A) CLASSES 25 hours SUBJECT: RULES AND REGULATIONS. INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
|
|
|
- Janis Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department: DEPARTMENT OF CANCER GENETICS WITH CYTOGENETIC LABATY Address: RADZIWILLOWSKA STREET 11 (COLLEGIUM MEDICUM BUILDING), LUBLIN, Course: MEDICAL GENETICS Head of Department: PROF. AGATA FILIP The course coordinator: DR. SZYMON ZMZYŃSKI, Telephone: Course description: 1. The Medical Genetics course includes 10 hours of lectures and 25 hours of classes during one semester for EUROPEAN PROGRAM 2. The course consists of the following parts: Human genome, Point mutations and polymorphisms, Chromosomal aberrations, Pathomechanisms of genetic diseases, Chromosomes, Immunogenetics, Oncogenesis, Molecular methods. 3. During the course students write short quizzes. 4. The course ends with the Final Test. 5. All information are available on the website of the Department: bookmark English Division. Topics covered in the course LAB 1 A) CLASSES 25 hours SUBJECT: RULES AND REGULATIONS. INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS I) Rules and regulations II) Basic terms: genetics, nucleic acid, DNA and RNA, DNA replication, DNA polymerase, helicase, DNA ligase, gene, allele (dominant and recessive), codominant alleles, exon, intron, transcription, reverse transcription, RNA polymerase, translation, homozygous (dominant and recessive), heterozygous, hemizygous, chromatin, chromosome, genome, genotype, phenotype, haplotype, haploid cells, diploid cells, mitosis, meiosis, mutation, polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), genetic anticipation. III) Types of genetic diseases: chromosome disorders, single-gene disorders, multifactorial disorders, mitochondrial disorders Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTER: Glossary CHAPTERS 1 and 2
2 LAB 2 SUBJECT: HUMAN GENOME I) DNA structure (nucleotides, base pairing, DNA as a double helix) II) Nuclear genome: -the structure of genes. Gene families. Protein coding genes, RNA-coding genes -non-coding DNA: satellite DNA, minisatellite DNA, microsatellite DNA, transposons (SINEs, LINEs, LTR, DNA transposons). Use of microsatellite DNA in forensic genetics. III) Mitochondrial genome: -mitochondrial function -protein coding genes, RNA-coding genes -mutation rate -mitochondrial inheritance -examples of mitochondrial disorders myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers syndrome (MERRF), Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KS). Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTERS: 2.1 DNA, 2.2 Genes, 2.3. Repetitive sequences, 5.5 Mitochondrial inheritance. GENETICS Ronald W. Dudek Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, ISBN CHAPTERS: 1. The human nuclear genome (I-General features; II-Proteincoding genes; III-RNA-coding genes; V-Non-coding DNA); 2. DNA packing (I-Biochemistry of nucleic acids; II-Double helix DNA) 3. Mitochondrial inheritance CHAPTERS 2 and 5
3 LAB 3 SUBJECT: POINT MUTATIONS AND POLYMPHISMS TEACHER: Dr. Sylwia Popek I) Terms: point mutation, somatic mutation, germline mutation, constitutional mutation, missense mutation, nonsense mutation, splice mutation, frameshift mutation, null mutation, silent mutation, de novo mutation, copy number variation, gene amplification, gain of function, loss of function, haploinsufficiency II) frameshift mutations in the case of Duchenne muscular dystrophy; in frame mutations in the case of Beckers muscular dystrophy II) Location of mutations and their possible effects (location within different part of a gene: promoter region, introns, exons, regulatory regions). III) Induced mutations - biological, chemical (base analogs, acridine dyes, nitrous acid) and physical factors (ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation, pyrimidine dimers). The effect of radiation on mutation rates. IV) Spontaneous mutations dynamic mutations, genetic anticipation, permutation status; genetic cause of fragile X syndrome and Huntington disease. V) Mutation vs. polymorphism. Single nucleotide polymorphisms. VI) Clinical consequences of mutation the hemoglobin disorders: sickle cell anemia, thalassemia (α and β). VII) DNA Repair (types and general overview). Xeroderma pigmentosum a disease of faulty DNA repair. Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTERS: 1.2. Frequency of genetic diseases, 3.1. Mutation or polymorphism? 3.5. Gene mutations, 3.6 Dynamic mutations, trinucleotide repeats CHAPTERS 3 and 5
4 LAB 4 SUBJECT: PATHOMECHANISMS OF GENETIC DISEASES I) Terms: pleiotropy, genetic heterogeneity, expressivity, variable expressivity, penetrance, epistasis, polyphenism, monogenic, digenic, polygenic, loss of heterozygosity II) Semidominance (incomplete dominance) in the case of familial hypercholesterolemia and complete dominance in the case of Huntington disease III) Heterozygote advantage in the case of sickle cell anemia IV) Codominance in the AB0 blood group system V) Dominant negative effect in the case of osteogenesis imperfecta and Marfan syndrome VI) DNA replication and aging effects function of enzymes involved in DNA replication (DNA topoisomerase, helicase, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase), leading strand and lagging strand; telomeres and function of telomerase; telomere shortening, accumulation of mitochondrial mutations. VII) Human progeria syndrome Werner syndrome. Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTERS: 2.1. DNA Replication of DNA, 4.1. From genotype to phenotype, 4.2. Dominant and recessive, 8. Aging and Genetics CHAPTER 4
5 LAB 5 SUBJECT: CHROMOSOMES AND THEIR ABERRATIONS TEACHER: Prof. Agata Filip I) Chromosome structure and classification (depending on centromere localization). II) Numerical chromosome abnormalities (aneuploidy, euploidy, meiotic nondisjunction, anaphase lag, mosaicism). III) Structural chromosome abnormalities (deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations, isochromosome, Robertsonian translocation, balanced/unbalanced aberrations), marker chromosomes. IV) Cytogenetic nomenclature. Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTERS: 2.7. Chromosomes, 3.2. Types of mutations, 3.3. Numerical chromosome abnormalities, 3.4. Structural chromosome abnormalities, 4.4 Mosaicism CHAPTERS 2 and 6
6 LAB 6 SUBJECT: CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS TEACHER: Prof. Agata Filip I) Methods of chromosome analysis II) Source of cells for chromosome analysis III) Cell cultures IV) Classical cytogenetics (G-banding, R-banding) V) Molecular cytogenetics FISH and its variants, CGH and array CGH. Human genetics: from molecules to medicine C.P. Schaaf, J. Zschocke, L. Potocki - Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer business, 2012 (first edition). ISBN-13: and ISBN- 10: CHAPTERS: Cytogenetics, Molecular cytogenetics CHAPTERS 2 and 6 SOURCE of LEARNING: Material from lecture (prof. Agata Filip)
7 LAB 7 SUBJECT: FROM GENES TO PROTEINS I) TERMS: promoter, enhancer, silencer, primary transcript, mature transcript, gene splicing, alternative splice sites, transcription factors, DNA-binding motifs, housekeeping genes, genetic code, codon and anticodon II) Posttranslational modifications in the case of Osteogenesis imperfecta (an inherited collagen disorder and its genetic cause). The process of collagen fibril formation. III) The concept of phenotype. Gene expression and mutations classes of CFTR gene mutations in cystic fibrosis. IV) Factors that affect expression of disease new mutations in the case of achondroplasia, age dependent penetrance in the case of Huntington disease, variable expression in the case of neurofibromatosis (type I and II), locus heterogeneity and germline mosaicism (both) in the case of osteogenesis imperfecta, pleiotropy in Marfan syndrome CHAPTERS 2, 3 and 4
8 LAB 8 SUBJECT: ONCOGENESIS PART I TEACHER: Prof. Agata Filip I) Oncogenic transformation definition, stages of transformation and their characteristics. II) Cancer cell characteristics. III) Tumor classification with respect to biology and histology. IV) Benign and malignant tumors differences. V) Apoptosis and necrosis VI) Molecular pathway of tumor development: oncogenes types, mechanisms of activation, examples. VII) Molecular pathway of tumor development: tumor suppressor genes types, mechanisms of activation, examples. VIII) microrna definition, structure and role in oncogenesis. XIX) Role of angiogenesis in tumor development, pro- and antiangiogenic factors. X) Metastases stages of development, sites CHAPTER 11
9 LAB 9 SUBJECT: ONCOGENESIS PART II TEACHER: Prof. Agata Filip I) Two-hit hypothesis for tumorgenesis II) Cancer predisposition role of germline mutations III) Familial cancer Lynch syndrome, retinoblastoma, breast cancer, familial adenomatous polyposis of colon, hereditary diffuse gastric cancer, Li-Fraumeni syndrome IV) molecular tests in cancer predisposition (germline mutations) V) molecular lesions as prognostic and predictive factors VI) targeted treatment CHAPTER 11
10 LAB 10 SUBJECT: IMMUNOGENETICS I) The humoral and cellular immune systems II) types of gene expression biallelic and monoallelic expression, allelic exclusion III) Immunoglobulin molecules and genes, the genetic basis of antibodies, structure and expression of immunoglobulin genes, synthesis of IgM and IgD in B-cells by alternate splicing, heavy chain class switching (another DNA rearrangement event), somatic mutation, random combinations of heavy and light chains IV) T-cell receptor molecules and genes V) The major histocompatibility complex CHAPTER 9 SOURCE of LEARNING: -Lecture immunogenetics (Dr. Szymon Zmorzyński)
11 LAB 11 SUBJECT: Molecular methods I) Examples of biological material for nucleic acid isolation II) Restriction enzymes: -names, types I-IV, blunt ends, sticky ends (5 -overhang and 3 -overhang) -examples: AluI, SmaI, BamHI, EcoRI, PstI, TaqI III) Detecting variation at DNA level: Southern blotting and restriction fragment analysis, tandem repeats polymorphisms, single nucleotide polymorphisms, copy number variants. IV) DNA sequencing technique, next generation sequencing (high-throughput DNA sequencing) V) PCR METHOD (general procedure and stages), PCR multiplex, reverse transcription PCR, real time PCR, PCR-RFLP -diagnostics of sickle cell anemia. VI) Genetic testing heterozygote screening, direct mutation analysis. Limitations of genetic testing CHAPTERS 3 and 13 SOURCE of LEARNING: -Lecture molecular methods (Dr. Szymon Zmorzyński)
12 LAB 12 SUBJECT: Medical cases Diagnosis of: I) CHROMOSOMAL DISDERS: -Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edward s syndrome, cat s cry syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Angelman syndrome. II) AUTOSOMAL DISDERS: -Oculocutaneous albinism (type I and II), cystic fibrosis, galactosemia (type I), Gaucher disease, hemochromatosis (type I), phenylketonuria, sickle-cell anemia, Tay-Sachs disease, the thalassemias, familial hypercholesterolemia, achondroplasia, Apert syndrome, Huntington disease, neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2, Marfan syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta. III) X-LINKED DISDERS: -glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD), hemophilia A, hemophilia B, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy, Menkes disease, Lesh-Nyhan syndrome, Bloch-Sulzberger disease (Incontinentia Pigmenti), Rett syndrome, hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets LAB 13 [1 hour] SUBJECT: Written quiz. Points calculation (before the final test). According to RULES and REGULATIONS a Student is obliged to take a written quiz (material from the whole semester), if the total score from the classes is less than 60% (60 points), but more than 40% (40points). [100% = 100 points]
13 B) LECTURES 10 hours 1.Types of RNA. Role of non-coding RNA. MicroRNAs their biogenesis and function, mirnas as prognostic and predictive factors; PROF. AGATA FILIP 2. Chromosome analysis meiosis and mitosis, cell cultures, classical cytogenetics (banding techniques), molecular cytogenetics FISH, CGH, array CGH; PROF. AGATA FILIP 3. Immunogenetics; DR. SZYMON ZMZYŃSKI 4. Prenatal diagnostics aims, indications, noninvasive and invasive testing techniques, preimplantation testing; PROF. AGATA FILIP 5. Molecular methods in medical genetics; DR. SZYMON ZMZYŃSKI
Basic Definitions. Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi MBChB MSc DCH (UK) MRCPCH
 Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity
 Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Genetic Disorders. SCPA 501: General Pathology. Amornrat Naranuntarat Jensen
 Genetic Disorders SCPA 501: General Pathology Amornrat Naranuntarat Jensen amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Human has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Sex chromosomes Human genome contains approximately 3 billion base
Genetic Disorders SCPA 501: General Pathology Amornrat Naranuntarat Jensen amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Human has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Sex chromosomes Human genome contains approximately 3 billion base
Lecture 17: Human Genetics. I. Types of Genetic Disorders. A. Single gene disorders
 Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
Genomics and Genetics in Healthcare. By Mary Knutson, RN, MSN
 Genomics and Genetics in Healthcare By Mary Knutson, RN, MSN Clinical Objectives Understand the importance of genomics to provide effective nursing care Integrate genetic knowledge and skills into nursing
Genomics and Genetics in Healthcare By Mary Knutson, RN, MSN Clinical Objectives Understand the importance of genomics to provide effective nursing care Integrate genetic knowledge and skills into nursing
BSC 2010C SI EXAM 3 REVIEW REVIEW SESSION AT: Wednesday, 12 2 PM In CB2 Room 105
 BSC 2010C SI EXAM 3 REVIEW REVIEW SESSION AT: Wednesday, 7/26 @ 12 2 PM In CB2 Room 105 Ch. 10 1) Where does the light cycle happen? Thylakoid membrane 2) Where does the calvin cycle happen? Stroma Ch.
BSC 2010C SI EXAM 3 REVIEW REVIEW SESSION AT: Wednesday, 7/26 @ 12 2 PM In CB2 Room 105 Ch. 10 1) Where does the light cycle happen? Thylakoid membrane 2) Where does the calvin cycle happen? Stroma Ch.
Classifications of genetic disorders disorders
 Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Human inherited diseases
 Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function. The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Chromosome loci. Organization of the Chromatin. Nucleotide Structure
 Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17
 Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Section Chapter 14. Go to Section:
 Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Chapter 16 Mutations. Practice Questions:
 Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 16 Mutations Practice Questions: Answer the following questions with one or two sentences. 1. List the name of one test that can be used to identify mutagens. 2. What is
Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 16 Mutations Practice Questions: Answer the following questions with one or two sentences. 1. List the name of one test that can be used to identify mutagens. 2. What is
Gene Expression and Mutation
 Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Gaucher disease 3/22/2009. Mendelian pedigree patterns. Autosomal-dominant inheritance
 Mendelian pedigree patterns Autosomal-dominant inheritance Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked Examples of AD inheritance Autosomal-recessive inheritance
Mendelian pedigree patterns Autosomal-dominant inheritance Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked Examples of AD inheritance Autosomal-recessive inheritance
Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont.
 Genetic Basis of Disease Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont. Traditional Mechanisms Chromosomal disorders Single-gene gene disorders Polygenic/multifactorial disorders Novel mechanisms Imprinting
Genetic Basis of Disease Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont. Traditional Mechanisms Chromosomal disorders Single-gene gene disorders Polygenic/multifactorial disorders Novel mechanisms Imprinting
Mutations. A2 Biology For WJEC
 12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
Human Genetic Mutations
 Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Course Title Form Hours subject
 Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Introduction to genetic variation. He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016
 Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Assessment and Counseling
 Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
BMS 6204 MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY & GENETICS SPRING 2010
 Week Date Cases Topic Subtopic/Class Activity Readings Jan 4th Course Introduction 1.1 Discussion of course organization, lecture format, quizzes, exams Unit I: Genetic Diseases: Structure and Function
Week Date Cases Topic Subtopic/Class Activity Readings Jan 4th Course Introduction 1.1 Discussion of course organization, lecture format, quizzes, exams Unit I: Genetic Diseases: Structure and Function
Chromosomal Mutations
 Notes 2/17 Chromosomal Mutations A chromosome mutation is an unpredictable change that occurs in a chromosome. These changes are most often brought on by problems that occur during meiosis or by mutagens
Notes 2/17 Chromosomal Mutations A chromosome mutation is an unpredictable change that occurs in a chromosome. These changes are most often brought on by problems that occur during meiosis or by mutagens
MUCOM Medical Genetics. Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi M.B.Ch.B M.Sc DCH (UK) MRCPCH
 MUCOM 2017-2018 Medical Genetics Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi M.B.Ch.B M.Sc DCH (UK) MRCPCH Single-Gene Disorders Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22)
MUCOM 2017-2018 Medical Genetics Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi M.B.Ch.B M.Sc DCH (UK) MRCPCH Single-Gene Disorders Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
Heredity and Genetics (8%)
 I. Basic Vocabulary a. G Phase Heredity and Genetics (8%) M G2 i. Chromosomes: Threadlike linear strands of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carry the genes and functions
I. Basic Vocabulary a. G Phase Heredity and Genetics (8%) M G2 i. Chromosomes: Threadlike linear strands of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carry the genes and functions
Welcome to the Genetic Code: An Overview of Basic Genetics. October 24, :00pm 3:00pm
 Welcome to the Genetic Code: An Overview of Basic Genetics October 24, 2016 12:00pm 3:00pm Course Schedule 12:00 pm 2:00 pm Principles of Mendelian Genetics Introduction to Genetics of Complex Disease
Welcome to the Genetic Code: An Overview of Basic Genetics October 24, 2016 12:00pm 3:00pm Course Schedule 12:00 pm 2:00 pm Principles of Mendelian Genetics Introduction to Genetics of Complex Disease
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Chromosome Abnormalities
 Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance. Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 Autosomal dominant (AD) a: Wild type (Wt) allele A: Mutant allele aa: Normal phenotype Aa: Affected (heterozygous) AA: Affected (homozygous)
Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 Autosomal dominant (AD) a: Wild type (Wt) allele A: Mutant allele aa: Normal phenotype Aa: Affected (heterozygous) AA: Affected (homozygous)
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Genetic Disorders. PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders. Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test
 Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
LIST OF INVESTIGATIONS
 Karyotyping: K001 K002 LIST OF INVESTIGATIONS SAMPLE CONTAINER TYPE cells For Karyotyping [Single] cells For Karyotyping [Couple] Vacutainer Vacutainer 7-8 7-8 K003 Fetal Blood Sample For Karyotyping Vacutainer
Karyotyping: K001 K002 LIST OF INVESTIGATIONS SAMPLE CONTAINER TYPE cells For Karyotyping [Single] cells For Karyotyping [Couple] Vacutainer Vacutainer 7-8 7-8 K003 Fetal Blood Sample For Karyotyping Vacutainer
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetics (Learning Objectives)
 Human Genetics (Learning Objectives) Recognize Mendel s contribution to the field of genetics. Review what you know about a karyotype: autosomes and sex chromosomes. Understand and define the terms: characteristic,
Human Genetics (Learning Objectives) Recognize Mendel s contribution to the field of genetics. Review what you know about a karyotype: autosomes and sex chromosomes. Understand and define the terms: characteristic,
A. Incorrect! Cells contain the units of genetic they are not the unit of heredity.
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill PS07: Mendelian Genetics Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The smallest unit of heredity is. Question #01 (A) Cell (B) Gene (C) Chromosome (D) Allele Cells contain the units of
MCAT Biology Problem Drill PS07: Mendelian Genetics Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The smallest unit of heredity is. Question #01 (A) Cell (B) Gene (C) Chromosome (D) Allele Cells contain the units of
Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Genetics Review. Alleles. The Punnett Square. Genotype and Phenotype. Codominance. Incomplete Dominance
 Genetics Review Alleles These two different versions of gene A create a condition known as heterozygous. Only the dominant allele (A) will be expressed. When both chromosomes have identical copies of the
Genetics Review Alleles These two different versions of gene A create a condition known as heterozygous. Only the dominant allele (A) will be expressed. When both chromosomes have identical copies of the
Human Genetics Notes:
 Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Biology Final Exam Review. SI Leader Taylor (Yeargain, MWF 1:30-2:20)
 Biology Final Exam Review SI Leader Taylor (Yeargain, MWF 1:30-2:20) General Information Review Session Please fill in any available space, and move to the front of the room! Thank you for coming Exam
Biology Final Exam Review SI Leader Taylor (Yeargain, MWF 1:30-2:20) General Information Review Session Please fill in any available space, and move to the front of the room! Thank you for coming Exam
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Learning Outcomes: The following list provides the learning objectives that will be covered in the lectures, and tutorials of each week:
 Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-306 Medical Genetics 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Spring (Semester 6) MED-103 Biology I MED-109 Biology II MED-204 Biochemistry I MED-209 Biochemistry
Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-306 Medical Genetics 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Spring (Semester 6) MED-103 Biology I MED-109 Biology II MED-204 Biochemistry I MED-209 Biochemistry
Recessive Genetic Disorders! A recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait.
 Section 1 Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance Recessive Genetic Disorders! A recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait. Section 1 Section 1 Table 11.2 Recessive
Section 1 Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance Recessive Genetic Disorders! A recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait. Section 1 Section 1 Table 11.2 Recessive
MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) assay validation; sensitivity; oligodendroglioma, FISH CAP lab accreditation;
 MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) assay validation; sensitivity; oligodendroglioma, FISH CAP lab accreditation; phase II deficiency oligodendroglioma; chemotherapy response
MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) assay validation; sensitivity; oligodendroglioma, FISH CAP lab accreditation; phase II deficiency oligodendroglioma; chemotherapy response
GENE EXPRESSION. Amoeba Sisters video 3pk9YVo. Individuality & Mutations
 Amoeba Sisters video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=giez 3pk9YVo GENE EXPRESSION Individuality & Mutations Complete video handout http://www.amoebasisters.com/uploads/ 2/1/9/0/21902384/video_recap_of_muta
Amoeba Sisters video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=giez 3pk9YVo GENE EXPRESSION Individuality & Mutations Complete video handout http://www.amoebasisters.com/uploads/ 2/1/9/0/21902384/video_recap_of_muta
Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics
 Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics Studying Human Genetics A pedigree is a chart for tracing genes in a family. Used to determine the chances of offspring having a certain genetic disorder. Karyotype=picture
Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics Studying Human Genetics A pedigree is a chart for tracing genes in a family. Used to determine the chances of offspring having a certain genetic disorder. Karyotype=picture
Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets
 Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets By Prof. K. K. Jain MD, FRACS, FFPM Jain PharmaBiotech Basel, Switzerland November 2018 A Jain PharmaBiotech Report A U T H O R ' S B I O G R A P H Y Professor
Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets By Prof. K. K. Jain MD, FRACS, FFPM Jain PharmaBiotech Basel, Switzerland November 2018 A Jain PharmaBiotech Report A U T H O R ' S B I O G R A P H Y Professor
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Exam #2 BSC Fall. NAME_Key correct answers in BOLD FORM A
 Exam #2 BSC 2011 2004 Fall NAME_Key correct answers in BOLD FORM A Before you begin, please write your name and social security number on the computerized score sheet. Mark in the corresponding bubbles
Exam #2 BSC 2011 2004 Fall NAME_Key correct answers in BOLD FORM A Before you begin, please write your name and social security number on the computerized score sheet. Mark in the corresponding bubbles
RAZAN AL-ZOUBI. Farah Albustanji BELAL AZAB. 1 P a g e
 . 21 RAZAN AL-ZOUBI Farah Albustanji BELAL AZAB 1 P a g e Last time we talked about Tay-sachs disease, and we said that the Dominance (complete, incomplete, codominance) is not s.th that is straight forward,
. 21 RAZAN AL-ZOUBI Farah Albustanji BELAL AZAB 1 P a g e Last time we talked about Tay-sachs disease, and we said that the Dominance (complete, incomplete, codominance) is not s.th that is straight forward,
Genetic Disorders. Students must provide an explanation for all problems. Students must have parent signature prior to submission.
 Name: Date: Students must provide an explanation for all problems. Students must have parent signature prior to submission. 1. A human hereditary disorder that may result in mental retardation is 1. A.
Name: Date: Students must provide an explanation for all problems. Students must have parent signature prior to submission. 1. A human hereditary disorder that may result in mental retardation is 1. A.
6.3 DNA Mutations. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 6.3 DNA Mutations SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau DNA Mutations Gene expression can be affected by errors that occur during DNA replication. Some errors are repaired, but others can become mutations (changes in the nucleotide
6.3 DNA Mutations SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau DNA Mutations Gene expression can be affected by errors that occur during DNA replication. Some errors are repaired, but others can become mutations (changes in the nucleotide
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.76 Genetic Counseling Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created Local Policy/ 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 2.04.76 Genetic Counseling Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created Local Policy/ 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases. Plan of the lecture
 Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases Plan of the lecture 1. Notion of variability. Different types of variability.
Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases Plan of the lecture 1. Notion of variability. Different types of variability.
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
A Presentation to: ABA. Howard M. Sandler, M.D. Sandler Occupational Medicine Associates, Inc. April 2008
 Genetics, Testing and Toxic Torts A Presentation to: ABA Howard M. Sandler, M.D. Sandler Occupational Medicine Associates, Inc. April 2008 Common Genetic Disorders Disorder Mutation Chromosome 22q11.2
Genetics, Testing and Toxic Torts A Presentation to: ABA Howard M. Sandler, M.D. Sandler Occupational Medicine Associates, Inc. April 2008 Common Genetic Disorders Disorder Mutation Chromosome 22q11.2
MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) analytical measurement range; CLSI MM06-A2 PCR assay performance and validation
 MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) analytical measurement range; CLSI MM06-A2 PCR assay performance and validation assay validation; sensitivity; PCR interpretation and
MOC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory 75-Question Module) analytical measurement range; CLSI MM06-A2 PCR assay performance and validation assay validation; sensitivity; PCR interpretation and
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Psych 3102 Lecture 5
 Psych 3102 Lecture 5 Extensions of Mendel - continued Multiple alleles where more than two alleles are present for the trait in the population Example: ABO blood group system in humans antigen antibody
Psych 3102 Lecture 5 Extensions of Mendel - continued Multiple alleles where more than two alleles are present for the trait in the population Example: ABO blood group system in humans antigen antibody
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT
 HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Chapter 15 Notes 15.1: Mendelian inheritance chromosome theory of inheritance wild type 15.2: Sex-linked genes
 Chapter 15 Notes The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mendel s hereditary factors were genes, though this wasn t known at the time Now we know that genes are located on The location of a particular gene
Chapter 15 Notes The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mendel s hereditary factors were genes, though this wasn t known at the time Now we know that genes are located on The location of a particular gene
Chapter 11. Chromosomes and Human Inheritance
 Chapter 11 Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomesand Sex Chromosomes Paired
Chapter 11 Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomesand Sex Chromosomes Paired
Molecular Genetic Pathology CC Exam Module Study Guide
 Registrants for the MGP only or combined Primary/MGP CC exam must take the mandatory general MGP module plus any elective HEM modules selected during registration. CC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory
Registrants for the MGP only or combined Primary/MGP CC exam must take the mandatory general MGP module plus any elective HEM modules selected during registration. CC MGP General Molecular Genetics I (Mandatory
Table of Contents. What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? How can gene mutations affect health and development?
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? How can gene mutations affect health and development? Do all gene mutations affect health and development? What kinds of
Chapter 3 Table of Contents What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? How can gene mutations affect health and development? Do all gene mutations affect health and development? What kinds of
Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis
 Name: Date: Block: 1 Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis Directions: Answer the questions and where indicated, draw a Punnett square and show all work! 1. Who was Gregor Mendel? Where did he live and
Name: Date: Block: 1 Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis Directions: Answer the questions and where indicated, draw a Punnett square and show all work! 1. Who was Gregor Mendel? Where did he live and
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Chapter 9. Cells Grow and Reproduce
 Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Gene Therapy. Definition: A disease resulting from a defect in individual genes. > 6000 inherited diseases 1:200 Births
 Inherited Disease (AKA Genetic Disease): A disease that is caused by a defect in the genome and that, like other genetic features, can be passed from parents to offspring. Epigenetics: A heritable change
Inherited Disease (AKA Genetic Disease): A disease that is caused by a defect in the genome and that, like other genetic features, can be passed from parents to offspring. Epigenetics: A heritable change
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
 CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring.
 Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring. Karyotype : picture of the actual chromosomes arranged in pairs, paired and arranged from largest to smallest. Human
Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring. Karyotype : picture of the actual chromosomes arranged in pairs, paired and arranged from largest to smallest. Human
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
12.1 X-linked Inheritance in Humans. Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12. X-linked Inheritance. X-linked Inheritance
 Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Essential Questions. Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How can genetic patterns be analyzed to determine dominant or recessive inheritance patterns? What are examples of dominant and recessive disorders? How can human pedigrees be constructed
Essential Questions How can genetic patterns be analyzed to determine dominant or recessive inheritance patterns? What are examples of dominant and recessive disorders? How can human pedigrees be constructed
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes
 Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK
 CHAPTER 6 DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK Genetic research aimed at the identification of new breast cancer susceptibility genes is at an interesting crossroad. On the one hand, the existence
CHAPTER 6 DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK Genetic research aimed at the identification of new breast cancer susceptibility genes is at an interesting crossroad. On the one hand, the existence
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics
 Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Mendelian and Atypical Patterns of Inheritance
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Mendelian and Atypical Patterns of Inheritance I MONOGENIC MENDELIAN INHERITANCE French I.1 SYNOPSIS I.2 AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE I.3
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Mendelian and Atypical Patterns of Inheritance I MONOGENIC MENDELIAN INHERITANCE French I.1 SYNOPSIS I.2 AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE I.3
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
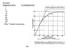 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
MENDELIAN INHERITANCE
 MENDELIAN INHERITANCE Mohammed El - Khateeb March 25 th. 2014 MGL- 6 Genetic Diseases (GD) Chromosomal Abnormalities Single Gene Defects Non-Traditional Inheritance Multifactorial Disorders Cancer Genetics
MENDELIAN INHERITANCE Mohammed El - Khateeb March 25 th. 2014 MGL- 6 Genetic Diseases (GD) Chromosomal Abnormalities Single Gene Defects Non-Traditional Inheritance Multifactorial Disorders Cancer Genetics
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Level 1, The Women s Centre John Radcliffe Hospital University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust OX3
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Level 1, The Women s Centre John Radcliffe Hospital University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust OX3
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
UNIT 2: GENETICS Chapter 7: Extending Medelian Genetics
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders. Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital
 Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Chromosomes and Human Inheritance. Chapter 11
 Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Chapter 11 11.1 Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Chapter 11 11.1 Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
