Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM Ref: GM038 Version: 1.1 (6 June 2018)
|
|
|
- Caroline Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM Ref: GM038 Version: 1.1 (6 June 2018)
2 Commissioning Statement Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning arrangements apply) Fitness for Surgery Policy Inclusion Criteria Treatment/procedures undertaken as part of an externally funded trial or as a part of locally agreed contracts / or pathways of care are excluded from this policy, i.e. locally agreed pathways take precedent over this policy (the EUR Team should be informed of any local pathway for this exclusion to take effect). NOTE: All patients should be assessed as fit for surgery before going ahead with treatment, even though funding has been approved. All patients with trigger finger / thumb should have been managed as follows before referral for surgical intervention: They have been given and followed advice on avoiding activities that cause pain, wherever possible. They have used a small splint to hold the finger or thumb straight at night, preferably fitted by a hand therapist when available. The splint should hold the finger straight at night. If indicated, they have been given a steroid injection in an appropriate clinical setting which would be expected to relieve the pain and triggering in up to 70% of cases (but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes). The risks of injection are small (it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection). Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. If clinically appropriate, the patient may be offered a second injection at the discretion of the treating clinician. Patients whose trigger finger has recurred and in whom steroid injections previously failed should be offered the injection but, if they are reluctant to try an injection again, then they may be referred for surgery without having been injected for the recurrence. Funding Mechanism Individual prior approval provided the patient meets the above criteria. Requests must be submitted with all relevant supporting evidence. Clinical Exceptionality Clinicians can submit an Individual Funding Request (IFR) outside of this guidance if they feel there is a good case for exceptionality. Exceptionality means a person to which the general rule is not applicable. Greater Manchester sets out the following guidance in terms of determining exceptionality; however the over-riding question which the IFR process must answer is whether each patient applying for exceptional funding has demonstrated that his/her circumstances are exceptional. A patient may be able to demonstrate exceptionality by showing that s/he is: Significantly different to the general population of patients with the condition in question. and as a result of that difference They are likely to gain significantly more benefit from the intervention than might be expected from the average patient with the condition. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 2 of 17
3 Contents Commissioning Statement... 2 Policy Statement... 4 Equality & Equity Statement... 4 Governance Arrangements... 4 Aims and Objectives... 4 Rationale behind the policy statement... 5 Treatment / Procedure... 5 Epidemiology and Need... 5 Adherence to NICE Guidance... 6 Audit Requirements... 6 Date of Review... 6 Glossary... 6 References... 7 Governance Approvals... 7 Appendix 1 Evidence Review... 9 Appendix 2 Diagnostic and Procedure Codes Appendix 3 Version History GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 3 of 17
4 Policy Statement Greater Manchester Shared Services (GMSS) Effective Use of Resources (EUR) Policy Team, in conjunction with the GM EUR Steering Group, have developed this policy on behalf of Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) within Greater Manchester, who will commission treatments/procedures in accordance with the criteria outlined in this document. In creating this policy GMSS/GM EUR Steering Group have reviewed this clinical condition and the options for its treatment. It has considered the place of this treatment in current clinical practice, whether scientific research has shown the treatment to be of benefit to patients, (including how any benefit is balanced against possible risks) and whether its use represents the best use of NHS resources. This policy document outlines the arrangements for funding of this treatment for the population of Greater Manchester. This policy follows the principles set out in the ethical framework that govern the commissioning of NHS healthcare and those policies dealing with the approach to experimental treatments and processes for the management of individual funding requests (IFR). Equality & Equity Statement GMSS/CCGs have a duty to have regard to the need to reduce health inequalities in access to health services and health outcomes achieved, as enshrined in the Health and Social Care Act GMSS/CCGs are committed to ensuring equality of access and non-discrimination, irrespective of age, gender, disability (including learning disability), gender reassignment, marriage and civil partnership, pregnancy and maternity, race, religion or belief, gender or sexual orientation. In carrying out its functions, GMSS/CCGs will have due regard to the different needs of protected characteristic groups, in line with the Equality Act This document is compliant with the NHS Constitution and the Human Rights Act This applies to all activities for which they are responsible, including policy development, review and implementation. In developing policy the GMSS EUR Policy Team will ensure that equity is considered as well as equality. Equity means providing greater resource for those groups of the population with greater needs without disadvantage to any vulnerable group. The Equality Act 2010 states that we must treat disabled people as more equal than any other protected characteristic group. This is because their starting point is considered to be further back than any other group. This will be reflected in GMSS evidencing taking due regard for fair access to healthcare information, services and premises. An Equality Analysis has been carried out on the policy. For more information about the Equality Analysis, please contact policyfeedback.gmscu@nhs.net. Governance Arrangements Greater Manchester EUR policy statements will be ratified by the Greater Manchester Association Governing Group (GMAGG) prior to formal ratification through CCG Governing Bodies. Further details of the governance arrangements can be found in the GM EUR Operational Policy. Aims and Objectives This policy document aims to ensure equity, consistency and clarity in the commissioning of treatments/procedures by CCGs in Greater Manchester by: reducing the variation in access to treatments/procedures. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 4 of 17
5 ensuring that treatments/procedures are commissioned where there is acceptable evidence of clinical benefit and cost-effectiveness. reducing unacceptable variation in the commissioning of treatments/procedures across Greater Manchester. promoting the cost-effective use of healthcare resources. Rationale behind the policy statement Whilst trigger finger is not a serious condition it can cause significant pain and functional issues. Although the majority will resolve spontaneously some cases will require interventions. Whilst surgical decompression and steroid injections have the same level of evidence available in support of their effectiveness, this policy is aimed at ensuring that the least invasive therapies are tried first before going on to surgery. Treatment / Procedure Trigger finger is a painful condition in which a finger or thumb clicks or locks as it is bent towards the palm. Thickening of the tendon sheath leads to roughness of the tendon surface which then causes the tendon to catch or trigger as it moves through the sheath. People with insulin dependent diabetes are especially prone to triggering, but most trigger digits occur in people without diabetes. Triggering occasionally appears to start after an injury such as a knock on the hand. There is little evidence that it is caused by work activities, but it can certainly be aggravated by hand use at work, at home, in the garden or at sport. Triggering is sometimes due to tendon nodules in people known to have rheumatoid arthritis. It is not caused by osteoarthritis. Symptoms Pain at the site of triggering in the palm (fingers) or on the palmar surface of the thumb at the middle joint. Tenderness if you press on the site of pain. Clicking of the digit during movement, or locking in a bent position, often worse on waking in the morning. The digit may need to be straightened with pressure from the opposite hand. Stiffness, especially in trigger thumb where movement at the end joint is reduced. Treatment Some mild cases recover over a few weeks without treatment. For those that don t resolve spontaneously the following treatments should be tried in order: 1. Advice on avoiding activities that cause pain, wherever possible. 2. Splinting the finger or thumb straight at night. Preferably fitted by a hand therapist, where this service can be provided in the community. The splint should hold the finger straight at night. 3. A course of steroid injections which would be expected to relieve the pain and triggering in about 70% of cases, but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes. The risks of injection are small, (it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection). Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. 4. Surgical decompression. Epidemiology and Need Trigger finger / thumb has a reported incidence of 28 cases per population per year, or a lifetime risk of 2.6% in the general population. This rises to 10% in patients with diabetes. Two peaks in incidence occur; the first under the age of eight and the second (more common) in the fifth and sixth GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 5 of 17
6 decades of life. This bimodal distribution represents two different clinical groups, not only for age but also in incidence, sex distribution, digit affected, treatment, and outcome. Expected annual numbers of cases and cases requiring surgery Area Population (2011 census) Incidence of trigger finger Assume 10% require surgery Bolton 276, Bury 185, HMR 211, Manchester 503, Oldham 224, Salford 233, Stockport 283, T&G 219, Trafford 226, Wigan 317, Totals 2,682, Adherence to NICE Guidance NICE have not currently issued guidance on this treatment. Audit Requirements There is currently no national database. Service providers will be expected to collect and provide audit data on request. Date of Review One year from the date of approval by Greater Manchester Association Governing Group and thereafter at a date agreed by the Greater Manchester EUR Steering Group, unless new evidence or technology is available sooner. The evidence base for the policy will be reviewed and any recommendations within the policy will be checked against any new evidence. Any operational issues will also be considered at this time. All available additional data on outcomes will be included in the review and the policy updated accordingly. The policy will be continued, amended or withdrawn subject to the outcome of that review. Glossary Term Bilateral Deformity Fascia Meaning Affecting both sides. The state of being deformed or misshapen. A structure of connective tissue that surrounds muscles and the overlying GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 6 of 17
7 affected skin. Flexion Hand dominance Incidence Nodule Osteoarthritis Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) Rheumatoid arthritis Subcutaneous tissue Surgical decompression Tendon Trigger finger / thumb Unilateral Bending. The preferred hand for fine motor functions e.g. writing. The rate at which a certain event occurs, as the number of new cases of a specific disease occurring during a certain period in a population at risk for that event. A small swelling or aggregation of cells in the body, especially an abnormal one. Degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying bone, most common from middle age onward. It causes pain and stiffness, especially in the hip, knee, and thumb joints. The joint between the bones of the finger closest to the hand. A chronic progressive disease causing inflammation in the joints and resulting in painful deformity and immobility, especially in the fingers, wrists, feet, and ankles Tissue found just below the surface of the skin. Operation to open the tendon sheath to avoid the tendon catching A flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone. A painful condition in which a finger or thumb clicks or locks as it is bent towards the palm On one side only. References 1. Greater Manchester Effective Use of Resources Operational Policy 2. NHS England Interim Clinical Commissioning Policy: Trigger Finger (stenosing tenosynovitis) Surgery, Prepared by Armed Forces Commissioning Policy Task and Finish Group, (November 2013) Governance Approvals Name Date Approved Greater Manchester Effective Use of Resources Steering Group 20/07/2016 Greater Manchester Chief Finance Officers / Greater Manchester Directors of Commissioning 12/09/2017 Greater Manchester Association Governing Group 02/10/2017 Bury Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Bolton Clinical Commissioning Group 27/10/2017 GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 7 of 17
8 Heywood, Middleton & Rochdale Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Manchester Clinical Commissioning Group 30/11/2017 Oldham Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Salford Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Stockport Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Tameside & Glossop Clinical Commissioning Group 02/10/2017 Trafford Clinical Commissioning Group 17/10/2017 Wigan Borough Clinical Commissioning Group 06/12/2017 GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 8 of 17
9 Appendix 1 Evidence Review Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM038 Search Strategy The following databases are routinely searched: NICE Clinical Guidance and full website search; NHS Evidence and NICE CKS; SIGN; Cochrane; York; BMJ Clinical Evidence; and the relevant Royal College websites. A Medline / Open Athens search is undertaken where indicated and a general google search for key terms may also be undertaken. The results from these and any other sources are included in the table below. If nothing is found on a particular website it will not appear in the table below: Database NHS Evidence and NICE CKS Cochrane CRD York BMJ Clinical Evidence General Search (Google) Other Result Database of clinical trials NCT study comparing 1 vs 2 corticosteroid injections still recruiting no completion date available no results at present. Cochrane Review: Corticosteroid injection for trigger finger in adults, Peters- Veluthamaningal C, van der Windt DAWM, Winters JC, Meyboom- de Jong B CRD Review: Corticosteroid injections in the treatment of trigger finger: a level I and II systematic review, Fleisch S B, Spindler K P, Lee D H Management and referral for trigger finger/thumb, Sohail Akhtar, Mary J Bradley, David N Quinton, Frank D Burke, BMJ Volume July 2005 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger, Benan M. Dala- Ali, MBBS, Amir Nakhdjevani, MBBS, Mary A. Lloyd, MBBS, Frederik B. Schreuder, MBBCH, Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4: Professional information leaflet: Trigger finger and trigger thumb, The British Society for Surgery of the Hand (BSSH) Summary of the evidence Evidence, although limited, suggests that most cases of trigger finger (incl. thumb) can be resolved using conservative measures or corticosteroid injections. For around 10% of patients a surgical tendon release is required. The evidence Levels of evidence Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Meta-analyses, systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials Randomised controlled trials Case-control or cohort studies Non-analytic studies e.g. case reports, case series Expert opinion GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 9 of 17
10 1. LEVEL1: SYSTEMATIC REVIEW CRD Review: Corticosteroid injections in the treatment of trigger finger: a level I and II systematic review, Fleisch S B, Spindler K P, Lee D H CRD summary The authors concluded that corticosteroid use was associated with an improvement in symptoms in 57% of patients. Limitations in the literature search, the poor quality and small number of included studies, and failure to appropriately synthesise the results mean that these findings should be interpreted with extreme caution. Authors' objectives: To assess the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection in the treatment of trigger finger. Searching: MEDLINE and the Cochrane CENTRAL Register were searched from inception to January 2006 for articles reported in English; the search terms were reported. The references of selected articles were screened. Study selection Study designs of evaluations included in the review: Studies of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) with at least 85% follow-up were eligible for inclusion. The duration of follow-up ranged from 1 to 27 months. Specific interventions included in the review: Studies of injectable corticosteroids were eligible for inclusion. The corticosteroids included were betamethasone sodium phosphate, methylprednisolone acetate and triamcinolone acetonide combined with varying doses of 1% lidocaine. Two trials were placebo-controlled, one compared corticosteroid alone with percutaneous release with corticosteroid, and the fourth compared intra-sheath corticosteroid with subcutaneous corticosteroid. Participants included in the review: Studies of adults with a diagnosis of trigger finger were included. The mean age of the participants ranged from 52 to 62 years. Seventy-five per cent of the participants were women. The majority of digits studied were fingers, although some patients with solely thumb involvement were included. Patients with co-morbid diabetes were included in one study; other studies excluded patients with diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis or previous injection. The duration of symptoms prior to enrolment and duration of follow-up varied within and between studies. Outcomes assessed in the review: Inclusion criteria were not defined in terms of the outcomes. The reported outcome was pain. The measures used varied between studies and were non-standardised. How were decisions on the relevance of primary studies made? The authors did not state how the papers were selected for the review, or how many reviewers performed the selection. Assessment of study quality: The validity of the included studies does not appear to have been systematically assessed. However, some judgement of methodological quality appears to have been made on the following criteria: percentage follow-up, method of randomisation, blinding and percentage of thumbs versus fingers. The authors also commented on potential sources of bias in the text. The authors did not state how the validity assessment was performed. Data extraction: The authors did not state how many reviewers performed the data extraction. The data were extracted onto a worksheet devised by a university-based research centre. The percentage of digits at follow-up, the digit being studied, the number of patients responding to treatment (unclear how a response to treatment was defined) and statistical significance were extracted. Methods of synthesis How were the studies combined? Individual study results were reported in a table and discussed in a narrative synthesis. The total percentage response to each treatment evaluated was calculated for all of the studies combined. How were differences between studies investigated? Differences between the studies were discussed in the text. Results of the review: Four studies were included (n=285, number of digits 297). Overall, 57% (range: 47 to 64) of patients treated with injectable corticosteroids responded to treatment. Corticosteroids were GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 10 of 17
11 significantly more effective than placebo in the two studies that evaluated this: 64% versus 20% (p<0.02) and 60% versus 15% (p<0.05). Corticosteroid injection with percutaneous release relieved pain in 91% of patients compared with 47% of patients who received corticosteroid alone (p=0.001). However, this study included patients with trigger thumb only and did not describe either the randomisation or blinding procedures. There was no significant difference between intra-sheath and subcutaneous corticosteroid injection (pvalue not reported). Authors' conclusions: Corticosteroids were effective in relieving pain in 57% of patients. CRD commentary: The review addressed a focused question that was supported by inclusion criteria defined in terms of the study design, population and intervention; the outcomes were defined more broadly. The search was limited to two databases and studies reported in English, and there were no attempts to locate unpublished studies. Relevant studies may therefore have been missed and the review may be subject to language and publication bias. Details of the review process were not reported, so it is not possible to determine whether any steps were taken to avoid error or bias. No formal validity assessment was carried out, although several methodological limitations of the included papers were highlighted in the review: inadequate reporting of study details, randomisation that is prone to bias, lack of blinding and use of non-standardised outcome measures. These limitations are likely to affect the reliability of the findings. There was a high level of clinical heterogeneity in the included studies in terms of corticosteroids administered, comparator treatments, duration of follow-up, participants and digits studied. The data were pooled to give a total percentage response rate and statistical heterogeneity was not formally assessed. Given that the response rates were similar across trials this may have been appropriate, however, pooling from single arms of the trials loses the effect of randomisation and the ability to make relevant comparisons. A more appropriate analysis would have focused on the difference between the two treatment groups in each trial. Given the limitations in the literature search, apparent poor quality and small number of included studies, and failure to appropriately synthesise the results, the authors conclusions should be interpreted with extreme caution, especially given that the value reported is obtained by pooling data from one arm of each trial. Implications of the review for practice and research: Practice: The authors did not state any implications for practice. Research: The authors stated that further RCTs evaluating both pharmacological and surgical interventions are needed. Future research should use standardised outcome measures: a classification system to assess severity of trigger finger, visual analogue scales to assess pain and a goniometer to assess mobility. 2. LEVEL1: SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Cochrane Review: Corticosteroid injection for trigger finger in adults, Peters- Veluthamaningal C, van der Windt DAWM, Winters JC, Meyboom- de Jong B ABSTRACT Background: Trigger finger is a disease of the tendons of the hand leading to triggering (locking) of affected fingers, dysfunction and pain. Available treatments include local injection with corticosteroids, surgery, or splinting. Objectives: To summarize the evidence on the efficacy and safety of corticosteroid injections for trigger finger in adults using the following endpoints: treatment success, frequency of triggering or locking, functional status of the affected fingers, and severity of pain of the fingers. Search methods: The databases CENTRAL, DARE, MEDLINE (1966 to November 2007), EMBASE (1956 to November 2007), CINAHL (1982 to November 2007), AMED (1985 to November 2007) and PEDro (a physiotherapy evidence database) were searched. Selection criteria: We selected randomized and controlled clinical trials evaluating efficacy and safety of corticosteroid injections for trigger finger in adults. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 11 of 17
12 Data collection and analysis: The databases were searched for titles of eligible studies. After screening abstracts of these studies, full text articles of studies which fulfilled the selection criteria were obtained. Data were extracted using a predefined electronic form. The methodological quality of included trials was assessed by using items from the checklist developed by Jadad and the Delphi list. We planned to extract data regarding information on the primary outcome measures: treatment success, frequency of triggering or locking, and functional impairment of fingers, severity of the trigger finger; and the secondary outcome measures: proportion of patients with side effects, types of side effects, and patient satisfaction with injection. Main results: Two randomized controlled studies were found that involved 63 participants: 34 were allocated to corticosteroids and lidocaine, and 29 were allocated to lidocaine alone. Corticosteroid injection with lidocaine was more effective than lidocaine alone on treatment success at four weeks (relative risk 3.15, 95% CI 1.34 to 7.40). The number needed to treat to benefit was 3. No adverse events or side effects were reported. The effectiveness of local corticosteroid injections was studied in only two small randomized controlled trials of poor methodological quality. Both studies showed better short-term effects of corticosteroid injection combined with lidocaine compared to lidocaine alone on the treatment success outcome. In one study the effects of corticosteroid injections lasted up to four months. No adverse effects were observed. The available evidence for the effectiveness of intra-tendon sheath corticosteroid injection for trigger finger can be graded as a silver level evidence for superiority of corticosteroid injections combined with lidocaine over injections with lidocaine alone. 3. LEVEL 4: CASE SERIES The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger, Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir Nakhdjevani, MBBS, Mary A. Lloyd, MBBS, Frederik B. Schreuder, MBBCH, Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4: Aim: investigate the efficacy of steroid injections for treating trigger digits. Methods: Ninety digits were investigated with at least a year follow up. The study mainly focused on the efficacy of the injections, as well as co-morbidities, presence of a nodule, actual digit injected and the severity at presentation using Green s classification. Results: The study found that 66% of trigger digits were effectively treated using steroid injections. There was a difference between the efficacy of the injection in the different digits, with a statistical significance between the thumb and the fingers. The results also showed that there was no statistical relationship between the severity of the condition, the presence of a nodule or co-morbidities and the efficacy of the steroid injections. Conclusions: The study found that steroid injections are an effective first-line intervention for the treatment of trigger digit. It also found an increased efficacy for treating the thumb compared to other digits. Both the severity of the condition at presentation and the presence of a nodule had no significant impact on the efficacy of the injections. 4. LEVEL: N/A (COMBINATION OF LITERATURE REVIEW AND EXPERT OPINION) Management and referral for trigger finger/thumb, Sohail Akhtar, Mary J Bradley, David N Quinton, Frank D Burke, BMJ Volume July 2005 Summary points: Children can present with trigger finger/thumb but it is less common than in adults; Presentation is usually a fixed flexion deformity of the thumb. In patients with diabetes, trigger finger is more common and less likely to respond to treatment than in patients without diabetes Steroid injection can produce a cure rate in excess of 90% in patients with a palpable nodule or with symptoms present for less than six months. With a suitable knowledge of the anatomy, giving a single steroid injection is safe and has few complications GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 12 of 17
13 Percutaneous trigger release is a safe and effective means of treating trigger finger and can be done in the outpatient clinic Sources and search criteria: We searched Medline and PubMed for relevant English language literature. We used the search terms trigger finger and stenosing tenosynovitis. We identified additional literature from the references of these papers. Epidemiology: The condition has a reported incidence of 28 cases per population per year, or a lifetime risk of 2.6% in the general population. This rises to 10% in patients with diabetes. Two peaks in incidence occur the first under the age of eight and the second (more common) in the fifth and sixth decades of life. This bimodal distribution represents two different clinical groups, not only for age but also in incidence, sex distribution, digit affected, treatment, and outcome. 5. LEVEL: N/A Professional information leaflet: Trigger finger and trigger thumb, The British Society for Surgery of the Hand (BSSH) What is it? Trigger finger is a painful condition in which a finger or thumb clicks or locks as it is bent towards the palm. What is the cause? Thickening of the mouth of a tendon tunnel leads to roughness of the tendon surface, and the tendon then catches in the tunnel mouth. People with insulin dependent diabetes are especially prone to triggering, but most trigger digits occur in people without diabetes. Triggering occasionally appears to start after an injury such as a knock on the hand. There is little evidence that it is caused by work activities, but the pain can certainly be aggravated by hand use at work, at home, in the garden or at sport. Triggering is sometimes due to tendon nodules in people known to have rheumatoid arthritis. It is not caused by osteoarthritis. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 13 of 17
14 What are the symptoms? 1. Pain at the site of triggering in the palm (fingers) or on the palm surface of the thumb at the middle joint, usually in a person over the age of Tenderness if you press on the site of pain. 3. Clicking of the digit during movement, or locking in a bent position, often worse on waking in the morning. The digit may need to be straightened with pressure from the opposite hand. 4. Stiffness, especially in trigger thumb where movement at the end joint is reduced. What is the treatment? Trigger finger and trigger thumb are not harmful, but can be a really painful nuisance. Some mild cases recover over a few weeks without treatment. The options for treatment are: 1. Avoiding activities that cause pain, if possible 2. Using a small splint to hold the finger or thumb straight at night. A splint can be fitted by a hand therapist, but even a lollipop stick held on with tape can be used as a temporary splint. Holding the finger straight at night keeps the roughened segment of tendon in the tunnel and makes it smoother. 3. Steroid injection relieves the pain and triggering in about 70% of cases, but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes. The risks of injection are small, but it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection. Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. A second injection is sometimes helpful, but surgery may be needed if triggering persists. 4. Percutaneous trigger finger release with a needle. Some surgeons prefer to release the tight mouth of the tunnel using a needle inserted under a local anaesthetic injection, but others feel that open surgery is more effective. The needle method is not suitable for all cases and all digits. Surgical decompression of the tendon tunnel. The anaesthetic may be local (injected under the skin at the site of operation) regional (injected in the armpit to numb the entire arm) or a general anaesthetic. Through a small incision, and protecting nerves that lie near the tunnel, the surgeon widens the mouth of the tendon tunnel by slitting its roof. The wound will require a small dressing for days, but light use of the hand is possible from the day of surgery and active use of the digit will aid the recovery of movement. Pain relief is usually rapid. Although the scar may be red and tender for several weeks, it is seldom troublesome in the longer term. Recurrence of triggering after surgery is uncommon. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 14 of 17
15 Appendix 2 Diagnostic and Procedure Codes Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM038 (All codes have been verified by Mersey Internal Audit s Clinical Coding Academy) GM076 - Correction of Trigger Finger OPCS-4 Procedure Codes: Release of constriction of sheath of tendon T72.3 Injection of therapeutic substance into tendon NEC T74.4 Specified muscle of hand NEC, or Z56.8 Muscle of hand NEC Z56.9 With the following ICD-10 diagnosis code(s): Trigger Finger M65.3 GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 15 of 17
16 Appendix 3 Version History Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM038 The latest version of this policy can be found here: GM Trigger Finger Policy Version Date Summary of Changes /03/2016 Initial draft /03/2016 The GM EUR Steering Group agreed the following changes: Under Definition, point 2, second sentence amended to read: 'Preferably fitted by a hand therapist, where this service can be provided in the community.' Commissioning Criteria: The 4 th paragraph under mandatory criteria amended from: 'They have been given a course of steroid injections which would be expected to relieve the pain and triggering in about 70% of cases, but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes. The risks of injection are small; (it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection). Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. The course is 2 serial injections for patients with diabetes and 3 serial injections for non-diabetic patients.' to: 'They have been given a course of 2 serial steroid injections which would be expected to relieve the pain and triggering in about 70% of cases, but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes. The risks of injection are small; (it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection). Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. In patients where trigger finger has recurred and in whom the course of steroid injections previously failed they should be offered the injections but if they are reluctant to try injections again then they may be referred for surgery without having the serial injections for the recurrence.' Funding mechanism of individual prior approval added to the policy. Following the above changes the GM EUR Steering Group agreed the policy could go out for a period of clinical engagement /07/2016 The GM EUR Steering Group reviewed the clinical engagement feedback and agreed the following changes to the policy: Under the Commissioning Recommendation and Mandatory Criteria the 4 th paragraph on steroid injections amended to read as follows: 'If indicated they have been given a steroid injection in an appropriate clinical setting, which would be expected to relieve the pain and triggering in up to 70% of cases, but the success rate is lower in people with diabetes). The risks of injection are small; (it very occasionally causes some thinning or colour change in the skin at the site of injection). Improvement may occur within a few days of injection, but may take several weeks. If clinically appropriate the patient may be offered a second injection at the discretion of the treating clinician.' 'Patients whose trigger finger has recurred and in whom steroid injections previously failed should be offered the injection but if they are reluctant to try an injection again then they may be referred for surgery without having been injected for the recurrence.' Following the above changes to the policy the GM EUR Steering Group agreed that the policy could progress through the governance process. 25/04/2017 Policy transferred to new template format. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 16 of 17
17 0.4 12/06/2017 Diagnostic and Procedure codes added to Appendix /10/2017 Approved by Greater Manchester Association Governing Group /06/2018 Appendix 2: Added OPCS-4 codes T74.4 Injection of therapeutic substance into tendon NEC, T691 Primary tenolysis & T692 Revision of tenolysis. GM Trigger Finger Policy v1.1 FINAL Page 17 of 17
Policy Statement. Title/Topic: Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Osteoarthritis Date: April 2014 Reference: GM037
 Policy Statement Title/Topic: Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Osteoarthritis Date: April 2014 Reference: GM037 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 09/09/2013 Initial draft N/A 0.2 19/09/2013
Policy Statement Title/Topic: Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Osteoarthritis Date: April 2014 Reference: GM037 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 09/09/2013 Initial draft N/A 0.2 19/09/2013
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Osteoarthritis Date: June 2014 Last Reviewed: May 2015 Reference: GM037 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Osteoarthritis Date: June 2014 Last Reviewed: May 2015 Reference: GM037 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Invasive Treatments for Snoring GM Ref: GM068 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Invasive Treatments for Snoring GM Ref: GM068 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Invasive Treatments for Snoring Policy Exclusions (Alternative
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Invasive Treatments for Snoring GM Ref: GM068 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Invasive Treatments for Snoring Policy Exclusions (Alternative
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement. Title/Topic: Surgical Revision of Scarring Date: June 2015 Reference: GM066
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Surgical Revision of Scarring Date: June 2015 Reference: GM066 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 02/09/2014 Initial draft N/A 0.2
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Surgical Revision of Scarring Date: June 2015 Reference: GM066 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 02/09/2014 Initial draft N/A 0.2
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Bunion (Hallux Valgus) Surgery GM Ref: GM052 Version: 3.0 (17 Jan 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Bunion (Hallux Valgus) Surgery GM Ref: GM052 Version: 3.0 (17 Jan 2018) Commissioning Statement Bunion (Hallux Valgus) Surgery Policy Exclusions Hallux Rigidus
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Bunion (Hallux Valgus) Surgery GM Ref: GM052 Version: 3.0 (17 Jan 2018) Commissioning Statement Bunion (Hallux Valgus) Surgery Policy Exclusions Hallux Rigidus
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement. Title/Topic: Tonsillectomy Date: April 2014 Last reviewed: May 2015 Reference: GM028
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Tonsillectomy Date: April 2014 Last reviewed: May 2015 Reference: GM028 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 09/09/2013 Initial draft
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Tonsillectomy Date: April 2014 Last reviewed: May 2015 Reference: GM028 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 09/09/2013 Initial draft
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Body Contouring GM Ref: GM011 & GM019 Version: 2.4 (6 June 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Body Contouring GM Ref: GM011 & GM019 Version: 2.4 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Body Contouring Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning arrangements
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Body Contouring GM Ref: GM011 & GM019 Version: 2.4 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Body Contouring Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning arrangements
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare. Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease
 Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease Hand Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with Dupuytren s disease and who are considering surgical
Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease Hand Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with Dupuytren s disease and who are considering surgical
Trigger Finger Release
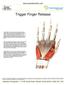 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Insert heading depending. cover options once. other cover options once you have chosen one. 20pt. Ref: N-SC/031
 Insert heading depending Insert Interim Insert heading Clinical Commissioning depending on line on on Policy: line length; length; please please delete delete on line line Spinal length; Surgery please
Insert heading depending Insert Interim Insert heading Clinical Commissioning depending on line on on Policy: line length; length; please please delete delete on line line Spinal length; Surgery please
TRIGGER FINGER CRITERIA BASED ACCESS POLICY
 TRIGGER FINGER CRITERIA BASED ACCESS POLICY Version: Discussion and Recommendation by the Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum 1617.v1b Date: 16 June 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Name of
TRIGGER FINGER CRITERIA BASED ACCESS POLICY Version: Discussion and Recommendation by the Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum 1617.v1b Date: 16 June 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Name of
Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) for Foot Drop GM Ref: GM036 Version: 2.
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) for Foot Drop GM Ref: GM036 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) for Foot Drop GM Ref: GM036 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Insert heading depending line on length; please delete delete. length; please delete other cover options once
 Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Labiaplasty GM Ref: GM027 Version: 3.0 (15 Nov 2017)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Labiaplasty GM Ref: GM027 Version: 3.0 (15 Nov 2017) Commissioning Statement Labiaplasty Policy Exclusions Labiaplasty carried out as the result of obstetric
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Labiaplasty GM Ref: GM027 Version: 3.0 (15 Nov 2017) Commissioning Statement Labiaplasty Policy Exclusions Labiaplasty carried out as the result of obstetric
Specialised Services Policy:
 Specialised Services Policy: CP35 Cochlear Implants Document Author: Specialised Planner for Women & Children s Services Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Executive Board Issue Date: 05
Specialised Services Policy: CP35 Cochlear Implants Document Author: Specialised Planner for Women & Children s Services Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Executive Board Issue Date: 05
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1.02 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol,
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1.02 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol,
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy. CP29: Bariatric Surgery
 Specialised Services Commissioning Policy CP29: Bariatric Surgery Document Author: Specialist Planner, Cardiothoracic Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 12 June
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy CP29: Bariatric Surgery Document Author: Specialist Planner, Cardiothoracic Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 12 June
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Specialised Services Policy Position PP104
 Specialised Services Policy Position PP104 Personalised External Aortic Root Support (PEARS) for surgical management of enlarged aortic root (adults) March 2019 Version 1.0 Document information Document
Specialised Services Policy Position PP104 Personalised External Aortic Root Support (PEARS) for surgical management of enlarged aortic root (adults) March 2019 Version 1.0 Document information Document
Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Cataract Surgery GM Ref: GM026 Version: 3.1 (15 Nov 2017)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Cataract Surgery GM Ref: GM026 Version: 3.1 (15 Nov 2017) Commissioning Statement Cataract Surgery Policy Exclusions Juvenile cataract, lens-induced disease
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Cataract Surgery GM Ref: GM026 Version: 3.1 (15 Nov 2017) Commissioning Statement Cataract Surgery Policy Exclusions Juvenile cataract, lens-induced disease
Acute Services Division. Information for patients. Carpal Tunnel. Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary
 Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Revised review: 30/04/2018 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Revised review: 30/04/2018 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Dupuytrens disease. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Dupuytrens disease Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Dupuytrens Disease Dupuytren s disease is a thickening of the tissue in the palm of the hand which may result in progressive flexion contractures
Dupuytrens disease Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Dupuytrens Disease Dupuytren s disease is a thickening of the tissue in the palm of the hand which may result in progressive flexion contractures
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis
 Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Rhiniplasty / Septoplasty / Septo- Rhinoplasty GM Ref: GM024 Version: 2.
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Rhiniplasty / Septoplasty / Septo- Rhinoplasty GM Ref: GM024 Version: 2.3 (6 June 2016) Commissioning Statement Rhiniplasty / Septoplasty / Septo-Rhinoplasty
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Rhiniplasty / Septoplasty / Septo- Rhinoplasty GM Ref: GM024 Version: 2.3 (6 June 2016) Commissioning Statement Rhiniplasty / Septoplasty / Septo-Rhinoplasty
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016
 Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement. Title/Topic: Correction of Eyelid Ptosis Reference: GM047 Date: December 2014 Last Reviewed: January 2016
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Correction of Eyelid Ptosis Reference: GM047 Date: December 2014 Last Reviewed: January 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 24/04/2014
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Correction of Eyelid Ptosis Reference: GM047 Date: December 2014 Last Reviewed: January 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 24/04/2014
Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia)
 Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia) Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The carpal tunnel is a tunnel found
Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia) Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The carpal tunnel is a tunnel found
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Radiofrequency Denervation for Back Pain GM Ref: GM004 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Radiofrequency Denervation for Back Pain GM Ref: GM004 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Radiofrequency Denervation for Back Pain Policy Exclusions
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Radiofrequency Denervation for Back Pain GM Ref: GM004 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Radiofrequency Denervation for Back Pain Policy Exclusions
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery. (Minor procedure in Primary Care)
 Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
Osteoarthritis of the Thumb
 Osteoarthritis of the Thumb A hand therapy resource booklet 1 of 12 Osteoarthritis of the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint in the thumb This booklet has been designed to provide you with information about your
Osteoarthritis of the Thumb A hand therapy resource booklet 1 of 12 Osteoarthritis of the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint in the thumb This booklet has been designed to provide you with information about your
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults Policy
 Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults Policy Version: 2016-19 Ratified by: NHS Leeds West CCG Assurance Committee on; 16 November 2016 NHS Leeds North CCG Governance on Performance and Risk Committee
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults Policy Version: 2016-19 Ratified by: NHS Leeds West CCG Assurance Committee on; 16 November 2016 NHS Leeds North CCG Governance on Performance and Risk Committee
The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture
 A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children
 Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
Dupuytren s Fasciectomy. Patient Information
 Dupuytren s Fasciectomy Patient Information Author ID: TG Leaflet Number: UL 015 Name of Leaflet: Dupuytren s Fasciectomy Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017 Review Date: October 2019 Introduction This
Dupuytren s Fasciectomy Patient Information Author ID: TG Leaflet Number: UL 015 Name of Leaflet: Dupuytren s Fasciectomy Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017 Review Date: October 2019 Introduction This
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery
 A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not
Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation
 Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation Document Author: Specialist Services Planning Manager for Neurosciences and Complex Conditions Executive Lead: Director of Planning and Performance
Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation Document Author: Specialist Services Planning Manager for Neurosciences and Complex Conditions Executive Lead: Director of Planning and Performance
West Suffolk Hospital
 For staff use only: Patient Details: First names: Hospital no: (Use hospital identification label) West Suffolk Hospital Patient information leaflet Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2-3 Patient agreement to investigation
For staff use only: Patient Details: First names: Hospital no: (Use hospital identification label) West Suffolk Hospital Patient information leaflet Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2-3 Patient agreement to investigation
OS05 Carpal Tunnel Release (under Local Anaesthetic)
 OS05 Carpal Tunnel Release (under Local Anaesthetic) What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition where there is increased pressure on the nerve that crosses the front of your
OS05 Carpal Tunnel Release (under Local Anaesthetic) What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition where there is increased pressure on the nerve that crosses the front of your
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement. Title/Topic: Cataract Surgery Reference: GM026 Date: September 2014 Last Reviewed: September 2015
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Cataract Surgery Reference: GM026 Date: September 2014 Last Reviewed: September 2015 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 07/01/2014
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Cataract Surgery Reference: GM026 Date: September 2014 Last Reviewed: September 2015 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 07/01/2014
Trigger Finger Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Trigger Finger Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Trigger Finger Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist
 ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
Study selection Study designs of evaluations included in the review Diagnosis.
 Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Labiaplasty Date: November 2014 Last Reviewed: November 2015 Reference: GM027
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Labiaplasty Date: November 2014 Last Reviewed: November 2015 Reference: GM027 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 12/05/2014 First
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Labiaplasty Date: November 2014 Last Reviewed: November 2015 Reference: GM027 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details Page number 0.1 12/05/2014 First
PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 18 March 2016
 Part 1 Part 2 PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 18 March 2016 Title of Report Supporting deaf patients to access primary care services Purpose of the Report The report is to provide the co-commissioning
Part 1 Part 2 PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 18 March 2016 Title of Report Supporting deaf patients to access primary care services Purpose of the Report The report is to provide the co-commissioning
Dupuytren s release. Turnberg Building Orthopaedics
 Dupuytren s release Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure Dupuytren s contracture is a common condition. In most cases, no cause
Dupuytren s release Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure Dupuytren s contracture is a common condition. In most cases, no cause
Specialised Services Policy: CP 44 Body Contouring
 Specialised Services Policy: CP 44 Body Contouring Document Author: Specialised Planner Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 11 July 2013 Review Date: 01 July
Specialised Services Policy: CP 44 Body Contouring Document Author: Specialised Planner Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 11 July 2013 Review Date: 01 July
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
 Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) First published:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) First published:
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Out of contract spinal procedures GM Ref: GM018 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Out of contract spinal procedures GM Ref: GM018 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Out of contract spinal procedures Policy Exclusions (Alternative
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Out of contract spinal procedures GM Ref: GM018 Version: 2.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Out of contract spinal procedures Policy Exclusions (Alternative
Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2015/2016
 Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2015/2016 Date of Meeting: 20 November 2015 Agenda Item: 8b Subject: Greater Manchester Effective Use of Resources Policies Reporting Officer: Dr C Duffy
Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2015/2016 Date of Meeting: 20 November 2015 Agenda Item: 8b Subject: Greater Manchester Effective Use of Resources Policies Reporting Officer: Dr C Duffy
Carpal tunnel decompression advice
 Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
DRAFT. Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement
 DRAFT Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Ultrasound and pulsed electromagnetic systems (PES) for bone healing Reference: GM063 Date: November 2015 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details
DRAFT Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement Title/Topic: Ultrasound and pulsed electromagnetic systems (PES) for bone healing Reference: GM063 Date: November 2015 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Details
Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2014/2015
 Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2014/2015 Date of Meeting: 16 January 2015 Agenda Item: 8d Subject: Approval of GM Effective Use of Resource (EUR) Policy Eyelid Ptosis Reporting Officer:
Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) Governing Body 2014/2015 Date of Meeting: 16 January 2015 Agenda Item: 8d Subject: Approval of GM Effective Use of Resource (EUR) Policy Eyelid Ptosis Reporting Officer:
BENIGN SKIN LESIONS INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUEST POLICY
 BENIGN SKIN LESIONS INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUEST POLICY Version: 1516.v3 Ratified by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 23 March 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name
BENIGN SKIN LESIONS INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUEST POLICY Version: 1516.v3 Ratified by: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 23 March 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 July 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta459
 Collagenase clostridium histolyticum for treating Dupuytren's contracture Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 July 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta459 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
Collagenase clostridium histolyticum for treating Dupuytren's contracture Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 July 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta459 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy. Information for patients MSK Outpatients - Women's Health (Therapy)
 Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy Information for patients MSK Outpatients - Women's Health (Therapy) What is carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common disorder of
Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy Information for patients MSK Outpatients - Women's Health (Therapy) What is carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common disorder of
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic assisted lung resection for primary lung cancer
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic assisted lung resection for primary lung cancer Reference: NHS England B10X03/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic assisted lung resection for primary lung cancer Reference: NHS England B10X03/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
London Choosing Wisely
 London Choosing Wisely Draft Policy Template: Knee arthroscopy Version Date Notes Draft for T&F Group 1 03/05/18 Initial draft Revised version post T&F Group 1 Revised version for Task & Finish Group 2
London Choosing Wisely Draft Policy Template: Knee arthroscopy Version Date Notes Draft for T&F Group 1 03/05/18 Initial draft Revised version post T&F Group 1 Revised version for Task & Finish Group 2
PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 8 SEPTEMBER 2015
 Part 1 Part 2 PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 8 SEPTEMBER 2015 Title of Report Trafford Palliative care Quality Premium Scheme 2015/16 Purpose of the Report The purpose of the report is to detail
Part 1 Part 2 PRIMARY CARE CO-COMMISSIONING COMMITTEE 8 SEPTEMBER 2015 Title of Report Trafford Palliative care Quality Premium Scheme 2015/16 Purpose of the Report The purpose of the report is to detail
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION. Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over, with Publications Gateway
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over, with Publications Gateway
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for adults with Parkinson's tremor and Familial Essential Tremor Version Number: NHS England B13X06/01 Information Reader Box
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for adults with Parkinson's tremor and Familial Essential Tremor Version Number: NHS England B13X06/01 Information Reader Box
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Placename CCG. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare. Policy for Managing Back Pain- Spinal Injections
 Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Managing Back Pain- Spinal Injections 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite of policies that the CCG uses to drive its
Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Managing Back Pain- Spinal Injections 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite of policies that the CCG uses to drive its
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Enhanced Service Specification. Childhood seasonal influenza vaccination programme 2018/19
 Enhanced Service Specification Childhood seasonal influenza vaccination programme 2018/19 Contents Childhood seasonal influenza vaccination programme... 1 Contents... 4 1 Introduction... 5 2 Background...
Enhanced Service Specification Childhood seasonal influenza vaccination programme 2018/19 Contents Childhood seasonal influenza vaccination programme... 1 Contents... 4 1 Introduction... 5 2 Background...
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Hernia Repair in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request Team - A partnership between
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Hernia Repair in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request Team - A partnership between
Translation and Interpretation Policy
 Translation and Interpretation Policy Version 1 Ratified By NHS West Cheshire Clinical Commissioning Group Governing Body Date Ratified 16 th November 2017 Author(s) Jonathan Taylor Responsible Committee
Translation and Interpretation Policy Version 1 Ratified By NHS West Cheshire Clinical Commissioning Group Governing Body Date Ratified 16 th November 2017 Author(s) Jonathan Taylor Responsible Committee
Data extraction. Specific interventions included in the review Dressings and topical agents in relation to wound healing.
 Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Closed reduction methods for acute anterior shoulder dislocation [Cochrane Protocol] Kanthan Theivendran, Raj Thakrar, Subodh Deshmukh,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Closed reduction methods for acute anterior shoulder dislocation [Cochrane Protocol] Kanthan Theivendran, Raj Thakrar, Subodh Deshmukh,
Commissioning Policy. The use of Acupuncture in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain. July 2013
 Commissioning Policy The use of Acupuncture in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain July 2013 This commissioning policy applies to patients within: South Worcestershire Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG)
Commissioning Policy The use of Acupuncture in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain July 2013 This commissioning policy applies to patients within: South Worcestershire Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG)
1. Purpose of this document
 Guideline Ref No: 0900 Version 4 Title: Document Author: Ratified by: Specialist Orthopaedic Physiotherapist Care and Clinical Policies Group Date: 13 February 2017 Date: 19 April 2017 Review date: 5 May
Guideline Ref No: 0900 Version 4 Title: Document Author: Ratified by: Specialist Orthopaedic Physiotherapist Care and Clinical Policies Group Date: 13 February 2017 Date: 19 April 2017 Review date: 5 May
DRAFT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION. Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Infliximab for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Infliximab for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over,
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Infliximab for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over,
Physiotherapy information for Achilles Tendinopathy
 Physiotherapy information for Achilles Tendinopathy What is Achilles Tendinopathy? Achilles Tendinopathy is a condition that can cause pain, swelling and weakness of the Achilles Tendon. This joins your
Physiotherapy information for Achilles Tendinopathy What is Achilles Tendinopathy? Achilles Tendinopathy is a condition that can cause pain, swelling and weakness of the Achilles Tendon. This joins your
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) Produced by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination Copyright 2017 University of York.
 A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults, Children and Young People Policy
 Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults, Children and Young People Policy Version: 2017-20 Ratified by: NHS Leeds West CCG Assurance Committee on; 16 November 2016 NHS Leeds North CCG Governance on
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors in Adults, Children and Young People Policy Version: 2017-20 Ratified by: NHS Leeds West CCG Assurance Committee on; 16 November 2016 NHS Leeds North CCG Governance on
WAHT-OCT-021 It is the responsibility of every individual to ensure this is the latest version as published on the Trust Intranet
 This guidance does not override the individual responsibility of health professionals to make appropriate decision according to the circumstances of the individual patient in consultation with the patient
This guidance does not override the individual responsibility of health professionals to make appropriate decision according to the circumstances of the individual patient in consultation with the patient
Cochrane Breast Cancer Group
 Cochrane Breast Cancer Group Version and date: V3.2, September 2013 Intervention Cochrane Protocol checklist for authors This checklist is designed to help you (the authors) complete your Cochrane Protocol.
Cochrane Breast Cancer Group Version and date: V3.2, September 2013 Intervention Cochrane Protocol checklist for authors This checklist is designed to help you (the authors) complete your Cochrane Protocol.
PALIPERIDONE LONG ACTING INJECTION PRESCRIBING GUIDELINE. Chief Pharmacist. Chief Pharmacist
 REFERENCE NUMBER: PALIPERIDONE LONG ACTING INJECTION PRESCRIBING GUIDELINE AREA: NAME OF RESPONSIBLE COMMITTEE / INDIVIDUAL NAME OF ORIGINATOR / AUTHOR Trust-wide Chief Pharmacist Chief Pharmacist DATE
REFERENCE NUMBER: PALIPERIDONE LONG ACTING INJECTION PRESCRIBING GUIDELINE AREA: NAME OF RESPONSIBLE COMMITTEE / INDIVIDUAL NAME OF ORIGINATOR / AUTHOR Trust-wide Chief Pharmacist Chief Pharmacist DATE
GOVERNING BOARD. Assisted Conception (IVF): Review of access criteria. Date of Meeting 21 January 2015 Agenda Item No 13. Title
 GOVERNING BOARD Date of Meeting 21 January 2015 Agenda Item No 13 Title Assisted Conception (IVF): Review of access criteria Purpose of Paper The SHIP (Southampton, Hampshire, Isle of Wight and Portsmouth)
GOVERNING BOARD Date of Meeting 21 January 2015 Agenda Item No 13 Title Assisted Conception (IVF): Review of access criteria Purpose of Paper The SHIP (Southampton, Hampshire, Isle of Wight and Portsmouth)
