Bronchial Asthma and COPD
|
|
|
- Gilbert Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bronchial Asthma and COPD Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Females doctor notes Grey: Males doctor notes OBJECTIVES: Different types of drugs used for treatment of asthma. Differentiate between treatment and prophylactic therapy for asthma. Recognize the different types of bronchodilators regarding pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, uses and side effects. Identify the different anti-inflammatory drugs for asthma in respect to kinetics, dynamics, uses and side effects. Editing File
2 Bronchial Asthma: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder (Obstructive diseases) of bronchial airways that result in airway obstruction in response to external stimuli or triggers. Characters of airways in asthmatic patients : Airway hyperreactivity: immunoglobulin is present in asthmatic patients). results in release of endogenous inflammatory mediators. Bronchospasm: 3 Is an abnormal sensitivity of the airways to any external stimuli. (Different (happens due to the release of histamine & leukotriens) 1 2 Constriction of the bronchial smooth muscles. Inflammation: e.g. histamine, leukotrienes Edema, swelling. Thick mucus production. * By antigen-antibody reaction (IgE) 2 Triggers of asthma: Exogenous chemicals or irritants 3 Symptoms of asthma Asthma produces recurrent episodic attack of : Acute bronchoconstriction Chest infections Shortness of breath Stress Chest tightness Exercise (in cold air) Wheezing Rapid respiration Pets Cough (mostly it is dry) Seasonal changes Emotional conditions Some drugs (as aspirin, β-bockers) Aspirin is NSAID which will inhibit the cyclooxygenase enzyme, so most of arachidonic acid will be converted through 5-lipoxygenase to leukotrienes instead which causes bronchoconstrictors, and they are important chemical mediators in the pathogenesis of asthma.. Symptoms can happen each time the airways are irritated by inhaled irritants or allergens.
3 Antimuscarinics Anti asthmatic drugs (Atropine substitutes) Bronchodilators (Quick relief) Treat acute episodic attack of Asthma. Short acting ß2-agonists Only ß2 agonists (Selective) used to reduce the side effects Xanthine preparations Reduce the frequency of attacks and nocturnal *night awakenings Corticosteroids The most potent anti-inflammatory drugs Mast cell stabilizers To stop the release of histamine Prophylactic (control) therapy (Anti-inflammatory) prophylactic means reduce the number of attack NOTE: long acting beta2 agonist is a bronchodilator (not anti-inflammatory) but is NEVER used for acute attacks, it s used as a control medication and is given with corticosteroids Leukotrienes antagonists Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody stops the effect of the allergen Long acting ß2-agonist First : Bronchodilators For better understanding of Bronchodilators, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the Innervations of the respiratory system -M3 receptors in smooth muscles and glands Action: Bronchoconstriction +Increase mucus secretion. Parasympathetic supply: Sympathetic supply: β- adrenoceptor agonists (Sympathomimetics) -B2 receptors in smooth muscles and glands. Action :Bronchodilation +Decrease mucus secretion. Mechanism of action for selective & Non-selective Sympathomimetics: stimulate β2 Directly stimulate adenyl cyclase camp **(a second messenger comes from ATP, bronchodilator, vasodilator) bronchodilation. Increase mucus clearance by increasing ciliary activity. (they have adrenergic receptors which upon their activation intracellular calcium, which ciliary activity) Stabilization of mast cell membrane **(therefore reducing histamine release).
4 A) Non-selective β-agonist Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Clinical uses Pharmacok inetics ADRs Contraindications Isoprenaline Epinephrine: Non-selective adrenergic agonist (α1, α2, β1, β2) Potent bronchodilator Adrenaline is the drug of choice for acute anaphylaxis (hypersensitivity reaction) can be used for asthma BUT selective B2 are better in case of asthma. Given S.C, I.M, inhalation Not effective orally *(any drug that can affect the heart is given S.C not I.V to reduce the side effects on the CVS). Rapid onset of action (maximum effect within 15 min). Has short duration of action (60-90 min). Hyperglycemia. Skeletal muscle tremor. CVS side effects (β1 actions): tachycardia, arrhythmia, hypertension. CVS patients :hypertension, heart failure. Diabetic patients, hyperthyroidism Asthmatic patient with hypertension. B) Selective β2 agonist Are mainly given by inhalation by: metered dose inhaler or nebulizer Short acting selective ß2 agonists Drugs Salbutamol (albuterol) : Mainly given by inhalation, orally, I.V. Terbutaline : Mainly given by inhalation, orally, s.c. Long acting selective ß2 agonists Are given by inhalation. Drugs of choice for acute episodic attack of asthma (especially salbutamol) Salmeterol. Formoterol Clinical uses Are NOT used to relieve acute episodes of asthma. Used for nocturnal asthma. combined with inhaled corticosteroids to control asthma prophylactic medication (to decrease the number and severity of asthma attacks). Suitable for asthmatic patients with CV disorders as hypertension or heart failure, due to Minimal CVS side effects. Pharmacok inetics ADRs Have rapid onset of action (15-30 min) Short duration of action (4-6 hr). Long acting bronchodilators (12 hours) due to high lipid solubility (creates depot effect). increased storage of drug in the body & gradually released. Skeletal muscle tremors. (A common characteristic. Activation of adrenergic receptors on skeletal muscles hypokalemia tremors) Nervousness, insomnia. Tolerance (β-receptors down regulation. Normally receptors are internalized into the cell to be recycled, repeated use can decrease the number of receptors beyond recycling Overdose may produce tachycardia due to β1 stimulation.
5 Muscarinic antagonists (2nd choice) Ipratropium Mechanism of action Tiotropium Act by blocking muscarinic receptors (non-selective). Inhibit bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion with no anti-inflammatory action. Less effective than β2-agonists. Does not diffuse into the blood. Does not enter CNS. (No CNS Effect) Pharmacodynamics Uses Pharmacokinetics Main choice in chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD). In asthma combined with β2 agonists & corticosteroids. given by aerosol inhalation. Have delayed onset of action. (Never used as rescue medications) *Short acting ß2 agonists are preferably used in cases of emergency because of the rapid onset of action. Duration has short duration of action (3-5 hrs) other characteristics - has longer duration of action (24 hrs) Quaternary derivatives of atropine (polar). Have minimal systemic side effects. Methylxanthines (Xanthine preparations) Theophylline Aminophylline are phosphodiestrase inhibitors: camp bronchodilation *phosphodiesterase break down camp camp, so we use these drugs to inhibit phosphodiesterase) Mechanism of action Adenosine receptors antagonists. one of the actions that adenosine does is bronchoconstriction, so blockade of adenosine leads to bronchodilation. Increase diaphragmatic contraction Stabilization of mast cell membrane Pharmacological effects Bronchial muscle relaxation contraction of diaphragm improve ventilation. CVS: heart rate, force of contraction GIT: gastric acid secretions contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcers. Kidney: renal blood flow, weak diuretic action CNS stimulation: stimulant effect on respiratory center. decrease fatigue & elevate mood. Overdose: tremors, nervousness, insomnia,convulsion.
6 Cont.. Administration Pharmacokinetics Uses Theophylline Aminophylline is given orally is given as slow infusion T ½= 8 hours metabolized by Cyt P450 enzymes in liver. has many drugs interactions: Cyt P450 Enzyme inducers (phenobarbitone & rifampicin): metabolism of theophylline T ½. Cyt P450 Enzyme inhibitors (erythromycin): metabolism of theophylline T ½. Second line drug in asthma Side Effects For status asthmaticus Low therapeutic index (narrow safety margin) monitoring of theophylline blood level is necessary. GIT effects: nausea & vomiting CVS effects: hypotension, arrhythmia. CNS side effects: tremors,nervousness,insomnia,convulsion. β- adrenoceptor agonists vs Methylxanthine : *same action different mechanism. Second : Anti-inflammatory Agents They are control medications / prophylactic therapy act by : bronchial hyperreactivity. inflammation of airways the spasm of airways
7 Glucocorticoids M.O.A - Anti-inflammatory action due to: Inhibition of phospholipase A2 prostaglandin and leukotrienes. Number of inflammatory cells in airways. Mast cell stabilization histamine release. capillary permeability and mucosal edema. Inhibition of antigen-antibody reaction. Upregulate β2 receptors (have additive effect to B2 agonists). *this means that glucocorticoids increase the effect of β2 agonists. Glucocorticoids in Asthma - Are not bronchodilators - Reduce bronchial inflammation Reduce bronchial hyperreactivity to stimuli Maximum action at 9-12 months. Effective in allergic, exercise, antigen and irritant-induced asthma. Have delayed onset of action (effect usually attained after 2-4 weeks). Given as prophylactic medications, used alone or combined with β2 agonists. (however they do reverse and provide a prophylactic effect in bronchoconstriction, and are mainly used to relieve the inflammatory effects). Pharmacological action - Anti-inflammatory actions Immunosuppressant effects *in case of transplantation, so that tissue rejection doesn t happen. Metabolic effects : Hyperglycemia + protein catabolism + protein anabolism + Stimulation of lipolysis (fat redistribution). Mineralocorticoid effects: sodium/fluid retention + potassium excretion (hypokalemia) + blood volume (hypertension) + Behavioral changes: depression Bone loss (osteoporosis) due to: Inhibited bone formation + calcium absorption from GIT. Administration - Inhalation: Given by inhalation (metered-dose inhaler). Have first pass metabolism therefore less side effects so it s the best choice in prophylaxis of asthma. e.g. Budesonide & Fluticasone,beclometasone. Orally: Prednisone, methyl prednisolone. Injection: Hydrocortisone, dexamethasone. because if some of the drug reached the esophagus it will be metabolized immediately by the liver
8 Cont... Clinical Uses of glucocorticoids Treatment of inflammatory disorders (asthma,rheumatoid arthritis). Treatment of autoimmune disorders (ulcerative colitis, psoriasis )اﻟﺻدﻓﯾﺔ and after organ or bone marrow transplantation as immunosuppressants. Antiemetics in cancer chemotherapy. ﻣﺿﺎد ﻟﻠﻘﻲء Systemic corticosteroids are reserved for: Status asthmaticus (i.v.) Side effects due to systemic (oral or injection) corticosteroids: Fluid Retention, Hypertension, Weight gain, Hyperglycemia Growth retardation in children Adrenal suppression Cataract (adrenal atrophy, most serious side effect) Osteoporosis Fat distribution Susceptibility to infections Psychosis Inhalation has very less side effects: but can cause the following: Oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush). fungal infection by Candida species caused by the suppression of normal flora and the pathogen Dysphonia (voice hoarseness) Rinse properly to reduce these effects. Withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids Abrupt stop of corticosteroids should be avoided and dose should be tapered (adrenal insufficiency syndrome). Administration and withdrawal should be gradual
9 Mast cell stabilizers act by stabilization of mast cell membrane. They are not bronchodilators, so they are not effective in acute attack of asthma. Prophylactic anti-inflammatory drugs. Reduce bronchial hyperreactivity. No histamine = no inflammation Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics Effective in exercise, antigen and irritant-induced asthma. Children respond better than adults. Cromoglycate (also called cromolyn), Nedocromil Prophylactic therapy in asthma especially in children. Allergic rhinitis. Conjunctivitis. given by inhalation (aerosol, nebulizer). Have poor oral absorption (10%). Bitter taste minor upper respiratory tract irritation (burning sensation, nasal congestion) Examples Uses Pharmacokinetics Side effects Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics a monoclonal antibody directed against human IgE. prevents IgE binding with its receptors on mast cells & basophiles. Decrease the release of allergic mediators. Uses used for treatment of moderate to severe allergic asthma which does not respond to high doses of corticosteroids. Examples Omalizumab Pharmacokinetics given by injection (s.c.). Disadvantage Expensive-not first line therapy.
10 Leukotrienes antagonists Target Leukotrienes: inflammatory mediators synthesized by inflammatory cells found in the airways (eosinophils, macrophages, mast cells), and produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase on arachidonic acid. Examples of Leukotrienes: Leukotriene B4: chemotaxis of neutrophils. Cysteinyl leukotrienes C4, D4 & E4: bronchoconstriction, bronchial hyperreactivity and mucosal edema and mucus secretion. selective, reversible antagonists of cysteinyl leukotriene receptors (CysLT1 receptors). bronchodilators but have delayed onset of action Have anti-inflammatory action Less effective than inhaled corticosteroids. Have glucocorticoids sparing effect. Zafirlukast, Montelukast and Pranlukast Prophylaxis of mild to moderate asthma (e.g. aspirin-induced asthma, antigen and exercise-induced asthma) Not effective in acute attack of asthma. Can be combined with glucocorticoids (additive effects, low dose of glucocorticoids can be used). Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics Examples Uses P.K Taken orally. Side effects Elevation of liver enzymes, headache, dyspepsia Glucocorticoids sparing effect: What this means is that when glucocorticoids are given with leukotrienes antagonists, we reduce the dose of glucocorticoids and therefore this will make the side effects less.
11 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) a chronic irreversible airflow obstruction, lung damage and inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli). characterized by chronic bronchitis and emphysema (destruction of walls of alveoli). Smoking is a high risk factor but air pollution and genetic factors can contribute. Treatment: supportive therapy only, it can t repair what has been damaged Inhaled bronchodilators Oxygen therapy Lung transplantation Inhaled glucocorticoids Antibiotics specifically macrolides such as azithromycin to reduce the number of exacerbations. Inhaled bronchodilators in COPD 1 Inhaled antimuscarinics Ipratropium & tiotropium. are superior to β2 agonists in COPD β2 agonists 2 -be used either alone or combined: salbutamol + ipratropium (short acting) salmeterol + Tiotropium (long acting-less dose frequency). Bronchial asthma Vs COPD (from 435) Obstructive diseases Definition Causes Treatment Bronchial asthma Chronic inflammatory disorder in bronchial airways result in airway obstruction Exogenous agents,stress,cold air, exercises,pets,seasonal changes, emotions, some drugs(like aspirin and β-blockers) *Bronchodilators: Short acting beta 2-agonists Antimuscarinics Xanthine preparations *Prophylactic therapy: Corticosteroids. Mast cell stabilizers. Leukotrienes antagonists Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody. Long acting ß2-agonis Helpful video COPD Chronic airflow obstruction caused by lung damage and inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli) Smoking. Air pollutant. *Bronchodilators: antimuscarinics : -unlike in asthma- antimuscarinic are superior to β2 agonists. β2 agonists. *Inhaled glucocorticoids *Oxygen therapy *Antibiotics *Lung transplantation Helpful video
12 Summary of drugs used to treat asthma taken from the doctor s lecture Bronchodilators (relievers) Drugs Characteristics β2 agonists -Salbutamol,terbutaline -Salmeterol, formoterol Target Short acting Main choices of acute asthma Inhalation - Adenyl cyclase and camp Long acting, Prophylaxis Nocturnal asthma Main drugs for COPD Inhalation Block muscarinic receptors orally or parenterally Inhibit phosphodiesterase camp Antimuscarinics -Ipratropium (short acting) -Tiotropium (long acting) Xanthine derivatives -Theophylline -Aminophylline inhibit phospholipase A2 Corticosteroids Anti-inflammatory drugs (prophylactic) Drugs Mode of administration Dexamethasone, Fluticasone, budesonide Inhalation prednisolone Orally Hydrocortisone parenterally Mast cell stabilizer Cromoglycate (Cromolyn), Nedocromil Cysteinyl LT1 Receptor antagonist Zafirlukast, montelukast Anti IgE antibody Omalizumab Inhalation, prophylaxis in Children Orally Injection (SC)
13 QUIZ MCQs: 1-One of these acts Selectively on Beta 2 receptors with long acting period? A-Isoprenaline. B-Epinephrine. C-Albuterol. D-Salmeterol 2-The best drug to be given for status asthmaticus cases is: A-Mast cell stabilizer. B-Leukotrienes antagonist. C-Sympathomimetics. D-Glucocorticoids. 3-A 30-years old patient came to the ER with severe Asthma, he was given Glucocorticoids but with no response, which drug may work effectively in this case? A-Prednisone. B-Anti IgE Antibody. C-Ipratropium. D-Nedocromil. 4-One of the ADRs of Pranlukast is : A-Elevation of liver Enzymes. B-Burning sensation. C-Bitter taste. D-Tremors. 5-In COPD which part of LRT is damaged: A-Alveoli. B-Air sacs C-Alveolar ducts. D-Respiratory bronchioles. Answers D, D, B, A, B SAQ: 1-What is the mechanism of action of Mast cell stabilizers? 2-Enumerate THREE drugs belong to glucocorticoids 3-List FOUR side effects of glucocorticoids 4-Name one condition in which Aminophylline is indicated Answers: 2-act by stabilization of mast cell membrane.they are not bronchodilators, so they are not effective in acute attack of asthma. 3-Budesonide & Fluticasone,beclometasone. 4-Adrenal suppression,cataract,psychosis, and Osteoporosis. 5-Status Asthmaticus.
14 GOOD LUCK Team Leaders: Nouf Alshammari Zyad Aldosari Team sub-leader: May Babaeer Team Members: Abdullah Alassaf Mohsen Almutairi Bader Aldhafeeri Sources: Team 435
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD
 Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
기관지확장제와기관지천식 치료에쓰이는약물 이종호 한림의대약리학교실
 기관지확장제와기관지천식 치료에쓰이는약물 이종호 한림의대약리학교실 천식치료제 기관지확장제 Beta2 adrenergic agonists; terbutaline, albuterol, metaproterenol, salmeterol Muscarinic antagonists; Ipratropium Methylxanthines; theophylline 예방및항염증약물
기관지확장제와기관지천식 치료에쓰이는약물 이종호 한림의대약리학교실 천식치료제 기관지확장제 Beta2 adrenergic agonists; terbutaline, albuterol, metaproterenol, salmeterol Muscarinic antagonists; Ipratropium Methylxanthines; theophylline 예방및항염증약물
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Asthma/COPD. Asthma synopsis. chronic inflammation of bronchial airways bronchi lining bronchi muscles mucus
 1 Asthma & COPD Asthma synopsis chronic inflammation of bronchial airways bronchi lining bronchi muscles mucus 2 Asthma synopsis chest tightness tachypnea wheezing acute broncho-constriction cough shortness
1 Asthma & COPD Asthma synopsis chronic inflammation of bronchial airways bronchi lining bronchi muscles mucus 2 Asthma synopsis chest tightness tachypnea wheezing acute broncho-constriction cough shortness
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Pharmacology Drugs of Respiratory system. Drugs acting on respiratory system. Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11
 Drugs acting on respiratory system Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11 Respiratory system is subjected to a lot of injurers and harms because it is nearly the only system which is in continuous contact with the
Drugs acting on respiratory system Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11 Respiratory system is subjected to a lot of injurers and harms because it is nearly the only system which is in continuous contact with the
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
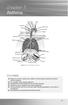 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Chapter 55. Changes in the Airway With COPD. Manifestations of Severe COPD. Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders
 Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
Anaphylaxis. Perceive the differences between anaphylactic shock and other types of shock. Recognize its nature, causes & characteristics.
 Anaphylaxis Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Females doctor notes Grey: Males doctor notes OBJECTIVES: By the end of this lecture,
Anaphylaxis Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Females doctor notes Grey: Males doctor notes OBJECTIVES: By the end of this lecture,
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
From the Text. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
Corticosteroids. Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology
 Corticosteroids Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be
Corticosteroids Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate) Composition Each actuation delivers: Salmeterol (as Salmeterol Xinafoate IP) 25 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA 134a.....q.s. Dosage Form
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate) Composition Each actuation delivers: Salmeterol (as Salmeterol Xinafoate IP) 25 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA 134a.....q.s. Dosage Form
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
Monocast Description Indications
 Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY
 Yerevan State Medical University Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Yerevan, Armenia RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY Dr. Armen VAROSYAN Associate Professor, DEAA, PhD Lecture Outline Drugs stimulating
Yerevan State Medical University Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Yerevan, Armenia RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY Dr. Armen VAROSYAN Associate Professor, DEAA, PhD Lecture Outline Drugs stimulating
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Lungs SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5
 Lungs SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5 1. A 15 year- old teen has asthma. A nebulizer treatment has been ordered. The type of medication most likely to be used in this treatment for asthma management
Lungs SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5 1. A 15 year- old teen has asthma. A nebulizer treatment has been ordered. The type of medication most likely to be used in this treatment for asthma management
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS
 Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Utibron Neohaler. (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow
 Utibron Neohaler (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Utibron Neohaler Generic name: Indacaterol, glycopyrrolate Pharmacological class: Long-acting beta2- agonist
Utibron Neohaler (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Utibron Neohaler Generic name: Indacaterol, glycopyrrolate Pharmacological class: Long-acting beta2- agonist
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Pathology of Asthma Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline Bronchial Asthma Definition: chronic, relapsing inflammatory lung disorder characterised by reversible
Pathology of Asthma Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline Bronchial Asthma Definition: chronic, relapsing inflammatory lung disorder characterised by reversible
Asthma - Chronic. Presentations of asthma Cough Wheeze Breathlessness Chest tightness
 Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
1. What is delayed sequence intubation? Can it be used for severe Asthma exacerbation? 2. What about pregnancy and Asthma is so important?
 Chapter 073 Asthma Episode Overview 1. 10 different causes of a wheeze. 2. List 8 risk factors for death from asthma 3. List 6 objective findings of severe asthma 4. 10 therapies for an acute severe asthma
Chapter 073 Asthma Episode Overview 1. 10 different causes of a wheeze. 2. List 8 risk factors for death from asthma 3. List 6 objective findings of severe asthma 4. 10 therapies for an acute severe asthma
Learning Objective. Asthma. Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Asthma 2/22/2017
 Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
ASTHMA ASTHMA DISEASE SUMMARY. Risk Factors
 ASTHMA Risk Factors Family history of asthma or other atopic diseases (eczema, hayfever) Having eczema or hayfever currently or as a child Living in an industrialised area more exposure to airborne pollutants,
ASTHMA Risk Factors Family history of asthma or other atopic diseases (eczema, hayfever) Having eczema or hayfever currently or as a child Living in an industrialised area more exposure to airborne pollutants,
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Atrovent Administration
 Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center
 Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center Outline Anatomy Common Diseases Interventions Oxygen Therapy Medications Nebulization Coupage Respiratory Tract
Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center Outline Anatomy Common Diseases Interventions Oxygen Therapy Medications Nebulization Coupage Respiratory Tract
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES. School Nurses November 2015
 ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
Pharmacology of Corticosteroids
 Pharmacology of Corticosteroids Dr. Aliah Alshanwani Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine, KSU Feb 2018 1 The Corticosteroids are steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. They consist of two
Pharmacology of Corticosteroids Dr. Aliah Alshanwani Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine, KSU Feb 2018 1 The Corticosteroids are steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. They consist of two
Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN
 Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN Goals of Therapy Asthma Prevent symptoms COPD Reduce COPD symptoms Decrease use of SABAs Maintain normal pulm function & prevent loss
Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN Goals of Therapy Asthma Prevent symptoms COPD Reduce COPD symptoms Decrease use of SABAs Maintain normal pulm function & prevent loss
Corticosteroids. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital,
 Corticosteroids Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa History 1855 Addison's disease 1856 Adrenal glands essential
Corticosteroids Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa History 1855 Addison's disease 1856 Adrenal glands essential
your breathing problems worsen quickly. you use your rescue inhaler, but it does not relieve your breathing problems.
 MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis
 Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
The Inflammatory Response
 RSPT 2317 The Inflammatory Response A general definition inflammation is the response of vascularized tissue to injury. First described in the first century A.D. and revised in the 20 th century as follows
RSPT 2317 The Inflammatory Response A general definition inflammation is the response of vascularized tissue to injury. First described in the first century A.D. and revised in the 20 th century as follows
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
Allergy and inflammation
 and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
AEROCORT Inhaler (Beclomethasone dipropionate + Levosalbutamol)
 Published on: 28 Jan 2016 AEROCORT Inhaler ( + ) Composition Each actuation delivers: IP. 50 mcg sulphate IP equivalent to levosalbutamol..50 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA-134a.. q.s. Dosage Form Inhalation
Published on: 28 Jan 2016 AEROCORT Inhaler ( + ) Composition Each actuation delivers: IP. 50 mcg sulphate IP equivalent to levosalbutamol..50 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA-134a.. q.s. Dosage Form Inhalation
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS*
 FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide
 Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Treatment Options for Complicated/Severe Asthma. Henry J. Kanarek, MD Kanarek Allergy Asthma Immunology
 Treatment Options for Complicated/Severe Asthma Henry J. Kanarek, MD Kanarek Allergy Asthma Immunology www.kallergy.com 913-451-8555 Asthma Epidemiology World Health Organization, Asthma is one of the
Treatment Options for Complicated/Severe Asthma Henry J. Kanarek, MD Kanarek Allergy Asthma Immunology www.kallergy.com 913-451-8555 Asthma Epidemiology World Health Organization, Asthma is one of the
Composition: Each tablet contain. Levocetirizine. Each 5ml contains. Montelukast. Pharmacokinetic properties:
 Composition: Each tablet contain Montelukast Levocetirizine 10mg 5mg Each 5ml contains Montelukast Levocetirizine 4mg 2.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Peak plasma concentrations of montelukast are achieved
Composition: Each tablet contain Montelukast Levocetirizine 10mg 5mg Each 5ml contains Montelukast Levocetirizine 4mg 2.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Peak plasma concentrations of montelukast are achieved
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/126654/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax, which details the measures
EMA/126654/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax, which details the measures
Asthma. - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness.
 Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications
 The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Management of COPD and CHF: drugs that should be preferred or avoided
 Management of COPD and CHF: drugs that should be preferred or avoided Dr John T. Parissis, Heart Failure Unit, Attikon University Hospital, Athens, Greece Disclosures: Research grants by Abbott USA and
Management of COPD and CHF: drugs that should be preferred or avoided Dr John T. Parissis, Heart Failure Unit, Attikon University Hospital, Athens, Greece Disclosures: Research grants by Abbott USA and
Pharmacotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis
 Pharmacotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College The Impact of Allergic Rhinitis Allergic rhinitis affects approximately 50 million
Pharmacotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College The Impact of Allergic Rhinitis Allergic rhinitis affects approximately 50 million
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Urticaria Moderate Allergic Reaction Mild signs/symptoms with any of following: Dyspnea, possibly with wheezes Angioneurotic edema Systemic, not local
 Allergic Reactions & Anaphylaxis Incidence In USA - 400 to 800 deaths/year Parenterally administered penicillin accounts for 100 to 500 deaths per year Hymenoptera stings account for 40 to 100 deaths per
Allergic Reactions & Anaphylaxis Incidence In USA - 400 to 800 deaths/year Parenterally administered penicillin accounts for 100 to 500 deaths per year Hymenoptera stings account for 40 to 100 deaths per
PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation
![PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation](/thumbs/74/71128680.jpg) PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - PHARMACOLOGY-
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - PHARMACOLOGY- PULSE - Mast cell stabilizers : a.have safe profile, so they're recommended for pregnant & children b.they work by blocking IgE receptors on mast cells - There is a case
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - PHARMACOLOGY- PULSE - Mast cell stabilizers : a.have safe profile, so they're recommended for pregnant & children b.they work by blocking IgE receptors on mast cells - There is a case
Respiratory Pharmacology. Pharmacology. Clinical Pharmacology. farmakon. pharmakon. Medicine Poison Magic Spell
 1 Respiratory Pharmacology Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand 2 Pharmacology is derived from a Greek word (pharmakon). The Greeks used this word
1 Respiratory Pharmacology Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand 2 Pharmacology is derived from a Greek word (pharmakon). The Greeks used this word
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Scope of Problem Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Marianne J. Davies, RN, MSN, APRN Yale University School of Medicine Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center Nevada Cancer Institute 2005 Hospitalizations
Scope of Problem Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Marianne J. Davies, RN, MSN, APRN Yale University School of Medicine Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center Nevada Cancer Institute 2005 Hospitalizations
10/6/2014. Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement. Disclosure. Objectives for this talk.
 Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
