MAJOR PAPER. Introduction
|
|
|
- Spencer Holland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; doi: /mrms.mp Published Online: October 11, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Benefit of 3T Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Comparison to Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging for the Evaluation of Disseminated Lesions in Primary Malignant Brain Tumors Yoshihito Kadota 1*, Toshinori Hirai 1, Hideo Nakamura 3, Keishi Makino 3, Shigetoshi Yano 3, Shinichiro Nishimura 2, Machiko Tateishi 2, Minako Azuma 2, Mika Kitajima 2, and Yasuyuki Yamashita 2 Purpose: We aimed to determine whether 3T diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has an additive value relative to contrast-enhanced MR imaging for the detection of disseminated lesions in patients with primary malignant brain tumors. Methods: We included consecutive 12 patients with nodular disseminated lesions of primary malignant brain tumors that were confirmed by surgery or follow-up MR imaging. All underwent conventional MR imaging, DWI at b = 1000 and 3000 s/mm 2, post-contrast T 1 -weighted and 3D gradient-echo imaging at 3T. For the largest lesion per person, two radiologists independently evaluated the presence of additional information on DWI compared with postcontrast MR images using a 4-point scoring system. On DW images, one radiologist measured the lesion-to-brain contrast ratio (LBCR). Results: Compared with postcontrast studies, radiologists 1 and 2, respectively, assigned more apparent lesion conspicuity in 2 (17%) and 1 (8%) DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 and 4 (33%) and 5 (42%) DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 studies. For one of them, the mean score was significantly higher for b = 3000 s/mm 2 than b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.05). Interobserver agreement for DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 and b = 3000 s/mm 2 was very good (κ = 0.85; 95% CI, ) and excellent (κ = 0.93; 95% CI, ), respectively. The mean LBCR was significantly higher for DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 than DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.01). Conclusion: In the detection of disseminated lesions in patients with primary malignant brain tumors, 3T DWI has an additive value relative to contrast-enhanced MR imaging. DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 may be more useful than DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2. Keywords: diffusion-weighted imaging, 3T MRI, dissemination, high-b value Introduction Primary malignant brain tumors represented by glioblastoma often develop local recurrence and disseminates throughout the central nervous system. Saito et al. 1 reported that 25% of patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or glioblastoma developed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dissemination. 1 Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Miyazaki, 5200 Kihara, Kiyotake, Miyazaki , Japan 2 Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and 3 Neurosurgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan *Corresponding author, Phone: , Fax: , yoshihito_kadota@med.miyazaki-u.ac.jp 2016 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives International License. Received: July 6, 2016 Accepted: September 9, 2016 The patients with dissemination at first relapse had significantly shorter survival times than a control group with local recurrence. 2 The MR imaging and CSF cytology techniques play a role of detecting CSF dissemination. Prompt and accurate diagnosis may have a significant impact on clinical treatment decision making because of poor prognosis of the patients with CSF dissemination. However, CSF cytology has a false negative rate of 40 to 50% in patients with clinically suspected neoplastic meningitis proven at the time of autopsy. 3 On the other hand, contrast-enhanced MRI has a > = 30% incidence of falsenegative results. 4 Diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI) is very useful for the diagnosis of various brain diseases (e.g., acute brain infarction, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, encephalitis). 5 7 High b-value DWI for these diseases has been also reported to be useful To our knowledge, however, the usefulness of Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences Vol. 16, No
2 Y. Kadota et al. DWI for the detection of disseminated lesions in patients with primary malignant brain tumors has not been investigated. The purpose of this study was to determine whether 3T DWI including high b-value DWI has an additive value relative to contrast-enhanced MR imaging for the detection of nodular disseminated lesions in patients with primary malignant brain tumors. Materials and Methods Subjects All human studies have been approved by the review board of the Medical Ethical Committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study. We reviewed and collected the record of having disseminated lesions of primary malignant brain tumors during post-treatment follow up in our MR database between March 2010 and March We found a total of 34 patients who met the record. The inclusion criteria were 1) patients with nodular disseminated lesions (type Ia, the presence of a mass lesion along the subarachnoid apace) based on the classification scheme of Bordignon 11 and 2) patients with lesions confirmed by pathology or follow-up MRI. The exclusion criteria were 1) patients with diffuse leptomeningeal (type Ib) and subepen dymal (type II) disseminated lesions, and very small nodular disseminated lesions that were not able to put a regionof-interest in a lesion and 2) patents with molecular treatment (e.g., bevacizumab) or administration of steroids. Thus, we finally included 12 patients (eight men, four women; age range, years old; mean age, 47 years) with disseminated lesions of primary malignant brain tumors in this study. According to the 2007 WHO classification, the malignant tumors included glioblastoma multiforme in five patients, anaplastic oligodendrglioma in two patients, and anaplastic ependymoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, giant cell glioblastoma, gliomatosis cerebri and primitive neuroectodermal tumor in one each. MR image acquisition We used 3T MR scanners (Magnetom Trio, Siemens; Achieva 3T, Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands) and an 8-channel head coil. The imaging sequences in this study included 3-plane scout localizers and axial spin-echo T 1 -weighted [TR/TE/number of signals averaged (NSA), 450 ms/10 ms/1; matrix, ; section thickness, 5 mm; intersection gap, 1 mm], turbo spin-echo T 2 -weighted (TR/ TE/NSA, 4060 ms/80 ms/1; turbo factor, 9; matrix, ; section thickness, 5 mm; intersection gap, 1 mm), and FLAIR images (TR/TE/NSA/TI, 9000 ms/120 ms/1/2500 ms; turbo factor 15; matrix, ; section thickness, 5 mm; intersection gap, 1 mm), DWI at b = 1000 and 3000 s/mm 2, and postcontrast T 1 -weighted and 3D gradient-echo images. The 3D gradient-echo MR imaging studies included 3D turbo field echo (TR/TE/NSA 450 ms/10 ms/1, matrix ) and magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition of gradient echo (TR/TE/TI 1900 ms/4.7 ms/900 ms, matrix ) sequences. DWI were acquired with a spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence (TR/TE/NSA, 3500 ms/63-74 ms/1; matrix, ; section thickness, 5 mm; intersection gap, 1 mm; sensitivity encoding factor, 2). The field of view was 23 cm on all MR images. The postcontrast 3D gradientecho MR images had a section thickness of 1 mm and no intersection gap. Image Evaluation Qualitative assessment The largest disseminated lesion per person was qualitatively and quantitatively assessed. Two radiologists (8 and 25 years of experience in neuroradiology, respectively) independently evaluated the presence of additional information on DWI at b = 1000 or 3000 s/mm 2 compared with postcontrast T 1 -weighted and 3D gradient-echo images. All DW images were analyzed in conjunction with the corresponding postcontrast MR images. All images were assessed on a PACS workstation. The presence of additional information on DW images compared with postcontrast MR images was evaluated with a 4-point scoring system, where 4 = The information about the presence of the lesions was provided only by using DW images, but not by using postcontrast studies, 3 = The conspicuity of the lesions was more apparent for DWI than postcontrast studies, 2 = DW images provided similar conspicuity of the lesions to postcontrast studies, 1 = The information about the presence of the lesions was provided only by using postcontrast studies, but not by using DW images. Quantitative assessment On DW images, one radiologist performed region-of-interest measurements of the signal intensity (SI) of nodular disseminated lesions and the adjacent cerebral cortex. The lesion-tobrain contrast ratio (LBCR) was calculated using the following formula: LBCR = SI lesion /SI brain, where SI lesion and SI brain are the SI of the lesion and adjacent cerebral cortex, respectively. Statistical Analysis The statistical significance of differences for the qualitative assessment was determined with the Wilcoxon-signed rank test. Measurement differences for the quantitative assessment were assessed with the paired t-test. Differences of P < 0.05 were considered significant. The levels of interobserver agreement between radiologist 1 and radiologist 2 were determined by calculating the κ coefficient (κ < 0.20 indicated poor agreement; κ = , fair agreement; κ = , moderate agreement; κ = , good agreement; κ = , very good agreement; and κ > 0.90, excellent agreement) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A statistical package (MedCalc; MediSoftware, Mariakerke, Belgium) was used to perform the calculations. 218 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
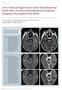
3 Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Disseminated Lesions Results The summary of the qualitative assessment for 12 disseminated lesions of 12 patients is shown in Table 1. Readers 1 and 2, respectively, assigned grade 3 in 2 (17%) and 1 (8%) DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 studies and 4 (33%) and 5 (42%) DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 studies (Figs. 1 and 2). For the reader 2, the mean score was significantly higher for b = 3000 s/mm 2 than b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.05). For the reader 1. there was no significant statistical difference between the two types of DWI. Interobserver agreement for DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 and b = 3000 s/mm 2 was very good (κ = 0.85; 95% CI, Table 1. Summary of the qualitative assessment in 12 patients with tumor dissemination DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 Interobserver DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 Case Reader 1 Reader 2 agreement* Reader 1 Reader Intermodality agreement* κ = κ = ( ) 3 3 ( ) Mean 1.75 ± ± 0.62* 2.08 ± ± 0.83* The number of readers indicates grading score, where 4 = The information about the presence of the lesions was provided only by using DW images, but not by using postcontrast studies, 3 = The conspicuity of the lesions was more apparent for DWI than postcontrast studies, 2 = DW images provided similar conspicuity of the lesions to postcontrast studies, 1 = The information about the presence of the lesions was provided only by using postcontrast studies, but not by using DW images. For the reader 2, the mean score was significantly higher for b = 3000 s/mm 2 than b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.05). For the reader 1. There was no significant statistical difference between the two types of DWI. *: interobserver agreement between reader 1 and reader 2, Data are κ statistics, with 95% CIs in parentheses. A C B D Fig 1. MR images at the level of the splenium of the corpus callosum in a 49-year-old woman with giant cell glioblastoma (case 8). Postcontrast 3D gradient-echo image (A) shows a small enhanced lesion (arrow) adjacent to the inferomedial part of the right parietal lobe. Diffusion-weighted image at b = 1000 s/mm 2 (B) demonstrates a slight hyperintense area (arrow) corresponding to the contrast-enhanced lesion. One reviewer ranked the image as grade 3 and the other as grade 2. Diffusion-weighted image at b = 3000 s/mm 2 (C) shows a definite hyperintense lesion (arrow) corresponding to the contrast-enhanced lesion. Both reviewers ranked the image as grade 3. Postcontrast 3D gradient-echo image (D) after 3 months reveals enlargement of the lesion (arrow). Vol. 16, No
4 Y. Kadota et al. A B Table 2. Summary of lesion-to-brain contrast ratio (LBCR) for 12 disseminated lesions Case DWI b = 1000 s/mm 2 b = 3000 s/mm Mean 1.33 ± ± 0.32 The lesion-to-brain contrast ratio (LBCR) was calculated using the following formula: LBCR = SI lesion /SI brain, where SI lesion and SI brain are the SI of the lesion and adjacent cerebral cortex, respectively. The mean LBCR score was significantly higher for DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 than DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.01). C ) and excellent (κ = 0.93; 95% CI, ), respectively. The quantitative assessment for 12 disseminated lesions is shown in Table 2. The mean LBCR score was significantly higher for DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 than DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 (P < 0.01). Fig 2. MR images at the level of the pons in an 11-year-old boy with primitive neuroectodermal tumor (case 12). Postcontrast 3D gradient-echo image (A) shows a lesion (arrow) adjacent to the anteromedial part of the left temporal lobe. The lesion adjacent to a vessel (arrow head) shows very subtle enhancement. Diffusion-weighted image at b = 1000 s/mm 2 (B) demonstrates a slight hyperintense lesion (arrow) corresponding to the slightly-enhanced lesion. The vessel adjacent to the lesion is completely suppressed. Both reviewers ranked the image as grade 2. Diffusion-weighted image at b = 3000 s/mm 2 (C) shows a remarkable hyperintense lesion (arrow) corresponding to the slightly-enhanced lesion. Both reviewers ranked the DWI as grade 3. This lesion was surgically resected and confirmed by pathological examination. Discussion For detecting nodular disseminated lesions of primary malignant brain tumors in our study, 3T DWI was able to provide additional information relative to postcontrast MR studies. This may be due to the following reasons. On postcontrast MR studies including postcontrast 3D gradient-echo images, insufficiently-enhanced disseminated lesions like our cases may be difficult to detect. In such situations, DWI may be especially useful for detecting the lesions. On the other hand, some well-enhanced disseminated lesions may be missed on postcontrast MR images because of their overlap with enhanced superficial vessels. As DWI suppresses the signal of intracranial vasculatures and provides a more uniform background, it may make disseminated lesions easier to detect. When evaluating disseminated lesions from primary malignant brain tumors, 3T DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 provided more additional information than at b = 1000 s/mm 2. In addition, interobserver agreement was higher at b = 3000 s/mm 2 than b = 1000 s/mm 2. This advantage of DWI at 3000 s/mm 2 is 220 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
5 Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Disseminated Lesions considered to be attributed to the following reasons. A higher b-value DWI provides better contrast with its reflection of more tissue diffusivity and less T 2 shine-through effect. 12,13 Then, DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 provide less signal of the cerebral cortices compared with DWI at b = 1000 s/mm 2 which would make more contrast between the disseminated lesion and the cortices. 10 Among various high-b-values on DWI, we selected b = 3000 s/mm 2. On DWI, the signal-to-noise ratio of the brain decreases as the b-value increases At b = 3000 s/mm 2, the signal of the gray matter is suppressed and the signal-tonoise ratio of the brain is appropriate at 3T. 10 Therefore, b = 3000 s/mm 2 was chosen as the most appropriate high-b-value in our study. Antiangiogenic therapies (e.g., bevacizumab) and steroid administration reduce the degree of contrast enhancement of gliomas. 16,17 In patients with such situations, DWI might be useful for evaluating disseminated lesions of primary malignant brain tumors. Further studies are required to clarify the clinical role of DWI in patients with antiangiogenic therapies and/or steroid administration. There are some limitations in our study. First, our patient population was relatively small and only the largest lesion was assessed. However, our study warrants further studies on large numbers of patients to clarify the clinical role of 3T DWI. Second, we did not assess the ADC value for the disseminated lesions. ADC maps have poorer tissue contrast than diffusion-weighted images. In patients with disseminated lesions, prompt and easy identification and localization of brain lesions are primarily important for making the accurate diagnosis. Therefore, we did not use ADC maps for this reader observation study. Third, we only evaluated nodular disseminated lesions (type Ia, the presence of a mass lesion along the subarachnoid apace) based on the classification scheme of Bordignon. 11 We did not include very small disseminated lesions and diffuse leptomeningeal (type Ib) and subependymal (type II) disseminated lesions in this study. DWI might have additional values for detecting these disseminated lesions. Further investigations with very small lesions and various types of disseminated lesion are needed to clarify the role of DWI in a clinical setting. Fourth, we did not evaluate the effect of tumor type on diffusion restriction. Some types of disseminated lesions (e.g., tumor with small round cell) may show high-signal intensity on DWI. Further studies are needed to clarify the effect of tumor type on the detection of disseminated lesions. Fifth, we did not evaluate postcontrast 3D fast spin-echo T 1 -weighted- and 3D FLAIR images. When evaluating leptomeningeal lesions, these 3D MR images may be more useful than 3D gradient-echo MR images. 18,19 Further investigations with the 3D MR images are needed to clarify the usefulness of DWI for detecting disseminated lesions. In conclusion, 3T DWI can provide additive information relative to contrast-enhanced MR imaging for the detection of nodular disseminated lesions from primary malignant brain tumors. In certain cases, 3T DWI at b = 3000 s/mm 2 may provide more additional information than b = 1000 s/mm 2. Although contrast-enhanced MR studies are the gold standard method for evaluating disseminated lesions, DWI may have a complementary role to the contrast-enhanced MR studies. Conflicts of Interest We declare that we have no conflict of interest. References 1. Saito R, Kumabe T, Jokura H, Shirane R, Yoshimoto T. Symptomatic spinal dissemination of malignant astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 2003; 61: Parsa AT, Wachhorst S, Lamborn KR, et al. Prognostic significance of intracranial dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme in adults. J Neurosurg 2005; 102: Glass JP, Melamed M, Chernik NL, Posner JB. Malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): the meaning of a positive CSF cytology. Neurology 1979; 29: Chamberlain MC. Neoplastic meningitis. Oncologist 2008; 13: Schaefer PW, Copen WA, Lev MH, Gonzalez RG. Diffusionweighted imaging in acute stroke. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2005; 15: Shiga Y, Miyazawa K, Sato S, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as an early diagnostic marker for Creutzfeldt- Jakob disease. Neurology 2004; 63: Schaefer PW. Diffusion-weighted imaging as a problemsolving tool in the evaluation of patients with acute stroke like syndromes. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 11: Hyare H, Thornton J, Stevens J, et al. High-b-value diffusion MR imaging and basal nuclei apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in variant and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010; 31: Toyoda K, Kitai S, Ida M, et al. Usefulness of high-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging in acute cerebral infarction. Eur Radiol 2007; 17: Iwashita K, Hirai T, Kitajima M, et al. Added value of highb-value (b = 3000 s/mm 2 ) diffusion-weighted imaging at 3T in relation to fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images for the evaluation of cortical lesions in inflammatory brain diseases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2013; 37: Bordignon KC, Neto MC, Ramina R, de Meneses MS, Zazula AD, de Almeida LG. Patterns of neuroaxis dissemination of gliomas: suggestion of a classification based on magnetic resonance imaging findings. Surg Neurol 2006; 65: DeLano MC, Cooper TG, Siebert JE, Potchen MJ, Kuppusamy K. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of adult brain: image contrast and apparent diffusion coefficient map features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000; 21: Vol. 16, No
6 Y. Kadota et al. 13. Burdette JH, Durden DD, Elster AD, Yen YF. High b-value diffusion-weighted MRI of normal brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2001; 25: Yoshiura T, Wu O, Zaheer A, Reese TG, Sorensen AG. Highly diffusion-sensitized MRI of brain: dissociation of gray and white matter. Magn Reson Med 2001; 45: Cihangiroglu M, Ulug AM, Firat Z, Bayram A, Kovanlikaya A, Kovanlikaya I. High b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of normal brain at 3T. Eur J Radiol 2009; 69: Gerstner ER, Frosh MP, Batchelor TT. et al. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging detects pathologically confirmed, nonenahncing tumor progression in a patient with recurrent gliomblastoma receiving bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28:e91 e Zaki HS, Jenkinson MD, Du Plessis DG, Smith T, Rainov NG. Vanishing contrast enhancement in malignant glioma after corticosteroid treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2004; 146: Kato Y, Higano S, Tamura H, et al. Usefulness of contrastenhanced T 1 -weighted sampling perfection with appli cationoptimized contrasts by using different flip angle evolutions in detection of small brain metastasis at 3T MR imaging: comparison with magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition of gradient echo imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009; 30: Fukuoka H, Hirai T, Okuda T, et al. Comparison of the added value of contrast-enhanced 3D fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition of gradient echo sequences in relation to conventional postcontrast T 1 -weighted images for the evaluation of leptomeningeal diseases at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010; 31: Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0098 Published Online: November 29, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0098 Published Online: November 29, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography at 3T
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 335 339, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2015-0081 TECHNICAL NOTE Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 335 339, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2015-0081 TECHNICAL NOTE Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a sensitive technique
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging in Pediatric Bell s Palsy
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
Masayuki Maeda, Tatsuya Yamamoto, Shouichiro Daimon, Hajime Sakuma, and Kan Takeda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time FLAIR at 3T
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:88-94 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.88 Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:88-94 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.88 Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer: Optimal B Value at 3T
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.61 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2013;14(1):61-69 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.61 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2013;14(1):61-69 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the
 Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4
 Biopsy Tracking and MRI Fusion to Enhance Imaging of Cancer Within the Prostate D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4 1 Dept. of Radiology, UCLA, Los
Biopsy Tracking and MRI Fusion to Enhance Imaging of Cancer Within the Prostate D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4 1 Dept. of Radiology, UCLA, Los
Perfusion MR imaging with the DSC method is widely used
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai M. Kitajima H. Nakamura T. Okuda A. Sasao Y. Shigematsu D. Utsunomiya S. Oda H. Uetani M. Morioka Y. Yamashita Quantitative Blood Flow Measurements in Gliomas Using Arterial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai M. Kitajima H. Nakamura T. Okuda A. Sasao Y. Shigematsu D. Utsunomiya S. Oda H. Uetani M. Morioka Y. Yamashita Quantitative Blood Flow Measurements in Gliomas Using Arterial
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Detection of skeletal metastasis is important in cancer staging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.J. Nemeth J.W. Henson M.E. Mullins R.G. Gonzalez P.W. Schaefer Improved Detection of Skull Metastasis with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Metastasis to the skull
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.J. Nemeth J.W. Henson M.E. Mullins R.G. Gonzalez P.W. Schaefer Improved Detection of Skull Metastasis with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Metastasis to the skull
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection?
 CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(1):24-29 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.1.24 Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection? Mohammed
CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(1):24-29 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.1.24 Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection? Mohammed
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors.
 Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
Ischemic strokes are estimated to happen during sleep in
 Can Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Mismatch (Positive Diffusion-Weighted Imaging/ Negative Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery) at 3 Tesla Identify Patients With Stroke
Can Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Mismatch (Positive Diffusion-Weighted Imaging/ Negative Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery) at 3 Tesla Identify Patients With Stroke
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
Meningiomas are the second most common primary intracranial
 Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke
 Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department
 298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality
 The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes
 JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
Comparison of MERGE and Axial T2-Weighted Fast Spin-Echo Sequences for Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in the Cervical Spinal Cord
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Role of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of intra and extra axial intracranial lesions
 International Surgery Journal Chakra VV et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3107-3112 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173897
International Surgery Journal Chakra VV et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3107-3112 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173897
Comparative Study of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Imaging at 3.0 Tesla in Brain Tumors
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-0376.100018 Neuro-Oncology: Open Access Comparative Study of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and Dynamic Susceptibility
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-0376.100018 Neuro-Oncology: Open Access Comparative Study of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and Dynamic Susceptibility
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms
 New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
Management of Tiny Meningiomas: To Resect or Not Resect
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1514 Management of Tiny Meningiomas: To Resect or Not Resect Julia R. Schneider 1, Kay O. Kulason 1, Tim White 2, Bidyut Pramanik 3, Shamik Chakraborty 1, Linda
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1514 Management of Tiny Meningiomas: To Resect or Not Resect Julia R. Schneider 1, Kay O. Kulason 1, Tim White 2, Bidyut Pramanik 3, Shamik Chakraborty 1, Linda
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls.
 Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study
 Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas: Does Lower ADC Predict a Worse Prognosis Independent of Grade of Tumor?
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
Waneerat Galassi, Warinthorn Phuttharak, John R. Hesselink, John F. Healy, Rosalind B. Dietrich, and Steven G. Imbesi
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Case 9 10/29/2018. CJD (Creutzfeldt -Jakob Disease) CJD (Creutzfeldt -Jakob Disease) CJD (Creutzfeldt -Jakob Disease)
 CJD (Creutzfeldt -Jakob Disease) Rare fatal neurodegen dz caused by infectious protein Prion (lacks nucleic acid)- causes spongiform changes of the brain and neuronal death. 4 types: scjd- 85% of cases
CJD (Creutzfeldt -Jakob Disease) Rare fatal neurodegen dz caused by infectious protein Prion (lacks nucleic acid)- causes spongiform changes of the brain and neuronal death. 4 types: scjd- 85% of cases
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Comparison of Different Post-Processing Algorithms for Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion Imaging of Cerebral Gliomas
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 129 136 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0036 Published Online: September 20, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Comparison of Different Post-Processing Algorithms for Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 129 136 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0036 Published Online: September 20, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Comparison of Different Post-Processing Algorithms for Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast
CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]
![CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE] CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]](/thumbs/86/94270487.jpg) ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
DWI that measures overall diffusivity in terms of directionally
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Altought liver (75%) and lung (15%) are the most commonly involved
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Biopsy-Proven Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging has been reported to be a sensitive and specific method in the diagnosis of disease of the sub-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
imri 2017;21:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
HNSCC accounts for 5% of all malignancies. 1 Head and
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H. Verhappen P.J.W. Pouwels R. Ljumanovic L. van der Putten D.L. Knol R. De Bree J.A. Castelijns Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer: Comparison between Half-Fourier
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H. Verhappen P.J.W. Pouwels R. Ljumanovic L. van der Putten D.L. Knol R. De Bree J.A. Castelijns Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer: Comparison between Half-Fourier
Enormous effort has been invested in clinical trials for malignant
 Published February 13, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0963 REVIEW ARTICLE J.W. Henson S. Ulmer G.J. Harris Brain Tumor Imaging in Clinical Trials SUMMARY: There are substantial challenges in the radiologic evaluation
Published February 13, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0963 REVIEW ARTICLE J.W. Henson S. Ulmer G.J. Harris Brain Tumor Imaging in Clinical Trials SUMMARY: There are substantial challenges in the radiologic evaluation
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Cholesteatoma is a collection of keratinous debris lined by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H.G. Dremmen P.A.M. Hofman J.R. Hof R.J. Stokroos A.A. Postma The Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Detection of Residual and/or Recurrent Cholesteatoma
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H.G. Dremmen P.A.M. Hofman J.R. Hof R.J. Stokroos A.A. Postma The Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Detection of Residual and/or Recurrent Cholesteatoma
High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI
 High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Objective: Compared to dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), image quality in diffusion-weighted
High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Objective: Compared to dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), image quality in diffusion-weighted
Meningiomas account for between 16% and 20% of primary
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
