Postpartum pneumomediastinum manifested by surgical emphysema. Should we always worry about underlying oesophageal rupture?
|
|
|
- Ruth York
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rare disease Postpartum pneumomediastinum manifested by surgical emphysema. Should we always worry about underlying oesophageal rupture? Dariusz Rafal Wozniak, Anna Blackburn Department of Respiratory Medicine, James Paget University Hospital, Great Yarmouth, UK Correspondence to Dr Dariusz Rafal Wozniak, Summary Spontaneous pneumomediastinum during labour is a rare, usually benign and self-limiting condition. It often presents with chest or neck pain and surgical emphysema. The latter sign is easy to demonstrate but often missed during clinical assessment if the condition is not included in the differential diagnosis of chest pain and dyspnoea in peripartum. The authors describe a case of 20-year-old primigravida who developed surgical emphysema following prolonged vaginal delivery. The chest x-ray revealed pneumomediastinum, and small left apical pneumothorax. She was investigated with CT of the chest and contrast swallow, both of which excluded oesophageal perforation. The management was conservative and she made a complete recovery. Spontaneous oesophageal rupture is a potential cause of pneumomediastinum and leads to high morbidity and mortality if not diagnosed early. However, it is extremely uncommon in labour, especially without a preceding history of vomiting. Unless a strong clinical suspicious exists, routine investigations and or treatment of suspected oesophageal perforation are unnecessary. BACKGROUND Subcutaneous emphysema originating in the mediastinum has an estimated incidence of 1 in deliveries. 1 Approximately 200 cases have been reported worldwide. 2 3 Despite its rarity and usually benign course it requires vigilance and prompt diagnosis. Therefore, both obstetricians and physicians should be familiar with this condition and understand its pathophysiology. It is often of concern to the attending clinician whether the pneumomediastinum has arisen from oesophageal rupture, as the latter carries high morbidity and mortality. Therefore, patients with spontaneous pneumomediastinum of various aetiologies are often subjected to further investigations and treatment for suspected oesophageal perforation. We review this approach and present a case where pneumomediastinum coincided with pneumopericardium and a small unilateral apical pneumothorax which has not previously been described. CASE PRESENTATION A 20-year-old primigravida developed mild retrosternal chest and neck pain associated with neck swelling 5 h after a prolonged, assisted vaginal delivery. Her medical history included eczema and mild asthma; she was a non-smoker and her pregnancy had been uneventful. She presented at 41 weeks and 3 days gestation in early spontaneous labour. She had a strong contractions throughout; however, her progress was slow and she required augmentation by artificial rupture of the membranes. Seven hours after presentation full dilatation was reached and active pushing began. She received 50 mg of pethidine and 50 mg of cyclizine. No nausea or vomiting was reported. She used entonox intermittently. An episiotomy was performed, but labour continued to progress slowly and at approximately two and a half hours of active pushing signs of fetal distress were detected. This prompted an immediate attempts at vacuum-assisted delivery which were unsuccessful and the baby was finally delivered using forceps. The baby girl was live, weighed 3225 g but required immediate resuscitation. Placenta and membranes were delivered by controlled cord traction. No postpartum haemorrhage occurred. Five hours later, the patient reported mild retrosternal chest pain associated with discomfort and swelling in the neck region. Clinical assessment revealed no obvious cause of the symptoms and simple analgesia was administered for the discomfort. Chest and neck pain occurred again on the following day and was accompanied by mild, transient breathlessness associated with a tachycardia of 130 beats per minute and mild tachypnoea at 20 breaths per minute. Blood pressure remained stable at 125/81 mm Hg and saturation were 96% on room air. A chest x-ray was requested and clinical review by the acute medical team instituted. At this time she was noted to have surgical emphysema palpable over the anterior neck, both supraclavicular fossae and the anterior chest wall. Lung fields were otherwise clear on auscultation with good bilateral air entry. INVESTIGATIONS ECG revealed sinus tachycardia with no other abnormalities and arterial blood gas analysis was normal. BMJ Case Reports 2011; doi: /bcr of 5
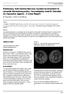
2 Figure 1 AP chest x-ray demonstrating surgical emphysema, small left apical pneumothorax (1) and pneumomediastinum (2). A chest x-ray confirmed pneumomediastinum and suggested a small left apical pneumothorax. The view was obscured by overlying surgical emphysema ( figure 1 ). The patient was placed nil by mouth and the following morning a CT thorax and barium contrast swallow were performed in order to exclude a spontaneous oesophageal rupture as the cause of pneumomediastinum. A CT confirmed chest x-ray findings and in addition revealed a small pneumopericardium. There was no evidence of free fluid in the mediastinum, pleural effusion or any other sign of oesophageal rupture ( figure 2 ). Barium oesophagogram was normal ( figure 3 ). DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Causes of pneumomediastinum include; Hamman s syndrome (spontaneous pneumomediastinum due to alveolar rupture), oesophageal rupture, pneumothorax with pleuro-mediastinal communication, intra-abdominal hollow viscus perforation with an associated hiatal defect, tracheo-oesophageal fistula with an air leak and mediastinal blunt force trauma with an airway injury. TREATMENT No treatment was required. OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP Normal oral intake was re-established and she was regularly clinically reviewed. Her pain settled, and tachycardia resolved. The white cell count fell from 17.2 after labour to Her chest and neck discomfort improved and the subcutaneous emphysema remained stable. Transfer to another hospital, where her baby was receiving additional care was facilitated. She was reviewed at 5 weeks and complete recovery was noted. DISCUSSION Since it was first formally reported by Simmons 4 in 1793 and then described by Hamman 5 in 1945, spontaneous pneumomediastinum remains an unusual phenomenon in labour. It usually occurs in the second stage of labour and is much uncommon in the first stage. 7 The signs and symptoms usually develop some time after the delivery. Clinical manifestation include retrosternal chest pain often radiating to the neck, mild dyspnoea and anxiety. Dysphagia, tachycardia, transient leucocytosis and fever may occur. 3 Surgical emphysema and Hamman s sign (a loud harsh sound over the precordium in systole) are pathognomonic. 2 of 5 BMJ Case Reports 2011; doi: /bcr
3 Figure 2 CT thorax demonstrating surgical emphysema (1), pneumomediastinum (2) and pneumopericardium (3). In this case the presenting symptoms were typical, but recognition was delayed. The diagnosis was established over 24 h after the delivery. However, the patient already reported first symptoms indicating development of surgical emphysema 5 h following the childbirth and it is very likely that pneumomediastinum occurred much earlier in the second stage of labour. There is no consensus on the predisposing factors leading to spontaneous pneumomediastinum in labour. Gordon, 6 who published first review of 130 cases stated that most often the patient was a healthy primigravida with a long labour. Reader et al 2 observed that, although 95% of women were primiparus the duration of labour was normal and the babies were of average size. Our case is consistent with the view that first pregnancy and prolonged, difficult labour carry a higher risk of this complication. The chest x-ray is usually diagnostic. However, the interpretation may be occasionally difficult in cases of extensive subcutaneous emphysema. In this instance, despite overlying surgical emphysema the chest x-ray clearly demonstrated both pneumomediastinum and tiny left apical pneumothorax. We acknowledge that CT has not contributed further to the management and in retrospective could have been avoided. The pathophysiology of spontaneous pneumomediastinum relates to Valsalva manoeuvre repeatedly generated during labour. Increased intra-alveolar pressure causes rupture of peripheral alveoli into perivascular tissue planes, with tracking of air into the mediastinum or pericardium. 5 6 Air subsequently dissects through facial planes in the neck and chest wall. This mitigates rises in intramediastinal pressure which could compromise venous return in the great veins and result in haemodynamic instability. Therefore, tension pneumomediastinum or tension pneumopericardium in Hamman s syndrome is very rare. Only a single case manifesting as a tension pneumomediastinum with cardiovascular instability in the second stage of labour has been reported. 8 The patient recovered following intravenous fluid resuscitation and no surgical intervention was required. Nevertheless, this rare, but potentially fatal complication should be noted. Pneumothorax can originate either from an independent rupture of peripheral alveoli or result from extension of free air from mediastinum to the pleural space. 2 3 Coexistence of spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium and pneumothorax in uncommon and to our knowledge has not been previously reported in labour. However, we suspect this is because of underdiagnosis as BMJ Case Reports 2011; doi: /bcr of 5
4 Figure 3 Normal barium oesophagogram. pneumopericardium may not always be apparent on the plain chest x-ray and CT is not necessarily undertaken. Although, the pathogenesis of pneumomediastinum and surgical emphysema outlined above has been widely accepted, establishing the final diagnosis for the clinician unfamiliar with the condition often poses a clinical dilemma. The most common concern is missing an oesophageal rupture, a condition which itself can lead to pneumomediastinum and carries a high morbidity and mortality if not diagnosed early. Many case reports reflect this and often oesophageal contrast studies and occasionally CT have been performed. 8 9 A management strategy we followed also confirms this practice. Interestingly our observations seem to be shared by others who investigated the occurrence of spontaneous pneumomediastinum in different cohorts of patients. Chapdelaine 10 found no oesophageal perforation in a group of 53 paediatric patients and advised caution when requesting further radiological investigations. Similarly, Abolnik 11 who studied an older group of patients with a mean age of 18.8 years found no incidence of oesophageal perforation, but 24% of patients were investigated with contrast swallow. Some investigators believe that the oesophagus in young patients, unlike the alveoli, is more tolerant of sudden pressure changes. 12 Spontaneous oesophageal rapture is a rare event in labour. If it occurs it is usually a consequence of repeated vomiting and only two confirmed cases of oesophageal perforation in labour are reported both of which describe preceding vomiting Investigations in this area can be difficult. A contrast study particularly in a case of small oesophageal tear may be normal. Endoscopy may be useful in the management of confirmed tears but may not be sufficiently sensitive to make the diagnosis. 15 We would recommend plain posteroanterior and lateral chest radiographs which can strongly suggest the diagnosis. Effusion in the mediastinum, a pleural effusion, hydropneumothorax, basal consolidations, emphysema located posteriorly and inferiorly along the lateral edge of the aorta and beneath the parietal pleura over the left hemidiaphragm are more suggestive of oesophageal perforation In contrast, surgical emphysema or pneumomediastinum alone are present in only 27% of patients with oesophageal rupture, whereas the chest x-ray was abnormal in 97% of cases. 17 Persistent fever, leucocytosis and systemic sepsis would strongly indicate acute mediastinitis 4 of 5 BMJ Case Reports 2011; doi: /bcr
5 while a transient leucocytosis alone may be a feature of surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum. 3 In conclusion, surgical emphysema and spontaneous pneumomediastinum are very rare events in labour. Oesophageal rupture is exceedingly unusual particularly in the absence of a history of vomiting when plain chest radiograph is otherwise normal and there are no signs of sepsis. Current evidence does not support the routine use of contrast enhanced CT or a contrast oesophagography. However, careful clinical assessment including a thorough history of the circumstances leading to a pneumomediastinum should be taken. We suggest that the risks of radiation exposure in a childbearing age woman should be carefully considered and the routine use of contrast enhanced CT with or without contrast swallow studies is not necessarily indicated in Hamman s syndrome. Learning points Spontaneous pneumomediastinum during labour is a rare condition. However, both physicians and obstetricians should be familiar with its pathophysiology and management. It is usually caused by a rupture of the alveoli. Spontaneous oesophageal rupture in labour is extremely rare. Unless strong clinical suspicion exists, routine investigations and or treatment of suspected oesophageal tear are unnecessary. REFERENCES 1. Crean PA, Stronge JM, FitzGerald MX. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in pregnancy. Case report. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1981 ;88 : Reeder SR. Subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and pneumothorax in labor and delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986 ;154 : Karson EM, Saltzman D, Davis MR. Pneumomediastinum in pregnancy: two case reports and a review of the literature, pathophysiology, and management. Obstet Gynecol 1984 ;64 (3 Suppl ):39S 43S. 4. Simmons ST. A case of emphysema brought on by severe labor pains. Lond Med Commun 1783 ;1 : Hamman L. Mediastinal emphysema. JAMA 1945 ; 128 : Gordon CA. Respiratory emphysema in labor. AM J Obstet Gynaecol 1927 ;14 : Miller HJ. Mediastinal and subcutaneous emphysema during the fi rst stage of labor. South Med J 1969 ;62 : Rafi J, Muppala H, Schaefer B. Cardiac instability due to pneumomediastinum during second stage of labour. Scott Med J 2009 ; 54 : Majer S, Graber P. Postpartum pneumomediastinum (Hamman s syndrome). Can Med Assoc Journal 2007 ; 177 : Chapdelaine J, Beaunoyer M, Daigneault P, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: are we overinvestigating? J Pediatr Surg 2004 ;39 : Abolnik I, Lossos IS, Breuer R. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum. A report of 25 cases. Chest 1991 ; 100 : Drakley MJ. The oesophagus in otolaryngology. In: Kerr AG, Stell PM,eds. Scott-Brown s Otolaryngology. Fifth edition. London : Butterworths Kennard HW. Rupture of oesophagus during childbirth. BMJ 1950 ;1 : Dresner SM, Bailey JL, Lamb PJ, et al. Spontaneous oesophageal perforation during vaginal delivery. J R Soc Med 2001 ; 94 : Brinster CJ, Singhal S, Lee L, et al. Evolving options in the management of esophageal perforation. Ann Thorac Surg 2004 ; 77 : Rogers LF, Puig AW, Dooley BN, et al. Diagnostic considerations in mediastinal emphysema: a pathophysiologic-roentgenologic approach to Boerhaave s syndrome and spontaneous pneumomediastinum. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1972 ;115 : Pate JW, Walker WA, Cole FH Jr, et al. Spontaneous rupture of the esophagus: a 30-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg 1989 ;47 : Competing interests None. Patient consent Obtained. This pdf has been created automatically from the fi nal edited text and images. Copyright 2011 BMJ Publishing Group. All rights reserved. For permission to reuse any of this content visit BMJ Case Report Fellows may re-use this article for personal use and teaching without any further permission. Please cite this article as follows (you will need to access the article online to obtain the date of publication). Wozniak DR, Blackburn A. A rare case of postpartum pneumomediastinum manifested by surgical emphysema. Should we always worry about underlying oesophageal rupture?. BMJ Case Reports 2011; /bcr , date of publication Become a Fellow of BMJ Case Reports today and you can: Submit as many cases as you like Enjoy fast sympathetic peer review and rapid publication of accepted articles Access all the published articles Re-use any of the published material for personal use and teaching without further permission For information on Institutional Fellowships contact consortiasales@bmjgroup.com Visit casereports.bmj.com for more articles like this and to become a Fellow BMJ Case Reports 2011; doi: /bcr of 5
Four cases of pneumomediastinum
 Avinash Aujayeb, Jonathan Miller, Mark Weatherhead, David Cooper aujayeb@doctors.net.uk North Tyneside General Hospital, Northumbria Health Care Foundation Trust, North Shields, UK. Four cases of pneumomediastinum
Avinash Aujayeb, Jonathan Miller, Mark Weatherhead, David Cooper aujayeb@doctors.net.uk North Tyneside General Hospital, Northumbria Health Care Foundation Trust, North Shields, UK. Four cases of pneumomediastinum
Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round. Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006
 Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006 Case Presentation 12 y/o female Presented to OSH after accidental swallowing of plastic fork in the bus, CXR/AXR form OSH did not
Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006 Case Presentation 12 y/o female Presented to OSH after accidental swallowing of plastic fork in the bus, CXR/AXR form OSH did not
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
Thoracic causes of pneumoperitoneum - it is not all about perforation
 Thoracic causes of pneumoperitoneum - it is not all about perforation Poster No.: C-2590 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ilieva; Sofia/BG Keywords: Education, Plain radiographic
Thoracic causes of pneumoperitoneum - it is not all about perforation Poster No.: C-2590 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ilieva; Sofia/BG Keywords: Education, Plain radiographic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Left Sided Chest Pain: A Case Report of Boerhaave Syndrome Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome
 664 Left Sided Chest Pain: A Case Report of Boerhaave Syndrome Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome Hoo F.K. 1 *, Lee S.H. 2, Shariful Hasan 1, Wan Aliaa WS 1, Mohd Sazlly Lim S 1, Hamidon Basri 1 1 Department
664 Left Sided Chest Pain: A Case Report of Boerhaave Syndrome Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome Hoo F.K. 1 *, Lee S.H. 2, Shariful Hasan 1, Wan Aliaa WS 1, Mohd Sazlly Lim S 1, Hamidon Basri 1 1 Department
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 9, September ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 9, September-2014 1196 Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema secondary to blunt laryngeal traumafavourable outcome with
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 9, September-2014 1196 Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema secondary to blunt laryngeal traumafavourable outcome with
Esophageal injuries. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Case Report Pneumomediastinum Associated with Pneumopericardium and Epidural Pneumatosis
 Case Reports in Emergency Medicine, Article ID 275490, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/275490 Case Report Pneumomediastinum Associated with Pneumopericardium and Epidural Pneumatosis Ozlem Bilir,
Case Reports in Emergency Medicine, Article ID 275490, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/275490 Case Report Pneumomediastinum Associated with Pneumopericardium and Epidural Pneumatosis Ozlem Bilir,
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal injuries. Pre-test /11/10. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119. O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries?
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
pulmonary and critical care pearls
 pulmonary and critical care pearls A 63-Year-Old Woman With Subcutaneous Emphysema Following Endotracheal Intubation* Bassam Hashem, MD; James K. Smith, MD, FCCP; and W. Bruce Davis, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2005;
pulmonary and critical care pearls A 63-Year-Old Woman With Subcutaneous Emphysema Following Endotracheal Intubation* Bassam Hashem, MD; James K. Smith, MD, FCCP; and W. Bruce Davis, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2005;
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Historical perspective
 Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks
 Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma but penetrating injuries also treated here (usually as single injuries, like stab wound)
 Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Swallowed Foreign Body
 Swallowed Foreign Body Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Swallowed foreign bodies can be divided into five distinct groups: 1 Small blunt objects 2 Large blunt objects 3 Potentially poisonous objects 4 Sharp objects
Swallowed Foreign Body Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Swallowed foreign bodies can be divided into five distinct groups: 1 Small blunt objects 2 Large blunt objects 3 Potentially poisonous objects 4 Sharp objects
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 04 Page April 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x A Rare Case of Boerhaaves Syndrome Managed Conservatively Authors Dr. Vinaya Ambore 1, Dr. Vikram Wagh 2, Dr. Prashant Turkar 3, Dr. Kapil
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x A Rare Case of Boerhaaves Syndrome Managed Conservatively Authors Dr. Vinaya Ambore 1, Dr. Vikram Wagh 2, Dr. Prashant Turkar 3, Dr. Kapil
Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation
 Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
RCH Trauma Guideline. Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax. Trauma Service, Division of Surgery
 RCH Trauma Guideline Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax Trauma Service, Division of Surgery Aim To describe safe and competent management of traumatic pneumothorax and haemothorax at RCH.
RCH Trauma Guideline Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax Trauma Service, Division of Surgery Aim To describe safe and competent management of traumatic pneumothorax and haemothorax at RCH.
Selective Nonoperative Management of Contained Intrathoracic Esophageal Disruptions
 Selective Nonoperative Management of Contained Intrathoracic Esophageal Disruptions John L. Cameron, M.D., Richard F. Kieffer, M.D., Thomas R. Hendrix, M.D., Denis G. Mehigan, M.., and R. Robinson aker,
Selective Nonoperative Management of Contained Intrathoracic Esophageal Disruptions John L. Cameron, M.D., Richard F. Kieffer, M.D., Thomas R. Hendrix, M.D., Denis G. Mehigan, M.., and R. Robinson aker,
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION
 CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE
 Thlorax (1950), 5, 369. PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE BY Fronm the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
Thlorax (1950), 5, 369. PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE BY Fronm the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Massive subcutaneous emphysema after domestic fall
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Massive subcutaneous emphysema after domestic fall Ida Carine Bø, Erik Waage Nielsen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Massive subcutaneous emphysema after domestic fall Ida Carine Bø, Erik Waage Nielsen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images
Thoracic Trauma The Spectrum
 Thoracic Trauma The Spectrum Joseph Mathew Consultant, s & Emergency dept. 2 Thoracic Trauma Responsible for 20-25% of all deaths attributed to trauma. Contributing cause of death in an additional 25%
Thoracic Trauma The Spectrum Joseph Mathew Consultant, s & Emergency dept. 2 Thoracic Trauma Responsible for 20-25% of all deaths attributed to trauma. Contributing cause of death in an additional 25%
Foreign Body Ingested
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Foreign Body Ingested Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Foreign Body Ingested Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
CHEST PAIN IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
 CHEST PAIN IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Quek Swee Chye, Wong May Ling Chest pain, previously a symptom prevalent in the elderly, is becoming an increasingly common complaint in children and adolescents.
CHEST PAIN IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Quek Swee Chye, Wong May Ling Chest pain, previously a symptom prevalent in the elderly, is becoming an increasingly common complaint in children and adolescents.
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL
 CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Pneumomediastinum and pneumoretroperitoneum PNEUMOMEDIASTINUM AND PNEUMORETROPERITONEUM ASSOCAITED WITH PERFORATED ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
 167 PNEUMOMEDIASTINUM AND PNEUMORETROPERITONEUM ASSOCAITED WITH PERFORATED ESOPHAGEAL CANCER Devadoss CW 1 *, Singla S 2, Mysorekar V 1, Dang M 1, Kenkare M 1, Harish K 3 1. Department of Pathology, M.S.
167 PNEUMOMEDIASTINUM AND PNEUMORETROPERITONEUM ASSOCAITED WITH PERFORATED ESOPHAGEAL CANCER Devadoss CW 1 *, Singla S 2, Mysorekar V 1, Dang M 1, Kenkare M 1, Harish K 3 1. Department of Pathology, M.S.
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
 Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
The ABC s of Chest Trauma
 The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
Traumatic Cardiac Arrest
 HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE Traumatic Cardiac Arrest HOP No: C/06 Issued: April 2013 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: 2 TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D13/5679 Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X Helicopter
HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE Traumatic Cardiac Arrest HOP No: C/06 Issued: April 2013 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: 2 TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D13/5679 Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X Helicopter
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems
 Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article
 Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
A unique case of esophageal perforation caused by prickly pears
 A unique case of esophageal perforation caused by prickly pears Abstract This is a report of a previously healthy 20-yearold male presenting with the sensation of a foreign object being stuck in the throat
A unique case of esophageal perforation caused by prickly pears Abstract This is a report of a previously healthy 20-yearold male presenting with the sensation of a foreign object being stuck in the throat
CHEST TRAUMA. Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS
 CHEST TRAUMA Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS Learning objectives Anatomy of chest wall and thoracic viscera Physiology of respiration and nerve pathways for pain Enumerate different thoracic conditions requiring
CHEST TRAUMA Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS Learning objectives Anatomy of chest wall and thoracic viscera Physiology of respiration and nerve pathways for pain Enumerate different thoracic conditions requiring
Drugs used in obstetrics
 Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Traumatic Tracheo-Oesophageal Fistula: A Case Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. II (Dec. 2017), PP 93-98 www.iosrjournals.org Traumatic Tracheo-Oesophageal Fistula:
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. II (Dec. 2017), PP 93-98 www.iosrjournals.org Traumatic Tracheo-Oesophageal Fistula:
Problem Based Learning Session. Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days.
 Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
ANESTHESIA FOR CHILDBIRTH
 Southwest Ob / Gyn Associates, L.L.P 16651 Southwest Freeway, Suite 200 Sugar Land, TX 77479 7737 Southwest Freeway, Suite 895 Houston, TX 77074 Telephone: (713) 774-5131 Fax: (713) 774-4336 ANESTHESIA
Southwest Ob / Gyn Associates, L.L.P 16651 Southwest Freeway, Suite 200 Sugar Land, TX 77479 7737 Southwest Freeway, Suite 895 Houston, TX 77074 Telephone: (713) 774-5131 Fax: (713) 774-4336 ANESTHESIA
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 71250 Computed tomography, thorax; without contrast material 71260 with contrast material(s) 71270 without
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 71250 Computed tomography, thorax; without contrast material 71260 with contrast material(s) 71270 without
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma Penetrating neck injury (PNI) comprises 5 to 10 percent of traumatic injuries
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma Penetrating neck injury (PNI) comprises 5 to 10 percent of traumatic injuries
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
UNC HOSPITALS CHAPEL HILL, NORTH CAROLINA REQUEST AND AUTHORIZATION FOR UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY AND BIOPSY MIM#180
 UNC HOSPITALS CHAPEL HILL, NORTH CAROLINA 27514 REQUEST AND AUTHORIZATION FOR UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY AND BIOPSY MIM#180 I request and authorize and/or associates or assistants of his/her choice
UNC HOSPITALS CHAPEL HILL, NORTH CAROLINA 27514 REQUEST AND AUTHORIZATION FOR UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY AND BIOPSY MIM#180 I request and authorize and/or associates or assistants of his/her choice
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Chest Pain
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Foreign Body Management
 Foreign Body Management NYSGE Fellows Summer Course Susana Gonzalez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine 1 Objectives Timing of endoscopy When? Anatomic location Where? High risk objects What? Choosing
Foreign Body Management NYSGE Fellows Summer Course Susana Gonzalez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine 1 Objectives Timing of endoscopy When? Anatomic location Where? High risk objects What? Choosing
Spotlight on Esophageal Perforation A multinational study using the Pittsburgh Esophageal Perforation Severity Scoring System
 Spotlight on Esophageal Perforation A multinational study using the Pittsburgh Esophageal Perforation Severity Scoring System Michael Schweigert Department of Thoracic Surgery Objective Esophageal perforation
Spotlight on Esophageal Perforation A multinational study using the Pittsburgh Esophageal Perforation Severity Scoring System Michael Schweigert Department of Thoracic Surgery Objective Esophageal perforation
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the
 Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Case 1. Technegas Case Studies. Prostate cancer. Finished treatment recently. Smoker. Angina. Presents sudden dyspnea and poorly defined chest pains.
 Case 1 Michel Leblanc MD; RCPSC; ABNM Head of the Nuclear Medicine Department, Centre Hospitalier Régional de Trois-Rivières. Clinical Professor, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Cannada.
Case 1 Michel Leblanc MD; RCPSC; ABNM Head of the Nuclear Medicine Department, Centre Hospitalier Régional de Trois-Rivières. Clinical Professor, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Cannada.
5 DIAGNOSIS. History taking
 5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications. Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University
 Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
Spontaneous Esophageal Perforation Presenting as a Right- Sided Pleural Effusion: A Case Report
 Case Report 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Spontaneous Esophageal Perforation Presenting as a Right- Sided Pleural Effusion: A
Case Report 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Spontaneous Esophageal Perforation Presenting as a Right- Sided Pleural Effusion: A
An unusual cause of pneumatocoele
 An unusual cause of pneumatocoele From Dr.N.C.Gowrishankar s Unit Pediatric Surgery and PICU Dr Shashi Ranjani DNB PG Mehta Children Hospital 13 year boy h/o RTA at 2.30 pm boy was under the rear wheel
An unusual cause of pneumatocoele From Dr.N.C.Gowrishankar s Unit Pediatric Surgery and PICU Dr Shashi Ranjani DNB PG Mehta Children Hospital 13 year boy h/o RTA at 2.30 pm boy was under the rear wheel
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Penetrating Neck Injuries. Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010
 Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro
 MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro Paul E. Van Schil, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic and Vascular Surgery University of Antwerp, Belgium Mediastinal staging Invasive techniques lymph node mapping cervical
MEDIASTINAL STAGING surgical pro Paul E. Van Schil, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic and Vascular Surgery University of Antwerp, Belgium Mediastinal staging Invasive techniques lymph node mapping cervical
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND
 Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND Thoracic Aortic Trauma In USA and CANADA 7500-8000 die of blunt thoracic aortic
Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND Thoracic Aortic Trauma In USA and CANADA 7500-8000 die of blunt thoracic aortic
Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017
 Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara
 SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Delayed-onset right-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia and group B streptococcal septicemia
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Delayed-onset right-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia and group B streptococcal septicemia September 2003 2 Saner C, Burtscher R, Hunziker U, Zimmermann-Bär U, Department
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Delayed-onset right-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia and group B streptococcal septicemia September 2003 2 Saner C, Burtscher R, Hunziker U, Zimmermann-Bär U, Department
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma
 Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN PHLEBECTASIA PRESENTING WITH HOARSENESS OF VOICE.
 ISSN: 2250-0359 VOLUME 4 ISSUE 2 2014 INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN PHLEBECTASIA PRESENTING WITH HOARSENESS OF VOICE. Sohini Chakraborty,Pranab Kumar Dey Amrita Roy Kolkatta Medical College India Abstract:- Internal
ISSN: 2250-0359 VOLUME 4 ISSUE 2 2014 INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN PHLEBECTASIA PRESENTING WITH HOARSENESS OF VOICE. Sohini Chakraborty,Pranab Kumar Dey Amrita Roy Kolkatta Medical College India Abstract:- Internal
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Acute Postpartum Pulmonary Edema: A Case Report
 Postpartum pulmonary edema 157 Acute Postpartum Pulmonary Edema: A Case Report Min-Po Ho 1, Wing-Keung Cheung 2, Kaung-Chau Tsai 1 Acute pulmonary edema after pregnancy is rare. Pulmonary emobolism, pneumonia,
Postpartum pulmonary edema 157 Acute Postpartum Pulmonary Edema: A Case Report Min-Po Ho 1, Wing-Keung Cheung 2, Kaung-Chau Tsai 1 Acute pulmonary edema after pregnancy is rare. Pulmonary emobolism, pneumonia,
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Case Report: Lightning-Induced Pneumomediastinum
 Case Report: Lightning-Induced Pneumomediastinum Blumenthal, Ryan PhD*; Saayman, Gert MD University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa. The authors report no conflict of interest. *Correspondence to:
Case Report: Lightning-Induced Pneumomediastinum Blumenthal, Ryan PhD*; Saayman, Gert MD University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa. The authors report no conflict of interest. *Correspondence to:
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
The Case Begins. The case continued. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
 Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Pain Relief Options for Labor. Providing you with quality care, information and support
 Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing you with quality care, information and support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery suite at Lucile Packard Children
Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing you with quality care, information and support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery suite at Lucile Packard Children
Foreign Body Airway Obstructions in Children Lessons Learnt from a Prospective Audit
 Foreign Body Airway Obstructions in Children Lessons Learnt from a Prospective Audit KL NARASIMHAN, SK CHOWDHARY, S SURI, JK MAHAJAN, R SAMUJH, KLN RAO Aim : To prospectively audit 75 consecutive children
Foreign Body Airway Obstructions in Children Lessons Learnt from a Prospective Audit KL NARASIMHAN, SK CHOWDHARY, S SURI, JK MAHAJAN, R SAMUJH, KLN RAO Aim : To prospectively audit 75 consecutive children
Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
