RESEARCH ARTICLE. Seyed Mohammad Razavi, Roya Yahyaabadi* Abstract. Introduction
|
|
|
- Laurence Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /APJCP RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with Behavior of Aggressive and Nonaggressive Central Giant Cell Granuloma with Immunohistochemistry Technique Seyed Mohammad Razavi, Roya Yahyaabadi* Abstract Background: The central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) is generally considered a non-neoplastic lesion. However, some cases show aggressive behavior like neoplasms. Based on clinical observations, a number of researchers have classified this lesion into aggressive and non- aggressive types. This study was aimed to investigate the association between clinical behavior and histopathological features using immunohistochemical vascular CD31 and cellular proliferation Ki67 markers. Materials and methods: In this descriptive-analytical, clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study, 50 CGCGs, including 25 aggressive and 25 non-aggressive types were selected according to Chuong s classification. The samples were then subjected to immunohistochemical staining to analyze positivity for CD31 and Ki67 markers. Numbers of blood vessels and percentage proliferation of underlying fibroendothelial cells were assessed, and the obtained results were analyzed with the t-test and the Mann-Whitney test. Results: The results showed a significant difference between aggressive and non-aggressive CGCG lesions in the mean incidences of Ki67 (p=0.044). and CD31 (p=0.003) positivity. Conclusion: The present evaluation of expression rates for the vascular CD31 and cellular proliferation Ki67 markers showed there might be a positive relation between the clinical features and histopathology of CGCG. Furthermore, clinical behavior may be predicted based on features such as the number of blood vessels and proliferation of fibroendothelial cells. Keywords: Aggressive central giant cell granuloma- non-aggressive central giant cell granuloma- vascular CD31- Ki 67 Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 19 (8), Introduction Central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) is an bone lesion with unknown etiology (Nevilel et al., 2016). This lesion was first introduced by Jaffe (1953). Recent studies have shown that jaw lesions are monoclonal (Nevilel et al., 2016). Clinically, CGCG occurs during an wide age range (2-80 years), approximately in 60% of cases before the age of 30. This lesion tends to occur in women, and about 70% of cases are seen in mandible (Jaffe, 1953; Peacock et al., 2012; Nevilel et al., 2016; AtarbashiMoghadam and Ghorbanpor, 2017). These lesions are more common in the anterior part of jaws and cross the middle line in the mandible (Jaffe, 1953; Ficarra et al., 1987; Nevilel et al., 2016; AtarbashiMoghadam and Ghorbanpour, 2017). Based on the clinical feature and radiography, CGCG can be classified into aggressive and non-aggressive types (O Malley et al., 1997; Peacock et al., 2012; El-Attar and Wahba, 2016; Nevilel et al., 2016; AtarbashiMoghadam and Ghorbanpour, 2017). Most of the lesions are non-aggressive. They are relatively small and have mild symptoms, or are asymptomatic. Their growth is slow, and they do not cause cortical bone perforation or root resorption in the adjacent teeth. They are usually detected during routin radiographic examination or based on the painless swelling of bone (O Malley et al., 1997; Peacock et al., 2012; El-Attar and Wahba, 2016; Nevilel et al., 2016; AtarbashiMoghadam and Ghorbanpour, 2017). Aggressive lesions are characterized by symptoms such as pain, rapid growth, cortical perforation, root resorption, tooth displacement, paresthesia and certain recurrence potential (Cowson et al., 1997; Nevilel et al., 2016; AtarbashiMoghadam and GHorbanpor, 2017). Spread to the soft tissue and mucosal ulceration may also occur in some cases (Nevilel et al., 2016). Radiographically, CGCG is an ionic lacunar or multi-lacunar radiolucency with defined outlines but non-cortical margins (Ficarra et al., 1987; Torabinia et al., 2011; Nevilel et al., 2016). Relationship between the histopathological features Dental Material Research Center. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial, Dental School, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. *For Correspondence: roksanarmcf@gmail.com Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
2 Seyed Mohammad Razavi and Roya Yahyaabadi and clinical behavior of this lesion has remained debatable. It is said that more aggressive lesions may be associated with a greater number of giant cells, more surface occupation by the giant cells and higher mitotic index (O Malley et al., 1997; Reddy et al., 2012; Nevilel et al., 2016). Few studies have suggested that increased vascular concentration and incidence of markers related to angiogenesis can be attributed to the aggressive clinical behavior of this lesion (Nevilel et al., 2016). For instance, Peacock et al., (2012) reported a higher level of angiogenesis in the aggressive giant cell lesions than non-aggressive ones. Also, Scholzen and Gerdes (2000) reported a higher expression of Ki67 marker in aggressive CGCGs than non-aggressive ones and called it a helpful criteria for diagnosis of these lesions. However, O Malley et al., (1997) reported that predicting the aggressive and non-aggressive central giant cell lesions based on histology is difficult. CD31 marker is a 130KD type I transmembrane glycoprotein from the large family of immunoglobulins (DeLisser et al., 1997; Peacock et al., 2012; Privratsky et al., 2012), which involves an extracellular site composed of six Ig-like homology domains, one Ig-residue transmembrane domain and one 118 residue cytoplasmic tail (El-Attar and Wahba, 2016). This marker is the most well-known immunohistochemical marker among vascular tumors (Ficarra et al., 1987). This marker, known as platelet endothelial cell adhesionmolecule1 (PEMCAM1), plays different roles in vascular biology, including angiogenesis (Li et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2010). Ki67 is an antigen with non-histone proteins in cell divisions. Presence in all active stages of mitosis is a significant characteristic of Ki67 so that it is present in all stages of cell cycle, including G1, S, G2 and mitosis, but it is not seen in the resting phase of the cell (Rosai and Ackerman, 2010). Due to contradictions regarding the relationship between clinical behavior and histological features in aggressive and non-aggressive CGCGs reported by studies up to now, the current study was conducted to investigate the association of histopathological features with clinical behavior of CGCGs via a comparative analysis of the incidence of CD31 and Ki67 markers in aggressive and non-aggressive CGCGs using immunohistochemistry method. Materials and Methods In this descriptive-analytical, cross-sectional study, the samples diagnosed with CGCG during in the archive of pathology department of Isfahan School of Dentistry were assessed, and clinical data, including the patients age, history of recurrence and effect on the adjacent structures like teeth and cortical bone were extracted from the patients files. From a total of 120 CGCGs, the other types of giant cells like cherubism and brown tumor were excluded from the study, and the remaining samples were included in the analysis. Then, 5 µ microscopic slides stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) staining method were analyzed by two oral pathologists to ensure the diagnosis. Finally, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19 non-aggressive and 25 aggressive CGCGs were confirmed by Chuong s classification (Chuong et al., 1986) (Table 1) and were coded randomly. All the selected slides were analyzed in terms of histological parameters such as the presence of fibroendothelial tissue and multinucleated giant cells in the background of lesion and were recorded in a specific table. For immunohistochemical staining by Biotin-avidin technique, antigen amplification, antigen retrieval, deparaffinization and rehydration and processing were performed, respectively. After irrigating the samples with PBS solution, the slides were put in monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal mouse Anti-human CD31 endothelial cell, JC70A, DAKO, USA) and (Ki67 bio care-sp6, USA) for 10 minutes. Finally, the samples were placed in ethanol with various concentrations for dehydration and then in xylene for clearing the slides, and were mounted by P.V-mounting system. In this study, pyogenic granuloma was used as the positive control for CD31 marker and Burkitt lymphoma was used as positive control for Ki67 marker. All the slides were survayed by two oral pathologists, who were blind to the samples, using an light microscope (Olympus BX41TF, Tokyo, Japan). The stained cells were randomly counted in 10 microscopic fields at 400 magnification (hpf). Then, the frequency of blood vessels was determined by counting the blood vessels stained with CD31 marker (as membrane and cytoplasmic staining), and the percentage of proliferation of mono nuclear stromal cells was calculated by counting the cells stained with Ki67 marker (as nuclear staining), Ki67 marker is staining only mono nuclear stroma cells but isn t staining giant cells because these don t proliferate. the results of which were recorded in tables. Next, the mean of 10 microscopic fields was determined as the rate of two markers. All data were fed into SPSS software (IBM-SPSS- Statistics22) and analyzed by Mann-Whitney and t-test. P<0.05 was considered significant. Results The results of this descriptive-analytical study on 50 CGCGs, including 25 aggressive and 25 non-aggressive CGCGs showed the mean expression of CD31 marker was 8.4% in non-aggressive CGCGs and 12.54% in aggressive CGCGs (Figure 1). Also, the mean expression of Ki67 marker was 16% in non-aggressive CGCGs and Table 1. Criteria for Classification of the GCLS of Jaws Major Criteria Recurrence after curettage Lesion size Minor Criteria Rapid growth Root resorption Cortical bone perforation Tooth displacement
3 DOI: /APJCP A B Figure 1. Expression of CD31 Marker in Stained Endothelial Cells of Capillaries in Non- Aggressive CGCG (A) and Aggressive CGCG (B) ( 400). Notice the higher expression of CD31 marker in aggressive CGCG. A B Figure 2. Expression of Ki67 Marker in Mono Nuclear Stromal Cells of Capillaries in Non- Aggressive CGCG (A) and Aggressive CGCG (B) ( 400). Notice the higher expression of Ki67 marker in aggressive CGCG. Table 2. Expression of CD31 and Ki67 Markers in Aggressive and Non-Aaggressive CGCGsa Tissue Ki67 CD31 Aggressive Mean % in aggressive CGCGs (Figure 2). The findings of t-test indicated a significant difference between the mean expression of CD31 and KI67 markers in nonaggressive and aggressive CGCGs (Pv Ki67=0.044 and Pv CD31=0.003) (Table 2). Discussion Minimum Maximum N Non-aggressive Mean Minimum Maximum N Total Mean Minimum Maximum N Central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) is considered a non-neoplastic lesion (Nevilel et al., 2016). Based on the clinical feature and radiography, CGCG can be divided into aggressive and non-aggressive types (Nevilel et al., 2016). There has always been disagreement on whether the clinical behavior of CGCG (aggressive or non-aggressive) can be determined according to the histopathological features of the lesion. This study investigated the association of histopathological features with clinical behavior of CGCG through analysis of the incidence of CD31 vascular marker and Ki67 proliferation marker in aggressive and non-aggressive CGCGs based on Chuong s classification. The findings showed the incidence of CD31 and Ki67 markers was higher in aggressive than non-aggressive CGCG. Further, the incidence rate of CD31 marker was 12.54% in aggressive CGCG and 8.4% in non-aggressive CGCG, indicating a significant difference between them (P=0.003). On the other hand, the increased vascular proliferation in aggressive CGCGs may be responsible for the aggressive behavior of this lesion. In line with this theory that vascular proliferation in aggressive CGCGs may be responsible for the aggressive behavior of this lesion, it can be argued that increased angiogenesis can differentiate the blood vessels into osteoclasts, which in turn induces the rapid growth, osteolysis and enlargement of this lesion. In a similar study, Peacock (2012) also evaluated the expression of VEGF, CD31 and CD34 markers in CGCGs. They found the angiogenesis level was higher in the aggressive samples than non-aggressive samples. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
4 Seyed Mohammad Razavi and Roya Yahyaabadi Therefore, the incidence rate of these markers can be a basis for predicting the clinical behavior of CGCG (Peacock et al., 2012). However, in another study these researchers carried out in the same year on 41 CGCG samples, use of histopathological criteria including, the number of giant cells or giant cell nuclei to differentiate the aggressive and non-aggressive CGCGs was not considered sufficient (Peacock et al., 2012). Moreover, in the study of El-Attar and Wahba (2016) on Ki67, P53, CD31 and CD68 markers in aggressive and non-aggressive lesions, the expression of CD31 and CD68 markers did not show a significant difference between the two groups, but the number of Ki67 and P53 markers was higher in aggressive lesions. Accordingly, it was concluded that the expression of Ki67 and P53 markers was helpful in determining the clinical behavior of CGCGs. On the other hand, AttarbashiMoghadam, (2016) reported no significant difference in expression of CD34 vascular marker between 16 aggressive and non-aggressive CGCG samples. Hence, it was concluded that CD34 vascular marker was of no use in determining the clinical behavior of CGCGs (AtarbashiMoghadam and Ghorbanpour, 2017). The positive point of the present study is that along with use of CD31 marker, as the most well-known immunohistochemical vascular marker, the researchers decided to use Ki67 marker, which is a sensitive cellular proliferation marker. An important characteristic of this marker is that it is present in all active stages of mitosis, so it can be well associated with cell proliferation (Gejman et al., 2008; Rosai and Ackerman, 2010). Based on the obtained results, the mean incidence of Ki67 was 22.15% in aggressive CGCG samples and 16% in non-aggressive samples, which indicated a significant difference between the two groups (p=0.044). On the other hand, the incidence of Ki67 marker in CGCG group was significantly higher than that of non-aggressive CGCG. Accordingly, cell proliferation by itself can be used as a reliable histopathological parameter to predict the clinical behavior of CGCG lesions. In this line, the study of El- Attar and Wahba (2016) on the expression of Ki67, P53, CD31 and CD68 markers in 10 CGCG non-aggressive samples and 8 aggressive CGCG samples showed estimating the expression rate of Ki67 and P53 markers could be helpful in determining the clinical behavior of CGCG lesions. However, Al Sheddi et al., (2004) conducted a study on 18 CGCG cases and investigated the expression of CD68, CD34 and Ki67 markers. They reported no difference between aggressive and non-aggressive CGCG lesions with regard to histopathological and immunohistochemical features; therefore, these indices could not be used for predicting the clinical behavior of CGCG (19). O Melly (1997) also reported the same point in their study in 1997 on 16 aggressive CGCG cases and 12 non-aggressive CGCG ones along with the expression of Ki67, P53, Cd68 and CD34. According to their results, the expression of Ki67 and CD34 showed no significant difference between the two groups, as P53 marker was not expressed in none of these two lesions. Hence, they concluded it is not possible to predict the 2282 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19 clinical behavior of CGCG by histological analyses and proliferation parameters. Although the results of these two studies are not in agreement with the findings of the present study, a point worth mentioning is that in the current study the number of studied samples was by far more than those of the aforementioned studies. Accordingly, it can be argued that the results of the present research are more reliable. Thus, considering the obtained results in the current study, it can be argued that the incidence of Ki67 marker can also be used as a reliable histopathological parameter to anticipate the clinical behavior of CGCG. In conclusion, the findings of this study showed that the clinical behavior of CGCG lesions can be partly predicted by using immunohistochemical markers and analyzing their expression in CGCG lesions. On the other hand, the histological criteria can probably be a proper index for early diagnosis of aggressive CGCG and consequently a guideline for the clinician or surgeon in making use of a proper treatment plan, including anti-angiogenesis treatments in order to prevent the outcomes occurring afterward, such as spread of lesion, destruction of the surrounding tissues and recurrence. References Al Sheddi M, Mosadomi H, Al Dayel F (2004). Central giant cell granuloma of the jaws and giant cell tumor of long bones.a clinicopathologic, cytometric, and immunohistochemical comparative study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol, 4, Atarbashi Moghadam S, Ghorbanpour M (2017). Central giant cell granuloma of the Jaws: Correlation between vascularity and biologic behavior. J Mashad Dent Sch, 1, Chuong R, Kaban LB, Kozakewich H, Perez-Atayde A (1986). Central giant cell lesions of the jaws: a clinicopathologic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 44, 708. Cowson RA, Binnie WH, Speight PM, Barrett AW (1999). Wright JM.Lucas pathology of tumors of the oral tissues.5thed. Philadelphia: Churchill living stone, pp DeLisser HM, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Strieter RM, et al (1997). Involvement of endothelial PECAM-1/CD31 in angiogenesis. J Pathol, 3, El-Attar RHM, Wahba OM (2016). Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in peripheral and central giant cell granuloma of the Jaws. Arch Cancer Res, 4, 2. Ficarra G, Kaban LB, Hansen LS (1987). Central giant cell lesions of the mandible and maxilla: a clinicopathologic and cytometric study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1, Gejman R, Swearingen B, Hedley-Whyte ET (2008). Role of Ki-67 proliferation index and p53 expression in predicting progression of pituitary adenomas. Hum Pathol, 5, Jaffe HL (1953). Giant-cell reparative granuloma, traumatic bone cyst, and fibrous (fibro-osseous) dysplasia of the jawbones. J Oral Pathol Med, 1, Kim H, Cho HJ, Kim SW, et al (2010). CD31+ cells represent highly angiogenic and vasculogenic cells in bone marrow: novel role of nonendothelial CD31+ cells in neovascularization and their therapeutic effects on ischemic vascular disease. Circ Res, 107, Li ZJ, Wang ZZ, Zheng YZ, et al (2005). Kinetic expression of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/ CD31) during embryonic stem cell differentiation. J Cell Biochem, 3,
5 Nevilel BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC (2016). Oral and maxillofacial pathology.4^thed saunders Co, pp O Malley M, Pogrel MA, Stewart JC, Silva RG, Regezi JA (1997). Central giant cell granulomas of the jaws: phenotype and proliferation-associated markers. J Oral Pathol Med, 4, Peacock ZS, Resnick CM, Susarla SM, et al (2012). Do histologic criteria predict biologic behavior of giant cell lesions?. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 11, Peacock ZS, Jordan RC, Schmidt BL (2012). Giant cell lesions of the jaws: does the level of vascularity and angiogenesis correlate with behavior?. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 8, Privratsky JR, Newman DK, Newman PJ (2012). PECAM-1: conflicts of interest in inflammation. Life Sci, 3, Reddy V, Saxena S, Aggarwal P, Sharma P, Reddy M (2012). Incidence of central giant cell granuloma of the jaws with clinical and histological confirmation: an archival study in Northern India. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 7, Rosai G, Ackerman LV (2010). Surgical pathology.4thed. Philadelphia: Mosby, pp Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000). The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol, 3, Torabinia N, Razavi SM, Shokrolahi Z (2011). A comparative immunohistochemical evaluation of CD68 and TRAP protein expression in central and peripheral giant cell granulomas of the jaws. J Oral Pathol Med, 4, DOI: /APJCP This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- Non Commercial 4.0 International License. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
 Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study)
 GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
JCDP ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology ISSN: Vol. 4 No. 4; April 2017
 Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
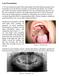 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives in Cancer Research Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws Radien HM El-Attar
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives in Cancer Research Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws Radien HM El-Attar
Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child
 Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 19/May 12, 2014 Page 5307
 PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation
 Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari
 Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report.
 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report. P.S Tripthi Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, ABSMIDS, Mangalore,
Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report. P.S Tripthi Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, ABSMIDS, Mangalore,
Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
 509 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 509-514, 2009 Original Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma Nasrollah Saghravanian
509 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 509-514, 2009 Original Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma Nasrollah Saghravanian
Case presentation. Central Giant Cell Granuloma. Case presentation
 Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports
 2018;24:182-186 The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2018007 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports Samir Abdelqader 1, Nicolas Roche 1,
2018;24:182-186 The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2018007 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports Samir Abdelqader 1, Nicolas Roche 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Anam Ali 1 *, Muhammad Asif 2, Bismah Ahmad 2, Shahid Jamal 3, Iram Ali 4, Muhammad Tahir Khadim 1. Abstract.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma
 IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma Shima Nafarzadeh 1,2, Maryam
IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma Shima Nafarzadeh 1,2, Maryam
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical Markers in Oral Pyogenic Granuloma: A Comparison with Hemangioma and Inflammatory Gingivitis
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 14, No. 2 Mar-Apr 2011, 185-189 Received: Mar 15, 2010; Accepted: Oct 25, 2010 Short communication Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 14, No. 2 Mar-Apr 2011, 185-189 Received: Mar 15, 2010; Accepted: Oct 25, 2010 Short communication Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report
 Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Case report. Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma. Open Access
 Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 109-114 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma Sepideh Vosoughhosseini
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 109-114 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma Sepideh Vosoughhosseini
Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report
 J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas. Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T
 Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case Report and Brief Review of Reported Cases
 J Oral Diag [online] 2017; 02:e20170005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aarfa Nasim 1 Ravi Prakash Sasankoti Mohan 1 * Nagaraju Kamarthi 1 Vijay Wadhwan 1 Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case
J Oral Diag [online] 2017; 02:e20170005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aarfa Nasim 1 Ravi Prakash Sasankoti Mohan 1 * Nagaraju Kamarthi 1 Vijay Wadhwan 1 Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented as Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw Bones. A Report of Three Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Original article J Bas Res Med Sci 2018; 5(3):49-51.
 Age related changes in clinicopathologic features of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) in Iranian patients: An epidemiologic study Ramin Ghafari 1, Noushin Jalayer Naderi 2*, Amirnader Emami Razavi 3
Age related changes in clinicopathologic features of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) in Iranian patients: An epidemiologic study Ramin Ghafari 1, Noushin Jalayer Naderi 2*, Amirnader Emami Razavi 3
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report
 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary. Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 16, No. (2), 2012
 Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study
 Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2017.01401 Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study Soudabeh
Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2017.01401 Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study Soudabeh
Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible
 Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A in Invasive Micropapillary Colorectal Carcinoma
 The coexpression of VEGF-A and CD31 may play a prominent role in the neoangiogenesis of IMPC. This Way to Gas. Photograph courtesy of Craig Damlo. www.soapboxrocket.com. Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial
The coexpression of VEGF-A and CD31 may play a prominent role in the neoangiogenesis of IMPC. This Way to Gas. Photograph courtesy of Craig Damlo. www.soapboxrocket.com. Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Detecting a sinus perforation.
 Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article Odontogenic s in Iran, Isfahan: A study of 0 cases Mahsa Kowkabi, Sayed Mohammad Razavi, Negin Khosravi, Amir Arsalan Navabi Torabinejad Dental Research Center
Dental Research Journal Original Article Odontogenic s in Iran, Isfahan: A study of 0 cases Mahsa Kowkabi, Sayed Mohammad Razavi, Negin Khosravi, Amir Arsalan Navabi Torabinejad Dental Research Center
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS
 EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS A Case of Recurrent Pyogenic Granuloma of Gingiva ABSTRACT A case of pyogenic granuloma of gingiva is presented. Aetiology factors, clinical presentations and different treatment
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS A Case of Recurrent Pyogenic Granuloma of Gingiva ABSTRACT A case of pyogenic granuloma of gingiva is presented. Aetiology factors, clinical presentations and different treatment
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma
 Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Spectrum of clinical presentations
 Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions
 Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 253 258 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions Seyed Mohammad RAZAVI, Maryam
Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 253 258 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions Seyed Mohammad RAZAVI, Maryam
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: ABSTRACT
 Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
Journal of American Science 2015;11(4)
 Expression of Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule PECAM -1 in Gingival Tissue of Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Ghada Bassiouny Department of periodontology and oral medicine, college of Dentistry,
Expression of Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule PECAM -1 in Gingival Tissue of Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Ghada Bassiouny Department of periodontology and oral medicine, college of Dentistry,
Treatment of Keratocysts: The Case for Decompression and Marsupialization
 CLINICAL CONTROVERSIES IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY: PART TWO J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1667-1673, 2005 Treatment of Keratocysts: The Case for Decompression and Marsupialization M. Anthony Pogrel,
CLINICAL CONTROVERSIES IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY: PART TWO J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1667-1673, 2005 Treatment of Keratocysts: The Case for Decompression and Marsupialization M. Anthony Pogrel,
Prognostic Values of Proliferative Markers ki-67 and repp86 in Breast Cancer
 Arch Iranian Med 2007; 10 (1): 27 31 Original Article Prognostic Values of Proliferative Markers ki-67 and repp86 in Breast Cancer Jaleh Mohsenifar MD*, Maryam Almassi-Aghdam MD*, Zohreh Mohammad-Taheri
Arch Iranian Med 2007; 10 (1): 27 31 Original Article Prognostic Values of Proliferative Markers ki-67 and repp86 in Breast Cancer Jaleh Mohsenifar MD*, Maryam Almassi-Aghdam MD*, Zohreh Mohammad-Taheri
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Aneurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 35-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.35 neurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization Department
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 35-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.35 neurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization Department
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Prevalence and Pattern of Congenital Missing Teeth in a Group of Iranian Adolescents
 Prevalence and Pattern of Congenital Missing Teeth in a Group of Iranian Adolescents Ajami B. a, Shabzendedar M. a*, Afzal Agaee M. b, Mehrjerdian M. c a Dept. of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry,
Prevalence and Pattern of Congenital Missing Teeth in a Group of Iranian Adolescents Ajami B. a, Shabzendedar M. a*, Afzal Agaee M. b, Mehrjerdian M. c a Dept. of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry,
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Ancient schwannoma of the mouth floor A case report and review
 Oral Oncology EXTRA (2006) 42, 281 285 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://intl.elsevierhealth.com/journal/ooex CASE REPORT Ancient schwannoma of the mouth floor A case report and
Oral Oncology EXTRA (2006) 42, 281 285 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://intl.elsevierhealth.com/journal/ooex CASE REPORT Ancient schwannoma of the mouth floor A case report and
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Evaluation of E-cadherin Expression in Gastric Cancer and Its Correlation with Clinicopathologic Parameters
 IJHOSCR International Journal of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Research Original Article Evaluation of E-cadherin Expression in Gastric Cancer and Its Correlation with Clinicopathologic Parameters
IJHOSCR International Journal of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Research Original Article Evaluation of E-cadherin Expression in Gastric Cancer and Its Correlation with Clinicopathologic Parameters
Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report. A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis)
 Diagnostic Pathology Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis) Veterinary Pathology 49(6) 1018-1023 ª The Author(s) 2012 Reprints and permission:
Diagnostic Pathology Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis) Veterinary Pathology 49(6) 1018-1023 ª The Author(s) 2012 Reprints and permission:
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic Features and Osseous-Dental Treatments
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
