ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES OSTEOPOROSIS
|
|
|
- Britney Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES OSTEOPOROSIS MPC ICD DEFINITION Osteoporosis is a disease of bone characterized by a reduction in bone density while maintaining the normal ratio of mineral to organic content. This decreased bone density leads to an increased risk of fracture. Osteoporosis, by World Health Organization (WHO) consensus, is considered to be present when bone mineral density is equal to or greater than 2.5 standard deviations below the mean bone density of young adult sex matched controls, or there is radiological evidence of osteoporotic fracture and reduced bone density in the region of the fracture. If the result is less than 2.5 standard deviations below the mean, a diagnosis of osteoporosis is not present. Osteopenia is a generic term for a general reduction in bone mass. It includes the conditions of osteoporosis and osteomalacia (softening of the bones due to impaired mineralization, with pain, tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia, and loss of weight). Where osteoporosis is secondary to a primary disease state, it may be claimed as part of the primary disease state or claimed as consequential to the disease state, depending on the circumstances. DIAGNOSTIC STANDARD Diagnosis by a qualified medical practitioner is required. Bone densitometry and/or x- ray showing osteoporotic compression/ fracture must be provided.
2 Entitlement Eligibility Guidelines OSTEOPOROSIS Page 2 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A distinguishing characteristic of osteoporosis is loss of bone mineralization and bone matrix resulting in thinner bone. The skeleton functions to provide structural support for muscles and organs, and to serve as a depot for the body s calcium and other essential minerals. The skeleton contains two types of bone: cortical bone (80%) which is concentrated in the appendicular skeleton and femoral neck, and the more metabolically active trabecular bone (20%), which is located in the spine, epiphysis, and pelvis. Bone consists of organic matrix and an inorganic mineral component (calcium and phosphate). Bone is constantly being broken down and reformed in order for growth, repair, and maintenance of the body to occur. Bone resorption and production is associated with the delicate balance of the actions of 2 types of cells found in body tissues. Osteoclast cells mediate bone resorption and are activated by concentrations of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D and parathyroid hormone, as well as other systemic hormones. Estrogen, estrogen receptor modulators, calcitonin, and biphosphonates are factors that inhibit bone resorption. Osteoblast cells make up the part of bone that undergoes mineralization. Under steady-state physiologic circumstances, the rate of osteoclastmediated bone resorption is equal and coupled with osteoblast-stimulated bone formation. The development of, or resistance to, osteoporosis is determined by this balance between bone resorption and formation. Local factors in bone that affect this balance include prostaglandins, insulin-like growth factors, interleukins (IL-1, IL-6, and IL-11), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and transforming growth factor. Osteoporosis is developed when there is a reduction in the amount of bone mass. Cortical bone becomes more porous and thin, while the structure of trabecular bone is impaired. This makes the bone weaker and more likely to fracture. The two primary types of osteoporosis for pension purposes are Type I and Type II. Type I, or high-turnover osteoporosis, occurs in some women between the ages of 50 and 75 because of sudden postmenopausal decreases in estrogen levels. This results in a rapid depletion of calcium from the skeleton. Type II, or low-turnover osteoporosis, results when the process of resorption and formation of bones is no longer coordinated and bone breakdown overcomes bone-building. This occurs with age in everyone to some degree. The determining factor for the diagnoses of either Type I or Type II osteoporosis is the amount of calcium left in the bone. A third type of osteoporosis is known as secondary osteoporosis and occurs secondary to certain diseases (e.g. chronic liver failure, hyperthyroidism, and renal failure) and to certain medications (e.g. corticosteroids, chronic heparin therapy).
3 Entitlement Eligibility Guidelines OSTEOPOROSIS Page 3 CLINICAL FEATURES Bone density normally reaches its peak after puberty and into the third decade of life. At menopause, there is an acceleration of bone loss. Factors that seem to confer the greatest risk of osteoporosis include low body mass index, previous fracture at less than 50 years of age, family history of osteoporosis, and current smoking. Other determinants related to the development of osteoporosis include non-modifiable risk factors such as advanced age, white race, and dementia. Modifiable risk factors include, but are not limited to, low calcium intake, eating disorder, low testosterone levels (men), premenopausal estrogen deficiency, amenorrhea for more than 1 year or menopause at less than 45 years, excessive alcohol intake, frail or poor health, physical inactivity, neurologic disorders, and lack of sunlight exposure. Osteoporosis usually becomes advanced before symptoms appear. It may present as a fracture of a vertebra, hip, forearm, or any bony site if sufficient bone mass is lost. Fractures frequently occur after apparently minor trauma such as bending over, lifting, jumping, or falling from the standing position. In the later stages of the disease, pain, disfigurement and debilitation are common. Early spinal compression fractures may go undetected for a long time, but after a large percentage of calcium has been lost the vertebrae in the spine start to collapse. This gradually causes a stooped posture called kyphosis or dowager s hump. As much as 6 inches in height may be lost. PENSION CONSIDERATIONS A. CAUSES AND/OR AGGRAVATION THE TIMELINES CITED BELOW ARE NOT BINDING. EACH CASE SHOULD BE ADJUDICATED ON THE EVIDENCE PROVIDED AND ITS OWN MERITS. 1. PRIMARY OSTEOPOROSIS While the causes of primary osteoporosis are currently unknown, i.e. idiopathic, the following are considered contributing factors: a) Smoking Smoking must occur prior to clinical onset or aggravation, and be in the amount of at least 10 pack-years* of cigarettes, or the equivalent in other tobacco products.
4 *One pack-year means 7,300 cigarettes, or 1,460 cigars, or 7.3 kg of pipe tobacco. b) Alcohol consumption Alcohol consumption is measured using 10 grams absolute alcohol per standard drink. 150 kg of alcohol is approximately equivalent to 4 standard drinks per day for 10 years. A standard drink is 175 cc wine, 350 cc/beer or 30 cc liquor. Alcohol consumption, for VAC pension purposes, differs for men and women as follows: MEN - consumption of at least 150 kg of alcohol over any 10 year period within approximately 20 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation; WOMEN - consumption of at least 75 kg of alcohol over any 10 year period within the 20 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. 2. SECONDARY OSTEOPOROSIS Secondary causes and/or aggravation factors of osteoporosis should be claimed as consequential to the primary disease state: a) Chronic renal failure or chronic cholestatic liver disease at the time of clinical onset or aggravation Chronic renal failure is a clinical condition resulting from a multitude of pathologic processes that lead to derangement and insufficiency of renal excretory and regulatory function. Chronic cholestatic liver disease is any chronic intrahepatic or extrahepatic disease which inhibits bile secretion into the gastrointestinal tract, allowing accumulation of biliary substances in the plasma and usually results in jaundice.
5 b) Use of a specified drug prior to clinical onset or aggravation A specified drug includes, but is not limited to, the following drugs taken as follows: phenytoin - daily for a minimum of 2 continuous months within approximately 2 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. Phenytoin interferes with the metabolism of vitamin D. glucocorticoids* (intravenous, intramuscular, oral) - daily or every second day for a minimum of 6 continuous months within approximately 2 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. Examples would include prednisone, prednisolone and cortisone. inhaled glucocorticoids* - dosages greater than 1200 ug/day of beclomethasone or its equivalent for a minimum of 12 continuous months within approximately 2 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. *Corticosteroids are either glucocorticoids or mineralcorticoids. The majority of corticosteroids are glucocorticoids, and are used to treat asthma and other conditions. The Compendium of Pharmaceuticals and Specialities (CPS) may assist in determining if a drug is a glucocortisteroid. corticotrophins - at least weekly dose for a minimum of 12 continuous months within approximately 2 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. Corticotrophins stimulate the secretion of coticosteroids. They are also known as adrenocorticotrophins (ACTH). heparin (intravenous, subcutaneous) - at least 20,000 units daily (a therapeutic dose) for a minimum of 3 continuous months within approximately 12 months prior to clinical onset or aggravation. The osteoporotic effect is felt to be reversible within several months upon discontinuation of heparin. thyroid hormone/throxine (oral) - any supraphysiologic dose for a minimum of 6 months within approximately 2 years prior to clinical onset or aggravation. Supraphysiologic dosages of thyroid hormone are an excessive quantity of thyroid hormone resulting from: (1) overproduction by the thyroid gland (e.g. Graves disease) (2) ingestion of greater than therapeutic dosages of thyroxine medication
6 (3) loss of storage function and leakage from the thyroid gland. immunosuppressive drugs - drugs such as cyclosporine used in solid organ transplantation (e.g. heart, lung, kidney), and used for a minimum of 6 months. c) Endocrine disease prior to clinical onset or aggravation For endocrine disease to cause or aggravate Osteoporosis, endocrine disease must have existed for at least 1 year within the 10 year period prior to clinical onset or aggravation of Osteoporosis. Endocrine disease includes, but is not limited to, the following: hypogonadism - This condition may be primary (associated with retardation of growth and sexual development) or secondary and may be the result of disease, trauma, surgical excision, chemical castration techniques, decreased estrogen, and decreased testosterone; hyperprolactinemia - This is associated with amenorrhea and galactorrhea in women; Cushing s syndrome; thyrotoxicosis or treatment for thyrotoxicosis; hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcuria. Loss of gonadal function may occur in men with hemacromatosis and thalassemia, which are associated with loss of bone density. d) Rheumatoid Arthritis or Ankylosing Spondylitis at the time of clinical onset or aggravation Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic multisystem disease primarily involving the joints. It is characterized by inflammatory synovitis, joint involvement, muscle atrophy, and bone destruction. Ankylosing Spondylitis can result in low bone density and fractures. (See Entitlement Eligibility Guidelines on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis) e) Infiltrative process of bone marrow at the time of clinical onset or aggravation Infiltrative processes include, but are not limited to, the following: multiple myeloma;
7 systemic mastocytosis; Gaucher s disease (an accumulation of glucocerebrosides in macrophages in the spleen, liver and bone marrow); leukemia. f) A chronic disease causing gastrointestinal malabsorption prior to clinical onset or aggravation For a chronic disease causing gastrointestinal malabsorption to cause or aggravate Osteoporosis, the chronic disease causing the gastrointestinal malabsorption must have existed for 1 year within the 10 year period prior to clinical onset or aggravation of Osteoporosis. Gastrointestinal malabsorption is a medical condition which may be caused by a range of diseases, all of which are characterized by faulty absorption from the intestine of essential food stuffs such as fat, vitamins and mineral salts, including the following: total or partial gastrectomy; total or partial small or large bowel resection; pancreatic insufficiency, including cystic fibrosis or chronic pancreatitis; celiac disease; primary biliary cirrhosis. g) Crohn s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis prior to clinical onset or aggravation For Crohn s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis to cause or aggravate Osteoporosis, Crohn s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis must have existed for 1 year within the 10 year period prior to clinical onset or aggravation of Osteoporosis. Crohn s Disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract, which is characterized by chronic inflammation. It may extend through all layers of the gastrointestinal tract wall, and may also be known as Regional Enteritis. Ulcerative Colitis is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, which primarily affects the large bowel and is usually limited to the mucosa and submucosa. h) Anorexia Nervosa at the time of clinical onset or aggravation Anorexia Nervosa is a psychiatric disorder defined in DSM-IV, which occurs predominantly in females, and is, usually, of adolescent onset. It is characterized by refusal to maintain a normal minimal body weight, intense fear of becoming
8 obese that is undiminished by weight loss, disturbance of self body image (resulting in a feeling of being fat even when extremely emaciated), and amenorrhea (in females). i) Immobility prior to clinical onset or aggravation For immobility to cause or aggravate Osteoporosis, immobility must exist for a continuous period of approximately 60 days within the year immediately prior to clinical onset or aggravation of Osteoporosis. Immobility means continuous restriction to a lying or sitting position as directed by a physician, including prolonged hospitalization with strict bed rest, quadriplegia and prolonged spinal traction. j) An inheritable connective tissue disorder at the time of clinical onset or aggravation An inheritable connective tissue disorder includes, but is not limited to, the following: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - characterized by hyperelasticity of the skin and hypermobile joints; Homocystinuria - which results in defects in the cross-linking of bone collagen; Osteogenesis imperfecta - which is characterized by bone fragility, blue sclerae, and premature deafness. Strictly speaking, the bone metabolism defect in osteogenesis imperfecta is osteoporosis.
9 B. MEDICAL CONDITIONS WHICH ARE TO BE INCLUDED IN ENTITLEMENT/ASSESSMENT osteomalacia C. COMMON MEDICAL CONDITIONS WHICH MAY RESULT IN WHOLE OR IN PART FROM OSTEOPOROSIS AND/OR ITS TREATMENT fractures at the site of the osteoporotic bone
10 REFERENCES FOR OSTEOPOROSIS 1. Amin, S. and D.T. Felson. Osteoporosis in Men. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America, vol 27, no 1. Toronto: W.B. Saunders, February Australia. Department of Veterans Affairs. Statement of Principles Concerning Osteoporosis [Instrument 61 of 1997]. 3. Fauci, Anthony S. and Eugene Braunwald, et al, eds. Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine. 14 th ed. Montreal: McGraw-Hill, Gray, Jean D., ed. January - February An Overview of the Pharmacological Management of Osteoporosis. Drugs and Therapeutics for Maritime Practitioners, vol 21, no Goroll, Allan H. and Albert G. Mulley, Jr., et al. Primary Care Medicine, Office Evaluation and Management of the Adult Patient. 4 th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Repchinsky, Carol, editor-in-chief, et al. CPS (Compendium of Pharmaceuticals and Specialties). 36 th ed. Ottawa: Canadian Pharmacists Association, Ruddy, Shaun, et al, eds. Kelley s Textbook of Rheumatology. 6 th ed. Toronto: W.B. Saunders, U.S. Preventative Services Task Force, Guidelines from Guide to Clinical Preventative Services. 2 nd ed. [N. p.]: Williams and Wilkins, Wilson, Jean D., Daniel W. Foster, et al. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 9 th ed. Toronto: W.B. Saunders, 1998.
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines DEXA Scan
 Policy: IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines IEHP considers bone mineral density testing using DEXA medically necessary for members who meet any of the following criteria: Women aged
Policy: IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines IEHP considers bone mineral density testing using DEXA medically necessary for members who meet any of the following criteria: Women aged
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis
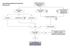 Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future
 www.worldosteoporosisday.org LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future Know your risk for osteoporosis www.iofbonehealth.org Osteoporosis is a problem worldwide, and in many countries, up to one in three women
www.worldosteoporosisday.org LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future Know your risk for osteoporosis www.iofbonehealth.org Osteoporosis is a problem worldwide, and in many countries, up to one in three women
BMD: A Continuum of Risk WHO Bone Density Criteria
 Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Academic Physician Assistants Volume 1 Number 1 Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options K Ihrke Citation K Ihrke.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Academic Physician Assistants Volume 1 Number 1 Osteoporosis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Methods And Treatment Options K Ihrke Citation K Ihrke.. The Internet Journal of
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 : assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
: assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis
 Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Osteoporosis The Silent Disease
 Joel Johnson, Yr, Subtask, Biology ER., 7/9/5 Osteoporosis The Silent Disease What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a disease which causes bones to become brittle, which increases the risk of broken bones.
Joel Johnson, Yr, Subtask, Biology ER., 7/9/5 Osteoporosis The Silent Disease What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a disease which causes bones to become brittle, which increases the risk of broken bones.
Disclosure and Conflicts of Interest Steven T Harris MD Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis
 Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Disclosure and Conflicts of Interest
Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Disclosure and Conflicts of Interest
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist
 VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention
 Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis. Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease
 Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture : A silent enemy of elderly people Islam MS
 Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture : A silent enemy of elderly people Islam MS The ORION Medical Journal 2005 Jan;20:229-231 Introduction As our life expectancy is increasing we are burdened with many
Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture : A silent enemy of elderly people Islam MS The ORION Medical Journal 2005 Jan;20:229-231 Introduction As our life expectancy is increasing we are burdened with many
Osteoporosis. Open Access. John A. Kanis. Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK
 Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS
 TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It!
 The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
 Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Osteoporosis - New Guidelines. Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011
 Osteoporosis - New Guidelines Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011 Outline What is Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? What treatments are available? Role of the Pharmacy technician Definition of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis - New Guidelines Michelle Glass B.Sc. (Pharm) June 15, 2011 Outline What is Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? What treatments are available? Role of the Pharmacy technician Definition of Osteoporosis
Learning Objectives. ! Students will become familiar with the 3 treatment solutions for osteoporosis. ! Students should be able to define osteoporosis
 Learning Objectives! Students should be able to define osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some risk factors of osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some of the people in the
Learning Objectives! Students should be able to define osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some risk factors of osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some of the people in the
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Mass Measurement BONE MASS MEASUREMENT HS-042. Policy Number: HS-042. Original Effective Date: 8/25/2008
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Section 1. What is osteoporosis? Your bones. Bones and osteoporosis. Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis
 4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
New 2010 Osteoporosis Guidelines: What you and your health provider need to know QUESTIONS&ANSWERS
 New 2010 Osteoporosis Guidelines: What you and your health provider need to know QUESTIONS&ANSWERS Wednesday, December 1, 2010 1:00 p.m. to 2:00 p.m. ET 1. I m 55 years old. I ve been taking Fosavance
New 2010 Osteoporosis Guidelines: What you and your health provider need to know QUESTIONS&ANSWERS Wednesday, December 1, 2010 1:00 p.m. to 2:00 p.m. ET 1. I m 55 years old. I ve been taking Fosavance
HIV and your Bones Osteopenia and Osteoporosis
 Osteopenia and Osteoporosis Background information For reasons not yet fully understood, higher rates of bone disease are starting to be seen in people living with HIV. These bone diseases include osteopenia
Osteopenia and Osteoporosis Background information For reasons not yet fully understood, higher rates of bone disease are starting to be seen in people living with HIV. These bone diseases include osteopenia
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource
 Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
nogg Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK
 nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
1
 www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
www.osteoporosis.ca 1 2 Overview of the Presentation Osteoporosis: An Overview Bone Basics Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Drug Therapies Risk Reduction Living with Osteoporosis 3 What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis:
Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio
 Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)? Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie. Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis
 BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations
 Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.RA10aC6 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician
Bone Mineral Density Studies in Adult Populations Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.RA10aC6 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician
An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice
 professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
Bone Densitometry Pathway
 Bone Densitometry Pathway The goal of the Bone Densitometry pathway is to manage our diagnosed osteopenic and osteoporotic patients, educate and monitor the patient population at risk for bone density
Bone Densitometry Pathway The goal of the Bone Densitometry pathway is to manage our diagnosed osteopenic and osteoporotic patients, educate and monitor the patient population at risk for bone density
Osteoporosis challenges
 Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
chapter Bone Density (Densitometry) RADIOPHARMACY INDICATIONS Radionuclide Localization Quality Control Adult Dose Range Method of Administration
 10766-04_CH04_redo.qxd 12/3/07 3:47 PM Page 17 chapter 4 Bone Density (Densitometry) RADIOPHARMACY Radionuclide Single radionuclide: 125 I t 1/2 : 60.1 days Energies: 23 31 kev Type: EC, x, γ, accelerator
10766-04_CH04_redo.qxd 12/3/07 3:47 PM Page 17 chapter 4 Bone Density (Densitometry) RADIOPHARMACY Radionuclide Single radionuclide: 125 I t 1/2 : 60.1 days Energies: 23 31 kev Type: EC, x, γ, accelerator
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Closing the Care Gap in Osteoporosis ICE Conference 2015
 Closing the Care Gap in Osteoporosis ICE Conference 2015 Pat McCarthy-Briggs RD, MHEd Thank You! What is osteoporosis? a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural
Closing the Care Gap in Osteoporosis ICE Conference 2015 Pat McCarthy-Briggs RD, MHEd Thank You! What is osteoporosis? a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis. for hospitals and General Practice
 Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Guideline for the investigation and management of osteoporosis for hospitals and General Practice Background Low bone density is an important risk factor for fracture. The aim of assessing bone density
Using the FRAX Tool. Osteoporosis Definition
 How long will your bones remain standing? Using the FRAX Tool Gary Salzman M.D. Director Banner Good Samaritan/ Hayden VAMC Internal Medicine Geriatric Fellowship Program Phoenix, Arizona Using the FRAX
How long will your bones remain standing? Using the FRAX Tool Gary Salzman M.D. Director Banner Good Samaritan/ Hayden VAMC Internal Medicine Geriatric Fellowship Program Phoenix, Arizona Using the FRAX
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging
 Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Quantitative CT (QCT) Bone Mineral Densitometry Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Quantitative CT (QCT) Bone Mineral Densitometry Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007
Name of Policy: Boniva (Ibandronate Sodium) Infusion
 Name of Policy: Boniva (Ibandronate Sodium) Infusion Policy #: 266 Latest Review Date: April 2010 Category: Pharmacology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews
Name of Policy: Boniva (Ibandronate Sodium) Infusion Policy #: 266 Latest Review Date: April 2010 Category: Pharmacology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Clinician Guide SEPTEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Clinician Guide SEPTEMBER 2017 Introduction This Clinician Guide was developed to assist Primary Care physicians
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Clinician Guide SEPTEMBER 2017 Introduction This Clinician Guide was developed to assist Primary Care physicians
To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan. To develop a better understanding of osteoporosis.
 Nutrition Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment t Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, OH. Objectives To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan.
Nutrition Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment t Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, OH. Objectives To understand bone growth and development across the lifespan.
454 Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis Mayo Clin Proc, May 2002, Vol 77 Table 1. Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis Endocrine disorders Acromegaly Adrenal
 Mayo Clin Proc, May 2002, Vol 77 Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis 453 Review Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis LORRAINE A. FITZPATRICK, MD Secondary causes of bone loss are not often considered in patients
Mayo Clin Proc, May 2002, Vol 77 Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis 453 Review Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis LORRAINE A. FITZPATRICK, MD Secondary causes of bone loss are not often considered in patients
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk. Costing report. Implementing NICE guidance
 Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Building Bone Density-Research Issues
 Building Bone Density-Research Issues Helping to Regain Bone Density QUESTION 1 What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? Symptoms Bone Fractures Osteoporosis 1,500,000 fractures a year Kyphosis
Building Bone Density-Research Issues Helping to Regain Bone Density QUESTION 1 What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis? Who is at risk? Symptoms Bone Fractures Osteoporosis 1,500,000 fractures a year Kyphosis
Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD. This program has been brought to you by PharmCon
 Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD This program has been brought to you by PharmCon Osteoporosis in Men Speaker: Dr. Wendy Rosenthal, President of MedOutcomes, will be the presenter for this webcast.
Osteoporosis in Men Wendy Rosenthal PharmD This program has been brought to you by PharmCon Osteoporosis in Men Speaker: Dr. Wendy Rosenthal, President of MedOutcomes, will be the presenter for this webcast.
Understanding Osteoporosis
 Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
DISCLAIMER DO NOT DISTRIBUTE
 DISCLAIMER The information contained in this presentation is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. It is provided for educational purposes only. You assume
DISCLAIMER The information contained in this presentation is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. It is provided for educational purposes only. You assume
Colin Beevor Matron & Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Colin Beevor Matron & Clinical Nurse Specialist Love your Bones 2016 10 years How our bones work Pelvis Periosteum Cartilage Spongy bone Structural support for body and protection of organs Store for
Colin Beevor Matron & Clinical Nurse Specialist Love your Bones 2016 10 years How our bones work Pelvis Periosteum Cartilage Spongy bone Structural support for body and protection of organs Store for
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
Conflict of Interest. Objectives. Learner Outcome
 Foundations of Orthopaedic Nursing Care, Part Four: Metabolic Bone Disease, highlighting Osteoporosis and Paget s Disease Conflict of Interest I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect
Foundations of Orthopaedic Nursing Care, Part Four: Metabolic Bone Disease, highlighting Osteoporosis and Paget s Disease Conflict of Interest I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect
All about Osteoporosis symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
 Health & Fitness Published : 07 Sep 2017, 14:41 All about Osteoporosis symptoms, diagnosis, treatment By : BD Post Desk Osteoporosis is a bone disease. Its name comes from the Latin for porous bones. The
Health & Fitness Published : 07 Sep 2017, 14:41 All about Osteoporosis symptoms, diagnosis, treatment By : BD Post Desk Osteoporosis is a bone disease. Its name comes from the Latin for porous bones. The
Page 1
 Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by weakened bones that fracture easily. After menopause many women are at risk of developing osteoporosis. Peak bone mass is usually reached during
Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by weakened bones that fracture easily. After menopause many women are at risk of developing osteoporosis. Peak bone mass is usually reached during
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
All about. Osteoporosis
 All about Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bone. It is a condition that causes bones to become thin and fragile, decreasing bone strength and making them more prone
All about Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bone. It is a condition that causes bones to become thin and fragile, decreasing bone strength and making them more prone
Osteoporosis is a huge taboo once you pass a certain age, but it really doesn t have to be that way. Even though it is a serious, irreversible,
 Osteoporosis is a huge taboo once you pass a certain age, but it really doesn t have to be that way. Even though it is a serious, irreversible, medical condition, people with osteoporosis can still have
Osteoporosis is a huge taboo once you pass a certain age, but it really doesn t have to be that way. Even though it is a serious, irreversible, medical condition, people with osteoporosis can still have
Sarena Ravi MD, MPH Endocrinologist. Franciscan Physicians Network Division of Endocrinology Chicago, IL
 Sarena Ravi MD, MPH Endocrinologist Franciscan Physicians Network Division of Endocrinology Chicago, IL Definition & Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Management of Osteoporosis in all Populations Long term Management
Sarena Ravi MD, MPH Endocrinologist Franciscan Physicians Network Division of Endocrinology Chicago, IL Definition & Diagnosis of Osteoporosis Management of Osteoporosis in all Populations Long term Management
CPT Codes: The following ICD-10-CM codes support the medical necessity of CPT code 82306:
 CPT s: 82306 Vitamin D; 25 hydroxy, includes fraction(s), if performed 82652 Vitamin D; 1, 25 dihydroxy, includes fraction(s), if performed The following ICD-10-CM codes support the medical necessity of
CPT s: 82306 Vitamin D; 25 hydroxy, includes fraction(s), if performed 82652 Vitamin D; 1, 25 dihydroxy, includes fraction(s), if performed The following ICD-10-CM codes support the medical necessity of
Diseases in which appear swelling, redness, pain and heat; aspects of the immune system (Inflammatory and immunologic conditions-imid)
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prednisolone is generally preferred amongst glucocorticoids for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive treatment. There are three
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prednisolone is generally preferred amongst glucocorticoids for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive treatment. There are three
Catch the HEDIS Buzz!
 Catch the HEDIS Buzz! Focus Area: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture Date: October 2014 HEDIS Performance Score In 2013, Humana At Home associates did a great job of promoting Osteoporosis
Catch the HEDIS Buzz! Focus Area: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture Date: October 2014 HEDIS Performance Score In 2013, Humana At Home associates did a great job of promoting Osteoporosis
Vitamin D Assay Testing For services performed on or after
 2018 MEDICARE LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (LCD) - L36692 CPT CODES: 82306, 82652 Vitamin D Assay Testing For services performed on or after 2-3-2017 DLS TEST CODE AND NAME 49907 (1,25 DIHYDROXY) (CPT
2018 MEDICARE LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (LCD) - L36692 CPT CODES: 82306, 82652 Vitamin D Assay Testing For services performed on or after 2-3-2017 DLS TEST CODE AND NAME 49907 (1,25 DIHYDROXY) (CPT
Cooking for bone health
 Cooking for bone health An interactive cooking session that includes instruction on how to prepare simple and nutritious meals that support healthy bones. Why is bone health important? Bones play many
Cooking for bone health An interactive cooking session that includes instruction on how to prepare simple and nutritious meals that support healthy bones. Why is bone health important? Bones play many
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
Bone Density Measurement in Women
 Bone Density Measurement in Women Revised 2005 Scope This guideline defines the medical necessity of bone mineral density (BMD) measurement using dualenergy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA), and applies
Bone Density Measurement in Women Revised 2005 Scope This guideline defines the medical necessity of bone mineral density (BMD) measurement using dualenergy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA), and applies
Objectives: What is Osteoporosis 10/8/2015. Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING
 Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING TIFFANY PAUL, APN, CNP, CCD Objectives: Review the diagnosis of Osteoporosis Describe the basics of a bone density exam Identify
Bone Health/ Osteoporosis: BASICS OF SCREENING, INTERPRETING, AND TREATING TIFFANY PAUL, APN, CNP, CCD Objectives: Review the diagnosis of Osteoporosis Describe the basics of a bone density exam Identify
New Osteoporosis Guidelines: What you and your health provider need to know QUESTION & ANSWER
 The first of the newsletters on these Qs and As should include a refresher on the Virtual Forums what they are, how they work, etc. The fact is that less than 5% of COPN members tune in for any given Forum.
The first of the newsletters on these Qs and As should include a refresher on the Virtual Forums what they are, how they work, etc. The fact is that less than 5% of COPN members tune in for any given Forum.
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health. Noah S. Schenkman, MD
 Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients. Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist
 Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets. Bone disorders
 Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets Bone disorders Thank You for Your comments Voice--- Ok Lecture too long--- this is in schedule??? More interaction--- I can do that inshalla Slides are crowded--- but
Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets Bone disorders Thank You for Your comments Voice--- Ok Lecture too long--- this is in schedule??? More interaction--- I can do that inshalla Slides are crowded--- but
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
Contractor Number 03201
 Local Coverage Article for Bone Mass Measurements Coverage - 2012 CPT Updates (A51577) Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Administrative Services, LLC opens in new window Contractor Number
Local Coverage Article for Bone Mass Measurements Coverage - 2012 CPT Updates (A51577) Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Administrative Services, LLC opens in new window Contractor Number
The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures.
 The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures. Measure Specifications for Registry Reporting MIPS #271: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive
The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures. Measure Specifications for Registry Reporting MIPS #271: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive
denosumab (Prolia ) Policy # Original Effective Date: 07/21/2011 Current Effective Date: 04/19/2017
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Based on review of available data, the Company may consider the use of denosumab (Prolia) for the
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
NO BONES ABOUT IT. What you need to know about osteoporosis _cov_a _cov_b _cov_c
 NO BONES ABOUT IT What you need to know about osteoporosis 210054900_cov_a 210054900_cov_b 210054900_cov_c WHAT S IT ALL ABOUT? Your bones have a thick, strong wall on the outside. Inside this wall, the
NO BONES ABOUT IT What you need to know about osteoporosis 210054900_cov_a 210054900_cov_b 210054900_cov_c WHAT S IT ALL ABOUT? Your bones have a thick, strong wall on the outside. Inside this wall, the
My joints ache. What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis?
 Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis means bones are less dense, more fragile, and at greater risk for breaking, even with small injuries. This problem often affects bones in the hip, spine,
Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis means bones are less dense, more fragile, and at greater risk for breaking, even with small injuries. This problem often affects bones in the hip, spine,
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
FORTEO (teriparatide) INJECTION
 FORTEO (teriparatide) INJECTION Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage
FORTEO (teriparatide) INJECTION Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to
 Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
A comprehensive guide brought to you by UNDERSTANDING. Osteoporosis
 A comprehensive guide brought to you by UNDERSTANDING Osteoporosis Contents What is osteoporosis? 2 About bone 2 Why is osteoporosis important? 4 How do I know whether or not I have osteoporosis? 6 Published
A comprehensive guide brought to you by UNDERSTANDING Osteoporosis Contents What is osteoporosis? 2 About bone 2 Why is osteoporosis important? 4 How do I know whether or not I have osteoporosis? 6 Published
1 of 10 5/14/15 2:48 PM
 Close window Guideline Synthesis: Screening and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Guidelines Being Compared: 1. The North American Menopause Society (). Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women:
Close window Guideline Synthesis: Screening and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Guidelines Being Compared: 1. The North American Menopause Society (). Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women:
Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease. Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017
 Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017 Learning outcomes Understand the structure and function of bone and articular cartilage Explain
Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017 Learning outcomes Understand the structure and function of bone and articular cartilage Explain
Osteoporosis. Skeletal System
 Osteoporosis Introduction Osteoporosis is a very common bone disease that causes bone to become weak. Bone weakness can lead to fractures of the spine, hip, and wrist from simple falls or even a sneeze
Osteoporosis Introduction Osteoporosis is a very common bone disease that causes bone to become weak. Bone weakness can lead to fractures of the spine, hip, and wrist from simple falls or even a sneeze
Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis
 Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis Miss Sarah Horn Consultant Oncoplastic Breast Surgeon April 2018 Aims Role of Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) in breast cancer treatment AI s effects on bone health Bone health
Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis Miss Sarah Horn Consultant Oncoplastic Breast Surgeon April 2018 Aims Role of Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) in breast cancer treatment AI s effects on bone health Bone health
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
8/6/2018. Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? Disclosure. Objectives. Overview
 Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Understanding the Development of Osteoporosis and Preventing Fractures: WHO Do We Treat Now?
 Understanding the Development of Osteoporosis and Preventing Fractures: WHO Do We Treat Now? Steven M. Petak, MD, JD, FACE, FCLM Texas Institute for Reproductive Medicine And Endocrinology, Houston, Texas
Understanding the Development of Osteoporosis and Preventing Fractures: WHO Do We Treat Now? Steven M. Petak, MD, JD, FACE, FCLM Texas Institute for Reproductive Medicine And Endocrinology, Houston, Texas
OSTEOPOROSIS PREVENTION THROUGH CHIROPRACTIC
 OSTEOPOROSIS PREVENTION THROUGH CHIROPRACTIC By Keith Wassung THE OSTEOPOROSIS EPIDEMIC Osteoporosis is a major public health threat for 28 million Americans, 80% of whom are women. Annual treatment costs
OSTEOPOROSIS PREVENTION THROUGH CHIROPRACTIC By Keith Wassung THE OSTEOPOROSIS EPIDEMIC Osteoporosis is a major public health threat for 28 million Americans, 80% of whom are women. Annual treatment costs
InfoSheet Osteoporosis
 InfoSheet Osteoporosis David M. Klein, M.D. Kennedy-White Orthopaedic Center INTRODUCTION TO BONE The bone that forms your skeleton is living tissue, comprised of protein that provides the foundation for
InfoSheet Osteoporosis David M. Klein, M.D. Kennedy-White Orthopaedic Center INTRODUCTION TO BONE The bone that forms your skeleton is living tissue, comprised of protein that provides the foundation for
Management of Osteoporosis : What Do the Guidelines Say? Robert D. Blank, MD, PhD Endocrinology, U of Wisconsin GRECC Service, Middleton VAMC
 Management of Osteoporosis : What Do the Guidelines Say? Robert D. Blank, MD, PhD Endocrinology, U of Wisconsin GRECC Service, Middleton VAMC Learning Goals Review guidelines for osteoporosis Consider
Management of Osteoporosis : What Do the Guidelines Say? Robert D. Blank, MD, PhD Endocrinology, U of Wisconsin GRECC Service, Middleton VAMC Learning Goals Review guidelines for osteoporosis Consider
