Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children
|
|
|
- Benedict Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children Zhenjiang Liu, Wei Yan, Lijun Zhang Department of Pediatric Orthopedics, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, People s Republic of China Received December 30, 2014; Accepted February 28, 2015; Epub March 15, 2015; Published March 30, 2015 Abstract: Objectives: To find the accurate incidence of the vacuum phenomenon in the hip and the best projection position for producing the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children. Methods: All pediatric anteroposterior (AP)-view and frog-leg-position plain hip joint radiographs obtained in our hospital between January 2003 and March 2013 were examined. The subjects ages ranged between 0 and 14 years (mean, 4.2 years). All of the plain radiographs showing crescent-, linear-, and irregular-shaped lucencies between the femoral head and acetabulum were included in the present study. Results: A total of 16,749 cases, including 12,422 cases (5,912 boys and 6,510 girls) with only AP-view plain radiographs and 4,327 cases (1,537 boys and 2,790 girls) with both AP-view and frog-leg-position plain radiographs that were assessed in our hospital between January 2003 and March 2013, were examined. None of the AP-view plain hip radiographs exhibited the vacuum phenomenon. Vacuum phenomenon of the hips was found in only 258 cases (321 hips) in the frog-leg-position plain radiographs of 4,327 cases, resulting in a constituent ratio of 5.96% (258/4327). A total of 1,738 normal children were assessed in the 4,327 frog-leg-position radiographs, and 150 cases of the vacuum phenomenon were found in the normal children; thus, the incidence of the vacuum phenomenon in normal children was 8.63% (150/1,738). In 2,360 children with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) who were assessed in the 4,327 frog-leg-position radiographs, 98 cases of vacuum phenomenon were found, yielding an incidence of 4.15% in children with DDH (98/2,360). Thus, the 258 cases with vacuum phenomenon included 150 normal hips (58.14%), 98 cases with DDH (37.98%), 5 cases with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (1.94%), and 1 case each of solitary eosinophilic granuloma in the left ischium (0.39%), polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of the left and right proximal femurs (0.39%), 1 case of hereditary multiple exostoses (0.39%), 1 case of congenital coxa vara (0.39%), and 1 fracture of the femoral neck after surgery (0.39%). The 321 hips in the 258 cases were classified as complete (121 hips, 37.69%) or partial (200 hips, 62.31%) types according to the proportion of the lucency area in the hip joints and as linear (159 hips, 49.53%), crescent (151 hips, 47.04%), or irregular (11 hips, 3.43%) lucencies according to the shape of the lucency area in the hips. Conclusions: The vacuum phenomenon of the hip in children is found in frog-leg-position plain radiographs. It is easier to find the vacuum phenomenon in normal hips compared to cases with DDH. Frog-leg-position plain radiographs provide a better projection position for obtaining the vacuum phenomenon of the hip in children compared to AP-view plain radiographs. Keywords: Vacuum phenomenon, hip, radiograph, children Introduction In 1910, Fick described for the first time the linear photic zone in X-ray images as the vacuum phenomenon [1], which is a self-forming phenomenon of intrajoint gas [2]. Clinical and experimental studies have shown that the vacuum phenomenon occurs only when there is no liquid inside the joint [3, 4]. The intrajoint vacuum phenomenon is most common in intradiscal spine fractures that are caused by cartilage degeneration [5]. It may also occur in other joints, including the shoulder, wrist, hip, sacroiliac joint, ankle, subtalar joint, and knee [3, 6-9]. Studies on the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon are very rare. Generally, the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon only occurs when traction or other forces have been applied to the hip joint [10-13] or in patients with severe osteoarthritis who attempt extreme abduction of their hip joints
2 Table 1. The disease distribution of VP in frog-leg position radiographs of 4327 cases Disease [14]. Some scholars believe that the occurrence of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon in children can exclude suppurative arthritis of the hip [13, 14], traumatic joint effusion, and recent severe hip trauma [3, 4], but this is controversial [15]. To date, the incidence rate of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon in children and the best X-ray projection position for viewing the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon are not clear. We performed a retrospective analysis of the X-ray images of 258 children (321 hips) with the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon that were obtained in the frog-leg hip position. This is the first study to report the incidence of the vacuum phenomenon in hip-joint X-ray images. In addition, we propose a morphological classification of the vacuum phenomenon that is based on the percentage and morphology of the photic zone. According to the literature, this was the largest case study of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon in the world. Material and methods Number of Cases In a review of all hip-joint anteroposterior and frog-leg position X-ray images in children recorded at the Pediatric Orthopaedics Department in Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University from January 2003 to March 2013, the VP Cases Percentage of VP Cases (%) Normal hip joint Developmental dysplasia of the hip Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease Femoral fractures Femur tumor Congenital coxa vara Ischial damage Slipped capital femoral epiphysis Pelvic fracture Hip infection Osteogenesis imperfecta Myositis ossificans Knee valgus Hypochondroplasia Total VP: vacuum phenomena. All of the hip-joint X-ray images showing crescent, linear, or irregular radioactive photic zones between the femoral head cartilage and the acetabular cartilage were included in this study. Dr. Zhenjiang Liu carefully read all of the included X-ray images and reviewed the clinical medical records of all of the patients. SPSS13.0 statistical software was applied, and Chi-square tests were used for the data analysis. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results ages of the patients ranged from 0 to 14 years, with an average of 4.2 years. Standard supine anteroposterior hip X-ray images and/or frog-leg position images were recorded. The distance between the films and the X-ray probes was 110 cm. The X-ray instrument was a Picture Archiving and Communications System and a Siemens digital X-ray workstation (Siemens AG, Munich, Germany). All of the X-ray images were collected by two pediatric orthopedic doctors (Zhenjiang Liu and Wei Yan) within one month at the same place. In the past 10 years, our hospital has recorded 16,749 hip-joint X-ray images in children, and these include 12,422 anteroposterior hip-joint X-ray images (5,912 male cases and 6,510 female cases) and 4,327 anteroposterior and frog-leg-position hip-joint X-ray images (1,537 male cases and 2,790 female cases). The disease distribution is shown in Table 1. In all of the 16,749 anteroposterior hip-joint X-ray images, no images of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon were found. The total constituent ratio of the vacuum phenomenon in anteroposterior hip-joint X-ray images was 0 (0/16,749). In 4,327 frog-leg-position hip-joint X-ray images, we found 258 (321 hips) cases of the hipjoint vacuum phenomenon with a constituent 3326 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
3 Table 2. The age distribution of the 258 cases with the hip-joint VP Age (years) Number Percentage (%) 1 40 (31 Normal hip/9 DDH) 15.50% (40/258) 2 62 (42 Normal hip/20 DDH) 24.03% (62/258) 3 36 (17 Normal hip/19 DDH) 13.95% (36/258) 4 23 (14 Normal hip/9 DDH) 8.91% (23/258) 5 29 (14 Normal hip/14 DDH/1 LCPD) 11.24% (29/258) 6 17 (9 Normal hip/6 DDH/1 LCPD/1 Congenital coxa vara) 6.59% (17/258) 7 13 (8 Normal hip/3 DDH/1 LCPD/1 FD) 5.04% (13/258) 8 5 (3 Normal hip/2 DDH) 1.94% (5/258) 9 8 (2 Normal hip/4 DDH/1 LCPD/1 HME) 3.10% (8/258) 10 7 (4 Normal hip/3 DDH) 2.71% (7/258) (4 Normal hip/6 DDH/1 LCPD/1 EG) 4.65% (12/258) 12 5 (2 Normal hip/2 DDH/1 fracture of femoral neck) 1.94% (5/258) % (0/258) 14 1 (1 DDH) 0.39% (1/258) Total % (258/258) VP: vacuum phenomena. DDH: developmental dysplasia of the hip. LCPD: Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. FD: Fibrous dysplasia. HME: hereditary multiple exostoses. EG: eosinophilic granuloma. ratio of 5.96% (258/4,327). The 4,327 frog-legposition hip-joint X-ray images included 1,738 normal hip joints with 150 cases of the vacuum phenomenon [incidence rate, 8.63% (150/ 1738)] and 2,360 patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip with 98 cases of the vacuum phenomenon [incidence rate, 4.15% (98/2,360)]. The Chi-square test showed P < 0.001, which was a significant difference. The age distribution of the 258 cases with the vacuum phenomenon is shown in Table 2. The medical records of all of the vacuum phenomenon patients showed no hip pain, swelling, or motion limitations, which excluded hip-joint infection and other diseases. The 258 cases of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon included 90 male cases (34.88%) and 168 female cases (65.12%) and 150 cases with a normal hip joint (58.14%) (Figures 1 and 2), 98 cases with developmental dysplasia of the hip (37.98%) (Figures 3 and 4), 5 cases with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (1.94%) (Figure 5), 1 case each of solitary eosinophilic granuloma in the left ischium (0.39%), polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of the left and right proximal femur (0.39%) (Figure 6), hereditary multiple exostoses (0.39%), congenital coxa vara (0.39%), and a fracture of the right femoral neck after surgery (0.39%). The 321 hips included 153 left hips and 168 right hips. According to the proportion of photic zones in the hip joint, these can be divided into complete or partial types. The complete type is defined by a photic zone with length larger than 50% of the length of the articular cartilage between the femoral head and the acetabulum. The partial type is defined by a photic zone with length smaller than 50% of the length of the articular cartilage between the femoral head and the acetabulum. Thus, the 321 hips included 121 complete-type hips (37.69%) and 200 partial-type hips (62.31%). According to the morphology of the hip-joint photic zone (linear, crescent, or irregular), the 321 hips included 159 hips with a linearshaped photic zone (49.53%), 151 hips with a crescent-shaped photic zone (47.04%), and 11 hips with an irregular-shaped photic zone (3.43%). Discussion In conventional X-ray images, small amounts of gathered gas are noticed in normal joints, and this is called the spontaneous vacuum phenomenon. This phenomenon is usually seen in babies and children. Ewans has suggested that healthy and normal children may show the vacuum phenomenon when they perform a strong hip abduction [10]. When traction is applied to the joint, the incidence rate of the vacuum phenomenon significantly increases [14]. In this study, among the 4,327 patients with frog-legposition hip-joint X-ray images, 258 showed dif Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
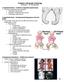
4 Figure 1. Typical frog-leg-position plain-film radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the normal hips of a 2-year-old boy. Note the crescent lucency and the complete type (arrows). Figure 2. Radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the normal hips of a 2-year-old boy. Note the linear lucency of the left hip (solid arrow) and the crescent lucency of the right hip (dotted arrow). Both are complete types. Figure 3. Radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the right hip of a 2-year-old girl with developmental dysplasia of the hip after close reduction in the right hip with avascular necrosis of the right femoral head. Note the irregular lucency and the partial type (arrow). mal hip joints was 8.63%, which was much higher than the 4.15% incidence rate found in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip, indicating that the hipjoint vacuum phenomenon more often occurred in normal hip joints. We did not detect even one vacuum phenomenon case in any of the anteroposterior hip-joint X-ray images, indicating that the vacuum phenomenon is hard to produce in hip-joint anteroposterior X-ray images without applying traction to the hip joint. Thus, we concluded that the external traction that is applied to the hip joint is a prerequisite of the vacuum phenomenon in hip-joint anteroposterior X-ray images. Compared to the hip-joint anteroposterior X-ray images, the hip-joint frog-leg position is a better X-ray projection position for observing the vacuum phenomenon. Our research results support the conclusions obtained by Ewans. What is the reason for the intrajoint vacuum phenomenon in the hip-joint frog-leg position? When the hip joint is in the frog-leg position, the stretch of the endogenous muscles, such as the muscles around the hip joint, leads to a sudden increase in the hip-jointcavity volume. The pressure in the joint cavity suddenly decreases, and the gases that are dissolved in the nearby tissues around the hip joint diffuse into the low-pressure joint cavity, thus producing the vacuum phenomenon. Thus, when the hip or shoulder joints are placed in an extreme abduc- ferent levels of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon, which was seen in the intrajoint photic zones with different sizes. The total constituent ratio of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon case in hip-joint frog-leg-position X-ray images in children was 5.96% (258/4,327), indicating that the vacuum phenomenon was not rare in hipjoint frog-leg-position X-ray images. The incidence rate of the vacuum phenomenon in nor- tion position for X-rays, the vacu- um phenomenon is usually more obvious. However, although the traction continues for a period of time, the gas that is diffused into the joint will be absorbed very quickly or replaced by liquids. Then, the vacuum phenomenon will disappear quickly [10]. Magnusson has suggested that, along with the decrease in intrajoint pressure, the gas that is 3328 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
5 Figure 4. Radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the right and left hips of a 3-year-old girl with developmental dysplasia of the hip after an open reduction, a Dega pelvis osteotomy, and a femoral shortening osteotomy in both hips. Note the irregular lucency of both hips, which are both partial types (arrows). 1/20 atm, the intrajoint liquid evaporates. The released gas leads to the vacuum phenomenon on X-ray images. In order to produce the intrajoint vacuum, it is necessary to overcome the soft-tissue elasticity and the external atmosphere traction [10]. Another prerequisite is that the soft tissues around the joint should be able to withstand the external pressure rather than be pressed into the enlarged joint cavity [10]. Nordheim has suggested that the intrajoint gas should include the evaporated synovial liquid that is at 37 C and 47 mmhg and previously dissolved gases in the blood and tissues, which diffused into the joint afterwards [10]. Figure 5. Radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the right and left hips of a 6-year-old girl with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease in the left femoral head. Note the crescent lucency in the left hip, which is a complete type (solid arrow). The linear lucency in the right hip is a partial type (dotted arrow). Figure 6. Radiographic appearance of the vacuum phenomenon in the right and left hips in a 7-year-old boy with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia in the left and right proximal femur. Note the linear lucency of the left hip (dotted arrows) and the linear lucency of the right hip (solid arrows), which are both partial types. dissolved in the synovium will be released. When the intrajoint pressure decreases to The factors involved in intrajoint gas formation mainly include traction applied to the joint, the extent of the joint capsule folding when the intrajoint vacuum forms, the relative inconsistency of the joint facets, and the existence of excessive intrajoint liquids and exudated or abnormal soft tissues [14]. When traction is applied, the joint capsule is folded, which can reduce the negative intrajoint pressure. Excessive liquids in the articular depression can replace the potential vacuum voids. Due to the effects of the liquid pressure, the facing joint facets are closely attached, with a resistance to external tractions. The vacuum phenomenon will not occur at this time. However, in patients with osteoarthritis, their rigid joint capsules restrict the applied tractions on the joint. When the traction is applied, their joint capsules cannot fold inward, which forms the joint vacuum and intrajoint gas release [14]. Radiation film technology has shown that the vacuum phenomenon is instantaneous. When the applied traction is great enough, 3329 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
6 intrajoint gas will be produced and then disappear very fast [14]. The major component of the intrajoint gas is a mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen, which is a similar constituent ratio as the ratio of the gas components in the circulating blood [2]. In fact, the term vacuum means the lack of gas, which is not accurate. Perhaps, the term spontaneous joint inflatable angiography that has been proposed by Fuiks and Grayson is more appropriate [3]. Does the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon have practical clinical value? Some scholars have proposed that the existence of the vacuum phenomenon can exclude the possibility of intrajoint exudates [2, 3]. Martel and Poznanski [14] have explained the diagnostic value of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon. When the distance between the femoral head and the acetabulum is larger than 1 mm and no intrajoint gas appears, the intrajoint exudate or other joint diseases can exist [15]. In a later study that was conducted by Martel et al. [16], traction applied to the hip joint can lead to intrajoint gas formation even when the intrajoint exudate exists, but the photic zone is not crescentshaped. If a crescent-shaped photic zone appears, the existence of exudate can be excluded [16]. In our clinical cases, 96.12% of the hipjoint vacuum phenomenon cases occurred in normal hip joints (58.14%) and in the follow-up period of cases with developmental dysplasia of the hip (37.98%). These cases did not involve any clinical manifestation of hip-joint exudate. For the vacuum phenomenon cases with noncrescent-shaped photic zones, their medical records did not provide any evidence of intrajoint exudates. Thus, we inferred that the hipjoint vacuum phenomenon was just an X-ray radiographic sign that occasionally occurred in X-rays. The hip-joint vacuum phenomenon has no special relationship with hip-joint diseases, and it has no practical clinical value. In this study, we were the first to propose a morphological classification of the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon, including the complete and partial types and the crescent, linear, and irregular-shaped photic zones. This morphological classification may be beneficial to future studies on the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon. This study was a preliminary investigation of the hipjoint vacuum phenomenon, and it could not determine its long-term clinical significance. Further studies on the hip-joint vacuum phenomenon are needed. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Zhenjiang Liu, Department of Pediatric Orthopedics, The Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, No. 36 Sanhao Street, Heping District, Shenyang City , People s Republic of China. Tel: ; lzjsdd@163.com References [1] Fick R. Handbuch der Anatomie und Mechanik der Gelenke. Teil II. Jena: Gustave Fischer; pp. 53. [2] Miller MD, Osborne JR. Spontaneous vacuum pneumarthrography revisited: the significance of the vacuum phenomenon in the lateral compartment of the knee. Arthroscopy 1998; 14: [3] Fuiks DM, Grayson CE. Vacuum pneumoarthrography and the spontaneous occurrence of gas in the joint spaces. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1950; 32: [4] Shogry ME, Pope TL Jr. Vacuum phenomenon simulating meniscal or cartilaginous injury of the knee at MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 180: [5] Wright DM, Sochart DH. Spontaneous vacuum phenomenon in the lateral compartment of the knee associated with a lateral tibial plateau fracture. Knee 2006; 13: [6] Hammar MV, Wintzell GB, Aström KG, Larsson S, Elvin A. Role of us in the preoperative evaluation of patients with anterior shoulder instability. Radiology 2001; 219: [7] Middleton WD, McAlister WH. Hip joint fluid in the presence of the vacuum phenomenon. Pediatr Radiol 1986; 16: [8] Sze MJ, Mulligan MJ. Reliability of vacuum phenomenon in the sacroiliac joint as a sign of traumatic injury. Emerg Radiol 2002; 9: [9] Lee TH, Wapner KL, Mayer DP, Hecht PJ. Computed tomographic demonstration of the vacuum phenomenon in the subtalar and tibiotalar joints. Foot Ankle Int 1994; 15: [10] Jerre T. The vacuum phenomenon in the hip joint. Acta Orthop Scand 1948; 17: [11] Arvidsson I. The hip joint: forces needed for distraction and appearance of the vacuum phenomenon. Scand J Rehabil Med 1990; 22: Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
7 [12] Vegter J, van den Broek JA. The diagnostic value of traction during radiography in diseases of the hip. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1983; 65: [13] van den Broek HA, Vegter J. Traction radiography of the hip and fluid in the hip joint. Diagn Imaging 1983; 52: [14] Martel W, Poznanski AK. The value of traction during roentgenography of the hip. Radiology 1970; 94: [15] Greenough CG. The vacuum arthrogram in the acutely injured knee: a case report. J Trauma 1989; 29: [16] Martel W, Poznanski AK, Kuhns LR. Further observations on the value of traction during roentgenography of the hip. Invest Adiol 1971; 6: Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies
 Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis?
 Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
 A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1661 1668 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1587-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip Michiel A. J. van de
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1661 1668 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1587-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip Michiel A. J. van de
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Childhood hip conditions. Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant
 Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults. Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015
 Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015 Objectives Develop a better understanding of the differential diagnosis of hip pain in active young adults Appreciate key points
Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015 Objectives Develop a better understanding of the differential diagnosis of hip pain in active young adults Appreciate key points
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
PEDIATRIC AND CONGENITAL IMAGING GUIDELINES MUSCULOSKELETAL 2009 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule
 Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
PEDIATRIC AND CONGENITAL IMAGING GUIDELINES: MUSCULOSKELETAL 2011 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
The surgical treatment of Perthes disease by
 Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Many fields are derived from the existing NJR. John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society
 Minimum Dataset for BHS Non Arthropasty Hip Surgery Database Please note: Many fields are derived from the existing NJR John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society 1
Minimum Dataset for BHS Non Arthropasty Hip Surgery Database Please note: Many fields are derived from the existing NJR John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society 1
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia
 Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:452-457 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.452 Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis Sung Soo Kim, MD, Chan Woo
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:452-457 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.452 Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis Sung Soo Kim, MD, Chan Woo
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session. DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips
 Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
The vacuum phenomenon in the ankle joint: Air bubbles on CT
 The vacuum phenomenon in the ankle joint: Air bubbles on CT by Christopher R. Hood JR. DPM 1*, Wesley A. Jackson DPM 2, Robert C. Floros DPM 3, David A. Bernstein, DPM 4 Gas or air bubbles in a joint space
The vacuum phenomenon in the ankle joint: Air bubbles on CT by Christopher R. Hood JR. DPM 1*, Wesley A. Jackson DPM 2, Robert C. Floros DPM 3, David A. Bernstein, DPM 4 Gas or air bubbles in a joint space
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Ultrasound Evaluation of Pavlik Harness in Treatment of Infants with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Prone Axial Approach to Harness in Situ
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Pavlik Harness in Treatment of Infants with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Prone Axial Approach to Harness in Situ C Fernández, MD; M Guasp, MD; J Gómez Fernández-Montes,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Pavlik Harness in Treatment of Infants with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Prone Axial Approach to Harness in Situ C Fernández, MD; M Guasp, MD; J Gómez Fernández-Montes,
7/1/2012. Repetitive valgus stresses cause microfractures in the apophyseal cartilage (weak link) Common in year olds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia
 Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia, MBChB, D Orth, MSc. Abstract: The aim of the study to determine the benefit of delaying appearance
Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia, MBChB, D Orth, MSc. Abstract: The aim of the study to determine the benefit of delaying appearance
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
The Hip from Cradle to Grave. Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital
 The Hip from Cradle to Grave Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital Developmental dysplasia hip DDH Irritable vs. septic hip Perthes disease Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
The Hip from Cradle to Grave Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital Developmental dysplasia hip DDH Irritable vs. septic hip Perthes disease Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
The Painful Hip. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4983-4989 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002634 Original Article Spatial changes of the peri-acetabular pelvic in developmental dysplasia of the hip---a combined 3-dimentional
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4983-4989 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002634 Original Article Spatial changes of the peri-acetabular pelvic in developmental dysplasia of the hip---a combined 3-dimentional
Case Developmental dysplasia of hip
 Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
Mohamed El-Sayed Tarek Ahmed Sameh Fathy Hosam Zyton. Introduction
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:471 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0451-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The effect of Dega acetabuloplasty and Salter innominate on acetabular remodeling monitored by the acetabular index
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:471 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0451-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The effect of Dega acetabuloplasty and Salter innominate on acetabular remodeling monitored by the acetabular index
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures. Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service
 Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service Disclosures Nothing to disclose Articular Fractures: Overview Require
Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service Disclosures Nothing to disclose Articular Fractures: Overview Require
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics. October 30, Name: Solution. This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions.
 BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics Exam 2 October 30, 2015 This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions. Grade: #1 / 16 #2 / 24 #3 / 32 #4 / 10 #5 / 18 Final Grade / 100 Page 1
BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics Exam 2 October 30, 2015 This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions. Grade: #1 / 16 #2 / 24 #3 / 32 #4 / 10 #5 / 18 Final Grade / 100 Page 1
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review
 Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011
 SUTTER MEDICAL FOUNDATION (SMF) 2800 L Street, 7 th Floor Sacramento, CA 95816 SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011 I. Shoulder Pain...Page
SUTTER MEDICAL FOUNDATION (SMF) 2800 L Street, 7 th Floor Sacramento, CA 95816 SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011 I. Shoulder Pain...Page
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis
 The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
Diagnostic Imaging Exams
 Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Effects of Immobilization. N24 Pedi Musculoskeletal Spring 2012, Week 14. Cabrillo ADN/C. Madsen RN, MSN 1. Physical effects on other systems
 Common Orthopedic Problems of Children Congenital Acquired Bones Neuromuscular Physical effects on other systems Pulmonary Cardiac Skin integrity Elimination GI GU 1 4 General Nursing Considerations any
Common Orthopedic Problems of Children Congenital Acquired Bones Neuromuscular Physical effects on other systems Pulmonary Cardiac Skin integrity Elimination GI GU 1 4 General Nursing Considerations any
What is a Hip Dysplasia?
 What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa
 Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa JAMES K. BRANNON, MD, FAAOS abstract Full article available online at ORTHOSuperSite.com. Search: 20120123-23 Hip arthroscopy
Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa JAMES K. BRANNON, MD, FAAOS abstract Full article available online at ORTHOSuperSite.com. Search: 20120123-23 Hip arthroscopy
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
KNEE DISLOCATION. The most common injury will be an anterior dislocation, and this usually results from a hyperextension mechanism.
 KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Supine and Standing AP Pelvis Radiographs in the Evaluation of Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid 3, Munir
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid 3, Munir
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian Citation V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian Citation V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian.
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit. Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care
 Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Disclosure. FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software. Acceptance of Hip Arthroscopy & FAI. Public. Payors. Orthopaedic Community
 2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Case Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent
 Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica o Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; H Hayashi, Tomayoshi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42 Issue Date 1997-12-20
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica o Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; H Hayashi, Tomayoshi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42 Issue Date 1997-12-20
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in the periadolescent period
 J Orthop Sci (2005) 10:15 21 DOI 10.1007/s00776-004-0850-z Original article Surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in the periadolescent period Vasilios A. Papavasiliou 1 and Athanasios
J Orthop Sci (2005) 10:15 21 DOI 10.1007/s00776-004-0850-z Original article Surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in the periadolescent period Vasilios A. Papavasiliou 1 and Athanasios
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule. (October 2016 February 2017)
 DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule (October 2016 February 2017) THEORY (3 PM 4 PM) 07.10.2016 CTEV and flat foot 14.10.2016 CDH 21.10.2016 Torticollis, congenital pseudoarthrosis of tibia and
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule (October 2016 February 2017) THEORY (3 PM 4 PM) 07.10.2016 CTEV and flat foot 14.10.2016 CDH 21.10.2016 Torticollis, congenital pseudoarthrosis of tibia and
Case Report Characteristics and outcomes of traumatic major extremity amputations in Chinese population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(3):6963-6967 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014520 Case Report Characteristics and outcomes of traumatic major extremity amputations in Chinese population Chenhao Dou 1,2*,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(3):6963-6967 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014520 Case Report Characteristics and outcomes of traumatic major extremity amputations in Chinese population Chenhao Dou 1,2*,
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion
 Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Surgical Technique. Hip System
 Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
A Patient s Guide to Perthes Disease of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Perthes Disease of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Perthes Disease of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
 UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
SC FE. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR
 SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
