GOUT disease spectrum including
|
|
|
- Henry Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GOUT disease spectrum including *hyperuricemia, *recurrent attacks of acute arthritis associated with monosodium urate crystals in leukocytes found in synovial fluid, *deposits of monosodium urate crystals in tissues (tophi), *interstitial renal disease, and *uric acid nephrolithiasis Pathophysiology **In humans, uric acid is the end product of the degradation of purines. It serves no known physiologic purpose and is regarded as a waste product. **The size of the urate pool is increased several folds in individuals with gout. **This excess accumulation may result from either overproduction or underexcretion. **The purines from which uric acid is produced originate from three sources : 1-dietary purine, 2-conversion of tissue nucleic acid to purine nucleotides, 3-de novo synthesis of purine bases. **About two-thirds of the uric acid produced each day is excreted in the urine. **The remainder is eliminated through the GI tract after enzymatic degradation by colonic bacteria. **A decline in the urinary excretion of uric acid to a level below the rate of production leads to hyperuricemia and an increased miscible pool of sodium urate. **Deposition of urate crystals in synovial fluid results in an inflammatory process involving chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, complement activation, and chemotactic activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. **Phagocytosis of urate crystals by leukocytes results in rapid lysis of cells and a discharge of proteolytic enzymes into the cytoplasm. **The ensuing inflammatory reaction is associated with intense joint pain, erythema, warmth, and swelling. **Most therapeutic strategies for gout involve lowering the uric acid level below the saturation point (6 mg/dl), thus preventing the deposition of urate crystals. **This can be accomplished by interfering with uric acid synthesis or increasing uric acid excretion. Diagnosis **The definitive diagnosis is accomplished by aspiration of synovial fluid from the affected joint and identification of intracellular crystals of monosodium urate monohydrate in synovial fluid leukocytes. **When joint aspiration is not a viable option, a presumptive diagnosis of acute gouty arthritis may be made on the basis of the presence of the characteristic signs and symptoms, as well as the response to treatment Desired outcomes **Terminate the acute attack, **Prevent recurrent attacks of gouty arthritis, and **Prevent complications associated with chronic deposition of urate crystals in tissues. Treatment of gout **Nonpharmacologic Therapy :- Patients may be advised to reduce their intake of foods high in purines (e.g., organ meats), avoid alcohol, increase fluid intake, and lose weight if obese. Joint rest for 1 to 2 days should be encouraged, and local application of ice may be beneficial (acute cases.) **Pharmacologic Therapy :- - Acute gout - Chronic gout #Treatment of acute gout *Acute gout attacks can result from a number of conditions, including excessive alcohol consumption, a diet rich in purines, and kidney disease. *NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or colchicine are effective alternatives for the management of acute gouty arthritis. *Indomethacin is considered the classic NSAID of choice, although all NSAIDs are likely to be effective in decreasing pain and inflammation. *Intraarticular administration of corticosteroids (when only one or two joints are affected) is also appropriate in the acute setting, with systemic corticosteroid therapy for more widespread joint involvement. *Patients are candidates for prophylactic urate-lowering therapy if they have more than two attacks per year or they have chronic kidney disease, kidney stones, or tophi (deposit of urate crystals in the joints, bones, cartilage, or other body structures). #Treatment of chronic gout *Urate-lowering therapy for chronic gout aims to reduce the frequency of attacks and complications of gout. *Treatment strategies include the use of xanthine oxidase inhibitors to reduce the synthesis of uric acid or use of uricosuric drugs to increase its excretion. *Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (allopurinol, febuxostat) are first-line urate-lowering agents. *Uricosuric agents (probenecid) may be used in patients who are intolerant to xanthine oxidase inhibitors or fail to achieve adequate response with those agents. [Note: Initiation of urate-lowering therapy can precipitate an acute gout attack due to rapid changes in serum urate concentrations. Medications for the prevention of an acute gout attack (low-dose colchicine, NSAIDs, or corticosteroids) should be initiated with urate-lowering therapy and continued for at least 6 months.]
2 Mechanism of action *Colchicine binds to tubulin, a microtubular protein, causing its depolymerization. This disrupts cellular functions, such as the mobility of granulocytes, thus decreasing their migration into the affected area. *Furthermore, colchicine blocks cell division by binding to mitotic spindles GOUT TREATMENT Colchicine Allopurinol Febuxostat Probenecid Pegloticase a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, is a purine analog. It reduces the production of uric acid by competitively inhibiting the last two steps in uric acid biosynthesis that are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase xanthine oxidase inhibitor, is structurally unrelated to allopurinol; however, it has the same indications *is a uricosuric drug. It is a weak organic acid that promotes renal clearance of uric acid by inhibiting the urateanion exchanger in the proximal tubule that mediates urate reabsorption. At therapeutic doses, it blocks proximal tubular reabsorption of uric acid *is a recombinant form of the enzyme urate oxidase or uricase. *It acts by converting uric acid to allantoin, a watersoluble nontoxic metabolite that is excreted primarily by the kidneys.. Therapeutic uses Pharmacokinet ics *The anti-inflammatory activity of colchicine is specific for gout, usually alleviating the pain of acute gout within 12 hours. [it must be administered within 36 hours of onset of attack to be effective] *NSAIDs replaced colchicine in the treatment of acute gouty attacks for safety reasons. * prophylactic agent to prevent acute attacks of gout in patients initiating uratelowering therapy * orally and is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. * is recycled in the bile and is excreted unchanged in feces or urine. * is an effective urate-lowering therapy in the treatment of gout and hyperuricemia secondary to other conditions, such as that associated with certain malignancies (those in which large amounts of purines are produced, particularly after chemotherapy) or in renal disease *completely absorbed after oral administration. The primary metabolite is alloxanthine (oxypurinol), which is also a xanthine oxidase inhibitor with a half-life of 15 to 18 hours. *Thus, effective inhibition of xanthine oxidase can be maintained with once-daily dosage. *The drug and its active metabolite are excreted in the feces and urine. *The dosage should be reduced if the creatinine clearance is less than 50 ml/min * blocks the tubular secretion of penicillin and is sometimes used to increase levels of β- lactam antibiotics. ****** *** * is indicated for patients with gout who fail treatment with standard therapies such as xanthine oxidase inhibitors. Febuxostat does not have the same degree of renal elimination as allopurinol and thus requires less adjustment in those with reduced renal function. *It also inhibits the excretion of methotrexate, naproxen, ketoprofen, and indomethacin. *Probenecid should be avoided if the creatinine clearance is less than 50 ml/min *It is administered as an IV infusion every 2 weeks
3 Adverse effects *nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea *Chronic administration may lead to myopathy, neutropenia, aplastic anemia, and alopecia. * should not be used in pregnancy, and it should be used with caution in patients with hepatic, renal, or cardiovascular disease. *Dosage adjustments are required in patients taking CYP3A4 inhibitors, like clarithromycin, itraconazole, and protease inhibitors. *For patients with severe renal impairment, the dose should be reduced. *well tolerated by most patients. *Hypersensitivity reactions, especially skin rashes, are the most common adverse reactions. *The risk is increased in those with reduced renal function. Because acute attacks of gout may occur more frequently during the first several months of therapy, colchicine, NSAIDs, or corticosteroids can be administered concurrently. *Allopurinol interferes with the metabolism of 6-mercaptopurine, the immunosuppressant azathioprine, and theophylline, requiring a reduction in dosage of these drugs * interactions with 6- mercaptopurine, azathioprine, and theophylline apply. *Its adverse effect profile is similar to that of allopurinol, although the risk for rash and hypersensitivity reactions may be reduced *** *** **Colchicine A plant alkaloid, is used for the treatment of acute gouty attacks. It is neither a uricosuric nor an analgesic agent, although it relieves pain in acute attacks of gout #Bone remodeling Throughout life, bone is continuously remodeled, with about 10% of the adult skeleton replaced each year. The purpose of bone remodeling is to remove and replace damaged bone and to maintain calcium homeostasis. Osteoclasts are cells that break down bone, a process known as bone resorption.following bone resorption, osteoblasts or bone-building cells synthesize new bone. Crystals of calcium phosphate known as hydroxyapatite are deposited in the new bone matrix during the process of bone mineralization. Bone mineralization is essential for bone strength. Lastly, bone enters a resting phase until the cycle of remodeling begins again.bone loss occurs when bone resorption exceeds bone formation during the remodeling process # Osteoporosis Characterized by progressive loss of bone mass and skeletal fragility.patients have an increased risk of fractures, which can cause significant morbidity. *Osteoporosis occurs in older men and women but is most pronounced in postmenopausal women TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS :- **Non-pharmacological: 1- Adequate dietary intake of calcium and vitamin D, 2-weight-bearing exercise,3-smoking cessation,4- avoid drugs that increase bone loss such as glucocorticoids **pharmacological:- 1- Bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates including alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, and zoledronicnacid are preferred agents for prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. These bisphosphonates, along with etidronate, pamidronate, and tiludronate, comprise an important drug group used for the treatment of bone disorders such as osteoporosis and Paget disease, as well as for treatment of bone metastases and hypercalcemia of malignancy 2- Selective estrogen receptor modulators Lower estrogen levels after menopause promote proliferation and activation of osteoclasts, and bone mass can decline rapidly. Estrogen replacement is effective for the prevention of postmenopausal bone loss. However, since estrogen may increase the risk of endometrial ancer (when used without a progestin in women with an intact uterus), breast cancer, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and coronary events, it is no longer recommended as a primary preventive therapy for osteoporosis
4 Bisphosphonates Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Adverse effects Relative decrease osteoclastic bone resorption mainly through an increase in osteoclastic apoptosis (programmed cell death) and inhibition of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway important for osteoclast function. The decrease in osteoclastic bone resorption results in a small increase in bone mass and a decreased risk of fractures in patients with osteoporosis. The beneficial effects of alendronate persist over several years of therapy, but discontinuation results in a gradual loss of effects The oral bisphosphonates (alendronate, risedronate, and ibandronate) are dosed on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis depending on the drug. Absorption after oral administration is poor, with less than 1% of the dose absorbed. Food and other medications significantly interfere with absorption of oral bisphosphonates, and specific guidelines for administration should be followed to maximize absorption rapidly cleared from the plasma, primarily because they avidly bind to hydroxyapatite in the bone., once bound to bone, they are cleared over a period of hours to years. Elimination is primarily via the kidney, and bisphosphonates should be avoided in severe renal impairment. For patients unable to tolerate oral bisphosphonates, intravenous ibandronate and zoledronic acid are alternatives *These include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and musculoskeletal pain. *Alendronate, risedronate, and ibandronate are associated with esophagitis and esophageal ulcers. *To minimize esophageal irritation, patients should remain upright after taking oral bisphosphonates. *Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported with bisphosphonates but is usually associated with higher intravenous doses used for hypercalcemia of malignancy. *Although uncommon, use of bisphosphonates may be associated with atypical fractures., The risk of atypical fractures may increase with long-term use of bisphosphonate therapy. *Etidronateis the only bisphosphonate that causes osteomalacia following long-term, continuous administration. potencies of the bisphosphonates
5 Selective estrogen receptor modulators Raloxifene Calcitonin Denosumab Teriparatide Salmon calcitonin is indicated for the treatment of osteoporosis in women who are at least 5 years postmenopausal. is a selective estrogen receptor modulator approved for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. It has estrogen-like effects on bone and estrogen antagonist effects on breast and endometrial tissue. It is an alternative for postmenopausal osteoporosis in women who are intolerant to bisphosphonates. Raloxifene increases bone density without increasing the risk of endometrial cancer. In addition, it decreases the risk of invasive breast cancer and also reduces levels of total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol. Adverse effects include hot flashes, leg cramps, and a risk of venous thromboembolism similar to estrogen. The drug reduces bone resorption, but it is less effective than bisphosphonates. A unique property of calcitonin is the relief of pain associated with osteoporotic fracture. Therefore, calcitonin may be beneficial in patients with a recent vertebral fracture. It is available in intranasal and parenteral formulations, but the parenteral formulation is rarely used for the treatment of osteoporosis. Common adverse effects of intranasal administration include rhinitis and other nasal symptoms. Resistance to calcitoninhas been observed with long-term use in Paget disease. Because of a potential increased risk of malignancy with calcitonin, this agent should be reserved for patients intolerant of other drugs for osteoporosis End Finally Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-b ligand and inhibits osteoclast formation and function. Denosumab is approved for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women at high risk of fracture. It is administered via subcutaneous injection every 6 months. Denosumab has been associated with an increased risk of infections, dermatological reactions, hypocalcemia, osteonecrosis of the jaw, and atypical fractures. It should be reserved for women at high risk of fracture and those who are intolerant of or unresponsive to other osteoporosis therapies. Teriparatide is a recombinant form of human parathyroid hormone that is administered subcutaneously daily for the treatment of osteoporosis. Teriparatide is the first approved treatment for osteoporosis that stimulates bone formation. Other drugs for osteoporosis inhibit bone resorption. Teriparatide promotes bone formation by stimulating osteoblastic activity. Teriparatide has been associated with an increased risk of osteosarcoma in rats. The safety and efficacy of this agent have not been evaluated beyond 2 years. Teriparatide should be reserved for patients at high risk of fractures and those who have failed or cannot tolerate other osteoporosis therapies.
Drugs for Gout, osteoarthritis and osteoporosis
 MMS Pharmacology Lecture 3 Drugs for Gout, osteoarthritis and osteoporosis Dr Sura Al Zoubi Revision Gout The term gout describes a disease spectrum including hyperuricemia, recurrent attacks of acute
MMS Pharmacology Lecture 3 Drugs for Gout, osteoarthritis and osteoporosis Dr Sura Al Zoubi Revision Gout The term gout describes a disease spectrum including hyperuricemia, recurrent attacks of acute
Drugs Used to Treat Gout. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used to Treat Gout Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of acute arthritis
Drugs Used to Treat Gout Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of acute arthritis
Case presentation. serum uric acid = 11.5 mg/dl 24-hour uric acid excretion = 300 mg
 GOUT 55 y/o male 12 hours pain in my big toe & ankle went to bed last night feeling fine felt as if had broken toe this morning similar problems in right ankle & left wrist Case presentation lab studies
GOUT 55 y/o male 12 hours pain in my big toe & ankle went to bed last night feeling fine felt as if had broken toe this morning similar problems in right ankle & left wrist Case presentation lab studies
What is Osteoporosis?
 What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
LECTURE 5: DRUGS IN GOUT
 Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Green : Dr s notes Grey: Extra information, explanation Editing File LECTURE 5: DRUGS IN GOUT
Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Green : Dr s notes Grey: Extra information, explanation Editing File LECTURE 5: DRUGS IN GOUT
Bisphosphonates. Making intelligent drug choices
 Making intelligent drug choices Bisphosphonates are a first choice for treating osteoporosis, according to Kedrin E. Van Steenwyk, DO, an obstetrician/gynecologist at Sycamore Women s Center, Miamisburg,
Making intelligent drug choices Bisphosphonates are a first choice for treating osteoporosis, according to Kedrin E. Van Steenwyk, DO, an obstetrician/gynecologist at Sycamore Women s Center, Miamisburg,
uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma
 73 uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma 1 Purines and uric acid Fig 2 JFI Uric acid is the major product of catabolism of the purine nucleosides adenosine and guanosine, Uric acid is sparingly soluble
73 uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma 1 Purines and uric acid Fig 2 JFI Uric acid is the major product of catabolism of the purine nucleosides adenosine and guanosine, Uric acid is sparingly soluble
Gout Treatment Guidelines
 Gout Treatment Guidelines Gout is a disorder that manifests as a spectrum of clinical and pathologic features built on a foundation of an excess body burden of uric acid, manifested in part by hyperuricemia,
Gout Treatment Guidelines Gout is a disorder that manifests as a spectrum of clinical and pathologic features built on a foundation of an excess body burden of uric acid, manifested in part by hyperuricemia,
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis. Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD
 The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD Definition A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase
The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD Definition A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase
Osteoporosis Agents Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Osteoporosis Agents Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of
Osteoporosis Agents Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of
Summary of the risk management plan by product
 Summary of the risk management plan by product 1 Elements for summary tables in the EPAR 1.1 Summary table of Safety concerns Summary of safety concerns Important identified risks Important potential risks
Summary of the risk management plan by product 1 Elements for summary tables in the EPAR 1.1 Summary table of Safety concerns Summary of safety concerns Important identified risks Important potential risks
S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
 S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Introduction Indication: Denosumab (Prolia ) is recommended in NICE TA204
S H A R E D C A R E G U I D E L I N E Drug: Denosumab 60mg injection Indication: treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Introduction Indication: Denosumab (Prolia ) is recommended in NICE TA204
Clinical Biochemistry department/ College of medicine / AL-Mustansiriyah University
 Clinical Biochemistry department/ College of medicine / AL-Mustansiriyah University Dr. Ali al-bayati NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM Lec. 3 The salvage pathway of purine synthesis Purines that result from the normal
Clinical Biochemistry department/ College of medicine / AL-Mustansiriyah University Dr. Ali al-bayati NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM Lec. 3 The salvage pathway of purine synthesis Purines that result from the normal
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the
PHARMACOLOGY ESSENTIALS FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS
 Focus on PHARMACOLOGY ESSENTIALS FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS CHAPTER 29 Drugs Used to Treat Musculoskeletal Conditions Multimedia Directory Slide 6 Slide 25 Slide 38 Osteoporosis Video Arthritis Video Mechanism
Focus on PHARMACOLOGY ESSENTIALS FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS CHAPTER 29 Drugs Used to Treat Musculoskeletal Conditions Multimedia Directory Slide 6 Slide 25 Slide 38 Osteoporosis Video Arthritis Video Mechanism
Gout 2.0. Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy
 Gout 2.0 Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy Case 48 year old man presents with swollen, painful left toe that started overnight. Didn t hurt when he went to bed. No
Gout 2.0 Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy Case 48 year old man presents with swollen, painful left toe that started overnight. Didn t hurt when he went to bed. No
Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis
 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis 1 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis Calcium and phosphate are the major mineral constituents of bone. They are also two of the most important minerals
Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis 1 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis Calcium and phosphate are the major mineral constituents of bone. They are also two of the most important minerals
AACE/ACE Osteoporosis Treatment Decision Tool
 AACE/ACE Osteoporosis Treatment Decision Tool What is Osteoporosis? OSTEOPOROSIS is defined as reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fracture. Osteoporosis, or porous bones, occurs when
AACE/ACE Osteoporosis Treatment Decision Tool What is Osteoporosis? OSTEOPOROSIS is defined as reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fracture. Osteoporosis, or porous bones, occurs when
CHAPTER:2 GOUT. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:2 GOUT BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY DEFINITION Gout is defined as a peripheral arthritis, resulting from the deposition of MSU crystals
CHAPTER:2 GOUT BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY DEFINITION Gout is defined as a peripheral arthritis, resulting from the deposition of MSU crystals
Osteoporosis. Definition
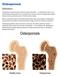 Osteoporosis Definition Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses like bending over or coughing can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures
Osteoporosis Definition Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses like bending over or coughing can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP
 Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Patients should receive supplemental calcium and vitamin D, if dietary intake is inadequate (see PRECAUTIONS).
 PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets Once Weekly 70 mg I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS Bisphosphonates are synthetic analogs of pyrophosphate that bind to the hydroxyapatite found in bone. is a bisphosphonate that acts as a
PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets Once Weekly 70 mg I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS Bisphosphonates are synthetic analogs of pyrophosphate that bind to the hydroxyapatite found in bone. is a bisphosphonate that acts as a
Osteoporosis Treatment Overview. Colton Larson RFUMS October 26, 2018
 Osteoporosis Treatment Overview Colton Larson RFUMS October 26, 2018 Burden of Disease Most common bone disease 9.9 million Americans + 43.1 million Americans have low bone mineral density (BMD) Stealthy
Osteoporosis Treatment Overview Colton Larson RFUMS October 26, 2018 Burden of Disease Most common bone disease 9.9 million Americans + 43.1 million Americans have low bone mineral density (BMD) Stealthy
Analgesics. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan March, 2014
 Analgesics Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan March, 2014 Mar-14 Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE 2 Feature Comparison of Analgesics Narcotic (Opioids) Nonnarcotic
Analgesics Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan March, 2014 Mar-14 Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE 2 Feature Comparison of Analgesics Narcotic (Opioids) Nonnarcotic
Elements for a Public Summary. Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Gout i Gout has a worldwide distribution. In the United Kingdom from 2000 to 2007, the estimated occurrence of gout is 5.9% in
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Gout i Gout has a worldwide distribution. In the United Kingdom from 2000 to 2007, the estimated occurrence of gout is 5.9% in
Download slides:
 Download slides: https://www.tinyurl.com/m67zcnn https://tinyurl.com/kazchbn OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW AND UPDATE Boca Raton Regional Hospital Internal Medicine Conference 2017 Benjamin Wang, M.D., FRCPC Division
Download slides: https://www.tinyurl.com/m67zcnn https://tinyurl.com/kazchbn OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW AND UPDATE Boca Raton Regional Hospital Internal Medicine Conference 2017 Benjamin Wang, M.D., FRCPC Division
1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential. 2. To understand the four stages of gout
 Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
1
 www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
New Developments in Osteoporosis: Screening, Prevention and Treatment
 Osteoporosis: Overview New Developments in Osteoporosis: Screening, Prevention and Treatment Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Definitions Risk factors
Osteoporosis: Overview New Developments in Osteoporosis: Screening, Prevention and Treatment Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Definitions Risk factors
Gout -revisited. Shrenik Shah
 Gout -revisited Shrenik Shah definition Monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition episodic and later persistent joint inflammation and tophi All MSU crystal deposition- broader definition EULAR- European
Gout -revisited Shrenik Shah definition Monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition episodic and later persistent joint inflammation and tophi All MSU crystal deposition- broader definition EULAR- European
Gout A rapid review. Jeremy Jones
 Gout A rapid review Jeremy Jones The Hyperuricemia Cascade Dietary purines Tissue nucleic acids Urate Endogenous purine synthesis Overproduction Hyperuricemia Underexcretion Silent tissue deposition Gout
Gout A rapid review Jeremy Jones The Hyperuricemia Cascade Dietary purines Tissue nucleic acids Urate Endogenous purine synthesis Overproduction Hyperuricemia Underexcretion Silent tissue deposition Gout
Osteoporosis. Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective. Old Definition of Osteoporosis
 Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective Dr Dicky T.K. Choy Physician Jockey Club Centre for Osteoporosis Care and Control, CUHK Osteoporosis Global public health
Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective Dr Dicky T.K. Choy Physician Jockey Club Centre for Osteoporosis Care and Control, CUHK Osteoporosis Global public health
A Patient s Guide to Gout. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Gout Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Gout Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Zainab Al-dabi - Shahd Alqudah - Dr. Malik
 - 4 - Zainab Al-dabi - Shahd Alqudah - Dr. Malik 1 In the USA there are 10 million cases of osteoporosis, most of which belong to women, this represents 3-4% of the population which is a relatively high
- 4 - Zainab Al-dabi - Shahd Alqudah - Dr. Malik 1 In the USA there are 10 million cases of osteoporosis, most of which belong to women, this represents 3-4% of the population which is a relatively high
Osteoporosis Update. Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist
 Osteoporosis Update Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist DEFINITION OSTEOPOROSIS is LOW BONE MASS (& micro-architectural deterioration) causing AN INCREASED RISK OF FRACTURE 23 years 82 years 23 y/o
Osteoporosis Update Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist DEFINITION OSTEOPOROSIS is LOW BONE MASS (& micro-architectural deterioration) causing AN INCREASED RISK OF FRACTURE 23 years 82 years 23 y/o
OSTEOPOROSIS: PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT
 OSTEOPOROSIS: OVERVIEW OSTEOPOROSIS: PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Definitions Key Risk factors Screening and Monitoring
OSTEOPOROSIS: OVERVIEW OSTEOPOROSIS: PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Definitions Key Risk factors Screening and Monitoring
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
 Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Lecture 8 Gout Hinch. Pathogenesis of acute attacks
 Gout: disease characterized by deposition of monosodium crystals in soft tissues (cartilage, tendons, bursa) recurrent episodes of acute joint pain & inflammation Pathogenesis of acute attacks Epidemiology:
Gout: disease characterized by deposition of monosodium crystals in soft tissues (cartilage, tendons, bursa) recurrent episodes of acute joint pain & inflammation Pathogenesis of acute attacks Epidemiology:
MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY. A story of the inflamed
 MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY A story of the inflamed 1 INFLAMMATION Pathophysiology Inflammation Reaction to tissue injury Caused by release of chemical mediators Leads to a vascular response Fluid and
MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY A story of the inflamed 1 INFLAMMATION Pathophysiology Inflammation Reaction to tissue injury Caused by release of chemical mediators Leads to a vascular response Fluid and
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Effective Health Care
 Number 12 Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments To Prevent Fractures in Men and Women With Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis Executive Summary Background Osteoporosis is a systemic
Number 12 Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments To Prevent Fractures in Men and Women With Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis Executive Summary Background Osteoporosis is a systemic
Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands. Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands
 Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands Calcium is an essential element for contraction of voluntary/smooth
Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands Calcium is an essential element for contraction of voluntary/smooth
Page 1
 Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by weakened bones that fracture easily. After menopause many women are at risk of developing osteoporosis. Peak bone mass is usually reached during
Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by weakened bones that fracture easily. After menopause many women are at risk of developing osteoporosis. Peak bone mass is usually reached during
Denosumab (Prolia 60 mg) Effective Shared Care Agreement For the treatment of Osteoporosis. Date: Date:
 Denosumab (Prolia 60 mg) Effective Shared Care Agreement For the treatment of Osteoporosis Section 1: Shared care arrangements and responsibilities Section 1.1 Agreement for transfer of prescribing to
Denosumab (Prolia 60 mg) Effective Shared Care Agreement For the treatment of Osteoporosis Section 1: Shared care arrangements and responsibilities Section 1.1 Agreement for transfer of prescribing to
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention
 Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Index. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 775 780 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AACE (American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists), bone mineral density recommendations of,
Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 775 780 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AACE (American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists), bone mineral density recommendations of,
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis. for hospitals and General Practice
 Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN OSTEOPOROSIS: SCREENING, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
 NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN OSTEOPOROSIS: SCREENING, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF OSTEOPOROSIS: OVERVIEW Definitions Risk factors
NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN OSTEOPOROSIS: SCREENING, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT Judith Walsh, MD, MPH Departments of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF OSTEOPOROSIS: OVERVIEW Definitions Risk factors
OSTEOPOROSIS MEDICINES
 Bone Basics 2010. NOF. All rights reserved. National Osteoporosis Foundation 1150 17th Street, NW, Suite 850 Washington, DC 20036 (800) 223-9994 www.nof.org OSTEOPOROSIS MEDICINES Although there is no
Bone Basics 2010. NOF. All rights reserved. National Osteoporosis Foundation 1150 17th Street, NW, Suite 850 Washington, DC 20036 (800) 223-9994 www.nof.org OSTEOPOROSIS MEDICINES Although there is no
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Hyperlipidemias. Hyperlipoproteinemias. Hyperlipemia. Hypercholestrolemia. Direct relationship with acute pancreatitis and atherosclerosis Structure Lipoprotein Particles Types
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Hyperlipidemias. Hyperlipoproteinemias. Hyperlipemia. Hypercholestrolemia. Direct relationship with acute pancreatitis and atherosclerosis Structure Lipoprotein Particles Types
Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline. Rheumatology January 2017
 Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline Rheumatology January 2017 Introduction Osteoporosis is a condition of low bone mass leading to an increased risk of low trauma fractures. The prevalence of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Clinical Guideline Rheumatology January 2017 Introduction Osteoporosis is a condition of low bone mass leading to an increased risk of low trauma fractures. The prevalence of osteoporosis
Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Meta-Analysis Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout Erika Bianca S. Villazor-Isidro, M.D.*; John Carlo G.
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Meta-Analysis Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout Erika Bianca S. Villazor-Isidro, M.D.*; John Carlo G.
BONEFOS 800 mg. Bonefos adalah obat baru yang terdaftar tahun Informasi di bawah ini merupakan informasi update tahun 2008.
 Bonefos adalah obat baru yang terdaftar tahun 2007. Informasi di bawah ini merupakan informasi update tahun 2008. BONEFOS 800 mg Important information, please read carefully! Composition 1 tablet contains
Bonefos adalah obat baru yang terdaftar tahun 2007. Informasi di bawah ini merupakan informasi update tahun 2008. BONEFOS 800 mg Important information, please read carefully! Composition 1 tablet contains
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS
 TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
Vol. 19, Bulletin No. 108 August-September 2012 Also in the Bulletin: Denosumab 120mg for Bone Metastases
 ה מ ר א פ הביטאון לענייני תרופות ISRAEL DRUG BULLETIN 19 years of unbiased and independent drug information P H A R x M A Vol. 19, Bulletin No. 108 August-September 2012 Also in the Bulletin: Denosumab
ה מ ר א פ הביטאון לענייני תרופות ISRAEL DRUG BULLETIN 19 years of unbiased and independent drug information P H A R x M A Vol. 19, Bulletin No. 108 August-September 2012 Also in the Bulletin: Denosumab
OSTEOFOS Tablets (Alendronate)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 OSTEOFOS Tablets (Alendronate) Composition OSTEOFOS 70 Each uncoated tablet contains: Sodium Alendronate, BP, equivalent to Alendronic Acid... 70 mg OSTEOFOS 35 Each uncoated
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 OSTEOFOS Tablets (Alendronate) Composition OSTEOFOS 70 Each uncoated tablet contains: Sodium Alendronate, BP, equivalent to Alendronic Acid... 70 mg OSTEOFOS 35 Each uncoated
Drugs Used in Gout. Knox Van Dyke. GENERIC NAME Allopurinol 445 Colchicine 443 Indomethacin 446 Oxyphenbutazone 446
 37 Drugs Used in Gout Knox Van Dyke DRUG LIST GENERIC NAME PAGE GENERIC NAME PAGE Allopurinol 445 Colchicine 443 Indomethacin 446 Oxyphenbutazone 446 Oxypurinol 446 Phenylbutazone 446 Probenecid 445 Sulfinpyrazone
37 Drugs Used in Gout Knox Van Dyke DRUG LIST GENERIC NAME PAGE GENERIC NAME PAGE Allopurinol 445 Colchicine 443 Indomethacin 446 Oxyphenbutazone 446 Oxypurinol 446 Phenylbutazone 446 Probenecid 445 Sulfinpyrazone
Update on Gout for GPs
 Update on Gout for GPs Dr Patrick Kiely PhD FRCP Consultant Physician and Rheumatologist St George s, London 2/3 1/3 Gut bacteria have uricase Chronic erosive arthropathy Clinical spectrum Making the diagnosis
Update on Gout for GPs Dr Patrick Kiely PhD FRCP Consultant Physician and Rheumatologist St George s, London 2/3 1/3 Gut bacteria have uricase Chronic erosive arthropathy Clinical spectrum Making the diagnosis
Kristen M. Nebel, DO PENN/ LGHP Geriatrics. Temple Family Medicine Review
 Kristen M. Nebel, DO PENN/ LGHP Geriatrics 10/3/17 Temple Family Medicine Review OBJECTIVES Define Revised 2017 American College of Physician Recommendations Screening, Prevention and Treatment Application
Kristen M. Nebel, DO PENN/ LGHP Geriatrics 10/3/17 Temple Family Medicine Review OBJECTIVES Define Revised 2017 American College of Physician Recommendations Screening, Prevention and Treatment Application
Greater Manchester Interface Prescribing Group Shared Care Template
 Greater Manchester Interface Prescribing Group Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline the use of Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. Author(s)/Originator(s):
Greater Manchester Interface Prescribing Group Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline the use of Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. Author(s)/Originator(s):
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices
 Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
Chapter 47. Media Directory. Calcium. Thyroid. Control of Calcium by Endocrine System. Drugs for Bone and Joint Disorders
 Chapter 47 Media Directory Slide 66 Calcitriol Animation Drugs for Bone and Joint Disorders Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Calcium Adequate levels in body necessary To transmit
Chapter 47 Media Directory Slide 66 Calcitriol Animation Drugs for Bone and Joint Disorders Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Calcium Adequate levels in body necessary To transmit
Osteoporosis - New Guidelines. Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011
 Osteoporosis - New Guidelines Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011 Outline What is Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? What treatments are available? Role of the Pharmacy technician Definition of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis - New Guidelines Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011 Outline What is Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? What treatments are available? Role of the Pharmacy technician Definition of Osteoporosis
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Febuxostat is a medicine used in adults with gout to reduce high levels of uric acid in the blood. Gout results from a build up
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Febuxostat is a medicine used in adults with gout to reduce high levels of uric acid in the blood. Gout results from a build up
Denosumab for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures
 APper apc15-0avgfh7 Shared Care Guideline Denosumab for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures For the latest information on interactions and adverse effects,
APper apc15-0avgfh7 Shared Care Guideline Denosumab for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures For the latest information on interactions and adverse effects,
Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP
 Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP Dr. Paul Doghramji is attending physician at the Pottstown Memorial Medical Center and medical director of Health Services
Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP Dr. Paul Doghramji is attending physician at the Pottstown Memorial Medical Center and medical director of Health Services
John J. Wolf, DO Family Medicine
 John J. Wolf, DO Family Medicine Objectives: 1. Review incidence & Risk of Osteoporosis 2.Review indications for testing 3.Review current pharmacologic & Non pharmacologic Tx options 4.Understand & Utilize
John J. Wolf, DO Family Medicine Objectives: 1. Review incidence & Risk of Osteoporosis 2.Review indications for testing 3.Review current pharmacologic & Non pharmacologic Tx options 4.Understand & Utilize
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Gout- Treatment Updates. Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA
 Gout- Treatment Updates Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA Gout Outline of purine metabolism: (1) amidophosphoribosyltransferase (2) hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
Gout- Treatment Updates Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA Gout Outline of purine metabolism: (1) amidophosphoribosyltransferase (2) hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
COPING A newsletter from COPN December 23, 2010 Remember: You can live well with osteoporosis!
 COPING A newsletter from COPN December 23, 2010 Remember: You can live well with osteoporosis! SEASONS GREETINGS! This issue of COPING draws to a close our series of articles on the 2010 Clinical Practice
COPING A newsletter from COPN December 23, 2010 Remember: You can live well with osteoporosis! SEASONS GREETINGS! This issue of COPING draws to a close our series of articles on the 2010 Clinical Practice
Chau Nguyen, D.O. Rheumatologist Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine at Western University of Health Sciences
 Chau Nguyen, D.O Rheumatologist Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine at Western University of Health Sciences I do not have any relationship with the manufacturer of any commercial products
Chau Nguyen, D.O Rheumatologist Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine at Western University of Health Sciences I do not have any relationship with the manufacturer of any commercial products
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
FOSAMAX (Alendronic acid as alendronate sodium trihydrate)
 CSP - UK/H/PSUR/0070 - March 2012 EUROPEAN UNION CORE SAFETY PROFILE FOSAMAX (Alendronic acid as alendronate sodium trihydrate) 4.2 Posology and method of administration The recommended dosage is one 70
CSP - UK/H/PSUR/0070 - March 2012 EUROPEAN UNION CORE SAFETY PROFILE FOSAMAX (Alendronic acid as alendronate sodium trihydrate) 4.2 Posology and method of administration The recommended dosage is one 70
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR
 1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Urinary Calculus Disease. Urinary Stones: Simplified Metabolic Evaluation. Urinary Calculus Disease. Urinary Calculus Disease 2/8/2008
 Urinary Stones: Simplified Metabolic Evaluation Marshall L. Stoller, M.D. Professor and Vice Chairman Department of Urology University of California San Francisco Incidence: 7-21/10,000 3 men: 1 woman
Urinary Stones: Simplified Metabolic Evaluation Marshall L. Stoller, M.D. Professor and Vice Chairman Department of Urology University of California San Francisco Incidence: 7-21/10,000 3 men: 1 woman
Bone Metastases. Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital
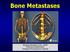 Bone Metastases Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital 1 Outline Pathophysiology Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Spinal Cord Compression 2 General Information
Bone Metastases Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital 1 Outline Pathophysiology Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Spinal Cord Compression 2 General Information
Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection
 Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection Policy #: 355 Latest Review Date: May 2011 Category: Pharmacy Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection Policy #: 355 Latest Review Date: May 2011 Category: Pharmacy Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
SpongeBone Menopants*
 SpongeBone Menopants* Adam Fershko, MD, FACP Kettering Health Network *Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Objectives O Epidemiology O Clinical significance O Pathophysiology O Screening and Diagnosis O Treatment
SpongeBone Menopants* Adam Fershko, MD, FACP Kettering Health Network *Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Objectives O Epidemiology O Clinical significance O Pathophysiology O Screening and Diagnosis O Treatment
ANNEX III SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX III SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Note: This SPC is the one that was annexed to the Commission Decision on this Article 7(5) referral for calcitonin and related names. The text was valid at
ANNEX III SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Note: This SPC is the one that was annexed to the Commission Decision on this Article 7(5) referral for calcitonin and related names. The text was valid at
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Zoledronic Acid A (zoledronic acid injection) for intravenous infusion This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when Zoledronic Acid A was
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Zoledronic Acid A (zoledronic acid injection) for intravenous infusion This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when Zoledronic Acid A was
FYI ONLY Generic Name. Generics available. zoledronic acid N/A
 Criteria Document: Reference #: PC/A011 Page 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community
Criteria Document: Reference #: PC/A011 Page 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community
GOUT. Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust
 GOUT Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust podagra Gout A disease of kings, the king of diseases History Louis XIV Emperor Augustus Henry VIII Introduction Gout an inflammatory arthritic condition that
GOUT Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust podagra Gout A disease of kings, the king of diseases History Louis XIV Emperor Augustus Henry VIII Introduction Gout an inflammatory arthritic condition that
BONIVA (ibandronate sodium)
 BONIVA (ibandronate sodium) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices
BONIVA (ibandronate sodium) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices
Osteoporosis challenges
 Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Cortical bone After age 40, gradually decreases % yearly, in both men and women Postmenopausally, loss accelerates to 2-3% yearly
 Osteoporosis POOLE, K.E.S. & COMPSTON, J.E. (2006): Osteoporosis and its management. BMJ 333:1251-6. Physiology Cortical bone After age 40, gradually decreases 0.3-0.5% yearly, in both men and women Postmenopausally,
Osteoporosis POOLE, K.E.S. & COMPSTON, J.E. (2006): Osteoporosis and its management. BMJ 333:1251-6. Physiology Cortical bone After age 40, gradually decreases 0.3-0.5% yearly, in both men and women Postmenopausally,
OBJECTIVES GOUT GOUTY INFLAMMATION 6/10/2016 GOUT INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE MONOSODIUM URATE CRYSTAL DEPOSITION DISEASE
 GOUT Lisa Talbert, MD Family Medicine Update June 15, 2016 OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gouty arthritis Be able to incorporate current guidelines when
GOUT Lisa Talbert, MD Family Medicine Update June 15, 2016 OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gouty arthritis Be able to incorporate current guidelines when
Gout: Update in therapeutics
 Summary Gout: Update in therapeutics 29/11/14 Caroline van Durme CHU de Liège Maastricht University Medical Centre+ Why treating gout? Guidelines: ACR 12 Drugs: Colchicine Allopurinol: what about the kidney?
Summary Gout: Update in therapeutics 29/11/14 Caroline van Durme CHU de Liège Maastricht University Medical Centre+ Why treating gout? Guidelines: ACR 12 Drugs: Colchicine Allopurinol: what about the kidney?
ALENDRONATE SODIUM FOSAMAX
 PRODUCT CIRCULAR PHL-MK0217-T-032010 ALENDRONATE SODIUM FOSAMAX Tablets Anti-Osteoporosis NAME AND STRENGTH OF ACTIVE INGREDIENT Each tablet of ALENDRONATE SODIUM (FOSAMAX) contains either 13.05 or 91.37
PRODUCT CIRCULAR PHL-MK0217-T-032010 ALENDRONATE SODIUM FOSAMAX Tablets Anti-Osteoporosis NAME AND STRENGTH OF ACTIVE INGREDIENT Each tablet of ALENDRONATE SODIUM (FOSAMAX) contains either 13.05 or 91.37
BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH
 BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH Rowena Ridout, MD, FRCPC Toronto Western Hospital Osteoporosis Program University Health Network / Mount Sinai Hospital rowena.ridout@uhn.ca None to declare Conflicts of Interest
BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH Rowena Ridout, MD, FRCPC Toronto Western Hospital Osteoporosis Program University Health Network / Mount Sinai Hospital rowena.ridout@uhn.ca None to declare Conflicts of Interest
Beyond the Break. After Breast Cancer: Osteoporosis in Survivorship. Dr Alexandra Ginty CCFP(EM) FCFP Regional Primary Care Lead CCO
 Beyond the Break After Breast Cancer: Osteoporosis in Survivorship Dr Alexandra Ginty CCFP(EM) FCFP Regional Primary Care Lead CCO Disclosures No disclosures Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Survivorship
Beyond the Break After Breast Cancer: Osteoporosis in Survivorship Dr Alexandra Ginty CCFP(EM) FCFP Regional Primary Care Lead CCO Disclosures No disclosures Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Survivorship
Dose of celecoxib in gout attack attack
 Dose of celecoxib in gout attack Gout is a disease characterized by an abnormal metabolism of uric acid, resulting in an excess of uric acid in the tissues and blood. People with gout either produce too
Dose of celecoxib in gout attack Gout is a disease characterized by an abnormal metabolism of uric acid, resulting in an excess of uric acid in the tissues and blood. People with gout either produce too
Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD. This program has been brought to you by PharmCon
 Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD This program has been brought to you by PharmCon Osteoporosis in Men Speaker: Dr. Wendy Rosenthal, President of MedOutcomes, will be the presenter for this webcast.
Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD This program has been brought to you by PharmCon Osteoporosis in Men Speaker: Dr. Wendy Rosenthal, President of MedOutcomes, will be the presenter for this webcast.
Zurampic. (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow
 Zurampic (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zurampic Generic name: Lesinurad Pharmacological class: URAT1 inhibitor Strength and Formulation: 200mg; tablets Manufacturer: Ironwood
Zurampic (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zurampic Generic name: Lesinurad Pharmacological class: URAT1 inhibitor Strength and Formulation: 200mg; tablets Manufacturer: Ironwood
