Mathematical biology From individual cell behavior to biological growth and form
|
|
|
- Elmer Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematical biology From individual cell behavior to biological growth and form Lecture 8: Multiscale models Roeland Merks (1,2) (1) Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, Amsterdam (2) Mathematical Institute, Leiden University
2 Examination Studiegids: Practicum assignment, 30% Final product, 30% Written exam, 40% - date will follow soon Seminars: prepare a short talk (15 mins + 5 mins discussion) on two papers Compare the two papers 18th November and 25th November
3 Paper seminars Two papers on a topic of your choice Prepare short seminar of ±15 mins, plus 5 minutes discussion What question do the papers study? What was the hypothesis? Did the papers propose alternative ideas? Did they work equally well? How was the hypothesis translated into a mathematical model?
4 Possible topics Mechanisms of phyllotaxis (upstream auxin transport vs. canalization) Gastrulation Blood vessel growth (angiogenesis) Reaction-diffusion models E.g. of finger prints Spiral waves in Dictyostelium discoideum Theory of cellular automata Morphogenesis due to differential growth
5 Mini-projects Small/tiny research project Typically based on a simulation you have seen during the computer labs Two guided afternoons and individual work Work in teams of two Work in three lab sessions: Nov. 18, Nov. 25, Dec. 2 Final presentation - December 9th ±30 mins. including discussion Introduce the problem, existing results, your research question, and your new results. Discuss the biological and mathematical relevance. What can biologists learn from your model?
6 Mini-projects Small research project (II) Final report: In the form of a paper: Introduction/Methods/Results/Discussion/Future work Figures, analysis of your model Size: around 8 pages Deadline: 31 January 2013 It s okay to choose the same topic for your seminar and research project
7 Potential topics Pattern formation (e.g. leaf venation, fur patterns, shell patterns) Theory of 1D/2D cellular automata Plant morphogenesis: interaction between reactiondiffusion and auxin pumping Blood vessel growth: extend models with additional cell types; angiogenesis in stromal tissues Branching growth (DLA): modify models with additional particle types, ballistic particle motion, aggregation probability: effect on? Models of tumor invasion Theory of cell sorting D f
8 Multiscale modeling Biological development: 1. Genes -> cell behavior 2. cell behavior->tissue shapes and patterns 3. tissue patterns-> genes and cell behavior How to model step 3? Multiscale modeling required Required levels: Gene regulatory networks Cell behavior Cell-cell signaling
9 Example of a multiscale model Dictyostelium discoideum
10 Dictyostelium discoideum Amoeba live independently When hungry, secrete camp pulse Also secrete camp if they sense camp Refractory period after camp secretion Chemotaxis against camp gradients Cells form Excitable medium (spiral waves,...) Aggregation, slug formation, culmination
11 Phenomena at all scales... Molecular level: camp sensing, camp secretion mechanism of cell motility mechanism of chemotaxis Cellular level Cell trajectories; cell velocity Cell-cell adhesion Tissue scale: aggregation slug motion
12 camp signaling in cell populations Full model would have many equations So population of m cells: m x n equations Models become complex: Expensive calculations Practically impossible to understand Can we simplify the single-cell level? Bottom line is: if cell senses camp, it secretes camp Excitable system minimal model, Fitzhugh-Nagumo
13 Simplified excitable model: Fitzhugh-Nagumo c t = D 2 c f (c) r inside amoebae c t = D 2 c d c (c c 0 ) outside amoebae r = ε(c)(kc r) t f (c) = C 1 c ε(c) = ε 1 for c < c 1 Null isoclines inside amoebae f (c) = C 2 c + a τ ε(c) = ε 2 for c 1 c c 2 f (c) = C 3 (c 1) ε(c) = ε 3 for c > c 2 Marée et al. JTB 1999
14 Model simulation (Savill and Hogeweg 1997, J. Theor. Biol. 184, 229)
15 Model simulation (Savill and Hogeweg 1997, J. Theor. Biol. 184, 229)
16 Model Simulation (Savill and Hogeweg 1997, J. Theor. Biol. 184, 229)
17 Slug moves to warm spot Warm Wave speeds up with temperature temperature Path of slug in absence of gradient Cold Marée and Hogeweg, J. Theor. Biol Pushes autocycling cell to left
18 Slug behavior is caused by the underlying genetics, but not necessarily explained by it
19 Heart modeling Sasha Panfilov - Ghent University
20 Multiscale models of tumor progression What makes cancer cells metastatic? Clonal evolution of tumor cells (Nowell, 1976) Cancer cells compete for glucose, oxygen, space What happens in harsh microenvironment? Stronger selections pressure? Relapses after cancer treatment? Model by Anderson et al., 2006 Tumor cell properties (adhesion, growth rate) affect tumor morphology
21 Tumor evolution Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Unbiased motility Motility to higher concentrations of ECM (haptotaxis)
22 Tumor evolution Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Tumor cells move randomly Tumor cells move up ECM gradients Cells produce matrix-degrading enzymes (MDE) E.g. MMPs Tumor cells consume oxygen Vasculature delivers oxygen: proportional to ECM
23 Tumor evolution Anderson et al. Cell Equations MMPs
24 Tumor evolution Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Cell-based model: possible to give each cell different properties Evolve cellular properties Exp. I: Vogelgram accumulation of mutations Fearon and Vogelstein, 1990
25 Phenotype I: Proliferative, adhesive, consumes little oxygen, produces few MMPs Phenotype IV: Slow proliferation, not adhesive, consumes lots of oxygen, produces lots of MMPs
26 Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Homogenous ECM
27 Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Homogenous ECM
28 Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Bumpy ECM
29 Anderson et al. Cell 2006 Grainy ECM
30 Progressive mutation Selection for aggressive phenotype IV (blue) Harsh environment (bumpy or grainy ECM) Fingering boundary In reality: tumors are genetically heterogeneous Alternative test for random mutation scheme; Cells jump between any of 100 parameter sets no progressive evolution possible
31 100 phenotypes Any combination of traits possible Selection rounds of oxygen limitation and oxygen excess
32
33 Selection for aggressive phenotypes Selected clones: no cell-cell adhesion low oxygen consumption high proliferation high haptotaxis Stronger selection in harsh environments
34 Model predictions Tumor microenvironment guides tumor shape Homogeneous ECM: smooth tumor boundary Grainy or bumpy ECM: fingering tumor boundary Harsh environment, e.g. hypoxia: Selection for more aggressive phenotypes Consequences for treatments? Do harsh treatments induce aggressive treatments? Relapse after therapies Some authors suggest to treat cancer as chronic disease : non-resistant cells outcompete resistant ones E.g. Gatenby and others
35 Conclusions Space matters for tumor growth! Tumors grow at edges: no exponential growth Cell-based models suggest causes of invasion / fingering growth Clonal selection in harsh micro-environments (Anderson et al.) Cancer Stem Cells (Sottoriva et al.) Further reading: e.g. Gatenby See reader
Mathematical biology From individual cell behavior to biological growth and form
 Mathematical biology From individual cell behavior to biological growth and form Lecture 6: Branching morphogenesis Roeland Merks (1,2) (1) Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, Amsterdam (2) Mathematical Institute,
Mathematical biology From individual cell behavior to biological growth and form Lecture 6: Branching morphogenesis Roeland Merks (1,2) (1) Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, Amsterdam (2) Mathematical Institute,
Cell-based modeling of angiogenic blood vessel sprouting
 Cell-based modeling of angiogenic blood vessel sprouting Roeland Merks Biomodeling & Biosystems Analysis Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica - Life Sciences Netherlands Institute for Systems Biology Netherlands
Cell-based modeling of angiogenic blood vessel sprouting Roeland Merks Biomodeling & Biosystems Analysis Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica - Life Sciences Netherlands Institute for Systems Biology Netherlands
Culturing embryonic tissues in the computer
 Culturing embryonic tissues in the computer Blood vessel development Roeland Merks Biomodeling & Biosystems Analysis CWI, Life Sciences and Netherlands Institute for Systems Biology Biological development
Culturing embryonic tissues in the computer Blood vessel development Roeland Merks Biomodeling & Biosystems Analysis CWI, Life Sciences and Netherlands Institute for Systems Biology Biological development
Evolution of cell motility in an. individual-based model of tumour growth
 Evolution of cell motility in an individual-based model of tumour growth P. Gerlee a,, A.R.A. Anderson b a Niels Bohr Institute, Center for Models of Life, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark b
Evolution of cell motility in an individual-based model of tumour growth P. Gerlee a,, A.R.A. Anderson b a Niels Bohr Institute, Center for Models of Life, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark b
Mathematical modelling of spatio-temporal glioma evolution
 Papadogiorgaki et al. Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling 213, 1:47 RESEARCH Open Access Mathematical modelling of spatio-temporal glioma evolution Maria Papadogiorgaki 1*, Panagiotis Koliou 2, Xenofon
Papadogiorgaki et al. Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling 213, 1:47 RESEARCH Open Access Mathematical modelling of spatio-temporal glioma evolution Maria Papadogiorgaki 1*, Panagiotis Koliou 2, Xenofon
Seminars in Cancer Biology
 Seminars in Cancer Biology 18 (2008) 338 348 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Seminars in Cancer Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/semcancer Review Invasion emerges from cancer
Seminars in Cancer Biology 18 (2008) 338 348 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Seminars in Cancer Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/semcancer Review Invasion emerges from cancer
Simulating the Tumor Growth with Cellular Automata Models
 Simulating the Tumor Growth with Cellular Automata Models S. Zouhri Université Hassan II- Mohammédia, Faculté des Sciences Ben M'sik Département de Mathématiques, B.7955, Sidi Othmane, Casablanca, Maroc
Simulating the Tumor Growth with Cellular Automata Models S. Zouhri Université Hassan II- Mohammédia, Faculté des Sciences Ben M'sik Département de Mathématiques, B.7955, Sidi Othmane, Casablanca, Maroc
Modeling Three-dimensional Invasive Solid Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironment under Chemotherapy
 Modeling Three-dimensional Invasive Solid Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironment under Chemotherapy Hang Xie 1, Yang Jiao 2, Qihui Fan 3, Miaomiao Hai 1, Jiaen Yang 1, Zhijian Hu 1, Yue Yang 4,
Modeling Three-dimensional Invasive Solid Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironment under Chemotherapy Hang Xie 1, Yang Jiao 2, Qihui Fan 3, Miaomiao Hai 1, Jiaen Yang 1, Zhijian Hu 1, Yue Yang 4,
Combination of The Cellular Potts Model and Lattice Gas Cellular Automata For Simulating The Avascular Cancer Growth
 Combination of The Cellular Potts Model and Lattice Gas Cellular Automata For Simulating The Avascular Cancer Growth Mehrdad Ghaemi 1, Amene Shahrokhi 2 1 Department of Chemistry, Teacher Training University,
Combination of The Cellular Potts Model and Lattice Gas Cellular Automata For Simulating The Avascular Cancer Growth Mehrdad Ghaemi 1, Amene Shahrokhi 2 1 Department of Chemistry, Teacher Training University,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28967 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Margaretha Maria (Margriet) Title: High-throughput simulation studies of
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28967 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Margaretha Maria (Margriet) Title: High-throughput simulation studies of
Volume Effects in Chemotaxis
 Volume Effects in Chemotaxis Thomas Hillen University of Alberta supported by NSERC with Kevin Painter (Edinburgh), Volume Effects in Chemotaxis p.1/48 Eschirichia coli Berg - Lab (Harvard) Volume Effects
Volume Effects in Chemotaxis Thomas Hillen University of Alberta supported by NSERC with Kevin Painter (Edinburgh), Volume Effects in Chemotaxis p.1/48 Eschirichia coli Berg - Lab (Harvard) Volume Effects
arxiv: v3 [q-bio.to] 9 Apr 2009
![arxiv: v3 [q-bio.to] 9 Apr 2009 arxiv: v3 [q-bio.to] 9 Apr 2009](/thumbs/83/87120684.jpg) MATHEMATICAL BIOSCIENCES AND ENGINEERING Volume xx, Number 0xx, xx 20xx http://www.mbejournal.org/ pp. 1 xx A SPATIAL MODEL OF TUMOR-HOST INTERACTION: APPLICATION OF CHEMOTHERAPY arxiv:0810.1024v3 [q-bio.to]
MATHEMATICAL BIOSCIENCES AND ENGINEERING Volume xx, Number 0xx, xx 20xx http://www.mbejournal.org/ pp. 1 xx A SPATIAL MODEL OF TUMOR-HOST INTERACTION: APPLICATION OF CHEMOTHERAPY arxiv:0810.1024v3 [q-bio.to]
Emergent Behaviors from a Cellular Automaton Model for Invasive Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironments
 Emergent Behaviors from a Cellular Automaton Model for Invasive Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironments Yang Jiao 1, Salvatore Torquato 1,2 * 1 Physical Science in Oncology Center, Princeton Institute
Emergent Behaviors from a Cellular Automaton Model for Invasive Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironments Yang Jiao 1, Salvatore Torquato 1,2 * 1 Physical Science in Oncology Center, Princeton Institute
A Cell-Based Model Exhibiting Branching and Anastomosis during Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis
 Biophysical Journal Volume 92 May 2007 3105 3121 3105 A Cell-Based Model Exhibiting Branching and Anastomosis during Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis Amy L. Bauer,* Trachette L. Jackson,* and Yi Jiang y *Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 92 May 2007 3105 3121 3105 A Cell-Based Model Exhibiting Branching and Anastomosis during Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis Amy L. Bauer,* Trachette L. Jackson,* and Yi Jiang y *Department
Date: Thursday, 1 May :00AM
 Cancer can give you Maths! Transcript Date: Thursday, 1 May 2008-12:00AM CANCER CAN GIVE YOU MATHS! Professor Philip Maini I would like to start off by thanking Gresham College for this invitation. I am
Cancer can give you Maths! Transcript Date: Thursday, 1 May 2008-12:00AM CANCER CAN GIVE YOU MATHS! Professor Philip Maini I would like to start off by thanking Gresham College for this invitation. I am
A Dynamic model of Pulmonary Vein Electrophysiology. Harry Green 2 nd year Ph.D. student University of Exeter
 A Dynamic model of Pulmonary Vein Electrophysiology Harry Green 2 nd year Ph.D. student University of Exeter Background to the Project Cardiac disease is the leading cause of death in most developed countries
A Dynamic model of Pulmonary Vein Electrophysiology Harry Green 2 nd year Ph.D. student University of Exeter Background to the Project Cardiac disease is the leading cause of death in most developed countries
Virtual Melanoma: When, Where and How Much to Cut Yang Kuang, Arizona State University
 Virtual Melanoma: When, Where and How Much to Cut Yang Kuang, Arizona State University Based on: Eikenberry S, Thalhauser C, Kuang Y. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009, 5:e1000362. Mathematical Modeling of Melanoma
Virtual Melanoma: When, Where and How Much to Cut Yang Kuang, Arizona State University Based on: Eikenberry S, Thalhauser C, Kuang Y. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009, 5:e1000362. Mathematical Modeling of Melanoma
Citation: Chen, Wei (2015) Modelling of Tumour-induced Angiogenesis. Doctoral thesis, Northumbria University.
 Citation: Chen, Wei (2015) Modelling of Tumour-induced Angiogenesis. Doctoral thesis, Northumbria University. This version was downloaded from Northumbria Research Link: http://nrl.northumbria.ac.uk/30235/
Citation: Chen, Wei (2015) Modelling of Tumour-induced Angiogenesis. Doctoral thesis, Northumbria University. This version was downloaded from Northumbria Research Link: http://nrl.northumbria.ac.uk/30235/
A Hybrid Mathematical Model of Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis with Blood Perfusion
 TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSNll1007-0214ll09/10llpp648-657 Volume 19, Number 6, December 2014 A Hybrid Mathematical Model of Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis with Blood Perfusion Junping Meng, Shoubin
TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSNll1007-0214ll09/10llpp648-657 Volume 19, Number 6, December 2014 A Hybrid Mathematical Model of Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis with Blood Perfusion Junping Meng, Shoubin
Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment
 Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment John Lowengrub Dept Math and Biomed Eng., UCI P. Macklin, Ph.D. 2007 (expected); Vittorio Cristini (UCI/UT Health
Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment John Lowengrub Dept Math and Biomed Eng., UCI P. Macklin, Ph.D. 2007 (expected); Vittorio Cristini (UCI/UT Health
Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment
 Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment John Lowengrub Dept Math and Biomed Eng., UCI P. Macklin, Ph.D. 2007 (expected); Vittorio Cristini (UCI/UT Health
Multiscale Models of Solid Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis: The effect of the microenvironment John Lowengrub Dept Math and Biomed Eng., UCI P. Macklin, Ph.D. 2007 (expected); Vittorio Cristini (UCI/UT Health
A hybrid cellular automaton model of clonal evolution in cancer: The emergence of the glycolytic phenotype
 Journal of Theoretical Biology 25 (28) 75 722 www.elsevier.com/locate/yjtbi A hybrid cellular automaton model of clonal evolution in cancer: The emergence of the glycolytic phenotype P. Gerlee, A.R.A.
Journal of Theoretical Biology 25 (28) 75 722 www.elsevier.com/locate/yjtbi A hybrid cellular automaton model of clonal evolution in cancer: The emergence of the glycolytic phenotype P. Gerlee, A.R.A.
Mathematics Meets Oncology
 .. Mathematics Meets Oncology Mathematical Oncology Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University November 12, 2011 Philippe B. Laval (Kennesaw State University)Mathematics Meets Oncology November 12, 2011
.. Mathematics Meets Oncology Mathematical Oncology Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University November 12, 2011 Philippe B. Laval (Kennesaw State University)Mathematics Meets Oncology November 12, 2011
In Silico Modelling of Tumour Margin Diffusion and Infiltration: Review of Current Status
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 672895, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/672895 Review Article In Silico Modelling of Tumour Margin Diffusion and Infiltration: Review
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 672895, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/672895 Review Article In Silico Modelling of Tumour Margin Diffusion and Infiltration: Review
3D-Tissue Microsystems for Tumor Microenvironments Designs for Basic and Translational Research
 3D-Tissue Microsystems for Tumor Microenvironments Designs for Basic and Translational Research Michael Phelan Biostatistics Shared Resource Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center UC, Irvine School of
3D-Tissue Microsystems for Tumor Microenvironments Designs for Basic and Translational Research Michael Phelan Biostatistics Shared Resource Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center UC, Irvine School of
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.cb] 7 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.cb] 7 Jun 2016 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.cb] 7 Jun 2016](/thumbs/88/115176718.jpg) 1 arxiv:1606.02167v1 [q-bio.cb] 7 Jun 2016 Integrative modeling of sprout formation in angiogenesis: coupling the VEGFA-Notch signaling in a dynamic stalk-tip cell selection Sotiris A.Prokopiou 1, Markus
1 arxiv:1606.02167v1 [q-bio.cb] 7 Jun 2016 Integrative modeling of sprout formation in angiogenesis: coupling the VEGFA-Notch signaling in a dynamic stalk-tip cell selection Sotiris A.Prokopiou 1, Markus
A Mathematical Model for Capillary Network Formation in the Absence of Endothelial Cell Proliferation
 Pergamon Appl. Math. Lett. Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 109-114, 1998 Copyright(~)1998 Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0893-9659/98 $19.00 + 0.00 PII: S0893-9659(98)00041-X A
Pergamon Appl. Math. Lett. Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 109-114, 1998 Copyright(~)1998 Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0893-9659/98 $19.00 + 0.00 PII: S0893-9659(98)00041-X A
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XXVII. Waves in Biology: Cardiac Arrhythmia. Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai
 Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XXVII. Waves in Biology: Cardiac Arrhythmia Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai The functional importance of biological waves Spiral Waves Cardiac Arrhythmias Arrhythmias:
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XXVII. Waves in Biology: Cardiac Arrhythmia Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai The functional importance of biological waves Spiral Waves Cardiac Arrhythmias Arrhythmias:
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
I TESSUTI: Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli Studi di Genova
 I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
Natural Selection Simulation: Predation and Coloration
 Name Period Date Natural Selection Simulation: Predation and Coloration This simulation was invented by G. Ledyard Stebbins, a pioneer in the evolution of plants. The purpose of the game is to illustrate
Name Period Date Natural Selection Simulation: Predation and Coloration This simulation was invented by G. Ledyard Stebbins, a pioneer in the evolution of plants. The purpose of the game is to illustrate
Biology Unit 3 Review. Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids
 Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Mathematical Methods for Cancer Invasion
 Mathematical Methods for Cancer Invasion Takashi Suzuki Osaka University Cell Movement Physiological morphogenesis wound healing cellular immunity Pathological inflammation arteriosclerosis cancer invasion,
Mathematical Methods for Cancer Invasion Takashi Suzuki Osaka University Cell Movement Physiological morphogenesis wound healing cellular immunity Pathological inflammation arteriosclerosis cancer invasion,
MODELING THE INFLUENCE OF COMPRESSIVE STRESSES ON THE EFFICACY OF ANTICANCER TREATMENTS
 Tuesday, July 24th, 10:30 MODELING THE INFLUENCE OF COMPRESSIVE STRESSES ON THE EFFICACY OF ANTICANCER TREATMENTS Pietro Mascheroni pietro.mascheroni@helmholtz-hzi.de Braunschweig Integrated Centre of
Tuesday, July 24th, 10:30 MODELING THE INFLUENCE OF COMPRESSIVE STRESSES ON THE EFFICACY OF ANTICANCER TREATMENTS Pietro Mascheroni pietro.mascheroni@helmholtz-hzi.de Braunschweig Integrated Centre of
A Multiscale Mathematical Model of Tumour Invasive Growth
 Bull Math Biol (2017) 79:389 429 DOI 10.1007/s11538-016-0237-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Multiscale Mathematical Model of Tumour Invasive Growth Lu Peng 1,2 Dumitru Trucu 1 Ping Lin 1 Alastair Thompson 3 Mark
Bull Math Biol (2017) 79:389 429 DOI 10.1007/s11538-016-0237-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Multiscale Mathematical Model of Tumour Invasive Growth Lu Peng 1,2 Dumitru Trucu 1 Ping Lin 1 Alastair Thompson 3 Mark
Research Article A Computational Model for Investigating Tumor Apoptosis Induced by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 26, Article ID 4963, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/55/26/4963 Research Article A Computational Model for Investigating Tumor Apoptosis Induced by Mesenchymal
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 26, Article ID 4963, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/55/26/4963 Research Article A Computational Model for Investigating Tumor Apoptosis Induced by Mesenchymal
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
 LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium. Rosita Winkler
 Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM. Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator
 Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Evolution and cancer therapy. Topics 8/18/2011. Carcinogenesis is somatic evolution
 Evolution and cancer therapy Robert Gatenby, MD Moffitt Cancer Center Tampa, Florida Topics 1. Evolutionary dynamics in cancer 2. Cancer therapy Evolution of resistance Experience in pest management Using
Evolution and cancer therapy Robert Gatenby, MD Moffitt Cancer Center Tampa, Florida Topics 1. Evolutionary dynamics in cancer 2. Cancer therapy Evolution of resistance Experience in pest management Using
UWA Research Publication
 UWA Research Publication Shrestha S. M. B. Joldes G. R. Wittek A. and Miller K. (2013) Cellular automata coupled with steady-state nutrient solution permit simulation of large-scale growth of tumours.
UWA Research Publication Shrestha S. M. B. Joldes G. R. Wittek A. and Miller K. (2013) Cellular automata coupled with steady-state nutrient solution permit simulation of large-scale growth of tumours.
Multiscale Cancer Modeling
 Preprint notes: This is a preprint of an article in review by Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. The preprint is posted in full accordance of the journal s copyright policies. Please note that this
Preprint notes: This is a preprint of an article in review by Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. The preprint is posted in full accordance of the journal s copyright policies. Please note that this
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment
 Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation How do plants and animals obtain the glucose they need? Plants: Animals: Cellular Respiration the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation How do plants and animals obtain the glucose they need? Plants: Animals: Cellular Respiration the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells
 Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.to] 31 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.to] 31 Mar 2017 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.to] 31 Mar 2017](/thumbs/72/66558296.jpg) Amoeboid-mesenchymal migration plasticity promotes invasion only in complex heterogeneous microenvironments Katrin Talkenberger 1,*, Elisabetta Ada Cavalcanti-Adam 2,3, Andreas Deutsch 1, and Anja Voss-Böhme
Amoeboid-mesenchymal migration plasticity promotes invasion only in complex heterogeneous microenvironments Katrin Talkenberger 1,*, Elisabetta Ada Cavalcanti-Adam 2,3, Andreas Deutsch 1, and Anja Voss-Böhme
Lab #2: Experimentation Lab
 Lab #2: Experimentation Lab INTRODUCTION: In this lab we are going to gain experience and practice using the scientific method. The first part of the lab will be focused on becoming familiar with the scientific
Lab #2: Experimentation Lab INTRODUCTION: In this lab we are going to gain experience and practice using the scientific method. The first part of the lab will be focused on becoming familiar with the scientific
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
 LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
What is the function of the cell membrane?
 What is the function of the cell membrane? 1. DIFFUSION: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Why do molecules move from high concentration to
What is the function of the cell membrane? 1. DIFFUSION: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Why do molecules move from high concentration to
B2 - Revision! Topic 3- Common Systems! Name:!
 B2 - Revision Topic 3- Common Systems Name: Lesson Topic B2.25 Fossils and Evolution B2.26 Growth B2.27 Blood B2.28 The Heart B2.29 The Circulatory System B2.30 The Digestive System B2.31 Breaking Down
B2 - Revision Topic 3- Common Systems Name: Lesson Topic B2.25 Fossils and Evolution B2.26 Growth B2.27 Blood B2.28 The Heart B2.29 The Circulatory System B2.30 The Digestive System B2.31 Breaking Down
Our Heart Rate. Measuring our heart rate at rest and after physical exercise
 Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Our Heart Rate USA Standards Correlation FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 The Dimension I practices listed below
Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Our Heart Rate USA Standards Correlation FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 The Dimension I practices listed below
Guided Cell Migration: A Dynamical Systems Perspective. Wolfgang Losert. Department of Physics, University of Maryland
 Guided Cell Migration: A Dynamical Systems Perspective Wolfgang Losert Department of Physics, University of Maryland Guided Cell Migration is Essential for Living Systems Phil Keller, Janelia Farm Development
Guided Cell Migration: A Dynamical Systems Perspective Wolfgang Losert Department of Physics, University of Maryland Guided Cell Migration is Essential for Living Systems Phil Keller, Janelia Farm Development
ANSWERS Problem Set 8
 ANSWERS Problem Set 8 Problem 1. All oxidation steps in the pathway from glucose to CO 2 result in the production of NADH, except the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) step in the TCA cycle, which yields FADH2.
ANSWERS Problem Set 8 Problem 1. All oxidation steps in the pathway from glucose to CO 2 result in the production of NADH, except the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) step in the TCA cycle, which yields FADH2.
The Phospholipids Between Us (Part 2) Transport through Cell Membranes
 The Phospholipids Between Us (Part 2) Transport through Cell Membranes Lesson Plan developed by Kai Orton, PhD and Apurva Naik, PhD (Northwestern University) and based on the PhET Interactive Simulation:
The Phospholipids Between Us (Part 2) Transport through Cell Membranes Lesson Plan developed by Kai Orton, PhD and Apurva Naik, PhD (Northwestern University) and based on the PhET Interactive Simulation:
Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I
 Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I 1. Which image best depicts the hot water, which the cold? 2. What is the relationship between temperature and the speed of molecular motion? 3. If a
Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I 1. Which image best depicts the hot water, which the cold? 2. What is the relationship between temperature and the speed of molecular motion? 3. If a
Mathematics and Physics of Cancer: Questions. Robijn Bruinsma, UCLA KITP Colloquium May 6, ) Cancer statistics and the multi-stage model.
 Mathematics and Physics of Cancer: Questions Robijn Bruinsma, UCLA KITP Colloquium May 6, 2009 1) Cancer statistics and the multi-stage model. 2) Cancer microevolution and clonal expansion. 3) Metastasis:
Mathematics and Physics of Cancer: Questions Robijn Bruinsma, UCLA KITP Colloquium May 6, 2009 1) Cancer statistics and the multi-stage model. 2) Cancer microevolution and clonal expansion. 3) Metastasis:
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output. Blood Vessels
 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Limiting the Development of Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in a Spatial Model of Micrometastases
 Limiting the Development of Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in a Spatial Model of Micrometastases arxiv:1601.03412v2 [q-bio.to] 2 Mar 2016 September 1, 2018 Ami B. Shah Department of Biology The College of
Limiting the Development of Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in a Spatial Model of Micrometastases arxiv:1601.03412v2 [q-bio.to] 2 Mar 2016 September 1, 2018 Ami B. Shah Department of Biology The College of
Multiscale modelling and nonlinear simulation of vascular tumour growth
 J. Math. Biol. (2009) 58:765 798 DOI 10.1007/s00285-008-0216-9 Mathematical Biology Multiscale modelling and nonlinear simulation of vascular tumour growth Paul Macklin Steven McDougall Alexander R. A.
J. Math. Biol. (2009) 58:765 798 DOI 10.1007/s00285-008-0216-9 Mathematical Biology Multiscale modelling and nonlinear simulation of vascular tumour growth Paul Macklin Steven McDougall Alexander R. A.
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer Winter 2019
 BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer Winter 2019 Lectures: Center Hall Room 119 Tuesdays/Thursdays; 3:30 4:50 PM January 9 March 15 Discussion Sections: Wednesday 12-1 CSB 001 Friday 12-1 CSB 001 Instructor:
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer Winter 2019 Lectures: Center Hall Room 119 Tuesdays/Thursdays; 3:30 4:50 PM January 9 March 15 Discussion Sections: Wednesday 12-1 CSB 001 Friday 12-1 CSB 001 Instructor:
Mathematical modeling of cancer cell invasion of tissue: biological insight from mathematical analysis and computational simulation
 J. Math. Biol. () 6:4 7 DOI.7/s85--69- Mathematical Biology Mathematical modeling of cancer cell invasion of tissue: biological insight from mathematical analysis and computational simulation Vivi Andasari
J. Math. Biol. () 6:4 7 DOI.7/s85--69- Mathematical Biology Mathematical modeling of cancer cell invasion of tissue: biological insight from mathematical analysis and computational simulation Vivi Andasari
Single-Cell Sequencing in Cancer. Peter A. Sims, Columbia University G4500: Cellular & Molecular Biology of Cancer October 22, 2018
 Single-Cell Sequencing in Cancer Peter A. Sims, Columbia University G4500: Cellular & Molecular Biology of Cancer October 22, 2018 Lecture will focus on technology for and applications of single-cell RNA-seq
Single-Cell Sequencing in Cancer Peter A. Sims, Columbia University G4500: Cellular & Molecular Biology of Cancer October 22, 2018 Lecture will focus on technology for and applications of single-cell RNA-seq
Mathematical Modelling of Tumour Invasion and Metastasis
 Journal of Theof-etical Med~cme. Vul 2, pp. 129-151 Reprints available drectly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only @ 2000 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license
Journal of Theof-etical Med~cme. Vul 2, pp. 129-151 Reprints available drectly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only @ 2000 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2015
 BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2015 Lectures: CENTR 214 Tuesdays/Thursdays, March 31 June 4 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2015 Lectures: CENTR 214 Tuesdays/Thursdays, March 31 June 4 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
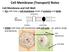 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Angiogenesis and vascular remodelling in normal and cancerous tissues
 J. Math. Biol. (29) 58:689 721 DOI 1.17/s285-8-213-z Mathematical Biology Angiogenesis and vascular remodelling in and cancerous tissues Markus R. Owen Tomás Alarcón Philip K. Maini Helen M. Byrne Received:
J. Math. Biol. (29) 58:689 721 DOI 1.17/s285-8-213-z Mathematical Biology Angiogenesis and vascular remodelling in and cancerous tissues Markus R. Owen Tomás Alarcón Philip K. Maini Helen M. Byrne Received:
Exercise for Health and Fitness
 Exercise for Health and Fitness Chapter 13 1 Figure 13.1 Current levels of physical activity among American adults 2 What is Physical Fitness? Definition: Five components of Physical Fitness: 3 Components
Exercise for Health and Fitness Chapter 13 1 Figure 13.1 Current levels of physical activity among American adults 2 What is Physical Fitness? Definition: Five components of Physical Fitness: 3 Components
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
Natural Selection. species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring
 Imagine that you and your classmates are taking a nature hike through a nearby desert ecosystem. The hot sun is beating down on you, and you begin to wonder how anything could live in this harsh climate.
Imagine that you and your classmates are taking a nature hike through a nearby desert ecosystem. The hot sun is beating down on you, and you begin to wonder how anything could live in this harsh climate.
Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0
 2017/2018 Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer Code: 101897 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2501230 Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other
2017/2018 Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer Code: 101897 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2501230 Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other
On the Possible Pitfalls in the Evaluation of Brain Computer Interface Mice
 On the Possible Pitfalls in the Evaluation of Brain Computer Interface Mice Riccardo Poli and Mathew Salvaris Brain-Computer Interfaces Lab, School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University
On the Possible Pitfalls in the Evaluation of Brain Computer Interface Mice Riccardo Poli and Mathew Salvaris Brain-Computer Interfaces Lab, School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University
Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) Experts Discuss Treatment Options. Part II: The Future Treatment of NMIBC
 Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) Experts Discuss Treatment Options Wednesday, June 14, 2017 Part II: The Future Treatment of NMIBC Presented by Dr. Arlene Siefer-Radtke is an Associate Professor
Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) Experts Discuss Treatment Options Wednesday, June 14, 2017 Part II: The Future Treatment of NMIBC Presented by Dr. Arlene Siefer-Radtke is an Associate Professor
CHEMOTACTIC SIGNALS AND RESPONSES ARE COORDINATED BY AN OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT IN DICTYOSTELIUM
 CHEMOTACTIC SIGNALS AND RESPONSES ARE COORDINATED BY AN OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT IN DICTYOSTELIUM Dr. William Loomis, UCSD (KITP Bio Networks Chemotaxis Workshop 3/12/03) 1 Dictyostelium is a social amoeba
CHEMOTACTIC SIGNALS AND RESPONSES ARE COORDINATED BY AN OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT IN DICTYOSTELIUM Dr. William Loomis, UCSD (KITP Bio Networks Chemotaxis Workshop 3/12/03) 1 Dictyostelium is a social amoeba
CA 2 : Cellular Automata Models and Self-Organized Chaos in Cancer Growth
 CA 2 : Cellular Automata Models and Self-Organized Chaos in Cancer Growth ADAM V. ADAMOPOULOS Medical Physics Laboratory, Department of Medicine Democritus University of Thrace GR-681 00, Alexandroupolis
CA 2 : Cellular Automata Models and Self-Organized Chaos in Cancer Growth ADAM V. ADAMOPOULOS Medical Physics Laboratory, Department of Medicine Democritus University of Thrace GR-681 00, Alexandroupolis
Modeling the Diffusion of TGF-β1 from a Fibrin Scaffold through Alveolar Bone Martin Barrio and Sindhu Raghunandan 10/28/2011 BENG221
 10/28/2011 BENG221 I. Background Periodontitis is defined as infection and inflammation of the primary tissues surrounding one or more teeth [5]. While the initial stages involve the infection and inflammation
10/28/2011 BENG221 I. Background Periodontitis is defined as infection and inflammation of the primary tissues surrounding one or more teeth [5]. While the initial stages involve the infection and inflammation
Contact-Inhibited Chemotaxis in De Novo and Sprouting Blood-Vessel Growth
 Contact-Inhibited Chemotaxis in De Novo and Sprouting Blood-Vessel Growth Roeland M. H. Merks 1,2,3 a *, Erica D. Perryn 4 b, Abbas Shirinifard 3, James A. Glazier 3 1 VIB Department of Plant Systems Biology,
Contact-Inhibited Chemotaxis in De Novo and Sprouting Blood-Vessel Growth Roeland M. H. Merks 1,2,3 a *, Erica D. Perryn 4 b, Abbas Shirinifard 3, James A. Glazier 3 1 VIB Department of Plant Systems Biology,
EDUCATION. Peripheral Artery Disease
 EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
UMBC REU Site: Computational Simulations of Pancreatic Beta Cells
 UMBC REU Site: Computational Simulations of Pancreatic Beta Cells Sidafa Conde 1, Teresa Lebair 2, Christopher Raastad 3, Virginia Smith 4 Kyle Stern, 5 David Trott 5 Dr. Matthias Gobbert 5, Dr. Bradford
UMBC REU Site: Computational Simulations of Pancreatic Beta Cells Sidafa Conde 1, Teresa Lebair 2, Christopher Raastad 3, Virginia Smith 4 Kyle Stern, 5 David Trott 5 Dr. Matthias Gobbert 5, Dr. Bradford
Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. - Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday 3-4 pm, Natural Sciences Building, Room 5316
 BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2014 Lectures: WLH 2204 Tuesdays/Thursdays, April 1 June 5 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2014 Lectures: WLH 2204 Tuesdays/Thursdays, April 1 June 5 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
Molecular Biology of Cancer. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester
 2017/2018 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
2017/2018 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
Cellular Transport. 1. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below.
 Name: Date: 1. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which diagram best represents the net movement of molecules?.. C. D. page 1 2. The following question(s) is/are
Name: Date: 1. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which diagram best represents the net movement of molecules?.. C. D. page 1 2. The following question(s) is/are
HOMEOSTASIS. Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis
 HOMEOSTASIS Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis As in all systems in nature, animal systems must maintain balance. We call this homeostasis. How do ecosystems maintain balance? In animal systems,
HOMEOSTASIS Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis As in all systems in nature, animal systems must maintain balance. We call this homeostasis. How do ecosystems maintain balance? In animal systems,
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Cell structure and function flash cards
 Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0
 2018/2019 Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer Code: 101897 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2501230 Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other
2018/2019 Molecular and Cell Biology of Cancer Code: 101897 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2501230 Biomedical Sciences OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other
CANCER is to be the leading cause of death throughout the
 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY AND BIOINFORMATICS, VOL. 9, NO. 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2012 169 Multiobjective Optimization Based-Approach for Discovering Novel Cancer Therapies Arthur W. Mahoney,
IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY AND BIOINFORMATICS, VOL. 9, NO. 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2012 169 Multiobjective Optimization Based-Approach for Discovering Novel Cancer Therapies Arthur W. Mahoney,
Molecular Biology of Cancer. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester
 2018/2019 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
2018/2019 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
Study of Early Tumour Development and its Glycolytic Properties
 Study of Early Tumour Development and its Glycolytic Properties Ariosto Siqueira Silva, Jose Andres Yunes Centro Infantil Boldrini Contacts: ariostosilva@i-genics.com,andres@boldrini.org.br It is believed
Study of Early Tumour Development and its Glycolytic Properties Ariosto Siqueira Silva, Jose Andres Yunes Centro Infantil Boldrini Contacts: ariostosilva@i-genics.com,andres@boldrini.org.br It is believed
Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana Juan Sebastián Munoz Arbeláez Cesar Nieto Londoño [0.5 min.] An optimal fin design and optimization process to get an efficient
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana Juan Sebastián Munoz Arbeláez Cesar Nieto Londoño [0.5 min.] An optimal fin design and optimization process to get an efficient
BMBF Forsys Partner Project: A Systems Biology Approach towards Predictive Cancer Therapy
 ling and ling and BMBF Forsys Partner Project: A Systems Biology Approach towards Predictive Cancer Therapy H. Perfahl, A. Lapin, M. Reuss Germany holger.perfahl@ibvt.uni-stuttgart.de 1 ling and Cooperation
ling and ling and BMBF Forsys Partner Project: A Systems Biology Approach towards Predictive Cancer Therapy H. Perfahl, A. Lapin, M. Reuss Germany holger.perfahl@ibvt.uni-stuttgart.de 1 ling and Cooperation
Cellular Respiration. How is energy in organic matter released for used for in living systems?
 Cellular Respiration How is energy in organic matter released for used for in living systems? Cellular Respiration Organisms that perform cellular respiration are called chemoheterotrophs Includes both
Cellular Respiration How is energy in organic matter released for used for in living systems? Cellular Respiration Organisms that perform cellular respiration are called chemoheterotrophs Includes both
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification
 icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
Activity Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
 Activity 8.1.2 Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Introduction The human body is an amazing machine that automatically monitors and adjusts itself in order to maintain equilibrium or homeostasis.
Activity 8.1.2 Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Introduction The human body is an amazing machine that automatically monitors and adjusts itself in order to maintain equilibrium or homeostasis.
Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas
 Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas Mathilde Badoual Paris Diderot University, IMNC lab 2nd HTE workshop: Mathematical & Computer Modeling to study tumors heterogeneity in its ecosystem,
Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas Mathilde Badoual Paris Diderot University, IMNC lab 2nd HTE workshop: Mathematical & Computer Modeling to study tumors heterogeneity in its ecosystem,
Cellular respiration and fermentation 04/18/2016 BI102
 Cellular respiration and fermentation 04/18/2016 BI102 Announcements Exam 1 after lecture Don t forget to do the online assignments every week! Quiz 2 and lab 2 review Cellular Respiration Cells require
Cellular respiration and fermentation 04/18/2016 BI102 Announcements Exam 1 after lecture Don t forget to do the online assignments every week! Quiz 2 and lab 2 review Cellular Respiration Cells require
