Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis, Classification, and Screening for Systemic Disease
|
|
|
- Lenard Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis, Classification, and Screening for Systemic Disease David A. Wetter, M.D. Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN) Cutaneous Lupus and Dermatomyositis Management Pearls and Pitfalls for the General Dermatologist, Forum Session (F114) American Academy of Dermatology, Annual Meeting, San Diego, California, February 18, MFMER
2 I have no conflicts of interest Disclosure Off-label use of systemic medications will be discussed 2016 MFMER
3 The scenario and clinical conundrum 2016 MFMER
4 A 36 year-old woman has this generalized eruption of the head, arms, and upper trunk. You are suspicious that this patient has discoid lupus. 1. What are the clinical and microscopic features that can help confirm the diagnosis of cutaneous lupus? 2. How should a patient be Initially evaluated for the presence of systemic involvement Monitored over time for the presence of systemic involvement 2016 MFMER
5 Overview How to diagnose cutaneous lupus How to classify the various subtypes of cutaneous lupus How to evaluate patients with cutaneous lupus for the possibility of systemic lupus (both at baseline and over time) 2016 MFMER
6 The Incidence of Cutaneous Lupus is 1. Greater than systemic lupus 2. The same as systemic lupus 3. Less than systemic lupus 2016 MFMER
7 Incidence Rate of Cutaneous Lupus is 4.30 per 100,000 Cutaneous lupus is as common as SLE 2016 MFMER
8 Incidence of Cutaneous Lupus is 3 Times Higher Than Systemic Lupus in Men 2016 MFMER
9 Which of the Following is an Example of Lupus Erythematosus-Specific Skin Disease? 1. Calcinosis cutis 2. Chilblain lupus 3. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis 4. Livedo reticularis 5. Periungual telangiectasia 2016 MFMER
10 Costner MI and Sontheimer RD Show characteristic histopathologic changes of lupus erythematosus (e.g. interface dermatitis) Do not show characteristic histopathology of lupus and can be seen in other diseases 2016 MFMER
11 What are the typical clinical findings of cutaneous lupus? 2016 MFMER
12 ACTIVITY: Erythema, scale/hypertrophy DAMAGE: Dyspigmentation, scarring, atrophy *Can help determine 1. How active disease is at time of evaluation (and thus influence your treatment approach) 2. Response to your treatment at follow-up Arch Dermatol 147(2):203, MFMER
13 Note presence of both ACTIVITY (erythema, scale) and DAMAGE (dyspigmentation, scarring) in this patient with discoid lupus 2016 MFMER
14 A few examples of lupus-specific skin disease 2016 MFMER
15 Localized acute cutaneous lupus ( malar rash ) Note: 1. Sparing of nasolabial fold 2. Involvement of malar cheeks extending over nasal dorsum ( butterfly rash ) 2016 MFMER
16 Patient had generalized DLE and although had 4/11 ACR criteria (discoid rash, oral ulcers, photosensitivity, positive ANA), she did not have clinically relevant SLE (per rheumatologic evaluation) Mucosal (oral) discoid lupus (DLE) 2016 MFMER
17 Hypertrophic/verrucous DLE 2016 MFMER
18 Note violaceous erythema and swelling of 2nd toe Chilblain lupus in setting of systemic lupus (SLE) 2016 MFMER
19 Definite chilblains lupus requires fulfilling BOTH major criteria and at least one of the minor criteria Cutis 54(6):395, MFMER
20 Proposed Diagnostic Criteria of Pernio Major criteria Localized erythema and swelling involving acral sites and persistent for >24 h Minor criteria Onset and/or worsening in cooler months (between November and March) Histopathologic findings of skin biopsy consistent with pernio (eg, dermal edema with superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate) and without findings of lupus erythematosus Response to conservative treatments (ie, warming and drying of affected areas) Pernio (chilblains) DIFFERENT entity than chilblain lupus 2016 MFMER
21 Lupus panniculitis 2016 MFMER
22 Which of the following conditions can closely mimic lupus panniculitis both clinically and microscopically? 1. Deep morphea 2. Erythema nodosum 3. Lymphoma 4. Nodular vasculitis 5. Pancreatic panniculitis 2016 MFMER
23 Lupus panniculitis and subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) can present very similarly both clinically and histopathologically 2016 MFMER
24 A few examples of lupus-nonspecific skin disease MFMER
25 Calcinosis cutis (in a patient with SLE) Ulcerations with focal extrusion of chalky granules because of calcinosis cutis in a patient with system lupus erythematosus Gutierrez Jr. and Wetter: Dermatologic Therapy 25:195, MFMER
26 2016 MFMER
27 Characteristics and Prevalence of ACTD Associated with Calcinosis Cutis Patients, No. (%) (n=78) Underlying ACTD Female sex Male sex Total Age at onset of calcinosis cutis, mean (range), y Time to onset of calcinosis cutis after diagnosis of ACTD, mean (range), mo Dermatomyositis 23 (77) 7 (23) 30 (38) 31 (4-75) 65 (3-216) Classic 11 (73) 4 (27) 15 (19) 48 (21-75) 94 (12-216) Amyopathic 1 (100) 0 1 (1) Juvenile 11 (79) 3 (21) 14 (18) 10 (4-21) 35 (3-84) Systemic sclerosis with limited cutaneous scleroderma 21 (88) 3 (13) 24 (31) 54 (28-73) 90 (0-372) Overlap CTD 5 (83) 1 (17) 6 (8) 39 (14-55) 128 (2-312) Undifferentiated CTD 5 (83) 1 (17) 6 (8) 51 (31-67) 32 (0-84) Lupus panniculitis 4 (100) 0 4 (5) 60 (39-74) 58 (5-108) Mixed CTD 2 (50) 2 (50) 4 (5) 50 (39-62) 75 (12-92) SLE 2 (100) 0 2 (3) 46 (35-57) 258 ( ) RA 1 (100) 0 1 (1) Polymyositis 1 (100) 0 1 (1) Range of ACTD s associated with calcinosis Dermatomyositis (38%) Systemic sclerosis with limited cutaneous scleroderma (31%) Lupus panniculitis (4 pts.), SLE (2 pts.) 2016 MFMER
28 Urticarial vasculitis Note bruise-like discoloration Can be associated with SLE particularly if associated with low complement levels 2016 MFMER
29 Etiologies of Cutaneous Small Vessel Vasculitis Infection (15-20%) Autoimmune connective tissue disease (15-20%) Drug (10-15%) Neoplasm (5%) Idiopathic (45-55%) Chung et al: Dermatology, 2008, Ch MFMER
30 What other conditions can appear clinically similar to cutaneous lupus? 2016 MFMER
31 Differential Diagnosis Acute cutaneous lupus/malar rash Rosacea (including corticosteroid-induced) Seborrheic dermatitis (especially photosensitive form) Sunburn Drug induced photosensitivity (phototoxic and photoallergic) Dermatomyositis Erysipelas Pemphigus erythematosus Dermatitis, atopic, contact and photocontact Acne vulgaris (rarely) Subacute cutaneous lupus Psoriasis Dermatophytosis, including tinea incognito Photolichenoid drug eruption Granuloma annulare Figurate erythemas (e.g. erythema annulare centrifugum) Dermatitis, atopic, contact and photocontact Permphigus foliaceus Discoid lesions Facial discoid dermatosis Tinea faciei, tinea capitis, tinea corporis Lichen planus and lichen planopilaris Jessner s lymphocytic infiltrate Polymorphous light eruption Sarcoidosis Lymphocytoma cutis Lymphoma cutis Granuloma faciale Dimorphic fungal infections, lupus vulgaris When single lesion, non-melanoma skin cancer Tumid lupus lesions Jessner s lymphocytic infiltrate Polymorphous light eruption Reticular erythematous mucinosis Lupus panniculitis Other panniculitides Lee and Werth: Dermatology, 2012, Ch MFMER
32 What is the histopathology of cutaneous lupus? 2016 MFMER
33 Low-Power Image Note Perivascular and Periadnexal Lymphocytic Infiltrate as well as Follicular Plugging Photo courtesy of Michael J. Camilleri, M.D. Mayo Clinic 2016 MFMER
34 Medium and High Power Images Note Interface Dermatitis With Basal Vacuolar Degeneration Photo courtesy of Michael J. Camilleri, M.D. Mayo Clinic 2016 MFMER
35 Direct Immunofluorescence Microscopy (DIF) Photo highlights granular deposits of IgM along basement membrane zone Lupus band continuous, strong, granular deposition of IgM, IgG, and complement (C3) along basement membrane zone Photo courtesy of Michael J. Camilleri, M.D. Mayo Clinic 2016 MFMER
36 Which of the following is associated with worse disease in this patient with discoid lupus? 1. Alcohol use 2. Hepatitis C 3. Malignancy 4. Positive PPD 5. Smoking 2016 MFMER
37 2016 MFMER
38 Can medications be associated with the onset of cutaneous lupus? 2016 MFMER
39 Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE) 2016 MFMER
40 SCLE Note Photodistribution in Current and Previous Photo 2016 MFMER
41 Drug-Induced SCLE Drug-Induced SLE (Usually Does Not Have Skin Involvement) Causes of Drug-Induced Lupus Drug-induced SCLE ACE inhibitors Phenytoin Hydroxychloroquine Griseofulvin Terbinafine Tetracycline Beta blockers Calcium channel blockers Tamoxifen Docetaxel Paclitaxel Anastrozole NSAIDS Thiazide diuretics Buproprion Leflunomide Proton Pump inhibitor Anti-TNF biologics Interferon-α Drug-Induced SLE (typically without skin involvement) Hydralazine Isoniazid Antihyperlipidemic agents Minocycline Procainamide Anti-TNF biologics Costner and Sontheimer: Dermatology in General Medicine, Ch. 155, 8 th ed MFMER
42 More than 1/3 of SCLE cases could be attributed to drug exposure 2016 MFMER
43 What is already known about this topic? Eighteen cases of proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-induced cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) have been reported in the literature since 2001 What does this study add? Nineteen new patients with 24 episodes of PPI-induced subacute CLE (SCLE) are reported Cross-reactivity between different PPIs is demonstrated Patients with previous CLE or other autoimmune diseases may be particularly prone to PPI-induced or exacerbated SCLE The diagnosis is challenged by the variation in time from prescription of the culprit drug to the appearance of SCLE Sandholdt et al: British Journal of Dermatology 170:342, MFMER
44 2016 MFMER
45 Antihypertensives 40 of 117 reported cases: 34.2% Calcium channel blockers Diltiazem 6 cases Verapamil 5 cases Nifedipine 3 cases Nitrendipine 1 case Diuretics Hydrochorothiazide 10 cases Hydrochlorothiazide + triamterene 3 cases Chlorthiazide 2 cases Beta blockers Oxprenolol 4 cases Acebutolol 1 case Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Enalapril 2 cases Lisnopril 1 case Captopril 1 case Cilazapril 1 case Antifungals 30 of 117 reported cases: 25.6% Terbinafine 29 cases Griseofulvin 1 case Chemotherapeutics 10 of 117 reported cases: 8.5% Docetaxel 3 cases Paclitaxel 3 cases Tamoxifen 2 cases Capecitabine 2 cases Antihistamines 9 of 117 reported cases: 7.7% Ranitidine 7 cases Brompheniramine 1 case Cinnarizine + thiethylperazine 1 case Immunomodulators 8 of 117 reported cases: 6.8% Leflunomide 5 cases Interferon α and β 3 cases Antiepileptics 3 of 117 reported cases: 2.6% Carbamazepine 2 cases Phenytoin 1 case Statins 3 of 117 reported cases: 2.6% Simvastatin 2 cases Pravastatin 1 case Biologics 2 of 117 reported cases: 1.7% Etanercept 2 cases Efalizumab 1 case Proton pump inhibitors 2 of 117 reported cases: 1.7% Lansoprazole 2 cases Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs 2 of 117 reported cases: 1.7% Naproxen 1 case Piroxicam 1 case Hormone-altering drugs 2 of 117 reported cases: 1.7% Leuprorelin 1 case Anastrozole 1 case Ultraviolet therapy 2 of 117 reported cases: 1.7% PUVA 1 case PUVA and UVB 1 case Others 4 of 117 reported cases: 3.4% Bupropion 1 case Tiotropium 1 case Ticlopidine 1 case Hay with fertilizer 1 case Answer: No (according to Lowe et al) 2016 MFMER
46 Approximately 80% of Patients With SCLE Will Have Positive Ro/SSA Antibodies (Does Not Differ Between Idiopathic and Drug-Induced Cases) Autoantibodies in drug-induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus Ro/SS-A, n/n (%) La/SS-B n/n (%) Antinuclear antibodies, n/n (%) Histone, n/n (%) Number reported positive at diagnosis 87/107 (81) 35/73 (48) 84/103 (82) 19/57 (33) Number reported positive after resolution of rash 28/42 (67) 5/9 (56) 19/23 (83) 3/6 (50): in one case antibody appeared after resolution Ro/SS-A autoantibody rates were not significantly different between DI-SCLE and idiopathic SCLE 2016 MFMER
47 2016 MFMER
48 SLE criteria ANA 14 (100) 57 (79) Arthritis 13 (93) 22 (31) Anti-dsDNA 10 (71) 52 (72) Cutaneous features 4 (29) 48 (67) Serositis 4 (29) 9 (12) Hematologic disorder 4 (29) 16 (22) Oral ulcers 4 (29) 3 (4) Antiphospholipid antibodies 1 (7) 8 (11) Renal disorder 0 (0) 5 (7) Neurologic disorder 0 (0) 2 (3) Anti-Smith antibodies 0 (0) 7 (10) Other features Hypocomplementemia 3 (21) 17% Antihistone antibodies 3 (21) NA Fever or general symptoms 11 (79) 23% Number of SLE critieria fulfilled 4 9 (64) 37 (51) 3 3 (21) 17 (24) (14) 18 (25) Outcome Improvement 13/13 (100) 71 (99) Time to improvement (mo) *High rate of arthritis and low rate of skin findings in our study *Do not need to fulfill ACR criteria to have an important lupus-like syndrome (ACR criteria developed more for clinical study classification, rather than establishing SLE diagnosis in given patient [Cutaneous Manifestations of Rheumatic Diseases, 2 nd ed.]) 2016 MFMER
49 Which laboratory evaluations should be performed in patients with cutaneous lupus? 2016 MFMER
50 Clinically Relevant Information About Cutaneous Lupus Eythematosus The development of systemic disease in patients with what seems to be a strictly cutaneous disease at diagnosis has been highlighted in this issue of the Archives. What is needed is a clear statement of how to monitor patients for this possibility. Is there predictive value of obtaining immunoflurescence microscopic findings on patients at diagnosis? Should we be performing repeated serologic testing in our patients, or should we only follow patients with a careful clinical history along with complete blood cell counts and urinalyses? How should patients with cutaneous lupus be monitored for systemic disease at (1) time of diagnosis and (2) over time? A CLEAR CONSENSUS DOES NOT YET EXIST Callen: Arch Dermatol 145(3):316, MFMER
51 My Typical Workup for Cutaneous Lupus (CLE) Goal: confirm diagnosis and assess for systemic involvement Thorough review of systems (use ACR criteria as guide) Skin biopsy: H&E and lesional DIF (I personally find the H&E to be the most helpful) Basic labs: CBC, LFT s, creatinine, inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP), urinalysis Autoimmune serologies, etc: ANA, ENA panel, dsdna, complement (C3, C4, total), anti-phospholipid Abs (anti-cardiolipin, beta-2-glycoprotein-1, lupus anticoagulant) If considering systemic therapy: Eye exam (antimalarials), hepatitis serologies (methotrexate), thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT; azathioprine) 2016 MFMER
52 Approach to newly diagnosed patient with cutaneous lupus 2016 MFMER
53 Costner M and Sontheimer R 2016 MFMER
54 SLICC, MFMER
55 SLICC (2012) criteria were more sensitive than ACR (1997) criteria in classifying a patient as having SLE 2016 MFMER
56 How Do I Monitor Patients With (Clinically Quiescent/Stable) CLE Over Time? Chronic CLE (CCLE) [DLE most common subtype] Annual skin exam and review of systems Laboratory studies based on: skin findings, review of systems (and if any abnormal baseline labs at time of diagnosis that are more concerning for higher chance of progression to SLE) SCLE Annual skin exam and review of systems For first 1-2 years consider annual labs (CBC, Cr, ESR, urinalysis, ENA panel, dsdna, complement levels); thereafter only if review of systems or skin exam concerning for SLE 2016 MFMER
57 In those with isolated discoid lupus, what is the risk of progression to systemic lupus over time? 1. 2% 2. 10% 3. 25% 4. 50% 5. 75% 2016 MFMER
58 13 of 129 patients (10.1%) with DLE progressed to SLE Mean time from cutaneous lupus diagnosis to progression to SLE was 8.2 years (this included all 19 [of 156 pts.] with cutaneous lupus that progressed to SLE) 2016 MFMER
59 2016 MFMER
60 Baseline Patient Characteristics and Symptoms Characteristic or Symptom CLE (n=64) SLE (n=13) P Age, mean (SD), y 51.0 (14.3) (14.80) 0.88 Time from CLE diagnosis to first visit, mean (SD), y 7.64 (8.52) 6.62 (6.10) 0.68 Follow-up time, mean (SD), y 2.33 (1.21) 2.81 (1.34) 0.20 No. of visits, median [range] 4 [2-12] 7 [2-13) Female sex, No. (%) 44 (69) 12 (92) 0.10 White race/ethnicity, No. (%) 46 (72) 12 (92) 0.18 CCLE, No. (%) 45 (70) 8 (62) 0.53 Discoid localized 22 (34) 1 (8) Discoid generalized 6 (9) 4 (31) 0.04 SCLE, No. (%) 19 (30) 5 (38) 0.53 Antibody test result, No. (%) Negative baseline ANA titer 54 (84) 5 (38) Baseline ANA titer, 1:80-1:160 3 (5) 4 (31) Baseline ANA titer, 1:320-1: (11) 4 (31) Positive for anti-dsdna 5 (8) 2 (15) 0.35 Positive for anti-smith 0 1 (8) 0.17 Positive for anti-cardiolipin or lupus anticoagulant 3 2 (15) 0.20 Therapeutic agent, No. (%) Topical or IL corticosteroid 18 (28) 2 (15) 0.50 Prednisone 6 (8) 1 (8) NA Antimalarials or dapsone 49 (77) 7 (54) 0.17 Immunomodulators 4 (6) 1 (8) NA Thalidomide 4 (6) 1 (8) NA No. of ACR criteria at baseline, mean (SD) 1.62 (0.92) 2.38 (0.78) Musculoskeletal, No. (%) 2 (3) 1 (8) 0.43 Renal, No. (%) 1 (2) 11 (8) 0.31 Hematologic, No. (%) 2 (3) 0 NA Overall severity, No. (%) None to mild 64 (100) 11 (85) Moderate/severe 0 2 (15) 0.03 P<0.005 = statistically significant 13 of 77 patients with cutaneous lupus (CLE) progressed to systemic disease (SLE): 16.8% 5/24 SCLE (20.8%) 8/53 DLE (15.1%) Those developing SLE were more likely to have ANA >1:80 at baseline (P=0.002) Mean time from CLE diagnosis to SLE diagnosis (n=13) was 8.03 years 2016 MFMER
61 Criteria Met by Patients Who Transitioned to SLE Severity of Systemic Symptoms Developed During the Study Criteria SLE, No. (%) (n=13) Photosensitivity 12 (92) ANA 9 (69) Discoid rash 8 (62) Oral ulcers 7 (54) Arthritis 6 (46) Malar rash 4 (31) Hematologic 4 (31) Antibodies 3 (23) Renal 2 (15) Pleuritis 0 Neurologic 0 Mucocutaneous criteria only 1 (8) Mucocutaneous criteria and antibodies 3 (23) Severity of systemic symptoms Musculoskeletal SLE, No. (%) (n=13) SLE (n=13) Mild 1 (2) 0 Moderate/severe 0 3 (23) Renal Mild 0 2 (15) Moderate/severe 0 2 (15) Hematologic Mild 5 (8) 4 (31) Moderate/severe 0 0 Overall severity Mild 64 (100) 8 (62) Moderate/severe 0 5 (38) P < <0.001 Most patients that developed SLE did so via mucocutaneous ACR criteria (Table 2) Of the 13 that developed SLE, only 5 (38.5%) developed new moderate to severe systemic disease (Table 3) 2016 MFMER
62 Wieczorek et al. concluded: Few patients with newly diagnosed CLE will go on to develop SLE (17%) Those that progress to SLE are likely to have mild systemic symptoms/disease (62%) Note: the 2 patients that developed renal involvement had the following baseline criteria (1 photosensitivity, ANA, discoid lesions; 2 photosensitivity, discoid lesions, and arthritis [patient 2 later developed positive ANA and other autoantibodies]) (Personal correspondence with Victoria Werth, M.D., 3/26/14) 2016 MFMER
63 A new SLE diagnosis in CLE may not require rheumatologic referral if primarily skin disease 31% of SLE patients only had mucocutaneous +/- ANA and other autoantibody titers Proposed monitoring 1. CBC with differential and urinalysis annually 2. Complete review of systems at each visit 3. Additional serologic tests based on positive review of systems (eg, ANA, anti-dsdna, anti-sm) Chong: JAMA Dermatology, MFMER
64 2016 MFMER
65 *** *** * Follow-up approach to patient with established cutaneous lupus 2016 MFMER
66 20% (18 of 90) SCLE patients met ACR criteria for SLE HOWEVER, only 1 with SLE had lupus nephritis (which developed 8.5 years prior to SCLE) and none of the others had renal, neurologic, or notable hematologic sequelae 14% (13 of 90) SCLE patients also had Sjögren syndrome 3 of 13 (23%) had systemic manifestations of Sjögren syndrome: pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, peripheral neuropathy, and inflammatory myopathy (1) Importance of evaluating SCLE patients not only for SLE, but also for Sjögren syndrome (2) Only rare serious systemic sequelae in SCLE patients with SLE may help guide clinicians on how to monitor their patients over time for SLE development 2016 MFMER
67 Not all patients that have SLE are managed the same Those that manifest SLE mainly due to mucocutaneous features are typically managed much differently than those with serious sequelae of SLE such as nephritis, cerebritis, or significant cytopenias 2016 MFMER
68 In a patient with lupus, which of the following cutaneous findings is associated with the highest risk of systemic involvement? 1. Generalized DLE 2. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis 3. Lupus panniculitis 4. SCLE 5. Tumid lupus 2016 MFMER
69 Lupus Erythematosus (LE)-Specific Skin Disease SCLE Generalized DLE ACLE Localized DLE Skin disease only Hypertrophic DLE Systemic disease LE-non-specific skin disease LE profundus Risk of systemic lupus: ACLE, LE-non-specific disease >>> SCLE > DLE (generalized > localized) Costner and Sontheimer, Dermatology in General Medicine, Ch. 155, 8 th ed MFMER
70 2012;166:29 Risk factors for both: (1) progression of DLE to SLE and (2) SLE patients with DLE Widespread DLE lesions Arthralgias/arthritis Nail changes (eg, periungual telangiectasia) Anemia Leukopenia High ESR (sedimentation rate) High-titer ANA 2016 MFMER
71 Summary of Studies Comparing DLE-Only Patients and SLE Patients With DLE Characteristics associated with systemic involvement Study, year Groups studied Clinical Laboratory Cardinali et al., DLE only, 19 DLE with SLE Generalized DLE Nail changes (i.e. periungual telan giectasias) None mentioned Ng et al., DLE only, 10 DLE with SLE Generalized DLE ANA ( 1:160) (+) C1q deposits Scott and Rees, SLE without DLE, 14 DLE with SLE, 11 DLE with systemic findings but no SLE, 77 DLE only Generalized DLE (+) LE test Callen, 1982, Callen, DLE only, 17 DLE with SLE Generalized DLE Periungual telangiectasias Arthritis Vera-Recabarren et al., CCLE only, 10 CCLE with SLE Generalized DLE Arthralgias/arthritis Nephropathy Xerophthalmia (+) Anti-nDNA Elevated ESR Hypocomplementemia (+) ANA Leucopenia Anemia Leucopenia (+) ANA ( 1:80) (+) Anti-Ro Lymphopenia (+) Anti-dsDNA Prystowsky and Gilliam, DLE without SLE, 15 DLE with systemic involvement, 13 SLE with proliferative glomerulonephritis None mentioned (+) ANA Low CH 50 (+) LBT 2016 MFMER
72 Summary of Studies Comparing DLE-Only Patients and Patients With DLE Who Progresses to SLE Risk factors for systemic spread Study, year Groups studied Clinical Laboratory Callen et al., DLE only, 4 DLE SLE Widespread DLE Periungual telangiectasias Arthralgias/arthritis Anemia High ANA titres Leucopenia High ESR Healy et al., localized DLE, 27 widespread DLE, 7 SLE, 3 DLE SLE Progression of localized DLE to generalized DLE Persistently anemia Persistently (+) ANA ( 1:80) Persistently abnormal ESR Persistently abnormal serum immunoglobins Insawang et al., DLE only, 59 DLE with SLE (including 27 DLE SLE) Arthralgia/arthritis Generalized DLE Presence of ANA Abnormal urinalysis Millard and Rowell, localized DLE, 19 disseminated DLE, 6 DLE SLE None mentioned Persistently (+) ANF titre (>1:50) Persistently low hemoglobin 2016 MFMER
73 2016 MFMER
74 Associations between discoid lupus erythematosus and other American College of Rheumatology criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus and end-stage renal disease SLE manifestation (n=positive finding of 1043) SLE without DLE (n=926), n(%) SLE with DLE (n=117), n (%) Unadjusted OR (95% CI) Adjusted OR (95%) Adjusted OR (95%) Anti-Smith 201(21.7) 45 (38.5) 2.25 ( ) 2.27 ( ) 2.41 ( ) Photosensitivity 374 (40.4) 60 (51.3) 1.55 ( ) 1.71 ( ) 1.63 ( ) Leukopenia 301 (32.5) 50 (42.7) 1.55 ( ) 1.50 ( ) 1.55 ( ) Pleuritis 349 (37.7) 31 (26.5) 0.59 ( ) 0.56 ( ) 0.56 ( ) Arthritis 738 (79.7) 79 (67.5) 0.53 ( ) 0.51 ( ) 0.49 ( ) Lupus nephritis 281 (30.3) 38 (32.5) 1.10 ( ) 1.09 ( ) 1.33 ( ) Pericarditis 112 (12.1) 10 (8.6) 0.68 ( ) 0.68 ( ) 0.68 ( ) Proteinuria 256 (27.7) 27 (23.1) 0.78 ( ) 0.70 ( ) 0.77 ( ) Casts 117 (12.6) 9 (77) 0.56 ( ) 0.53 ( ) 0.57 ( ) End-stage renal 48 (5.1) 7 (6.0) 1.16 ( ) 0.96 ( ) 1.24 ( ) disease Oral ulcers 240 (25.9) 37 (31.6) 1.32 ( ) 1.35 ( ) 1.32 ( ) Malar rash 406 (43.8) 46 (39.3) 0.82 ( ) 0.86 ( ) 0.88 ( ) Seizure 100 (10.8) 14 (12) 1.12 ( ) 1.14 ( ) 1.20 ( ) Psychosis 16 (1.7) 3 (2.6) 1.50 ( ) 1.45 ( ) 1.50 ( ) Anemia 181 (19.5) 26 (22.2) 1.17 ( ) 1.12 ( ) 1.15 ( ) Lymphopenia 340 (36.7) 51 (43.6) 1.33 ( ) 1.32 ( ) 1.38 ( ) Thrombocytopenia 110 (11.9) 18 (15.4) 1.35 ( ) 1.45 ( ) 1.54 ( ) Anti-dsDNA 610 (65.9) 83 (70.9) 1.27 ( ) 1.25 ( ) 1.33 ( ) Antiphospholipid antibodies 225 (24.3) 24 (20.5) 0.80 ( ) 0.85 ( ) 0.87 ( ) Capsule Summary Prior studies suggest that discoid lupus erythematosus among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus is a marker for less severe disease, often offered as reassurance We did not observe any associations (either positive or negative) with discoid lupus erythematosus and severe lupus manifestations (ie, renal or neurologic) These findings have important implications for counseling our patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and discoid lupus erythematosus regarding prognosis DLE in SLE (compared to SLE without DLE): Increased risk of photosensitivity, leukopenia, and anti-smith antibodies Decreased risk of pleuritis and arthritis No association (positive or negative) with nephritis or neurologic disease 2016 MFMER
75 Summary of Cutaneous Lupus (CLE) Diagnosis of CLE requires clinicopathologic correlation CLE classified as Lupus-specific skin disease (multiple subtypes) Lupus-nonspecific skin disease Risk of systemic disease varies according to the type of skin disease present Smoking is associated with worse CLE Medications can trigger CLE (particularly SCLE) Patients with CLE should be monitored for progression to systemic disease, but consensus guidelines lacking Risk factors for SLE in those with DLE include Widespread DLE, arthralgias/arthritis, periungual telangiectasias, anemia, leukopenia, high ESR, high-titer ANA 2016 MFMER
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus. Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016
 Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS LUPUS 101 SLE SUBSETS AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 11/4/2013 HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS
 LUPUS 101 LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS SLE SUBSETS SUBACUTE CUTANEOUS LUPUS DRUG INDUCED LUPUS NEONATAL LUPUS LATE ONSET LUPUS ANTI-PHOSPHOLIPID
LUPUS 101 LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS SLE SUBSETS SUBACUTE CUTANEOUS LUPUS DRUG INDUCED LUPUS NEONATAL LUPUS LATE ONSET LUPUS ANTI-PHOSPHOLIPID
Ask the Expert: Photosensitivity in Cutaneous Lupus
 Ask the Expert: Photosensitivity in Cutaneous Lupus Victoria P. Werth, MD Department of Dermatology & Medicine University of Pennsylvania ; Philadelphia VA Hospital Overview Definition Impact of photosensitivity
Ask the Expert: Photosensitivity in Cutaneous Lupus Victoria P. Werth, MD Department of Dermatology & Medicine University of Pennsylvania ; Philadelphia VA Hospital Overview Definition Impact of photosensitivity
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Bernard Rubin, DO MPH Case 1: History A 45-year-old woman presents with severe dyspnea and cough. She was in excellent health until 4 weeks ago when
High Impact Rheumatology Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Bernard Rubin, DO MPH Case 1: History A 45-year-old woman presents with severe dyspnea and cough. She was in excellent health until 4 weeks ago when
Autoimmune diseases. SLIDE 3: Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic
 SLIDE 3: Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Autoimmune diseases Sometimes relapsing : and remitting. which means that they present as attacks Progressive damage Epitope spreading more and more
SLIDE 3: Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Autoimmune diseases Sometimes relapsing : and remitting. which means that they present as attacks Progressive damage Epitope spreading more and more
Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE
 Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE Dr. John H. Yost Pediatric Rheumatology Children s Hospital at Dartmouth Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth john.h.yost@hitchcock.org
Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE Dr. John H. Yost Pediatric Rheumatology Children s Hospital at Dartmouth Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth john.h.yost@hitchcock.org
MANAGING THE PATIENT WITH POSITIVE ANA
 MANAGING THE PATIENT WITH POSITIVE ANA Rafael F. Rivas-Chacon, M.D. Disclosures Grant/Research support for: Pfizer Study JIA A3921104 Tofacitinib not related to this presentation 1 Positive Antinuclear
MANAGING THE PATIENT WITH POSITIVE ANA Rafael F. Rivas-Chacon, M.D. Disclosures Grant/Research support for: Pfizer Study JIA A3921104 Tofacitinib not related to this presentation 1 Positive Antinuclear
COMPLEX CUTANEOUS LUPUS CASES PEARLS AND PITFALLS
 COMPLEX CUTANEOUS LUPUS CASES PEARLS AND PITFALLS Benjamin F. Chong, MD, MSCS February 17, 2018 CONFLICTS OF INTEREST D I S CLOSURE OF R E LATI ONSHIPS W I T H I NDUSTRY Benjamin Chong, MD, MSCS F059 Complex
COMPLEX CUTANEOUS LUPUS CASES PEARLS AND PITFALLS Benjamin F. Chong, MD, MSCS February 17, 2018 CONFLICTS OF INTEREST D I S CLOSURE OF R E LATI ONSHIPS W I T H I NDUSTRY Benjamin Chong, MD, MSCS F059 Complex
SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Susan Y. Ritter MD, PhD Associate Physician Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy Department of Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor in Medicine
SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Susan Y. Ritter MD, PhD Associate Physician Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy Department of Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor in Medicine
Medical Dermatology Society
 A Mashup of Instructive Cases Presenting With Subacute Cutaneous LE (SCLE) Skin Lesions Medical Dermatology Society Denver, Colorado March 20, 2014 Rick Sontheimer, M.D. Professor of Dermatology University
A Mashup of Instructive Cases Presenting With Subacute Cutaneous LE (SCLE) Skin Lesions Medical Dermatology Society Denver, Colorado March 20, 2014 Rick Sontheimer, M.D. Professor of Dermatology University
Conflict of Interest. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital.
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None Overview Diagnostic Classification Criteria of SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None Overview Diagnostic Classification Criteria of SLE
Definition Chronic autoimmune disease The body s immune system starts attacking itself Can affect most organs and tissues in the body Brain, lungs, he
 LIVING WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. Rowan Diagnostic Clinic Salisbury, N.C. May 11, 2013 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement
LIVING WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. Rowan Diagnostic Clinic Salisbury, N.C. May 11, 2013 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement
Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary
 Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, NetResults F series and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, NetResults F series and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
9/25/2013 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
Cutaneous manifestations and systemic correlation in patients with lupus erythematosus and its subsets: a study of 40 cases
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Mahajan R et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2018 Nov;4(4):479-483 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20183407
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Mahajan R et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2018 Nov;4(4):479-483 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20183407
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW. Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center
 RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
Disclosures. Rheumatological Approaches to Differential Diagnosis, Physical Examination, and Interpretation of Studies. None
 Rheumatological Approaches to Differential Diagnosis, Physical Examination, and Interpretation of Studies Sarah Goglin MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Disclosures None 1 [footer
Rheumatological Approaches to Differential Diagnosis, Physical Examination, and Interpretation of Studies Sarah Goglin MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Disclosures None 1 [footer
.,Dr Ali Alkazzaz Babylon collage of medicine 2016
 .,Dr Ali Alkazzaz Babylon collage of medicine 2016 Lupus history Lupus is the Latin word for wolf 1 st used medically in the 10 th century Described clinically in the 19 th century Butterfly rash in 1845
.,Dr Ali Alkazzaz Babylon collage of medicine 2016 Lupus history Lupus is the Latin word for wolf 1 st used medically in the 10 th century Described clinically in the 19 th century Butterfly rash in 1845
ONE of the following:
 Medical Coverage Policy Belimumab (Benlysta) EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 01 2012 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11 21 2017 OVERVIEW Belimumab (Benlysta ) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active, autoantibody-positive,
Medical Coverage Policy Belimumab (Benlysta) EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 01 2012 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11 21 2017 OVERVIEW Belimumab (Benlysta ) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active, autoantibody-positive,
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Head, Division of Rheumatology University of Maryland School of Medicine CASE: HISTORY A 26-year-old woman is seen for migratory
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Head, Division of Rheumatology University of Maryland School of Medicine CASE: HISTORY A 26-year-old woman is seen for migratory
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis, Relationship to SLE and Management
 Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis, Relationship to SLE and Management Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) Chief, Division of Dermatology Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Disclosure (previous
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis, Relationship to SLE and Management Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) Chief, Division of Dermatology Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Disclosure (previous
Seeing the Signs: Visual Recognition of Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases
 Seeing the Signs: Visual Recognition of Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases Utah Association of Family Practitioners CME Meeting at Snowbird, UT 1:00-1:30 pm, Saturday, February 13, 2016 Snowbird/Alta
Seeing the Signs: Visual Recognition of Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases Utah Association of Family Practitioners CME Meeting at Snowbird, UT 1:00-1:30 pm, Saturday, February 13, 2016 Snowbird/Alta
CUTIS Do not copy. Anastrozole-Induced Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
 nastrozole-induced Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Juliya Fisher, MD; Mital Patel, MD; Michael Miller, MD; Katy urris, MD PRCTICE POINTS There are numerous cases of drug-induced subacute cutaneous
nastrozole-induced Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Juliya Fisher, MD; Mital Patel, MD; Michael Miller, MD; Katy urris, MD PRCTICE POINTS There are numerous cases of drug-induced subacute cutaneous
CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF CUTANEOUS LUPUS PATIENTS
 CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF CUTANEOUS LUPUS PATIENTS Benjamin F. Chong, MD, MSCS February 19, 2018 CONFLICTS OF INTEREST D I S CLOSURE OF R E LATI ONSHIPS W I T H I NDUSTRY Benjamin Chong,
CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF CUTANEOUS LUPUS PATIENTS Benjamin F. Chong, MD, MSCS February 19, 2018 CONFLICTS OF INTEREST D I S CLOSURE OF R E LATI ONSHIPS W I T H I NDUSTRY Benjamin Chong,
Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2006) 14, 120-128 Original Article Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus Cutaneous manifestations are important aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2006) 14, 120-128 Original Article Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus Cutaneous manifestations are important aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus
CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK F Type 3 Hypersensitivity Reaction
 CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK F Type 3 Hypersensitivity Reaction Setting: ER Mr. Smith I ve just felt so weak for so long, and I ve lost so much weight, and now I m having trouble breathing it s affecting
CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK F Type 3 Hypersensitivity Reaction Setting: ER Mr. Smith I ve just felt so weak for so long, and I ve lost so much weight, and now I m having trouble breathing it s affecting
PS + MPs PS - MPs 37% 36% 64% 64%
 Supplementary Figure 1. Amount and distribution of phosphatidylserine negative (PS - ) and phosphatidylserine positive (PS + ) MPs in 280 SLE patients and 280 controls. Circles are proportional to the
Supplementary Figure 1. Amount and distribution of phosphatidylserine negative (PS - ) and phosphatidylserine positive (PS + ) MPs in 280 SLE patients and 280 controls. Circles are proportional to the
UPDATES ON PEDIATRIC SLE
 UPDATES ON PEDIATRIC SLE BY ANGELA MIGOWA, PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGIST/SENIOR INSTRUCTOR AKUHN MBCHB-UON, MMED-AKUHN,PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGY- MCGILL UNIVERSITY HEALTH CENTRE ROSA PARKS OBJECTIVES RECOGNIZE
UPDATES ON PEDIATRIC SLE BY ANGELA MIGOWA, PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGIST/SENIOR INSTRUCTOR AKUHN MBCHB-UON, MMED-AKUHN,PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGY- MCGILL UNIVERSITY HEALTH CENTRE ROSA PARKS OBJECTIVES RECOGNIZE
Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital
 Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical application Common autoantibody in ANA diseases Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical
Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical application Common autoantibody in ANA diseases Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
Summary Article: Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) from Harvard Medical School Health Topics A-Z
 Topic Page: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Summary Article: Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) from Harvard Medical School Health Topics A-Z What Is It? Lupus is thought to develop when the immune system
Topic Page: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Summary Article: Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) from Harvard Medical School Health Topics A-Z What Is It? Lupus is thought to develop when the immune system
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes. Mark S. Box, MD
 Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes Mark S. Box, MD Overlap Syndromes As many as 25% of patients with rheumatic diseases with systemic symptoms cannot be definitely diagnosed
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes Mark S. Box, MD Overlap Syndromes As many as 25% of patients with rheumatic diseases with systemic symptoms cannot be definitely diagnosed
UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. October 20, 2012 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement Diagnosis Treatment Pregnancy
UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. October 20, 2012 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement Diagnosis Treatment Pregnancy
Dr.MD.IMRAN KAZMI ASST PROF.DEPT OF DVL,KIMS
 Dr.MD.IMRAN KAZMI ASST PROF.DEPT OF DVL,KIMS Lupus erythematosus is a multisystem disorder whose spectrum runs from a relatively benign, self-limited cutaneous eruption to a severe, often fatal, systemic
Dr.MD.IMRAN KAZMI ASST PROF.DEPT OF DVL,KIMS Lupus erythematosus is a multisystem disorder whose spectrum runs from a relatively benign, self-limited cutaneous eruption to a severe, often fatal, systemic
Essential Rheumatology. Dr Ellen Bruce Consultant Rheumatologist CMFT
 Essential Rheumatology Dr Ellen Bruce Consultant Rheumatologist CMFT Saving the best for last! Apparently people recall best the first and last thing they re told. Far too difficult to include everything.
Essential Rheumatology Dr Ellen Bruce Consultant Rheumatologist CMFT Saving the best for last! Apparently people recall best the first and last thing they re told. Far too difficult to include everything.
Cutaneous manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 11 (May. 2018), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Cutaneous manifestations of Systemic Lupus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 11 (May. 2018), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Cutaneous manifestations of Systemic Lupus
Development of SLE among Possible SLE Patients Seen in Consultation: Long-Term Follow-Up. Disclosures. Background. Evidence-Based Medicine.
 Development of SLE among Patients Seen in Consultation: Long-Term Follow-Up Abstract # 1699 May Al Daabil, MD Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Alexander Fine Hsun Tsao Patricia Ho Joseph F. Merola, MD Peter H. Schur,
Development of SLE among Patients Seen in Consultation: Long-Term Follow-Up Abstract # 1699 May Al Daabil, MD Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Alexander Fine Hsun Tsao Patricia Ho Joseph F. Merola, MD Peter H. Schur,
What will we discuss today?
 Autoimmune diseases What will we discuss today? Introduction to autoimmune diseases Some examples Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Sometimes relapsing Progressive damage Epitope spreading more
Autoimmune diseases What will we discuss today? Introduction to autoimmune diseases Some examples Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Sometimes relapsing Progressive damage Epitope spreading more
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Policy. Section: Medicine Effective Date: January 15, 2015 Subsection: Pathology/Laboratory Original Policy Date: December 5, 2014 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 10 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 10 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
S003 CPC Self-Assessment
 S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases
 Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Rheumatology Primer: What Labs and When
 Rheumatology Primer: What Labs and When Irina Konon, MD Department of Internal Medicine Division of Rheumatology Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosures None 1 Objective Discuss principles of laboratory
Rheumatology Primer: What Labs and When Irina Konon, MD Department of Internal Medicine Division of Rheumatology Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosures None 1 Objective Discuss principles of laboratory
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy
 Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Belimumab Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 4 References... 4 Effective Date... 11/15/2017 Next
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Belimumab Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 4 References... 4 Effective Date... 11/15/2017 Next
LUPUS (SLE) MEDICAL SOURCE STATEMENT
 LUPUS (SLE) MEDICAL SOURCE STATEMENT From: Re: (Name of Patient) (Social Security No.) Please answer the following questions concerning your patient s impairments. Attach relevant treatment notes, radiologist
LUPUS (SLE) MEDICAL SOURCE STATEMENT From: Re: (Name of Patient) (Social Security No.) Please answer the following questions concerning your patient s impairments. Attach relevant treatment notes, radiologist
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Lupus. Fast facts. What is lupus? What causes lupus? Who gets lupus?
 Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015!
 Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Table S1: Dubois Guidelines for Diagnosis of DrugInduced Lupus 1. Continuous treatment with a known lupusinducing drug for 1month and usually much longer 2. Presenting symptoms:
Supplementary material Table S1: Dubois Guidelines for Diagnosis of DrugInduced Lupus 1. Continuous treatment with a known lupusinducing drug for 1month and usually much longer 2. Presenting symptoms:
Rheumatology 101 A Pediatrician s Guide
 Rheumatology 101 A Pediatrician s Guide Pediatric Staff and Alumni Day 2016 Dawn M. Wahezi, Yonit Sterba, Tamar Rubinstein Disclosures None Pick a Group Group 1 A child with a limp Group 2 ANA To test
Rheumatology 101 A Pediatrician s Guide Pediatric Staff and Alumni Day 2016 Dawn M. Wahezi, Yonit Sterba, Tamar Rubinstein Disclosures None Pick a Group Group 1 A child with a limp Group 2 ANA To test
REVIEW. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Allison Chabassol Class of 2013, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University
 REVIEW Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Allison Chabassol Class of 2013, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University Lupus erythematosus (LE) is a heterogeneous group of chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases,
REVIEW Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Allison Chabassol Class of 2013, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University Lupus erythematosus (LE) is a heterogeneous group of chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases,
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Disease. Autoimmunity. Epidemiology. ACR Criteria for Diagnosis. Signs and Symptoms. Autoreactivity: Reactivity to self antigens:
 Autoimmunity Reactivity to self antigens: Autoreactivity: Autoimmune Disease T cells B cells Leading to tissue damage or dysfunction Occurring in the absence of ongoing infection Epidemiology SLE Pathogenesis
Autoimmunity Reactivity to self antigens: Autoreactivity: Autoimmune Disease T cells B cells Leading to tissue damage or dysfunction Occurring in the absence of ongoing infection Epidemiology SLE Pathogenesis
Autoimmunity. Autoimmune Disease
 Autoimmunity Reactivity to self antigens: T cells B cells Autoimmune Disease Autoreactivity: Leading to tissue damage or dysfunction Occurring in the absence of ongoing infection 1 SLE Pathogenesis Immune
Autoimmunity Reactivity to self antigens: T cells B cells Autoimmune Disease Autoreactivity: Leading to tissue damage or dysfunction Occurring in the absence of ongoing infection 1 SLE Pathogenesis Immune
Objectives. Joint Pain. Case 1. Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) 12/4/2010
 Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Autoimmune (AI) Disorders
 Autoimmune (AI) Disorders Affect up to 50 million people in the U.S. 80 100 types, dozens more suspected #2 cause of chronic illness Women are more likely to be affected than men Symptoms overlap and are
Autoimmune (AI) Disorders Affect up to 50 million people in the U.S. 80 100 types, dozens more suspected #2 cause of chronic illness Women are more likely to be affected than men Symptoms overlap and are
Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Nithya Gayathri Devi D et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2018 May;4(2):142-148 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20181095
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Nithya Gayathri Devi D et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2018 May;4(2):142-148 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20181095
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital
 Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
Drug-induced cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 88 new cases
 Clinical report Eur J Dermatol 2017; 27(1): 28-33 Rasa LAURINAVICIENE Linda Holm SANDHOLDT Anette BYGUM Department of Dermatology and Allergy Centre, Odense University Hospital, DK-5000, Odense C, Denmark
Clinical report Eur J Dermatol 2017; 27(1): 28-33 Rasa LAURINAVICIENE Linda Holm SANDHOLDT Anette BYGUM Department of Dermatology and Allergy Centre, Odense University Hospital, DK-5000, Odense C, Denmark
AAM Case Discussion Guide Key Learning Objectives
 AAM Case Discussion Guide Key Learning Objectives List the differential diagnosis for a systemic disease presentation in a young person. Discuss the key elements of diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus
AAM Case Discussion Guide Key Learning Objectives List the differential diagnosis for a systemic disease presentation in a young person. Discuss the key elements of diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus
Update in deposition diseases
 Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
PGALS: Approach to Child with Arthritis. Prof Chris Scott Paediatric Rheumatology
 PGALS: Approach to Child with Arthritis Prof Chris Scott Paediatric Rheumatology Introduction In a prospective study from The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, every 58th child presented with
PGALS: Approach to Child with Arthritis Prof Chris Scott Paediatric Rheumatology Introduction In a prospective study from The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, every 58th child presented with
CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: RETIRED. Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: &
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: & HSCT type: o autologous o allogeneic, o
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: & HSCT type: o autologous o allogeneic, o
Cases I have Learned From. Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) University of Louisville
 Cases I have Learned From Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) University of Louisville Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Disclosure (previous 12 months) Consultant/Advisory board Auxilium Consultant
Cases I have Learned From Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) University of Louisville Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Disclosure (previous 12 months) Consultant/Advisory board Auxilium Consultant
Clinical Study A Study on Clinical and Pathologic Features in Lupus Nephritis with Mainly IgA Deposits and a Literature Review
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 289316, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/289316 Clinical Study A Study on Clinical and Pathologic Features in Lupus Nephritis with Mainly
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 289316, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/289316 Clinical Study A Study on Clinical and Pathologic Features in Lupus Nephritis with Mainly
Early diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in primary care by family doctors
 ISSN 2229-5518 2,302 Early diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in primary care by family doctors Saad Ali Alalyani, Abdullah Saad Alalyani, Sultan Salem Algethami, Hamad Sulayyih Alosaimi, Abdullah
ISSN 2229-5518 2,302 Early diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in primary care by family doctors Saad Ali Alalyani, Abdullah Saad Alalyani, Sultan Salem Algethami, Hamad Sulayyih Alosaimi, Abdullah
10/6/08. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. SLE Epidemiology: who is at risk? Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC.
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE Epidemiology: who is at risk? One of the most common autoimmune diseases affecting women of all ages Predominantly women in child-bearing years (M:F ratio is 1:10) Incidence
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE Epidemiology: who is at risk? One of the most common autoimmune diseases affecting women of all ages Predominantly women in child-bearing years (M:F ratio is 1:10) Incidence
Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Section: Medicine Effective Date: January 15, 2016 Subsection: Pathology/Laboratory Original Policy Date: December 5, 2014 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Page: 1 of 11 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Page: 1 of 11 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience Ala M. AlHeresh MD* ABSTRACT Objectives: To study the characteristics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Jordan and
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience Ala M. AlHeresh MD* ABSTRACT Objectives: To study the characteristics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Jordan and
Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective
 Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective Pamela Thorpe, MD, FACP Lupus Foundation of America, Inc. Philadelphia Tri-State Chapter Volunteer May 2014 My Own Story Is it Lupus Yet? The What What is this?
Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective Pamela Thorpe, MD, FACP Lupus Foundation of America, Inc. Philadelphia Tri-State Chapter Volunteer May 2014 My Own Story Is it Lupus Yet? The What What is this?
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
To live with lupus, we need to know about lupus.
 To live with lupus, we need to know about lupus. Zineb Aouhab, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Loyola University Medical Center Division of Rheumatology 1 Where did the word lupus come from? The word
To live with lupus, we need to know about lupus. Zineb Aouhab, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Loyola University Medical Center Division of Rheumatology 1 Where did the word lupus come from? The word
Tips on Evaluation and Diagnosis of Scarring Alopecias. Melissa Peck Piliang, MD Dermatology and Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic
 Tips on Evaluation and Diagnosis of Scarring Alopecias Melissa Peck Piliang, MD Dermatology and Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Disclosures I do not have any relevant relationships with industry Investigator:
Tips on Evaluation and Diagnosis of Scarring Alopecias Melissa Peck Piliang, MD Dermatology and Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Disclosures I do not have any relevant relationships with industry Investigator:
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval
 135091662 Age 45 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100215AM 29/8/2017 110825AM Ref By Final RHEUMATOID AUTOIMMUNE COMREHENSIVE ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF), SERUM ----- 20-60
135091662 Age 45 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100215AM 29/8/2017 110825AM Ref By Final RHEUMATOID AUTOIMMUNE COMREHENSIVE ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF), SERUM ----- 20-60
Policy. Background
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2016 Page: 1 of 11 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
Last Review Status/Date: December 2016 Page: 1 of 11 Summary Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that can be difficult to diagnose because patients often present
Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus
 REVIEW ARTICLE Drug Saf 2011; 34 (5): 357-374 0114-5916/11/0005-0357/$49.95/0 ª 2011 Adis Data Information BV. All rights reserved. Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus Incidence, Management and Prevention
REVIEW ARTICLE Drug Saf 2011; 34 (5): 357-374 0114-5916/11/0005-0357/$49.95/0 ª 2011 Adis Data Information BV. All rights reserved. Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus Incidence, Management and Prevention
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Pediatric Rheumatology: A Case-based Approach to the Basics. Hilary M. Haftel, MD, MHPE University of Michigan Department of Pediatrics
 Pediatric Rheumatology: A Case-based Approach to the Basics Hilary M. Haftel, MD, MHPE University of Michigan Department of Pediatrics Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s)
Pediatric Rheumatology: A Case-based Approach to the Basics Hilary M. Haftel, MD, MHPE University of Michigan Department of Pediatrics Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s)
Dermatology GP Referral Guidelines
 Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
 Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of. Connective Tissue Disease
 Connective Tissue Disease Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Connective Tissue Disease Connective Tissue Disease High quality assays and novel tests Inova offers a complete array of assay methods,
Connective Tissue Disease Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Connective Tissue Disease Connective Tissue Disease High quality assays and novel tests Inova offers a complete array of assay methods,
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) ... PRESENTATIONS... Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Based on a presentation by Susan Manzi, MD, MPH
 ... PRESENTATIONS... Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on a presentation by Susan Manzi, MD, MPH Presentation Summary Tracking the epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus is problematic
... PRESENTATIONS... Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on a presentation by Susan Manzi, MD, MPH Presentation Summary Tracking the epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus is problematic
OBSERVATION. Golimumab-Exacerbated Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
 OBSERVATION Golimumab-Exacerbated Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Eric Wilkerson, BS; Matthew A. Hazey, MD; Soon Bahrami, MD; Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Background: Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
OBSERVATION Golimumab-Exacerbated Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Eric Wilkerson, BS; Matthew A. Hazey, MD; Soon Bahrami, MD; Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Background: Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091593 Age 25 Years Gender Male 30/8/2017 91600AM 30/8/2017 93946AM 31/8/2017 84826AM Ref By Final COLLAGEN DISEASES ANTIBODY ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF),
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091593 Age 25 Years Gender Male 30/8/2017 91600AM 30/8/2017 93946AM 31/8/2017 84826AM Ref By Final COLLAGEN DISEASES ANTIBODY ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF),
Hair and Scalp Changes in Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Am J Clin Dermatol https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-018-0363-8 REVIEW ARTICLE Hair and Scalp Changes in Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Siriorn Udompanich 1 Kumutnart Chanprapaph 1 Poonkiat Suchonwanit
Am J Clin Dermatol https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-018-0363-8 REVIEW ARTICLE Hair and Scalp Changes in Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Siriorn Udompanich 1 Kumutnart Chanprapaph 1 Poonkiat Suchonwanit
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adolescents Beth S. Gottlieb and Norman T. Ilowite. DOI: /pir
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adolescents Beth S. Gottlieb and Norman T. Ilowite Pediatr. Rev. 2006;27;323-330 DOI: 10.1542/pir.27-9-323 The online version of this article, along with updated
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adolescents Beth S. Gottlieb and Norman T. Ilowite Pediatr. Rev. 2006;27;323-330 DOI: 10.1542/pir.27-9-323 The online version of this article, along with updated
Jessner Kanof disease induced by leflunomide: a dermal variant of cutaneous lupus?
 Jessner Kanof disease induced by leflunomide: a dermal variant of cutaneous lupus? Laëtitia Sparsa, Naji Afif, Joëlle Goetz, Christelle Sordet, Emmanuel Chatelus, Dan Lipsker, Jean Sibilia To cite this
Jessner Kanof disease induced by leflunomide: a dermal variant of cutaneous lupus? Laëtitia Sparsa, Naji Afif, Joëlle Goetz, Christelle Sordet, Emmanuel Chatelus, Dan Lipsker, Jean Sibilia To cite this
Skin Manifestations of Systemic Disease. Approach to Dermatalogic Diagnosis 9/6/2016. Go Ahead---Judge a Book by its Cover!
 Go Ahead---Judge a Book by its Cover! Skin Manifestations of Systemic Disease Amelie Hollier, DNP, FNP-BC, FAANP Lafayette, LA President, APEA Objectives Compare diseases of the skin with reactions of
Go Ahead---Judge a Book by its Cover! Skin Manifestations of Systemic Disease Amelie Hollier, DNP, FNP-BC, FAANP Lafayette, LA President, APEA Objectives Compare diseases of the skin with reactions of
A48-year-old Hispanic woman
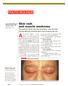 Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
The Diagnosis of Lupus
 The Diagnosis of Lupus LUPUSUK 2017 This information booklet has been produced by LUPUS UK 2017 LUPUS UK LUPUS UK is the registered national charity for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and
The Diagnosis of Lupus LUPUSUK 2017 This information booklet has been produced by LUPUS UK 2017 LUPUS UK LUPUS UK is the registered national charity for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and
Lupus and Friends Perspectives on common syndromes and Primary care responses
 Lupus and Friends Perspectives on common syndromes and Primary care responses Paul H Caldron DO, PhD, FACP, FACR, MBA Arizona Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates, PC University of Arizona College of
Lupus and Friends Perspectives on common syndromes and Primary care responses Paul H Caldron DO, PhD, FACP, FACR, MBA Arizona Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates, PC University of Arizona College of
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin
 Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Controversies in Women s Health: Clinical Dilemmas in Arthritis
 Controversies in Women s Health: Clinical Dilemmas in Arthritis Jonathan Graf, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine, UCSF Division of Rheumatology, SFGH December, 2008 Approximate Prevalence of Rheumatic
Controversies in Women s Health: Clinical Dilemmas in Arthritis Jonathan Graf, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine, UCSF Division of Rheumatology, SFGH December, 2008 Approximate Prevalence of Rheumatic
