Neuroradiology Original Research
|
|
|
- Emily Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords: contrast media, multiple sclerosis, neuroradiology DOI: /AJR Received December 22, 2005; accepted after revision June 7, Department of Radiology, Sisli Etfal Hospital, Etfal Sok, Istanbul 80220, Turkey. Address correspondence to E. Uysal (enderuysaltr@yahoo.com). 2 Department of Neurology, Sisli Etfal Hospital, Istanbul 80220, Turkey. AJR 2007; 188: X/07/ American Roentgen Ray Society Sensitivity of Immediate and Delayed Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI After Injection of 0.5 M and 1.0 M Gadolinium Chelates for Detecting Multiple Sclerosis Lesions OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to compare the efficacy of cranial MR images obtained immediately after, 5 minutes after, and 10 minutes after the injection of 0.5-mol/L (Magnevist) and 1.0-mol/L (Gadovist) gadolinium chelates in the detection of active multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions. MATERIALS AND METHODS. Thirty patients with MS were examined with MRI first with 0.5-mol/L and then, after hours, with 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelates. T1-weighted spin-echo images with magnetization transfer were obtained immediately, 5 minutes, and 10 minutes after the injection of the contrast material. Three radiologists evaluated the gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images on a remote MR console (Advantage Windows) in six separate sessions and counted the number of enhancing lesions in consensus. RESULTS. Significantly fewer enhancing lesions were seen on MR images immediately after the injection of 0.5- and 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelates (n = 18 and n = 36, respectively; p < 0.05) than at 5 minutes (n = 32 and n = 54; p < 0.05) and 10 minutes (n = 34 and n =55; p < 0.05) after the injection (p < 0.05). Likewise, significantly fewer patients with at least one enhancing lesion after the injection of 0.5- and 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelates (n = 10 and n = 16; p < 0.05) were found immediately after injection than were found 5 minutes (n = 18 and n = 24; p < 0.05) and 10 minutes (n = 18 and n = 24; p < 0.05) after injection (p < 0.01). CONCLUSION. The use of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate enables us to detect an increased number of enhancing lesions and patients with active disease. A delay of 5 minutes after the injection of the gadolinium chelate might be sufficient to detect active lesions in patients with MS. adolinium-enhanced brain MRI G has become the most sensitive tool for confirming the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) and for monitoring MS treatment trials [1]. In longitudinal clinical studies, the presence of at least one enhancing (i.e., active) lesion at screening is an established entry criterion for therapy [2, 3]. Hence, to show one or no enhancing lesions is an important clinical and research goal [4]. The sensitivity of gadolinium-enhanced MRI may be improved by means of magnetization transfer or by increasing the concentration of gadolinium in the tissues by increasing the injected volume of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelates or by increasing the delay between injection and the imaging sequences [1, 5, 6]. Although the use of magnetization transfer has become commonplace for patients with MS, the optimal gadolinium dose and the optimal scan timing are still controversial. Furthermore, a new MRI contrast agent with double gadolinium concentration (molarity) has recently been introduced into clinical practice and deserves to be investigated in this context. In this study, our aim was to compare the ability of cranial MR images obtained immediately, 5 minutes, and 10 minutes after the injection of 0.5-mol/L (Magnevist [gadopentetate dimeglumine], Schering) and 1.0- mol/l (Gadovist [gadobutrol], Schering) gadolinium chelates in the detection of active MS lesions. To our knowledge, ours is the first study to compare 0.5- and 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelates in the clinical setting of MS. Materials and Methods Patients Thirty patients (21 women, nine men; mean age, years) who had clinically proven MS and who were classified as relapsing remitting according to the criteria of McDonald et al. [6] were included in the study. None of the patients were under steroid treatment for at least 3 months before the study. Approval was obtained from our AJR:188, March
2 A C Fig year-old man with multiple sclerosis. A, Axial fast spin-echo T2-weighted image (TR/TE, 4,800/102; inversion time, 2 milliseconds) shows plaque lesion at left side of pons near tectum. B, Ten minutes after IV administration of 0.5-mol/L contrast medium (0.1 mmol/kg), no contrast enhancement attributable to this lesion is detectable on magnetization transfer contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image (560/15; inversion time, 1 millisecond). C, Immediately after administration of 1.0-mol/L contrast medium (0.2 mmol/kg), focal contrast enhancement (arrowhead) is barely detectable. (Fig. 1 continues on next page) B institutional review board, and informed consent was obtained from each patient before entering the study. MRI Technique Brain MR images were obtained with a 1.5-T unit (Signa Excite 2.0, GE Healthcare) using a standard head coil. Axial spin-echo T1-weighted images with a magnetization transfer pulse (TR/TE, 560/15; number of excitations, 1; 5-mm-thick slices with 0.5-mm 698 AJR:188, March 2007
3 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Fig. 1 (continued) 35-year-old man with multiple sclerosis. D and E, However, 5 (D) and 10 (E) minutes after administration of 1.0-mol/L contrast medium (0.2 mmol/kg), enhancement is clearly visible in this lesion. gap; matrix; 24-cm field of view) were obtained before and after the injection of 0.1 ml of 0.5- mol/l gadolinium chelate (0.1 mmol of gadolinium) per kilogram of body weight. In each patient, contrast-enhanced images were obtained immediately after, 5 minutes after, and 10 minutes after the manual injection of contrast material through an antecubital vein. Twenty-four to 48 hours (mean ± SD, 39.9 ± 7.0 hours) after the first MR examination, all patients underwent a second MR examination with the same protocol as the first but after the injection of 0.1 ml of 1.0 mol/l gadolinium chelate (0.2 mmol of gadolinium) per kilogram of body weight. Thus, a total of six cranial MRI sets were obtained for each patient. Axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo (4,800/102; number of excitations, 2; 5-mm-thick slices with 0.5-mm gap; matrix; 24-cm field of view) and FLAIR sequences (8,800/102; number of excitations, 2; 5-mm-thick slices with 0.5-mm gap; matrix; 24-cm field of view) were also obtained at the first session to achieve a complete MR examination for clinical purposes. Safety Assessment Blood urea and creatinine levels were evaluated in all patients as part of the clinical management of MS patients in our neurology clinic; no abnormality was detected. Furthermore, all patients were D asked whether they had renal disease before the MR examination and were asked about any discomfort or side effects related to contrast administration at the end of the each scanning session. The patients were called back to our clinic 1 day after study and the questions were posed by the same observers. Both contrast agents were well tolerated by all patients and no adverse reaction was detected. Image Analysis Three radiologists evaluated the gadoliniumenhanced T1-weighted images and the unenhanced T1- and T2-weighted images on a remote MR console (Advantage Windows, GE Healthcare) in six separate sessions and counted the number of enhancing lesions in consensus. An enhancing lesion was defined as a well-demarcated area of unequivocally increased signal intensity as compared with normal-appearing white matter. We tried to detect false enhancement, enhancing vessels, and flow artifacts by evaluating unenhanced and contrast-enhanced images together on the remote MR console. An equal number of MRI sets were randomly assigned to the reviewing sessions, so that in each session the radiologists evaluated 30 image sets obtained with different gadolinium chelates and different scanning times. The radiologists were blinded to patients identity, the molarity of the gadolinium chelate, and the timing of MRI. The reviewing sessions were 2 weeks apart to avoid a learning bias. Statistical Analysis The number of enhancing lesions on MR images obtained with different time delays after the injection of 0.5- or 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate were compared using Friedman and Dunn post hoc tests. The number of the patients who had at least one enhancing lesion was compared between the image sets with different scanning times using the McNemar test. The number of enhancing lesions and the number of patients who had at least one enhancing lesion were compared between the image sets obtained after the administration of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate and the corresponding image sets obtained after the administration of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate using Wilcoxon s matched pairs and McNemar tests, respectively. Results The number (n = 18) of enhancing lesions on MR images obtained immediately after the injection of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate was significantly less than those obtained 5 minutes (n = 32) and 10 minutes (n = 34) after the injection (p < 0.05). Likewise, the E AJR:188, March
4 A C Fig year-old woman with multiple sclerosis (MS). A, Millimetric MS plaque lesions are seen in subcortical white matter and at periventricular region on axial fast spin-echo T2-weighted image. B, Ten minutes after IV administration of 0.5-mol/L contrast medium (0.1 mmol/kg), no contrast enhancement attributable to a white matter lesion is detectable on magnetization transfer contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image. C, Immediately after administration of 1.0-mol/L contrast medium (0.2 mmol/kg), there is also no contrast enhancement. (Fig. 2 continues on next page) B number of enhancing lesions on MR images obtained immediately after the injection of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate was significantly less than those obtained 5 minutes (n = 54) and 10 minutes (n = 55) after the injection (p < 0.05). In both gadolinium chelate groups, the number of enhancing lesions did not differ significantly between the images obtained 5 and 10 minutes after the injection. 700 AJR:188, March 2007
5 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions The number of patients with at least one enhancing lesion (n = 10) was significantly less on the MR images obtained immediately after the injection of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate than on those obtained 5 minutes (n = 18) and 10 minutes (n = 18) after the injection (p < 0.01). Likewise, the number of patients with at least one enhancing lesion (n = 16) was significantly less on the MR images obtained immediately after the injection of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate than on those obtained 5 minutes (n = 24) and 10 minutes (n = 24) after the injection (p < 0.01). Significantly fewer enhancing lesions were seen on MR images obtained immediately, 5 minutes, and 10 minutes after the injection of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate than at corresponding times after the injection of 1.0- mol/l gadolinium chelate (p < 0.05), and significantly fewer patients had at least one enhancing lesion on MR images obtained after the injection of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate than on those obtained at corresponding times after the injection of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate (p < 0.05). D Fig. 2 (continued) 27-year-old woman with multiple sclerosis (MS). D and E, However, 5 (D) and 10 (E) minutes after administration of 1.0-mol/L contrast medium (0.2 mmol/kg), one enhancing lesion (arrowhead) is detectable in frontal left lobe. Note that enhancement is more prominent on latest image. Discussion Our results show that the use of a 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate significantly increases the sensitivity of contrast-enhanced MRI in detecting active lesions in patients with MS compared with the use of a 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate. On MR images obtained immediately, 5 minutes, and 10 minutes after the injection of gadolinium chelate, we detected more active lesions with the 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate (Figs. 1 and 2). Furthermore, for every scanning time, we detected significantly more patients who had at least one enhancing lesion with the 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate. More critically, in our study the clinical management has been changed in six patients who had no enhancing lesions after the administration of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate but at least one enhancing lesion after the administration of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate. Gadovist is a hydrophilic, electrically neutral macrocyclic contrast agent. The T1 relaxivity of Gadovist is 5.6 L/mmol per second in plasma at 39 C and 20 MHz. Magnevist, a standard extracellular paramagnetic MR contrast agent, has a T1 relaxivity of 4.8 L/mmol second in plasma at 39 C and 20 Hz. Elimination of gadobutrol occurred predominantly via the renal route, and 12 hours after administration, 92.5%, 98.0%, and 96.6% of the dose had already been recovered from the urine for the low, medium, and high doses, respectively [7]. Approximately 80% of the dose was excreted in the urine within 6 hours and 93% within 24 hours after injection of a 0.1 mmol/kg dose of Magnevist [8]. Enhanced MRI is the most sensitive measure of short-term MS activity and is widely used to monitor disease evolution, both natural and modified by treatment [4]. Thus, optimization of image timing, sequences, and contrast dose is essential. Increasing the delay between injection and scanning time (20 30 minutes after injection) to make use of the cumulative effect of gadolinium in the extracellular space is an efficient technique, but it is time-consuming [9] and hard to apply in a busy clinical setting. In our study, the last contrast-enhanced scan was started 10 minutes after the gadolinium injection. We found significantly more enhancing lesions and more patients with at least one enhancing lesion on MR images obtained 5 E AJR:188, March
6 and 10 minutes after the injection of gadolinium than on those obtained immediately after injection with both gadolinium chelate concentrations. No difference was seen in the number of lesions or the number of patients with at least one lesion between the 5- and 10- minute postinjection groups. Visible enhancement of MS lesions depends on the local concentration of gadolinium, which in turn depends on the vascular concentration of gadolinium, the permeability of the blood brain barrier, and the size of the leakage space [10]. Thus, increasing the dose of contrast material is another method for identifying more enhancing lesions on brain MR images in MS patients. Previous longitudinal studies have emphasized that triple-dose gadolinium-enhanced MRI maximizes the harvest of enhancing lesions in MS patients [11, 12]; and its use, in combination with other strategies such as delayed scanning and a magnetization transfer pulse, can lead to increased sensitivity of about 130% over standard techniques [13]. But the clinical use of triple-dose gadolinium is limited by cost benefit considerations. Another shortcoming of the triple dose is the increased procedure time. Furthermore, several studies have documented that a double dose of gadopentetate dimeglumine is as sensitive as a triple dose [14, 15]. Although the gadolinium dose (0.2 mmol/kg) we used in the 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate group was double the standard dose of 0.1 mmol per kilogram of body weight, the 0.5- mol/l gadolinium chelate group received a standard single dose of gadolinium. Few studies have compared the number of enhanced lesions seen with single and double doses of gadolinium. Our results differ from those of a recent study in which three subsequent single doses of gadolinium chelate were administered in 10 patients with MS, with imaging delays of 5, 13, and 21 minutes after injection [16]. The authors reported no significant difference in the number of enhancing lesions between the single dose and the fractionated double dose. In contrast to that study, we found significantly more enhancing lesions using 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate (i.e., a double dose of gadolinium) than using 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate (i.e., a single dose). A possible explanation of this discrepancy is that we used not a fractionated but a single injection of both 0.5- and 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelates. The relatively small sample size (n = 10) of the study of Sardanelli et al. [16] might also have contributed to this discrepancy. Our study has some limitations. Higher relaxivity of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate has been reported in some studies [7]. However, because we did not use a double dose of 0.5- mol/l gadolinium chelate, we could not evaluate a possible difference in relaxivity after the administration of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate and a double dose of 0.5-mol/L gadolinium chelate, which contain equal total amounts of gadolinium. We were not able to randomize patients in this study. Thus, there might be potential residual gadolinium in the system just before the administration of Gadovist. However, 93% of the gadolinium is excreted within 24 hours after injection. Furthermore, we used the magnetization transfer technique, and lesions may show high signal intensity even on unenhanced T1- weighted images. Thus, we asked our reviewers to mark the lesions that showed a definite signal enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images compared with unenhanced T1-weighted images regardless of the signal intensity of lesions on unenhanced images. Another limitation is our relatively small sample size. Finally, we did not acquire images 20 or 30 minutes after injection; in our opinion, this approach is not feasible in the busy clinical setting of our institution. In conclusion, the use of 1.0-mol/L gadolinium chelate enables us to detect more enhancing lesions and more patients with active disease. A delay of 5 minutes after injection of gadolinium chelate may be sufficient to detect active lesions in patients with MS. References 1. Gavra MM, Voumvourakis C, Gouliamos AD, Sfagos C, Vlahos LJ. Brain MR post-gadolinium contrast in multiple sclerosis: the role of magnetization transfer and image subtraction in detecting more enhancing lesions. Neuroradiology 2004; 46: Miller DH, Barkhof F, Albert PS, et al. Guidelines for the use of magnetic resonance techniques to monitor the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 1996; 39: Sardanelli F, Losacco C, Iozzelli A, et al. Evaluation of Gd-enhancement in brain MR of multiple sclerosis: image subtraction with and without magnetization transfer. Eur Radiol 2002; 12: Molyneux PD, Miller DH. Magnetic resonance imaging techniques to monitor phase III treatment trials. In: Filippi M, Grossman RI, Comi G, eds. Magnetic resonance techniques in clinical trials in multiple sclerosis. Milan, Italy: Springer-Verlag, 1999: McFarland HF, Frank JA. The application of magnetic resonance imaging to phase II trials in multiple sclerosis. In: Filippi M, Grossman RI, Comi G, eds. Magnetic resonance techniques in clinical trials in multiple sclerosis. Milan, Italy: Springer-Verlag, 1999: McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: Goyen M, Lauenstein TC, Herborn CU, Debatin JF, Bosk S, Ruehm SG. 0.5 M Gd chelate (Magnevist) versus 1.0 M Gd chelate (Gadovist): dose-independent effect on image quality of pelvic three-dimensional MR-angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001; 14: Magnevist monograph. Berlin, Germany: Schering AG, Filippi M, Capra R, Campi A, et al. Triple dose of gadolinium-dtpa and delayed MRI in patients with benign multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1996; 60: Tofts PS, Kermode AG. Measurement of the blood brain barrier permeability and leakage space using dynamic MR imaging. 1. Fundamental concepts. Magn Reson Med 1991; 17: Filippi M, Rovaris M, Capra R, et al. A multi-centre longitudinal study comparing the sensitivity of monthly MRI after standard and triple dose gadolinium-dtpa for monitoring disease activity in multiple sclerosis: implications for phase II clinical trials. Brain 1998; 121(Pt 10): Wolansky LJ, Bardini JA, Cook SD, Zimmer AE, Sheffet A, Lee HJ. Triple-dose versus single-dose gadoteridol in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimaging 1994; 4: Silver NC, Good CD, Barker GJ, et al. Sensitivity of contrast enhanced MRI in multiple sclerosis: effects of gadolinium dose, magnetization transfer contrast and delayed imaging. Brain 1997; 120(Pt 7): Gasperini C, Paolillo A, Rovaris M, et al. A comparison of the sensitivity of MRI after double- and triple-dose Gd-DTPA for detecting enhancing lesions in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 18: Stecco A, Migazzo E, Saponaro A, et al. Gadolinium dose optimisation in patients with multiple sclerosis: intra- and inter-individual comparisons. Eur J Radiol 2006; 57:37 42; Epub 2005 Jul Sardanelli F, Iozzelli A, Losacco C, Murialdo A, Filippi M. Three subsequent single doses of gadolinium chelate for brain MR imaging in multiple sclerosis. Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24: AJR:188, March 2007
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Single-Dose Gadolinium with Magnetization Transfer versus Triple- Dose Gadolinium in the MR Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 Single-Dose Gadolinium with Magnetization Transfer versus Triple- Dose Gadolinium in the MR Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions J. H. T. M. van Waesberghe, J. A. Castelijns, W. Roser, N. Silver, T.
Single-Dose Gadolinium with Magnetization Transfer versus Triple- Dose Gadolinium in the MR Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions J. H. T. M. van Waesberghe, J. A. Castelijns, W. Roser, N. Silver, T.
gadolinium-dtpa for detection of MRI
 540 50ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1995;59:540-544 SHORT REPORT Neurology M Filippi V Martinelli B Colombo N Canal G Comi Neuroradiology, Scientific Institute Ospedale San Raffaele,
540 50ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1995;59:540-544 SHORT REPORT Neurology M Filippi V Martinelli B Colombo N Canal G Comi Neuroradiology, Scientific Institute Ospedale San Raffaele,
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
Clinical trials of multiple sclerosis monitored with enhanced MRI: new sample size calculations based on large data sets
 494 Neuroimaging Research Unit, Department of Neuroscience, Scientific Institute Ospedale San RaVaele, University of Milan, Via Olgettina 6, 2132 Milan, Italy M P Sormani M Rovaris M Filippi Clinical Trials
494 Neuroimaging Research Unit, Department of Neuroscience, Scientific Institute Ospedale San RaVaele, University of Milan, Via Olgettina 6, 2132 Milan, Italy M P Sormani M Rovaris M Filippi Clinical Trials
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
 Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
High-Resolution MR Lymphangiography in Patients with Primary and Secondary Lymphedema
 Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice?
 Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Comparison of MERGE and Axial T2-Weighted Fast Spin-Echo Sequences for Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in the Cervical Spinal Cord
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Multiple sclerosis: High prevalence of the central vein sign in white matter lesions on susceptibility-weighted images
 Original article Multiple sclerosis: High prevalence of the central vein sign in white matter lesions on susceptibility-weighted images The Neuroradiology Journal 0(00) 1 6! The Author(s) 2018 Reprints
Original article Multiple sclerosis: High prevalence of the central vein sign in white matter lesions on susceptibility-weighted images The Neuroradiology Journal 0(00) 1 6! The Author(s) 2018 Reprints
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate dimeglumine
 Eur. Radiol. 10, 1068±1072 (2000) Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 European Radiology Original article Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate
Eur. Radiol. 10, 1068±1072 (2000) Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 European Radiology Original article Improving postoperative MR imaging of pituitary macroadenomas: comparison of full and reduced dose of gadopentetate
Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the product information
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis
 APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
High b Value Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Detecting Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Preliminary Results
 Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Ovid: Barkhof: Neurology, Volume 49(6).December Copyright 1997 American Academy of Neurology. Volume 49(6) December 1997 pp
 Page 1 of 11 Copyright 1997 American Academy of Neurology Volume 49(6) December 1997 pp 1682-1688 Improving interobserver variation in reporting gadolinium-enhanced MRI lesions in multiple sclerosis [Articles]
Page 1 of 11 Copyright 1997 American Academy of Neurology Volume 49(6) December 1997 pp 1682-1688 Improving interobserver variation in reporting gadolinium-enhanced MRI lesions in multiple sclerosis [Articles]
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS
 MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS Ambesh Deshar *, Gyanendra KC and Zhang Lopsang *Department of Medical Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, First
MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS Ambesh Deshar *, Gyanendra KC and Zhang Lopsang *Department of Medical Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, First
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects of Interferon Beta-1b in the BENEFIT Study
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects of Interferon in the BENEFIT Study Integrated 2-Year Results Frederik Barkhof, MD, PhD; Chris H. Polman, MD, PhD; Ernst-Wilhelm Radue, MD; Ludwig
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects of Interferon in the BENEFIT Study Integrated 2-Year Results Frederik Barkhof, MD, PhD; Chris H. Polman, MD, PhD; Ernst-Wilhelm Radue, MD; Ludwig
Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief Investigative Radiology
 Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief Investigative Radiology Patients First RSNA 2012 The classical model of medical care which portrays the authoritative physician evaluating and treating an obedient, non-inquisitive
Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief Investigative Radiology Patients First RSNA 2012 The classical model of medical care which portrays the authoritative physician evaluating and treating an obedient, non-inquisitive
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions
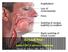 Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
MR of Intraparotid Masses
 MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Achilles Tendon After Percutaneous Surgical Repair: Serial MRI Observation of Uncomplicated Healing
 MRI of Achilles Tendon Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Akira Fujikawa 1 Yukishige Kyoto 1 Masahisa Kawaguchi 2 Yutaka Naoi 1 Yo Ukegawa 2 Fujikawa A, Kyoto Y, Kawaguchi M, Naoi Y, Ukegawa Y Keywords:
MRI of Achilles Tendon Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Akira Fujikawa 1 Yukishige Kyoto 1 Masahisa Kawaguchi 2 Yutaka Naoi 1 Yo Ukegawa 2 Fujikawa A, Kyoto Y, Kawaguchi M, Naoi Y, Ukegawa Y Keywords:
Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
Pseudo Washout Sign in High-Flow Hepatic Hemangioma on Gadoxetic Acid Contrast-Enhanced MRI Mimicking Hypervascular Tumor
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Doo et al. Pseudo Washout Sign on MRI of Hemangioma Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kyung Won Doo 1 Chang Hee Lee Jae Woong Choi Jongmee Lee
Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Doo et al. Pseudo Washout Sign on MRI of Hemangioma Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kyung Won Doo 1 Chang Hee Lee Jae Woong Choi Jongmee Lee
A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates
 Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol. for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS. David K.B.
 Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Computer-Assisted Quantitation of Enhancing Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis: Correlation with Clinical Classification
 Computer-Assisted Quantitation of Enhancing Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis: Correlation with Clinical Classification Yukio Miki, Robert I. Grossman, Jayaram K. Udupa, Supun Samarasekera, Mark A. van Buchem,
Computer-Assisted Quantitation of Enhancing Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis: Correlation with Clinical Classification Yukio Miki, Robert I. Grossman, Jayaram K. Udupa, Supun Samarasekera, Mark A. van Buchem,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Efficacy of Azathioprine on Multiple Sclerosis New Brain Lesions Evaluated Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Efficacy of Azathioprine on Multiple Sclerosis New Brain Lesions Evaluated Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Luca Massacesi, MD; Alessandro Parigi, MD; Alessandro Barilaro, MD; Anna
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Efficacy of Azathioprine on Multiple Sclerosis New Brain Lesions Evaluated Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Luca Massacesi, MD; Alessandro Parigi, MD; Alessandro Barilaro, MD; Anna
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update
 MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple sclerosis diagnosis
 Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2017; 16(4): 168-72 The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple
Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2017; 16(4): 168-72 The relationship of multiple sclerosis and cerebral developmental venous anomaly with an advantageous role in the multiple
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018)
 Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Use of MRI Technology in Determining Prognosis and Tracking Therapeutic Benefit in Multiple Sclerosis
 Use of MRI Technology in Determining Prognosis and Tracking Therapeutic Benefit in Multiple Sclerosis Timothy Vollmer, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Yale School of Medicine New Haven, Connecticut
Use of MRI Technology in Determining Prognosis and Tracking Therapeutic Benefit in Multiple Sclerosis Timothy Vollmer, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Yale School of Medicine New Haven, Connecticut
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7
 PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Francesco Manfredonia, MD; Olga Ciccarelli, PhD; Zhaleh Khaleeli, MRCP;
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Normal-Appearing Brain T1 Relaxation Time Predicts Disability in Early Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Francesco Manfredonia, MD; Olga Ciccarelli, PhD; Zhaleh Khaleeli, MRCP;
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
Report on the Investigation Results
 This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1
 A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. imaging (MRI) provides
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Annex II. Scientific conclusions
 Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Short-Term Correlations between Clinical and MR Imaging Findings in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:75 81, January 2003 Short-Term Correlations between Clinical and MR Imaging Findings in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris, Giancarlo Comi, David Ladkani, Jerry
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:75 81, January 2003 Short-Term Correlations between Clinical and MR Imaging Findings in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris, Giancarlo Comi, David Ladkani, Jerry
Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis
 43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES. M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly
 LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians
 Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 129 133 Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians 1 Heng-Thay CHONG MRCP, 1 Norlisah RAMLI FRCR, 2 Kwang-Ho LEE MD, 2 Byung-Joon
Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 129 133 Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians 1 Heng-Thay CHONG MRCP, 1 Norlisah RAMLI FRCR, 2 Kwang-Ho LEE MD, 2 Byung-Joon
Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Whole body magnetic resonance imaging (WB MRI) has become feasible and enables fast
 Continuing Education Column Clinical Application of Whole-body MRI Chin A Yi, MDKyung Soo Lee, MDJi Hye Kim, MD Department of Radiology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine E - mail : jhkate@skku.edu
Continuing Education Column Clinical Application of Whole-body MRI Chin A Yi, MDKyung Soo Lee, MDJi Hye Kim, MD Department of Radiology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine E - mail : jhkate@skku.edu
The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis
 The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis William T. C. Yuh, E. Turgut Tali, Hoang D. Nguyen, Tereasa M. Simonson, Nina A. Mayr, and David
The Effect of Contrast Dose, Imaging Time, and Lesion Size in the MR Detection of Intracerebral Metastasis William T. C. Yuh, E. Turgut Tali, Hoang D. Nguyen, Tereasa M. Simonson, Nina A. Mayr, and David
Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI
 Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
T he spinal cord is frequently affected, both pathologically
 51 PAPER Increasing cord atrophy in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 3 year study W Rashid, G R Davies, D T Chard, C M Griffin, D R Altmann, R Gordon, A J Thompson, D H Miller... See end
51 PAPER Increasing cord atrophy in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 3 year study W Rashid, G R Davies, D T Chard, C M Griffin, D R Altmann, R Gordon, A J Thompson, D H Miller... See end
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
Long-term effects of cladribine tablets on MRI activity outcomes in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: the CLARITY Extension study
 753365TAN0010.1177/1756285617753365Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersG Comi, S CooK research-article2018 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Original Research Long-term effects of
753365TAN0010.1177/1756285617753365Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersG Comi, S CooK research-article2018 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Original Research Long-term effects of
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging has been reported to be a sensitive and specific method in the diagnosis of disease of the sub-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Arch Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 November 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
Perfusion MRI. Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute
 Perfusion MRI Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute Perfusion The delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue Perfusion
Perfusion MRI Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute Perfusion The delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue Perfusion
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an
 Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Signal Intensity as a Predictor of Gadolinium Enhancement in Relapsing- Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Mihail Guranda, MD; Marco Essig, MD, PhD; Ariane Poulin, MD; Reza
Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Signal Intensity as a Predictor of Gadolinium Enhancement in Relapsing- Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Mihail Guranda, MD; Marco Essig, MD, PhD; Ariane Poulin, MD; Reza
Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
Venous compression to reduce peripheral venous contamination in gadofosveset-enhanced first-pass wholebody
 Venous compression to reduce peripheral venous contamination in gadofosveset-enhanced first-pass wholebody MRA Poster No.: C-3421 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: Y.
Venous compression to reduce peripheral venous contamination in gadofosveset-enhanced first-pass wholebody MRA Poster No.: C-3421 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: Y.
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Evolution of T 1 black holes in patients with multiple sclerosis imaged monthly for 4 years
 DOI: 10.1093/brain/awg182 Advanced Access publication June 23, 2003 Brain (2003), 126, 1782±1789 Evolution of T 1 black holes in patients with multiple sclerosis imaged monthly for 4 years Francesca Bagnato,
DOI: 10.1093/brain/awg182 Advanced Access publication June 23, 2003 Brain (2003), 126, 1782±1789 Evolution of T 1 black holes in patients with multiple sclerosis imaged monthly for 4 years Francesca Bagnato,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research
 University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline
 Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Brain MRI With Single-Dose (0.1 mmol/kg) Gadobutrol at 1.5 T and 3 T: Comparison With 0.15 mmol/kg Gadoterate Meglumine
 euroradiology/head and eck Imaging riginal Research Kramer et al. rain MRI With Gadobutrol Versus Gadoterate Meglumine euroradiology/head and eck Imaging riginal Research Harald Kramer 1 Val M. Runge 2
euroradiology/head and eck Imaging riginal Research Kramer et al. rain MRI With Gadobutrol Versus Gadoterate Meglumine euroradiology/head and eck Imaging riginal Research Harald Kramer 1 Val M. Runge 2
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
A Multiple Classifier System for Classification of Breast Lesions Using Dynamic and Morphological Features in DCE-MRI
 A Multiple Classifier System for Classification of Breast Lesions Using Dynamic and Morphological Features in DCE-MRI Roberta Fusco 1, Mario Sansone 1, Antonella Petrillo 2, and Carlo Sansone 3 1 Department
A Multiple Classifier System for Classification of Breast Lesions Using Dynamic and Morphological Features in DCE-MRI Roberta Fusco 1, Mario Sansone 1, Antonella Petrillo 2, and Carlo Sansone 3 1 Department
