Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages)
|
|
|
- Cecily West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1711P 1
2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning Nursing Trans. & Corp. Ops. Commissioning Strategy Finance Publications Gateway Reference: 763 Document Purpose Document Name Author Publication Date Target Audience Policy Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages) Specialised Commissioning Team 21 December 218 CCG Clinical Leaders, Care Trust CEs, Foundation Trust CEs, Medical Directors, Directors of PH, Directors of Nursing, NHS England Regional Directors, NHS England Directors of Commissioning Operations, Directors of Finance, NHS Trust CEs Additional Circulation List #VALUE! Description Routinely Commissioned - NHS England will routinely commission this specialised treatment in accordance with the criteria described in this policy. Cross Reference Superseded Docs (if applicable) Action Required Timing / Deadlines (if applicable) Contact Details for further information By January 19 england.specialisedcommissioning@nhs.net Document Status This is a controlled document. Whilst this document may be printed, the electronic version posted on the intranet is the controlled copy. Any printed copies of this document are not controlled. As a controlled document, this document should not be saved onto local or network drives but should always be accessed from the intranet. 2
3 Standard Operating Procedure: Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages) First published: December 218 Prepared by NHS England Specialised Services Clinical Reference Group for Chemotherapy Published by NHS England, in electronic format only. 3
4 Contents 1 Introduction Definitions Aims and Objectives Epidemiology and Needs Assessment Evidence Base Criteria for Commissioning Patient Pathway Governance Arrangements Mechanism for Funding Audit Requirements Documents Which Have Informed this Policy Date of Review References
5 Policy Statement NHS England will commission gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer in accordance with the criteria outlined in this document. In creating this policy NHS England has reviewed this clinical condition and the options for its treatment. It has considered the place of this treatment in current clinical practice, whether scientific research has shown the treatment to be of benefit to patients, (including how any benefit is balanced against possible risks) and whether its use represents the best use of NHS resources. This policy document outlines the arrangements for funding of this treatment for the population in England. Equality Statement Promoting equality and addressing health inequalities are at the heart of NHS England s values. Throughout the development of the policies and processes cited in this document, we have: given due regard to the need to eliminate discrimination, harassment and victimisation, to advance equality of opportunity, and to foster good relations between people who share a relevant protected characteristic (as cited under the Equality Act 21) and those who do not share it; and given regard to the need to reduce inequalities between patients in access to, and outcomes from healthcare services and to ensure services are provided in an integrated way where this might reduce health inequalities. Plain Language Summary About pancreatic cancer The pancreas is part of the digestive system and is a large gland in the body that produces digestive juices, insulin and other hormones to do with digestion. Around 5
6 9,6 people in the United Kingdom (UK) are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer each year and it is the eleventh most common cancer (Cancer Research UK, 218). It is more common in older adults and almost half of all new cases are diagnosed in people aged 75 and over (Cancer Research UK, 218). In the past 1 years, pancreatic cancer rates have increased and this trend is expected to continue over the next decade (Cancer Research UK, 218). When pancreatic cancer is detected at an early stage, there is a much greater chance that it can be cured with surgery, which is also referred to as a resection. However, only about 1% of people with pancreatic cancer have potentially curative surgery because most pancreatic cancers have spread too far at the point of diagnosis to enable surgery to be effective. A pathologist will examine and grade the cancerous tumour that has been removed to help guide further treatment options. This policy relates to cases of pancreatic cancer where, following surgical resection, a pathologist has determined that there are no remaining cancer cells visible to the naked eye. This is termed microscopic clearance or microscopic infiltration of the resection margin and is graded by the pathologist as either R or R1. About current treatments The current treatment options for pancreatic cancer include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Treatment options depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer (a way of describing where the cancer is located, if or where it has spread, and whether it is affecting other parts of the body), possible side effects, overall health and individual preference. Surgery for pancreatic cancer may be combined with radiation therapy and / or chemotherapy to reduce the chances of the cancer returning; if given after surgery, this is called adjuvant therapy. In England, currently gemcitabine is given alone as an adjuvant chemotherapy treatment for people that have undergone potentially curative surgery for pancreatic cancer and who do not have any remaining cancer cells visible to the naked eye (R and R1). It is usually started within three months of surgery and continued for six months. 6
7 About the new treatment The new treatment combines a chemotherapy medicine called capecitabine with gemcitabine which is currently available. This combination is intended to further improve outcomes compared to gemcitabine alone. Both medicines are given at the same time and both work by stopping cells making and repairing DNA, which they need to grow and multiply. What we have decided NHS England has carefully reviewed the evidence to treat resected pancreatic cancer, where either microscopic clearance (R) or microscopic infiltration (R1) of the margins has been achieved, with adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine, and has concluded that there is enough evidence to make the treatment available. 7
8 1 Introduction Pancreatic cancer is cancer that starts in the pancreas, a large gland in the body that produces digestive juices, insulin and other hormones to do with digestion. The majority of pancreatic cancers start in the cells that produce digestive juices and are called exocrine pancreatic cancers. Less commonly, pancreatic cancers start in the cells that produce insulin and hormones and are known as endocrine pancreatic cancers. Pancreatic cancer can also start in other types of cells but this is rare. The current treatment options for pancreatic cancer include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer (a way of describing where the cancer is located, if or where it has spread, and whether it is affecting other parts of the body), possible side effects, and the patient s preferences and overall health. When detected early (also called resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer), pancreatic cancer has a much higher chance of being cured with surgery. However, only about 1% of people with pancreatic cancer are able to have potentially curative surgery because most pancreatic cancers have already spread too far at the point of diagnosis. Surgery for pancreatic cancer may be combined with radiation therapy and / or chemotherapy to reduce the chances of the cancer returning; if given after surgery, this is called adjuvant therapy. Examination and grading of the resection margins by a pathologist after surgery helps to guide further treatment options. There are three classifications used: (i) R microscopic tumour clearance; (ii) R1 microscopic tumour infiltration; and (iii) R2 macroscopic residual tumour. In England, currently gemcitabine is given alone as an adjuvant chemotherapy treatment for patients who have undergone potentially curative surgery for pancreatic cancer. Gemcitabine belong to a family of drugs called antimetabolites. The drug works by stopping cells making and repairing DNA which they need to grow and multiply. Gemcitabine is usually started within three months of surgery and continued 8
9 for six months. Common side effects include neutropenia, anaemia, bruising and bleeding, feeling sick, loss of appetite and tiredness. Capecitabine, which is not licensed to treat this indication, is another chemotherapy drug that can be given in combination with gemcitabine to improve outcomes further after surgery. The drug is given concurrently with gemcitabine and for the same treatment duration. It belongs to the same family of drugs as gemcitabine and acts in the same way, preventing cancerous cells from re-producing. It is proposed to treat cases of surgically resected pancreatic cancer with gemcitabine and capecitabine, where either microscopic clearance (R) or microscopic infiltration (R1) of the margins has been achieved with surgery. 2 Definitions Adjuvant therapy any therapy, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy, given after initial treatment to suppress the cancer from returning. Antimetabolites a group of drugs that interfere with the normal dividing and functions of cells. Cancer abnormal cells that divide in an uncontrolled way. Chemotherapy a type of cancer treatment where medication is used to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy also affects healthy cells and this can cause sideeffects, which will vary depending on the type of cell affected. Pancreatic cancer a cancer that starts in the pancreas. The pancreas is part of the digestive system and is a large gland that produces digestive juices, insulin and other hormones to do with digestion. Radiotherapy a treatment where radiation is used to kill cancer cells. There are many different ways radiotherapy can be given, but they all work in a similar way. They damage cancer cells and stop them from growing or spreading in the body. 9
10 Side-effects may occur and are caused by radiation affecting the surrounding healthy tissues. These will vary depending on the healthy tissue affected and amount of radiation received. Resectable pancreatic cancer is pancreatic cancer that has been diagnosed when it is at an early stage and is potentially curable with surgery. R grading system is used after surgery to guide further treatment. The removed cancer is examined and graded by a pathologist using the following system: R microscopic tumour clearance; R1 microscopic tumour infiltration; and R2 macroscopic residual tumour. Staging for pancreatic cancer this describes the size of the cancer, where it is and whether it has spread. It is used to help guide treatment. Scans and other tests, such as biopsies, will give information about the staging. Type of pancreatic cancer this is the type of cell the pancreatic cancer started in. The majority of pancreatic cancers start in the cells that produce digestive juices and are called exocrine pancreatic cancers. Less commonly, pancreatic cancers start in the cells that produce insulin and hormones and are known as endocrine pancreatic cancers. Pancreatic cancer can also start in other types of cells but this is rare. 3 Aims and Objectives This policy considered gemcitabine and capecitabine combination chemotherapy following surgery for pancreatic cancer. The objectives were to establish, via an evidence review the efficacy and safety of using gemcitabine and capecitabine combination chemotherapy compared with gemcitabine given alone following pancreatic cancer surgery. 1
11 4 Epidemiology and Needs Assessment Around 9,6 people in the UK get pancreatic cancer each year and it is the 11th most common cancer. In the past 1 years, pancreatic cancer rates have increased and it is thought they will continue to increase over the next decade (Cancer Research UK, 218). Pancreatic cancer is more common in older people and almost half of all new cases are diagnosed in people aged 75 and over; pancreatic cancer is uncommon in people under 4 years old. It is more common in people living in poorer areas and it affects men and women equally. In the past 1 years, pancreatic cancer rates have increased and it is thought they will continue to increase over the next decade (Cancer Research UK, 218). Common risk factors for pancreatic cancer include smoking, obesity, consuming foods high in fat, heavy alcohol use, diabetes and chronic pancreatitis (an inflammation of the pancreas which can occur for a variety of reasons). It can also run in families and is associated with rare inherited conditions. It is estimated that approximately 1% of patients with pancreatic cancer will have surgery (Pancreatic Cancer UK, 215). In England, this equates to approximately 845 patients a year. All cases of surgically resected pancreatic cancer where microscopic clearance (R) or microscopic infiltration (R1) of the resection margins has been achieved with surgery would be assessed to determine if gemcitabine and capecitabine is able to be given (i.e., ability to tolerate the chemotherapy). Of the 845 people undergoing potentially curative surgery, it is estimated that approximately 5% will have either R or R1 margins and will therefore be eligible for treatment under the criteria within the policy. The remaining 5% of cases will have R2 margins and fall outside the scope of this policy. 5 Evidence Base NHS England has concluded that there is sufficient evidence to support the routine commissioning of this treatment for the indication. 11
12 An evidence review assessed the clinical and cost-effectiveness of using gemcitabine and capecitabine in combination as adjuvant therapy following potentially curative surgery for pancreatic cancer compared with gemcitabine alone. The evidence review was based on 1 open label randomised controlled trial which compared adjuvant treatment with gemcitabine plus capecitabine with gemcitabine alone in 73 people who had undergone complete macroscopic resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (R or R1 resections). The main outcome of the study was overall survival, defined as the time from randomisation until death from any cause. Relapse-free survival, which was defined as the minimum time from randomisation to date of local tumour recurrence, lymph node spread, distant metastases or death from any cause, was a secondary outcome. Participants in the study were followed-up for a median of 43.2 months. The study included people with the indication and characteristics of interest and the results are generalisable to a UK population (76% of participants were from the UK). Although the study was generally well-conducted, it was open label and participants and study investigators knew which treatment had been allocated, which is a source of bias. However, the primary outcome of overall survival is unlikely to be influenced by bias. Compared with gemcitabine alone there was a statistically significant increase of 2.5 months in the median overall survival time with gemcitabine plus capecitabine. The median overall survival time was 25.5 months in the gemcitabine group compared with 28. months in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group. Gemcitabine plus capecitabine had a statistically significant treatment effect on overall survival in people who had negative resection margins (R resections). In people who had positive resection margins (R1 resections) gemcitabine plus capecitabine had no statistically significant treatment effect on overall survival. However, the study was powered for the primary outcome of overall survival for the whole group; while the analysis of the R and R1 resection subgroups was prespecified, caution should be exercised when interpreting the results of these individual subgroups. In this study, positive resection margins (R1) were defined as any tumour cell within 1 millimetre of any surface of the specimen. In people who had R resections, gemcitabine plus capecitabine increased median overall survival by 11.6 months compared with gemcitabine alone (from 27.9 months 12
13 to 39.5 months). In people who had R1 resections, there was a.7 month difference between the 2 treatment groups for median overall survival (23. months in the gemcitabine group compared with 23.7 months in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group). Compared with gemcitabine alone, estimated overall survival at 5 years was found to be 12.5% higher with gemcitabine plus capecitabine (16.3% compared with 28.8%). These results are only estimates as not all people still alive at the end of the study would have had 5 years of follow-up. The study ran for approximately 7.5 years but participants could be recruited to the study at any time during the first 6 years. There was no statistically significant difference between gemcitabine plus capecitabine and gemcitabine alone for median relapse-free survival time. So although an increase in overall survival was seen, no difference was seen in how long it took for the pancreatic cancer to relapse or progress in the people who were still alive. The median relapse-free survival time was 13.1 months in the gemcitabine group compared with 13.9 months in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group. Three-year relapse-free survival was 2.9% in the gemcitabine group compared with 23.8% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group and 5 year relapse-free survival was 11.9% in the gemcitabine group compared with 18.6% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group. Fourteen percent of participants in the gemcitabine group and 22% of participants in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group stopped treatment early due to side-effects. There was no statistical significant difference between gemcitabine plus capecitabine and gemcitabine alone for the percentage of participants who had at least 1 treatment-related serious adverse event (26% in the gemcitabine group compared with 24% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group), although the study did not report how it defined treatment-related serious adverse events. Adverse events were graded according to the National Cancer Institute common toxicity criteria, version 4.3. This grades adverse events on a scale of 1 to 5 with 4 being the most serious adverse event and 5 being death. Grade 3 4 adverse events were reported by 54% of participants in the gemcitabine group compared with 63% of participants in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group. There was a statistically significant higher percentage of participants who had grade 3 4 adverse events of 13
14 diarrhoea, neutropenia and hand-foot syndrome in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group compared with the gemcitabine group. There was a statistically significant lower percentage of participants who had grade 3 4 adverse events of infection and other infestations (adverse event category not defined in the paper) in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group compared with the gemcitabine group: Diarrhoea: 2% in the gemcitabine group compared with 5% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group Neutropenia: 24% in the gemcitabine group compared with 38% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group Hand-foot syndrome: No participants in the gemcitabine group compared with 7% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group Infections and other infestations: 7% in the gemcitabine group compared with 3% in the gemcitabine plus capecitabine group. 6 Criteria for Commissioning Capecitabine with gemcitabine combination therapy should be considered as adjuvant treatment in cases of pancreatic cancer, where either microscopic clearance (R) or microscopic infiltration (R1) of the margins has been achieved following surgical resection. Treatment should commence within 12 weeks of surgery and continue for six months. When used to treat this indication, both drugs are given concurrently in the following way: Gemcitabine is administered intravenously. Each patient will receive six cycles of treatment, each cycle comprising 1 mg/m 2 given intravenously once a week for three of every four weeks; and Capecitabine is given orally. Each patient will receive six cycles of treatment, each cycle comprising 166 mg/m 2 given daily for twenty-one days followed by seven days rest. 14
15 The decision to select the patient for adjuvant treatment with gemcitabine and capecitabine must be made by the hepatobiliary and pancreatic multi-disciplinary team and the patient. The first cycle must be prescribed by a consultant specialist specifically trained and accredited in the use of systemic anti-cancer therapy. A decision to continue or stop treatment should be made by the multi-disciplinary team and the patient. 7 Patient Pathway The patient pathway in accessing this treatment will be through the hepatobiliary and pancreatic multi-disciplinary team. This reflects existing care pathway arrangements for patients with pancreatic cancer. 8 Governance Arrangements As capecitabine is not a licensed medicine for this indication, any provider organisation treating patients with this intervention will be required to assure itself that the internal governance arrangements have been completed before the medicine is prescribed. These arrangements may be through the trust s Drugs and Therapeutics committee (or similar) and NHS England may ask for assurance of this process. Providers will be expected to follow trust and Cancer Alliance policies for the safe prescribing and monitoring of off-label licensed medications including compliance with MHRA safety alerts. Prescribers need to also be aware of their responsibilities as specified in MHRA Drug Safety Update volume 1 issue, 12 July 217:2. 9 Mechanism for Funding Gemcitabine and capecitabine will be funded by local specialised commissioning teams, through established chemotherapy funding arrangements. 1 Audit Requirements Systemic Anti-Cancer Treatment (SACT) dataset. 15
16 11 Documents Which Have Informed this Policy NHS England Evidence Review for Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer. 12 Date of Review This document will be reviewed when information is received which indicates that the policy requires revision. 16
17 References Cancer Research UK About Pancreatic Cancer. January [Accessed January 218] Neoptolemos JP, Palmer DH, Ghaneh P et al. (217). Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): a multicentre, openlabel, randomised, phase 3 trial. The Lancet 389: Pancreatic Cancer UK. Surgery for Operable Pancreatic Cancer. January 215. London: Pancreatic Cancer UK. [Accessed March 218] 17
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170054P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170054P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16042/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16042/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170029P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170029P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae Reference: NHS England: 16062/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae Reference: NHS England: 16062/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16029/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16029/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Reference: NHS England: 16017/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Reference: NHS England: 16017/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Reference: NHS England 1602
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Clofarabine for refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) as a bridge to stem cell transplantation Reference: NHS England 1602 First published: TBC
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Clofarabine for refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) as a bridge to stem cell transplantation Reference: NHS England 1602 First published: TBC
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1736P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1736P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Levofloxacin nebuliser solution for chronic Pseudomonas lung infection in cystic fibrosis (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Levofloxacin nebuliser solution for chronic Pseudomonas lung infection in cystic fibrosis (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1732P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Levofloxacin nebuliser solution for chronic Pseudomonas lung infection in cystic fibrosis (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1732P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult) Reference: NHS England B01/P/d NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult) Reference: NHS England B01/P/d NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.14 Shingles immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.14 Shingles immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a.
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease Reference: NHS England: 16032/P 2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease Reference: NHS England: 16032/P 2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) Reference: NHS England 1607 1 First published: TBC Prepared by NHS England
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Bendamustine with rituximab for relapsed indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) Reference: NHS England 1607 1 First published: TBC Prepared by NHS England
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pegvisomant for acromegaly as a third-line treatment (adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pegvisomant for acromegaly as a third-line treatment (adults) Reference: NHS England: 16050/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pegvisomant for acromegaly as a third-line treatment (adults) Reference: NHS England: 16050/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 17088P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 17088P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical
Insert heading depending line on length; please delete delete. length; please delete other cover options once
 Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
Clinical commissioning policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of advanced indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages)
 Clinical commissioning policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of advanced indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170055P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER
Clinical commissioning policy: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of advanced indolent non-hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170055P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex Reference: NHS England E09X04/01 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex Reference: NHS England E09X04/01 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Reference No: Author(s) 12/05/16. Approval date: committee. June Operational Date: Review:
 Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist & on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist & on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bortezomib for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bortezomib for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1735P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bortezomib for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1735P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy First published:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy First published:
Reference No: Author(s) Approval date: 12/05/16. Committee. June Operational Date: Review:
 Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Biliary Tract Cancer (BTC) Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Biliary Tract Cancer (BTC) Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
The incidence of pancreatic cancer is rising in India and is higher in the urban male population in the western and northern parts of India.
 Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Pancreatic Cancer (1 of 5)
 i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
Using selective internal radiation therapy to treat bowel cancer that has spread to the liver
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Using selective internal radiation therapy to treat bowel cancer that has spread to the liver NICE interventional procedures guidance
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Using selective internal radiation therapy to treat bowel cancer that has spread to the liver NICE interventional procedures guidance
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps. Martin Lee
 National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer
 Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer Based on findings from the National Bowel Cancer Audit Background How are patients diagnosed?
Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer Based on findings from the National Bowel Cancer Audit Background How are patients diagnosed?
Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Pembrolizumab for drug-resistant gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. NHS England Reference: P
 Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Pembrolizumab for drug-resistant gestational trophoblastic neoplasia NHS England Reference: 170027P 1 Equality statement Promoting equality and addressing
Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Pembrolizumab for drug-resistant gestational trophoblastic neoplasia NHS England Reference: 170027P 1 Equality statement Promoting equality and addressing
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care
 CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care Technical guidance NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care Technical guidance NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP)
 Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Information for patients This information is for people with cancer of unknown primary (CUP) and covers symptoms, investigations/tests and treatment options. If there is
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Information for patients This information is for people with cancer of unknown primary (CUP) and covers symptoms, investigations/tests and treatment options. If there is
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: 18Fflourodeoxyglucose
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: 18Fflourodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) as part of radical radiotherapy treatment planning for oesophageal cancer
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: 18Fflourodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) as part of radical radiotherapy treatment planning for oesophageal cancer
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Human coagulation factor X for hereditary factor X deficiency (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Human coagulation factor X for hereditary factor X deficiency (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170105P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Human coagulation factor X for hereditary factor X deficiency (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170105P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
OFFICIAL. Document Status. NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX
 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX OFFICIAL Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning Nursing Trans. & Corp. Ops. Strategy & Innovation Finance Publications Gateway Reference:
NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX OFFICIAL Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning Nursing Trans. & Corp. Ops. Strategy & Innovation Finance Publications Gateway Reference:
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
Mucinous breast cancer
 Mucinous breast cancer This booklet is for people who would like more information about mucinous breast cancer. It describes what mucinous breast cancer is, its symptoms, how a diagnosis is made and possible
Mucinous breast cancer This booklet is for people who would like more information about mucinous breast cancer. It describes what mucinous breast cancer is, its symptoms, how a diagnosis is made and possible
Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment
 Cancer treatments Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment What are the main treatments? Hormone therapy Surgery Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Targeted anti-cancer therapy (immunotherapy)
Cancer treatments Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment What are the main treatments? Hormone therapy Surgery Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Targeted anti-cancer therapy (immunotherapy)
Commissioning Urology Services in New NHS
 Commissioning Urology Services in New NHS Oct 2013 Commissioning Urology Services NHS England s Role Role of the new Clinical Reference Groups Current Issues / Work Programme for Urology Clinical Reference
Commissioning Urology Services in New NHS Oct 2013 Commissioning Urology Services NHS England s Role Role of the new Clinical Reference Groups Current Issues / Work Programme for Urology Clinical Reference
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Trastuzumab, as monotherapy and in combination with a taxane, for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer (to include
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Trastuzumab, as monotherapy and in combination with a taxane, for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer (to include
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pasireotide for acromegaly as thirdline treatment (adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pasireotide for acromegaly as thirdline treatment (adults) Reference: NHS England: 16003/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Pasireotide for acromegaly as thirdline treatment (adults) Reference: NHS England: 16003/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
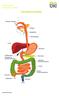 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of localised prostate cancer (adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of localised prostate cancer (adults) Reference: NHS England: 170021/P Standard NHS England INFORMATION READER
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of localised prostate cancer (adults) Reference: NHS England: 170021/P Standard NHS England INFORMATION READER
Guideline for the Management of Patients Suitable for Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Version History Guideline for the Management of Patients Suitable for Immediate Breast Reconstruction Version Summary of change Date Issued 2.0 Endorsed by the Governance Committee 20.02.08 2.1 Circulated
Version History Guideline for the Management of Patients Suitable for Immediate Breast Reconstruction Version Summary of change Date Issued 2.0 Endorsed by the Governance Committee 20.02.08 2.1 Circulated
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children. January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X.
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X England 1 NHS England Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X England 1 NHS England Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for
Phyllodes tumours: borderline and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information about borderline or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the symptoms, how a diagnosis
Phyllodes tumours: borderline and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information about borderline or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the symptoms, how a diagnosis
Clinical commissioning policy statement: Arsenic trioxide for the treatment of high risk acute promyelocytic leukaemia (all ages)
 Clinical commissioning policy statement: Arsenic trioxide for the treatment of high risk acute promyelocytic leukaemia (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170072P 1 Contents 1 Plain language summary... 3
Clinical commissioning policy statement: Arsenic trioxide for the treatment of high risk acute promyelocytic leukaemia (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170072P 1 Contents 1 Plain language summary... 3
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy. Issued by the Breast Team
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
Reference: NHS England 1605
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of advanced indolent non- Hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) Reference: NHS England 1605 First published: TBC
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Bendamustine with rituximab for first line treatment of advanced indolent non- Hodgkin s lymphoma (all ages) Reference: NHS England 1605 First published: TBC
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476
 Paclitaxel as albumin-bound nanoparticles with gemcitabine for untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476 NICE 2018. All
Paclitaxel as albumin-bound nanoparticles with gemcitabine for untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476 NICE 2018. All
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170065P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170065P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV positive adults and adolescents
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV positive adults and adolescents Reference: NHS England F03/P/b NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV positive adults and adolescents Reference: NHS England F03/P/b NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Concomitant (without adjuvant) temozolomide and radiation to treat glioblastoma: A retrospective study
 Concomitant (without adjuvant) temozolomide and radiation to treat glioblastoma: A retrospective study T Sridhar 1, A Gore 1, I Boiangiu 1, D Machin 2, R P Symonds 3 1. Department of Oncology, Leicester
Concomitant (without adjuvant) temozolomide and radiation to treat glioblastoma: A retrospective study T Sridhar 1, A Gore 1, I Boiangiu 1, D Machin 2, R P Symonds 3 1. Department of Oncology, Leicester
Interim Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Adalimumab for Severe Refractory Uveitis. Reference: NHS England: /PS
 Interim Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Adalimumab for Severe Refractory Uveitis Reference: NHS England: 170010/PS Publications Gateway Reference: Document Purpose Policy 05527s Document Name
Interim Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Adalimumab for Severe Refractory Uveitis Reference: NHS England: 170010/PS Publications Gateway Reference: Document Purpose Policy 05527s Document Name
Lymphoma accounts for 10-20% of all canine cancers and is by far the most common canine blood cancer.
 Lymphoma What is cancer? Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
Lymphoma What is cancer? Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sapropterin for Phenylketonuria (all ages) NHS England Reference: P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sapropterin for Phenylketonuria (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1713P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sapropterin for Phenylketonuria (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1713P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV infection (all ages) Reference: NHS England F03/P/b
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV infection (all ages) Reference: NHS England F03/P/b NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Use of cobicistat as a booster in treatment of HIV infection (all ages) Reference: NHS England F03/P/b NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Head and Neck Cancer surgeon level data - first report. Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Head and Neck Cancer surgeon level data - first report Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 1 of 8 Foreword This report for the first time presents data for individual surgeons relating to head
Head and Neck Cancer surgeon level data - first report Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 1 of 8 Foreword This report for the first time presents data for individual surgeons relating to head
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma AProf Lara Lipton 28 April 2018 Percentage alive 5 years after diagnosis for men and women Epidemiology 6% of cancer related deaths worldwide 4 th highest cause of cancer death
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma AProf Lara Lipton 28 April 2018 Percentage alive 5 years after diagnosis for men and women Epidemiology 6% of cancer related deaths worldwide 4 th highest cause of cancer death
Chronic conditions explained
 Chronic conditions explained The limits of your cover for treatment of chronic medical conditions April 2015 Contents Undertanding chronic conditions Why it s important for you to understand 3 about chronic
Chronic conditions explained The limits of your cover for treatment of chronic medical conditions April 2015 Contents Undertanding chronic conditions Why it s important for you to understand 3 about chronic
Pancreas Quizzes c. Both A and B a. Directly into the blood stream (not using ducts)
 Pancreas Quizzes Quiz 1 1. The pancreas produces hormones. Which type of hormone producing organ is the pancreas? a. Endocrine b. Exocrine c. Both A and B d. Neither A or B 2. Endocrine indicates hormones
Pancreas Quizzes Quiz 1 1. The pancreas produces hormones. Which type of hormone producing organ is the pancreas? a. Endocrine b. Exocrine c. Both A and B d. Neither A or B 2. Endocrine indicates hormones
Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg81
 Advanced breast cancer: diagnosis and treatment Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg81 NICE 20. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Advanced breast cancer: diagnosis and treatment Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg81 NICE 20. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Alemtuzumab for treating relapsingremitting. sclerosis third cycle (all ages)
 Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Alemtuzumab for treating relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis third cycle (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170075P 1 Equality statement Promoting equality
Urgent Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Alemtuzumab for treating relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis third cycle (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170075P 1 Equality statement Promoting equality
RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION
 RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Francesco Sclafani Medical Oncologist, Clinical Research Fellow The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK esmo.org Disclosure I have nothing to declare
RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Francesco Sclafani Medical Oncologist, Clinical Research Fellow The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK esmo.org Disclosure I have nothing to declare
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY:
 PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Dabrafenib-Trametinib PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Dabrafenib-Trametinib PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL
Single Technology Appraisal (STA)
 Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Durvalumab for maintenance treatment of locally advanced unresectable non-small cell lung cancer that has not progressed after platinum-based chemoradiation therapy Response
Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Durvalumab for maintenance treatment of locally advanced unresectable non-small cell lung cancer that has not progressed after platinum-based chemoradiation therapy Response
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY:
 PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Pembrolizumab PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL NAME/STAMP:
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Pembrolizumab PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL NAME/STAMP:
Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009
 HIGHLIGHT ARTICLE - Slide Show Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009 Muhammad Wasif Saif
HIGHLIGHT ARTICLE - Slide Show Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009 Muhammad Wasif Saif
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC THERAPY: CONSENT FORM FERRERI / IELSG PROTOCOL. Patient s first names. Date of birth
 Page 1 of 6 FORM FERRERI / IELSG PROTOCOL Patient s surname/family name Patient s first names Date of birth Hospital Name: Guy s Hospital St. Thomas Hospital King s College Hospital Lewisham Hospital NHS
Page 1 of 6 FORM FERRERI / IELSG PROTOCOL Patient s surname/family name Patient s first names Date of birth Hospital Name: Guy s Hospital St. Thomas Hospital King s College Hospital Lewisham Hospital NHS
Paget s disease of the breast
 Paget s disease of the breast This booklet is for people who d like more information about Paget s disease of the breast (also known as Paget s disease of the nipple). It describes what Paget s disease
Paget s disease of the breast This booklet is for people who d like more information about Paget s disease of the breast (also known as Paget s disease of the nipple). It describes what Paget s disease
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY:
 PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Atezolizumab PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL NAME/STAMP:
PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC ANTI- CANCER THERAPY: Atezolizumab PATIENT DETAILS PATIENT S SURNAME/FAMILY NAME: PATIENT S FIRST NAME(S): DATE OF BIRTH: NHS NUMBER: (or other identifier) HOSPITAL NAME/STAMP:
Horizon Scanning Centre November Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887
 Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a
Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Everolimus in combination with exemestane for the treatment of advanced or metastatic HER2 negative, oestrogen
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Everolimus in combination with exemestane for the treatment of advanced or metastatic HER2 negative, oestrogen
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
Louisa Fleure. Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist. Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust
 Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
Patient guide to Capecitabine chemotherapy with radiotherapy for rectal cancer
 Patient Name: Patient guide to chemotherapy with radiotherapy for rectal cancer Chemotherapy This guide should only be given to patients who have been prescribed capecitabine chemotherapy in conjunction
Patient Name: Patient guide to chemotherapy with radiotherapy for rectal cancer Chemotherapy This guide should only be given to patients who have been prescribed capecitabine chemotherapy in conjunction
Pancreatic Cancer Action Patient and Carer Survey 2015
 Pancreatic Cancer Action Patient and Carer Survey 2015 The survey was conducted online using Survey Monkey between 17 th August and 16 th October 2015 190 respondents made up of: Men: 56% Women: 44% Carers:
Pancreatic Cancer Action Patient and Carer Survey 2015 The survey was conducted online using Survey Monkey between 17 th August and 16 th October 2015 190 respondents made up of: Men: 56% Women: 44% Carers:
Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy
 Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy Information for patients Excellent Care with Compassion What is sentinel node? The sentinel node (gland) is the first lymph node or nodes in
Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy Information for patients Excellent Care with Compassion What is sentinel node? The sentinel node (gland) is the first lymph node or nodes in
Educator Navigation Guide
 Decoding Breast Cancer Virtual Lab Educator Navigation Guide Decoding Cancer Nav Guide 2 Introduction In this virtual lab, students test tissue samples from different patients with breast cancer in order
Decoding Breast Cancer Virtual Lab Educator Navigation Guide Decoding Cancer Nav Guide 2 Introduction In this virtual lab, students test tissue samples from different patients with breast cancer in order
Progress in improving cancer services and outcomes in England. Report. Department of Health, NHS England and Public Health England
 Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General Department of Health, NHS England and Public Health England Progress in improving cancer services and outcomes in England HC 949 SESSION 2014-15 15 JANUARY
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General Department of Health, NHS England and Public Health England Progress in improving cancer services and outcomes in England HC 949 SESSION 2014-15 15 JANUARY
Patient identifier/label: Page 1 of 6 PATIENT AGREEMENT TO SYSTEMIC THERAPY: CONSENT FORM CYTARABINE (HIGH DOSE)
 Patient identifier/label: Page 1 of 6 CYTARABINE Patient s surname/family name Patient s first names Date of birth Hospital Name: Guy s Hospital St. Thomas Hospital King s College Hospital Lewisham Hospital
Patient identifier/label: Page 1 of 6 CYTARABINE Patient s surname/family name Patient s first names Date of birth Hospital Name: Guy s Hospital St. Thomas Hospital King s College Hospital Lewisham Hospital
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gastroelectrical stimulation for gastroparesis
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gastroelectrical stimulation for gastroparesis Reference: NHS England: 16025/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gastroelectrical stimulation for gastroparesis Reference: NHS England: 16025/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised
Photodynamic therapy for bile duct cancer. Issue date: July 2005
 Issue date: July 2005 Photodynamic therapy for bile duct cancer Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information about NICE Interventional Procedure
Issue date: July 2005 Photodynamic therapy for bile duct cancer Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information about NICE Interventional Procedure
Aligning the Publication of Performance Data Statistics Consultation
 Aligning the Publication of Performance Data Statistics Consultation NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information Nursing Trans. & Corp. Ops.
Aligning the Publication of Performance Data Statistics Consultation NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information Nursing Trans. & Corp. Ops.
Clinical commissioning policy: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for malignant otitis externa (all ages) For implementation from 1 April 2019
 Clinical commissioning policy: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for malignant otitis externa (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1745P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical commissioning policy: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for malignant otitis externa (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1745P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY...
 Colorectal Pathway Board: Non-Surgical Oncology Guidelines October 2015 Organization» Table of Contents ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY... 2 DUKES C/ TNM STAGE 3... 2 DUKES B/ TNM STAGE 2... 3 LOCALLY ADVANCED
Colorectal Pathway Board: Non-Surgical Oncology Guidelines October 2015 Organization» Table of Contents ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY... 2 DUKES C/ TNM STAGE 3... 2 DUKES B/ TNM STAGE 2... 3 LOCALLY ADVANCED
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 15 February 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
Intended for use by Clinicians and Health Care Providers involved in the Management or Referral of adult patients with pancreatic
 Intended for use by Clinicians and Health Care Providers involved in the Management or Referral of adult patients with pancreatic cancer Section AA Cancer Centre Referrals In the absence of metastatic
Intended for use by Clinicians and Health Care Providers involved in the Management or Referral of adult patients with pancreatic cancer Section AA Cancer Centre Referrals In the absence of metastatic
