Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome as the Initial Clinical Manifestation of an Antisynthetase Syndrome
|
|
|
- Brent Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT ISSN: (Print)/ (Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2016;79: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome as the Initial Clinical Manifestation of an Antisynthetase Syndrome Seo-Hyun Kim, M.D. and I-Nae Park, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea Antisynthetase syndrome has been recognized as an important cause of autoimmune inflammatory myopathy in a subset of patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. It is associated with serum antibody to aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases and is characterized by a constellation of manifestations, including fever, myositis, interstitial lung disease, mechanic s hand-like cutaneous involvement, Raynaud phenomenon, and polyarthritis. Lung disease is the presenting feature in 50% of the cases. We report a case of a 60-year-old female with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which later proved to be an unexpected and initial manifestation of anti-jo-1 antibody positive antisynthetase syndrome. The present case showed resolution of ARDS after treatment with high-dose corticosteroids. Given that steroids are not greatly beneficial in the treatment of ARDS, it is likely that the improvement of the respiratory symptoms in this patient also resulted from the prompt suppression of the inflammatory systemic response by corticosteroids. Keywords: Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult; Immunoglobulins; Antisynthetase Syndrome Introduction The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a rare group of heterogeneous connective tissue diseases affecting skeletal muscle and other organ systems. Subsets of IIM are clinically and pathologically assigned to one of three general subcategories: polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and inclusion body myositis. The lung is one of the most common extramuscular targets in IIM, and interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a prevalent and often devastating manifestation of Address for correspondence: I-Nae Park, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, 9 Mareunnae-ro, Jung-gu, Seoul 04551, Korea Phone: , Fax: eanee@hanmail.net Received: Jun. 1, 2015 Revised: Jun. 24, 2015 Accepted: Sep. 19, 2015 cc It is identical to the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( Copyright 2016 The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved. IIM. IIM-associated ILD (IIM-ILD) contributes to nearly 80% of the mortality in IIM with a reported prevalence of 65% of newly diagnosed IIM cases 1-3. The antisynthetase syndrome is characterized by the presence of any one of several antisynthetase autoantibodies (perhaps occurring in up to one-third of DM and PM patients) in combination with fever, Raynaud s phenomenon, polyarthritis, myositis, ILD, and mechanic hands 4,5. ILD often dominates the clinical picture and may be the presenting feature of the syndrome, as the acute onset of fever and respiratory distress occurs in nearly 50% of patients 3,6,7. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the most acute form of presentation, with rapid progressive respiratory failure; however, very few cases have been reported in association with IIM or the antisynthetase syndrome 8,9. We report a case with antisynthetase syndrome, presenting with ARDS. Case Report A 60-year-old woman was admitted to the Emergency Department (ED) of our hospital for cough, shortness of breath, chills, and myalgia. There was no sputum. She was a tourist from Japan and had come to Korea three days earlier. The patient had been in good health until the past week, when 188
2 ARDS and antisynthetase syndrome she developed a fever and headache. In response, she took acetaminophen for 3 days. She had no history of smoking and was not on any continuous therapy. On arrival to the ED, the patient s body temperature was 37.8 o C, blood pressure 130/74 mm Hg, pulse rate 82 beats per minute, respiratory rate 24 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation 86% while breathing ambient air. Crackles were heard at the base of lungs. Respiratory failure was confirmed by the arterial blood gas: PO 2 51 mm Hg, PCO 2 32 mm Hg, and ph The white blood cell count was 7,500/μL (neutrophils, 80%; lymphocytes, 12%; monocytes, 5%) and a hemoglobin value of 13.0 g/dl. C-reactive protein was increased to 12.7 mg/dl (normal, mg/ dl). Procalcitonin was <0.05 ng/ml (normal, <0.05 ng/ml). Chest radiography (Figure 1B) showed bilateral infiltrates in both lower fields. The patient was admitted to the Respiratory Department, where she received antibiotics (intravenous levofloxacin plus piperacillin-tazobactam plus oral clarithromycin) and oxygen. Further blood tests were conducted, which showed elevations of creatinine kinase (448 IU/L), lactate dehydrogenase (596 IU/L), aspartate aminotransferase (144 IU/ L), and alanine aminotransferase (128 IU/L). On the second day of hospitalization, the patient s respiratory failure worsened, and she was transferred to the intensive care unit, where endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation were performed. As she progressed to respiratory failure (Figure 1C), we thought she had severe community-acquired pneumonia, and we administered hydrocortisone intravenously (100 mg then 50 mg every 6 hours) for 3 days. After 4 days on the ventilator (Figure 1D), we removed the endotracheal tube. However, two days later, the patient s body temperature was 39 o C, her respiratory rate was 35 breaths per minute, and she complained of general weakness and dyspnea. Due to the development of ARDS (Figure 1E), we re-intubated the patient and began mechanical ventilation again. We thought her condition may be ventilator-associated pneumonia, and changed antibiotics from levofloxacin plus piperacillin-tazobactam to meropenem plus vancomycin. However, the patient s high fever persisted and her chest radiography worsened. On the eighth day of hospitalization, there was still no improvement and the microbiological evaluation provided no evidence for bacterial, fungal, or viral infection under repeated endotracheal aspiration cultures and protected bronchial washing culture. We suspected inflammatory myopathy with ILD due to the increased muscle and liver enzyme values. Especially, creatinine kinase was elevated to >2,000 IU/L. Thus, we checked specific markers for connective tissue diseases. In addition, we reviewed her past medical history from her daughter. Before admission, the patient had suffered from frequent oral ulcers and eye dryness for several weeks. Two months ago, she underwent chest radiography (Figure 1A) at a Japanese hospital and the results were normal. One week before she arrived in Korea, she underwent a blood test due to multiple arthralgias, which showed a high value of lactate dehydrogenase (422 IU/L). While we screened for the specific markers for inflammatory myopathy, an empirical therapy with high-dose corticosteroids was started (intravenous pulses of 125 mg every 6 hours for one day tapered 60 mg/day). The therapy led to a significant improvement of PaO 2 /FIO 2 ratio, and enabled to wean the patient from mechanical ventilation on the 11th day after intubation. On the 13th day of hospitalization, laboratory results revealed positive anti Jo-1 antibody with 6.4 index (normal range, <1.0 index), aldolase with 22.9 U/L A B C D E F Figure 1. Chest X-ray film at 2 months prior to admission (A), on admission (B), before the first intubation (C), after the first extubation (D), after the second intubation (E), and at discharge (F)
3 SH Kim et al. (normal range, U/L), and anti-ro (SSA) antibody with >240 U/mL (normal range, <10 U/mL). Rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody, anti-la (SSB) antibody, anti-centromere antibody, anti Scl-70 antibody, anti ds-dna antibody, antiribonucleoprotein antibody, and anti-sm antibody were all negative. On high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) (Figure 2) after extubation, there were still irregular diffuse ground-glass opacity in both upper lungs and irregular patchy consolidation on both lower lungs without honeycombing. Although a histologic diagnosis was not made, we provisionally diagnosed the patient with ARDS as the initial clinical manifestation of an anti Jo-1 antibody positive antisynthetase syndrome. After 25 days of hospitalization (Figure 1F), the patient was discharged without oxygen. Figure 3 shows the whole course of laboratory values, clinical course, and treatments. Discussion Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) is a family of cytoplasmic enzymes that catalyze the formation of aminoacyl-trna from a specific amino acid and its cognate trna and play a crucial role in protein synthesis. Eight anti-ars autoantibodies have been identified to date. These include antihistidyl (anti Jo-1), anti-threonyl (anti PL-7), anti-alanyl (anti PL-12), anti-isoleucyl (anti-oj), anti-glycyl (anti-ej), anti-asparaginyl (anti-ks), anti-phenylalanyl (anti-zo), and anti tyrosyl-trna synthetases 7. Based on a unique combination of clinical features commonly observed in patients with anti-ars autoantibodies, Targoff 4 proposed a disease entity termed antisynthetase syndrome. Antihistidyl trna synthetase antibody, often referred to as anti Jo-1 antibody, is the most frequently detected antisynthetase autoantibody and is strongly associated with the presence of ILD in both PM and DM. In one large cohort study, ILD was identified in 86% of anti Jo-1 antibody positive myositis patients 10. The breadth of presentation in IIM-ILD ranges from asymptomatic basilar lung fibrosis to an acute, rapidly progressive condition associated with ARDS and respiratory failure 3,6. The most common presenting symptoms are cough and dyspnea; however, IIM-ILD may be associated with asymptomatic lung disease, as evidenced by the high frequency of radiographi- A B Figure 2. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) after the second extubation when the patient was on prednisolone. On HRCT, there were still irregular diffuse ground glass opacities in both upper lobes (A) and irregular patchy consolidation in both lower lobes without honeycombing (B). 2,500 2,000 LDH CK AST LDH/CK (IU/L) 1,500 1, AST (IU/L) Hospitalization day Fever Fever Ventilator Ventilator Hydrocortisone Methylprednisolone IV oral prednisolone 0 Figure 3. The time course of laboratory values including creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and history of ventilator use and medications. Intravenous methylprednisolone was administered at a dose of 125 mg every 6 hours for 1 day, followed by oral prednisolone at a dose of 60 mg/day. 190 Tuberc Respir Dis 2016;79:
4 ARDS and antisynthetase syndrome cally documented ILD 10. Of clinical importance, there is no correlation between the severity of lung involvement and the degree of myositis disease activity; yet, the severity of respiratory symptoms at presentation appears to correlate with the outcome in IIM-ILD 11,12. In particular, acute and rapidly progressive ILD, corresponding to ARDS with the histopathology of diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), can occur in any patient with IIM-ILD but is frequently seen with the antisynthetase syndrome, regardless of whether patients manifest complete forms of the syndrome or formes frustes 4. Several histopathologic patterns have been described in IIM-ILD 3,13. The most common histology in IIM-ILD is nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), with a prevalence of approximately 80% 3. Usual interstitial pneumonia is less common than NSIP in IIM-ILD 3. DAD is the most rapidly progressive pathologic subset and carries worst prognosis. DAD, resembling the histological appearance associated with ARDS, is diffuse interstitial inflammation with edema and hyaline membrane production ultimately leading to organizing fibrosis. On HRCT, it is diffuse in appearance with ground glass consolidations and, in later stages, traction bronchiectasis and honeycombing may appear. Any initial HRCT pattern can rapidly deteriorate to ARDS, often leading to patient demise 3. In one retrospective case study, ILD patients with anti- ARS antibodies showed a chronic clinical course, lung-base predominant ground glass opacity with volume loss, NSIP and/or organizing pneumonia patterns, and a good response to corticosteroid treatment; however, some had a rapidly worsening courses and recurrence, despite therapy 7. In terms of prognosis, Yousem et al. 13, studying the clinicopathologic pattern of 20 antisynthetase syndrome patients, found that the subgroup of patients presenting with an acute rapidly progressive hypoxemia had a worst prognostic histologic pattern due to the presence of DAD in five cases. This analysis highlights that a significant portion of these patients present with acute respiratory decompensation manifesting as pure DAD or DAD superimposed on underlying chronic symptomatic or asymptomatic fibrosing lung disease 13. Our patient followed a fulminant course, with fever, rapid progression of radiographic changes, and respiratory failure. Her clinical course was all consistent with acute interstitial pneumonia, although we did not obtain a surgical lung biopsy. There are no approved agents in the treatment of IIM, and this lack of established treatment regimen extends to IIM- ILD. Nevertheless, corticosteroids remain the cornerstone of early treatment with initial doses at 1 mg/kg of the ideal body weight. In an effort to reduce treatment-related side effects, other immunosuppressive, steroid-sparing agents should be considered at the outset of therapy, particularly, when treating antisynthetase syndrome and other severe and progressive manifestations of ILD 3. Especially, given the relative rarity of ARDS complicating IIM, there is a paucity of studies to guide therapy 8,14. Perhaps the best approach for now is to increase the intensity of pulse cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, or other immunosuppressive therapy earlier, especially in patients who have responded poorly, if at all, to conventional pulse steroid therapy. Tacrolimus, 100-fold more potent than cyclosporine in inhibiting T-cell activation, has also been used in concert with other immunosuppressive agents 15. Fortunately, our patient s ARDS secondary to antisynthetase syndrome was resolved under treatment with a high dose of steroids, resulting in the patient s discharge without oxygen. In conclusion, given that steroids are not greatly beneficial in the treatment of ARDS, it is likely that the improvement of the respiratory symptoms in this patient also resulted from the prompt suppression of the inflammatory systemic response by corticosteroid. Conflicts of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. References 1. Fathi M, Vikgren J, Boijsen M, Tylen U, Jorfeldt L, Tornling G, et al. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: longitudinal evaluation by pulmonary function and radiology. Arthritis Rheum 2008;59: Fathi M, Dastmalchi M, Rasmussen E, Lundberg IE, Tornling G. Interstitial lung disease, a common manifestation of newly diagnosed polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63: Saketkoo LA, Ascherman DP, Cottin V, Christopher-Stine L, Danoff SK, Oddis CV. Interstitial lung disease in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2010;6: Targoff IN. Immune manifestations of inflammatory muscle disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1994;20: Friedman AW, Targoff IN, Arnett FC. Interstitial lung disease with autoantibodies against aminoacyl-trna synthetases in the absence of clinically apparent myositis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1996;26: Tillie-Leblond I, Wislez M, Valeyre D, Crestani B, Rabbat A, Israel-Biet D, et al. Interstitial lung disease and anti-jo-1 antibodies: difference between acute and gradual onset. Thorax 2008;63: Koreeda Y, Higashimoto I, Yamamoto M, Takahashi M, Kaji K, Fujimoto M, et al. Clinical and pathological findings of interstitial lung disease patients with anti-aminoacyl-trna synthetase autoantibodies. Intern Med 2010;49: Bajocchi G, Piro R, Lombardini C, Cavazza A, Facciolongo N. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: an undercover antisynthetase syndrome: a case report and a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2012;30:
5 SH Kim et al. 9. Polosa R, Di Mauro C, Spampinato B, Castelli L, D Amico G, Edwards CJ, et al. A patient with antihistidyl-trna synthetase positive polymyositis presenting as acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Rheumatol 2008;14: Richards TJ, Eggebeen A, Gibson K, Yousem S, Fuhrman C, Gochuico BR, et al. Characterization and peripheral blood biomarker assessment of anti-jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60: Marie I, Hachulla E, Cherin P, Dominique S, Hatron PY, Hellot MF, et al. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 2002;47: Huh JW, Kim DS, Lee CK, Yoo B, Seo JB, Kitaichi M, et al. Two distinct clinical types of interstitial lung disease associated with polymyositis-dermatomyositis. Respir Med 2007;101: Yousem SA, Gibson K, Kaminski N, Oddis CV, Ascherman DP. The pulmonary histopathologic manifestations of the anti- Jo-1 trna synthetase syndrome. Mod Pathol 2010;23: Lee CS, Chen TL, Tzen CY, Lin FJ, Peng MJ, Wu CL, et al. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy with diffuse alveolar damage. Clin Rheumatol 2002;21: Guglielmi S, Merz TM, Gugger M, Suter C, Nicod LP. Acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to antisynthetase syndrome is reversible with tacrolimus. Eur Respir J 2008;31: Tuberc Respir Dis 2016;79:
Myositis and Your Lungs
 Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan
 CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies. publication is available at link.sp
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Comparison of Pulmonary Involvement PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies Tomonaga, Masaomi; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomoyuki; Harada, Tatsuhiko; Nakash Shintaro; Horai,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Comparison of Pulmonary Involvement PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies Tomonaga, Masaomi; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomoyuki; Harada, Tatsuhiko; Nakash Shintaro; Horai,
CTD-related Lung Disease
 13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
Clinical and Pathological Findings of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Anti-Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Autoantibodies
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Pathological Findings of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Anti-Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Autoantibodies Yoshimizu Koreeda 1, Ikkou Higashimoto 1, Masuki Yamamoto 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Pathological Findings of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Anti-Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Autoantibodies Yoshimizu Koreeda 1, Ikkou Higashimoto 1, Masuki Yamamoto 1,
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
 Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than
 TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8955-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Noriaki Sunaga 1,2, Chiharu
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8955-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Noriaki Sunaga 1,2, Chiharu
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9553-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Rapidly Progressive Unclassifiable Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia with Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9553-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Rapidly Progressive Unclassifiable Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia with Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction
 CASE REPORT The Clinical Characteristics of Two Anti-OJ (Anti-IsoleucyltRNA Synthetase) Autoantibody-Positive Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis Kei Kunimasa 1,8, Machiko
CASE REPORT The Clinical Characteristics of Two Anti-OJ (Anti-IsoleucyltRNA Synthetase) Autoantibody-Positive Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis Kei Kunimasa 1,8, Machiko
myopathy and interstitial lung dise
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of primary Sjögren's syndrom myopathy and interstitial lung dise Koga, Tomohiro; Kouhisa, Yukiko; Na Akinari; Motomura, Masakatsu; Kawak
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of primary Sjögren's syndrom myopathy and interstitial lung dise Koga, Tomohiro; Kouhisa, Yukiko; Na Akinari; Motomura, Masakatsu; Kawak
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates
 Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091593 Age 25 Years Gender Male 30/8/2017 91600AM 30/8/2017 93946AM 31/8/2017 84826AM Ref By Final COLLAGEN DISEASES ANTIBODY ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF),
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091593 Age 25 Years Gender Male 30/8/2017 91600AM 30/8/2017 93946AM 31/8/2017 84826AM Ref By Final COLLAGEN DISEASES ANTIBODY ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF),
Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University
 9 ORIGINAL Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University Hospital Kenji Tani, Reiko Tomioka,KeikoSato, Chiyuki Furukawa, Takeshi Nakajima,
9 ORIGINAL Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University Hospital Kenji Tani, Reiko Tomioka,KeikoSato, Chiyuki Furukawa, Takeshi Nakajima,
CASE REPORT JOURNAL OF MEDICAL. Ellen De Langhe 1*, Jan Lenaerts 1, Xavier Bossuyt 2, Rene Westhovens 1 and Wim A Wuyts 3
 De Langhe et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2015) 9:82 DOI 10.1186/s13256-015-0571-2 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mechanic s hands in a woman with undifferentiated connective
De Langhe et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2015) 9:82 DOI 10.1186/s13256-015-0571-2 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mechanic s hands in a woman with undifferentiated connective
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure
 A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure Case report On November 24, 2004, a 72-year-old male was admitted to the medical intensive care unit (ICU) with a history
A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure Case report On November 24, 2004, a 72-year-old male was admitted to the medical intensive care unit (ICU) with a history
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Clinical features of seven Japanese patients with anti-pl- antibody frequent positivity for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody
 Cace report Clinical features of seven Japanese patients with anti-pl- antibody frequent positivity for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody Yoichiro Akiyama 1, Takao Nagashima 1, Masahiro Iwamoto
Cace report Clinical features of seven Japanese patients with anti-pl- antibody frequent positivity for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody Yoichiro Akiyama 1, Takao Nagashima 1, Masahiro Iwamoto
Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 2/0/20 Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague Diagnosis Polymyositis Juvenile DM (JPM) Paraneoplastic Myositis in overlap
2/0/20 Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague Diagnosis Polymyositis Juvenile DM (JPM) Paraneoplastic Myositis in overlap
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Autoantibodies andprognosis. Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic
 Autoantibodies andprognosis Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic HeterogeneityofIIMs Diagnosis Polymyositis Dermatomyositis IBM Necrotising myopathy Paraneoplastic Amyopathic
Autoantibodies andprognosis Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic HeterogeneityofIIMs Diagnosis Polymyositis Dermatomyositis IBM Necrotising myopathy Paraneoplastic Amyopathic
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy
 Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Citation Clinical rheumatology (2011), 30(3)
 A case of antisynthetase syndrome i Titlepatient with anti-pl-12 antibody fo etanercept. Ishikawa, Yuki; Yukawa, Naoichiro; Author(s) Ohmura, Koichiro; Fujii, Takao; Usu Tsuneyo Citation Clinical rheumatology
A case of antisynthetase syndrome i Titlepatient with anti-pl-12 antibody fo etanercept. Ishikawa, Yuki; Yukawa, Naoichiro; Author(s) Ohmura, Koichiro; Fujii, Takao; Usu Tsuneyo Citation Clinical rheumatology
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte
 IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis
 CHEST Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis Hiroshi Mukae, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Ishimoto, MD; Noriho Sakamoto,
CHEST Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis Hiroshi Mukae, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Ishimoto, MD; Noriho Sakamoto,
Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment
 Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION!
 UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18
![Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18 Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18](/thumbs/95/125595183.jpg) Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis
 Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 1005 1012 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00038806 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis T. Suda*, T. Fujisawa*, N. Enomoto*,
Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 1005 1012 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00038806 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis T. Suda*, T. Fujisawa*, N. Enomoto*,
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 Myositis and cancer Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Primary idiopathic polymyositis Primary idiopathic dermatomyositis Juvenile poly/dermatomyositis Myositis associated with another CTD Myositis associated
Myositis and cancer Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Primary idiopathic polymyositis Primary idiopathic dermatomyositis Juvenile poly/dermatomyositis Myositis associated with another CTD Myositis associated
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Anti-synthetase syndrome
 Anti-synthetase syndrome Floranne C. Ernste, M.D. The Myositis Association Annual Conference Louisville, KY September 7, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Octapharma: clinical trial support Genentech:
Anti-synthetase syndrome Floranne C. Ernste, M.D. The Myositis Association Annual Conference Louisville, KY September 7, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Octapharma: clinical trial support Genentech:
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
Significance of Myositis Autoantibody in Patients with Idiopathic Interstitial Lung Disease
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.676 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 56(3):676-683, 2015 Significance of Myositis Autoantibody in Patients with Idiopathic Interstitial
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.676 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 56(3):676-683, 2015 Significance of Myositis Autoantibody in Patients with Idiopathic Interstitial
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case Report of Serial Computed Tomographic Findings in a Young Male Patient
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
Case 4 History. 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar
 Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report
 CASE REPORT Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report Yusuke Tomita 1,2, Shunsuke Mori 3, Nobuyuki Arima 4,
CASE REPORT Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report Yusuke Tomita 1,2, Shunsuke Mori 3, Nobuyuki Arima 4,
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Clinical Laboratory. [None
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
P olymyositis (PM) and dermatomyositis (DM) are systemic
 297 EXTENDED REPORT Interstitial lung disease, a common manifestation of newly diagnosed polymyositis and dermatomyositis M Fathi, M Dastmalchi, E Rasmussen, I E Lundberg, G Tornling... See end of article
297 EXTENDED REPORT Interstitial lung disease, a common manifestation of newly diagnosed polymyositis and dermatomyositis M Fathi, M Dastmalchi, E Rasmussen, I E Lundberg, G Tornling... See end of article
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval
 135091660 Age 44 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100219AM 29/8/2017 105510AM Ref By Final EXTRACTABLENUCLEAR ANTIGENS (ENA), QUANTITATIVE ROFILE CENTROMERE ANTIBODY, SERUM 20-30 Weak ositive
135091660 Age 44 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100219AM 29/8/2017 105510AM Ref By Final EXTRACTABLENUCLEAR ANTIGENS (ENA), QUANTITATIVE ROFILE CENTROMERE ANTIBODY, SERUM 20-30 Weak ositive
Interstitial lung disease and anti-jo-1 antibodies: difference between acute and gradual onset
 1 Service de Pneumologie et Réanimation Respiratoire, Hôpital Tenon, Paris, France; 2 Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Avicenne, Bobigny, France; 3 Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Bichat, Paris, France;
1 Service de Pneumologie et Réanimation Respiratoire, Hôpital Tenon, Paris, France; 2 Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Avicenne, Bobigny, France; 3 Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Bichat, Paris, France;
Key words: CT scanners; interstitial lung diseases; polymyositis-dermatomyositis; x-ray
 Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease
 Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis
 Rheumatology Advance Access published June 21, 2005 Rheumatology 2005; 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh723 Concise Report Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and
Rheumatology Advance Access published June 21, 2005 Rheumatology 2005; 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh723 Concise Report Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and
Faculty of Medicine, Titu Maiorescu University, Bucharest, Romania b. Dr. Ion Stoia Clinical Center for Rheumatic Diseases, Bucharest, Romania c
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2016; 11(6): 130-135 STATE OF THE ART New Insights into Antisynthetase Syndrome Manole COJOCARU a,b ; Inimioara Mihaela COJOCARU
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2016; 11(6): 130-135 STATE OF THE ART New Insights into Antisynthetase Syndrome Manole COJOCARU a,b ; Inimioara Mihaela COJOCARU
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and the lung
 EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and the lung Jean-Christophe Lega 1,2, Quitterie Reynaud 1, Alexandre Belot 3, Nicole Fabien 4, Isabelle
EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and the lung Jean-Christophe Lega 1,2, Quitterie Reynaud 1, Alexandre Belot 3, Nicole Fabien 4, Isabelle
Clinical Diagnosis & Management of SARS
 Clinical Diagnosis & Management of SARS Joseph SUNG MD, PhD Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Hospital Authority of Hong Kong SAR Diagnosis
Clinical Diagnosis & Management of SARS Joseph SUNG MD, PhD Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Hospital Authority of Hong Kong SAR Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
A Case of Statin-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis due to Rosuvastatin
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.281 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2015;78:281-285 A Case of Statin-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis due to Rosuvastatin
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.281 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2015;78:281-285 A Case of Statin-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis due to Rosuvastatin
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
International consensus statement on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Disclosures. Clinical Approach: Evaluating CTD-ILD for the pulmonologist. ILD in CTD. connective tissue disease or collagen vascular disease
 Disclosures Clinical Approach: Evaluating CTD-ILD for the pulmonologist Industry relationships: Actelion, atyr Pharma, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech- Roche, Gilead Aryeh Fischer, MD Associate Professor
Disclosures Clinical Approach: Evaluating CTD-ILD for the pulmonologist Industry relationships: Actelion, atyr Pharma, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech- Roche, Gilead Aryeh Fischer, MD Associate Professor
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Bras Pneumol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 09.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Bras Pneumol. 2011 February ; 37(1): 100 109. Myositis-related interstitial lung disease and antisynthetase syndrome*,,** Joshua
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Bras Pneumol. 2011 February ; 37(1): 100 109. Myositis-related interstitial lung disease and antisynthetase syndrome*,,** Joshua
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
IPF - Inquadramento clinico
 IPF - Inquadramento clinico Sergio Harari Unità Operativa di Pneumologia UTIR Servizio di Fisiopat. Resp. e Emodinamica Polmonare Ospedale S. Giuseppe, Milano Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal
IPF - Inquadramento clinico Sergio Harari Unità Operativa di Pneumologia UTIR Servizio di Fisiopat. Resp. e Emodinamica Polmonare Ospedale S. Giuseppe, Milano Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Fever in Lupus. 21 st April 2014
 Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Acute Onset Anti-Synthetase Syndrome With Pericardial Effusion and Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia
 Elmer ress Case Report J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9):683-687 Acute Onset Anti-Synthetase Syndrome With Pericardial Effusion and Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia Aditya Shah a, b, Samir R. Patel a Abstract
Elmer ress Case Report J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9):683-687 Acute Onset Anti-Synthetase Syndrome With Pericardial Effusion and Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia Aditya Shah a, b, Samir R. Patel a Abstract
Mortality in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 Mortality in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies I.E. Lundberg 1, C.J. Forbess 2 1 Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine at Karolinska University Hospital in Solna, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm,
Mortality in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies I.E. Lundberg 1, C.J. Forbess 2 1 Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine at Karolinska University Hospital in Solna, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm,
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports
 Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(9B):928-932 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(9B):928-932 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Severe Acute Fibrinous and Organizing Pneumonia with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2011.71.5.368 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;71:368-372 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2011.71.5.368 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;71:368-372 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
Multidisciplinary Diagnosis in Action: Challenging Case Presentations
 Multidisciplinary Diagnosis in Action: Challenging Case Presentations Interstitial Lung Disease: Advances in Diagnosis and Management UCSF CME November 8, 2014 Case 1 69 yo M 3 year history of intermittent
Multidisciplinary Diagnosis in Action: Challenging Case Presentations Interstitial Lung Disease: Advances in Diagnosis and Management UCSF CME November 8, 2014 Case 1 69 yo M 3 year history of intermittent
Favorable rituximab response in patients with refractory idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 de Souza et al. Advances in Rheumatology (2018) 58:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-018-0030-z Advances in Rheumatology RESEARCH Favorable rituximab response in patients with refractory idiopathic inflammatory
de Souza et al. Advances in Rheumatology (2018) 58:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-018-0030-z Advances in Rheumatology RESEARCH Favorable rituximab response in patients with refractory idiopathic inflammatory
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease
 Challenges in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Overview New Classification of IIP Prior classification Modifications for new classification
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Overview New Classification of IIP Prior classification Modifications for new classification
Life-threatening respiratory failure requiring extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation secondary to the anti-synthetase syndrome
 Case report Life-threatening respiratory failure requiring extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation secondary to the anti-synthetase syndrome Journal of the Intensive Care Society 0(0) 1 5! The Intensive Care
Case report Life-threatening respiratory failure requiring extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation secondary to the anti-synthetase syndrome Journal of the Intensive Care Society 0(0) 1 5! The Intensive Care
Case Report Primary Sjogren s Syndrome Presenting as Acute Interstitial Pneumonitis/Hamman-Rich Syndrome
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 4136765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4136765 Case Report Primary Sjogren s Syndrome Presenting as Acute Interstitial Pneumonitis/Hamman-Rich
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 4136765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4136765 Case Report Primary Sjogren s Syndrome Presenting as Acute Interstitial Pneumonitis/Hamman-Rich
Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma tests/panels.
 February 20, 2017 Client Letter Test Update February 2017 Dear Colleague: This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma
February 20, 2017 Client Letter Test Update February 2017 Dear Colleague: This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma
Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis
 Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis Steven Ytterberg, M.D. TMA Annual Patient Conference New Orleans, LA Sept. 2, 2016 Disclosures Financial: Dynavax Corp. Pfizer Mallinckrodt American Board
Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis Steven Ytterberg, M.D. TMA Annual Patient Conference New Orleans, LA Sept. 2, 2016 Disclosures Financial: Dynavax Corp. Pfizer Mallinckrodt American Board
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases: Is There Really Anything New?
 : Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
: Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease. Mark Gourley, MD
 What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
Atlas of Antinuclear Antibodies
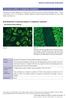 Fluorescence patterns of cytoplasmic autoantigens There are many important organelles in the cytoplasm which fulfill various functions of the cell as described in section 1. Various autoantibodies, known
Fluorescence patterns of cytoplasmic autoantigens There are many important organelles in the cytoplasm which fulfill various functions of the cell as described in section 1. Various autoantibodies, known
Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital
 Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) Heterogeneous group of systemic autoimmune syndromes
Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) Heterogeneous group of systemic autoimmune syndromes
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 648570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/648570 Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 648570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/648570 Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
