Gadolinium in Humans: A Family of Disorders
|
|
|
- Marlene Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana Ramalho 1,4 Semelka RC, Ramalho M, AlObaidy M, Ramalho J Keywords: gadolinium, MRI, toxicity DOI: /AJR Received November 14, 2015; accepted after revision February 14, Department of Radiology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, CB Old Clinic Bldg, 101 Manning Dr, Chapel Hill, NC Address correspondence to R. C. Semelka (richsem@med.unc.edu). 2 Department of Radiology, Hospital Garcia de Orta, Almada, Portugal. 3 Department of Radiology. King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. 4 Department of Neuroradiology, Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Lisbon, Portugal. AJR 2016; 207: X/16/ American Roentgen Ray Society Gadolinium in Humans: A Family of Disorders OBJECTIVE. The literature informs us that gadolinium can cause health issues. At least four major gadolinium disorders, including the two well-recognized nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and severe acute adverse event, have been identified. CONCLUSION. We propose naming the histopathologically proven presence of gadolinium in brain tissue gadolinium storage condition, and we describe a new entity that represents symptomatic deposition of gadolinium in individuals with normal renal function, for which we propose the designation gadolinium deposition disease. G adolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) have been used extensively since their introduction into clinical practice in More than 200 million doses are estimated to have been administered worldwide [1]. All GBCAs approved for clinical use have been considered extremely safe when used at low doses ( mmol/kg) in patients with normal renal function. The accumulated safety record is excellent, with serious adverse reactions occurring in roughly 0.03% of all administrations [2, 3]. However, despite the lack of clinical findings, evidence of in vivo gadolinium deposition has long been recognized [4 7]. The first major study reporting gadolinium deposition in patients with renal failure was published in 1998 [4]. In that study, 25% of administered gadodiamide ( Omniscan, GE Healthcare) was not recovered. The first report regarding gadolinium deposition in patients with normal renal function came in 2004, when Gibby et al. [5] described the presence of gadolinium in resected femoral head specimens after administration of both gadodiamide and gadoteridol (ProHance, Bracco), with the greater amount seen after administration of gadodiamide. The first serious side effects seen after gadolinium administration were only reported 18 years after GBCAs were approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when nephrologists connected the administration of GBCAs to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) [8, 9]. NSF is a debilitating condition observed in patients with renal failure. Most reported cases have been associated with the administration of nonionic, linear gadodiamide (Omniscan), although reports also described numerically important incidents with another nonionic linear agent, gadoversetamide (OptiMARK, Mallinckrodt Imaging), and with an ionic linear agent, gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist, Bayer HealthCare) [10 15]. To our knowledge, no new cases of NSF have been reported since 2009, which we suspect reflects use of more stable GBCAs and limitation of use of GBCAs in patients with renal failure [16]. As a result, from 2009 to 2014, confidence in the safety profile of GBCAs has been largely restored, with the exception of less stable chelates used in patients with advanced renal failure. In early 2014, an investigation by Kanda et al. [17] described the development of high signal intensity in brain tissue on T2-weighted images of patients with normal renal function after repeated administrations of a GBCA (Omniscan, Magnevist, or both). This caught many radiologists by surprise, as many had thought that deposition of gadolinium could not occur in patients with normal renal function. This deposition results in signal-intensity increase on unenhanced T1-weighted images in different regions of the brain, primarily in the dentate nucleus (DN) and globus pallidus (GP). As with NSF, the agent most associated with this finding is Omniscan [17 20]. To our knowledge, neither the bone deposition first reported by Gibby et al. [5] nor the brain deposition first reported by Kanda et al. [17] have been AJR:207, August
2 Semelka et al. associated with recognized disease. We propose to name these storage entities gadolinium storage condition. Along a separate avenue of inquiry, patient advocacy groups have formed, with an online presence in which individual members report that they have experienced severe disease following the administration of GBCAs [21]. Some of these patients have reported persistent presence of gadolinium in their systems, as shown by continued elevated gadolinium in their urine. All experience a variety of symptoms including pain in both the torso and the extremities; the latter location is associated with skin thickening and discoloration. These physical features are similar, but lesser in severity, to those reported for NSF [22]. Our preliminary investigation has convinced us that this phenomenon is a true disease process, which we propose naming gadolinium deposition disease. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis NSF is the best known and most written about of the gadolinium-induced disease entities. NSF is a debilitating and potentially life-threatening disease characterized by widespread progressive tissue fibrosis that predominantly involves the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Initial symptoms typically involve the distal arms and legs, including skin thickening, skin reddening, woody texture of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, and occasionally pruritus. Symptoms and signs may develop and progress rapidly, with some affected patients developing contractures and joint immobility. Onset of NSF symptoms occurs within days to months after injection of GBCA in most patients [8, 9, 11, 13, 23, 24]; however, in rare cases, symptoms have appeared years after the last reported exposure [25, 26]. Two factors are critical to the development of NSF: severe renal failure and IV administration of the GBCA. Most unconfounded, also termed solitary use, cases have been reported after exposure to Omniscan, Opti- MARK, and Magnevist, which are responsible for most cases of NSF. We prefer to use the trade names Omniscan rather than gadodiamide because Omniscan is formulated with 5% free diamide ligand and OptiMARK rather than gadoversetamide because OptiMARK is formulated with 10% free versetamide ligand. Both of these agents are linear chelates, and Omniscan and OptiMARK are nonionic, which further lessens their stability. GBCAs that are more stable chelates by virtue of macrocyclic design (gadoteridol [ProHance, Bracco], gadobutrol [Gadavist, Bayer HealthCare], and gadoterate meglumine [Dotarem, Guerbet]) or that have additional hepatobiliary elimination while being ionic linear agents (gadoxetate disodium [Eovist, Bayer HealthCare; Primovist, Bayer Schering Pharma; MultiHance, Bracco]) have been associated with few to no cases of NSF with solitary use. Stability of the chelate seems to be the factor critical to avoiding NSF. A recent article reported that patients with poor renal function or renal transplantation who received MultiHance did not develop NSF subsequent to MRI [27]. NSF occurs most commonly in patients who have received high doses of GBCA, either as a single administration or cumulatively in multiple administrations over months to years [13, 26, 28]. The reason why some patients with severe acute or chronic kidney diseases develop NSF following exposure to GBCAs while others do not is not known [26]. The most commonly held theory for the pathophysiology of NSF is that gadolinium ions dissociate from their chelating ligands while the agent is in the interstitial space because of the combination of prolonged retention of gadolinium in the body from decreased renal elimination and the greater opportunity for dechelation because of decreased elimination. The released (also termed free ) gadolinium then binds with native anions such as phosphate, and the resulting insoluble precipitate is deposited in various tissues [29, 30]. A fibrotic reaction is stimulated, involving the activation of circulating fibrocytes (cluster of differentiation 34 positive fibroblasts) [30, 31]. This concept is supported by the greater presence of gadolinium in affected tissues relative to unaffected tissues in patients with NSF [32]. To date, successful treatment has been elusive. Renal transplant and the resultant improved renal function may stabilize the condition and perhaps result in some improvement. The fact that only 3% of patients in the worst category of renal failure (stage V) and receiving the weakest chelate (Omniscan) experience this condition belies the notion that host immunologic factors are important in the disease [16]. Avoiding the use of weak chelates and limiting the number of gadolinium-enhanced studies in individuals with poor renal function has largely eliminated this condition since Severe Acute Adverse Event Acute adverse events can be categorized as either allergiclike or physiologic and organized according to severity (mild, moderate, or severe). The adverse event rate for GBCAs administered at clinical doses (typically mmol/kg of body weight) ranges from 0.07% to 2.4%. Most reactions are mild and physiologic, including coldness, warmth, or pain at the injection site; nausea with or without vomiting; headache; paresthesia; and dizziness. Allergiclike reactions are uncommon and vary in frequency from 0.004% to 0.7%. The manifestations of an allergiclike reaction to a GBCA are similar to those of an allergiclike reaction to an iodinated contrast medium. Severe life-threatening anaphylactic reactions occur [33 39] but are exceedingly rare ( %) [26, 38, 40, 41]. Severe anaphylactic reaction that results in death has been reported in approximately 1 in 300,000 administrations of GBCAs, with 40 deaths per 51 million administered GBCA doses reported between 2004 and 2009 [42, 43]. Such rates are about one-third as common as reaction rates recorded with nonionic iodine-based contrast agents. Patients with asthma and various allergies may have a mildly increased risk for an allergiclike reaction to GBCAs compared with the general population, as may patients who have had immediate hypersensitivity reactions to MRI contrast media [42]. The frequency of severe anaphylactic reaction resulting in death is comparable and extremely low for all GBCAs. The reason why the frequency of such events is lower for GBCAs than for iodine-based contrast agents is unclear but may be attributable to difference in volumes administered for the two types of media (typically, 15 vs 100 ml, respectively). Allergiclike reactions occur immediately to within 24 hours of GBCA administration, with the most occurring within minutes of the injection, suggesting an immune response to the entire GBCA or part of it. The acuity of the onset reflects that this is an acute immunologic event, but the exact pathogenesis is unclear [26]. Gadolinium Storage Condition Gadolinium storage condition is the term we propose for gadolinium tissue deposition. Even in patients with normal renal function, in vivo clinical exposure to gadolinium chelates results in gadolinium incorporation into body tissues such as bone matrix [5 7] or brain tissues [44, 45]. As early as 1991, Rocklage et al. 230 AJR:207, August 2016
3 Gadolinium in Humans [46] noted the potential for minute amounts of chelated or unchelated metals to remain in the body for an extended period as well as the potential for a toxic effect. Multiple recent reports that observe deposition in the DN and GP represent the largest body of literature on gadolinium storage condition. As mentioned above, the most commonly reported GBCA to result in this condition has been Omniscan, but it has also been seen with Magnevist [17, 47, 48]. The more stable macrocyclic GBCAs, such as ProHance [47] and Dotarem [48, 49], were not associated with significant MRI changes, supporting the concept that gadolinium accumulation varies depending on the stability of the agent used. MultiHance, a more intermediate stable agent but with additional hepatobiliary elimination, was associated with lesser MRI changes when compared with the linear Omniscan and only appreciated in the DN [20]. Recently, Weberling et al. [50] suggested that this agent releases less gadolinium than Magnevist but more than Dotarem. In two studies published in March and April 2015, McDonald et al. [44] and Kanda et al. [45] showed in cadavers that gadolinium deposition within the brain tissue causes the reported increased signal intensity on T1-weighted images. Confirming human studies, an animal study [49] also found that repeated administration of Omniscan to healthy rats was associated with progressive and persistent signal hyperintensity on T1-weighted images in the DN and with histologic gadolinium deposits in the cerebellum; no such effects were seen in subjects who received Dotarem. As is the case with NSF, the least stable GBCAs appear to be most likely to result in gadolinium storage condition, and stable agents either do not cause it or cause it at a very low level. On the basis of anecdotal reporting, ProHance, a macrocyclic agent, may deposit as a fully intact chelate in bone, as opposed to the dechelated deposition seen with Omniscan [3, 51]. It should not be surprising that simple storage should be predominantly based on how likely the chelate is to release the gadolinium atom. The clinical significance of gadolinium tissue deposition remains incompletely understood. As stated in the recent FDA safety announcement regarding brain deposit of gadolinium: [i]t is unknown whether these gadolinium deposits are harmful or can lead to adverse health effects [52]. The FDA recommends that health care professionals should consider limiting GBCA use to clinical circumstances in which the additional information provided by the contrast is necessary [52]. It may be imperative to consider gadolinium retention potential when deciding which GBCA to administer. Gadolinium Deposition Disease Gadolinium deposition disease is the name we propose for a disease process observed in subjects with normal or near normal renal function who develop persistent symptoms that arise hours to 2 months after the administration of GBCAs. In these cases, no preexistent disease or subsequently developed disease of an alternate known process is present to account for the symptoms. Some of these patients are likely to have coexistent gadolinium storage condition, as described above, but gadolinium deposition disease is also described after a single administration of GBCA. The causal relationship has not been fully established, but it is under investigation. The aforementioned MRI gadolinium-toxicity support group has reported symptoms that they considered to be consistent with the known toxic effects of gadolinium. In a recent survey performed in 17 patients, an association between chronic effects and GBCA exposure was suggested [21]. Their internal investigation of members showed that the symptoms appeared within 1 month after the last contrast-enhanced MRI, and pain in the lower arms and legs persisted to the present time without resolving [53]. In our experience, symptoms of gadolinium deposition disease are similar but not identical to those observed in NSF. Typical clinical features include persistent headache and bone and joint pain. Patients often complain of clouded mentation that many describe as a brain fog. More distinctive features are comparable with those observed in NSF but of lesser severity; patients often experience subcutaneous soft-tissue thickening that clinically appears somewhat spongy or rubbery without the hardness and redness observed in NSF. Tendons and ligaments in a comparable distribution may also be painful and have a thickened appearance. Patients may complain of tightness of the hands and feet that resembles the feeling of being fitted with extremely tight gloves or socks. Patients may experience excruciating pain, typically in a distal distribution, of the arms and legs but that may also be in the torso or generalized in location. This pain is often described as feeling like sharp pins and needles, cutting, or burning. As with NSF, it is unknown why only some patients have symptoms after gadolinium administration. From previous experience with NSF, we assume that less stable GBCAs are more likely associated with symptoms, but this assumption needs further validation. Host factors such as genetic susceptibility, adaptive immune response, or both may determine whether patients with gadolinium storage condition will develop gadolinium deposition disease. The extent of overlap between patients with gadolinium deposition disease and subjects who have shown gadolinium storage condition in the brain is not known; further research is needed. Other areas of research interest include whether different tissue gadolinium deposition results in different symptoms and whether different immune cell components cause different symptoms. Additionally, a greater range of GBCAs may cause gadolinium deposition disease compared with NSF or gadolinium storage condition. The contribution of acute immune effects may explain why this condition may also be observed even with more stable agents. Our opinion at present is that gadolinium deposition disease is likely uncommon. We believe that radiologists and clinicians must be attentive to the development of NSF-like disease in patients with normal renal function and not dismiss patients with severe symptoms after GBCA administration. Our opinion is that in patients who describe symptoms that suggest the diagnosis of gadolinium deposition disease, confirmation of the presence of gadolinium is necessary to establish the diagnosis. We recommend 24-hour urine testing for gadolinium, 30 days or more after the most recent GBCA administration. Early recognition will facilitate early treatment of the disease before it becomes more chronic and likely less responsive to therapy. A recent report described gadolinium-associated plaques [54]. Sclerotic bodies (eosinophilic, collagenous, round or ovoid bodies) thought to be pathognomonic for NSF were found in histopathologic examination of the skin of patients exposed to Omniscan without NSF or even renal disease. We would put this condition under the rubric of gadolinium deposition disease if the patients have normal or near normal renal function and show symptoms from the lesions. Future Directions It is important to improve the understanding of the family of disorders related to gado- AJR:207, August
4 Semelka et al. linium in humans. Genetic testing may hold the key to predict who is likely to have NSF, severe acute adverse event, gadolinium storage condition, or gadolinium deposition disease, but it is uncertain if such testing will occur or be practical. As genetic testing is not currently a reality to prevent these diseases, early detection and treatment are the focus of management. A number of adverse processes occur from the presence of gadolinium in humans. Because of mounting concern from health care workers and patients, agents that are the least likely to cause harm should be used. Because macrocyclic agents are more stable than linear agents and have been shown to have fewer instances of disease or deposition states, it would be prudent to employ predominantly macrocyclic agents in children and in subjects for whom multiple studies are anticipated (e.g., patients with Crohn disease or multiple sclerosis). Roles still exist for linear agents that possess properties of hepatobiliary elimination (Eovist, MultiHance) or prolonged intravascular dwell time (MultiHance), but continuing to use linear agents that are purely nonspecific and extracellular may be unjustified. References 1. Hao D, Ai T, Goerner F, Hu X, Runge VM, Tweedle M. MRI contrast agents: basic chemistry and safety. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012; 36: Bleicher AG, Kanal E. A serial dilution study of gadolinium-based MR imaging contrast agents. AJNR 2008; 29: Kanal E, Tweedle MF. Residual or retained gadolinium: practical implications for radiologists and our patients. Radiology 2015; 275: Joffe P, Thomsen HS, Meusel M. Pharmacokinetics of gadodiamide injection in patients with severe renal insufficiency and patients undergoing hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Acad Radiol 1998; 5: Gibby WA, Gibby KA, Gibby WA. Comparison of Gd DTPA-BMA (Omniscan) versus Gd HP-DO3A (ProHance) retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Invest Radiol 2004; 39: White GW, Gibby WA, Tweedle MF. Comparison of Gd(DTPA-BMA) (Omniscan) versus Gd(HP-DO3A) (ProHance) relative to gadolinium retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy. Invest Radiol 2006; 41: Darrah TH, Prutsman-Pfeiffer JJ, Poreda RJ, Campbell ME, Hauschka PV, Hannigan RE. Incorporation of excess gadolinium into human bone from medical contrast agents. Metallomics 2009; 1: Grobner T. Gadolinium: a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: [Erratum in Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21:1745] 9. Marckmann P. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative role of gadodiamide used for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: Thomsen HS. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: history and epidemiology. Radiol Clin North Am 2009; 47: Broome DR. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: a summary of the medical literature reporting. Eur J Radiol 2008; 66: Abujudeh HH, Kaewlai R, Kagan A, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after gadopentetate dimeglumine exposure: case series of 36 patients. Radiology 2009; 253: Wertman R, Altun E, Martin DR, et al. Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: evaluation of gadolinium chelate contrast agents at four American universities. Radiology 2008; 248: Hope TA, Herfkens RJ, Denianke KS, LeBoit PE, Hung YY, Weil E. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease who received gadopentetate dimeglumine. Invest Radiol 2009; 44: Fretellier N, Idée JM, Guerret S, et al. Clinical, biological, and skin histopathologic effects of ionic macrocyclic and nonionic linear gadolinium chelates in a rat model of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Invest Radiol 2011; 46: Altun E, Martin DR, Wertman R, Lugo- Somolinos A, Fuller ER, Semelka RC. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: change in incidence following a switch in gadolinium agents and adoption of a gadolinium policy report from two U.S. universities. Radiology 2009; 253: Kanda T, Ishii K, Kawaguchi H, Kitajima K, Takenaka D. High signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: relationship with increasing cumulative dose of a gadolinium-based contrast material. Radiology 2014; 270: Errante Y, Cirimele V, Mallio CA, Di Lazzaro V, Zobel BB, Quattrocchi CC. Progressive increase of T1 signal intensity of the dentate nucleus on unenhanced magnetic resonance images is associated with cumulative doses of intravenously administered gadodiamide in patients with normal renal function, suggesting dechelation. Invest Radiol 2014; 49: Quattrocchi CC, Mallio CA, Errante Y, et al. Gadodiamide and dentate nucleus T1 hyperintensity in patients with meningioma evaluated by multiple follow-up contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance examinations with no systemic interval therapy. Invest Radiol 2015; 50: Ramalho J, Castillo M, AlObaidy M, et al. High signal intensity in globus pallidus and dentate nucleus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: evaluation of two linear gadolinium-based contrast agents. Radiology 2015; 276: Gadolinium Toxicity website. The lighthouse project. Accessed April 20, Williams S, Grimm H. Gadolinium toxicity: a survey of the chronic effects of retained gadolinium from contrast MRIs. Gadolinium Toxicity website. gdtoxicity.files.wordpress.com/2014/09/ gd-symptom-survey.pdf. Published April 2, Accessed November 1, Broome DR, Girguis MS, Baron PW, Cottrell AC, Kjellin I, Kirk GA. Gadodiamide-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: why radiologists should be concerned. AJR 2007; 188: Sadowski EA, Bennett LK, Chan MR, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: risk factors and incidence estimation. Radiology 2007; 243: Shabana WM, Cohan RH, Ellis JH, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a report of 29 cases. AJR 2008; 190: American College of Radiology (ACR) Committee on Drugs and Contrast Media. ACR manual on contrast media, version Reston, VA: American College of Radiology, Nandwana SB, Moreno CC, Osipow MT, Sekhar A, Cox KL. Gadobenate dimeglumine administration and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: is there a real risk in patients with impaired renal function? Radiology 2015; 276: Kallen AJ, Jhung MA, Cheng S, et al. Gadolinium-containing magnetic resonance imaging contrast and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a casecontrol study. Am J Kidney Dis 2008; 51: Collidge TA, Thomson PC, Mark PB, et al. Gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: retrospective study of a renal replacement therapy cohort. Radiology 2007; 245: Abraham JL, Thakral C, Skov L, Rossen K, Marckmann P. Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Br J Dermatol 2008; 158: Rosenkranz AR, Grobner T, Mayer GJ. Conventional or gadolinium containing contrast media: the choice between acute renal failure or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Wien Klin Wochenschr 2007; 119: Christensen KN, Lee CU, Hanley MM, Leung N, MD, Moyer TP, Pittelkow MR. Quantification of gadolinium in fresh skin and serum samples from patients with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011; 64: Weiss KL. Severe anaphylactoid reaction after i.v. 232 AJR:207, August 2016
5 Gadolinium in Humans Gd-DTPA. Magn Reson Imaging 1990; 8: media. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2001; 12: trast agent. Radiology 2015; 275: Omohundro JE, Elderbrook MK, Ringer TV. La- 42. Jung JW, Kang HR, Kim MH, et al. Immediate hy- 49. Robert P, Lehericy S, Grand S, et al. T1-weighted hy- ryngospasm after administration of gadopentetate persensitivity reaction to gadolinium-based MR persignal in the deep cerebellar nuclei after repeated dimeglumine. J Magn Reson Imaging 1992; contrast media. Radiology 2012; 264: administrations of gadolinium-based contrast agents 2: Kanal E, Maravilla K, Rowley HA. Gadolinium in healthy rats: difference between linear and macro- 35. Tardy B, Guy C, Barral G, Page Y, Ollagnier M, contrast agents for CNS imaging: current concepts cyclic agents. Invest Radiol 2015; 50: Bertrand JC. Anaphylactic shock induced by intravenous gadopentetate dimeglumine. (letter) Lancet 1992; 339: Takebayashi S, Sugiyama M, Nagase M, Matsubara S. Severe adverse reaction to IV gadopentetate dimeglumine. (letter) AJR 1993; 160: Witte RJ, Anzai LL. Life-threatening anaphylactoid reaction after intravenous gadoteridol administration in a patient who had previously received gadopentetate dimeglumine. AJNR 1994; 15: Murphy KJ, Brunberg JA, Cohan RH. Adverse reactions to gadolinium contrast media: a review of 36 cases. AJR 1996; 167: Beaudouin E, Kanny G, Blanloeil Y, Guilloux L, Renaudin JM, Moneret-Vautrin DA. Anaphylactic shock induced by gadoterate meglumine ( D O TA R E M ). Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 35: Runge VM. Safety of approved MR contrast media for intravenous injection. J Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 12: Runge VM. Safety of magnetic resonance contrast and clinical evidence. AJNR 2014; 35: McDonald RJ, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, et al. Intracranial gadolinium deposition after contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2015; 275: Kanda T, Fukusato T, Matsuda M, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agent accumulates in the brain even in subjects without severe renal dysfunction: evaluation of autopsy brain specimens with inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy. Radiology 2015; 276: Rocklage SM, Worah D, Kim SH. Metal ion release from paramagnetic chelates: what is tolerable? Magn Reson Med 1991; 22: ; discussion, Kanda T, Osawa M, Oba H, et al. High signal intensity in dentate nucleus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: association with linear versus macrocyclic gadolinium chelate administration. Radiology 2015; 275: Radbruch A, Weberling LD, Kieslich PJ, et al. Gadolinium retention in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus is dependent on the class of con- 50. Weberling LD, Kieslich PJ, Kickingereder P, et al. Increased signal intensity in the dentate nucleus on unenhanced T1-weighted images after gadobenate dimeglumine administration. Invest Radiol 2015; 50: Birka M, Wentker KS, Lusmöller E, et al. Diagnosis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis by means of elemental bioimaging and speciation analysis. Anal Chem 2015; 87: U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. FDA evaluating the risk of brain deposits with repeated use of gadolinium-based contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). downloads/drugs/drugsafety/ucm pdf. Accessed November 1, Ramalho J, Semelka RC, Ramalho M, Nunes RH, AlObaidy M, Castillo M. Gadolinium-based contrast agent accumulation and toxicity: an update. AJNR 2015 Dec 10 [Epub ahead of print] 54. Gathings RM, Reddy R, Santa Cruz D, Brodell RT. Gadolinium-associated plaques. JAMA Dermatol 2015; 151: AJR:207, August
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
 Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates
 Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018)
 Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline
 Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
 Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects
 Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Reviews and Commentary n Opinion Carlo Cosimo Quattrocchi, MD, PhD Aart J. van der Molen, MD Published online 10.1148/radiol.2016161626
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Reviews and Commentary n Opinion Carlo Cosimo Quattrocchi, MD, PhD Aart J. van der Molen, MD Published online 10.1148/radiol.2016161626
Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions
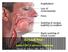 Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Gadolinium Retention in the Dentate Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Is Dependent on the Class of Contrast Agent 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research
 University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
Frequency and Severity of Acute Allergic-Like Reactions to Gadolinium-Containing IV Contrast Media in Children and Adults
 Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
INTRODUCTION CLINICAL EXPERIENCE CLINICAL EFFICACY PEDIATRIC EXPERIENCE DOSING SUMMARY
 1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
Incidence of Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions
 Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
Report on the Investigation Results
 This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
Received: 16 October 2015, Accepted: 3 December 2015, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 11 January 2016
 Short communication Received: 16 October 2015, Accepted: 3 December 2015, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 11 January 2016 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/cmmi.1683 High signal intensity
Short communication Received: 16 October 2015, Accepted: 3 December 2015, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 11 January 2016 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/cmmi.1683 High signal intensity
NSF Coming and Going
 NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
Annex II. Scientific conclusions
 Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Figure 1 Figure 1: Energy diagram illustrates formation of a chelate (ML) created by combining two chemicals free Gd 3 (M), which is a metal ion, and
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Gadolinium Deposition:
 Gadolinium Deposition: Imaging Phenomenon or Should we change practice? Gregory Brown FSMRT MR Radiographer, PhD student Centre for Advanced Imaging, University of Queensland, Australia ORCID: 0000-0001-7994-2743
Gadolinium Deposition: Imaging Phenomenon or Should we change practice? Gregory Brown FSMRT MR Radiographer, PhD student Centre for Advanced Imaging, University of Queensland, Australia ORCID: 0000-0001-7994-2743
Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice?
 Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (marketed as Magnevist, MultiHance, Omniscan, OptiMARK, ProHance)
 Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist and Magnevist below.
 August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR
 William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist, Eovist and Magnevist on the following pages.
 Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document. Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013
 FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents
 Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Public Assessment Report
 Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
Central nervous system gadolinium accumulation in patients undergoing periodical contrast MRI screening for hereditary tumor syndromes
 Vergauwen et al. Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice (2018) 16:2 DOI 10.1186/s13053-017-0084-7 RESEARCH Central nervous system gadolinium accumulation in patients undergoing periodical contrast MRI
Vergauwen et al. Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice (2018) 16:2 DOI 10.1186/s13053-017-0084-7 RESEARCH Central nervous system gadolinium accumulation in patients undergoing periodical contrast MRI
Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be used
 Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7
 PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS
 DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA.
 ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
Summary. Correspondence Jerrold L. Abraham. Accepted for publication 17 September 2007
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies
 Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Special Articles Original Research
 Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the product information
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media
 HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Imaging in the time of NFD/NSF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency?
 DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges
 REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM. (gadoterate meglumine) Injection. For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing theory
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
Safety of Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) as a Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance
 Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. flow rate of approximately 2 ml/second for adults and 1-2 ml/second for pediatric
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. 1.1 Central Nervous System. 1.2 Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues. 1.3 Body
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
Contrast controversies and confusion
 Contrast controversies and confusion Mariya Kobi 1 ; Meir H Scheinfeld 1 ; Seymour Sprayregen 1 ; R Joshua Dym 2 * 1 Department of Radiology, Montefiore Medical Center, USA 2 Department of Radiology, Rutgers
Contrast controversies and confusion Mariya Kobi 1 ; Meir H Scheinfeld 1 ; Seymour Sprayregen 1 ; R Joshua Dym 2 * 1 Department of Radiology, Montefiore Medical Center, USA 2 Department of Radiology, Rutgers
IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI
 11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are significantly
 Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: Possible Association with a Predisposing Infection
 MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
ARTICLE IN PRESS European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx
 European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Tolerability and diagnostic value
European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Tolerability and diagnostic value
Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern
 Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
ASKLEPIOS Course. July 20 21, 2018 Bangkok/Thailand
 This ASKLEPIOS course is implemented with great support and partnership of Guerbet and RCRT Education in partnership Course information This ESOR course aims to discuss the most important topics in neuroradiology.
This ASKLEPIOS course is implemented with great support and partnership of Guerbet and RCRT Education in partnership Course information This ESOR course aims to discuss the most important topics in neuroradiology.
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
CONTRAINDICATIONS History of severe hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM. Gadoterate meglumine injection. (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
October 23, Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs. Dear Dr. Hamburg:
 October 23, 2012 Commissioner Margaret A. Hamburg, M.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue WO Bldg. 1, Room 2217 Silver Springs, MD 20993 Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs Dear
October 23, 2012 Commissioner Margaret A. Hamburg, M.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue WO Bldg. 1, Room 2217 Silver Springs, MD 20993 Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs Dear
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST. gadoxetate disodium injection mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml)
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
Instructions for the safe administration of gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCA). 1. PREADMINISTRATION PRECAUTIONS:
 POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
During the past decade, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 Low Risk for Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Nondialysis Patients Who Have Chronic Kidney Disease and Are Investigated with Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Constantina Chrysochou,* Albert
Low Risk for Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Nondialysis Patients Who Have Chronic Kidney Disease and Are Investigated with Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Constantina Chrysochou,* Albert
T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents in Human Whole Blood at 1.5, 3, and 7 T
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
 Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are of great value for
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology and Gadolinium Distribution in the Rodent Brain After the Administration of Cumulative High Doses of Linear and Macrocyclic Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents Jessica Lohrke, PhD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology and Gadolinium Distribution in the Rodent Brain After the Administration of Cumulative High Doses of Linear and Macrocyclic Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents Jessica Lohrke, PhD,*
Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Scientific Paper. Authors: E. De Kerviler 1, S. Gaillard 2 ; 1 Paris/FR, 2 Villepinte/FR
 Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. DOTAREM mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid)
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
Policy #: 291 Latest Review Date: February 2013
 Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
flow rate of approximately 2 ml/second for adults and 1-2 ml/second for pediatric patients. The dose is delivered by manual or power injection.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
CONTRAINDICATIONS Clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM. (4)
 M120177AB HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
M120177AB HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
Who Should Be Premediciated for Contrast-Enhanced Exams?
 Who Should Be Premediciated for Contrast-Enhanced Exams? Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Types of Intravenous Contrast Media Iodinated Contrast Agents
Who Should Be Premediciated for Contrast-Enhanced Exams? Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Types of Intravenous Contrast Media Iodinated Contrast Agents
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient
 Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient About DOTAREM: DOTAREM is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain
Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient About DOTAREM: DOTAREM is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain
Update. Drug Safety. Welcome to the first issue of the newly launched Drug Safety Update. This
 Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Induction of a type I interferon signature in normal. human monocytes by gadolinium-based contrast agents: comparison of linear and macrocyclic
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Jefferson Institute of Molecular Medicine Papers and Presentations Jefferson Institute of Molecular Medicine 1-2014 Induction of a type I interferon
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Jefferson Institute of Molecular Medicine Papers and Presentations Jefferson Institute of Molecular Medicine 1-2014 Induction of a type I interferon
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC
 DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively.
DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively.
Reference ID: MultiHance Injection, NDA , SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov _CLEAN.
 MultiHance Injection, NDA 21-357, SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov-18-2010_CLEAN.doc HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
MultiHance Injection, NDA 21-357, SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov-18-2010_CLEAN.doc HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.
![FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA. FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.](/thumbs/77/75534485.jpg) Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Primovist 0.25 mmol/ml, solution for injection Gadoxetate disodium Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine. - Keep this leaflet.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Primovist 0.25 mmol/ml, solution for injection Gadoxetate disodium Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine. - Keep this leaflet.
PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM
 PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM NAME OF THE MEDICINE DOTAREM (gadoteric acid) paramagnetic contrast medium for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The structural formula of gadoteric acid is shown below: The
PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM NAME OF THE MEDICINE DOTAREM (gadoteric acid) paramagnetic contrast medium for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The structural formula of gadoteric acid is shown below: The
