Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI): More than a skin deep review. Vicky Parente, MD Sea Pines Conference July 12th, 2018
|
|
|
- Claire McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI): More than a skin deep review Vicky Parente, MD Sea Pines Conference July 12th, 2018
2 Objectives To review the anatomy and classification of SSTIs To understand the approach to diagnosis and management of commonly encountered pediatric SSTIs To incorporate recent evidence into management of SSTIs in children Role of antibiotics Role of adjunctive laboratory testing
3 ANATOMY AND CLASSIFICATION
4 Anatomy
5 Classification Superficial Impetigo Cellulitis Erysipelas Abscess (furuncles, carbuncles) Deep/Necrotizing Necrotizing fasciitis Pyomyositis Osteomyelitis Non-necrotizing Mild/moderate Responsive to abx alone Necrotizing Life-threatening Systemic toxicity Tissue necrosis Requires surgical management Miscellaneous Animal Contact Orbital cellulitis Immunocompromised Hosts Surgical Site Infections (SSI)
6 Challenges in Management of SSTI Diagnosis Overlap in clinical presentation Severity of illness Can be subtle Antibiotic resistance patterns
7 SUPERFICIAL SSTI
8 Impetigo Anatomy: Epidermis Clinical Features Most common skin infection in the world Non-bullous (>70% of cases) Typically on face and extremities Follows local skin trauma Early vesicle/pustule becomes classic honeycrusted plaque Minimal surrounding erythema and few systemic sx Diagnosis Clinical
9 Impetigo Microbiology S. pyogenes (GAS) classic cause of non-bullous impetigo S. aureus now the most common cause of impetigo Management No labs necessary Mupirocin 2% ointment for limited number of lesions Indications for oral antibiotics : Multiple lesions, deeper involvement (cellulitis), perioral lesions
10 Erysipelas Anatomy: Superficial dermis Clinical Features: Prominent lymphatic involvement Raised, sharply demarcated borders Indurated and peau d orange appearance Young infants/children, older adults Classic: butterfly area of face; legs also common Microbiology: GAS most common Management: Penicillin Cephalosporin (1 st generation)
11 Cellulitis Acute spreading infection of the skin that extends deeper than erysipelas and involves the subcutaneous tissues Anatomy: Deep Dermis and Subcutaneous Tissues Clinical Features Diffuse inflammation with pain, warmth, erythema, edema Lack of sharply demarcated borders Regional lymphangitis and systemic symptoms possible Systemic symptoms may start hours before skin manifestations Hospital Pediatrics 2013;3;103
12 Diagnosis Cellulitis Diffuse cellulitis typically not amenable to culture Needle aspirates and punch biopsies not recommended 1-2 Ultrasound consider to help exclude occult abscess 6 Blood cultures low-yield in children and adults with cellulitis 3-4 Jeng A, Medicine (Baltimore) 2010;89: Stevens DL, Clin Infect Dis 2005;41: Sadow KB, Pediatrics 1998;101(3). Swartz MN, NEJM 2004;350(9): Squire BJ, Acad Emerg Med 2005;12:
13 Abscess Anatomy: Deep dermis and subcutaneous tissues Clinical Features Pus collection with painful, tender, fluctuant nodules Surface pustule with surrounding erythema and edema Furuncle, aka boil = infection of hair follicle Carbuncle = coalescence of furuncles to an inflamed mass
14 Abscess Diagnosis Clinical examination important but findings may be unreliable 5 Ultrasound can increase diagnostic accuracy 6 Culture of purulent fluid critical Microbiology S. aureus is primary pathogen in 25-50% of cases Often polymicrobial skin flora, bugs (GNR, anaerobes) from adjacent mucous membranes (e.g., perioral, perianal, groin)
15 Abscess Management Warm compresses Adequate for small furuncles I&D I&D alone adequate for simple abscesses Wound packing also may not be necessary Antibiotics Simple abscesses do not require antibiotics after I&D Adjunctive abx after I&D in certain situations Tailor abx based on culture and susceptibility patterns Include CA-MRSA coverage Hospitalization If rapidly progressive infection or systemic toxicity
16 EVIDENCE UPDATE: MANAGEMENT OF SSTI
17 Evidence Update: Management of SSTI Commonly encountered clinical questions: 1. When are antibiotics necessary? IV vs PO? 2. Is one class of antibiotics preferred over another? (Should I cover for MRSA?) 3. What additional testing is useful/high-yield?
18 I. Evidence Update: Antibiotics for SSTI SSTI are common (>14M clinic visits + >850K admissions annually) Serious complications can occur (bacteremia, need for surgical procedures, morbidity/mortality) Clinical presentation and severity of illness can be subtle Miller LG, N Engl J Med 2015;372: Lopez MA, Pediatrics 2013;131:e718
19 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: MRSA is common MRSA is most prevalent organism in SSTIs (59%) Many w/ca-mrsa have no RF Presence of RF for CA-MRSA raise suspicion but are not 100% reliable Moran GJ, NEJM 2006;366:
20 Peds study of empiric antibiotics Studies: for SSTIs Trends in invasive MRSA (infants!) Common cause of bacteremia in infants Empiric antibiotics often have gram negative coverage Page 20
21 Staph vs Strep: Classic Clinical Features CA-MSSA ( classic S. aureus) Pyogenic infections Localized swelling and erythema Less rapid with less systemic toxicity Streptococcus (usually GAS) Rapid onset (hours) Progressive, well-demarcated erythema along tissue planes Often associated lymphangitis Systemic symptoms (chills, fever) and toxicity CA-MRSA Mimics GAS rapid onset, systemic toxicity Very pyogenic infection
22 Community Acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) Oral Antibiotic Options Clindamycin TMP-SMX No activity against GAS Tetracyclines (Doxycycline, Minocycline) Linezolid Triple Coverage only with clindamycin or linezolid
23 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: Beta-lactams work just fine in the CA-MRSA era Diffuse, Non-culturable SSTIs Case-control study of 2096 patients at PCP clinic and ED sites All enrolled patients had non-drained, non-cultured SSTI High prevalence of MRSA (>50%) Conclusion: β-lactams are reasonable first-line agents for non-culturable outpatient SSTIs TMP-SMX associated with higher odds of treatment failure than β-lactams Clindamycin provides no additional benefit over β-lactams Elliott DJ, et al, Pediatrics 2009;123:e95
24 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: Draining pus matters more than the antibiotic Purulent, Culturable SSTIs RCT of 161 children with uncomplicated skin abscess at large peds ED Randomized to placebo vs TMP-SMX x 7-10 days after I&D No difference high success rate in both arms (94.7% vs 95.9%) More new lesions at 10 days in placebo (26% vs 13%) but not at 3 mo 129/161 (80.1%) had CA-MRSA, 13/161 (8.1%) MSSA Conclusion: I&D alone is adequate for simple abscess Placebo non-inferior to TMP-SMX after I&D of simple abscess Adjunctive abx are not necessary for drained simple abscesses Ann Emerg Med 2010; 55:
25 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: Even abx that don t work for MRSA are just fine as long as you drain pus Purulent, Culturable SSTIs RCT 200 patients with uncomplicated, PURULENT outpatient SSTI Randomized to clindamycin vs cephalexin 69% of cultured wounds MRSA+ 96% had drainage procedure (manual expression of pus or I&D) No difference in clinical outcomes (2-3 days and 7 days) Improvement in 94% of cephalexin and 97% of clindamycin groups Chen AE, et al, Pediatrics 2011;127:e573
26 Fine. MRSA is a common cause of abscesses and draining pus when present gives you more bang for your buck than antibiotics. But if MRSA is so common, shouldn t it also be a big cause of non-purulent cellulitis as well?
27 GABHS still the most common cause of cellulitis Design Prospective cohort 248 adults at an LA county hospital with diffuse cellulitis High prevalence of MRSA (>50%) 179 completed acute + convalescent titers for β-hemolytic strep (BHS) Results 73% had evidence (serology or +blood culture) of BHS infection 96% of patients who got 1 dose anti-mrsa abx responded to β-lactams Includes 27% of patients who had no evidence of BHS Bottom Line BHS is still predominant cause of diffuse, non-culturable cellulitis MSSA more important than MRSA in diffuse cellulitis Empiric treatment with β-lactams effective for most cases
28 Cellulitis Jeng, A; Medicine (Baltimore) 2010;89:217
29 2011 IDSA Guidelines Mgmt of MRSA I&D alone for simple cutaneous abscesses Antibiotics only for certain situations when treating abscess Definitive conclusion on role of antibiotics (if any) unknown Purulent cellulitis empiric anti-mrsa abx x 5-10 days Non-purulent cellulitis empiric anti-strep abx x 5-10 days Expand to cover CA-MRSA if no response or systemic toxicity
30 Abscess
31 Newest Guideline 2014 IDSA SSTI Guideline Clarity around cellulitis gone is the purulent cellulitis term Skin abscess with surrounding redness, warmth, tenderness = abscess with surrounding inflammation, not abscess with surrounding cellulitis Is this an important distinction or just semantics? Primary therapy for pus = drainage Primary therapy for cellulitis = antibiotics aimed at streptococci (except in specific circumstances) MRSA is an unusual cause of typical cellulitis, even if MRSA SSTI rates are high For cellulitis, cover for MRSA only if: Penetrating trauma, MRSA elsewhere (including nasal swab), IVDU, immunosuppressed?, SIRS? Recommended duration for cellulitis: 5 days, as long as patient improving Slide courtesy of Dr. Tom Holland
32
33 Recent studies also supportive of guidelines Clindamycin vs TMP-SMX for uncomplicated SSTI RCT of 524 patients at urgent cares, EDs, and 4 US sites 6 months 85 years old; mean age 27; 30% children Cellulitis and/or abscess (30% abscess only; 15% abscess + cellulitis) Clindamycin or TMP-SMX given for 10 days to primary outcome of clinical cure at 7-10 days post-treatment Conclusion: no difference in cure rates or adverse events N Engl J Med 2015;372: Ann Int Med; ACP Journal Club Jul 21, 2015
34 Wait now TMP-SMX is maybe better than I&D?!? TMP-SMX vs Placebo for Uncomplicated Skin Abscess RCT of 1265 patients at 5 US sites with uncomplicated skin abscess that were incised and drained Following I&D, randomized to TMP-SMX or placebo x 7 days Median age 35 (range 14-73); 45% +MRSA wound cultures Primary outcome: clinical cure at 7-14 days post-treatment TMP-SMX group cure rate 6.9% higher than placebo group N Engl J Med 2016;374:
35 Enough with the evidence what s the bottom line?
36 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: Clinical Bottom Line Pus matters If purulent think Staph (include MRSA) If non-purulent think Strep Always I&D and obtain culture data whenever possible Antibiotics not absolutely necessary after I&D of uncomplicated abscesses If given, tailor abx based on culture results
37 I. Antibiotics for SSTI: Clinical Bottom Line Cephalosporins are reasonable first-line agents for uncomplicated SSTI (especially if nonpurulent, nonculturable) Expand to cover CA-MRSA if no response in first 48 hrs Use local micro/epi data to guide empiric abx selection Rates of CA-MRSA resistance to clindamycin and TMP-SMX Follow-up ( wound checks ) and anticipatory guidance is key
38 II. Additional Testing for SSTI: Cellulitis Bacteremia Blood cultures commonly done for children admitted with cellulitis, esp those who will receive IV abx Prevalence SSTI-associated bacteremia ~20% (pre-hib era) Following introduction of Hib vaccine, SSTIassociated bacteremia rates fell to ~2% Largely driven by superinfection of active VZV lesions Pediatrics 2013;132: Pediatrics 1998;101(3):
39 II. Additional Testing for SSTI: Cellulitis Bacteremia Two recent studies evaluated prevalence of SSTI-associated bacteremia in the modern (MRSA) era Prevalence in ED patients with uncomplicated cellulitis: 0% Prevalence in inpatients admitted with uncomplicated SSTI: 0% Ratio of contaminant:pathogen in +Bcx: 3-4:1 Cost of 4 contaminated Bcx (in one study): $2280 Sending a Bcx in SSTI inpatients increases LOS by 1 day Clinical bottom line: Bacteremia rare in ED and inpatients with uncomp SSTI (<1%) Unnecessary Bcx are costly and increase hospital LOS No role for routine Bcx in uncomplicated SSTI Pediatrics 2013;132: Hospital Pediatrics 2013;3;103
40 DEEP/NECROTIZING SSTI
41 Necrotizing Fasciitis Anatomy: All layers from skin to underlying muscle Clinical Features Severe pain out of proportion to exam Erythema Ecchymosis and bullae (late) Crepitus Cutaneous anesthesia Woody/firm feeling of skin Systemic toxicity, fever, AMS Can develop after initial minor skin lesions Microbiology Type I = Polymicrobial (mixed aerobes and anaerobes) Type II = Monomicrobial usually GAS
42 Necrotizing Fasciitis Diagnosis Clinical/Labs Hard signs often absent Maintain a high clinical suspicion Risk scores can aid in decision for surgical exploration Imaging XR (tissue gas very specific), CT, MRI Imaging should NOT delay surgery Operative Gold standard for diagnosis Management Medical Broad spectrum abx Surgical prompt surgery saves lives
43 Common Pitfalls in Management of SSTIs 1. Typical cellulitis caused by MRSA is unusual 2. TMP-SMX does not reliably cover streptococcus 3. Pay close attention to susceptibility pattern on cultures if Clinda-S + Erythro-R, look for D-Test 4. Routine blood cx unnecessary for uncomplicated SSTI 5. Necrotizing SSTIs cause high mortality call surgery early
44 Case #1 6 yo healthy female brought to SDC 2 days redness and swelling of foot No fevers/chills, n/v Exam: Afebrile Mild erythema Normal gait Management?
45 Case #1 6 yo healthy female brought to SDC 2 days redness and swelling of foot No fevers/chills, n/v Exam: Afebrile Mild erythema Normal gait Management? Case Considerations Classification? Cellulitis Management? Antibiotics? PO e.g., cephalexin Blood cultures? No Imaging? No Dispo Admit vs DC? DC What type of follow-up? F/U if no response/worsens
46 Case #2 11 yo healthy M w/2 days redness and pain to L arm Subjective fever last night Exam Afebrile / Rest of VS normal 3 x 5 cm area of warmth, tenderness, and erythema L arm Central area of ~2 cm fluctuance Management?
47 Case #2 11 yo healthy M w/2 days redness and pain to L arm Subjective fever last night Exam Afebrile / Rest of VS normal 3 x 5 cm area of warmth, tenderness, and erythema L arm Central area of ~2 cm fluctuance Management? Case Considerations Classification? Abscess + infllammation Management? Antibiotics? No (if drained) Blood cultures? No Imaging? +/- U/S Dispo Admit vs DC? DC What type of follow-up? Wound check in 1-2 days
48 Case #3 18 yo healthy male with 2-3 days of progressive erythema, edema, and pain of LUE Associated fevers, chills, malaise starting same day as onset of skin sx Exam: T 39/ BP 115/70 / HR 120 LUE diffusely swollen, firm, and red Exquisitely tender with minimal palpation on exam No crepitus Management?
49 Case #3 18 yo healthy male with 2-3 days of progressive erythema, edema, and pain of LUE Associated fevers, chills, malaise starting same day as onset of skin sx Exam: T 39/ BP 115/70 / HR 120 LUE diffusely swollen, firm, and red Exquisitely tender with minimal palpation on exam No crepitus Case Considerations Classification? Deep/complicated SSTI Management? Antibiotics? Yes include MRSA coverage Blood cultures? Yes Imaging? Maybe, but not at expense of urgent surgical C/S Management? Dispo Admit vs DC? Admit What type of follow-up? Serial evaluations as IP (potentially SICK patient)
50 QUESTIONS? Page 50
51 References 1. Jeng A, et al, The Role of β-hemolytic Streptococci in Causing Diffuse, Nonculturable Cellulitis, Medicine (Baltimore) 2010;89: Stevens DL, et al, Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections, Clin Infect Dis 2005;41: Sadow KB, Chamberlain, JM, Blood Cultures in the Evaluation of Children with Cellulitis, Pediatrics 1998;101(3). 4. Swartz MN, Cellulitis, NEJM 2004;350(9): Marin JR, et al, Reliability of Clinical Examinations for Pediatrics Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections, Pediatrics 2010;126: Squire BJ, et al, ABSCESS: Applied Bedside Sonography for Convenient Evaluation of Superficial Soft Tissue Infections, Acad Emerg Med 2005;12: Liu C, et al, Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Adults and Children, Clin Infect Dis 2011; Duong M, et al, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Antibiotics in the Management of Community-Acquired Skin Abscesses in the Pediatric Patient, Ann Emerg Med 2010;55: Moran GJ, et al, Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Infections among Patients in the Emergency Department, NEJM 2006;355: Miller LG, et al, Clinical and Epidemiologic Characteristics cannot distinguish CA-MRSA Infection from CA-MSSA Infection: A Prospective Investigation, Clin Infect Dis 2007;44: Elliott DJ, et al, Empiric Antimicrobial Therapy for Pediatric Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections in the Era of Methicillin- Resistant Staphyloccus aureus, Pediatrics 2009;123:e Chen AE, et al, Randomized Controlled Trial of Cephalexin versus Clindamycin for Uncomplicated Pediatric Skin Infections, Pediatrics 2011;127:e Williams DJ, et al, Comparative Effectiveness of Antibiotic Treatment Strategies for Pediatric Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections, Pediatrics 2011;128:e Baker, CJ. Large CA-MRSA disease burden mandates prompt diagnosis, appropriate management. AAP News 2007; 28: Baddour LM, Skin Abscesses, Furuncle, and Carbuncles, Up to Date, Kaplan SL, Evaluation and Management of Suspected Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in Children, Up to Date, Baddour LM, Cellulitis and Erysipelas, Up to Date, Morelli JG, Impetigo, Chapter 657.1, Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19 th ed, edited by Kliegman RM, et al, published by Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, 2011.
52 7/9/2018
Objectives. Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection
 Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH
 Eric Bosley, MD Laura Stadler, MD John MD J h Draus, D MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH PART I: OUTPATIENT ISSUES AND MANAGEMENT NOT REQUIRING I&D OR HOSPITALIZATION Eric L. Bosley, MD, FAAP Pediatric Associates,
Eric Bosley, MD Laura Stadler, MD John MD J h Draus, D MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH PART I: OUTPATIENT ISSUES AND MANAGEMENT NOT REQUIRING I&D OR HOSPITALIZATION Eric L. Bosley, MD, FAAP Pediatric Associates,
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH)
 Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
 SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS ZAIN CHAGLA SEA COURSES - PATAGONIA COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in
SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS ZAIN CHAGLA SEA COURSES - PATAGONIA COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in
-> Education -> Excellence
 Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
13/10. Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan
 13/10 Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan Salam soul, this is the first Microbiology lecture of this system given by Dr.hani masaadeh. I ll do my best to make it easy
13/10 Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan Salam soul, this is the first Microbiology lecture of this system given by Dr.hani masaadeh. I ll do my best to make it easy
Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections. Sally Williams MD
 Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections Sally Williams MD Cellulitis: A very common infection 25 cases per 1000 patient years More common in men, obese patients 60% occurs in the lower extremities 74% handled
Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections Sally Williams MD Cellulitis: A very common infection 25 cases per 1000 patient years More common in men, obese patients 60% occurs in the lower extremities 74% handled
DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition.
 DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition. Cellulitis may be further classified by the unique area
DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition. Cellulitis may be further classified by the unique area
Skin and so* +ssue infec+on. N.Nuntachit MD.
 Skin and so* +ssue infec+on N.Nuntachit MD. Non purulent SSTI Impe+go, ecthyma Celluli+s, Erysipelas Erysipeloid Necro+zing infec+on Etc eg Glanders, bubonic plaque Purulent SSTI Furuncle Carbuncle Abscess
Skin and so* +ssue infec+on N.Nuntachit MD. Non purulent SSTI Impe+go, ecthyma Celluli+s, Erysipelas Erysipeloid Necro+zing infec+on Etc eg Glanders, bubonic plaque Purulent SSTI Furuncle Carbuncle Abscess
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
ID Emergencies. BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu
 ID Emergencies BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
ID Emergencies BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
Update in Management of Skin and So1 Tissue Infec7ons. Disclosures. None 4/23/15
 Update in Management of Skin and So1 Tissue Infec7ons Catherine Liu, MD Associate Professor UCSF, Division of Infec7ous Diseases None Disclosures 1 Overview Purulent SSTI (abscesses) Non- purulent SSTI
Update in Management of Skin and So1 Tissue Infec7ons Catherine Liu, MD Associate Professor UCSF, Division of Infec7ous Diseases None Disclosures 1 Overview Purulent SSTI (abscesses) Non- purulent SSTI
Abscess cellulitis pus
 Abscess cellulitis pus An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body.. If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess,. 13-2-2018 Patients with skin
Abscess cellulitis pus An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body.. If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess,. 13-2-2018 Patients with skin
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated
 Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS. Sports Medicine
 COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
ID Emergencies. BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu
 ID Emergencies BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
ID Emergencies BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems
 StudentL 1 Lower Limb Cellulitis University of Washington School of Nursing Nurse- Midwifery Education Program NCLIN 512 Fall 2012 Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health
StudentL 1 Lower Limb Cellulitis University of Washington School of Nursing Nurse- Midwifery Education Program NCLIN 512 Fall 2012 Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health
Disclosure. Patient Case. Objectives. Patient Case. Patient Case 7/25/2015. An update on the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections
 Disclosure 49th Annual Meeting An update on the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections I do not have a vested interest in or affiliation with any corporate organization offering financial support
Disclosure 49th Annual Meeting An update on the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections I do not have a vested interest in or affiliation with any corporate organization offering financial support
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University
 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University Usual Skin Flora Skin flora consists of those microbes able to adapt to the high salt
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University Usual Skin Flora Skin flora consists of those microbes able to adapt to the high salt
Osteomyelitis and Septic Joints; Practical Considerations. Coleen K. Cunningham
 Osteomyelitis and Septic Joints; Practical Considerations Coleen K. Cunningham Goals/objectives To improve understanding of the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of pediatric bone and joint infections
Osteomyelitis and Septic Joints; Practical Considerations Coleen K. Cunningham Goals/objectives To improve understanding of the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of pediatric bone and joint infections
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
S t a p h i n f e c t i o g r o i n p i c t u r e s
 S t a p h i n f e c t i o g r o i n p i c t u r e s When someone is under an infection either in any area of the body or in the groin to be specific, the lymph nodes will swell up. Lymph nodes are located
S t a p h i n f e c t i o g r o i n p i c t u r e s When someone is under an infection either in any area of the body or in the groin to be specific, the lymph nodes will swell up. Lymph nodes are located
Alabama Medicaid Pharmacist
 Alabama Medicaid Pharmacist Published Quarterly by Health Information Designs, LLC, Winter 015 edition A Service of Alabama Medicaid PDL Update Effective January 5, 015, the Alabama Medicaid Agency will
Alabama Medicaid Pharmacist Published Quarterly by Health Information Designs, LLC, Winter 015 edition A Service of Alabama Medicaid PDL Update Effective January 5, 015, the Alabama Medicaid Agency will
Skin and soft tissue (SSTI) sepsis (surgery, antimicrobial therapy and more)
 Skin and soft tissue (SSTI) sepsis (surgery, antimicrobial therapy and more) Christian Eckmann Antibiotic Stewardship Expert ECDC Chief of Staff Department of General, Visceral and Thoracic Surgery Klinikum
Skin and soft tissue (SSTI) sepsis (surgery, antimicrobial therapy and more) Christian Eckmann Antibiotic Stewardship Expert ECDC Chief of Staff Department of General, Visceral and Thoracic Surgery Klinikum
Staph infection groin pictures
 Staph infection groin pictures Search TheBody.com fills you in on the topic, staph infections on the groin, with a wealth of fact sheets, expert advice, community perspective, the latest news/research.
Staph infection groin pictures Search TheBody.com fills you in on the topic, staph infections on the groin, with a wealth of fact sheets, expert advice, community perspective, the latest news/research.
Cellulitis: a practical guide
 Cellulitis: a practical guide Dr John Day Consultant in Infectious Diseases & General Medicine Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 77 yr old retired civil servant A&E presentation c/o rigors
Cellulitis: a practical guide Dr John Day Consultant in Infectious Diseases & General Medicine Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 77 yr old retired civil servant A&E presentation c/o rigors
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines
 ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122)
 (NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
Case 2. Case 3 - course. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60
 Case 2 42 y/o man c/o painful right arm and shoulder x 3 days. Hx of IDU ( skin popping heroin ). No other trauma or bite. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60 PMH: HCV, HBV, HIV negative,
Case 2 42 y/o man c/o painful right arm and shoulder x 3 days. Hx of IDU ( skin popping heroin ). No other trauma or bite. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60 PMH: HCV, HBV, HIV negative,
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam
 Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Osteomieliti STEOMIE
 OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
Foot infections are now among the most
 Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center. Daniel Kaufman, MD
 Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS. Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA. University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014
 SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
Clinical Case. ! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital. ! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis: ! Need of HBOT?
 Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS: SURVEILLANCE & PREVENTION
 SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS: SURVEILLANCE & PREVENTION Facts There were an estimated 157,500 surgical site infections associated with inpatient surgeries in 2011. SSIs were the most common healthcare-associated
SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS: SURVEILLANCE & PREVENTION Facts There were an estimated 157,500 surgical site infections associated with inpatient surgeries in 2011. SSIs were the most common healthcare-associated
CRACKCast Episode 137: Skin Infections (Ch th )
 CRACKCast Episode 137: Skin Infections (Ch. 129 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Skin infections are common and are rarely life-threatening. Deadly necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections are
CRACKCast Episode 137: Skin Infections (Ch. 129 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Skin infections are common and are rarely life-threatening. Deadly necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections are
Common bacterial skin infections
 Common bacterial skin infections Cellulitis A localized area of soft tissue inflammation with skin infiltration with white cells, capillary dilatation and proliferation of bacteria. Staph aureus and Strep
Common bacterial skin infections Cellulitis A localized area of soft tissue inflammation with skin infiltration with white cells, capillary dilatation and proliferation of bacteria. Staph aureus and Strep
Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification
 Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification Muhammad Hussein Gasem Div Infectious Disease, TropMed, and Immunology Dr. Kariadi Hospital, Diponegoro University Semarang,
Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification Muhammad Hussein Gasem Div Infectious Disease, TropMed, and Immunology Dr. Kariadi Hospital, Diponegoro University Semarang,
Pediatric Infections: Treatment of Resistant Pathogens. Focus : MRSA and DRSP Infections, Including Pneumonia. Blaise L. Congeni M.D.
 Pediatric Infections: Treatment of Resistant Pathogens Focus : MRSA and DRSP Infections, Including Pneumonia Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Patient 1-LP 8 yo with 8 days of fever and 6 days of cough. She had consistently
Pediatric Infections: Treatment of Resistant Pathogens Focus : MRSA and DRSP Infections, Including Pneumonia Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Patient 1-LP 8 yo with 8 days of fever and 6 days of cough. She had consistently
In the absence of underlying edema or other skin abnormalities, erysipelas
 ERYSIPELAS Erysipelas is a distinct type of superficial cutaneous cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic vessel involvement caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (very uncommonly group C or G streptococcus)
ERYSIPELAS Erysipelas is a distinct type of superficial cutaneous cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic vessel involvement caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (very uncommonly group C or G streptococcus)
Common Bedside Procedures in Pediatric Emergency Medicine
 Common Bedside Procedures in Pediatric Emergency Medicine James Luckey M.D. Children Hospital of the King s Daughters/ EVMS April 12, 2018 Objectives 1. Identify the indications, contraindications, and
Common Bedside Procedures in Pediatric Emergency Medicine James Luckey M.D. Children Hospital of the King s Daughters/ EVMS April 12, 2018 Objectives 1. Identify the indications, contraindications, and
Fighting Infection in Diabetes
 I have no disclosures Fighting Infection in Diabetes Emily Abdoler, MD Division of Infectious Diseases GomerBlog. http://gomerblog.com/2018/02/nystatin-statin/ Does DM Increase Risk of Infections? Diabetic
I have no disclosures Fighting Infection in Diabetes Emily Abdoler, MD Division of Infectious Diseases GomerBlog. http://gomerblog.com/2018/02/nystatin-statin/ Does DM Increase Risk of Infections? Diabetic
Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network. Comments for Query: Osteomyelitis in Children
 Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network Comments for Query: Osteomyelitis in Children Choice of antimicrobial At our institution, we typically start with clindamycin (unless
Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network Comments for Query: Osteomyelitis in Children Choice of antimicrobial At our institution, we typically start with clindamycin (unless
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint. Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department
 Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) guidelines for management of skin and soft tissue infections
 Sartelli et al. World Journal of Emergency Surgery 2014, 9:57 WORLD JOURNAL OF EMERGENCY SURGERY REVIEW World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) guidelines for management of skin and soft tissue infections
Sartelli et al. World Journal of Emergency Surgery 2014, 9:57 WORLD JOURNAL OF EMERGENCY SURGERY REVIEW World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) guidelines for management of skin and soft tissue infections
Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview
 Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview M Al Madadha Sources : Harrisons infectious diseases 2 nd edition, Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology 2 nd edition Anatomic relationships:
Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview M Al Madadha Sources : Harrisons infectious diseases 2 nd edition, Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology 2 nd edition Anatomic relationships:
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) S urveillance Report 2008 Background Methods
 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2008 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2008 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services
Cellulitis of the lower limbs: Incidence, Diagnosis and Management
 Cellulitis of the lower limbs: Incidence, Diagnosis and Management Leanne Atkin, Lecturer practitioner/vascular Nurse Specialist, School of Human and Health Sciences, University of Huddersfield and Mid
Cellulitis of the lower limbs: Incidence, Diagnosis and Management Leanne Atkin, Lecturer practitioner/vascular Nurse Specialist, School of Human and Health Sciences, University of Huddersfield and Mid
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Buccal Cellulitis in 3 Infants Martin W Stallings Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2016;8:e252 http://dx.doi.org/10.17334/jps.78460 How to cite this article: Stallings MW. Buccal
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Buccal Cellulitis in 3 Infants Martin W Stallings Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2016;8:e252 http://dx.doi.org/10.17334/jps.78460 How to cite this article: Stallings MW. Buccal
GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE
 GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE Laboratory confirmation of infection with or without clinical evidence of invasive disease: isolation of group A streptococcus (Streptococcus
GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE Laboratory confirmation of infection with or without clinical evidence of invasive disease: isolation of group A streptococcus (Streptococcus
The Curious Intersection of HIV and Staphylococcus aureus with a Focus on MRSA
 The Curious Intersection of HIV and Staphylococcus aureus with a Focus on MRSA Franklin D. Lowy, MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY Topics to Be Covered Background Some
The Curious Intersection of HIV and Staphylococcus aureus with a Focus on MRSA Franklin D. Lowy, MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY Topics to Be Covered Background Some
Antibiotic Stewardship for Skin and Soft Tissue Infection and Respiratory Tract Infections
 Antibiotic Stewardship for Skin and Soft Tissue Infection and Respiratory Tract Infections Ghinwa Dumyati, MD Professor of Medicine Center for Community Health and Infectious Diseases Division University
Antibiotic Stewardship for Skin and Soft Tissue Infection and Respiratory Tract Infections Ghinwa Dumyati, MD Professor of Medicine Center for Community Health and Infectious Diseases Division University
Hot Topics in Infectious Diseases
 Hot Topics in Infectious Diseases Penelope H. Dennehy, MD Director, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Hasbro Children s Hospital Professor and Vice Chair for Academic Affairs Department of Pediatrics
Hot Topics in Infectious Diseases Penelope H. Dennehy, MD Director, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Hasbro Children s Hospital Professor and Vice Chair for Academic Affairs Department of Pediatrics
SURGICAL ANTISEPSIS. Overview FOUNDATIONS OF OPTOMETRIC SURGERY. Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO Consultative Ophthalmology and Procedural Optometry
 SURGICAL ANTISEPSIS FOUNDATIONS OF OPTOMETRIC SURGERY Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO Consultative Ophthalmology and Procedural Optometry Professor & Assistant Dean for Surgical Training and Education Director,
SURGICAL ANTISEPSIS FOUNDATIONS OF OPTOMETRIC SURGERY Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO Consultative Ophthalmology and Procedural Optometry Professor & Assistant Dean for Surgical Training and Education Director,
Severe β-lactam allergy. Alternative (use for mild-moderate β-lactam allergy) therapy
 Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Staph Infections. including MRSA
 Staph Infections including MRSA What is a Staph infection? STAPH Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as staph, are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. SYMPTOMS
Staph Infections including MRSA What is a Staph infection? STAPH Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as staph, are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. SYMPTOMS
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations
 Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations Mark Beilke, M.D. Professor of Medicine Chief of Infectious Diseases Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center Objectives Diagnose and treat water
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations Mark Beilke, M.D. Professor of Medicine Chief of Infectious Diseases Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center Objectives Diagnose and treat water
Case Presentation and Discussion on Posterior Neck Mass. Martin Joseph S. Cabahug
 Case Presentation and Discussion on Posterior Neck Mass Martin Joseph S. Cabahug General Data: C.A, 60 y/o male Sta. Ana, Mla Chief Complaint: Posterior Neck Mass History and Physical Exam 2 wks PTA mass,
Case Presentation and Discussion on Posterior Neck Mass Martin Joseph S. Cabahug General Data: C.A, 60 y/o male Sta. Ana, Mla Chief Complaint: Posterior Neck Mass History and Physical Exam 2 wks PTA mass,
Foot infections in persons with diabetes are
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
The effect of bedside ultrasound on diagnosis and management of soft tissue infections in a pediatric ED,
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2012) 30, 1347 1351 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution The effect of bedside ultrasound on diagnosis and management of soft tissue infections in
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2012) 30, 1347 1351 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution The effect of bedside ultrasound on diagnosis and management of soft tissue infections in
Should I prescribe antibiotics after draining an abscess in a young child? Should I pack his wound? Do I prescribe decolonizing measures?
 EIA is a recurring EIA section is a of recurring Hospital section Pediatrics of Hospital where expert Pediatrics pediatric hospitalists where expert pediatric give their hospitalists interpretation give
EIA is a recurring EIA section is a of recurring Hospital section Pediatrics of Hospital where expert Pediatrics pediatric hospitalists where expert pediatric give their hospitalists interpretation give
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy"
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29
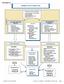 PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE:
 HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE: MYCOBACTERIUM ON THE ROUTINE BENCH Christina Partington MT(ASCP) ACL Laboratory 1 Introduction The importance of the possibility of AFB appearing in a routine culture. How to recognize
HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE: MYCOBACTERIUM ON THE ROUTINE BENCH Christina Partington MT(ASCP) ACL Laboratory 1 Introduction The importance of the possibility of AFB appearing in a routine culture. How to recognize
DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin.
 DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin. Nonbullous impetigo Formation of vesiculopustules that ruptures, leading to crusting with a characteristic
DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin. Nonbullous impetigo Formation of vesiculopustules that ruptures, leading to crusting with a characteristic
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
 The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
Group B streptococcal infection;. Bacteremia without a focus occurs in 80-85%,. July has been recognised as Group B Strep Awareness Month,.
 Group B streptococcal infection;. Bacteremia without a focus occurs in 80-85%,. July has been recognised as Group B Strep Awareness Month,. 12-10-2017 Group B streptococci are uniformly sensitive to penicillin
Group B streptococcal infection;. Bacteremia without a focus occurs in 80-85%,. July has been recognised as Group B Strep Awareness Month,. 12-10-2017 Group B streptococci are uniformly sensitive to penicillin
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent. 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens
 Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Community- Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections In Chinese Neonates
 Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Community- Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections In Chinese Neonates Xuzhuang Shen Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University,
Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Community- Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections In Chinese Neonates Xuzhuang Shen Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University,
Staph Infection Fact Sheet
 What is Staphylococcus aureus (staph)? Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as staph, are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Approximately 25% to 30% of
What is Staphylococcus aureus (staph)? Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as staph, are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Approximately 25% to 30% of
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE
 Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE Professor, Department of Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Director, Division of Hospital Medicine Attending Physician in Infectious Diseases
Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE Professor, Department of Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Director, Division of Hospital Medicine Attending Physician in Infectious Diseases
clear evidence of the signs and symptoms of infection, simply a breast cancer that looks like infection.
 Hello, and welcome to The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center lecture series on Inflammatory Breast Cancer. In this section we ll discuss the clinical diagnosis of IBC. My name is Wendy Woodward
Hello, and welcome to The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center lecture series on Inflammatory Breast Cancer. In this section we ll discuss the clinical diagnosis of IBC. My name is Wendy Woodward
Molluscum BOTE Sign: A Predictor of Imminent Resolution
 Molluscum BOTE Sign: A Predictor of Imminent Resolution abstract Molluscum contagiosum is a common self-limited viral skin infection. The course of the infection often includes tender, crusted, erythematous
Molluscum BOTE Sign: A Predictor of Imminent Resolution abstract Molluscum contagiosum is a common self-limited viral skin infection. The course of the infection often includes tender, crusted, erythematous
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Streptococcus pyogenes
 Streptococcus pyogenes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Streptococcus pyogenes S. pyogenes bacteria at 900x magnification. Scientific classification Kingdom: Eubacteria Phylum: Firmicutes Class: Cocci
Streptococcus pyogenes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Streptococcus pyogenes S. pyogenes bacteria at 900x magnification. Scientific classification Kingdom: Eubacteria Phylum: Firmicutes Class: Cocci
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Persons with HIV: Increased Prevalence, Increased Mortality
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Persons with HIV: Increased Prevalence, Increased Mortality Jason E. Farley, PhD, MPH, NP Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Persons with HIV: Increased Prevalence, Increased Mortality Jason E. Farley, PhD, MPH, NP Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing
POLICY FOR TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: July 2013 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: April 2016 Implementation
POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: July 2013 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: April 2016 Implementation
Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh.
 Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh. This sheet is complete slides + Dr Comments, so you don t need to go back to the slides. Here is some dermatological
Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh. This sheet is complete slides + Dr Comments, so you don t need to go back to the slides. Here is some dermatological
Healthy Skin and Skin Infections. Prepared by the Midland Region Child Health Action Group Skin Subgroup
 Healthy Skin and Skin Infections Prepared by the Midland Region Child Health Action Group Skin Subgroup Objectives of this presentation This presentation will: Support health professional knowledge development
Healthy Skin and Skin Infections Prepared by the Midland Region Child Health Action Group Skin Subgroup Objectives of this presentation This presentation will: Support health professional knowledge development
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery
 Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Bone and Joint Infections Oh, My
 Bone and Joint Infections Oh, My Dale Jarka, MD,CM, FRCSC The Children s Mercy Hospitals & Clinics The Children's Mercy Hospital 2016 1 Disclosures A: I have no relevant financial relationships with the
Bone and Joint Infections Oh, My Dale Jarka, MD,CM, FRCSC The Children s Mercy Hospitals & Clinics The Children's Mercy Hospital 2016 1 Disclosures A: I have no relevant financial relationships with the
Antibiotic Management of Pediatric Osteomyelitis
 Reprinted from www.antimicrobe.org Sandra Arnold, M.D. Antibiotic Management of Pediatric Osteomyelitis Several points uncertainty exist regarding the antimicrobial management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis,
Reprinted from www.antimicrobe.org Sandra Arnold, M.D. Antibiotic Management of Pediatric Osteomyelitis Several points uncertainty exist regarding the antimicrobial management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis,
Learn Connect Succeed. JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017
 Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 Financial Disclosure Evaluation and Treatment of Orbital Cellulitis Thomas E. Johnson, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute University of Miami School of
Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 Financial Disclosure Evaluation and Treatment of Orbital Cellulitis Thomas E. Johnson, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute University of Miami School of
Staphylococci. What s to be Covered. Clinical Scenario #1
 Staphylococci Micrococcus, which, when limited in its extent and activity, causes acute suppurative inflammation (phlegmon), produces, when more extensive and intense in its action on the human system,
Staphylococci Micrococcus, which, when limited in its extent and activity, causes acute suppurative inflammation (phlegmon), produces, when more extensive and intense in its action on the human system,
POLICY FOR TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: Date: July 2018 The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Implementation
POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: Date: July 2018 The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Implementation
Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia
 Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia Amanda Guth 1 Amy Slenker MD 1,2 1 Department of Infectious Diseases, Lehigh Valley Health Network
Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia Amanda Guth 1 Amy Slenker MD 1,2 1 Department of Infectious Diseases, Lehigh Valley Health Network
Prevention and Management of Hysterectomy-Related Infectious Morbidity DR. S. FOULEM BSC, MD, FRSCS
 Prevention and Management of Hysterectomy-Related Infectious Morbidity DR. S. FOULEM BSC, MD, FRSCS Objectives Definition and epidemiology of surgical site infections (SSI) What are the most common infectious
Prevention and Management of Hysterectomy-Related Infectious Morbidity DR. S. FOULEM BSC, MD, FRSCS Objectives Definition and epidemiology of surgical site infections (SSI) What are the most common infectious
Pott s Puffy Tumor. Shahad Almohanna 15/1/2018
 Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H.
 Felon The superficial The deep cutaneous paronychial hyponychial subcutaneous furuncle of the finger osteal tendinous articular pandactilitis a At a paronychial it is necessary cut epidermis and pathological
Felon The superficial The deep cutaneous paronychial hyponychial subcutaneous furuncle of the finger osteal tendinous articular pandactilitis a At a paronychial it is necessary cut epidermis and pathological
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014
 Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge
 Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge Keith F Cutting Merimbula, 5 th November 2010 Wound infection microbial load immune system microbial load + + + immune system infection host response Diagnosing
Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge Keith F Cutting Merimbula, 5 th November 2010 Wound infection microbial load immune system microbial load + + + immune system infection host response Diagnosing
