The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis
|
|
|
- Valentine Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Tropical Medicine Volume 3 Number 1 The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis N Moorchung, A Srivastava, N Gupta, S Bandopadhyay, B Achyut, B Mittal Citation N Moorchung, A Srivastava, N Gupta, S Bandopadhyay, B Achyut, B Mittal. The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis. The Internet Journal of Tropical Medicine Volume 3 Number 1. Abstract Chronic gastritis is a multifactorial disorder, which is influenced primarily by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In addition to the density of the organism, the CagA pathogenicity island (PAI) of H pylori is thought to be a primary factor contributing to the antral inflammation. Endoscopic findings are believed to be non contributory in the diagnosis. In this study, we have shown that endoscopic features like erythema, erosions and nodularity maybe contributory in predicting the presence of H pylori in the biopsy specimen. The primary factor influencing the degree of inflammation in gastritis appears to be the density of H pylori in the antrum. The CagA pathogenicity island does not appear to have a role in influencing the severity of the antral inflammation. The role of other H pylori antigens remains undetermined. INTRODUCTION Although gastritis was first interpreted to be due to ageing and lifelong exposure to various insults, it is now clear that the most common cause of this inflammatory condition is infection with Helicobacter pylori ( 1 ). It has been shown that this organism is strongly associated with chronic active gastritis as well as gastric adenocarcinoma and MALT (Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue) lymphomas ( 2 ). Although H pylori infection is extremely common, only a small proportion of those infected develop chronic gastritis. Thus the clinical outcome is dependant on a complex interplay between the bacterium and the host. Several bacterial virulence factors have been implicated in influencing the severity of gastritis. The CagA island which encodes a high molecular weight antigen (CagA) is believed to stimulate gastric mucosal cells to produce high levels of interleukin 8 that has a pivotal role in the inflammatory responses to infection ( 3, 4, 5 ). H pylori strains that express the CagA protein are considered to be endowed with increased pathogenecity. Studies have shown that the prevalence of antibodies to the CagA protein is higher in patients with peptic ulcer disease than in H pylori gastritis without ulcer ( 6, 7, 8, 9 ). However it is not clear if increased titres of Cag A antibodies are associated with a severe phenotype of chronic gastritis. The endoscope has been used extensively in visualizing antral gastritis but histopathological examination remains the gold standard for the diagnosis. ( 10, 11 ). Various gastroscopic features may be interpreted as signs of gastritis. These include erythema (diffuse, spotty, linear), erosions, absence of rugae in the gastric corpus, and presence of visible vessels ( 12 ). It remains uncertain if any of the endoscopic features are a predictor for the presence of H pylori or any particular histological features of gastritis. The Sydney system for grading and classifying chronic gastritis was devised to provide a standardised approach to the histological interpretation of biopsies in 1990 ( 13 ) and it was later upgraded in 1994 ( 14 ). Several parameters are assessed in this system including the density of H pylori. The parameters are graded on a visual analogue scale as normal, mild, moderate and marked. This system remains an excellent predictor for evaluating the presence of H pylori and the severity of gastritis. In this study, we gauged if the density of H pylori in biopsy specimens and the presence of anti CagA antibodies were significantly associated with the severity of gastritis as evaluated by histopathology. We also studied the role of endoscopy in predicting the severity of gastritis. The aim of the study was two fold; Firstly, we wished to evaluate the role of H pylori and its main antigen in the pathogenesis of the disease. Secondly, we attempted to assess if a careful endoscopic examination would obviate the need of 1 of 7
2 histopathological examination in assessing for the presence of H pylori and the severity of the disease. MATERIALS AND METHODS PATIENTS Between August 2004 and August 2005, 120 patients with non ulcer dyspepsia who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy were studied. The duration of the illness and history of tobacco and alcohol consumption were recorded. Dietary habits noted included a vegetarian or non-vegetarian diet and history of excessive consumption of spices. Vegetarians included patients who consumed only grain, vegetables and milk or milk products with the total exclusion of meat, fish or eggs in their food. A non-vegetarian diet included patients who consumed meat, fish or eggs regularly in addition to grain, vegetables and milk products. Exclusion criteria were present or past history of gastric neoplasm's or gastric surgery, long term therapy with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, liver disease and previous treatment with antibiotics or bismuth salts. All subjects had given informed consent for the study and the local ethics committee had approved the protocol. Endoscopy was performed after an overnight fast with standard upper gastrointestinal endoscopes (Olympus Optical Co Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and biopsy specimens were obtained with standard biopsy forceps. On endoscopy, the features noted were the presence or absence of erythema, nodularity, exudates, mucosal edema and excessive friability of the mucosa. A visible vascular pattern, intramucosal bleeding and the presence of erosions were also recorded. A special mention was made of the presence of rugal atrophy or hypertrophy. The endoscopic evaluation was done by an experienced endoscopist (NKG) who had performed more than 15,000 endoscopies. Two to three antral biopsies were taken for histological examination from the distal lesser and greater curvature, 2 to 3 cm from the pylorus. The biopsies were immediately fixed in formalin for histopathological examination. In addition to the biopsy samples, 3-4 ml of peripheral blood was collected from each patient. The blood was collected in a sterile tube and allowed to clot. The tubes were then centrifuged at rpm for 5 minutes to separate the serum. The separated serum was then stored at - 20 C and used for the anti CagA ELISA. HISTOLOGY All biopsies were oriented and fixed in 10% buffered formalin. They were processed by routine techniques and stained by the haematoxylin and eosin stain, the modified Giemsa stain for the detection of H pylori and the Cookes stain for the detection of mast cells ( 15 ). The modified Giemsa stain was used for the evaluation of H pylori because it has been reported to be a reliable, cheap and reproducible method for the detection of the organism ( 16 ). The slides were evaluated by three pathologists (NM, ANS and SB) according to the Updated Sydney System ( 14 ). The pathologists were unaware of the clinical, endoscopic and serological data. A score of 0 to 3 (absent, mild, moderate, marked) was assigned to each of the morphological variables: H pylori density, density of neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils and mast cells. Glandular atrophy, glandular shortening, intestinal metaplasia and the presence or absence of fibrosis was also noted and graded into the above three categories. The presence of micro ulceration, activity, and foveolar hyperplasia was noted and graded as present or absent. The grading of the presence of lymphoid follicles was done as per the histological scoring index as proposed by Wotherspoon et al ( 17 ). For each variable, the highest score was given among the antral biopsies. To minimize the interobservor variability in grading the histopathological features, we used the scoring system as proposed by Aydin et al ( 18 ) SEROLOGY Serum samples stored at -20 C were tested for the presence of IgG antibodies against the CagA antigenic fraction of H pylori using standard ELISA (Genesis diagnostics, UK). Eight controls were run with each set of samples. In addition to the positive and negative control, six serial dilutions of the CagA antigen were included. The dilutions were 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 U/ml. A standard curve was constructed based upon the OD of the controls. The OD of the test samples were then read off the curve. Repeat ELISA's were done as and when required. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The association between the clinical, endoscopic and histological findings was assessed by means of the χ2 test for trend ( 19 ). A probability value of p 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS DEMOGRAPHIC DATA 69 males and 51 females were included in the study. The 2 of 7
3 mean age of the patients was yrs with a range of 16 yrs to 70 yrs. The mean age of the male patients was yrs with a range of 16 yrs to 67 yrs. The mean age of the female patients was with a range of 16 yrs to 70 yrs. There was no significant difference in age and sex with regard to the colonization by H pylori or the severity of gastritis as evaluated by histopathological examination. There were fifteen smokers and five reformed smokers in the study. One of the female patients was a smoker. The rest of the smokers were males. Of the reformed smokers, one patient was a female and four were males. Ten patients gave a history of alcohol consumption. All the ten patients were male. Five patients were reformed drinkers, which included one female and four male patients. The numbers of the smokers and drinkers was too small to reach a statistical conclusion ), eosinophils (p = 0.00), micro ulceration (p = 0.00) and activity (p = 0.037). (Table 2). It was also was associated with the density of lymphocytes (p = 0.097) and the presence of lymphoid follicles (p = 0.098) at a p value of p 0.1. The presence of erosions was the third endoscopic feature, which was associated strongly with the presence of H pylori (p = 0.02) (data not shown). Figure 2 Table 2: Prevalance of severe histological features in patients with nodularity on endoscopy Fifty patients were non-vegetarians. There was no significant difference between the vegetarian and non-vegetarian group with any of the endoscopic or histopathological features. ENDOSCOPIC FEATURES The commonest endoscopic finding noted was the presence of erythema, which was seen in 49 patients. The presence of erythema was associated with the presence of H pylori (p = 0.03). It was also associated with the presence of lymphoid follicles (p = 0.038) and micro ulceration (p = 0.028). At a p value of p 0.1, erythema was associated with the density of neutrophils (p = 0.071) and active lesions (0.081).(Table 1) Figure 1 Table 1: Prevalance of and other histological features in patients with erythema on endoscopy The presence of edema, friability, mucosal exudates, rugal atrophy and hypertrophy was seen in an insignificant population of patients to have any statistical significance. HISTOPATHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS 67 antral biopsies showed H pylori on histopathological examination. The density of H pylori as visualized by histopathology (Fig 1) was strongly associated with the density of neutrophils (p = 0.00), lymphocytes (p = 0.050), plasma cells (p = 0.01), eosinophils (p = 0.08)(Fig 2), ulceration (p = 0.04) and active lesions (p = 0.00). In this study, the number of cases of intestinal metaplasia was too small to reach a statistical conclusion. Mast cells did not show any significant association with the density of H pylori (Fig 3). The presence of nodularity was also associated with the density of H pylori (p = 0.045). It was also associated with the density of neutrophils (p = 0.039), plasma cells (p = 3 of 7
4 Figure 3 Figure 1 Figure 5 Figure 3: Box Plot showing the lack of a relationship between density and the density of Mast cells as visualized by the Cookes stain Serological association - No association between the CagA antibody levels and the density of H pylori as visualized by the Giemsa stain was noted. The scatter plot of the CagA antibody levels is shown in Fig 4. Figure 4 Figure 2: Bar diagrams showing an increase in density as visualized on histopathology with various inflammatory parameters (neutrophils, plasma cell, lymphocyte and eosinophil density) Figure 6 Figure 4: Scatter plot showing a lack of correlation of anti CagA antibodies with the density of as visualized on histopathology DISCUSSION The use of endoscopy in the diagnosis of gastritis is debatable. Redeen et al ( 12 ) studied 488 patients with gastritis and attempted to correlate the endoscopic features. They concluded that the absence of rugae and the presence of visible vessels correlated with histological gastritis in the corpus and the antrum. No endoscopic features showed a sensitivity of more than 57 % for H. pylori infection. They 4 of 7
5 concluded that except for the absence of rugae and visible vessels, macroscopic features as observed during gastroscopy are of very limited value in the evaluation of gastritis. In our study, the presence of erythema, nodularity and erosions were statistically associated with the H pylori density and other inflammatory parameters. Our findings suggest that a careful endoscopic examination maybe a useful predictor for the presence of H pylori although further studies are needed to confirm our findings. A strong association has been reported between the H pylori density and inflammatory activity on gastritis ( 20 ). It has been noted that the presence of H pylori in a biopsy specimen was associated with acute and chronic inflammation ( 21, 22 ). However, the same studies have reported that there was no correlation between the density of H pylori and the degree of inflammation ( 21 ). In our study, there was a strong association between the degree of infiltration by various inflammatory cells and H pylori density in chronic gastritis. The neutrophillic infiltrate, activity and micro ulceration showed a significant association with the H pylori density. This is in concordance with the study by Sobala et al who have noted that some degree of neutrophillic infiltration is an almost constant companion of persisting infection ( 23 ). There was also a significant association of the H pylori density with the chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate. However, there was no correlation of the density of the organism with parameters like glandular atrophy and glandular shortening. Atrophy maybe a consequence of auto destructive products such as neutrophils and monocyte activation such as reactive oxygen metabolites and proteases ( 24 ). Glandular atrophy and intestinal metaplasia are probably not hospitable environments for the bacteria ( 25 ) and are hence associated with a decrease in the density of the organism. In Caucasian populations it has been reported that strains that contain the CagA pathogenic island are associated with a more severe disease than strains that lack CagA ( 26, 27, 28 ). CagA positive isolates are associated with a higher grade of antral polymorphonuclear inflammation. ( 27 ). It has also been reported that there is a strong correlation between the presence of serum antibodies to CagA and the isolation of CagA positive strains from a patient ( 27 ). In our study, although there was a strong association between the density of H pylori and the density of various inflammatory cells, there was no association between the CagA antibody levels and the degree of inflammation. This suggests that the presence of the organism is the primary factor influencing the inflammatory response and not the presence of the CagA pathogenic island. It has been reported that in Asian populations, the association of CagA positivity and disease risk is much weaker or not present ( 29, 30 ). This finding was also seen in this study. The existence of distinct variants of certain genes of the Cag pathogenicity island may offer an explanation for this discrepancy. Analysis of H pylori strains from East Asian patients suggested that in some strains, only a part of the Cag pathogenicity island is present ( 31, 32 ). Maeda et al ( 32 ) reported that 6% of the H pylori strains they had studied lacked the CagI or CagII islands although all of them retained the CagA gene. All the patients who lacked the complete pathogenicity island presented with non ulcer dyspepsia. 41 of 59 patients with the complete Cag pathogenic island presented with peptic ulcer or gastric cancer. It is possible that the absence of a part of the Cag pathogenic island may confer less pathogenicity than in patients who harbor the complete pathogenic island. Ikenoue et al ( 31 ) have reported similar findings. In their patients, the strains containing CagA but lacking CagE and/or CagT were less pathogenic than the strains with the complete pathogenic island. The CagA protein is strongly immunogenic and most patients colonized with a CagA positive strain show a high titre of anti CagA antibodies ( 33 ). Truncated proteins which do not contain the CagE or CagT components are likely to confer a strong immunogenicity but low pathogenicity. This would explain why the antibody titres against CagA have no relationship to the H pylori density or the degree of the inflammatory response. The existence of variant specific antibodies remains unknown. In conclusion, we suggest that endoscopic features like the presence of erythema, erosions and nodularity maybe a useful predictor for the presence of H pylori in the antrum. The degree of infiltration by H pylori is the primary mediator of the degree of inflammation in chronic gastritis and not the presence or absence of the CagA pathogenicity island. In the Indian context, it appears that the presence of the Cag pathogenicity island does not have a role in influencing the severity of gastritis. It fuctions more as an immunogenicity island rather than a pathogenicity island. Other host or bacterial factors need to be evaluated in order to define the primary factor leading to severe gastritis. 5 of 7
6 CORRESPONDENCE TO Dr Balraj Mittal PhD Phone: Ext 2322 Fax Department of Medical Genetics Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences Rae Bareilly Road Lucknow Uttar Pradesh, INDIA References 1. Soll A H. Gastritis and Helicobacter pylori. In : Goldman L, Bennet J C eds. Cecil Textbook of Medicine, 21st ed. Philadelphia: Saunders 2000: Peterson W L, Graham D Y. Helicobacter pylori. In: Feldman M, Scharschmidt B F, Sleisenger M F, eds. Sleisinger and Fordtrans Gastrointestinal and Liver disease. Pathophysiology (Diagnosis) and Management, 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders 1998: Crabtree J E, Covacci A, Farmery S M et al. Helicobacter pylori induced interleukin 8 expression in gastric epithelial cells is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J Clin Pathol 1995; 48: Crabtree J E, Farmery S M, Lindley I J et al.cag A / cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin 8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol 1994; 47: Censini S, Lange C, Xiang Z at al. CagA pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori encodes type 1 specific and disease associated virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: Tummuru M K R, Cover T L, Blaser M J. Cloning and expression of a high molecular weight major antigen of Helicobacter pylori: evidence of linkage to cytotoxin production. Infect Immunol 1993; 61: Covacci A, Censini S, Bugnoli M et al. Molecular characterization of the 128 KDa imunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: Oderda G, Figura N, Bayeli P F et al. Serological IgG recognition of Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin associated protein, peptic ulcer and gastroduodenal pathology in childhood. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1993; 5: Cover T L, Dooley C P, Blaser M J. Characterisation of human serological responses to proteins in Helicobacter pylori broth culture supernatants with vacuolising cytotoxin activity. Infect Immunol 1990; 58: Tepes B, Ferlan Marolt V, Jutersek A, Kausic B, Zaletel - Kragelj L. Interobservor variation in the assessment of gastritis reversibility after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Histopathology 1999; 34: Genta R M. Pathology of Helicobacter pylori infection. In: Weinstein R S ed. Advances in Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. St Louise Mosby 1994: Redeen S, Petersson F, Johnsson KA, Borch K, Relationship of gastroscopic features to histological findings in gastritis and Helicobacter pylori infection in a general population sample. Endoscopy 2003 Nov;35(11): Misiewice J J, Tytgat G N J, Goodwin C S. The Sydney system: a new classification of gastritis. J Hepatol Gastroenterol 1991: 6; Dixon M F, Genta R M, Yardley J H et al. Classification and Grading of Gastritis. The Updated Sydney System. Am J Surg Pathol 20(10) : , Cooke H C. A modified thionin technique for mast cells in tissue sections. J Med Laboratory 1961; 18: Rotini O, Cairns A, Gray S, Moayyedi P, Dixon M F. Histological identification of Helicobacter pylori: comparison of the staining methods. J Clin Pathol 2000; 53: Wotherspoon A C, Dogilioni C, Diss C D et al. Regression of primary low grade B cell gastric lymphoma of mucosal associated lymphoid tissue type after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet 1993:342(4); Aydin O, Reyhan E, Karabacak T, Kanok A. Interobserver variation in histopathological assessment of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. World J Gastroenterol 2003: 9(10); Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical methods in medical research. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. 1987: Holck S, Norgaard A, Bennedsen M, Permin H, Norn S, Andersen L P. Gastric mucosal cytokine responses in Helicobacter pylori infected patients with gastritis and peptic ulcers. Association with inflammatory parameters and bacterial load. Immunol and Med Microbiol 2003; 36: Hansing R L, D'Amico H, Levy M, Gullian R A. Prediction of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric specimens by Inflammatory and Morphological histological evaluation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992; 87: Marshall B J, Warren J R. Unidentified curved bacteria in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984; 1: Sobala G M, Axon A T R, Dixon M F. Morphology of chronic gastritis; relationship to age, Helicobacter pylori status and peptic ulceration. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1992; 4: Dixon M F. Pathophysiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Scan J Gastroenterol 1994; 29 Suppl 201: Zhang C, Yamada N, Wu Y L, Wen M, Matsuhisa T, Matsukura N. Helicobacter pylori infection, glandular atrophy and intestinal metaplasia in superficial gastritis, gastric erosion, erosive gastritis, gastric ulcer and early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: Blaser M J. Intra strain differences in Helicobacter pylori: a key question in mucosal damage? Ann Med 1995; 27: Cover T L, Glupczynski Y, Lage A P et al. Serological detection of infection with CagA positive Helicobacter pylori strains. J Clin Microbiol 1995; 33: van Doorn L J, Figueiredo C, Sanna R, Blaser M J, Quint W G V. Distinct variants of Helicobacter CagA are associated with VacA subtypes. J Clin Microbiol 1999; 37 (7): Ogura K, Kanai F, Maeda S et al. High prevalence of cytotoxin positive Helicobacter pylori in patients unrelated to the presence of peptic ulcers in Japan. Gut 1997; 41: Pan Z J, van der Hulst R W, Feller M et al. Equally high prevalence of infection with CagA positive Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients with peptic ulcer disease and those with chronic gastritis associated dyspepsia. J Clin Microbiol 1997; 35: Ikenoue T, Maeda K, Ogura H et al. Simple and practical methods to study cag pathogenicity island: usage of cage and cagt gene amplifications. Gastroenterology 114: A157 (abstr G0641). 32. Maeda S, Ikenoue K, Ogura H et al. Structure of cag pathogenicity island in Japanese and Western Helicobacter pylori isolates. Gastroenterology 114: A210 (abstr G0861). 33. Perez - Perez G I, Bhat N, Gaensbauer A et al. Country specific constancy by age in CagA + proportion of Helicobacter pylori infections. Int J Cancer 1997; 72: of 7
7 Author Information Nikhil Moorchung, MD, DNB, MNAMS (Pathology) A. N. Srivastava, MD (Pathology) N. K. Gupta, MD (Medicine) S. Bandopadhyay, MD(Path), MD (Biochem) B. R. Achyut, MSc Balraj Mittal, PhD 7 of 7
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
the pathology of chronic gastritis
 Original Article Singapore Med12007,48(5):447 Cytokine gene polymorphisms and the pathology of chronic gastritis Moorchung N, Srivastava A N, Gupta N K, Ghoshal U C, Achyut B R, Mittal B Department of
Original Article Singapore Med12007,48(5):447 Cytokine gene polymorphisms and the pathology of chronic gastritis Moorchung N, Srivastava A N, Gupta N K, Ghoshal U C, Achyut B R, Mittal B Department of
Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
Immunoglobulin G Antibody against Helicobacter pylori: Clinical Implications of Levels Found in Serum
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 1044 1048 Vol. 9, No. 5 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.5.1044 1048.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 1044 1048 Vol. 9, No. 5 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.5.1044 1048.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Original Article. Abstract
 Original Article Association of helicobacter pylori with carcinoma of stomach Muhammad Arif, Serajuddaula Syed Department of Pathology, Sindh Medical College, Karachi Abstract Objective: To note the association
Original Article Association of helicobacter pylori with carcinoma of stomach Muhammad Arif, Serajuddaula Syed Department of Pathology, Sindh Medical College, Karachi Abstract Objective: To note the association
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI DETECTION IN CHRONIC GASTRITIS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Histopathological profile of gastritis in adult patients seen at a referral hospital in Kenya
 Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 27 August 14; 13(3): 4117-4121 World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com 27 WJG. All rights reserved. RAPID COMMUNICATION Histopathological
Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 27 August 14; 13(3): 4117-4121 World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com 27 WJG. All rights reserved. RAPID COMMUNICATION Histopathological
Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization and Severity of Gastritis
 Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8320496, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8320496 Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization
Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8320496, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8320496 Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization
Determination of Helicobacter pylori Virulence by Simple Gene Analysis of the cag Pathogenicity Island
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 181 186 Vol. 8, No. 1 1071-412X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.1.181 186.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 181 186 Vol. 8, No. 1 1071-412X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.1.181 186.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen
 Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY. Robin Warren
 - Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Anti-CagA IgG Antibody Is Independent from Helicobacter pylori VacA and CagA Genotypes
 Anti-CagA IgG Antibody Is Independent from Helicobacter pylori VacA and CagA Genotypes Hashem Fakhre Yaseri 1, 2*, Mehdi Shekaraby 3, Hamid Reza Baradaran 4, Seyed Kamran Soltani Arabshahi 5 1 Gastroenterology,
Anti-CagA IgG Antibody Is Independent from Helicobacter pylori VacA and CagA Genotypes Hashem Fakhre Yaseri 1, 2*, Mehdi Shekaraby 3, Hamid Reza Baradaran 4, Seyed Kamran Soltani Arabshahi 5 1 Gastroenterology,
MOSAIC APPEARANCE OF GASTRIC MUCOSA AS A PREDICTOR FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
 Basrah Journal Original Article Of Surgery MOSAIC APPEARANCE OF GASTRIC MUCOSA AS A PREDICTOR FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION Ali Adnan Mohsin* & Sarkis K Strak @ *MBChB Registrar, @ MBChB, MRCP, FRCP,
Basrah Journal Original Article Of Surgery MOSAIC APPEARANCE OF GASTRIC MUCOSA AS A PREDICTOR FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION Ali Adnan Mohsin* & Sarkis K Strak @ *MBChB Registrar, @ MBChB, MRCP, FRCP,
Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 3, September 2010, pp. 345-350 original article Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 3, September 2010, pp. 345-350 original article Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit
 H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Variants of the 3 Region of the caga Gene in Helicobacter pylori Isolates from Patients with Different H. pylori-associated Diseases
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1998, p. 2258 2263 Vol. 36, No. 8 0095-1137/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Variants of the 3 Region of the caga
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1998, p. 2258 2263 Vol. 36, No. 8 0095-1137/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Variants of the 3 Region of the caga
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States
 Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia, Acid Peptic Disease, Helicobacter Pylori, Urease, Giemsa, Peptic Ulcer, Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia.
 INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Relation between clinical presentation, Helicobacter pylori density, interleukin 1β and 8 production, and caga status
 84 Department of Medicine, Veterans AVairs Medical Centre and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA Y Yamaoka D Y Graham Third Department of Internal Medicine, Kyoto Prefectural University of
84 Department of Medicine, Veterans AVairs Medical Centre and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA Y Yamaoka D Y Graham Third Department of Internal Medicine, Kyoto Prefectural University of
The effect of CagA status on response to Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in Western Turkey
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2001) 34: 1435-1439 CagA status affects H. pylori eradication rate ISSN 0100-879X 1435 The effect of CagA status on response to Helicobacter pylori
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2001) 34: 1435-1439 CagA status affects H. pylori eradication rate ISSN 0100-879X 1435 The effect of CagA status on response to Helicobacter pylori
H.Pylori IgG Cat # 1503Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
Original Article. Is There Any Association between Helicobacter pylori CagA Status and Patient's Habits with Gastric Carcinoma
 Faridpur Med. Coll. J. 2015;10(1):09-13 Original Article Is There Any Association between Helicobacter pylori CagA Status and Patient's Habits with Gastric Carcinoma MA Hassan 1, MA Ahad 2, MH Rahman 3,
Faridpur Med. Coll. J. 2015;10(1):09-13 Original Article Is There Any Association between Helicobacter pylori CagA Status and Patient's Habits with Gastric Carcinoma MA Hassan 1, MA Ahad 2, MH Rahman 3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF H. PYLORI IN PATIENTS OF GASTRIC CANCER IN SOUTHERN ODISHA
 ROLE OF H. PYLORI IN PATIENTS OF GASTRIC CANCER IN SOUTHERN ODISHA Kalandi Barik 1, I.C. Muduli 2, S.N. Mallick 3,Lachhaman Bag 4, Anower Hossen Halder 5, Rupesh Sondawle 6, Sarada Prasanna Sahoo 7, Sanjit
ROLE OF H. PYLORI IN PATIENTS OF GASTRIC CANCER IN SOUTHERN ODISHA Kalandi Barik 1, I.C. Muduli 2, S.N. Mallick 3,Lachhaman Bag 4, Anower Hossen Halder 5, Rupesh Sondawle 6, Sarada Prasanna Sahoo 7, Sanjit
caga Positive Helicobacter pylori in Brazilian Children Related to Chronic Gastritis
 254 BJID 2006; 10 (August) caga Positive Helicobacter pylori in Brazilian Children Related to Chronic Gastritis Luciano Lobo Gatti 1,2, Roger de Lábio¹, Luiz Carlos da Silva 3, Marília de Arruda Cardoso
254 BJID 2006; 10 (August) caga Positive Helicobacter pylori in Brazilian Children Related to Chronic Gastritis Luciano Lobo Gatti 1,2, Roger de Lábio¹, Luiz Carlos da Silva 3, Marília de Arruda Cardoso
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs Prof. Sheila Crowe
 Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients with Dyspepsia
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 184806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/184806 Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 184806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/184806 Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients
~Helicobacter pylori, gastritis, and peptic ulceration
 17 Department of Pathology J I Wyatt Department of Medicine T M Shallcross J E Crabtree RV Heatley St James University Hospital, Leeds LS9 7TF Correspondence to: Dr J I Wyatt. Accepted for publication
17 Department of Pathology J I Wyatt Department of Medicine T M Shallcross J E Crabtree RV Heatley St James University Hospital, Leeds LS9 7TF Correspondence to: Dr J I Wyatt. Accepted for publication
H.Pylori IgG
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Duodenal histology, ulceration, and Helicobacter pylori in the presence or absence of non-steroidal
 1162 Departments of Gastroenterology, A S Taha I Nakshabendi R I Russell Pathology, S Dahill F D Lee and Rheumatology, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow R D Sturrock Correspondence to: Dr A S Taha, Gastroenterology
1162 Departments of Gastroenterology, A S Taha I Nakshabendi R I Russell Pathology, S Dahill F D Lee and Rheumatology, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow R D Sturrock Correspondence to: Dr A S Taha, Gastroenterology
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter pylori status in Western Turkey
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 747-751 Dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori ISSN 0100-879X 747 Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 747-751 Dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori ISSN 0100-879X 747 Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report.
 Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
T M Peters, R J Owen, E Slater, R Varea, E L Teare, S Saverymuttu
 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:219 223 219 Public Health Laboratory, Chelmsford CM2 0YX, UK T M Peters E L Teare Helicobacter Reference Unit, Laboratory of Enteric Pathogens, Central Public Health Laboratory, 61
J Clin Pathol 2001;54:219 223 219 Public Health Laboratory, Chelmsford CM2 0YX, UK T M Peters E L Teare Helicobacter Reference Unit, Laboratory of Enteric Pathogens, Central Public Health Laboratory, 61
Association between Helicobacter pylori, caga, and vaca Status and Clinical Presentation in Iranian Children
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Oct 2013; Vol 23 (No 5), Pp: 551-556 Association between Helicobacter pylori, caga, and vaca Status and Clinical Presentation in Iranian Children Mandana Rafeey, MD; Reza
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Oct 2013; Vol 23 (No 5), Pp: 551-556 Association between Helicobacter pylori, caga, and vaca Status and Clinical Presentation in Iranian Children Mandana Rafeey, MD; Reza
A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic and Histological Diagnoses in Gastroduodenitis
 000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
H.Pylori IgM Cat # 1504Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Density of Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo as Assessed by Quantitative Culture and Histology
 552 Density of Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo as Assessed by Quantitative Culture and Histology John C. Atherton,* Kyi T. Tham, Richard M. Peek, Jr., Timothy L. Cover, and Martin J. Blaser Divisions
552 Density of Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo as Assessed by Quantitative Culture and Histology John C. Atherton,* Kyi T. Tham, Richard M. Peek, Jr., Timothy L. Cover, and Martin J. Blaser Divisions
H. pylori IgM. Cat # H. pylori IgM ELISA. ELISA: Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ELISA - Indirect; Antigen Coated Plate
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
M Frezza, N Gorji, M Melato. The chronic use of non-steroidal antiinflammatory
 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:521 525 521 Unit of Gastroenterology, General Hospital, I-34149 Trieste, Italy M Frezza Department of Pathological Anatomy, General Hospital and University of Trieste N Gorji M Melato
J Clin Pathol 2001;54:521 525 521 Unit of Gastroenterology, General Hospital, I-34149 Trieste, Italy M Frezza Department of Pathological Anatomy, General Hospital and University of Trieste N Gorji M Melato
Relationship between Helicobacter pylori icea, caga, and vaca Status and Clinical Outcome: Studies in Four Different Countries
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1999, p. 2274 2279 Vol. 37, No. 7 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Relationship between Helicobacter
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1999, p. 2274 2279 Vol. 37, No. 7 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Relationship between Helicobacter
H elicobacter pylori infection causes duodenal ulcers, most
 797 STOMACH Helicobacter pylori infection induces duodenitis and superficial duodenal ulcer in Mongolian gerbils T Ohkusa, I Okayasu, H Miwa, K Ohtaka, S Endo, N Sato... See end of article for authors
797 STOMACH Helicobacter pylori infection induces duodenitis and superficial duodenal ulcer in Mongolian gerbils T Ohkusa, I Okayasu, H Miwa, K Ohtaka, S Endo, N Sato... See end of article for authors
Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) Online Ahead of Print Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection ISSN 0100-879X 1 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) Online Ahead of Print Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection ISSN 0100-879X 1 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter
The Association of CagA + Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Carcinoma
 The Association of CagA + Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Carcinoma PRESENTER: Dr. Md. Khalilur Rahman Student of M.D.(Internal Medicine) Sylhet MAG Osmani Medical College Gastric Cancer- ranked
The Association of CagA + Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Carcinoma PRESENTER: Dr. Md. Khalilur Rahman Student of M.D.(Internal Medicine) Sylhet MAG Osmani Medical College Gastric Cancer- ranked
Table 2.9. Case control studies of helicobacter pylori infection and oesophageal adenocarcinoma
 Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
Helicobacter pylori Seroprevalence in Patients with Mild Asthma
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2005, 207, Helicobacter 287-291pylori Infection in Athmatic Patients 287 Helicobacter pylori Seroprevalence in Patients with Mild Asthma ZHAO JIAN JUN, 1, 2 YANG LEI, 2 YASUO SHIMIZU,
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2005, 207, Helicobacter 287-291pylori Infection in Athmatic Patients 287 Helicobacter pylori Seroprevalence in Patients with Mild Asthma ZHAO JIAN JUN, 1, 2 YANG LEI, 2 YASUO SHIMIZU,
Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification
 Journal of Digestive Diseases 2011; 12; 436 442 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00532.x Original article Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification Ryo NAKASHIMA,* Naoyoshi
Journal of Digestive Diseases 2011; 12; 436 442 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00532.x Original article Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification Ryo NAKASHIMA,* Naoyoshi
Introduction. Original articles. Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra Huertas, 2 Rosario Albis, 3 Diego Aponte, 4 Luis Carlos Sabbagh. 5
 Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
See external label 2 C-8 C Σ=96 tests Cat # 1505Z. MICROWELL ELISA H.Pylori IgA Cat # 1505Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
H.pylori IgA Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy Success Regarding Different Treatment Period Based on Clarithromycin or Metronidazole Triple-Therapy Regimens
 Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF H. PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRIC LESIONS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA
 408 East African Medical Journal December 2012 East African Medical Journal Vol. 89 No. 12 December 2012 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF H. PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRIC LESIONS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA M. O.
408 East African Medical Journal December 2012 East African Medical Journal Vol. 89 No. 12 December 2012 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF H. PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRIC LESIONS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA M. O.
Epithelial cell proliferation and glandular atrophy in lymphocytic gastritis: Effect of H pylori treatment
 P.O.Box 2345, Beijing 100023,China World J Gastroenterol 2003;9(12):2706-2710 Fax: +86-10-85381893 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail: wjg@wjgnet.com www.wjgnet.com Copyright 2003 by The WJG Press
P.O.Box 2345, Beijing 100023,China World J Gastroenterol 2003;9(12):2706-2710 Fax: +86-10-85381893 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail: wjg@wjgnet.com www.wjgnet.com Copyright 2003 by The WJG Press
RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS
 RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS Gurjeet Kaur 1, Manoharan Madhavan 1, Amir Hakim Basri 2, Abdul Hamid Mat Sain 3, Mohd Shaiful Bahrun Hussain 3, Mohd Kamal Yatiban
RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS Gurjeet Kaur 1, Manoharan Madhavan 1, Amir Hakim Basri 2, Abdul Hamid Mat Sain 3, Mohd Shaiful Bahrun Hussain 3, Mohd Kamal Yatiban
ISSN X (Print) Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(2B):631-637 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(2B):631-637 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug users presenting with dyspepsia at the Kenyatta National Hospital
 Research Article Department of Clinical Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr. G O Oyoo. Email: geomondi@hotmail. com Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in
Research Article Department of Clinical Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr. G O Oyoo. Email: geomondi@hotmail. com Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in
Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
The significance of Helicobacter pylori in the approach of dyspepsia in primary care Arents, Nicolaas Lodevikus Augustinus
 University of Groningen The significance of Helicobacter pylori in the approach of dyspepsia in primary care Arents, Nicolaas Lodevikus Augustinus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen The significance of Helicobacter pylori in the approach of dyspepsia in primary care Arents, Nicolaas Lodevikus Augustinus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis
 Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Helicobacter Pylori Infection Can Be Linked to Low Levels of Serum Cobalamins
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(3): 1898-1902, 2009 ISSN 1991-8178 Helicobacter Pylori Infection Can Be Linked to Low Levels of Serum Cobalamins 1,4 2 3 4 Jamil R. AL-Alami; Kamal Bani-Hani;
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(3): 1898-1902, 2009 ISSN 1991-8178 Helicobacter Pylori Infection Can Be Linked to Low Levels of Serum Cobalamins 1,4 2 3 4 Jamil R. AL-Alami; Kamal Bani-Hani;
Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease
 Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 427-43 I 1998, British Geriatrics Society Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease HELENA KEMPPAINEN, ISMO MIHA, HARRY KUJARI 1, LEIF SOURANDER
Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 427-43 I 1998, British Geriatrics Society Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease HELENA KEMPPAINEN, ISMO MIHA, HARRY KUJARI 1, LEIF SOURANDER
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Analysis of Helicobacter pylori vaca and caga genotypes and serum antibody profile in benign and malignant gastroduodenal diseases
 182 Department of Laboratory Medicine D Basso F Navaglia L Brigato M G Piva A Toma E Greco G Roveroni M Plebani Department of Gastroenterology F Di Mario II Divisione Chirurgica, University Hospital of
182 Department of Laboratory Medicine D Basso F Navaglia L Brigato M G Piva A Toma E Greco G Roveroni M Plebani Department of Gastroenterology F Di Mario II Divisione Chirurgica, University Hospital of
Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy
 Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
H. pylori IgM CLIA kit
 H. pylori IgM CLIA kit Cat. No.:DEEL0251 Pkg.Size:96 tests Intended use Helicobacter pylori IgM Chemiluminescence ELISA is intended for use in evaluating the serologic status to H. pylori infection in
H. pylori IgM CLIA kit Cat. No.:DEEL0251 Pkg.Size:96 tests Intended use Helicobacter pylori IgM Chemiluminescence ELISA is intended for use in evaluating the serologic status to H. pylori infection in
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Gastric Antral Mucosa Before and After Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment
 Original papers The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment Yen-Chun Peng,,, A F, Lan-Ru Huang, A, C, E, Hui-Ching Ho, C, Chi-Sen Chang, C, E, Shou-Wu Lee, E, Ching-Chang
Original papers The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment Yen-Chun Peng,,, A F, Lan-Ru Huang, A, C, E, Hui-Ching Ho, C, Chi-Sen Chang, C, E, Shou-Wu Lee, E, Ching-Chang
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 3, Issue 19,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 3, Issue 19, 295-301 Original Article Helicobacter pylori infection, glandular atrophy, intestinal metaplasia and topography of chronic active gastritis
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 3, Issue 19, 295-301 Original Article Helicobacter pylori infection, glandular atrophy, intestinal metaplasia and topography of chronic active gastritis
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
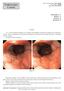 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN
 THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN Ahed J. Al-Khatib Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan Ahmed Saber Abu-zaiton Al-albayt University Abstract
THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN Ahed J. Al-Khatib Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan Ahmed Saber Abu-zaiton Al-albayt University Abstract
The association of and -related gastroduodenal diseases
 The association of and -related gastroduodenal diseases N. R. Hussein To cite this version: N. R. Hussein. The association of and -related gastroduodenal diseases. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology
The association of and -related gastroduodenal diseases N. R. Hussein To cite this version: N. R. Hussein. The association of and -related gastroduodenal diseases. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology
CagA-Positive Helicobacter Pylori and the Gastroduodenal Pathology
 Thammasat Int. J. Sc. Tech., Vol. 10. No. l. January-March 2005 CagA-Positive Helicobacter Pylori and the Gastroduodenal Pathology Sasichai Kangsadalampair, Panadda Rojpibulstitt Treetip Ratanavalachair,
Thammasat Int. J. Sc. Tech., Vol. 10. No. l. January-March 2005 CagA-Positive Helicobacter Pylori and the Gastroduodenal Pathology Sasichai Kangsadalampair, Panadda Rojpibulstitt Treetip Ratanavalachair,
Conservation of the cag pathogenicity island is associated with vaca alleles and gastroduodenal disease in South African Helicobacter pylori isolates
 Gut 2001;49:11 17 11 PAPERS GI Clinic and Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town, South Africa M Kidd J A Louw Department of Medical Microbiology, University
Gut 2001;49:11 17 11 PAPERS GI Clinic and Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town, South Africa M Kidd J A Louw Department of Medical Microbiology, University
Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach. Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK. Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract
 Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract 1 Some facts about Histopathology and the upper GI tract
Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract 1 Some facts about Histopathology and the upper GI tract
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師
 Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
The New England Journal of Medicine. Patients
 HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER NAOMI UEMURA, M.D., SHIRO OKAMOTO, M.D., SOICHIRO YAMAMOTO, M.D., NOBUTOSHI MATSUMURA, M.D., SHUJI YAMAGUCHI, M.D., MICHIO YAMAKIDO,
HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER NAOMI UEMURA, M.D., SHIRO OKAMOTO, M.D., SOICHIRO YAMAMOTO, M.D., NOBUTOSHI MATSUMURA, M.D., SHUJI YAMAGUCHI, M.D., MICHIO YAMAKIDO,
Bcl-2 Expression in CagA Strain H. Pylori Gastritis (Immunohistochemical and Insitu Hybridization Study)
 CAGA THE IRAQI STRAIN POSTGRADUATE H. PYLORI MEDICAL GASTRITIS JOURNAL Bcl- Expression in CagA Strain H. Pylori Gastritis (Immunohistochemical and Insitu Hybridization Study) Hussam Hasson Ali *, Hassan
CAGA THE IRAQI STRAIN POSTGRADUATE H. PYLORI MEDICAL GASTRITIS JOURNAL Bcl- Expression in CagA Strain H. Pylori Gastritis (Immunohistochemical and Insitu Hybridization Study) Hussam Hasson Ali *, Hassan
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Campylobacter pylori in non-specific abdominal pain in childhood
 Gut, 1989, 3, 912-916 Serum pepsinogen I and IgG antibody to Campylobacter pylori in non-specific abdominal pain in childhood GIUSEPPINA ODERDA, D VAIRA, J HOLTON, J F DOWSETT, AND NICOLETTA ANSALDI From
Gut, 1989, 3, 912-916 Serum pepsinogen I and IgG antibody to Campylobacter pylori in non-specific abdominal pain in childhood GIUSEPPINA ODERDA, D VAIRA, J HOLTON, J F DOWSETT, AND NICOLETTA ANSALDI From
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations
 Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Intestinal metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori: an
 16 Department of Internal Medicine, St Elisabeth's of Groote Gasthuis, Haarlem, The Netherlands M E Craanen W Dekker J Ferwerda Department of Pathology, Public Health Laboratory, Haarlem, The Netherlands
16 Department of Internal Medicine, St Elisabeth's of Groote Gasthuis, Haarlem, The Netherlands M E Craanen W Dekker J Ferwerda Department of Pathology, Public Health Laboratory, Haarlem, The Netherlands
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic variation in Helicobacter pylori Pan, Z. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic variation in Helicobacter pylori Pan, Z. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Pan, Z. (1999). Genetic variation in Helicobacter pylori
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic variation in Helicobacter pylori Pan, Z. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Pan, Z. (1999). Genetic variation in Helicobacter pylori
Role of Helicobacter pylori in ulcer healing and
 22 Departments of Gastroenterology G Bianchi Porro F Parente V Imbesi and Rheumatology F Montrone I Caruso L Sacco University Hospital, Milan, Italy Correspondence to: Professor G Bianchi Porro, Gastrointestinal
22 Departments of Gastroenterology G Bianchi Porro F Parente V Imbesi and Rheumatology F Montrone I Caruso L Sacco University Hospital, Milan, Italy Correspondence to: Professor G Bianchi Porro, Gastrointestinal
