Original Research Article
|
|
|
- Karin Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Article Tushar Kalekar 1, Pooja Shriramwar 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, DY Patil Medical College, 2 Consultant Radiologist Megavision Scan Centre, Pimpri, Pune, Maharashtra, India Corresponding author: Dr Tushar Kalekar, Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, DY Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune, Maharashtra, India How to cite this article: Tushar Kalekar, Pooja Shriramwar. MRI evaluation of non traumatic painful hip joint. International Journal of Contemporary Medicine Surgery and Radiology. 2018;3(1): A B S T R A C T Introduction: MR imaging is a valuable tool in the evaluation of hip disorders because it enables assessment of articular structures, extra-articular soft tissues, and the osseous structures that can be affected by hip disease. Trauma, infection, arthritis, avascular necrosis, tumor, and hip dysplasia can all manifest with extremely subtle radiographic abnormalities. Study aimed to assess the role of MRI in early evaluation of painful hip joint, to establish a differential diagnosis of various painful hip joint conditions on MRI and to assess the severity and extent of the lesion in various conditions of painful hip joint. Material and methods: A prospective study was carried out on 50 patients over a period of 2 years from Dec 2014 to September Institute Ethics Committee Clearance was obtained before the start of the study. Result: Our study shows all positive findings. Out of 50 cases almost 48% were had avascular necrosis, 20% of the patient had osteoarthritis, 16% of the patient had only joint effusion, 12% patient showed features of infection and only 4% had Perthes's disease. Conclusion: MR imaging is a valuable tool in the evaluation of hip disorders because it enables assessment of articular structures, extra-articular soft tissues, and osseous structures that can be affected by the hip disease. MRI of the hips should be performed early in patients with persistent pain and negative radiographic findings. Key words: MRI, Painful Hip Joint INTRODUCTION Imaging of the hip was among the earliest reported applications of musculoskeletal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. MR imaging is a valuable tool in the evaluation of hip disorders because it enables assessment of articular structures, extra-articular soft tissues, and the osseous structures that can be affected by hip disease. In the setting of chronic hip pain, a normal appearing radiograph, a nonspecific history and clinical findings can be a difficult diagnostic dilemma. Trauma, infection, arthritis, avascular necrosis, tumor, and hip dysplasia can all manifest with extremely subtle radiographic abnormalities. 1 The principal benefit of the true coronal and axial planes is that they provide symmetric, bilateral images, which can be important in the diagnosis and can greatly accelerate the time required to evaluate both hips. Normal hip anatomy can be routinely demonstrated on coronal and axial MR images. The femoral head and neck and the intertrochantric region are best appreciated on coronal MR images. Axial MR images provide good visualization of the articular space, hip musculature, and supporting ligaments. 2-8 The diagnostic ability of MR imaging in the evaluation of AVN is evolving. MR imaging is performed to detect AVN in its early stages, thus allowing early treatment and prevention of subsequent bone destruction. MR imaging has been shown to be the most sensitive modality for imaging AVN. Screening of asymptomatic, high-risk patients may enable early intervention. The principal role of MR imaging is in establishing the diagnosis of AVN in symptomatic patients before radiographic changes become apparently visible MR imaging is becoming increasingly useful in diagnosis and management of pediatric hip disorders. MR imaging offers several advantages that are especially important in the pediatric hip population. Because much of pediatric hip is cartilaginous, it is often not optimally imaged with other modalities such as plain radiography, ultrasound (US) (after 6 months of age), and computed tomography (CT). MR imaging is unique in its ability to depict cartilage and is, therefore, especially efficacious in the evaluation of the pediatric hip Currently, high-resolution direct MR imaging of the hip provides the best means for evaluating intra-articular pathology. However, radiography remains important for the diagnosis of subtle bony irregularities associated with femoro-acetabular impingement. Therefore, a comprehensive imaging strategy requires conventional radiographs and MRI to evaluate intra- and extra-articular sources of pain Study aimed to assess the role of MRI in early evaluation of painful hip joint, to establish a differential diagnosis of various painful hip joint conditions on MRI and to assess the severity and extent of the lesion in various conditions of painful hip joint. 155
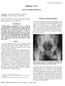
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS Study population A prospective study was carried out on 50 patients over a period of 2 years from Dec 2014 to September Institute Ethics Committee Clearance was obtained before the start of the study. Patient selection criteria The study included patients from all age groups including both men and women presenting with acute or chronic unilateral or bilateral hip pain without recent history of trauma (less than one month). Patients with congenital hip conditions or tumour were not a part of this study. Also patients with history of claustrophobia or history of metallic implants insertion, cardiac pacemakers and metallic foreign body insitu were excluded from this study. Method MRI was performed using SIEMENS 1.5 Tesla MAGNETOM AVANTO Machine. The size of bore was 60 cm and overall length of the system was 160 cm. A body coil was used. Detailed clinical history, physical and systemic examination findings were noted in addition to the laboratory investigations. All the patients were subjected to radiograph of Hip AP View. Scanning technique Patient was positioned in supine position with head pointing towards the magnet. A body coil was placed over the pelvis to provide a uniform signal to nose ratio. Standrad sequences prformed namely. Coronal T1W, Coronal STIR, Axial T1, Axial STIR, Sagital T1, Axial GRE. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Microsoft office 2007 was used for the analysis. Descriptive statistics like mean and percentages were used for the analysis. RESULTS Sex distribution Out of the 50 patients included in our study, 36 (72%) were males and 14(28%) were females. Age wise distribution Age of the patients ranged from 6 to 65 years with the highest incidence seen in the age group (as seen in the table -1) comprising of 12 patients each in the and age groups. Out of these 60% patients that means 30 were positive on radiography and rest were negative MRI findings All these 50 patients had positive findings on MRI (100%). These are as follows 1. Avascular necrosis of femoral head Out of 50 cases 24 (48%) cases were diagnosed as avascular necrosis of femoral head. In 24 cases of AVN, only 10 (42%) cases were detected on radiography whereas all 24 (100%) cases were detected on MRI. Out of 24 cases, 14 (58%) cases which were normal {stage I and stage II of FICAT Classification} on radiography were proved to have AVN on MRI. Thus MRI is more sensitive than plain radiography. Out of the 10 (42%) cases which were detected both on radiography and MRI, 6 (25%) that were reported as stage II on radiography {FICATS} were staged as stage III on MRI {MITCHELL S} and 4 (16%) cases which were reported as stage III on radiography {FICATS} were staged as stage III or more on MRI {MITCHELL S}. In 42% of the patients AVN was correctly diagnosed on radiography and all 100% were diagnosed on MRI MRI findings of AVN Commonest finding seen on MRI in cases with AVN was that of bone marrow edema which was seen in 25 cases followed by subchondral cysts seen in 16 patients. Joint space Figure-1: Axial T2W image showing well demarcated geographic lesions with typical peripheral low signal intensity rim (arrow) on the antero-superior aspect of the left femoral head(avn grade II) Figure-2: Coronal T2W image showing double line sign (arrow) as a high signal intensity inner border with a low intensity peripheral rim. of stage III AVN Age Number of patient Percentage total Table-1: Age wise distribution 156
3 MRI Findings Number of Patients Percentage % (n=24) Bone marrow edema Femoral head % Acetabulum 4 16 % Double line sign % Subchondral cysts Femoral head % Acetabulum 1 4 % Joint Effusion % Joint space reduction 1 4 % Femoral head altered contour 9 37 % Femoral head fragmentation with collapse 1 4 % Table-2: Showing MRI findings of AVN Serial No. Pathology No. of Patients Percentage 1. AVN % 2. Osteoarthritis % 3. Joint Effusion 8 16 % 4. TB Arthritis 6 12 % 5. Perthe s 2 4 % Total % Table-3: Pathology Figure-5: Tuberculosis of right hip showing bone marrow edema in right acetabulum, right femoral head and neck with large erosion along articular surface of right acetabulum. Right hip joint space is narrowed and associated synovial effusion Figure-3a and 3b: Showing Crescent sign on both coronal T1W) images suggestive Figure-4: Osteoarthritic changes in right hip with thinning of articular cartilage with reduction of the right hip joint space. Marginal osteophytes with multiple subchondral cysts reduction was not commonly seen and was found in only one patient (table-2). 2. Osteoarthritis Out of 50 cases ten (20%) showed osteoarthritis. All the ten cases were detected both on plain radiography as well as on MRI. But, out of ten cases three (30%) appeared to be stage I on radiograph and stage II or III on MRI. Of the ten cases 3 (30%) showed stage II on radiography and stage III on MRI. Out of ten cases detected on radiography stage I (4 cases), stage II (4 cases) and stage III (2 cases). On MRI stage I (1 case), stage II (4 cases), stage III (3 cases) and stage IV (2 cases). MRI findings of osteorthritis Commonest MRI abnormality seen in cases of osteoarthritis was signal loss in the femoral head and neck on T1W images which was found in 90% cases. 3. Joint effusion Out of 50 cases, 8 (16%) cases showed isolated joint effusion. Of these, three (37%) cases were detected on radiography alone and all eight cases (100%) were positive for joint effusion on MRI. Findings on radiograph: widening tear drop distance. Findings on MRI: T2W and STIR hyperintensity within the joint space which is graded as mild, moderate and severe. 4. Tuberculosis of hip joint 6 cases (12%) were diagnosed as Tuberculosis of hip, out of which five (83%) cases were correctly detected on radiography, where as all six (100%) cases were detected on MRI. Out of five cases detected on radiograph stage I (1 case), stage II (1 case), stage III (2 cases), stage IV (0) and stage 157
4 V (1 case). Out of six cases detected on MRI shows stage I (1 case), stage II (1 case), stage III (1 case), stage IV (2) and stage V (1 case). MRI findings in TB hip joint Commonest findings of TB hip seen on MRI were adjacent soft tissue hyperintensity and joint effusion each seen in 5 (83%) cases followed by bone marrow edema seen in 4(67%) cases. 5. Perthe s disease Two cases (4%) of Perthe s disease were seen in our study. Both of the cases were correctly detected on radiograph (100%) as well as MRI (100%). MRI findings of Perthe s were T2 weighted epiphyseal hyperintensity and bone marrow edema (table-3). DISCUSSION Our study aims at early detection of the disease before the appearance of signs on radiography or in patients having subtle findings on plain radiography by using MR imaging. It also aims at the accurate staging of the disease and assessment of involvement of pathology in cases which are already detected on plain radiography. This helps the clinician to treat the patient at an early stage and to improvise treatment according to the stage of involvement of the pathology thereby limiting further progression of the disease. 30 Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head In our study, AVN of femoral head was the commonest pathology identified as the cause for painful hip joint. In 24 (48%, n=50) cases of AVN diagnosed on MRI only 10 (20%, n=50) cases were identified on plain radiography. Out of 10 (42%, n=24) cases diagnosed on plain radiography, 6 (25%, n=24) cases showed subchondral cysts and osteoporosis suggestive of stage I AVN {FICATS staging}. Rest of the 4 (16%, n=24) cases showed crescent sign, altered head morphology and osteoporosis suggestive of stage II AVN {FICATS staging}. Of all the 24 cases detected on MRI, 21 (87%, n=24) cases showed bone marrow edema in femoral head, 4 cases (16%, n=24) cases showed bone marrow edema in acetabulum suggesting it to be a common associated feature that can be detected only on MRI as radiography has its limitation in diagnosing bone marrow edema. MRI demonstrated double line sign i.e, on T2W sequences inner bright line representing granulation tissue and outer dark line suggestive of sclerotic bone in 19 (79%, n=24) cases. Fourteen (58%, n=24) cases were diagnosed as normal or stage I (FICATS) on plain radiography and stage I or II on MRI. Out of a total of 10 (42%, n=24) cases detected on plain radiography; 6 (25%, n=24) cases were staged as stage I (FICATS) which showed stage III (MITCHELL S) with intermediate fluid signal on T1W images and bright signal on T2W images. Four (16%, n=24) cases which were staged as stage II (FICATS) turned out to be stage III or stage IV on MRI (MITCHELL S) giving fibrous signal, dark on both T1W and T2W sequences, revealing that MRI is better than radiography in staging and assessing the extent of the pathological involvement in already proven cases of AVN on plain radiography. In comparison to the study done by Robinson HJ et al. 30 in which twenty-three of the ninety-six hips that were suspected of having early-stage necrosis of the femoral head but showed slight or no radiographic changes were studied by repeat radiographs. Of the twenty-three hips, eighteen (78 per cent) had positive changes on magnetic resonance imaging. In our study out of 24 hips, MRI detected 24 cases (100%), where as radiography could detect only 10 cases (42%). Osteoarthritis In this study, 10 (20%, n=50) cases of osteoarthritis were diagnosed. All of the 10 cases were correctly detected on plain radiography and on MRI. On plain radiography, four (40%, n=10) cases showed stage I (Kellgren and Lawrence staging) in the form of possible narrowing of the joint space and osteophytes. Four (40%, n=10) cases were diagnosed as stage II with definite narrowing of the joint space inferiorly, minimal sclerosis and osteophytes. Two (20%, n=10) cases showed stage III with marked narrowing of the joint space, definite osteophytes, cyst formation, deformation of femoral head and acetabulum. On MRI, one (10%, n=10) case showed stage I (Higgs and Aiesen staging) that is inhomogeneous high signal on T2W images within the cartilage. Four (40%, n=10) cases showed stage II that is inhomogenity of articular cartilage seen as high signal on T2Wsequences and indistinct trabeculae or signal intensity loss in femoral head and neck on T1W sequences. Three (30%, n=10) cases were diagnosed as stage III having criteria of stage I and II as mentioned above and indistinct zone between femoral head and acetabulum associated with subchondral signal loss due to bone sclerosis. In our study Articular cartilage abnormalities were seen in 5 (50%) cases, joint effusion in 8 (80%) cases and osteophytes at various sites around the joint were noted in 6(60%) cases. Similar findings were noted in the study conducted by Horii et al 15 in 2000 who found articular cartilage abnormalities such as stripping and high signals in the antero-superior portions of the hip joint in about 90% cases, joint effusion in 29 cases and osteophye formation in 80% cases. Joint Effusion On MRI, joint effusion was seen as high signal intensity within the joint space on T2W and STIR sequences suggestive of fluid collection within the joint capsule. Also MRI demonstrated an added advantage of better and correct evaluation of the amount of fluid within the joint and grading to the effusion as minimal, moderate and severe joint effusion. Four (50%, n=8) cases had minimal joint effusion, 3 (38%, n=8) moderate and 1 (12%, n=8) case had severe joint effusion. Five (62.5%, n=8) cases diagnosed as normal on plain radiography showed joint effusion on MRI. Reviewing the above findings, MRI proved to be more sensitive in detection of joint effusion particularly in cases where plain radiography showed normal or subtle changes Tuberculosis of Hip joint In the six cases (100%, n=6) diagnosed on MRI, 1 (17%, n=6) case showed only synovial T2W hyperintensity and joint effusion in the form of high signal intensity within the joint 158
5 space in T2W and STIR sequences. This was diagnosed as normal on plain radiography. On MRI, 1 (17%, n=6) case showed synovial hyper intensity, joint effusion and bone marrow edema as high signal intensity within the marrow on STIR sequence. Another single (17%, n=6) case showed sub articular T2 hyper intense cysts and joint space reduction. Joint deformity along with bone marrow edema, joint space reduction and para articular soft tissue hyper intense signal on T2W sequence was seen in two (33%, n=6) cases. Thus, MRI helped in better delineation of synovial involvement and detection of joint effusion in early stages of TB hip where plain radiography has limitation in diagnosis. MRI also proved beneficial in detection of bone marrow edema in early stages of the disease. In the radiologically diagnosed cases, MRI helped in better evaluation of the extent of the articular cartilage destruction and also para articular soft tissue involvement. Sawlani V. et al. 24 described the MRI findings of Tuberculous hip which included synovitis, effusion, central and peripheral erosions, active and chronic pannus, abscess, bone chips and hypo-intense synovium. They also emphasized the importance of early diagnosis of the condition in order to salvage the affected limb which is possible only with MR imaging. Similar MR findings were seen in the our study in the cases that were diagnosed as tuberculosis of the hip. Perthes Disease In our study 2 (4%, n=50) cases were diagnosed as Perthes disease. Both the cases could be diagnosed on radiography as well as on MRI (100%, n=2) The plain radiographic findings included cessation of femoral epiphyseal growth in the form of small epiphysis seen in one case and complete resorption of femoral epiphyses in healed/ residual stage which was also seen in just one of the two cases. On MRI, one of the cases, showed epiphyseal abnormality in the form of T1 hypo intensity, T2W hyper intensity and bone marrow edema in the form of STIR hyper intensity and metaphyseal T2W hyper intensities which was seen as cessation of femoral epiphyses growth on plain radiography Similar findings were seen in a study done by Toby EB et. al. 9 who assessed pediatric hip disease by scanning the hips of 24 children (30 scans). They found twelve patients with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (17 hips) showed characteristic areas of lowintensity signal representative of necrotic areas of the capital epiphysis. In our study both the cases showed small epiphyses which were seenas hypo intense on T1W and hyperintense on T2W sequences. Thus, MRI helps in better evaluation of femoral epiphyses along with detection of bone marrow edema on STIR sequence. CONCLUSION Plain film radiography is used in the initial evaluation of any cause of hip pain, including suspected avascular necrosis, arthritis, infection, dysplasia and tumour. Plain film cannot accurately characterize the articular cartilage pathology and soft tissue involvement. MR imaging is a valuable tool in the evaluation of hip disorders because it enables assessment of articular structures, extra-articular soft tissues, and osseous structures that can be affected by the hip disease. MRI of the hips should be performed early in patients with persistent pain and negative radiographic findings. MR imaging is becoming increasingly useful in the diagnosis and management of pediatric hip disorders. It offers several advantages that are especially important in the pediatric population. MR imaging is performed to detect avascular necrosis in its early stages, thus allowing early treatment and intervention to prevent or delay subsequent bone destruction. It has been shown to be the most sensitive modality for imaging avascular necrosis. Joint effusion and synovial proliferation can be better detected by MRI than by conventional radiography. In proven cases on plain radiography such as Perthe s and infectious diseases of hip, MRI helps in better staging of the disease, assessing the extent of pathological involvement and soft tissue extension. Additionally, MRI is extremely sensitive to alteration in the bone marrow that may represent pathology occult to plain radiography of the hips. REFERENCES 1. Manster B.J. MD, PhD. Adult Chronic Hip Pain: Radiographic Evaluation. Radiographics 2000;20(2):S3- S Gabriel H, Fitzgerald SW, Myers MT, Donaldson JS, Poznanski AK. MR Imaging of Hip Disorders. Radiographics 1994;14(1): Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5 th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Berquist H. Thomas. MRI of the Musculoskeletal system: Hip, 6 th ed.philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Drake RL, Vogl WA, Mitchell AW, Schmitt W, Gruliow R. Lower limb. In: 6. Gray's anatomy for students. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone; p Ficat RP, Arlet J. Necrosis of the femoral head. In: Hungerford DS, editor. 8. Ischemia and Necrosis of Bone. 3 rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Steinberg ME, Hayken GD. A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(2): Bassett LW, Gold RH, Reicher M, Bennett LR, Tooke SM. MRI in the Early Diagnosis of Ischemic Necrosis of the Femoral Head. Clin. Ortho. 1987;214(3): Toby EB, Komal La, Bechtold RE. Magnetic resonance imaging of paediatric hip disease, J Pediatrc Orthop 1985: Swagerty D and Hellinger D. Radiographic Assessment of Osteoarthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2001;64(3): Cicuttini FM, Spector T, Baker J. Risk factors for osteoarthritis in the tibiofemoral and the patellofemoral joints of the knee. J Rheumatol. 1997;24(4): Buckland-Wright C, Verbruggen G, Haraoui PB. Imaging: radiological assessment of hand osteoarthritis. In: Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000;8(5):
6 15. Terjesen T, Gunderson RB. Radiographic evaluation of osteoarthritis of the hip: an inter-observer study of 61 hips treated for late-detected developmental hip dislocation. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(4): upper femoral epiphysis in Hashimoto s thyroiditis in a 29-year-old man. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2009;91(5): Horii M, Kubo T, Hirasawa Y. Radial MRI of the hip with moderate osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2000;82(2): Riad J, Bajelidze G, Gabos PG. Bilateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis: Predictive factors for contralateral slip. J Pediatr Orthop 2007;27(1): McAfee PC, Cady RB. Endocrinologic and metabolic factorsin atypical presentations of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;180(6): Tins B, Cassar-Pullicino V, McCall I.The role of pretreatment MRI in established cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Eur J Radiol 2009;70(5): Gholve PA, Cameron DB, Millis MB. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis update. Curr Opin Pediatr 2009;21(6): Tehranzadeh J, Fung Y, Donohue M, Anavim A, Pribram HW. Computed tomography of Paget disease of the skull versus fibrous dysplasia. Skeletal Radiol 1998;27(1): Loneragan R. Digital subtraction angiography demonstration of bone hypervascularity in Paget s disease. Australas Radiol 1999;43(6): Vande Berg BC, Malghem J, Lecouvet FE, Maldague B. Magnetic resonance appearance of uncomplicated Paget s disease of bone. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 2001;5(6): Babhulkar S, Pande S, Sonali. Tuberculosis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;398(2): Sawlani V, Chandra T, Mishra RN, Aggarwal A, Jain UK, Gujral RB. MRI features of tuberculosis of peripheral joints. Clin Radiol 2003;58(3): Karchevsky M, Schweitzer ME, Morrison WB, Parellada JA. MRI Findings of septic arthritis and associated osteomyelitis in adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(5): Malizos KN, Zibis AH, Dailiana Z, Hantes M, Karachalios T, Karantanas AH. MR imaging findings in transient osteoporosis of the hip. Eur J Radiol 2004;50(6): Ragab Y, Emad Y, Abou-Zeid A. Bone marrow edema syndromes of the hip: MRI features in different hip disorders. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(4): Ganz R, Leunig M, Leunig-Ganz K, Harris. The etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip: an integrated mechanical concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(6): Houghton KM. Review for the generalist: evaluation of pediatric hip pain. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2009;7(2): Robinson H, Hartleben P, Lund G, Schreiman J. Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: accuracy compared with radiographs, core biopsy, and intraosseous pressure measurements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71(1): Source of Support: Nil; Conflict of Interest: None Submitted: ; Published online:
Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General
 Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General Hospital Osteonecrosis pathophysiology epidemiology imaging
Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General Hospital Osteonecrosis pathophysiology epidemiology imaging
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
 A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when?
 Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients. Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015
 Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion
 Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA
 Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA Don t Miss Acquired Hip Disorders SCFE Posterior Hip Dislocation Osteoid
Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA Don t Miss Acquired Hip Disorders SCFE Posterior Hip Dislocation Osteoid
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD
 Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Case Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case.
 Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule
 Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Case Dysbaric osteonecrosis of the humerus
 Case 14398 Dysbaric osteonecrosis of the humerus Magdalena Posadzy 1, Nicolas De Vos 2, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker2, 3, 4 1. W. Dega Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation University Hospital, Karol Marcinkowski University
Case 14398 Dysbaric osteonecrosis of the humerus Magdalena Posadzy 1, Nicolas De Vos 2, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker2, 3, 4 1. W. Dega Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation University Hospital, Karol Marcinkowski University
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions. Claudio Mella, MD
 Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies
 Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
SC FE. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR
 SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
The Role of MR Imaging in Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head
 The Role of MR Imaging in Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head Apostolos H. Karantanas, M.D., Ph.D. 1 and Eleni E. Drakonaki, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Due to the pattern of its blood supply, the femoral
The Role of MR Imaging in Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head Apostolos H. Karantanas, M.D., Ph.D. 1 and Eleni E. Drakonaki, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Due to the pattern of its blood supply, the femoral
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Brain Atrophy. Brain Atrophy
 Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Medial circumflex artery Lateral circumflex artery
 Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip
 Original Article MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13995.6967 Radiology Section Madhavi Nori 1, Sravan Kumar Marupaka 2, Swathi Alluri
Original Article MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13995.6967 Radiology Section Madhavi Nori 1, Sravan Kumar Marupaka 2, Swathi Alluri
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders. Nisha Patel, MD
 MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa
 Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Beyond the Bump: The Spectrum of Extra-articular Pathology in Hip MRI for Clinical Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Beyond the Bump: The Spectrum of Extra-articular Pathology in Hip MRI for Clinical Femoroacetabular Impingement Poster No.: C-2239 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K.
Beyond the Bump: The Spectrum of Extra-articular Pathology in Hip MRI for Clinical Femoroacetabular Impingement Poster No.: C-2239 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K.
MRI of the Hips and Pelvis
 MRI of the Hips and Pelvis Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI
MRI of the Hips and Pelvis Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP
 O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP "2" L. Ditri, F. Grigoletto, Y. Melamed, D. Reis, L. Cucci, P. Germonprè, T. Mesimeris,
O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP "2" L. Ditri, F. Grigoletto, Y. Melamed, D. Reis, L. Cucci, P. Germonprè, T. Mesimeris,
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN. Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
Unilateral osteonecrosis. imaging findings
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis
 The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
MRI of the Hip. Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
 MRI of the Hip Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Take Home Points Joint effusion: does not collect dependently Imaging
MRI of the Hip Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Take Home Points Joint effusion: does not collect dependently Imaging
Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture
 Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture Joey Chan Yiing Beh 1*, Ehab Shaban Mahmoud Hamouda 1 1. Department of Diagnostic Imaging, KK Women's and Children's Hospital,
Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture Joey Chan Yiing Beh 1*, Ehab Shaban Mahmoud Hamouda 1 1. Department of Diagnostic Imaging, KK Women's and Children's Hospital,
Sacroiliac joint infection
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014
![Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014 Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014](/thumbs/89/100531147.jpg) Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Radiology Corner. Femoroacetabular Impingement. Summary of Imaging Findings. Introduction. History
 Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review
 Radiology Case Reports Volume II, Issue 1, 2007 Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review Jason C. Naples,
Radiology Case Reports Volume II, Issue 1, 2007 Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review Jason C. Naples,
GALEN ADVANCED Course
 GALEN ADVANCED Course Education in partnership Course information The course is aimed at senior residents, board-certified radiologists and fellows and is designed to advance the knowledge of an array
GALEN ADVANCED Course Education in partnership Course information The course is aimed at senior residents, board-certified radiologists and fellows and is designed to advance the knowledge of an array
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Guidelines, Policies and Statements. Statement on the Use of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Developmental Hip Dysplasia and Dislocation
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements Statement on the Use of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Developmental Hip Dysplasia and Dislocation Approved by Council June 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards
Guidelines, Policies and Statements Statement on the Use of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Developmental Hip Dysplasia and Dislocation Approved by Council June 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards
Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review
 Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2542 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords:
Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2542 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords:
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3325-3331 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005361 Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children Zhenjiang Liu, Wei Yan, Lijun Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3325-3331 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005361 Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children Zhenjiang Liu, Wei Yan, Lijun Zhang
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
