Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome*
|
|
|
- Warren Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
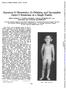
1 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 322. Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome* MIRIAM G. WILSONt, JOHN MELNYK, and JOSEPH W. TOWNER Fronm University of Southern California School of Medicine, Los Angeles County- University of Southern California Medical Center, and Children's Hospital of Los Angeles, U.S.A. Retinoblastoma has been reported in 3 subjects whose karyotypes showed partial deletion of the long arm of a D (13-15) chromosome (Lele, Penrose, and Stallard, 1963; Thompson and Lyons, 1965; Van Kempen, 1966). The child reported here is an additional case of retinoblastoma with partial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 14. Case Report A Caucasian girl was first seen at this hospital at 18 months of age with bilateral retinoblastoma, complete midline cleft of the secondary palate, and eczematoid dermatitis. There was moderate retardation of development and growth. This child had been born at term, weighing 3150 g., after an uncomplicated gestation and delivery. She was born to a healthy 20-year-old primigravida mother. The age of the father is unknown. Since the birth of this child, the mother has had two normal children. The three children have had different fathers. There was no maternal family history of retinoblastoma, congenital malformations, or mental retardation. Information about the father was unknown or withheld. The infant ate poorly and gained weight slowly. At 1 year of age, clouding of the right pupil was noted. The child crawled at 15 months, stood with support at 17 months, and walked alone at 20 months. Medical history included two episodes of uncomplicated pneumonia, recurrent otitis media, intermittent asthma, and persistent eczematoid dermatitis. On admission at 18 months of age, the child's right eye, which was extensively invaded by tumour, was enucleated. Post-operative treatment included irradiation with 3250 rads (total) to both orbits, intracarotid artery injection of triethylenemelamine (0-08 mg./kg.), and photocoagulations of the tumour in the left eye, followed by enucleation. Microscopical examination of the enucleated tissue from both eyes showed active retinoblastoma extending into the choroid and vitreous. Physical Examination. At this time (January, 1968) the child is 51 years of age and presents an attractive appearance, except for temporary orbital prostheses (Fig. 1). Height and weight are less than the 3rd percentile for age. The teeth are at a normal developmental stage for age, but are irregularly shaped, stubby, and carious. There are transverse palmar creases. The only other evident anomaly is the cleft palate. She feeds herself without assistance and is toilet trained. Her motor abilities represent her least retarded behaviour; she runs and participates in games. Her vocabulary, however, is less than 10 words, and her general behavioural quotient is estimated at by Gesell developmental testing. Laboratory and Investigative Studies. Normal laboratory studies included blood counts, urine analysis, serum proteins, serum bilirubin, prothrombin, and alkaline phosphatase. Blood type was AjRh positive. Normal percentages of haemoglobins F and A2 in peripheral blood were found by column chromatographic techniques. Amino acid screening tests of urine and plasma yielded normal results. X-rays of the skull, Received December 5, * This study was supported by project grants 322 and 422 from the Children's Bureau. t Address: Department of Pediatrics, Los Angeles County- University of Southern California Medical Center, 1200 North State FIG. 1. Patient at 5* years of age. Temporary orbital prostheses Street, Los Angeles, California 90033, U.S.A. are in place. 322
2 .~~~~~~~~ 3 Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome A...~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... *3.: ' xx 22; (; Sl FIG. 2. Karyotype of leucocyte culture from the patient. The arrow indicates the deleted D chromosome. cervical and thoracic vertebrae, chest, and limbs were normal. An electroencephalogram was normal. Cytogenetic Studies. The buccal smear was sex chromatin positive. The Barr bodies in the positive cells were single and of normal size. Karyotypes were examined from three peripheral blood cultures; the results are summarized in Table I. The modal number of chromosomes was 46, and the karyotype showed an XX female pattern. In all 87 cells analysed, there were only 5 normal appearing chromosomes of the D (13-15) group. An unpaired acrocentric chromosome which TABLE I CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS FROM PATIENT AND MOTHER Chromosome No. of Cells No./Cell 4444r or Coun--An- Ana-I Analysis fewer ted lysed Patient Leucocyte cultures 4* 4* ,XX,?14p- (No. =3) Mother Leucocyte culture 1* ,XX (No. = 1) *Random loss. a. 323 was intermediate in size between a D-group and G- group chromosome was assumed to be a D chromosome with about one-quarter deletion of the long arm (Fig. 2). Autoradiographic studies were done on the peripheral blood cultures by the technique described by Schmid (1965) which uses continuous labelling with tritiated thymidine. A total of 30 cells was considered satisfactory for analysis. Autoradiography did not always clearly differentiate the three labelling patterns of the D chromosomes; however, the majority of analyses indicated that the deleted D was most likely chromosome 14 (Table II). These interpretations were based on the previously described labelling patterns of the D-group chromosomes (Yunis, Hook, and Mayer, 1964; Giannelli, 1965). Autoradiographic labelling of the D-group of chromosomes from 5 cells is illustrated in Fig. 3. The karyotype of the patient is expressed as 46,XX, 14q -, according to the notation of the Chicago TABLE II AUTORADIOGRAPHIC IDENTIFICATION OF DELETED D CHROMOSOME 13 Chromosome 13 or or No. of Cells Total=30
3 324 Conference (1966). Cytogenetic studies from other tissues of the patient were not permitted. Chromosomal analysis from the mother's peripheral blood culture showed a normal 46,XX pattern (Table I). The father and the two half-sibs were not available for examination. Dermatoglyphs. The dermatoglyphs of the patient are illustrated in Fig. 4. The dermatoglyphs were unusual in that the total ridge count was only 31, average for females being 127, with a standard deviation of 53 (Holt, 1961). The low ridge count was due to arches on five fingers, a vestigial radial loop on the second finger of FIG. 3. Autoradiographs of five D-group chromosomes. Labelling pattern is most consistent with chromosome 14. Wilson, Melnyk, and Towner the right hand, and a vestigial ulnar loop on the fifth finger of the right hand. The case reported by Lele et al. (1963) had four arches. Only the thumbs and the fourth right finger of our patient had patterns; these were small ulnar loops. There were a single transverse palmar crease and a less developed transverse crease distally on both palms. The proximal axial triradii were not elevated distally. Both hypothenar regions showed loops opening towards the ulnar side. There was a loop in the third interdigital area. The hallucal area of both feet showed distal loops. The case reported by Lele et al. (1963) showed a whorl on one foot and a loop opening towards the tibial margin on the other. Discussion Descriptions of the four children with retinoblastoma associated with partial deletion of a D chromosome are in Table III. These children were retarded in growth and development, with the possible exception of the patient described by Lele et al. (1963), who appeared normal except for an initial delay in development. The extent of followup is, however, not known in this instance. Cleft palate and transverse palmar creases were found in our patient and in the patient described by Thompson and Lyons (1965). An increased proportion of arches on the fingers was found in our patient and the child described by Lele et al. (1963). There were no other congenital anomalies that these patients had in common. Our patient and the child described by Lele et al. (1963) were the least affected. Except for poor feeding and slow weight gain, these two children seemed generally healthy up to the time that the diagnosis of retinoblastoma was made. It has been believed that detectable autosomal deletions are usually associated with non-viability or severe abnormality in the affected subject (Lancet, 1965). The relatively few congenital defects in these two patients show that a detectable amount of chromosomal material may be missing from chromosome 14 without severe, multiple abnormalities. An alternative explanation is that some of the deleted material has been translocated to another chromosome where it is not noticeable. The cases reported by Thompson and Lyons (1965) and Van Kempen (1966) showed many congenital anomalies. Karyotypes from peripheral blood cultures from these two patients were interpreted as showing abnormalities in addition to the deleted D chromosome. Chromosomal analyses of the parents and sibs in the above cases were not always reported. The
4 Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome FIG. 4. Dermatoglyphs from hand and foot prints. TABLE III DESCRIPTION OF 4 CASES OF RETINOBLASTOMA AND DELETION-D SYNDROME Present Case Lele el al. (1963) Thomson and Lyons Van Kempen (1966) l l (1965) Sex F F M M Maternal age (yr.) Paternal age (yr.) Unknown Gestation Term Not stated 40 wk. Term Birthweight (g.) 3150 Not stated Status at time of report Alive at 54 yr. Alive at 10 + mth. Death at 3 yr. Alive at 6 yr. Abnormalities* Retinoblastoma, bilat. Retinoblastoma, bilat. Retinoblastoma, OD Retinoblastoma, bilat. (Dx at 18 mth.); (Dx at 10 mth.); (Dx at 19 mth.); (Dx at 6 mth.); mental retardation slow development mental retardation (severe); mental retardation (est. IQ 30-50); Growth retardation; (moderate to severe); growth retardation; hypotonia; Growth retardation; cleft palate; convulsions; antimongoloid slants; transverse palmar hirsutism; epicanthal folds; creases; microcephaly; dental caries; eczematoid dermatitis; micropthalmia; high arched palate; dental dysplasia colobomata; small testes; malformed ears; multiple skeletal anomalies high arched and cleft palate; cryptorchidism; hypospadias; multiple skeletal anomalies; transverse palmar creases Dermatoglyphs Arches on 5 fingers Arches on 4 fingers; Stated to be abnormal Not reported arch tibial on one foot Chromosome studies Tissue Blood Blood, skin, tumour, Blood Blood conjunctiva Analysis 46,XX,D(14)q - 46,XX,Dq - 46,XY,Dq - /46,XY,t(C;D) 46,XY,Dq-,t(2;C) Sex chromatin Positive Not reported Not reported Negative Chromosome studies Mother normal; Normal Mother 46,XX/46,XX,Dq-; Not reported on parents father not available father normal *Significant features found in more than one patient are in italics. Dx = diagnosis. 325
5 326 father of our patient was not available for examination. Van Kempen (1966) reported no chromosomal studies from the parents of his case. The karyotypes of the parents of the case reported by Lele et al. (1963) were normal. The mother of the child reported by Thompson and Lyons (1965) showed a partial deletion of one of the D chromosomes in some cells; therefore, in this instance it is assumed that the deleted D was an inherited abnormality. Retinoblastoma has not been associated with deletion short arm D (Grouchy et al., 1966; Bias and Migeon, 1967), deletion of long arm D (Bloom, Gerald, and Diamond, 1966; Laurent et al., 1967; Taylor, 1968); and ring-d chromosomes (Wang et al., 1962; Turner, 1963; Bain and Gauld, 1963; Macintyre et al., 1964; Adams, 1965; Reisman, Darnell, and Murphy, 1965; Jacobsen, 1966; Gerald et al., 1967; Teplitz et al., 1967; Sparkes, Carrel, and Wright, 1967; Lejeune et al., 1968). Autoradiography was done in 5 cases; two deletions and two ring chromosomes appeared to consist of a No. 13 (Bias and Migeon, 1967; Bloom et al., 1966; Gerald et al., 1967; Reisman et al., 1965; Bloom, Gerald, and Reisman, 1967); while the ring reported by Sparkes et al. (1967) was a chromosome 14. Presumably a ring chromosome is formed after deletions at both ends of a single chromosome; the ends then unite in a ring. A different portion of the chromosome may be lost if a deletion is intercalary in position. The clinical features of the child described by Sparkes et al. (1967) did not resemble our patient. Retinoblastoma is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. This is the fourth report in which the tumour has been found in association with a gross chromosomal abnormality. In these patients, congenital abnormalities and mental retardation were found, but were not always so severe as to interfere with reproduction by the affected subject. Most patients with retinoblastoma do not show congenital abnormalities and those who have been studied have normal karyotypes; thus the syndrome of deletion of chromosome D (14) does not contribute significantly to the total number of cases of retinoblastoma (Lele et al., 1963; Wiener, Reese, and Hyman, 1963; Fraser and Friedmann, 1967). Summary A girl with retinoblastoma, cleft palate, and retardation of growth and development is described. All the karyotypes from peripheral blood cultures of the patient showed a partial deletion of the long arm of a D chromosome. This is the fourth reported instance in which retinoblastoma has been Wilson, Melnyk, and Towner associated with this chromosomal structural defect, and the first in which the deleted chromosome was shown by autoradiography to be chromosome 14. Retinoblastoma and deletion of chromosome D (14) appears to be a verified chromosomal deletion syndrome, in which there may not be multiple severe anomalies. We are grateful to Mr. Paul Brager and Mr. William George for technical assistance; to Dr. Jamshed Mavalwala for analysing the dermatoglyphs; to Dr. Kenneth N. F. Shaw for amino acid screening; and to the numerous physicians who participated in the medical management of this child. REFERENCES Adams, M. S. (1965). Palm-prints and a ring-d chromosome. Lancet, 2, 494. Bain, A. D., and Gauld, I. K. (1963). Multiple congenital abnormalities associated with ring chromosome. ibid., 2, 304. Bias, W. B., and Migeon, B. R. (1967). Haptoglobin: A locus on the D1 chromosome? Amer. 7. hum. Genet., 19, 393. Bloom, G. E., Gerald, P. S., and Diamond, L. K. (1966). Autoradiographic analysis of the specific D chromosome bearing the haptoglobin locus. Soc. Pediat. Res. 36th Annual Meeting (Abstract).,-, and Reisman, L. E. (1967). Ring D chromosome: A second case associated with anomalous haptoglobin inheritance. Science, 156, Chicago Conference (1966). Standardization in Human Cytogenetics, Birth Defects: Original article series, 2, 1. Ed. by D. Bergsma, J. L. Hamerton, and H. P. Klinger. Fraser, G. R., and Friedmann, A. I. (1967). The Causes of Blindness in Childhood, pp Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore. Gerald, P. S., Warner, S., Singer, J. D., Corcoran, P. A., and Umansky, I. (1967). A ring D chromosome and anomalous inheritance of haptoglobin type. J7. Pediat., 70, 172. Giannelli, F. (1965). Autoradiographic identification of the D (13-15) chromosome responsible for D1 trisomic Patau's syndrome. Nature (Lond.), 208, 669. Grouchy, J. de, Salmon, C., Salmon, D., and Maroteaux, P. (1966). Deletion du bras court d'un chromosome 13-15, hypertelorism et phenotype haptoglobine Hp 0 dans une meme famille. Ann. Genit., 9, 80. Holt, S. B. (1961). Quantitative genetics of finger-print patterns. Brit. med. Bull., 17, 247. Jacobsen, P. (1966). A ring chromosome in the group associated with microcephalic dwarfism, mental retardation and emotional immaturity. Hereditas (Lund), 55, 188. Lancet (1965). Leading article. Chromosome deletions. 1, 472. Laurent, C., Cotton, J.-B., Nevelon, A., and Freycon, M-Th. (1967). Deletion partielle du bras lond d'un chromosome du groupe D (13-15). Ann. Genet., 10, 25. Lejeune, J., Lafourcade, J., Berger, R., Cruveiller, J., Rethore, M.-O., Dutrillaux, B., Abony, D., and Jerome, H. (1968). Le phenotype (Dr.). Atude de trois cas de chromosomes D en anneau. ibid., 11, 79. Lele, K. P., Penrose, L. S., and Stallard, H. B. (1963). Chromosome deletion in a case of retinoblastoma. Ann. hum. Genet., 27, 171. Macintyre, M. N., Hempel, J. M., Staples, W. I., and Stenchever, M. A. (1964). A ring chromosome in a human male with congenital anomalies. Anat. Rec., 148, 386. Reisman, L. E., Darnell, A., and Murphy, J. W. (1965). Abnormalities with ring chromosome. Lancet, 2, 445. Schmid, W. (1965). Autoradiography of human chromosomes. In Human Chromosome Methodology, pp Ed. by J. J. Yunis. Academic Press, New York. Sparkes, R. S., Carrel, R. E., and Wright, S. W. (1967). Absent thumbs with a ring D2 chromosome. A new deletion syndrome. Amer. j. hum. Genet., 19, 644. Taylor, A. I. (1968). Autosomal trisomy syndromes: A detailed study of 27 cases of Edwards' syndrome and 27 cases of Patau's syndrome. J. med. Genet., 5, 227.
6 Teplitz, R. L., Miller, D., Hansson, K. M., and Rundall, T. S. (1967). A human ring D chromosome associated with multiple congenital abnormalities. 7. Pediat., 70, 936. Thompson, H., and Lyons, R. B. (1965). Retinoblastoma and multiple congenital anomalies, associated with complex mosaicism with deletion of D-chromosome and probable D/C translocation. Hum. Chromos. Newsl., 15, 21. Turner, B. (1963). Cytogenetic studies in mental retardation. Proc. Aust. Ass. Neurol., 1, 41. Van Kempen, C. (1966). A case of retinoblastoma, combined with Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome 327 severe mental retardation and a few other congenital anomalies, associated with complex aberrations of the karyotype. Maandschr. Kindergeneesk., 34, 92. Wang, H.-C., Meinyk, J., McDonald, L. T., Uchida, I. A., Carr, D. H., and Goldberg, B. (1962). Ring chromosomes in human beings. Nature (Lond.), 195, 733. Wiener, S., Reese, A. B., and Hyman, G. A. (1963). Chromosome studies in retinoblastoma. Arch. Ophthal., 69,311. Yunis, J. J., Hook, E. B., and Mayer, M. (1964). Deoxyribonucleicacid replication pattern of trisomy D1. Lancet, 2, 935. J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 September Downloaded from on 17 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Ring 13 Chromosome with Normal Haptoglobin -Inheritance*
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 222. Ring 13 Chromosome with Normal Haptoglobin -Inheritance* JOSEPH G. HOLLOWELL,t L. GAYLE LITTLEFIELD, AYUT DHARMKRONG-AT, GORDON M. FOLGER, CLARK W. HEATH Jr,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 222. Ring 13 Chromosome with Normal Haptoglobin -Inheritance* JOSEPH G. HOLLOWELL,t L. GAYLE LITTLEFIELD, AYUT DHARMKRONG-AT, GORDON M. FOLGER, CLARK W. HEATH Jr,
Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males*
 J. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 112. Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males* H. HUNTER From Balderton Hospital, Balderton, Nr. Newark, Notts. Holt in 1955 provided evidence that total finger ridge
J. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 112. Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males* H. HUNTER From Balderton Hospital, Balderton, Nr. Newark, Notts. Holt in 1955 provided evidence that total finger ridge
Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages,
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 345. Comments on Patients with Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages, Xga Blood Group DIGAMBER S. BORGAONKAR and EMILIE MULES From the Division
Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 345. Comments on Patients with Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages, Xga Blood Group DIGAMBER S. BORGAONKAR and EMILIE MULES From the Division
Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 457. Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family RINA SCHMIDT, GEORGE MUNDEL, MALKA ROSENBLATT, and MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON
Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 457. Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family RINA SCHMIDT, GEORGE MUNDEL, MALKA ROSENBLATT, and MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON
XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 140. Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of the Long Arm of Chromosome No. 18* J. INSLEY From the Institute of Child Health, Francis Road, Birmingham 16 In 1964
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 140. Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of the Long Arm of Chromosome No. 18* J. INSLEY From the Institute of Child Health, Francis Road, Birmingham 16 In 1964
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships of the Blood Groups and Types with Hand Patterns and Handedness
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 43, Issue 4 (July, 1943) 1943-07 An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 43, Issue 4 (July, 1943) 1943-07 An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships
Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome Associated with an Unusual Abnormality of Chromosome No. 4*
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 164. Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome Associated with an Unusual Abnormality of Chromosome No. 4* MIRIAM G. WILSON,t JOSEPH W. TOWNER, and LYNN D. NEGUS From University of
Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 164. Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome Associated with an Unusual Abnormality of Chromosome No. 4* MIRIAM G. WILSON,t JOSEPH W. TOWNER, and LYNN D. NEGUS From University of
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab
 Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Case 1B. 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21)
 Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Educational Items Section
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Chromosome Disease. The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental
 Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 195. Mental Retardation, Unusual Facies, and Abnormal Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases VICTOR DUBOWITZ, PATRICIA
Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 195. Mental Retardation, Unusual Facies, and Abnormal Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases VICTOR DUBOWITZ, PATRICIA
A. Definitions... CD-157. B. General Information... CD-158
 CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
Down's syndrome phenotype and. child with presumed (X;21) de novo. autosomal gene inactivation in a. translocation
 144 Down's syndrome phenotype and autosomal gene inactivation in a child with presumed (X;21) de novo translocation SUMMARY A 32-year-old female with clinical features of Down's syndrome was found to have
144 Down's syndrome phenotype and autosomal gene inactivation in a child with presumed (X;21) de novo translocation SUMMARY A 32-year-old female with clinical features of Down's syndrome was found to have
Immunological Profile in a Chromosome 18 Deletion Syndrome with IgA Deficiency
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 388. Immunological Profile in a Chromosome 18 Deletion Syndrome with IgA Deficiency SARA C. FINLEY, MAX D. COOPER, WAYNE H. FINLEY, IRENE A. UCHIDA, THOMAS A. NOTO, and ROY F.
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 388. Immunological Profile in a Chromosome 18 Deletion Syndrome with IgA Deficiency SARA C. FINLEY, MAX D. COOPER, WAYNE H. FINLEY, IRENE A. UCHIDA, THOMAS A. NOTO, and ROY F.
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
ISSN CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR
 J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
A RING D CHROMOSOME IN ASSOCIATION WITH DOWN'S
 A RING D CHROMOSOME IN ASSOCIATION WITH DOWN'S SYNDROME-LIKE PHENOTYPE A. WAJNTAL*; A. J. DIAMENT**; P. H. SALDANHA* The first ring chromosome was described by Morgan (1933) 9 and originated from a crossing-over
A RING D CHROMOSOME IN ASSOCIATION WITH DOWN'S SYNDROME-LIKE PHENOTYPE A. WAJNTAL*; A. J. DIAMENT**; P. H. SALDANHA* The first ring chromosome was described by Morgan (1933) 9 and originated from a crossing-over
Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia*
 J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 96. Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia* P. H. FITZGERALD, P. E. CROSSEN, A. C. ADAMS, C. V. SHARMAN, and F. W. GUNZ From the Cytogenetics Unitt, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 96. Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia* P. H. FITZGERALD, P. E. CROSSEN, A. C. ADAMS, C. V. SHARMAN, and F. W. GUNZ From the Cytogenetics Unitt, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
Title. Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Chromosome Studies in 2 Patients with Suspected Cri Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 15(4): 706-711 Issue
Title Chromosome Studies in 2 Patients with Suspected Cri Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 15(4): 706-711 Issue
LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS PALACKIANAE OLOMUCENSIS FACULTAS RERUM NATURALIUM (2001 2002) BIOLOGICA 39 40 LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION Václav Hajn Department of Zoology
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS PALACKIANAE OLOMUCENSIS FACULTAS RERUM NATURALIUM (2001 2002) BIOLOGICA 39 40 LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION Václav Hajn Department of Zoology
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
and duodenal atresia. Two other families reported may have had the same syndrome. Case reports CASE 1 (III.8, FAMILY 1)
 JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Superior Intelligence in Sighted Retinoblastoma
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 331. Superior Intelligence in Sighted Retinoblastoma Patients and their Families* ROSWELL ELDRIDGE, KATHY O'MEARA, and DAVID KITCHIN From the Section on Genetics
Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 331. Superior Intelligence in Sighted Retinoblastoma Patients and their Families* ROSWELL ELDRIDGE, KATHY O'MEARA, and DAVID KITCHIN From the Section on Genetics
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns
 Am J Hum Genet 28:280-289, 1976 The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns HERMAN M. SLATIS,1 MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON,2 AND BATSHEVA BONNE-TAMIR3 Although there have been a few reports on the inheritance
Am J Hum Genet 28:280-289, 1976 The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns HERMAN M. SLATIS,1 MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON,2 AND BATSHEVA BONNE-TAMIR3 Although there have been a few reports on the inheritance
Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2001) : 24-31 24 Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension PS Igbigbi, BC Msamati, TM Ng ambi
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2001) : 24-31 24 Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension PS Igbigbi, BC Msamati, TM Ng ambi
Chromosome Mutations
 Chromosome Mutations Variation in Chromosome Number Euploidy: having full sets of chromosomes Haploid Diploid Triploid Aneuploidy: having anything other than full sets of chromosomes Monosomy Trisomy Variation
Chromosome Mutations Variation in Chromosome Number Euploidy: having full sets of chromosomes Haploid Diploid Triploid Aneuploidy: having anything other than full sets of chromosomes Monosomy Trisomy Variation
Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Chapter 15 Chromosomal Basis for Inheritance AP Biology Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed
Exam Chapter 15 Chromosomal Basis for Inheritance AP Biology Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed
Chapter 15 Chromosomes
 Chapter 15 Chromosomes Chromosome theory of inheritance Genes located on chromosomes = gene locus Thomas Hunt Morgan, Columbia Univ. Fly room Drosophila 100s of offspring 2n = 8 3 prs autosomes X and Y
Chapter 15 Chromosomes Chromosome theory of inheritance Genes located on chromosomes = gene locus Thomas Hunt Morgan, Columbia Univ. Fly room Drosophila 100s of offspring 2n = 8 3 prs autosomes X and Y
A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia
 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
Focal dermal hypoplasia
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 620 Focal dermal hypoplasia G. S. WILLETTS The County Hospital, York Attention was drawn by Goltz, Peterson, Gorlin, and Ravits (1962) to a rare syndrome of multiple congenital
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 620 Focal dermal hypoplasia G. S. WILLETTS The County Hospital, York Attention was drawn by Goltz, Peterson, Gorlin, and Ravits (1962) to a rare syndrome of multiple congenital
Human Genetic Mutations
 Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Familial Retinoblastoma: Segregation of Chromosome 13
 Am J Hum Genet 32:194-201, 1980 Familial Retinoblastoma: Segregation of Chromosome 13 in Four Families LOUISE A. KNIGHT,' H. ALLEN GARDNER,1 AND BRENDA L. GALLIE2 SUMMARY Fluorescent markers on chromosome
Am J Hum Genet 32:194-201, 1980 Familial Retinoblastoma: Segregation of Chromosome 13 in Four Families LOUISE A. KNIGHT,' H. ALLEN GARDNER,1 AND BRENDA L. GALLIE2 SUMMARY Fluorescent markers on chromosome
Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype
 Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype The Normal Human Karyotype The normal human karyotype is composed of SEVEN groups of chromosomes A G plus the sex chromosomes X and Y. The
Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype The Normal Human Karyotype The normal human karyotype is composed of SEVEN groups of chromosomes A G plus the sex chromosomes X and Y. The
Click on Karyotyping under human biology and read the Introduction page: 1. What causes a dark band on the chromosome?
 Karyotyping Activity Name: In this activity, you will use a computer model to look at chromosomes and prepare a karyotype. You will diagnose patients for abnormalities and learn the correct notation for
Karyotyping Activity Name: In this activity, you will use a computer model to look at chromosomes and prepare a karyotype. You will diagnose patients for abnormalities and learn the correct notation for
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Hirschsprung's disease
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
autosomal dominant mode of inheritance
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1982, 19, 104-109 A new variant of spondylometaphyseal dysplasia with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance J M GARCIA-CASTRO, C M ISALES-FORSYTHE, AND P DIAZ DE GARAU From
Journal of Medical Genetics 1982, 19, 104-109 A new variant of spondylometaphyseal dysplasia with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance J M GARCIA-CASTRO, C M ISALES-FORSYTHE, AND P DIAZ DE GARAU From
De Lange Syndrome: Report of a Case with an
 J. med. Genet. (1967). 4, 184. De Lange Syndrome: Report of a Case with an Unusual Karyotype J. M. BERG*, G. F. SMITH, M. A. C. RIDLER, B. D. McCREARYt, JANET A. FAUNCH, FAITH N. FARNHAM, and MARY L. ALLEN
J. med. Genet. (1967). 4, 184. De Lange Syndrome: Report of a Case with an Unusual Karyotype J. M. BERG*, G. F. SMITH, M. A. C. RIDLER, B. D. McCREARYt, JANET A. FAUNCH, FAITH N. FARNHAM, and MARY L. ALLEN
Chromosome pathology
 Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Longevity of a Woman With Down Syndrome: A Case Study. Brian Chicoine and Dennis McGuire
 Longevity of a Woman With Down Syndrome: A Case Study Brian Chicoine and Dennis McGuire Abstract: A case of a woman who is among the longest surviving people with Down Syndrome was described. The life
Longevity of a Woman With Down Syndrome: A Case Study Brian Chicoine and Dennis McGuire Abstract: A case of a woman who is among the longest surviving people with Down Syndrome was described. The life
Genetic Disorders. PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders. Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test
 Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Chromosomes and Gene Expression. Exceptions to the Rule other than sex linked traits
 Chromosomes and Gene Expression Exceptions to the Rule other than sex linked traits Chromosome Inactivation If girls have two X chromosomes, do they produce more proteins than boys with only one X chromosome???
Chromosomes and Gene Expression Exceptions to the Rule other than sex linked traits Chromosome Inactivation If girls have two X chromosomes, do they produce more proteins than boys with only one X chromosome???
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
chromosomal anomalies and mental pdf Chapter 8: Chromosomes and Chromosomal Anomalies (PDF) Chromosomal abnormalities -A review - ResearchGate
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALIES AND MENTAL RETARDATION FROM GENOTYPES TO NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL PHENOTYPES OF GENETIC SYNDROMES AT HIGH INCIDENCEGENOTYPE TO PHENOTYPE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page
DOWNLOAD OR READ : CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALIES AND MENTAL RETARDATION FROM GENOTYPES TO NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL PHENOTYPES OF GENETIC SYNDROMES AT HIGH INCIDENCEGENOTYPE TO PHENOTYPE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page
I handedness are in general agreement in finding slight but nevertheless 'real
 GENETIC INTERRELATIONSHIPS OF DERMATOGLYPHICS AND FUNCTIONAL HANDEDNESS' DAVID C. RIFE Ohio Stale University Received July 18, 1942 NVESTIGATORS of the relationships of dermatoglyphics and functional I
GENETIC INTERRELATIONSHIPS OF DERMATOGLYPHICS AND FUNCTIONAL HANDEDNESS' DAVID C. RIFE Ohio Stale University Received July 18, 1942 NVESTIGATORS of the relationships of dermatoglyphics and functional I
The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease Group (The Human Masukake- Gata) at Minangkabau Ethnic, West Sumatra, Indonesia
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2199 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (1): 9-14 (2016) Research Article The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2199 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (1): 9-14 (2016) Research Article The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 2: 16, December Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma
 Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Symphalangism. Symphalangism usually involves the proximal, interphalangeal
 Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION
 Original Research Article DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION Esther Yamuna N * 1, Dhanalakshmi V 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2017, Vol
Original Research Article DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION Esther Yamuna N * 1, Dhanalakshmi V 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2017, Vol
Finding New Friends Down Syndrome. Pedicases
 Finding New Friends Down Syndrome Pedicases Objectives List the diagnostic features of Down syndrome and its associated complications. Describe the role of the clinician in management of Down syndrome,
Finding New Friends Down Syndrome Pedicases Objectives List the diagnostic features of Down syndrome and its associated complications. Describe the role of the clinician in management of Down syndrome,
Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal
 Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Bio 100 Guide 08.
 Bio 100 Guide 08 http://images.andrewsmcmeel.com/media/3820/medium.jpg http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/n100/images/11nondisjunction.gif http://www.unm.edu/~vscience/images/hela%20karyotype%203%20(1000x).jpg
Bio 100 Guide 08 http://images.andrewsmcmeel.com/media/3820/medium.jpg http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/n100/images/11nondisjunction.gif http://www.unm.edu/~vscience/images/hela%20karyotype%203%20(1000x).jpg
Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY OF HAND: " MIRROR HAND " By M. MUKERJI, F.R.C.S. Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta Case Report.--S. B., aged 4 months, was born with eight fingers and no thumb on the left hand and
CONGENITAL ANOMALY OF HAND: " MIRROR HAND " By M. MUKERJI, F.R.C.S. Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta Case Report.--S. B., aged 4 months, was born with eight fingers and no thumb on the left hand and
Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness
 Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness Jerry G. Petroff & Madeline Appell Based on the work of.. Dr. Sarah Cawthon, M.D. What is Deaf-Blindness? the term deaf-blind, with respect to
Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness Jerry G. Petroff & Madeline Appell Based on the work of.. Dr. Sarah Cawthon, M.D. What is Deaf-Blindness? the term deaf-blind, with respect to
Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
with Orthopaedic Abnormalities
 7. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 215. XYY Sex Chromosomes in a Jamaican with Orthopaedic Abnormalities MARIGOLD J. THORBURN, WINSTON CHUTKAN, ROLF RICHARDS, and RUTH BELL From the University of the West Indies,
7. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 215. XYY Sex Chromosomes in a Jamaican with Orthopaedic Abnormalities MARIGOLD J. THORBURN, WINSTON CHUTKAN, ROLF RICHARDS, and RUTH BELL From the University of the West Indies,
Mutations. New inherited traits, or mutations, may appear in a strain of plant or animal.
 Genetic Mutations Mutations New inherited traits, or mutations, may appear in a strain of plant or animal. The first individual showing the new trait is called a mutant. 2 Types of Mutations Chromosomal
Genetic Mutations Mutations New inherited traits, or mutations, may appear in a strain of plant or animal. The first individual showing the new trait is called a mutant. 2 Types of Mutations Chromosomal
The basic methods for studying human genetics are OBSERVATIONAL, not EXPERIMENTAL.
 Human Heredity Chapter 5 Human Genetics 5:1 Studying Human Genetics Humans are not good subjects for genetic research because: 1. Humans cannot ethically be crossed in desired combinations. 2. Time between
Human Heredity Chapter 5 Human Genetics 5:1 Studying Human Genetics Humans are not good subjects for genetic research because: 1. Humans cannot ethically be crossed in desired combinations. 2. Time between
Tagawa, Masato; Harada, Naoki; Mori. is available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Mirror duplication of chromosome 21 syndrome. Egashira, Masanori; Kondoh, Tatsuro Tagawa, Masato; Harada, Naoki; Mori Pediatrics international,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Mirror duplication of chromosome 21 syndrome. Egashira, Masanori; Kondoh, Tatsuro Tagawa, Masato; Harada, Naoki; Mori Pediatrics international,
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE. Dr Rasime Kalkan
 SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
Dermatoglyphic patterns, very low birth weight, and blood pressure in adolescence
 F18 FSID Unit of Perinatal and Paediatric Epidemiology, Department of Public Health, Muspratt Building, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GB, UK C J Stevenson CRWest P O D Pharoah Correspondence
F18 FSID Unit of Perinatal and Paediatric Epidemiology, Department of Public Health, Muspratt Building, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GB, UK C J Stevenson CRWest P O D Pharoah Correspondence
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
A contribution to the natural history of neural crest tumors. Geiser, C. F. and Schindler, A. M. (1969). Long survival in a male
 122 Case Reports neoplastic disease. Leukaemia has been reported in 2 patients with D group chromosomal aberrations (Schade et al, 1962; Zuelzer et al, 1968). The present cases of D-trisomy each had, at
122 Case Reports neoplastic disease. Leukaemia has been reported in 2 patients with D group chromosomal aberrations (Schade et al, 1962; Zuelzer et al, 1968). The present cases of D-trisomy each had, at
Facts About Down Syndrome. National Association for Down Syndrome (NADS)
 Facts About Down Syndrome National Association for Down Syndrome (NADS) What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is a genetic condition that causes delays in physical and intellectual development. It occurs
Facts About Down Syndrome National Association for Down Syndrome (NADS) What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is a genetic condition that causes delays in physical and intellectual development. It occurs
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Bio 105 Guide 08.
 Bio 105 Guide 08 http://images.andrewsmcmeel.com/media/3820/medium.jpg The chromosomes present in 1 cell nucleus! http://www.unm.edu/~vscience/images/hela%20karyotype%203%20(1000x).jpg karyotype http://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucbhjow/medicine/images/human_karyotype.gif
Bio 105 Guide 08 http://images.andrewsmcmeel.com/media/3820/medium.jpg The chromosomes present in 1 cell nucleus! http://www.unm.edu/~vscience/images/hela%20karyotype%203%20(1000x).jpg karyotype http://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucbhjow/medicine/images/human_karyotype.gif
De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities. Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD. Pediatric Genetics Team
 Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Familial Mental Retardation
 Behavior Genetics, Vol. 14, No. 3, 1984 Familial Mental Retardation Paul L. Nichols ~ Received 18 Aug. 1983--Final 2 Feb. 1984 Familial patterns of mental retardation were examined among white and black
Behavior Genetics, Vol. 14, No. 3, 1984 Familial Mental Retardation Paul L. Nichols ~ Received 18 Aug. 1983--Final 2 Feb. 1984 Familial patterns of mental retardation were examined among white and black
Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism
 Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition.
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2003) Vol. 1, No. 4, Issue 4, 267-271 Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition. Gupta UK 1
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2003) Vol. 1, No. 4, Issue 4, 267-271 Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition. Gupta UK 1
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
An Inherited Small Extra Chromosome: A Mother with 46,XX,t(17;22)
 REFERENCES Bobrow, M., Jones, L. F. and Clarke, G. (1971). A complex chromosomal rearrangement with formation of a ring 4. Journal of Medical Genetics, 8, 235-239. Bobrow, M. and Pearson, P. L. (1971).
REFERENCES Bobrow, M., Jones, L. F. and Clarke, G. (1971). A complex chromosomal rearrangement with formation of a ring 4. Journal of Medical Genetics, 8, 235-239. Bobrow, M. and Pearson, P. L. (1971).
Lecture 17: Human Genetics. I. Types of Genetic Disorders. A. Single gene disorders
 Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
Ring 18. Our Mission: To help individuals. they face so they might lead healthy, happy, and productive lives. Normal Chromosomes
 The Chromosome 18 Registry & Research Society Ring 18 There are five major conditions involving large changes of chromosome 18. Each of these conditions has a wide variety of characteristics. Additionally,
The Chromosome 18 Registry & Research Society Ring 18 There are five major conditions involving large changes of chromosome 18. Each of these conditions has a wide variety of characteristics. Additionally,
ijifm case report ABSTRACT
 ijifm case report 1p36 Deletions 10.5005/jp-journals-10016-1085 in Two Cases with Thalassemia 1p36 Deletions in Two Cases with Thalassemia 1 Puspal De, 2 Sudipa Chakravarty, 3 Amit Chakravarty ABSTRACT
ijifm case report 1p36 Deletions 10.5005/jp-journals-10016-1085 in Two Cases with Thalassemia 1p36 Deletions in Two Cases with Thalassemia 1 Puspal De, 2 Sudipa Chakravarty, 3 Amit Chakravarty ABSTRACT
Genetic Disorders. and. blood vessels the and. How many genes are affected by this deletion? Turner s Syndrome- An incomplete or missing chromosome
 Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is an abnormality in the. They can range for a deletion of a gene to the deletion of an entire chromosome. List the types of genetic disorders. Williams Syndrome- A
Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is an abnormality in the. They can range for a deletion of a gene to the deletion of an entire chromosome. List the types of genetic disorders. Williams Syndrome- A
STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 04 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 05/01/13 Revised on: 26/01/13 Accepted on: 18/02/13 STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA OF CERVIX Balsurkar Smita Kashinathappa
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 04 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 05/01/13 Revised on: 26/01/13 Accepted on: 18/02/13 STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA OF CERVIX Balsurkar Smita Kashinathappa
Common Genetic syndromes. Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria
 Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
176 N. TAKAGI, S. MAKINO, S. TAKAI, and M. HIKITA [Vol. 41,
 No. 2] 175 39. A Phenotypical XXYY Human Male with Notes on Two Regular Kline f elter Cases*' By Nobuo TAKAGI, Sajiro MAKINO, Shudo TAKAI, **~ and Masahiro HIKITA**) (Comm. by Yoshimaro TANAKA, M.J.A.,
No. 2] 175 39. A Phenotypical XXYY Human Male with Notes on Two Regular Kline f elter Cases*' By Nobuo TAKAGI, Sajiro MAKINO, Shudo TAKAI, **~ and Masahiro HIKITA**) (Comm. by Yoshimaro TANAKA, M.J.A.,
