons performed cataract surgery by pushing a thin needle through the eye to break up the cataract. Then the small pieces were suctioned through the small hole in the needle, restoring at least a moderate amount of sight to the patient. 15
6 FIGURE 5: Obstetrical hooks/ sharp hooks Other operations involved plastic surgery. One report discusses an individual getting his earlobes repaired after years of wearing heavy earrings. The excess lobe was trimmed, and the hole sewn together. Freed slaves prompted another common, but expensive, plastic surgery. The brandings and scars of the freed slave could be removed for a price. This would minimize the recognition and stigma of having been a slave in this ancient society. 13 Perhaps the most amazing operations were performed on the brain. Trepanation, the name of the procedure used, provided relief to patients with incurable headaches and relieved pressure on the brain resulting from head injuries. The surgeon used a cylindrical drill bit to cut a circle in the skull. He would rotate the drill using a bow-like device, much like the ones used to rub sticks together in making a fire. Patients had a high survival rate, and, amazingly, no anesthetic was needed. 13 When used, anesthestics in ancient Roman times could not compare to today s standards. Surgeons wanted to minimize the screaming and fighting of patients during surgery; the pain of the patient, however, still scared many. They used opium, henbane, and mandrake. Opium numbed the patient and limited movement. Henbane induced sleeping and a slight amnesia. Finally, mandrake slowed the heart rate and deadened pain. Even with the help of these anesthetics, the standard for a good surgeon was speed! 12 It was perhaps because of this and the lowsurvival rates of many surgeries that led Roman society to place such a high value on diet, gymnastics, exercise, massage, and sea-bathing. Surgical instruments The surgical tools found by researchers, especially those discovered in the remains of Pompeii, the city buried by volcanic lava from Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE, provide insight into the tools used by surgeons in Rome. In the home of one Pompeiian surgeon, many surgical instruments, including scalpels, scissors, and bone forceps, were found in pristine condition under the ash of the volcano. Much of what we know about Roman medicine is because of the House of the Surgeon. 13 The instruments found at Pompeii represent the normal range that a surgeon of the time would have needed. They were mostly bronze, brass or copper, but blades and needles were almost invariably made of iron or steel. Most of the instruments could be heated up and used for cautery. By heating the instruments, the surgeons were, without realizing it, sterilizing them. 3 Instruments found Scalpels, usually were manufactured of either steel or bronze, or a combination of the two (for example, steel blade and a bronze handle). They were used to make incisions and were typically stored and carried in a wooden box, laid head to tail and separated by small, fixed partitions. The Surgical Technologist AUGUST
7 Hooks, both sharp and blunt, were employed regularly by Roman physicians in much the same way that surgeons today use them. Blunt hooks were primarily used as probes for dissection and for raising blood vessels. Sharp hooks were used to hold and lift small pieces of tissue so that they could be extracted and to retract the edges of wounds. 7 Bone drills, which resembled modern cork screws, were used to remove diseased bone tissue from the skull and to extract foreign objects, such as weapons, from bones. Bone forceps were utilized to extract small objects that were otherwise difficult to remove with the surgeon s fingers. During trepanation of the skull, the surgery described above to relieve headaches, was performed in such a way so that the drill did not penetrate quickly into the dura matter. The surgeon frequently plunged the drill into cold water to avoid overheating the bone. Catheters, like their modern successors, were employed by Roman surgeons to open up blocked urethra to treat urinary tract infections. Uvula crushing forceps were often used by the famous physician Galen for treating coughs. Galen used the forceps to crush the uvula and then cut it off. This harmless, but senseless, operation was one of Galen s primary sources of income as well as a popular treatment in ancient Rome. Several types of vaginal specula have been discovered, and they generally demonstrate the high degree of engineering skill available to the ancient doctors. Most of the vaginal specula consist of a screw device, which, when turned, forces a cross-bar to push the blades outwards. 7 Bleeding cups collected blood from a patient in a diseased area of the body. It was thought that removal of the blood would rid that area of the disease. The larger cupping vessel was selected for larger areas of the body, such as the back or thighs, while the smaller cup was likely chosen for smaller areas, such as the arms. Roman physicians carried wooden medicine boxes to contain their forceps, scalpels, catheters, and even arrow-extractors. Instrument sterility It is unclear whether Romans understood the importance of sterilizing their surgical instruments, but they did use many techniques to kill germs that were not formally invented until much later. For example, they boiled their tools before use and would not reuse the same tool on a patient without placing it into boiling water a second time. Wounds were typically washed with acetum, which is actually a better antiseptic than the carbolic acid used by Joseph Lister more than 1,500 years later. Conclusion The lack of truly sterile equipment, few if any painkillers or anesthetics, and the reliance on superstitions and myths would probably make any modern-day surgeon cringe when reading FIGURE 6: Tile cautery 17
8 about the medical practices of ancient Rome. In many respects, though, the Romans laid the foundation for certain areas of modern medicine. From the Romans, surgical methods began to be based on their extensive study of anatomy and physiology as well as their examinations of the human body s reactions to disease and injury. The use of physical examinations improved as more detailed patient histories began to be kept, which allowed surgeons to eventually compare cases and share information. In addition, the vast experience that Roman physicians gained on the battlefield from treating wounded and ailing soldiers, led to a tremendous advancement in knowledge and surgical practices. Furthermore, the bureaucracy of Rome insisted that the treatments and knowledge perfected by military physicians be taught in the new medical schools being formed. Although physicians still were not regarded highly in Roman society, and many citizens continued to believe that the head of the household was more capable than a doctor of tending to the care of his family, the field of medicine expanded tremendously during the time of the Roman Empire. About the author Margaret Sterling, cst, lpn, ma, is the educational coordinator for surgery at Shore Memorial Hospital in Somers Point, New Jersey. She is responsible for planning, implementation and evaluation of formal and informal learning and assisting surgical services personnel to perform competently. She also serves on hospital committees that deal with clinical ladders, clinical competency and cultural diversity. Sterling has been working in the O.R. exclusively since 1982 and began her perioperative career in I have been involved in the miracle of medicine for the last 35 years. At the AST Annual Conference in Las Vegas she presented Ancient Surgery. Editor s Note: The notations BCE (Before the Common Era) and CE (Common Era) are terms that refer to BC (Before Christ) and AD (Anno Domini) as time references. More information about these terms is available online at For more information on Galen (also known as Claudius Galenus), see the September 2004 and November 2001 issues of this journal. For more information on ancient medicine, visit system.virginia.edu/internet/library/historical/artifacts/antiqua/. Images: All images are courtesy of Historical Collections & Services, Claude Moore Health Sciences Library, University of Virginia. The editors want to express appreciation to Andrew Jacobs, BA, who is pursuing a Masters degree in Secondary English Education, and Claudia Sueyras, BA, Historical Collections Specialist, who is pursuing a Masters degree in Library Science. Their assistance in obtaining the high resolution imagery greatly facilitated the publication of this article. Both are affiliated with the Historical Collections and Services at the University of Virginia. References 1. Adkins L, Adkins R, eds. Handbook to Life in Ancient Rome. New York, NY: Oxford University; Ancient Roman Doctors. Available online at: Accessed July 3, Ancient Surgery. Available online at: html. Accessed July 3, Asclepion. Available online at: Accessed July 5, Bishop WJ. The Early History of Surgery. New York, NY; Barnes and Noble Publishers: Galen. Available online at: Galen. Accessed July 5, Greek and Roman Surgical Instruments. Available online at: Accessed July 5, Haeger K. The Illustrated History of Surgery. New York, NY; Crown Publishers: Medicine in Ancient Rome. Available online at: htm. Accessed July 3, Milne JS. Surgical Instruments in Greek and Roman Times. Oxford, England; Claredon Press: Roman Hospitals. Available online at: com/culture/roman-hospitals.php. Accessed July 3, Roman Medicine Drugs. Available online at: Accessed July 5, Roman Medicine Surgery. Available online at: Accessed July 5, Surgical Instruments from Ancient Rome. Available online at: historical/artifacts/roman_surgical/ Accessed July 3, The Surgical Technologist AUGUST
9 CEExam 272 AUGUST CE CREDIT Surgery in ancient Rome Earn CE credits at home You will be awarded continuing education (CE) credit(s) for recertification after reading the designated article and completing the exam with a score of 70% or better. If you are a current AST member and are certified, credit earned through completion of the CE exam will automatically be recorded in your file you do not have to submit a CE reporting form. A printout of all the CE credits you have earned, including Journal CE credits, will be mailed to you in the first quarter following the end of the calendar year. You may check the status of your CE record with AST at any time. If you are not an AST member or are not certified, you will be notified by mail when Journal credits are submitted, but your credits will not be recorded in AST s files. Detach or photocopy the answer block, include your check or money order made payable to AST, and send it to the Accounting Department, AST, 6 West Dry Creek Circle, Suite 200, Littleton, CO Members: $6 per CE, nonmembers: $10 per CE 272 AUGUST CE CREDIT Surgery in ancient Rome 1. One of the most influential Roman physicians was: a. Celsus c. Galen b. Pergamum d. Aesculapius 2. The Romans were influenced by whose belief that diseases had natural causes? a. Egyptians c. Mayans b. Greeks d. Turks 3. Which of the following were Roman beliefs? a. A healthy mind equals a healthy body. b. Physical fitness is important. c. Gods control health and healing. d. All of the above 4. Romans are credited with being the first civilization to... a. Perform plastic surgery b. Implement public health programs that benefited all citizens c. Discover natural causes for diseases d. Believe in pagan rites and sacrifices as methods of healing 5. Roman baths... a. Were available only to wealthy citizens b. Were built near aqueducts c. Were recommended for healing diseases d. All of the above 6. Facilities resembling modern-day hospitals... a. Weren t seen until after the rise of Christianity b. Were called valetudinaria c. Were prevalent throughout Roman society d. Were introduced to the Romans by the Greeks 7. In ancient Rome... a. Public vivisections were considered vulgar and were prohibited b. Trepanations were performed to remove cataracts c. Physicians prevented gangrene with amputation d. Anesthetics weren t used due to high cost 8. As the population of Roman cities increased... a. Pipes and aqueducts were built to transport water overland b. Sewage system pipes were made from sturdy cast iron c. Military forts were built near marshes d. Plastic surgery became too expensive for most citizens 9. Romans use of sterilization included... a. Misting the surgical table with carbolic acid b. Washing wounds with acetum c. Storing blood in sterilized bleeding cups d. Wearing washed-wool gloves during examinations 10. Which of the following is not true of Roman society? a. Surgeons demonstrated a high degree of skill despite crude instruments. b. Romans believed cleanliness contributed to good health and healing. c. Exercise, diet, mental health and massage were valued highly. d. Their use of detailed patient histories wasn t replicated until modern times. a b c d a b c d Certified Member Certified Nonmember 1 6 Certification No. Name Address City State ZIP Telephone Mark one box next to each number. Only one correct or best answer can be selected for each question. 19
The History of Health and Medicine
 The History of Health and Medicine Roman Medicine 400 BC AD 500 The History of Health and Medicine Roman Medicine 400 AD 500 These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available
The History of Health and Medicine Roman Medicine 400 BC AD 500 The History of Health and Medicine Roman Medicine 400 AD 500 These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available
1. Who was Imhotep? Where did Imhotep live? When did he live? What kinds of work did he do? 2. Who was Hippocrates? Where did he live?
 Chapter 1: Supplemental Questions 1. Who was Imhotep? Where did Imhotep live? When did he live? What kinds of work did he do? 2. Who was Hippocrates? Where did he live? When did he live? 3. What new medical
Chapter 1: Supplemental Questions 1. Who was Imhotep? Where did Imhotep live? When did he live? What kinds of work did he do? 2. Who was Hippocrates? Where did he live? When did he live? 3. What new medical
The Development of Scientific Medicine
 The Development of Scientific Medicine A. EARLY HUMANS: (before 3000 B.C.) 1. Supernatural Belief Systems: magical-religious or supernatural explanations of disease. Causes of disease: by direct intervention
The Development of Scientific Medicine A. EARLY HUMANS: (before 3000 B.C.) 1. Supernatural Belief Systems: magical-religious or supernatural explanations of disease. Causes of disease: by direct intervention
Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs
 Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs What is a labor epidural? A labor epidural is a thin tube (called an epidural catheter) placed in a woman s lower back by an anesthesia provider.
Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs What is a labor epidural? A labor epidural is a thin tube (called an epidural catheter) placed in a woman s lower back by an anesthesia provider.
E-book Code: REAU4041
 E-book Code: REAU4041 Written by Sally Young. Illustrated by Melinda Brezmen. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2008) Ready-Ed Publications - 2008. P.O. Box 276 Greenwood Perth W.A. 6024 Email: info@readyed.com.au
E-book Code: REAU4041 Written by Sally Young. Illustrated by Melinda Brezmen. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2008) Ready-Ed Publications - 2008. P.O. Box 276 Greenwood Perth W.A. 6024 Email: info@readyed.com.au
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse. Patient decision aid
 Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
Enhanced Recovery Programme
 Enhanced Recovery Programme Enhanced Recovery Programme This leaflet should increase your understanding of the programme and how you can play an active part in your recovery. If there is anything you are
Enhanced Recovery Programme Enhanced Recovery Programme This leaflet should increase your understanding of the programme and how you can play an active part in your recovery. If there is anything you are
Why was there so much change in this period?
 Why was there so much change in this period? Germ Theory: Summary? 1) 1861: Germ Theory Bacteria in the air turned things bad (working to find why beer was going sour). Pasteur wondered if this could make
Why was there so much change in this period? Germ Theory: Summary? 1) 1861: Germ Theory Bacteria in the air turned things bad (working to find why beer was going sour). Pasteur wondered if this could make
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
History GCSE. Question Guidance for: The History of Medicine Time for the exam: 1hr 15 mins
 History GCSE Question Guidance for: The History of Medicine Time for the exam: 1hr 15 mins Medicine and Public Health Question 1 8 marks, 12 minutes This is compulsory and it is a change question: use
History GCSE Question Guidance for: The History of Medicine Time for the exam: 1hr 15 mins Medicine and Public Health Question 1 8 marks, 12 minutes This is compulsory and it is a change question: use
Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)
 Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us
Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us
Hygiene and Medicine in the Middle Ages. Make sure you re taking notes!
 Hygiene and Medicine in the Middle Ages Make sure you re taking notes! Disease - During the Middle Ages, most people were sick with something for most of their lives. - There were no treatments for most
Hygiene and Medicine in the Middle Ages Make sure you re taking notes! Disease - During the Middle Ages, most people were sick with something for most of their lives. - There were no treatments for most
KS 2 (Upper) KS 3. Ebook Code: REUK4041. * The Working Body * The Growing Body ISBN
 Ebook Code: REUK4041 * The Working Body * The Growing Body KS 2 (Upper) KS 3 Written by Sally Young. Illustrated by Melinda Brezmen. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2010) Ready-Ed Publications P.O.
Ebook Code: REUK4041 * The Working Body * The Growing Body KS 2 (Upper) KS 3 Written by Sally Young. Illustrated by Melinda Brezmen. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2010) Ready-Ed Publications P.O.
SURGERY IN ANCIENT TIMES. Rebeka Stevenson University of Calgary. Preceptor: None
 SURGERY IN ANCIENT TIMES by Rebeka Stevenson University of Calgary Preceptor: None Abstract In our modern world, invasive surgeries and organ transplantations are common: machines circulate and oxygenate
SURGERY IN ANCIENT TIMES by Rebeka Stevenson University of Calgary Preceptor: None Abstract In our modern world, invasive surgeries and organ transplantations are common: machines circulate and oxygenate
Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement)
 Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a half hip replacement. It gives information about the
Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a half hip replacement. It gives information about the
Operational Guideline
 1 of 6 PURPOSE Prevention of the spread of sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections (STBBI) through distribution of harm reduction supplies SCOPE & GOAL Harm reduction supplies and condoms will
1 of 6 PURPOSE Prevention of the spread of sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections (STBBI) through distribution of harm reduction supplies SCOPE & GOAL Harm reduction supplies and condoms will
Recovering at home. How will I feel when I get home? How should I look after my wound?
 How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
9-1 GCSE SURGERY 18 TH & 19 TH CENTURY
 9-1 GCSE www.stchistory.com SURGERY 18 TH & 19 TH CENTURY SURGERY IN 1800: What can you infer from this source about surgery in 1800? SURGERY IN 1900: Amputation Clip What can you infer from this source
9-1 GCSE www.stchistory.com SURGERY 18 TH & 19 TH CENTURY SURGERY IN 1800: What can you infer from this source about surgery in 1800? SURGERY IN 1900: Amputation Clip What can you infer from this source
Alternative Health. A New Look at an Old Way. A free report by:
 Alternative Health A New Look at an Old Way of Life A free report by: http://natural-remediesinfo.com Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Concepts of Eastern Medicine... 2 Combining Alternative Methods
Alternative Health A New Look at an Old Way of Life A free report by: http://natural-remediesinfo.com Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Concepts of Eastern Medicine... 2 Combining Alternative Methods
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery
 Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF)
 Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
Who is this leaflet for? What is a fistula? How is the fistula formed?
 Your fistula Who is this leaflet for? Your doctor has told you that your kidneys are not working properly. One of the many functions of the kidneys is to get rid of waste products from your body. If your
Your fistula Who is this leaflet for? Your doctor has told you that your kidneys are not working properly. One of the many functions of the kidneys is to get rid of waste products from your body. If your
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
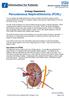 Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Complex Limb Injury. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
The History of Health Care
 The History of Health Care Ancient Times Prevention of injury from predators Illness/disease caused by supernatural spirits Ancient Times Herbs and plants were used as medicine examples: Digitalis from
The History of Health Care Ancient Times Prevention of injury from predators Illness/disease caused by supernatural spirits Ancient Times Herbs and plants were used as medicine examples: Digitalis from
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw)
 Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Las Vegas Urogynecology
 Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Physician's Surgical Procedure Disclosure and Patient s Consent TO THE PATIENT: You
Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Physician's Surgical Procedure Disclosure and Patient s Consent TO THE PATIENT: You
THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital
 BACLOFEN PUMP THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital PAGER: 617-355-6369 and ask to page #7867 (PUMP) 1 Contents What is spasticity?... 3 What is baclofen?... 3 The evaluation for
BACLOFEN PUMP THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital PAGER: 617-355-6369 and ask to page #7867 (PUMP) 1 Contents What is spasticity?... 3 What is baclofen?... 3 The evaluation for
Circumcision Excerpted from Gentle Baby Care by Elizabeth Pantley
 Male Circumcision Circumcision Dr. Morris Elstein is the only doctor (that we are aware of) who will perform this surgery on your homebirthed son. He is not only a doctor but also, a special religious
Male Circumcision Circumcision Dr. Morris Elstein is the only doctor (that we are aware of) who will perform this surgery on your homebirthed son. He is not only a doctor but also, a special religious
Laser Away Peripheral Neuropathy Pain?
 Demand soars for neuropathy treatment offered in Pasco Laser Away Peripheral Neuropathy Pain? What Every Peripheral Neuropathy Sufferer Should Know About This Popular Laser Treatment If you suffer with
Demand soars for neuropathy treatment offered in Pasco Laser Away Peripheral Neuropathy Pain? What Every Peripheral Neuropathy Sufferer Should Know About This Popular Laser Treatment If you suffer with
Patient Information. Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE)
 Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Bilateral Wilms Tumor: New Protocols and Procedures by Dawn Wolf
 www.complexchild.com Bilateral Wilms Tumor: New Protocols and Procedures by Dawn Wolf Masses...tumors...oncologist...straight to the ER... Those were the words the doctor was using as he talked about our
www.complexchild.com Bilateral Wilms Tumor: New Protocols and Procedures by Dawn Wolf Masses...tumors...oncologist...straight to the ER... Those were the words the doctor was using as he talked about our
Elizabethan medicine. Bubonic plague (Black Death) Smallpox. Sewage. Clean water. Operations. Relay race cards
 Relay race cards Bubonic plague (Black Death) The bubonic plague was a painful disease, with black buboes, or swellings, in the groin and armpits, which lasted up to a week. There was some chance of surviving
Relay race cards Bubonic plague (Black Death) The bubonic plague was a painful disease, with black buboes, or swellings, in the groin and armpits, which lasted up to a week. There was some chance of surviving
Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide. Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon
 Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon www.drbuckparker.com Thanks! Thanks so much for downloading my laparoscopic appendectomy guide! This guide
Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon www.drbuckparker.com Thanks! Thanks so much for downloading my laparoscopic appendectomy guide! This guide
This booklet has been developed to help guide you through your post-operative rehabilitation.
 Patient Information Physiotherapy following Breast Surgery Physiotherapy Directorate Keep this booklet as a reminder with your exercises long term. If you start to develop stiffness, pain, weakness, or
Patient Information Physiotherapy following Breast Surgery Physiotherapy Directorate Keep this booklet as a reminder with your exercises long term. If you start to develop stiffness, pain, weakness, or
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide)
 Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth.
 For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Many people use a combination of the standard 17mm cannula and the shorter 13mm cannula length depending where on their body they are inserting.
 There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
Pain Relief in Labour Epidurals and Spinals
 Pain Relief in Labour Epidurals and Spinals Information for woman Maternity Services For more information, please contact: Anaesthetics Department Telephone Scarborough: 01723 385202 Telephone York: 01904
Pain Relief in Labour Epidurals and Spinals Information for woman Maternity Services For more information, please contact: Anaesthetics Department Telephone Scarborough: 01723 385202 Telephone York: 01904
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Anesthesia and You. Planning Your Childbirth
 Anesthesia and You Planning Your Childbirth Anesthesia Options for Labor and Delivery There are many medications available to women during labor and childbirth. However, some pain relief choices may be
Anesthesia and You Planning Your Childbirth Anesthesia Options for Labor and Delivery There are many medications available to women during labor and childbirth. However, some pain relief choices may be
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair
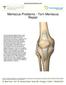 Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
Epidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal
 Information for patients pidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal This leaflet has been made using information from the Royal College
Information for patients pidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal This leaflet has been made using information from the Royal College
Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367
 364 Problems of the Urine System Chapter 23 In this chapter: Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367 Other Problems of the Urine System
364 Problems of the Urine System Chapter 23 In this chapter: Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367 Other Problems of the Urine System
Unexplained Illness Patient Scenario
 Diagnosis and Management of Foodborne Illnesses A Primer for Physicians and Other Health Care Professionals Unexplained Illness Patient Scenario Unexplained Illness Patient Scenario American Medical Association
Diagnosis and Management of Foodborne Illnesses A Primer for Physicians and Other Health Care Professionals Unexplained Illness Patient Scenario Unexplained Illness Patient Scenario American Medical Association
Your Homeopathic Questions Answered
 Your Homeopathic Questions Answered Betty Magill, ND CNHP, CHS, CAT, BS Bioenergetics Practitioner WHY HOMEOPATHIES? WHAT ARE HOMEOPATHIES? I have been involved with natural alternatives for my own health
Your Homeopathic Questions Answered Betty Magill, ND CNHP, CHS, CAT, BS Bioenergetics Practitioner WHY HOMEOPATHIES? WHAT ARE HOMEOPATHIES? I have been involved with natural alternatives for my own health
Patient information. Retinal Detachment Surgery St. Paul s Eye Unit PIF 024 V7
 Patient information Retinal Detachment Surgery St. Paul s Eye Unit PIF 024 V7 Your eye specialist has advised you to have retinal detachment surgery. This leaflet gives you information that will help you
Patient information Retinal Detachment Surgery St. Paul s Eye Unit PIF 024 V7 Your eye specialist has advised you to have retinal detachment surgery. This leaflet gives you information that will help you
21. Getting Tested for HIV
 21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
Nephrostomy. Radiology Department. Patient information leaflet
 Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Opening a Medical Weight Loss Practice in Middle-Class, High-Competition Areas
 Opening a Medical Weight Loss Practice in Middle-Class, High-Competition Areas A White Paper August 20, 2013 INTRODUCTION Obesity is nothing new. In fact, it has been a health epidemic for several years
Opening a Medical Weight Loss Practice in Middle-Class, High-Competition Areas A White Paper August 20, 2013 INTRODUCTION Obesity is nothing new. In fact, it has been a health epidemic for several years
Managing Pain and Sickness after Surgery
 Managing Pain and Sickness after Surgery This pamphlet explains about pain relief after surgery. There are many effective treatments to help keep you comfortable after your operation. The different ways
Managing Pain and Sickness after Surgery This pamphlet explains about pain relief after surgery. There are many effective treatments to help keep you comfortable after your operation. The different ways
Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Subacromial Decompression
 PATIENT INFORMATION Subacromial Decompression You will be admitted for surgery to your shoulder as a result of a subacromial impingement syndrome. The subacromial impingement syndrome is a condition where
PATIENT INFORMATION Subacromial Decompression You will be admitted for surgery to your shoulder as a result of a subacromial impingement syndrome. The subacromial impingement syndrome is a condition where
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Tuesday, September 25, Ethnomedicine
 Ethnomedicine What is ethnomedicine? those beliefs and practices relating to disease which are the products of indigenous cultural development and are not explicitly derived from the conceptual system
Ethnomedicine What is ethnomedicine? those beliefs and practices relating to disease which are the products of indigenous cultural development and are not explicitly derived from the conceptual system
Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing)
 Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Penile implants What to expect and how to prepare
 Penile implants What to expect and how to prepare Penile implants can restore erectile function. Explore your choices and find out what to expect from this procedure. Penile implants are artificial devices
Penile implants What to expect and how to prepare Penile implants can restore erectile function. Explore your choices and find out what to expect from this procedure. Penile implants are artificial devices
Bunion Surgery. Patient information Leaflet
 Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
Origins of Bio-Medical Science
 Origins of Bio-Medical Science Greek and Roman Legacy Physicians in Mesopotamia and Egypt 3000 years ago used herbal drugs, salts and physical therapy Hippocrates (460-375 BCE) - Greek physician father
Origins of Bio-Medical Science Greek and Roman Legacy Physicians in Mesopotamia and Egypt 3000 years ago used herbal drugs, salts and physical therapy Hippocrates (460-375 BCE) - Greek physician father
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
Skip Navigation Links Latest Numbers
 Skip Navigation Links Latest Numbers http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos072.htm Dentists Nature of the Work Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement Employment Job Outlook Projections Data Earnings OES
Skip Navigation Links Latest Numbers http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos072.htm Dentists Nature of the Work Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement Employment Job Outlook Projections Data Earnings OES
The Secret To A Great Butt
 Share this guide The Secret To A Great Butt 4 TIPS TO GET STARTED The Secret To A Great Butt: 4 Tips To Get Started Without question the number 1 request I get today, is finding the best way to get a great
Share this guide The Secret To A Great Butt 4 TIPS TO GET STARTED The Secret To A Great Butt: 4 Tips To Get Started Without question the number 1 request I get today, is finding the best way to get a great
ARTERIAL BYPASS GRAFTS IN THE LEG
 The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY
 MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY The Treatment of Skin Cancer What is Mohs Micrographic Surgery? Mohs Micrographic surgery is a specialized, highly effective technique used to treat skin cancer. The goal of Mohs
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY The Treatment of Skin Cancer What is Mohs Micrographic Surgery? Mohs Micrographic surgery is a specialized, highly effective technique used to treat skin cancer. The goal of Mohs
Anterior cervical discectomy and replacement / fusion
 Anterior cervical discectomy and replacement / fusion Advice sheet for patients by Mr Alexander Montgomery, Consultant Spinal Surgeon This advice sheet is intended specifically for patients of Mr Alexander
Anterior cervical discectomy and replacement / fusion Advice sheet for patients by Mr Alexander Montgomery, Consultant Spinal Surgeon This advice sheet is intended specifically for patients of Mr Alexander
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
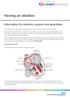 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Hepatitis C Information Sheet.
 Department of Gastroenterology 4225 Hoyt Avenue, Suite A Everett, Washington 98203-2318 (425) 259-3122 * (425) 252-9860 fax Hepatitis C Information Sheet. What you should know about having HCV infection:
Department of Gastroenterology 4225 Hoyt Avenue, Suite A Everett, Washington 98203-2318 (425) 259-3122 * (425) 252-9860 fax Hepatitis C Information Sheet. What you should know about having HCV infection:
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
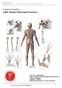 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks
 This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
Insertion of a Haemodialysis Catheter
 Insertion of a Haemodialysis Catheter Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction This leaflet is about the procedure required to put in a temporary dialysis catheter. It is intended to give
Insertion of a Haemodialysis Catheter Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction This leaflet is about the procedure required to put in a temporary dialysis catheter. It is intended to give
ISPUB.COM. Epidural For Pain Control After Surgery. A Kowalski, O Wenker WHAT IS AN EPIDURAL? WHY SHOULD I HAVE AN EPIDURAL?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pain, Symptom Control and Palliative Care Volume 2 Number 1 A Kowalski, O Wenker Citation A Kowalski, O Wenker.. The Internet Journal of Pain, Symptom Control and Palliative
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pain, Symptom Control and Palliative Care Volume 2 Number 1 A Kowalski, O Wenker Citation A Kowalski, O Wenker.. The Internet Journal of Pain, Symptom Control and Palliative
Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT)
 Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Total Hip Replacement
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE and on each subsequent page Forename.. Male Female Surname Hospital Number... Consultant D.O.B.././ OPERATION: Total Hip Replacement PROCEDURE: The hip joint is a ball
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE and on each subsequent page Forename.. Male Female Surname Hospital Number... Consultant D.O.B.././ OPERATION: Total Hip Replacement PROCEDURE: The hip joint is a ball
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting
 Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Instrument inspection and testing
 Lesson No. CIS 271 (Instrument Continuing Education - ICE) Sponsored by: Tonsillectomy & Adenoidectomy Instrumentation JON WOOD, BAAS, CST, CRCST CLINICAL EDUCATOR, IAHCSMM Instrument Continuing Education
Lesson No. CIS 271 (Instrument Continuing Education - ICE) Sponsored by: Tonsillectomy & Adenoidectomy Instrumentation JON WOOD, BAAS, CST, CRCST CLINICAL EDUCATOR, IAHCSMM Instrument Continuing Education
Kidney Biopsy. Patient Information. Working together for better patient information. Health & care information you can trust. The Information Standard
 Kidney Biopsy Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information This leaflet is designed to answer some
Kidney Biopsy Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information This leaflet is designed to answer some
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Contents
 DENTAL IMPLANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS Contents Dental Implants History 1 Dental Implants Now 2 The Process 3 How to Care for Implants 5 Potential Complications 6 Roger Moore Contact Details 7 DENTAL IMPLANTS
DENTAL IMPLANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS Contents Dental Implants History 1 Dental Implants Now 2 The Process 3 How to Care for Implants 5 Potential Complications 6 Roger Moore Contact Details 7 DENTAL IMPLANTS
"Easy-On" Caponizing Set. Instruction Book. Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON. Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds.
 BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds Instruction Book "Easy-On" Caponizing Set Copyright 1922 Published for Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. Dallas, Tex. Philadelphia, Pa. Seattle,
BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds Instruction Book "Easy-On" Caponizing Set Copyright 1922 Published for Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. Dallas, Tex. Philadelphia, Pa. Seattle,
How varicose veins occur
 Varicose veins are a very common problem, generally appearing as twisting, bulging rope-like cords on the legs, anywhere from groin to ankle. Spider veins are smaller, flatter, red or purple veins closer
Varicose veins are a very common problem, generally appearing as twisting, bulging rope-like cords on the legs, anywhere from groin to ankle. Spider veins are smaller, flatter, red or purple veins closer
Mommy Makeover
 Mommy Makeover Many women experience significant physical changes following pregnancy and breast-feeding, many of which can be persistent and difficult to correct with diet and exercise alone. Changes
Mommy Makeover Many women experience significant physical changes following pregnancy and breast-feeding, many of which can be persistent and difficult to correct with diet and exercise alone. Changes
Reversed geometry shoulder replacement
 Information and exercises Reversed geometry shoulder replacement Introduction The reversed geometry total shoulder replacement is designed for use in shoulders that have a deficient rotator cuff, arthritis
Information and exercises Reversed geometry shoulder replacement Introduction The reversed geometry total shoulder replacement is designed for use in shoulders that have a deficient rotator cuff, arthritis
UNDERSTANDING DENTAL IMPLANTS Comfort and Confidence Again
 502 Jefferson Highway N. Champlin, MN 55316 763 427-1311 www.moffittrestorativedentistry.com UNDERSTANDING DENTAL IMPLANTS Comfort and Confidence Again NEW TEETH FOR A NEW SMILE Do you avoid laughing aloud,
502 Jefferson Highway N. Champlin, MN 55316 763 427-1311 www.moffittrestorativedentistry.com UNDERSTANDING DENTAL IMPLANTS Comfort and Confidence Again NEW TEETH FOR A NEW SMILE Do you avoid laughing aloud,
Patient information. Information for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Disc Surgery. Trauma and Orthopaedic Directorate PIF 1359/V3
 Patient information Information for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Disc Surgery Trauma and Orthopaedic Directorate PIF 1359/V3 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Lumbar Microdiscectomy. What
Patient information Information for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Disc Surgery Trauma and Orthopaedic Directorate PIF 1359/V3 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Lumbar Microdiscectomy. What
M A H O M E W O R K # 2 P a g e Outpatient surgery is generally limited to procedures requiring less than 60
 M A 2 0 5 H O M E W O R K # 2 P a g e 1 NAME: DATE: CHAPTER 42 Assisting with Minor Surgery True/False: 1. Outpatient surgery is generally limited to procedures requiring less than 60 minutes to perform.
M A 2 0 5 H O M E W O R K # 2 P a g e 1 NAME: DATE: CHAPTER 42 Assisting with Minor Surgery True/False: 1. Outpatient surgery is generally limited to procedures requiring less than 60 minutes to perform.
Total ankle replacement. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS IN THE WORKPLACE
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS IN THE WORKPLACE Purpose In the event of an emergency, are you prepared to lend a helping hand? Workplace accidents, automobile accidents, injuries at home or during recreation can
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS IN THE WORKPLACE Purpose In the event of an emergency, are you prepared to lend a helping hand? Workplace accidents, automobile accidents, injuries at home or during recreation can
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
Temperature Extremes
 Temperature Extremes A SAFETY TALK FOR DISCUSSION LEADERS This safety talk is designed for discussion leaders to use in preparing safety meetings. Set a specific time and date for your safety meeting.
Temperature Extremes A SAFETY TALK FOR DISCUSSION LEADERS This safety talk is designed for discussion leaders to use in preparing safety meetings. Set a specific time and date for your safety meeting.
About your graft for dialysis. Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit)
 About your graft for dialysis Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 12 You will have discussed with your doctor that your kidney condition means that you need to have
About your graft for dialysis Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 12 You will have discussed with your doctor that your kidney condition means that you need to have
Coronary angioplasty and stents
 Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
