Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis
|
|
|
- Denis McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) Online Ahead of Print Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection ISSN X 1 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis X.B. Li 1, Z.Z. Ge 1, X.Y. Chen 2 and W.Z. Liu 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology, 2 Department of Pathology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Institute of Digestive Diseases, Medical College of Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China Correspondence X.B. Li Shandong Zhong Road, , Shanghai China Fax: lxb1969@gmail.com Research supported by Shanghai leading academic discipline project (No. Y0205). Received April 28, 2006 Accepted April 26, 2007 Abstract Whether the regression of gastric metaplasia in the duodenum can be achieved after eradication of Helicobacter pylori is not clear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between H. pylori infection and gastric metaplasia in patients with endoscopic diffuse nodular duodenitis. Eighty-six patients with endoscopically confirmed nodular duodenitis and 40 control patients with normal duodenal appearance were investigated. The H. pylori-positive patients with duodenitis received anti-h. pylori triple therapy (20 mg omeprazole plus 250 mg clarithromycin and 400 mg metronidazole, all twice daily) for one week. A control endoscopy was performed 6 months after H. pylori treatment. The H. pylori-negative patients with duodenitis received 20 mg omeprazole once daily for 6 months and a control endoscopy was performed 2 weeks after treatment. The prevalence of H. pylori infection was 58.1%, and the prevalence of gastric metaplasia was 57.0%. Seventy-six patients underwent endoscopy again. No influence on the endoscopic appearance of nodular duodenitis was found after eradication of H. pylori or acid suppression therapy. However, gastric metaplasia significantly decreased and complete regression was achieved in 15/28 patients (53.6%) 6 months after eradication of H. pylori, accompanied by significant improvement of other histological alterations. Only mild chronic inflammation, but not gastric metaplasia, was found in the control group, none with H. pylori infection in the duodenal bulb. Therefore, H. pylori infection is related to the extent of gastric metaplasia in the duodenum, but not to the presence of diffuse nodular duodenitis. Key words Nodular duodenitis Helicobacter pylori Gastric metaplasia Introduction Helicobacter pylori infection is a major cause of many gastroduodenal diseases, especially chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer, and duodenitis. Since the colonization of the duodenum by H. pylori occurs only in regions of gastric metaplasia (GM), the development of duodenal GM is critically important in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer
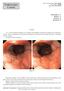
2 2 X.B. Li et al. Figure 1. Diffuse nodularity in the duodenal bulb. and duodenitis. In previous studies, the prevalence of GM was 72 to 90% in patients with duodenal ulcer, 40 to 95% in patients with duodenitis, and 0 to 33% in patients with normal endoscopic duodenal appearance (1,2). GM is generally believed to occur as a non-specific response to acid/peptic damage. It has been speculated that H. pylori infection induces a high level of acid burden in the duodenum by increasing gastrin secretion, which may influence the development of GM. It has been shown that the amount of H. pylori in the duodenal bulb may be related to the extent of GM (3). Theoretically, regression of GM may be induced by eradication of H. pylori or acid-suppression therapy. However, published results are conflicting and few studies have focused on the relationship between H. pylori infection and GM in the pathogenesis of duodenitis (4-11). Clinically, we observed quite a few patients with endoscopic diffuse nodularity, which is independent of duodenal ulceration, in the duodenal bulb. This alteration may be a special type of chronic duodenitis. The purpose of the present prospective study was to investigate the association between H. pylori infection and GM in patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis. Patients and Methods Patients Between January 2002 and June 2005, 86 patients with endoscopically confirmed diffuse nodular duodenitis (Figure 1) were enrolled, including 50 patients (22 males; median age 49.0 years, range years) with H. pylori infection and 36 patients (13 males; median age 52.6 years, range years) without H. pylori infection. Forty patients (14 males; median age 51.6 years, range years) with normal appearance of the duodenum were used as controls. Patients were excluded who had 1) evidence of gastroduodenal malignancies, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, or scar on gastroscopy; 2) liver, biliary, or pancreatic diseases on ultrasound examination; 3) received proton pump inhibitors (PPIs, such as omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, and pantoprazole, etc.), bismuth, antibiotics, aspirin, or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) in the preceding 2 weeks; 4) Zollinger-Ellison syndrome or Crohn s disease involving the duodenum; 5) previous upper gastrointestinal surgery; 6) pregnancy, or 7) renal insufficiency or other severe concomitant illnesses. This study was approved by the Medicine Ethics Committee of Shanghai Renji Hospital and signed informed consent was obtained from all patients. Clinical procedures Patients with endoscopically confirmed diffuse nodular duodenitis were treated with anti-h. pylori triple therapy consisting of 20 mg omeprazole twice daily, 250 mg clarithromycin twice daily, and 400 mg metronidazole twice daily for one week when H. pylori infection was diagnosed either in the duodenal bulb or in the gastric antrum. A control endoscopy was performed 6 months after the anti-h. pylori treatment. The H. pylori-negative (both in the duodenal bulb
3 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection 3 and in the gastric antrum) patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis received 20 mg omeprazole once daily for 6 months and a control endoscopy was performed 2 weeks after treatment. During the follow-up period after eradication treatment, intermittent short courses of hydrotalcite or sucralfate were prescribed to avoid symptoms and PPIs were avoided when possible. Endoscopy and biopsy sampling Endoscopic findings of duodenal morphology were defined according to the criteria of endoscopic duodenitis described by the Sydney classification (12), including the subjective assessment of severity as mild, moderate or severe. During each endoscopic examination, three antral biopsies were taken from the lesser and the greater curvature within 2-3 cm from the pylorus, and two duodenal biopsies were taken from the diffuse nodular lesion in the duodenal bulb. Among these biopsies, one antral specimen was used to detect H. pylori by the rapid urease test, and the others were used for histological assessment. Histology The biopsy specimens for histological examination were fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin on the oriented edge, and cut into 4-µm thick sequential sections. The tissue sections were then stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological examination, with Alcian blue periodic acid- Schiff (AB/PAS) for identifying and assessing the extent of GM, and with Giemsa for H. pylori assessment. The slides were evaluated by an experienced pathologist who was blind to clinical, endoscopic and other tests for H. pylori. Gastric antral and duodenal biopsy specimens were assessed according to the updated Sydney System (12). In each duodenal biopsy specimen, the infiltration of the duodenal mucosa by mononuclear cells (chronic inflammation) and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (neutrophilic activity) was graded as follows: 0, none; 1, mild; 2, moderate; 3, severe. GM was defined by the presence of surface epithelial cells containing PAS-positive neutral mucin in the duodenal bulb. The extent of gastric type epithelium in duodenal biopsy specimens was arbitrarily graded on a scale of 0-3 as follows: grade 0, no GM observed; grade 1, GM involving a few villi; grade 2, GM involving several villi, and grade 3, GM involving almost all villi (12). The lymphoid follicles were considered to be positive when aggregates of lymphocytes with a germinal center (secondary lymphoid follicles) or accumulations of lymphocytes and plasma cells without a germinal center (primary lymphoid aggregates) were observed. Villus atrophy was defined as flattening or widening of villi. H. pylori infection was diagnosed when the rapid urease test, hematoxylin and eosin stain, and Giemsa stain were all positive. Statistical analysis Data are reported as means ± SD. Differences were evaluated by the Fisher exact test, t-test, or Wilcoxon signed rank test. P values of <0.05 were considered significant. Results Helicobacter pylori status Fifty patients (50/86, 58.1%) were H. pylori positive. Among the 76 patients who completed the study, 48 were H. pylori positive. After eradication treatment, 9 patients were still H. pylori positive. Pre-treatment endoscopic appearance and histological findings No common pathogenic factors, such as renal transplantation or duodenal parasitic
4 4 X.B. Li et al. Table 1. Severity of diffuse nodular duodenitis in Helicobacter pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative groups before and after treatment. Severity of diffuse nodular duodenitis None Mild Moderate Severe H. pylori-positive (N = 50) H. pylori-negative (N = 36) Successful eradication of H. pylori (N = 39) Before eradication* After eradication PPI treatment (N = 28) Before treatment** After treatment P > 0.05 compared with the H. pylori-negative group; *P > 0.05 compared with the group after H. pylori eradication; **P > 0.05 compared with the group after treatment with proton pump inhibitors (PPI; Wilcoxon signed rank test). Table 2. Extent of duodenal gastric metaplasia in the Helicobacter pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative groups before and after treatment. Table 3. Post-treatment histological changes of diffuse nodular duodenitis in the Helicobacter pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative groups. Histological alterations Extent of duodenal metaplasia Grade 0 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Successful eradication of H. pylori (N = 39) Before eradication + * After eradication PPI treatment (N = 28) Before treatment** After treatment Grade 0, no gastric metaplasia observed; grade 1, gastric metaplasia involving a few villi; grade 2, gastric metaplasia involving several villi; grade 3, gastric metaplasia involving almost all villi. + P = compared with the group before proton pump inhibitors (PPI) treatment; *P = compared with the group after eradication of H. pylori; **P > 0.05 compared with the group after treatment with PPI (Wilcoxon signed rank test). Post-treatment histological changes Successful Failure of H. pylori negative eradication of eradication of (after PPI treatment) H. pylori (N = 39) H. pylori (N = 9) (N = 28) Gastric metaplasia 13/28 (46.4%) + 6/6 (100%) 12/15 (80%) Lymphoid follicles 0/26* 6/6 (100%) 5/8 (62.5%) Villus atrophy 16/39 (41.0%)* 9/9 (100%) 14/15 (93.3%) Goblet cell decrease 0/25* 6/6 (100%) 8/8 (100%) Ectopic gastric mucosa 0 0 6/6 (100%) PPI = proton pump inhibitors. + P = 0.033, *P < compared with the H. pylori-negative group (Fisher exact test). infestation, were present in patients with nodular duodenitis. There was no significant difference in the severity of endoscopic nodular duodenitis between the H. pylori-positive and -negative groups (P = 0.144, Table 1). GM was detected in 49 of the 86 patients (57.0%). The prevalence of GM, villus atrophy, goblet cell reduction, and lymphoid follicles was significantly higher in patients with H. pylori infection than in patients without H. pylori infection (P < 0.05 for all). The extent of GM was also greater in H. pyloripositive patients than that in H. pylori-negative patients (P = 0.032, Table 2). Furthermore, different degrees of chronic duodenal inflammation (average score, 3.4 ± 1.3) and neutrophilic activity (average score, 2.3 ± 1.9) were found in most of the patients with nodular duodenitis. Only mild duodenal chronic inflammation (average score 0.8 ± 1.0) was found in 30 of 40 control patients with normal appearance of the duodenum. The values were significantly lower than those in H. pyloripositive or -negative patients in the treatment group (both P < ). No other histological alterations, including GM, were found in this group. Post-treatment endoscopic appearance and histological changes Seventy-six patients completed the study, including 48 patients with H. pylori eradication treatment (successful in 39) and 28 patients with PPI treatment. Neither the successful eradication treatment nor PPI treatment could improve the endoscopic appearance of nodular duodenitis (both P > 0.05, Table 1). Six months after successful eradication of H. pylori, both the values of chronic inflammation and neutrophilic activity were significantly decreased (2.2 ± 1.2 vs 4.0 ± 1.5, P < , and 0.1 ± 0.3 vs 3.8 ± 1.5, P < , respectively). Furthermore, the
5 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection 5 extent of duodenal GM was significantly reduced (P = , Table 2), and regression of histological alterations was achieved in most or all patients (Table 3). However, no significant change in histological findings, including GM, was found in H. pylori-negative patients on PPI treatment or in patients with persistent H. pylori infection after eradication treatment (Table 3). Discussion An association between GM, H. pylori infection and duodenitis has been reported (13-15). GM of the duodenum is characterized by the metaplastic replacement of the normal duodenal epithelial cells with those displaying a phenotype similar to that of mucus-secreting cells of the gastric mucosa. It resembles gastric foveolar epithelium in many respects, including H. pylori colonization (16,17). It has been suggested that the presence of GM may create a suitable environment for H. pylori colonization in the duodenum, resulting in chronic duodenitis (13,14,17,18). The development of metaplastic tissue is a necessary prerequisite for H. pylori colonization because the bacterium may survive in the gastric mucosa but it cannot grow on normal duodenal epithelium (13,16,18). When spread to the duodenal mucosa, H. pylori is believed to exert a cytotoxic effect on mucosal cells. The inflammatory injury to duodenal mucosa by H. pylori may eventually lead to the development of further GM (13,14,19). H. pylori infection was confirmed to be one of the independent risk factors of GM (20), and an inductive role of H. pylori in the development of GM was suggested recently (21). However, there are conflicting reports concerning the relationship between the extent of GM and H. pylori infection. It has been reported that neither the prevalence nor the extent of GM was affected by H. pylori status (5,6,9,22). In contrast, some studies found such a relationship between the extent of GM in the duodenum and the amount of H. pylori in the gastric antrum or in the duodenal bulb (3,4,13,17). Our study showed that both the presence and the extent of GM in nodular duodenitis are related to the presence of H. pylori infection. There are also conflicting reports as to whether the extent of GM decreases after eradication of H. pylori. Some studies have shown no decrease in the extent of GM after eradication of H. pylori (5-7,9-11), whereas a significant reduction in the extent of GM was demonstrated in others (4,8). In agreement with the latter reports, the results of the present study showed that the extent of GM significantly decreased and complete regression occurred in more than half (15/28) the patients 6 months after eradication of H. pylori. In addition, the patients with successful eradication of H. pylori show a significantly higher prevalence of GM regression than those with no eradication. These findings further confirm the important contributory role of H. pylori infection in the development and persistence of GM. In addition to H. pylori infection, it was speculated that the presence of duodenal GM is most likely caused by duodenal injury or high acidity (14,15), and is considered to be a protective mechanism to excess acid (23). But long-term acid inhibition treatment with H 2 -receptor antagonists could not decrease the extent of GM (5). It was shown in another study that acid suppression alone produced a 43% reduction in GM, similar to the effect of H. pylori eradication. The authors concluded that the extent of GM was partly due to H. pylori and partly to acid (4). In the present study, only 20% regression in GM could be achieved with long-term acid inhibition treatment alone in patients without H. pylori infection. However, the results of PPI treatment should be interpreted with caution because the acidity levels were not evaluated. This aspect deserves further investigation. Diffuse nodular duodenitis is a special
6 6 X.B. Li et al. type of chronic duodenitis. Up to now, we know little about its pathogenesis. It was speculated that the appearance of endoscopic findings of duodenitis may result from H. pylori infection or from an acid-pepsin attack and is usually accompanied with some histopathologic abnormalities, including GM (17). However, few studies had focused on the association between the appearance of duodenitis and H. pylori infection. It has been reported that no significant difference exists in the severity of endoscopic duodenitis between H. pylori-positive and -negative patients, and successful eradication of H. pylori did not lead to any change in endoscopic appearance (9). In agreement with this finding, we found that neither the eradication of H. pylori nor the acid suppression treatment could change the appearance of endoscopic nodular duodenitis in a significant manner. In conclusion, the present results suggest that H. pylori infection is related to the extent of GM in the duodenum, but not to the presence of diffuse nodular duodenitis. References 1. Heikkinen M, Pikkarainen P, Vornanen M, Hollmen S, Julkunen R. Prevalence of gastric metaplasia in the duodenal bulb is low in Helicobacter pylori positive non-ulcer dyspepsia patients. Dig Liver Dis 2001; 33: Chen XY, Shi Y, Peng YS, Ma YZ, Xiao SD. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric metaplasia in the mucosa of duodenal bulb. Chin J Dig 2004; 9: Futami H, Takashima M, Furuta T, Hanai H, Kaneko E. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric metaplasia in the duodenal bulb in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999; 14: Khulusi S, Badve S, Patel P, Lloyd R, Marrero JM, Finlayson C, et al. Pathogenesis of gastric metaplasia of the human duodenum: role of Helicobacter pylori, gastric acid, and ulceration. Gastroenterology 1996; 110: Noach LA, Rolf TM, Bosma NB, Schwartz MP, Oosting J, Rauws EA, et al. Gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 1993; 34: Harris AW, Gummett PA, Walker MM, Misiewicz JJ, Baron JH. Relation between gastric acid output, Helicobacter pylori, and gastric metaplasia in the duodenal bulb. Gut 1996; 39: Savarino V, Mela GS, Zentilin P, Mele MR, Bisso G, Pivari M, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on 24-hour gastric ph and duodenal gastric metaplasia. Dig Dis Sci 2000; 45: Ciancio G, Nuti M, Orsini B, Iovi F, Ortolani M, Palomba A, et al. Regression of duodenal gastric metaplasia in Helicobacter pylori positive patients with duodenal ulcer disease. Dig Liver Dis 2002; 34: Urakami Y, Sano T. Endoscopic duodenitis, gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001; 16: Urakami Y, Sano T. Long-term follow-up of gastric metaplasia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. J Med Invest 2003; 50: Bago J, Strinic D, Halle ZB, Jandric D, Tomic M, Bilic A, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on extent of duodenal gastric metaplasia and grade of gastritis. Coll Antropol 2002; 26: Tytgat GN. The Sydney System: endoscopic division. Endoscopic appearances in gastritis/duodenitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1991; 6: Madsen JE, Vetvik K, Aase S. Helicobacter-associated duodenitis and gastric metaplasia in duodenal ulcer patients. APMIS 1991; 99: Satoh K, Kimura K, Yoshida Y, Kasano T, Kihira K, Taniguchi Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori colonization and acute inflammation of the duodenal mucosa. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88: Fitzgibbons PL, Dooley CP, Cohen H, Appleman MD. Prevalence of gastric metaplasia, inflammation, and Campylobacter pylori in the duodenum of members of a normal population. Am J Clin Pathol 1988; 90: Carrick J, Lee A, Hazell S, Ralston M, Daskalopoulos G. Campylobacter pylori, duodenal ulcer, and gastric metaplasia: possible role of functional heterotopic tissue in ulcerogenesis. Gut 1989; 30: Wyatt JI, Rathbone BJ, Sobala GM, Shallcross T, Heatley RV, Axon AT, et al. Gastric epithelium in the duodenum: its association with Helicobacter pylori and inflammation. J Clin Pathol 1990; 43: Johan G, Offerhaus A, Molyvas EN, Hoedemaeker PJ. Helicobacter pylori infection of gastric mucin cell metaplasia: the duodenum revisited. J Pathol 1990; 162: Walker MM, Dixon MF. Gastric metaplasia: its role in duodenal ulceration. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1996; 10 (Suppl 1): Voutilainen M, Juhola M, Farkkila M, Sipponen P. Gastric metaplasia and chronic inflammation at the duodenal bulb mucosa. Dig Liver Dis 2003; 35: Van De Bovenkamp JH, Korteland-Van Male AM, Buller HA, Einerhand AW, Dekker J. Metaplasia of the duodenum shows a Helicobacter pylori-correlated differentiation into gastric-type protein expression. Hum Pathol 2003; 34: Suriani R, Venturini I, Actis GC, Rocca G, Rizzetto M, Cerutti E, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on bulbitis and duodenal gastric metaplasia. Hepatogastroenterology 2004; 51: James AH. Gastric epithelium in the duodenum. Gut 1964; 5:
Duodenal histology, ulceration, and Helicobacter pylori in the presence or absence of non-steroidal
 1162 Departments of Gastroenterology, A S Taha I Nakshabendi R I Russell Pathology, S Dahill F D Lee and Rheumatology, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow R D Sturrock Correspondence to: Dr A S Taha, Gastroenterology
1162 Departments of Gastroenterology, A S Taha I Nakshabendi R I Russell Pathology, S Dahill F D Lee and Rheumatology, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow R D Sturrock Correspondence to: Dr A S Taha, Gastroenterology
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy Success Regarding Different Treatment Period Based on Clarithromycin or Metronidazole Triple-Therapy Regimens
 Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
Pathogenesis of Gastric Metaplasia of the Human Duodenum: Role of Helicobacter pylori, Gastric Acid, and Ulceration
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;110:452 458 Pathogenesis of Gastric Metaplasia of the Human Duodenum: Role of Helicobacter pylori, Gastric Acid, and Ulceration SAM KHULUSI,* SUNIL BADVE, PRAFUL PATEL,* REBECCA LLOYD,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;110:452 458 Pathogenesis of Gastric Metaplasia of the Human Duodenum: Role of Helicobacter pylori, Gastric Acid, and Ulceration SAM KHULUSI,* SUNIL BADVE, PRAFUL PATEL,* REBECCA LLOYD,*
COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION
 Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
~Helicobacter pylori, gastritis, and peptic ulceration
 17 Department of Pathology J I Wyatt Department of Medicine T M Shallcross J E Crabtree RV Heatley St James University Hospital, Leeds LS9 7TF Correspondence to: Dr J I Wyatt. Accepted for publication
17 Department of Pathology J I Wyatt Department of Medicine T M Shallcross J E Crabtree RV Heatley St James University Hospital, Leeds LS9 7TF Correspondence to: Dr J I Wyatt. Accepted for publication
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report.
 Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Immunoglobulin G Antibody against Helicobacter pylori: Clinical Implications of Levels Found in Serum
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 1044 1048 Vol. 9, No. 5 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.5.1044 1048.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 1044 1048 Vol. 9, No. 5 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.5.1044 1048.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Gastric metaplasia and duodenal ulcer disease in children infected by Helicobacter pylori
 Gut 1996;38: 513-517 Gastric metaplasia and duodenal ulcer disease in children infected by Helicobacter pylori 513 Department of Paediatrics S M Gormally B Bourke B Drumm and Public Health Medicine and
Gut 1996;38: 513-517 Gastric metaplasia and duodenal ulcer disease in children infected by Helicobacter pylori 513 Department of Paediatrics S M Gormally B Bourke B Drumm and Public Health Medicine and
Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs Prof. Sheila Crowe
 Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen
 Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment
 Original papers The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment Yen-Chun Peng,,, A F, Lan-Ru Huang, A, C, E, Hui-Ching Ho, C, Chi-Sen Chang, C, E, Shou-Wu Lee, E, Ching-Chang
Original papers The effect of proton pump inhibitors on the gastric mucosal microenvironment Yen-Chun Peng,,, A F, Lan-Ru Huang, A, C, E, Hui-Ching Ho, C, Chi-Sen Chang, C, E, Shou-Wu Lee, E, Ching-Chang
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Gastric Antral Mucosa Before and After Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease
 Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 427-43 I 1998, British Geriatrics Society Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease HELENA KEMPPAINEN, ISMO MIHA, HARRY KUJARI 1, LEIF SOURANDER
Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 427-43 I 1998, British Geriatrics Society Characteristics of Helicobacter pylorinegative and -positive peptic ulcer disease HELENA KEMPPAINEN, ISMO MIHA, HARRY KUJARI 1, LEIF SOURANDER
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Helicobacter 2008;13:1-6. Am J Gastroent 2007;102: Am J of Med 2004;117:31-35.
 An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
Role of Helicobacter pylori in ulcer healing and
 22 Departments of Gastroenterology G Bianchi Porro F Parente V Imbesi and Rheumatology F Montrone I Caruso L Sacco University Hospital, Milan, Italy Correspondence to: Professor G Bianchi Porro, Gastrointestinal
22 Departments of Gastroenterology G Bianchi Porro F Parente V Imbesi and Rheumatology F Montrone I Caruso L Sacco University Hospital, Milan, Italy Correspondence to: Professor G Bianchi Porro, Gastrointestinal
Maastricht Ⅴ /Florence
 2016 21 10 577 Maastricht Ⅴ /Florence 200001 2015 10 8 9 Maastricht V 1 / 2 3 4 / 5 Maastricht Ⅴ Interpretation of Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection the Maastricht Ⅴ / Florence Consensus Report
2016 21 10 577 Maastricht Ⅴ /Florence 200001 2015 10 8 9 Maastricht V 1 / 2 3 4 / 5 Maastricht Ⅴ Interpretation of Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection the Maastricht Ⅴ / Florence Consensus Report
Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY. Robin Warren
 - Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
The prevalence of lymphoid follicles in Helicobacter pylon associated gastritis in patients
 I Clin Pathol 1995;48:325-329 Department of Histopathology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab mirates A M Zaitoun Correspondence to: Dr A M Zaitoun, Mayday Healthcare NHS Trust, Mayday Road Thornton
I Clin Pathol 1995;48:325-329 Department of Histopathology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab mirates A M Zaitoun Correspondence to: Dr A M Zaitoun, Mayday Healthcare NHS Trust, Mayday Road Thornton
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA
 A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
Duodenal Ulcer / Duodenitis
 Duodenal Ulcer / Duodenitis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with duodenitis and/or a duodenal ulcer. The information below
Duodenal Ulcer / Duodenitis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with duodenitis and/or a duodenal ulcer. The information below
Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients with Dyspepsia
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 184806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/184806 Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 184806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/184806 Research Article Performance of Routine Helicobacter pylori Invasive Tests in Patients
Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification
 Journal of Digestive Diseases 2011; 12; 436 442 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00532.x Original article Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification Ryo NAKASHIMA,* Naoyoshi
Journal of Digestive Diseases 2011; 12; 436 442 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00532.x Original article Histological features of nodular gastritis and its endoscopic classification Ryo NAKASHIMA,* Naoyoshi
Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on nutrition
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16: 799 806. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on nutrition T. FURUTA*, N. SHIRAI*, F. XIAO*, M. TAKASHIMA* & H. HANAI *First Department of Medicine
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16: 799 806. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on nutrition T. FURUTA*, N. SHIRAI*, F. XIAO*, M. TAKASHIMA* & H. HANAI *First Department of Medicine
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia, Acid Peptic Disease, Helicobacter Pylori, Urease, Giemsa, Peptic Ulcer, Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia.
 INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
Epithelial cell proliferation and glandular atrophy in lymphocytic gastritis: Effect of H pylori treatment
 P.O.Box 2345, Beijing 100023,China World J Gastroenterol 2003;9(12):2706-2710 Fax: +86-10-85381893 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail: wjg@wjgnet.com www.wjgnet.com Copyright 2003 by The WJG Press
P.O.Box 2345, Beijing 100023,China World J Gastroenterol 2003;9(12):2706-2710 Fax: +86-10-85381893 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail: wjg@wjgnet.com www.wjgnet.com Copyright 2003 by The WJG Press
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis
 Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug users presenting with dyspepsia at the Kenyatta National Hospital
 Research Article Department of Clinical Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr. G O Oyoo. Email: geomondi@hotmail. com Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in
Research Article Department of Clinical Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr. G O Oyoo. Email: geomondi@hotmail. com Prevalence of gastroduodenal lesions in
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations
 Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:841-848 Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis J I WYATT,* B J RATHBONE,t M F DIXON,: R V HEATLEYt From the Departments of *Pathology
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:841-848 Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis J I WYATT,* B J RATHBONE,t M F DIXON,: R V HEATLEYt From the Departments of *Pathology
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD. Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School
 PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School No disclosures Disclosures Overview Causes of peptic ulcer disease
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School No disclosures Disclosures Overview Causes of peptic ulcer disease
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori?
 What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori? Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy for Helicobacter pylori
What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori? Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy for Helicobacter pylori
ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ
 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ 205 206 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ EPITHELIAL CELL TURNOVER IN NON-DYSPLASTIC GASTRIC MUCOSA ADJACENT TO EARLY AND
ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ 205 206 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ EPITHELIAL CELL TURNOVER IN NON-DYSPLASTIC GASTRIC MUCOSA ADJACENT TO EARLY AND
Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in Detecting Helicobacter pylori Infection ABSTRACT
 Original Article Rojborwonwitaya J, Vijitjunyakul N THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 55 Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in
Original Article Rojborwonwitaya J, Vijitjunyakul N THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 55 Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Patients with End Stage Renal Disease
 2000;20:97-102 Helicobacter pylori Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Patients with End Stage Renal Disease Do Ha Kim, M.D., Hwoon-Yong Jung, M.D., Suk-Kyun Yang, M.D. Weon-Seon Hong, M.D. and Young
2000;20:97-102 Helicobacter pylori Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Patients with End Stage Renal Disease Do Ha Kim, M.D., Hwoon-Yong Jung, M.D., Suk-Kyun Yang, M.D. Weon-Seon Hong, M.D. and Young
Histopathological study of gastric carcinoma with associated precursor lesions
 Original Research Article Histopathological study of gastric carcinoma with associated precursor lesions Manasa G C 1,*, Sunila 2, Manjunath GV 3 1 Assistant Professor, JJM Medical College, Tharalabalu
Original Research Article Histopathological study of gastric carcinoma with associated precursor lesions Manasa G C 1,*, Sunila 2, Manjunath GV 3 1 Assistant Professor, JJM Medical College, Tharalabalu
Helicobacter pyloni and upper gastrointestinal
 314 Helicobacter pyloni and upper gastrointestinal disease: a survey of gastroenterologists in the United Kingdom Gut 1995; 37: 314-318 R Milne, R P H Logan, D Harwood, J J Misiewicz, D Forman Health Services
314 Helicobacter pyloni and upper gastrointestinal disease: a survey of gastroenterologists in the United Kingdom Gut 1995; 37: 314-318 R Milne, R P H Logan, D Harwood, J J Misiewicz, D Forman Health Services
High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland
 High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland K Bennett, H O Connor, M Barry, C O Morain, J Feely Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Department of Gastroenterology Trinity
High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland K Bennett, H O Connor, M Barry, C O Morain, J Feely Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Department of Gastroenterology Trinity
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Peptic Ulcer Disease Update
 Peptic Ulcer Disease Update Col Pat Storms RAM 2005 Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Col Patrick Storms I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will discuss the following
Peptic Ulcer Disease Update Col Pat Storms RAM 2005 Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Col Patrick Storms I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will discuss the following
Assessment of symptomatic response as predictor of Helicobacter pylori status following eradication therapy in patients with ulcer
 618 University Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow G11 6NT, UK K E L McColl A El-Nujumi L S Murray E M El-Omar A Dickson A W Kelman T E Hilditch Correspondence to: Professor
618 University Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow G11 6NT, UK K E L McColl A El-Nujumi L S Murray E M El-Omar A Dickson A W Kelman T E Hilditch Correspondence to: Professor
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.38 Genetic Testing for Helicobacter pylori Treatment Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return
MP 2.04.38 Genetic Testing for Helicobacter pylori Treatment Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS
 RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS Gurjeet Kaur 1, Manoharan Madhavan 1, Amir Hakim Basri 2, Abdul Hamid Mat Sain 3, Mohd Shaiful Bahrun Hussain 3, Mohd Kamal Yatiban
RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION IN GASTRIC IMPRINT SMEARS Gurjeet Kaur 1, Manoharan Madhavan 1, Amir Hakim Basri 2, Abdul Hamid Mat Sain 3, Mohd Shaiful Bahrun Hussain 3, Mohd Kamal Yatiban
T he secretion of acid is an important function of the
 927 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrin (G) cells and somatostatin (D) cells in patients with dyspeptic symptoms: Helicobacter pylori associated and non-associated gastritis Y Liu, G D C Vosmaer, G N J Tytgat, S-d
927 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrin (G) cells and somatostatin (D) cells in patients with dyspeptic symptoms: Helicobacter pylori associated and non-associated gastritis Y Liu, G D C Vosmaer, G N J Tytgat, S-d
Rpts. GENERAL General Schedule (Code GE) Program Prescriber type: Dental Medical Practitioners Nurse practitioners Optometrists Midwives
 Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
Gilles Jequier. Commercial Director Organobalance, a Novozymes Company
 "Latest clinical Evidences showing that a proprietary Lactobacillus reuteri Strain can reduce the Symptoms associated with a Helicobacter pylori Infection" Gilles Jequier Commercial Director Organobalance,
"Latest clinical Evidences showing that a proprietary Lactobacillus reuteri Strain can reduce the Symptoms associated with a Helicobacter pylori Infection" Gilles Jequier Commercial Director Organobalance,
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA MANAGEMENT Dyspepsia refers to a spectrum of usually intermittent upper gastrointestinal symptoms, including epigastric pain and heartburn. For the majority
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA MANAGEMENT Dyspepsia refers to a spectrum of usually intermittent upper gastrointestinal symptoms, including epigastric pain and heartburn. For the majority
Gastric Ulcer / Gastritis
 Gastric Ulcer / Gastritis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with gastritis and/or a gastric ulcer. The information below outlines
Gastric Ulcer / Gastritis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with gastritis and/or a gastric ulcer. The information below outlines
Omeprazole 10mg. Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form OMEPRAZOLE omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Max. Qty.
 Omeprazole 10mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole
Omeprazole 10mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole
Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia
 Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia ianbrown@envoi.com.au Topics for discussion Classification of gastritis Minimal diagnostic criteria for gastritis H.pylori negative
Gastritis (and gastropathy) Dr Ian Brown Envoi Pathology Brisbane, Australia ianbrown@envoi.com.au Topics for discussion Classification of gastritis Minimal diagnostic criteria for gastritis H.pylori negative
Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report. Kimitoshi Kubo 1, Noriko Kimura 2, Katsuhiro Mabe 1, Yusuke Nishimura 1 and Mototsugu Kato 1
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0842-18 Intern Med 57: 2951-2955, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synchronous Triple Gastric Cancer Incorporating Mixed Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumor Completely
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0842-18 Intern Med 57: 2951-2955, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synchronous Triple Gastric Cancer Incorporating Mixed Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumor Completely
Rpts. GENERAL General Schedule (Code GE)
 Pantoprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form Pantoprazole 20mg enteric tablet, 30 (8399C) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form
Pantoprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form Pantoprazole 20mg enteric tablet, 30 (8399C) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form
Introduction. Original articles. Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra Huertas, 2 Rosario Albis, 3 Diego Aponte, 4 Luis Carlos Sabbagh. 5
 Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
The long-term management of patients with bleeding duodenal ulcers
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther (1997); 11: 505±510. The long-term management of patients with bleeding duodenal ulcers M. E. MCALINDON, J. S. W. TAYLOR & S. D. RYDER Department of Medicine, University Hospital,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther (1997); 11: 505±510. The long-term management of patients with bleeding duodenal ulcers M. E. MCALINDON, J. S. W. TAYLOR & S. D. RYDER Department of Medicine, University Hospital,
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師
 Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection
 Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences
 JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences Volume 4, Number 2, June 2011 ISSN 1995-6673 Pages 71-76 Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis at the North of Jordan N. M. Abu-Ahmad, A. Odeh and A-K.
JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences Volume 4, Number 2, June 2011 ISSN 1995-6673 Pages 71-76 Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis at the North of Jordan N. M. Abu-Ahmad, A. Odeh and A-K.
The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Tropical Medicine Volume 3 Number 1 The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis N Moorchung, A Srivastava, N Gupta,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Tropical Medicine Volume 3 Number 1 The Role Of Helicobacter Pylori And Cag A Antibody Titers In The Pathology Of Chronic Gastritis N Moorchung, A Srivastava, N Gupta,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Relation between reflux of bile acids into the stomach and gastric mucosal atrophy, intestinal metaplasia in biopsy specimens
 Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn11-90 10.3164/jcbn.11-90 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Relation
Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn11-90 10.3164/jcbn.11-90 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Relation
The yield of UGIE: a study of a ten-year period in the Zaanstreek
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The yield of UGIE: a study of a ten-year period in the Zaanstreek R.J.L.F. Loffeld *, A.B.M.M. van der Putten Department of Internal Medicine, De Heel Zaans Medical Centre, PO BOX 21,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The yield of UGIE: a study of a ten-year period in the Zaanstreek R.J.L.F. Loffeld *, A.B.M.M. van der Putten Department of Internal Medicine, De Heel Zaans Medical Centre, PO BOX 21,
Histopathological profile of gastritis in adult patients seen at a referral hospital in Kenya
 Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 27 August 14; 13(3): 4117-4121 World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com 27 WJG. All rights reserved. RAPID COMMUNICATION Histopathological
Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 27 August 14; 13(3): 4117-4121 World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com 27 WJG. All rights reserved. RAPID COMMUNICATION Histopathological
A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic and Histological Diagnoses in Gastroduodenitis
 000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI DETECTION IN CHRONIC GASTRITIS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Proton Pump Inhibitors Drugs: Aciphex Sprinkle (rabeprazole), Dexilant (dexlansoprazole), Lansoprazole, Nexium (esomeprazole capsule, esomeprazole granules), Omeprazole, Pantoprazole,
Drug Class Monograph Class: Proton Pump Inhibitors Drugs: Aciphex Sprinkle (rabeprazole), Dexilant (dexlansoprazole), Lansoprazole, Nexium (esomeprazole capsule, esomeprazole granules), Omeprazole, Pantoprazole,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection William D. Chey, MD, FACG 1, Grigorios I. Leontiadis, MD, PhD 2, Colin W. Howden, MD, FACG 3 and Steven F. Moss, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection William D. Chey, MD, FACG 1, Grigorios I. Leontiadis, MD, PhD 2, Colin W. Howden, MD, FACG 3 and Steven F. Moss, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs Yuki Sakamoto, Tadashi Shimoyama, Satoru Nakagawa,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs Yuki Sakamoto, Tadashi Shimoyama, Satoru Nakagawa,
Disclosures. Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab
 H. pylori testing Disclosures Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab Learning Objectives Evaluate the appropriate testing methodology by balancing performance, economics, and workflow. Discuss the
H. pylori testing Disclosures Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab Learning Objectives Evaluate the appropriate testing methodology by balancing performance, economics, and workflow. Discuss the
