CASE REPORT INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Dwight Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Allergology International. ; : - DOI: allergolint.10-cr-0251 CASE REPORT Centrilobular Opacities in the Asthmatic Lung Successfully Treated with Inhaled Ciclesonide and Tiotropium: With Assessment of Alveolar Nitric Oxide Levels Hirofumi Kiyokawa 1, Hisako Matsumoto 1,HitoshiNakaji 1, Akio Niimi 1,IsaoIto 1, Kikuko Ono 2, Tomoshi Takeda 1, Tsuyoshi Oguma 1, Kojiro Otsuka 1 and Michiaki Mishima 1 ABSTRACT Background: Despite the fact that bronchioles are involved in asthma, there have been limited asthmatic cases showing marked centrilobular opacities on computed tomography (CT) chest scans. Systemic corticosteroids have been administered in such cases, but the efficacy of extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroids has not been assessed. Case Summary: A previously healthy 64-year-old man presented with a four-month history of productive cough and progressive dyspnea despite a combination therapy with inhaled salmeterol (50 μg bid) and fluticasone (500 μg bid), sustained-release theophylline, and pranlukast because of suspicion of asthma. Physical examination revealed wheezing at the end of forced expiration. High resolution CT chest scan showed diffuse centrilobular opacities, bronchiectatic changes, and bronchial wall thickening. Transbronchial lung biopsy, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and transbronchial biopsy all showed predominant eosinophil infiltrates, suggesting that eosinophilic inflammation across the entire airway tree caused the abnormal CT findings. Alveolar fraction of exhaled nitric oxide level, a non-invasive marker of eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation, was also elevated. Because he refused systemic corticosteroids, inhaled ciclesonide (400 μg bid) and inhaled tiotropium were added on to his current medication under careful observation. His symptoms, pulmonary function and CT findings promptly improved, and he had fully recovered at follow-up. Discussion: Extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroids could be an alternative approach in centrilobular opacities caused by eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation. KEY WORDS alveolar nitric oxide, asthma, centrilobular opacities, eosinophilic bronchiolitis, extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroids INTRODUCTION In 2001, Takayanagi et al. have proposed a new disease entity of eosinophilic bronchiolitis that shows centrilobular opacities on computed tomography (CT) scans, 1 which was followed by several similar reports of eosinophilic bronchiolitis with or without asthma. 2 Accumulation of such cases may provide deeper understanding of links between peripheral airway dysfunction and eosinophilic inflammation. In the previous cases, however, details of peripheral airway function and its responses to treatment have been poorly described. In addition, the efficacy of extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroids that may allow better access to the peripheral airways has not been assessed. We here report that the addition of an 1Department of Respiratory Medicine and 2 Department of Pediatrics, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan. Correspondence: Hisako Matsumoto, MD, PhD, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, 54 Kawahara-cho, Shogoin, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan. hmatsumo@kuhp.kyoto u.ac.jp Received 28 July Accepted for publication 3 October Japanese Society of Allergology Allergology International Vol 00, No0,
2 Kiyokawa H et al. Table 1 Pulmonary function results and markers of eosinophilic inflammation before and after intensifying treatment Before intensifi cation 2 wk after intensifi cation 2 mo after 4 mo after 1 yr after VC, L (%pred) 2.43 (72.8) 2.97 (88.9) 3.74 (112.0) 3.99 (119.5) 4.22 (126.3) FEV 1, L (% pred) 0.88 (35.2) 1.34 (53.6) 2.52 (100.4) 3.03 (120.7) 3.23 (129.2) PEF, L/min RV/TLC, % ΔN 2, % Blood eosinophils, % Fe NO50, ppb CA NO,TMAD, ppb Treatment intensifi cation = Addition of inhaled ciclesonide and tiotropium. VC, vital capacity; FEV 1, forced expiratory volume in one second; PEF, peak expiratory fl ow; RV/TLC, residual volume/total lung capacity; ΔN 2, slope of alveolar plateau of the single-breath nitrogen washout curve; FeNO50, Fraction of exhaled nitric oxide (NO) at 50 ml/s; CANO,TMAD, Alveolar fraction of exhaled NO adjusted for trumpet shape airways and axial diffusion. extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroid and an inhaled tiotropium was effective for treating asthma with marked centrilobular opacities on a CT scan, by showing responses of peripheral airway function and alveolar fraction of exhaled nitric oxide (NO) levels, a non-invasive marker of eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation, to the treatment. CLINICAL SUMMARY A previously healthy 64-year-old man presented with a four-month history of productive cough and progressive dyspnea despite a combination therapy with inhaled salmeterol (50 μg) and fluticasone (500 μg bid), sustained-release theophylline, and pranlukast because of suspicion of asthma. These medications did not sufficiently improve his symptoms. He had a smoking history of 20 pack-years, but had quit smoking more than 20 years before. He had experienced allergic rhinitis symptoms during Japanese cedar pollen season for 8 years. Physical examination revealed wheezing at the end of forced expiration. Blood tests showed eosinophilia (13.1%), elevated IgE (630 IU ml), and mild hypoxemia while breathing room air (PaO2 = 66.5 mmhg). He was sensitized to multiple inhaled allergens. Other serological tests showed no remarkable findings. Pulmonary function tests revealed severe airflow limitation (pre- and post- bronchodilator FEV1 of 0.88 L and 0.89 L, respectively), increased residual volume and increased slope of the alveolar plateau during single-breath nitrogen washout test(δn2) (Table 1). The alternative indices of small airway caliber and reactance measured using the impulse oscillometry system (MasterScreen TM ; Erich Jaeger, Hoechberg, Germany) were also impaired; The frequency dependence of respiratory resistance (Rrs) between 5 and 20 Hz, i.e., Rrs5-Rrs20, was 0.25 kpa L -1 s; the reactance at 5 Hz, i.e., Xrs 5, was kpa L -1 s; and the reactance area, i.e., the integral of Xrs from 5 Hz to the resonant frequency AX was 3.39 kpa L -1. On admission methacholine challenge test was not performed because of the severe airflow limitation. Sputum showed predominant eosinophils and yielded no growth of microorganisms, including fungi and Mycobacteria. High resolution CT chest scan showed diffuse centrilobular or tree-in-bud opacities, bronchiectatic changes, and bronchial wall thickening, but no airspace consolidation or emphysematous changes (Fig. 1a-c). Sinusitis was not observed on a CT scan of the sinuses. The exhaled NO level was measured at three flow rates, 50 ml s, 100 ml s, and 200 ml s, using a chemiluminescence analyzer (NOA280, Sievers, CO, USA), and alveolar fraction of exhaled NO level was determined by a trumpet model with axial diffusion (CANO,TMAD). 3,4 CANO,TMAD level was numerically higher than median (3.9 ppb) or average (5.5 ppb) of the measured values of 70 patients with stable asthma in our institution. 4 The elevation of CANO,TMAD strongly suggested the presence of eosinophilic inflammation in the peripheral airways. Transbronchial lung biopsy (TBLB) revealed eosinophilic infiltration into alveolar septa (Fig. 2a), and eosinophils (60%) were predominant in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Transbronchial biopsy obtained at the bifurcation of anterior basal segmental bronchus and lateral basal segmental bronchus of the right lung also showed eosinophil infiltrates, basement membrane thickening, and an increased area of airway smooth muscle (Fig. 2b). Based on these clinico-pathophysiological findings, we speculated that eosinophilic inflammation associated with asthma might have involved the bronchioles, which could explain the centrilobular opacities on a CT scan. Because he refused systemic corticosteroids use, inhaled ciclesonide (400 μg bid), an extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroid, and inhaled tiotropium were added on to his current medication under careful observation. Within 2 weeks, the patient s symptoms and pulmonary function promptly improved. One year later, he had fully recovered (Ta- 2 Allergology International Vol 00, No0,
3 Centrilobular Nodules in Asthmatic Lung Fig. 1 Computed tomography chest scans on admission (a, b, c) and at 2 months after intensifying the treatment (d). ble 1 and Fig. 1d), showing improvement of airway impedance; an Rrs5-Rrs20 of 0.03 kpa L -1 s, Xrs5 of kpa L -1 s, and AX of 0.37 kpa L -1.Onsubsequent evaluation, he showed airway hyperresponsiveness to inhaled methacholine (Astograph TM ; Chest, Tokyo, Japan; Dmin, 10.4 Units). DISCUSSION Despite the fact that the bronchioles are involved in asthma, 5 there have been a limited number of cases with asthma or eosinophilic lung disease that showed marked centrilobular opacities on chest CT scans, except for recent reports of eosinophilic bronchiolitis with or without asthma. 1,2 Here we presented an asthmatic case showing diffuse centrilobular or tree-inbud opacities on a CT scan that was successfully treated with an extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroid and an inhaled tiotropium. Although a definitive lesion involving bronchioles was not obtained in this case due to technical issues with the transbronchial approach, the presence of eosinophilic bronchiolitis was highly suspected as eosinophil infiltrates were observed across the entire airway tree (i.e., in TBLB, BALF and bronchial biopsy samples). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report showing that the addition of an extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroid, as well as inhaled tiotropium, was effective for treating asthma with marked centrilobular opacities on a CT scan. We carefully observed the patient s condition to avoid under-treatment, because previous cases with eosinophilic bronchiolitis with or without asthma 1,2 consistently used medium to high doses of systemic corticosteroids. Previously we have also found that inhaled chlorofluorocarbonbeclomethasone dipropionate alone failed to treat chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. 6 Despite these concerns, our patient promptly responded to medications without the administration of systemic corticosteroids and did not deteriorate thereafter. The addition of inhaled ciclesonide to the medication may have exerted anti-inflammatory effects, possibly because its particle size was adequately small for it to reach the peripheral airways, but also because of its delivery system. This patient might have had reduced inspiratory flow rates, in which case the use of the aerosol formulation, such as of ciclesonide, may be advantageous over the dry powder formulation. In addition, the increase in the total amount of inhaled corticosteroids may have suppressed the remaining inflammation throughout the airways. The additive effects of inhaled tiotropium should also be acknowledged, since cholinergic tone increases particularly in asthmatics Allergology International Vol 00, No0,
4 Kiyokawa H et al. Fig. 2 Transbronchial lung biopsy (a) and transbronchial biopsy (b). Arrow heads indicate eosinophil infiltrates. with moderate to severe disease. 7 Further studies are necessary, since we did not use any placebo control in this case; nonetheless, from the results obtained we can conclude that extra-fine particle inhaled corticosteroids may be an alternative approach for treating eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation. 8,9 Unlike previous reports of eosinophilic bronchiolitis, 1,2 we have clearly shown physiological abnormalities in the peripheral airways and their responses to treatment. Peripheral airway obstruction and ventilation heterogeneity at baseline as expressed in elevated RV TLC and ΔN2 were improved in parallel with the improvement of symptoms and CT findings after intensifying the treatment. Moreover we showed improvement of alveolar NO level, a noninvasive marker of eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation, after intensifying the treatment. Alveolar NO level determined by a two compartment model (CANO) 10 has been used as a non-invasive tool to assess eosinophilic inflammation of peripheral airway alveolar regions. Recently corrected models of CANO, i.e., CANO,TMAD that incorporated trumpet shaped airways and axial diffusion have been developed to correct the effect of axial contamination by small airway NO diffusion on CANO. 3,11 Changes in CANO,TMAD levels in our case may suggest the usefulness of multiple expiratory flow measurements of NO to determine alveolar NO levels particularly when eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation is suspected. NO level at an expiratory flow of 50 ml s (FeNO50) before intensifying the treatment was unexpectedly low (Table 1). The low FeNO50 level can be explained by an elegant simulation model that shows that increased ventilation heterogeneity and predominant NO production in the peripheral airways decreases FeNO50 levels when compared to levels under uniform ventilation and NO production. 12 Indeed, the FeNO50 level paradoxically increased when ventilation heterogeneity was partially resolved. It was important to determine whether or not this patient had asthma. On admission to the hospital, 200 μg of inhaled salbutamol was administered, but it did not change his FEV1 level. We believe that the reason for this was the dose of salbutamol administered, which was insufficient to be delivered throughout the airways, since his airways were severely obstructed because of inflammation accompanied by airway edema and mucus plugging. After bronchoscopic examination, when the wheezing and dyspnea worsened, 300 μg salbutamol followed by 50 μg nebulized procaterol was administered, and the patient s condition improved. This may suggest that the airway obstruction in this patient was reversible with bronchodilators. Furthermore, airway hyperresponsiveness to inhaled methacholine, eosinophilic inflammation in the central airway, and partial improvement of symptoms by asthma medication, including sustained-release theophylline and pranlukast, suggest that this patient had asthma. In conclusion, we have comprehensively reported a rare case of asthma that presented with centrilobular opacities on a CT scan. The presence of eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation was suspected due to an elevated alveolar NO level, which was confirmed by the findings of TBLB and BALF. Addition of extrafine particle inhaled corticosteroids may attenuate eosinophilic peripheral airway inflammation. REFERENCES 1. Takayanagi N, Kanazawa M, Kawabata Y, Colby TV. Chronic bronchiolitis with associated eosinophilic lung disease (eosinophilic bronchiolitis). Respiration 2001;68: Fukushima Y, Kamiya K, Tatewaki M et al. Apatientwith bronchial asthma in whom eosinophilic bronchitis and bronchiolitis developed during treatment. Allergol Int 2010;59: Condorelli P, Shin HW, Aledia AS, Silkoff PE, George SC. A simple technique to characterize proximal and peripheral nitric oxide exchange using constant flow exhalations andanaxialdiffusionmodel.j Appl Physiol 2007;102:417-4 Allergology International Vol 00, No0,
5 Centrilobular Nodules in Asthmatic Lung Matsumoto H, Niimi A, Jinnai M et al. Association of alveolar nitric oxide levels with pulmonary function and its reversibility in stable asthma. Respiration. Epub 2010 Oct Balzar S, Wenzel SE, Chu HW. Transbronchial biopsy as a tool to evaluate small airways in asthma. EurRespirJ 2002;20: Minakuchi M, Niimi A, Matsumoto H, Amitani R, Mishima M. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: Treatment with inhaled corticosteroids. Respiration 2003;70: Gelb AF, Karpel J, Wise RA, Cassino C, Johnson P, Conoscenti CS. Bronchodilator efficacy of the fixed combination of ipratropium and albuterol compared to albuterol alone in moderate-to-severe persistent asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2008;21: Cohen J, Douma WR, ten Hacken NH, Vonk JM, Oudkerk M, Postma DS. Ciclesonide improves measures of small airway involvement in asthma. EurRespirJ2008; 31: Yamaguchi M, Niimi A, Ueda T et al. Effect of inhaled corticosteroids on small airways in asthma: Investigation using impulse oscillometry. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2009;22: Tsoukias NM, George SC. A two-compartment model of pulmonary nitric oxide exchange dynamics. J Appl Physiol 1998;85: Kerckx Y, Michils A, Van Muylem A. Airway contribution to alveolar nitric oxide in healthy subjects and stable asthma patients. J Appl Physiol 2008;104: Suresh V, Shelley DA, Shin HW, George SC. Effect of heterogeneous ventilation and nitric oxide production on exhaled nitric oxide profiles. J Appl Physiol 2008;104: Allergology International Vol 00, No0,
Title montelukast on small airways inflam.
 Title Effects of 24-week add-on treatment montelukast on small airways inflam Nakaji, Hitoshi; Petrova, Guergana; Author(s) Toshiyuki; Ito, Isao; Oguma, Tsuyos Tomoko; Nagasaki, Tadao; Kanemitsu, Akio;
Title Effects of 24-week add-on treatment montelukast on small airways inflam Nakaji, Hitoshi; Petrova, Guergana; Author(s) Toshiyuki; Ito, Isao; Oguma, Tsuyos Tomoko; Nagasaki, Tadao; Kanemitsu, Akio;
A Patient with Bronchial Asthma in Whom Eosinophilic Bronchitis and Bronchiolitis Developed during Treatment
 Allergology International. 2010;59:87-91 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.09-cr-0114 CASE REPORT A Patient with Bronchial Asthma in Whom Eosinophilic Bronchitis and Bronchiolitis Developed during Treatment Yasutsugu
Allergology International. 2010;59:87-91 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.09-cr-0114 CASE REPORT A Patient with Bronchial Asthma in Whom Eosinophilic Bronchitis and Bronchiolitis Developed during Treatment Yasutsugu
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pathological and radiological approach to the small airway disease in asthma: Limitation of current inhaled corticosteroid therapy
 Allergology International (2004) 53: 1 6 Review Article Pathological and radiological approach to the small airway disease in asthma: Limitation of current inhaled corticosteroid therapy Hiroshi Tanaka,
Allergology International (2004) 53: 1 6 Review Article Pathological and radiological approach to the small airway disease in asthma: Limitation of current inhaled corticosteroid therapy Hiroshi Tanaka,
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Small Airways : How To Confident Diagnosis and Management?
 Small Airways : How To Confident Diagnosis and Management? Assistant Prof. Siwasak Juthong. M.D. Division of Respiratory and Respiratory Critical Care Medicine Faculty of Medicine Prince of Songkla University
Small Airways : How To Confident Diagnosis and Management? Assistant Prof. Siwasak Juthong. M.D. Division of Respiratory and Respiratory Critical Care Medicine Faculty of Medicine Prince of Songkla University
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Small Airways Disease. Respiratory Function In Small Airways And Asthma. Pathophysiologic Changes in the Small Airways of Asthma Patients
 Small Airways Disease Respiratory Function In Small Airways And Relevant Questions On Small Airway Involvement In How can small airway disease be defined? What is the link between small airway abnormalities
Small Airways Disease Respiratory Function In Small Airways And Relevant Questions On Small Airway Involvement In How can small airway disease be defined? What is the link between small airway abnormalities
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Importance of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in diagnosis of bronchiectasis accompanied with bronchial asthma
 Original Article Importance of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in diagnosis of bronchiectasis accompanied with bronchial asthma Feng-Jia Chen, Huai Liao, Xin-Yan Huang, Can-Mao Xie Department of Respiratory
Original Article Importance of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in diagnosis of bronchiectasis accompanied with bronchial asthma Feng-Jia Chen, Huai Liao, Xin-Yan Huang, Can-Mao Xie Department of Respiratory
4.6 Small airways disease
 4.6 Small airways disease Author: Jean-Marc Fellrath 1. INTRODUCTION Small airways are defined as any non alveolated and noncartilaginous airway that has an internal diameter of 2 mm. Several observations
4.6 Small airways disease Author: Jean-Marc Fellrath 1. INTRODUCTION Small airways are defined as any non alveolated and noncartilaginous airway that has an internal diameter of 2 mm. Several observations
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
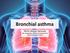 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers?
 Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
LUNG FUNCTION TESTING: SPIROMETRY AND MORE
 LUNG FUNCTION TESTING: SPIROMETRY AND MORE OBJECTIVES 1. To describe other lung function testing for toddlers and those who cannot perform spirometry 2. To describe a lung function test on infants 3. To
LUNG FUNCTION TESTING: SPIROMETRY AND MORE OBJECTIVES 1. To describe other lung function testing for toddlers and those who cannot perform spirometry 2. To describe a lung function test on infants 3. To
Coexistence of confirmed obstruction in spirometry and restriction in body plethysmography, e.g.: COPD + pulmonary fibrosis
 Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yueyue Li *, Yang Chen *, Ping Wang
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):1271-1275 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002365 Original Article Application of impulse oscillometry and bronchial dilation test for analysis in patients with asthma and
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):1271-1275 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002365 Original Article Application of impulse oscillometry and bronchial dilation test for analysis in patients with asthma and
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Lecture Notes. Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
COPD/ Asthma. Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer
 COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values
 PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives : Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
New Therapies for Asthma
 New Therapies for Asthma Tracy Bridges, MD Speaker Disclosure: Dr. Bridges participates in speaker bureaus for Teva, Genetech & Astra Zeneca. Objectives: Discuss the use of LAMA s for Asthma Detail the
New Therapies for Asthma Tracy Bridges, MD Speaker Disclosure: Dr. Bridges participates in speaker bureaus for Teva, Genetech & Astra Zeneca. Objectives: Discuss the use of LAMA s for Asthma Detail the
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Goals and Learning Objectives
 Small Airways (SAW) Symposium: Asthma Treatment Issues. New Bronchodilator for Asthma: A Patient Centric Approach for Treating Asthma Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis
Small Airways (SAW) Symposium: Asthma Treatment Issues. New Bronchodilator for Asthma: A Patient Centric Approach for Treating Asthma Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis
Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing. Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum deflation. Total lung capacity at maximum inflation
 r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Overview of Obstructive Diseases of the Lung, Lung Physiology and Imaging Modalities
 Overview of Obstructive Diseases of the Lung, Lung Physiology and Imaging Modalities Jann Mortensen Final Phil meeting, 29 april 2004 Obstructive disease Definition Epidemiologi Mechanisms Natural history
Overview of Obstructive Diseases of the Lung, Lung Physiology and Imaging Modalities Jann Mortensen Final Phil meeting, 29 april 2004 Obstructive disease Definition Epidemiologi Mechanisms Natural history
This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Increased peak expiratory flow variation in asthma: severe persistent increase but not nocturnal worsening of airway inflammation
 Eur Respir J 998; : 5655 DOI:.83/93936.98.356 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-936 Increased peak expiratory flow variation in asthma:
Eur Respir J 998; : 5655 DOI:.83/93936.98.356 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-936 Increased peak expiratory flow variation in asthma:
Update on heterogeneity of COPD, evaluation of COPD severity and exacerbation
 Update on heterogeneity of COPD, evaluation of COPD severity and exacerbation Yung-Yang Liu, MD Taipei Veterans General Hospital Aug 29, 2015 G O lobal Initiative for Chronic bstructive L D ung isease
Update on heterogeneity of COPD, evaluation of COPD severity and exacerbation Yung-Yang Liu, MD Taipei Veterans General Hospital Aug 29, 2015 G O lobal Initiative for Chronic bstructive L D ung isease
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD. AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07
 Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
COPD or not COPD, that is the question.
 COPD or not COPD, that is the question. Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome: ACOS Do we really need this? Michelle Harkins Disclosure Slide Slide help - William Busse, MD Organizational Interests ATS, ACCP, ACP
COPD or not COPD, that is the question. Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome: ACOS Do we really need this? Michelle Harkins Disclosure Slide Slide help - William Busse, MD Organizational Interests ATS, ACCP, ACP
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Acinar effect of inhaled steroids evidenced by exhaled nitric oxide
 Acinar effect of inhaled steroids evidenced by exhaled nitric oxide Alain Van Muylem, PhD, Yannick Kerckx, PhD, and Alain Michils, PhD Brussels, Belgium Background: The effects of inhaled corticosteroids
Acinar effect of inhaled steroids evidenced by exhaled nitric oxide Alain Van Muylem, PhD, Yannick Kerckx, PhD, and Alain Michils, PhD Brussels, Belgium Background: The effects of inhaled corticosteroids
#POMAD8 #ChoosePOMA #POMAD8 #ChoosePOMA #POMAD8 #ChoosePOMA
 Where There s Smoke There s Obstruction Stephen G. Basheda, D.O., F.C.C.P. 1 Disclosures Dr. Basheda is an independent contractor for AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, LP and GlaxoSmithKline and on the speaker
Where There s Smoke There s Obstruction Stephen G. Basheda, D.O., F.C.C.P. 1 Disclosures Dr. Basheda is an independent contractor for AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, LP and GlaxoSmithKline and on the speaker
Impulse Oscillometry; Therapeutic Impacts of Transdermal Long-Acting Beta-2 Agonist Patch in Elderly Asthma with Inhaled Corticosteroid Alone
 Allergology International. 212;61:385-392 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.12-rai-465 Review Series: Non-Invasive Monitoring of Airway Inflammation in Asthma REVIEW ARTICLE Impulse Oscillometry; Therapeutic Impacts
Allergology International. 212;61:385-392 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.12-rai-465 Review Series: Non-Invasive Monitoring of Airway Inflammation in Asthma REVIEW ARTICLE Impulse Oscillometry; Therapeutic Impacts
Meeting the Challenges of Asthma
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
The role of lung function testing in the assessment of and treatment of: AIRWAYS DISEASE
 The role of lung function testing in the assessment of and treatment of: AIRWAYS DISEASE RHYS JEFFERIES ARTP education Learning Objectives Examine the clinical features of airways disease to distinguish
The role of lung function testing in the assessment of and treatment of: AIRWAYS DISEASE RHYS JEFFERIES ARTP education Learning Objectives Examine the clinical features of airways disease to distinguish
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
KEY WORDS airflow limitation, airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation, airway lability, peak expiratory flow rate
 Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
COPD and Asthma Update. April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute
 COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8965-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function Daisuke Minami, Chihiro Ando, Takamasa Nakasuka,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8965-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function Daisuke Minami, Chihiro Ando, Takamasa Nakasuka,
Interesting cases in fungal asthma
 Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Distal airways are classically defined as. Update on the roles of distal airways in asthma REVIEW
 Eur Respir Rev 2009; 18: 112, 80 95 DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00001109 CopyrightßERSJ Ltd 2009 REVIEW Update on the roles of distal airways in asthma P-R. Burgel, J. de Blic, P. Chanez, C. Delacourt, P. Devillier,
Eur Respir Rev 2009; 18: 112, 80 95 DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00001109 CopyrightßERSJ Ltd 2009 REVIEW Update on the roles of distal airways in asthma P-R. Burgel, J. de Blic, P. Chanez, C. Delacourt, P. Devillier,
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Asthma Update I have no professional or personal financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
 Asthma Update 2018 Disclosures Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center I have
Asthma Update 2018 Disclosures Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center I have
Asthma Update Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP
 Asthma Update 2018 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures I have
Asthma Update 2018 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures I have
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype. Phenotypes of Severe Asthma. Cellular Phenotypes 12/7/2012
 Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Objectives. Pulmonary Assessment 12/13/2017
 Pulmonary Assessment Reid Blackwelder, MD, FAAFP Professor and Chair, Family Medicine Quillen Colege of Medicine, ETSU Objectives Understand anatomy and physiology of pulmonary assessment techniques Remember
Pulmonary Assessment Reid Blackwelder, MD, FAAFP Professor and Chair, Family Medicine Quillen Colege of Medicine, ETSU Objectives Understand anatomy and physiology of pulmonary assessment techniques Remember
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD
 Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Pulmonary Function Test
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel GMC Spirometry Pulmonary Function Test! Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel GMC Spirometry Pulmonary Function Test! Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after
Prof Neil Barnes. Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital
 Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
C ough variant asthma, gastro-oesophageal reflux associated
 14 ASTHMA Comparison of atopic cough with cough variant asthma: is atopic cough a precursor of asthma? M Fujimura, H Ogawa, Y Nishizawa, K Nishi... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
14 ASTHMA Comparison of atopic cough with cough variant asthma: is atopic cough a precursor of asthma? M Fujimura, H Ogawa, Y Nishizawa, K Nishi... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Asthma and COPD in the ICU
 Asthma and COPD in the ICU Prescott Woodruff, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Medicine in Residence Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine Acute Exacerbations of Asthma Asthma exacerbations
Asthma and COPD in the ICU Prescott Woodruff, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Medicine in Residence Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine Acute Exacerbations of Asthma Asthma exacerbations
Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012
 Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012 Recognize the importance of Pulmonary Function Testing in Cystic Fibrosis Be aware of different types
Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012 Recognize the importance of Pulmonary Function Testing in Cystic Fibrosis Be aware of different types
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
Usefulness of Colored 3D Imaging of Respiratory Impedance in Asthma
 Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013 September;5(5):322-328. http://dx.doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.5.322 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Usefulness of Colored 3D Imaging of Respiratory Impedance
Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013 September;5(5):322-328. http://dx.doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.5.322 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Usefulness of Colored 3D Imaging of Respiratory Impedance
Asthma in Day to Day Practice
 Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
7/7/2015. Somboon Chansakulporn, MD. History of variable respiratory symptoms. 1. Documented excessive variability in PFT ( 1 test)
 Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma
 The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
Spirometry. Obstruction. By Helen Grim M.S. RRT. loop will have concave appearance. Flows decreased consistent with degree of obstruction.
 1 2 Spirometry By Helen Grim M.S. RRT 3 4 Obstruction loop will have concave appearance. Flows decreased consistent with degree of obstruction. Volumes may be normal, but can decrease with severity of
1 2 Spirometry By Helen Grim M.S. RRT 3 4 Obstruction loop will have concave appearance. Flows decreased consistent with degree of obstruction. Volumes may be normal, but can decrease with severity of
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care
 Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
