CHAPTER 5 CRYSTALLISATION OF HYDRATED AND ANHYDROUS URIC ACID AND AMMONIUM ACID URATE CRYSTALS IN GEL
|
|
|
- Alison Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 61 CHAPTER 5 CRYSTALLISATION OF HYDRATED AND ANHYDROUS URIC ACID AND AMMONIUM ACID URATE CRYSTALS IN GEL 5.1 INTRODUCTION Uric acid is an important constituent of human stones. Under normal circumstances uric acid is a minor serum constituent. However, certain reptiles and birds excrete most of their nitrogenous waste in the form of uric acid. In the normal, urea is the main form of nitrogenous waste product and, except in humans, apes, new world monkeys and Dalmatian dogs almost all uric acid is converted into allantoin prior to excretion (Smith et al, 1969). Uric acid stones are known to occur in patients in whom urinary uric acid excretion is raised, due to primary or secondary gout and the incidence rises with increasing urinary uric acid (Gutman 1963). Henneman et al (1962) indicated a tendency for uric acid stone formation to be associated with the passage of an unusually acid urine. An increase of uric acid levels in blood leads to the deposition of uric acid in joints which result in gout causing pain and swelling. Uric acid is often found as a constituent of urinary calculi and has high incidence in nephrolithiasis resulting in severe kidney damage. Hence studies on nucleation and crystal growth of uric acid play a vital role in medicine and pharmaceutical research. Several workers have grown crystals of uric acids from solution (Rinaudo and Boistelle 1980, Boistelle and Rinaudo 1981). Anhydrous uric acid is known to crystallize in monoclinic system with unit cell constants a = nm, b = nm and c = nm with/3 = 65.10*. There is an increasing interest in growing urinary crystals as a model system for studying crystals deposition diseases in human beings. A method
2 62 suitable for use under practical conditions based on diffusion and crystallization in gels has been developed (Henisch 1970, Bisaillon and Tawashi 1973, Legeros and Morales 1973, Phaneuf-mimeault and Tawashi 1977). There have been several studies on the solubilities of uric acid and the degree of supersaturation attained under various conditions (Porter 1963 a, Marshall and Robertson 1976, Vermueien et al 1964). Babic-Ivacic et al (1987) studied the solubility of uric acid dihydrate (UA.2H2O) and the precipitation of UA.2H20 and anhydrous uric acid (UA) from solutions containing sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. Boistelle and Rinaudo (1981) grew (0.6 x 0.4 x 0.2 mm3) crystals of anhydrous uric acid in solution. The experimental study on dissolution of uric acid by Vermeulen and Fried (1965) indicates that uric acid stone formation is also due to precipitation from a supersaturated solution. Little is known about the factors which may influence the crystallization of uric acid from gel. In the present work, crystallization of both uric acid and uric add dihydrate using the gel technique have been investigated. The conditions for growing these crystals of uric acids using silica gel and to obtain good crystals for X- ray diffraction and other studies have been enumerated. Crystals of linear dimensions ranging from 0.2 to 1 mm have been grown in the present investigation. The general growth aspects of uric acids as a contribution to the knowledge of uric acid stone growth which grow in a synovial medium (gout, joints) have also been investigated. Ammonium acid urate crystals (C5H7N5O3) have been found as one of the compositions of urinary calculi (Tsay 1961, prien 1963). Ammonium urate is a pure state of urinary calculi. The most important type of bladder stones from developing countries consists mainly of ammonium acid urate. Ammonium acid urate was the most common constituent of the stones from Dalmatians dog (Sutor and Wooley 1970 b). Teotia and Sutor (1971) have shown that excess of both uric acid and the ammonium ion is essential for the formation of Ammonia acid urate from urine over the ph range of It is chiefly found in the endemic bladder stones and which are still prevalent in certain areas of some of the developing countries such as India, Turkey etc. (Lonsdale et al 1968). Because of their interest in biological system we have studied the growth and morphology of these crystals.
3 63 Despite the biological interest in Ammonium acid urate crystals, surprisingly little is known about its growth and characterisation, although the solubility has been more interestingly studied (Marshalf and Robertson 1976, Porter 1963 b). The present work describes the growth conditions of these crystals in sodium metasilicate gel under ambient conditions. The effects due to the change of concentration of the reactions, the density of gel and the ph of the gel solution impregnated with the inner reactants on the growth of the crystals have also been investigated and discussed. In view of the varied occurrence of ammonium acid urate and its importance in endemic children s bladder stone formation, a knowledge of its precipitation from gel technique would be useful to study growth conditions of crystals found in urinary systems. 5.2 EXPERIMENTAL A sodium meta silicate solution (Baker analysed) of densities ranging from 1.03 to 1.06 g/cc were prepared from the stock solution. Uric acid solution was prepared (200mg in 100ml) in hot water. The ph of the solution was maintained between 3 to 6 by treating it with glacial acetic acid (BDH-Analar). The sodium meta silicate solution of known density 1.03 g/cc and the uric acid solutions (United States chemical) were mixed in the ratio 2:1. The gel solutions thus prepared were transferred into 25 x 300 mm Borosil test tubes adding about 30 ml mixtures to each tube. Sometimes small test tubes were also used. After the gelation along with the mixtures at room temperature (25 *C), 20 ml of 10% acetic acid is poured carefully over the gel. The tubes were covered with cork stoppers and allowed to stand at room temperature for crystallization. Completion of crystallization took about 30 to 40 days. White tabular crystals of different sizes are obtained for the above case. The crystals grown in test tubes are shown in Fig 5.1. Because of the continuous diffusion of outer solution into the gel medium white precipitate is formed just below the interface. At the same time within a period of 2 to 3 weeks tabular crystals of anhydrous uric acid are formed throughout the bottom portion of the test tube. The same result was obtained when we used U tube apparatus.
4 64 In a variation of the above procedure, uric acid-gel mixtures, ph 5, were used to set the gel as above in U tubes. Then the solution of the uric acid (20ml) prepared by taking 250mg of uric acid in 50 cc of 0.2 N NaOH solution (Merk-purified pellet) was poured on the top of the gel in one leg of the U tube, while in the other leg a 10% HC1 acid solution was poured. The reaction takes place slowly and within a fortnight, tiny crystallites are found to grow just below the gel solution interface of the leg which had uric acid solution and later in the bent portion of the U tube. In one experiment with the gel solution of density 1.03 g/cc acetone was mixed in a ratio 5:1 and the ph of the gel solution was adjusted to 4 or 4.5 with 3M acetic acid and taken in a test tube or U tube and allowed to set. The supernatant solution UA/NaOH was poured carefully on the set gel. In this case hydrated uric acid crystals are found to grow (Fig.5.2). After the completion of each experiment, crystalline products were harvested from the gels by decanting of the supernatant solution and washed in distilled water. The harvested crystals are observed by optical microscopy and separated into various groups. X-ray patterns were obtained for a portion of each group to enable identification of the phases using a Philips APD 3600 automated powder diffractometer (CuKa radiation = nm), by scanning electron microscopy and by infrared absorption spectroscopy with a P.E. 980, ratio recording dispersive instrument. In order to minimise dehydration of UA 2H2O, X- ray diffraction patterns were recorded from moist samples. In order to grow ammonium acid urate crystals in sodium meta silicate gel, a gel solution of density 1.04 gm/cc is prepared from the stock solution. In the growth of ammonium acid urates 20 ml of ammonium chloride is used as the inner reactant. The gel solutions impregnated with the inner reactant are acidified with 3M acetic acid and taken in straight tubes of 2.5 cm diameter and 23 cm length. The period of gelation varied from 12 hours to 24 hours. A solution of uric acid is used as the outer reactant. The outer
5 65 reactant diffused into the gel medium and immediately the reactions are taking place between inner and outer reactants. The expected reaction during the process of crystallization is C5H4N403 + NH4C > C5H7N5O3 + HC1 The experiment is repeated by changing various parameters like the concentration of reactants, the ph of the gel solution and the density of the gel solution. The effects of these parameters on the growth of ammonium acid urate crystals are discussed. The gel grown crystals were characterised by powder X-ray diffraction pattern and identified as C5H7N5O3 by comparison with known patterns from the ASTM index. 5.3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Crystal Growth The anhydrous crystals grew throughout the gel as white tabular reaching diameter up to 1 mm over 4 to 6 weeks period. The hydrated crystals of maximum size 0.8 mm are also grown in our experiment for the above period. Table 5.1 summarises the results of the experiments with and without uric acid in gel phase and dilute acids or uric acid in the overlying solution. It also gives the amounts of uric acid that are to be chosen to crystallize the hydrate or anhydrous phase. When uric acid dissolved in hot water was taken with the gel at ph=5 and UA/NaOH in one arm of the U tube and dil. HC1 (10%) in the other arm, it was observed that minute crystallites are formed first in the portion below the gel interface of UA/NaOH solution side at a temperature below 20 C. When the crystals grown with the above conditions are allowed for fairly a longer time it was found that the minute crystallites in the upper region of gel column grew into agglomerated orthorhombic uric acid crystals. At the same time, low solution concentration of the uric acid in the bent portion of the U tube facilitates the growth of anhydrous monoclinic uric acid crystals and has the similar situation as the growth of
6 Figure 5-3 Figure 5-2
7 67 anhydrous uric acid crystals grown in test or U tube at ph = 5, when UA/hot was taken as inner reactant and dil. HCI as the outer reactant. Table 5.1 Product with various reagents in U - tube experiments ph Inner reactants Outer reactants 3.5 UA/NaOH dil. HCI (on both limbs) 4.0 UA/NaOH dil. acetic (on both limbs) 4.0 Acetone UA/NaOH (both limbs) Product uric acid Anhydrous Anhydrous Hydrated Size of the crystal up to 1 mm.3 to.8 mm.2 to.6 mm 4.5 Acetone UA/NaOH Hydrated.2 to.8 mm 5.0 UA/hot dil. HCI (on both limbs) 5.0 UA/hot UA/NaOH (on one limb) dil. HCI (on the other limb) Anhydrous Hydrated Anhydrous.2 to.6 mm.2 to.6 mm.2 to.6 mm 6.0 UA/hot dil. HCI Anhydrous.2 to.8 mm UA/hot - 200mg in 100ml hot water; UA/NaOH - 250mg in 50ml 0.2 NaOH, dil NaOH = 10%, dilute acetic acid = 10%, acetone = 10ml. Thus it is observed that uric acids of both the phases are found to grow in the same experiment (Fig.5.3). Moreover, the hydrated orthorhombic uric acid crystals whose solubility is greater than anhydrous uric acid are formed first. This is true because when the formation of several phases is possible the one with the highest solubility will form first and transform sooner or later to the thermodynamically most stable phase (Ostwald, 1897, Lamerwin and Nancollas
8 ). In the present investigation, however, the author has not observed the modification of orthorhombic uric acid to monoclinic uric acid and vice versa because the crystals formed are more stable in the medium. The monoclinic anhydrous crystals that appear in the bent portion remain as the stable anhydrous uric acid because of the acidic environment (Rinaudo ef al 1984) that prevail in the bent portion of the U tube and the hydrated uric acid crystals just below the gel interface are stable in alkaline or neutral environment at low temperature (Babic-Ivancic et al 1987, Shirley 1966). X-ray diffraction analysis of crystals extracted from gel confirmed that the crystals harvested from the upper portion of the tube and bent portion of the tube are respectively the hydrated and anhydrous crystals. Thus the simultaneous growth of two phases of uric acid crystals are found in gel growth experiment (Irusan et al 1993 c). The same process occurs in human stones made up of both the uric acids (Lonsdale and Mason 1966). The spherulitic types of crystals grown in our study have been viewed by SEM (Fig.5.4) and these crystals are found to consist of number of needle like crystals showing the characteristic behaviour of the grown crystals in gel (Morse and Donnay 1936). The size and crystal habit of uric acid grown in gels are affected by temperature, concentration of reactant and ph. In the present study, at far below the room temperature (20* C) in silica gel medium, the sole crystalline products are tabular or spherulitic and at a higher temperature they are needle shaped. The crystallization of ammonium acid urate in gel is due to the chemical reaction between the inner reactant impregnated into the gel solution and the outer reactant diffused into the gel medium. In respect of ammonium acid urate due to the chemical reaction between the inner and outer reactants, pale yellow crystals are formed just below the interface. Crystals of platelet and hexagonal morphology were found to grow within two to three weeks (Irusan et al 1993 a). In the U tube method suggested by Henisch et al (1965 b), it is found that a few crystals are formed as clusters. Crystals that grow at or near the surface of the gel tend to form spherical aggregates of ammonium urate rather than growing
9 uniformly. However, at a depth ranging from 1-30 mm beneath the gel interface crystals show hexagonal morphology. The crystals are lemon yellow in colour and transparent with perfect edges as shown in Fig.5.5. Most of the crystals are prismatic and well faceted. The maximum size of the harvested crystals in straight tube is 8.9 x 2.8 x 1 mm Effects due to change of growth parameters Effect of ph ph is the key factor in gel technique producing interesting effect on the growth of uric acid systems in sodium metasilicate gel at ambient temperature. The crystallization is possible in case when the ph of the gel solution is between 3 to 6. Tabular and spherulitic types of crystals are obtained when the ph is 3.5 to 5.5 and for ph 6 twin crystals are formed. When the ph is less than 3 or greater than 6 crystallization is not at all possible. Hence in the case of uric acid, the change of ph has control over the growth phenomenon. At very low ph values only single hair-like crystals are obtained. The crystals grown at various ph values are tabulated. The ph of the gel solution impregnated with the inner reactants is varied in the range of 3.5 to 7 in steps of 0.5 in the growth of ammonium acid urate. Even though the crystallization is obtained in all the above ph ranges larger number of single crystals of smooth surfaces are obtained when the ph is 5. The crystallization is very poor at higher ph values. A number of well defined crystals of Ammonium acid urate are obtained when the ph is 4. In general there is no pronounced effect due to the variation of the ph of the gel solution impregnated with the inner reactant in the range of 4 to 5. Both the hexagonal and rhombohedral crystals are obtained in this range. Figure 5.6 shows the SEM photograph of the Ammonium acid urate crystals harvested in 30 days (ph = 4).
10 Effect of gel density The gel densities ranging from 1.02 to 1.08 were prepared from the stock solution keeping the gel ph constant at 5. When the gel density is 1.06 g/cc, the number of crystals is reduced very much. Decrease in the nucleation density has been observed when we increase the gel density. The gelation has also its effective role in the growth of uric acid crystals. The effects due to the variation of gel density on the growth of ammonium urate crystals were studied. The density of the gel solution is varied in the range of 1.02 to 1.0 gm/cc. Crystallisation of Ammonium acid urate crystals is observed in the range between 1.02 to But the most favourable gel density for obtaining good crystals is 1.04 gm/cc. Above this concentration the gel inclusions are observed and the growth rate is small. Most of the crystals formed are hexagonal and their size varies from the interface to deep inside gel column. The ageing of gels has profound effect on the quality and morphology of the crystals. The outer electrolyte was added after different ageing of the gel. Only very small crystals were seen and the growth rate is also low. Since the pore size distribution of the gel is affected by ageing: the growth rate is drastically reduced (Henisch 1970). But it is observed that the more aged gels produced more perfect crystals. Experiments on the growth of Ammonium urate results in excessive nucleation and the successful growth of these crystals depends on the supersaturation Effect of temperature The growth of uric acid crystals in gel is temperature dependent. The crystals can only be grown in gel when the temperature of the growth system is less than 38 *C. No nucleation can be observed when the temperature is above 38 *C. Growth is favourable when the temperature is between 20 C to 25 *C. Number of crystals formed becomes lesser and lesser when the temperature is increased
11 71 from 30 to 38 * C. Hydrated crystals are grown well at a temperature of 20 C. The modification from hydrated uric acid phase to anhydrous is very much influenced by the change of temperature. This investigation has shown that uric acids of both the phases can be crystallized using silica gel under proper conditions of ph, temperature and the reactant concentrations Effect of concentration of the reactants If the concentration of the inner reactant (Ammonium chloride) for the growth of ammonium urate is changed in the range of 0.25M to 1 M it is observed that the crystallization is effective. Crystals of hexagonal, rhombohedral and platelet morphology have been found to grow when the concentration of inner reactant is kept constant and the outer reactants are varied from 0.25M to 0.75M. Crystallisation is observed to be mainly depending upon the relative concentration of the outer reactant. It is noticed that when the concentration of the outer reactant (uric add) is less than 0.25M crystallization is not at all observed. A number of isolated, transparent good crystals are obtained when the concentration of inner and outer are 0.75M and 0.5M respectively. Platelet crystals were obtained when 0.25M ammonium chloride was used as the inner and 0.5M uric acid as outer reactant. Thus the concentration of inner and outer electrolyte have distinct influence on the growth of Ammonium urate crystals Effect of impurities The effect of different ions such as lead, cadmium, magnesium and pyrophosphate and juices of some medicinal plants like ocimum sanctum on the growth of ammonium urate crystals were also studied. The presence of magnesium and pyrophosphate produced an alteration of crystal habit and stunting of the growth. No appreciable effects had been noted with other ions.
12 CONCLUSION It has been proved by experiment that the difficultly soluble crystals of uric acids and ammonium acid urate can be grown from gel under ambient conditions. The uric acid crystals are found to be white in colour with spherulitic and platelet morphology. But ammonium acid urate crystal is pale yellow in colour with shining surfaces. The hydrated orthorhombic modification is obtained only when the ph and the temperatures are very low. Experiments showed that uric acid which has a low aqueous and organic solubility can be used to determine the conditions under which crystals already formed can be dissolved, modified or inhibited from the view point of devising new treatment and means to control the disease. X - ray diffraction studies have been done and the lattice parameters of respective crystals are found to be in good agreement with the reported values.
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
CRYSTAL GROWTH, MORPHOLOGICAL, THERMAL AND DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTAL
 CRYSTAL GROWTH, MORPHOLOGICAL, THERMAL AND DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTAL R. Selvaraju 1, & S. Sulochana 2 Engineering physics (FEAT), Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608002
CRYSTAL GROWTH, MORPHOLOGICAL, THERMAL AND DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTAL R. Selvaraju 1, & S. Sulochana 2 Engineering physics (FEAT), Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608002
Engineering Physics, FEAT, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar
 Crystal Growth, Functional, Thermal and Optical Characterizations of Pure and Cobalt Doped Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystals by Single Diffusion Gel Method R. Selvaraju 1, S. Sulochana 2, M. Bhuwaneswari
Crystal Growth, Functional, Thermal and Optical Characterizations of Pure and Cobalt Doped Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystals by Single Diffusion Gel Method R. Selvaraju 1, S. Sulochana 2, M. Bhuwaneswari
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
» Croscarmellose Sodium is a cross linked polymer of carboxymethylcellulose sodium.
 BRIEFING Croscarmellose Sodium, NF 22 page 2856 and page 702 of PF 30(2) [Mar. Apr. 2004]. A modification is made in the test for Degree of substitution to correct the endpoint color to agree with the
BRIEFING Croscarmellose Sodium, NF 22 page 2856 and page 702 of PF 30(2) [Mar. Apr. 2004]. A modification is made in the test for Degree of substitution to correct the endpoint color to agree with the
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases. (Phenolphthalein)
 Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
MONOGRAPHS (USP) Saccharin Sodium
 Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR
 1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. NCERT
 Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Pectins. Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Pectins This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive Specifications.
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Pectins This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive Specifications.
Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN
 Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN PRINCIPLE SCOPE Many modifications of the Kjeldahl method have been accepted for the estimation of protein in organic materials. It comprises sample oxidation and conversion
Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN PRINCIPLE SCOPE Many modifications of the Kjeldahl method have been accepted for the estimation of protein in organic materials. It comprises sample oxidation and conversion
Topic Objectives. Physical Examination LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE. Appearance. Odor Specific Gravity Volume
 LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
(Writing model for laboratory note book)
 Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
TECHNICAL METHODS GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN. aspirated and examined as well.
 J. clin. Path. (1950), 3, 152. TECHNICAL METHODS THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE BY From the Pathological Depariment, Salisbury General Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
J. clin. Path. (1950), 3, 152. TECHNICAL METHODS THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE BY From the Pathological Depariment, Salisbury General Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
The organic matrix of gallstones
 Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
INTERNATIONAL ŒNOLOGICAL CODEX. BENTONITES Bentonita N SIN: 558 (Oeno 11/2003 modified Oeno )
 BENTONITES Bentonita N SIN: 558 (Oeno 11/2003 modified Oeno 441-2011) 1. OBJECT, ORIGIN AND FIELD OF APPLICATION Bentonites are hydrous aluminium silicates belonging to the montmorillonite group. The brute
BENTONITES Bentonita N SIN: 558 (Oeno 11/2003 modified Oeno 441-2011) 1. OBJECT, ORIGIN AND FIELD OF APPLICATION Bentonites are hydrous aluminium silicates belonging to the montmorillonite group. The brute
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg CAUTION. Abnormal Crystals of Metabolic Origin. Unit 2; Session 5. Abnormal crystals
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
MONOGRAPHS (NF) Pharmacopeial Forum 616 HARMONIZATION Vol. 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]
![MONOGRAPHS (NF) Pharmacopeial Forum 616 HARMONIZATION Vol. 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005] MONOGRAPHS (NF) Pharmacopeial Forum 616 HARMONIZATION Vol. 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]](/thumbs/86/93540561.jpg) 616 HARMONIZATION Vol. 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005] the recorder. The substances are eluted in the following order: o-toluenesulfonamide, p-toluenesulfonamide, and caffeine. The test is not valid unless the
616 HARMONIZATION Vol. 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005] the recorder. The substances are eluted in the following order: o-toluenesulfonamide, p-toluenesulfonamide, and caffeine. The test is not valid unless the
Biochemical Techniques 06 Salt Fractionation of Proteins. Biochemistry
 . 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
. 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units
 6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units Change 1. Content Uniformity, 3. Criteria and Table 6.02-2 as follows: 1. Content Uniformity Select not less than 30 units, and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units Change 1. Content Uniformity, 3. Criteria and Table 6.02-2 as follows: 1. Content Uniformity Select not less than 30 units, and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
Purity Tests for Modified Starches
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones. Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019
 The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019 Urinary Calculi Prevalence and incidence of kidney stones increasing across the world Environmental
The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019 Urinary Calculi Prevalence and incidence of kidney stones increasing across the world Environmental
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム
 Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Date... Name... Group... Urine sample (Tube No 2)
 Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products)
 Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
» Monohydrate Citric Acid contains one molecule of water of hydration. It contains not less than 99.5 percent and not more than 100.
 BRIEFING Citric Acid, Monohydrate. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Citric Acid, Monohydrate monograph,
BRIEFING Citric Acid, Monohydrate. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Citric Acid, Monohydrate monograph,
SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 ISBN 978-0-626-31165-0 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Water Sulfide content Published by SABS Standards Division 1 Dr Lategan Road Groenkloof Private Bag X191 Pretoria 0001 Tel: +27 12 428 7911 Fax: +27
ISBN 978-0-626-31165-0 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Water Sulfide content Published by SABS Standards Division 1 Dr Lategan Road Groenkloof Private Bag X191 Pretoria 0001 Tel: +27 12 428 7911 Fax: +27
Effect of fluoride on the crystallization and spectral properties of cholesterol
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 49, August 2011, pp. 539-544 Effect of fluoride on the crystallization and spectral properties of cholesterol P Kanchana 1 & C Sekar 2 * 1 Department of Physics,
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 49, August 2011, pp. 539-544 Effect of fluoride on the crystallization and spectral properties of cholesterol P Kanchana 1 & C Sekar 2 * 1 Department of Physics,
Petrolatum. Stage 4, Revision 1. Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum.
 1 001-1208PDG.pdf Petrolatum Stage 4, Revision 1 Definition Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum. It may contain a suitable antioxidant. Description and Solubility
1 001-1208PDG.pdf Petrolatum Stage 4, Revision 1 Definition Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum. It may contain a suitable antioxidant. Description and Solubility
Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: 1. Introduction 1.1. Nature, Mechanism of Action, and Biological Effects (Fig. 1)
 7 Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: Nitrate; nitrite; methemoglobin; blood pressure; asphyxia; spinach; spongy cadmium column; zinc metal; sodium nitrate; sodium nitrite; ammonia buffer solution; Jones reductor.
7 Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: Nitrate; nitrite; methemoglobin; blood pressure; asphyxia; spinach; spongy cadmium column; zinc metal; sodium nitrate; sodium nitrite; ammonia buffer solution; Jones reductor.
HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- REDUCING SUGARS. MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF
 XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF REDUCING SUGARS. By CHARLES SAMUEL HANES (Junior Scholar of the Exhibition of 1851). From the Botany
XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF REDUCING SUGARS. By CHARLES SAMUEL HANES (Junior Scholar of the Exhibition of 1851). From the Botany
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Sample Paper 2 Solution
 Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Sample Paper 2 Solution I. 1. (b) When elements or compounds are mixed, a mixture is obtained. The proportion of the constituents of a mixture is not fixed. The
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Sample Paper 2 Solution I. 1. (b) When elements or compounds are mixed, a mixture is obtained. The proportion of the constituents of a mixture is not fixed. The
E55A GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina
 00-0PDG.pdf 0 0 0 0 EA GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina DEFINITION Purified protein obtained from collagen of animals (including fish and poultry) by partial alkaline and/or acid hydrolysis, by enzymatic
00-0PDG.pdf 0 0 0 0 EA GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina DEFINITION Purified protein obtained from collagen of animals (including fish and poultry) by partial alkaline and/or acid hydrolysis, by enzymatic
Methotrexate. (Ph. Eur. monograph 0560) C 20 H 22 N 8 O Action and use. Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor; cytostatic.
 Browse: British Pharmacopoeia 2013 British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances Methotrexate Methotrexate General Notices (Ph. Eur. monograph 0560) C 20 H 22
Browse: British Pharmacopoeia 2013 British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances Methotrexate Methotrexate General Notices (Ph. Eur. monograph 0560) C 20 H 22
--> Buy True-PDF --> Auto-delivered in 0~10 minutes. GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB1886.
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB1886.235-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA National Food
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB1886.235-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA National Food
SALIVA TEST Introduction
 SALIVA TEST Introduction This is a practical lesson using saliva to learn digestive enzyme activity. We can check the existence of reducing sugars clearly by Benedict s reaction after salivary enzyme decomposes
SALIVA TEST Introduction This is a practical lesson using saliva to learn digestive enzyme activity. We can check the existence of reducing sugars clearly by Benedict s reaction after salivary enzyme decomposes
19 Nosiheptide S O. For chickens (excluding broilers) For broilers. Finishing period broilers Growing period broilers. Stating chicks Growing chicks
 19 osiheptide H S H H S S H H 2 H S S H S H H H [Summary of nosiheptide] C 51 H 43 13 12 S 6 MW: 1222 CAS o.: 56377-79-8 osiheptide (H) is a polypeptide antibiotic obtained by the incubation of Streptomyces
19 osiheptide H S H H S S H H 2 H S S H S H H H [Summary of nosiheptide] C 51 H 43 13 12 S 6 MW: 1222 CAS o.: 56377-79-8 osiheptide (H) is a polypeptide antibiotic obtained by the incubation of Streptomyces
EFFECT OF SOLVENTS ON PARTICLE STRUCTURE, MORPHOLOGY AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLES
 EFFECT OF SOLVENTS ON PARTICLE STRUCTURE, MORPHOLOGY AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLES A.Vanaja 1 and K.Srinivasa Rao 2 1 Department of Physics, Lingayya s University, Old Faridabad, Haryana,
EFFECT OF SOLVENTS ON PARTICLE STRUCTURE, MORPHOLOGY AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLES A.Vanaja 1 and K.Srinivasa Rao 2 1 Department of Physics, Lingayya s University, Old Faridabad, Haryana,
Management of common uroliths through diet
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERIZATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANO- PARTICLES
 88 CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERIZATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANO- PARTICLES 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the characterization of ZnO nano-particles using FTIR, XRD, PSA & SEM. The results analysis and interpretations
88 CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERIZATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANO- PARTICLES 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the characterization of ZnO nano-particles using FTIR, XRD, PSA & SEM. The results analysis and interpretations
This revision also necessitates a change in the table numbering in the test for Organic Impurities.
 Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 27 Jul 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 27 Jul 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical
BRIEFING. Nonharmonized attributes: Identification, Heavy metals, Characters, Labeling, Bacterial endotoxins, Sterility, Storage.
 BRIEFING Citric Acid, Anhydrous, page 872 of PF 28(3) [May June 2002]. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the
BRIEFING Citric Acid, Anhydrous, page 872 of PF 28(3) [May June 2002]. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
How do we detect PEDs?
 How do we detect PEDs? Drug Testing https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dq5pvabzpxq Urine sample Blood sample Detection of drug metabolites The Excretory System Urine is excreted from bladder via the urethra
How do we detect PEDs? Drug Testing https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dq5pvabzpxq Urine sample Blood sample Detection of drug metabolites The Excretory System Urine is excreted from bladder via the urethra
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* Previous studies (1, 2) have shown that after the ingestion of caffeine
 A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES.
 XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI)
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(1), 2013, 457463 ISSN 0972768X www.sadgurupublications.com PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI) SUMAN PARIHAR a, PRASOON HADA
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(1), 2013, 457463 ISSN 0972768X www.sadgurupublications.com PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI) SUMAN PARIHAR a, PRASOON HADA
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, iv. J.
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN III. PREPARATION OF ACTIVE CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM INACTIVE DENATURED PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton,
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN III. PREPARATION OF ACTIVE CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM INACTIVE DENATURED PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton,
NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention
 NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Epidemiology Prevalence 2-3%, maybe in
NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Epidemiology Prevalence 2-3%, maybe in
ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) ARTESUNATI COMPRESSI ARTESUNATE TABLETS
 December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human
 3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
G/LITRE 5.0 g KOH g 0.5 g 0.05 g 0.01 g MgS047H20 NaCl CaCl2
 A P P E N D IX -V III COMPOSITION OF USED MEDIA AND CHEMICAL REAGENTS 1. NITROGEN FREE BROMOTHYMOL BLUE (NFB) MEDIUM Dobereiner et al (1976) Same media was also used to check the effect of temperature
A P P E N D IX -V III COMPOSITION OF USED MEDIA AND CHEMICAL REAGENTS 1. NITROGEN FREE BROMOTHYMOL BLUE (NFB) MEDIUM Dobereiner et al (1976) Same media was also used to check the effect of temperature
THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE
 THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE BY P. A. LEVENE AND R. STUART TIPSON (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York) (Received for publication, March 13, 1935) The 2-desoxy-ribose
THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE BY P. A. LEVENE AND R. STUART TIPSON (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York) (Received for publication, March 13, 1935) The 2-desoxy-ribose
EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH
 Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN)
 CJ Shuster AP2 Lab Addenum Kidney Dissection 1 The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN) BACKGROUND INFORMATION The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary
CJ Shuster AP2 Lab Addenum Kidney Dissection 1 The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN) BACKGROUND INFORMATION The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS ABSTRACT
 EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
Quantitative Identification of Urinary Calculi
 Quantitative Identification of Urinary Calculi Reid H. Leonard and Arthur J. Butt HE USUAL METHODS of identification of urinary calculi are based upon qualitative chemical reactions (1, 2, 3). These methods
Quantitative Identification of Urinary Calculi Reid H. Leonard and Arthur J. Butt HE USUAL METHODS of identification of urinary calculi are based upon qualitative chemical reactions (1, 2, 3). These methods
HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE
 002-0901PDG.pdf HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE Compared to the Stage 4, document the following changes are proposed: 1. Assay: a determination of the
002-0901PDG.pdf HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE Compared to the Stage 4, document the following changes are proposed: 1. Assay: a determination of the
CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM
 79 CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM 5.1 INTRODUCTION Urea and Uric acid are the metabolic nitrogenous wastes present in the body that can be measured in blood and urine. Serum
79 CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM 5.1 INTRODUCTION Urea and Uric acid are the metabolic nitrogenous wastes present in the body that can be measured in blood and urine. Serum
BRIEFING. Pharmacopeial Discussion Group Sign Off Document Attributes EP JP USP Definition Identification B Identification C + + +
 BRIEFING Edetate Calcium Disodium, USP 29 page 779. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Edetate Calcium Disodium
BRIEFING Edetate Calcium Disodium, USP 29 page 779. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Edetate Calcium Disodium
Compliance. Should you have any questions, please contact Behnaz Almasi, Associate Scientific Liaison ( or
 Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 30 Mar 2018 Official Date 01 Apr 2018 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 30 Mar 2018 Official Date 01 Apr 2018 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Preparation of Penicillins by Acylation of 6-Aminopenicillanic acid with Acyl Chlorides Week One: Synthesis
 Preparation of Penicillins by Acylation of 6-Aminopenicillanic acid with Acyl Chlorides Week One: Synthesis Wear gloves during this experiment. Dissolve 1.05g of sodium bicarbonate in 12mL of acetone:
Preparation of Penicillins by Acylation of 6-Aminopenicillanic acid with Acyl Chlorides Week One: Synthesis Wear gloves during this experiment. Dissolve 1.05g of sodium bicarbonate in 12mL of acetone:
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.85-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.85-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.85-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.85-2016
10 Sulfaquinoxaline H N O S O. 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: CAS No.:
 10 Sulfaquinoxaline N N H N O S O NH 2 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: 300.33 CAS No.: 59-40-5 Outline of sulfaquinoxaline Sulfaquinoxaline is light yellow to brownish
10 Sulfaquinoxaline N N H N O S O NH 2 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: 300.33 CAS No.: 59-40-5 Outline of sulfaquinoxaline Sulfaquinoxaline is light yellow to brownish
Supporting information for the manuscript
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for the manuscript Toward enhanced photoactivity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for the manuscript Toward enhanced photoactivity
Structural and luminescent properties of ZnO flower-like microstructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method
 Structural and luminescent properties of ZnO flower-like microstructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, FB Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University
Structural and luminescent properties of ZnO flower-like microstructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, FB Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University
RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
Lesson Overview. The Excretory System. Lesson Overview The Excretory System
 Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Revision Bulletin 23 Feb Mar 2018 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Compliance
 Esomeprazole Magnesium Delayed-Release Capsules Type of Posting Posting Date Official Date Expert Committee Reason for Revision Revision Bulletin 23 Feb 2018 01 Mar 2018 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3
Esomeprazole Magnesium Delayed-Release Capsules Type of Posting Posting Date Official Date Expert Committee Reason for Revision Revision Bulletin 23 Feb 2018 01 Mar 2018 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords.
 The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 28, No. 3. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords. MASAMI BY SUZUKI. (From the Medico-Chemical Institute, Hokkaido Imperial
The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 28, No. 3. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords. MASAMI BY SUZUKI. (From the Medico-Chemical Institute, Hokkaido Imperial
STABILITY INDICATING ASSAY. differentiate an intact drug from its potential decomposition products 425.
 .1. INTRODUCTION.1.1 STABILITY INDICATING ASSAY The stability - indicating assay is a method that is employed for the analysis of stability samples in pharmaceutical industry. It is essential to validate
.1. INTRODUCTION.1.1 STABILITY INDICATING ASSAY The stability - indicating assay is a method that is employed for the analysis of stability samples in pharmaceutical industry. It is essential to validate
URINARY CRYSTALS. by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown
 URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
CHEMO-IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON CONJUGATED CARBOHYDRATE-PROTEINS IV. Tm~ SX~TI~SlS of Tm~ p-amn~obenzx~ ETm~R OF THE SOLUBLE
 Published Online: 1 September, 1931 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.54.3.431 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 31, 2018 CHEMO-IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON CONJUGATED CARBOHYDRATE-PROTEINS IV.
Published Online: 1 September, 1931 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.54.3.431 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 31, 2018 CHEMO-IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON CONJUGATED CARBOHYDRATE-PROTEINS IV.
FIXATION OF TISSUES MODULE 5.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 5.2 AIMS OF FIXATION 5.3 PRINCIPLE OF FIXATION. Notes
 MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers
 The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers Yimin Qin, Huiqun Hu, Aixiang Luo The Biochemical Materials Research and Development Center, Jiaxing College,
The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers Yimin Qin, Huiqun Hu, Aixiang Luo The Biochemical Materials Research and Development Center, Jiaxing College,
SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine
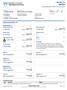 1-800-533-1710 SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine Patient ID Patient Name SAMPLEREPORT, SAT24 NORMAL Birth Date 1976-05-13 Gender M Age 40 Order Number Client Order Number Ordering Physician
1-800-533-1710 SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine Patient ID Patient Name SAMPLEREPORT, SAT24 NORMAL Birth Date 1976-05-13 Gender M Age 40 Order Number Client Order Number Ordering Physician
By Authority Of THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Legally Binding Document
 By Authority Of THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Legally Binding Document By the Authority Vested By Part 5 of the United States Code 552(a) and Part 1 of the Code of Regulations 51 the attached document has
By Authority Of THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Legally Binding Document By the Authority Vested By Part 5 of the United States Code 552(a) and Part 1 of the Code of Regulations 51 the attached document has
Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x
 J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
PAPER No.5: Forensic Chemistry & Explosives MODULE No. 12 : Blood Alcohol Estimation
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag PAPER: 5, Forensic Chemistry & Explosives MODULE: M12, Blood alcohol estimation FS_P5_M12 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Sample Collection
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag PAPER: 5, Forensic Chemistry & Explosives MODULE: M12, Blood alcohol estimation FS_P5_M12 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Sample Collection
BIOL 347L Laboratory Three
 Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
The Nitrofurantoin Capsules Revision Bulletin supersedes the currently official monograph.
 Nitrofurantoin Capsules Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 28 Dec 2018 Official Date 01 Jan 2019 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 1 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
Nitrofurantoin Capsules Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 28 Dec 2018 Official Date 01 Jan 2019 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 1 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: Vol.8, No.6, pp , 2015
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.8, No.6, pp 297-302, 2015 Effect on Annealing Temperature on Zno Nanoparticles Sugapriya S* 1, Lakshmi S 1, Senthilkumaran
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.8, No.6, pp 297-302, 2015 Effect on Annealing Temperature on Zno Nanoparticles Sugapriya S* 1, Lakshmi S 1, Senthilkumaran
